Abstract
Zinc is an essential trace metal element in the human body, but it also constitutes a variety of proteins in the body of the important elements necessary; this element plays an important role in physiological metabolism. Disturbances in the metabolism of zinc ions in the body can significantly threaten human health, especially neurological diseases. Therefore, developing a rapid and straightforward method for determining zinc ions is important. Fluorescent probe technology has been widely used for detecting and labeling zinc ions. Among many fluorescent probes, the rhodamine derivative LPDQ fluorescent probe has unique application scenarios, for example, it plays an important role in the detection of zinc white in oil colors, and its advantages are simplicity, rapidity, and real-time operation. This paper introduces the types of fluorescent probes for zinc ions and the three main mechanisms of fluorescent probe detection. The characteristics, design strategies, and application effects of the three fluorescent probes for zinc ions, as well as their advantages and limitations, are reviewed and summarized, which are intended to provide valuable references for the development of new probes for zinc ions detection in the future and for the future direction of research in this field.
1. Introduction
As the environmental pollution problem is getting more and more attention, the environmental awareness of human beings has gradually improved, and people have begun to pay attention to the harm of metal pollution to human beings [1]. However, some trace metal elements essential to the human body are often overlooked and not given enough attention [2]. For example, metallic elements such as iron, zinc, and copper are essential elements in the human body, but excessive intake can also seriously jeopardize human life and health [3,4].
Zinc is the second most abundant trace metal element in the human body and an important element necessary for the composition of many proteins [5]. Most of the zinc in the body is in the form of zinc ions (Zn2+) and this element plays an important role in physiological metabolism [6,7]. Zinc ions are important cofactors in the catalytic process of constructing many biological enzymes that regulate protein and nucleic acid synthesis, gene expression, cell growth, differentiation, and transmission of neural signals [8,9]. The disturbance of zinc ion metabolism in the body can pose a significant threat to the life and health of the human body, especially neurological diseases, which can induce Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, epileptic diseases, etc. [10,11]. Zhang et al. [12] prepared a peptide-based ratiometric fluorescent probe, HcZ9, by solid-phase peptide synthesis for the quantification of zinc ions in biological solutions, which showed promising applications in cellular and human semen studies. Therefore, monitoring the concentration of zinc ions in the body in real-time is of great significance.
The primary detection methods of trace metal elements include electrochemical analysis, atomic spectrometry, isotope mass spectrometry, and chromatography [13,14,15,16]. Despite the high sensitivity of these traditional methods, the high requirements for samples, time-consuming operation, reliance on large-scale equipment and professional operators, and unsuitability for on-site rapid detection have primarily limited the application in real life. In recent years, fluorescence detection technology has been widely used in chemistry, medicine, and life sciences. It has been developed considerably because of its advantages of simple sample preparation, fast response, higher sensitivity, better selectivity, and ease of operation [17,18,19]. Rivera-Fuentes et al. [20] developed the far-red light probe SpiroZin2, which has a nanomolar affinity for zinc ions and is insensitive in the physiological pH range, and can be used for the precise detection and imaging of zinc ions in cells and tissues, providing a reliable tool for the study of zinc dynamics in acidic vesicles and neural synapses. Fluorescence detection techniques have been applied to detect metal ions in the environment and living organisms. In particular, fluorescent probe-targeted detection, labeling, and imaging techniques have received tremendous attention and have become a specialized field of research. In recent years, fluorescent probe detection has been significantly developed, mainly including fluorescent molecular probes for recognizing and detecting relevant metal ions, small molecules, etc. [21,22]. At the same time, the detection target can be labeled and imaged in the cell, which has an important reference significance for the study of related diseases [23]. The coumarin platform is widely used to design and synthesize small-molecule fluorescent probes. The backbone has been used to develop fluorescent chemosensors for various applications in molecular recognition, molecular imaging, bioorganic chemistry, analytical chemistry, materials chemistry, and biological and medical sciences. Goldberg et al. [24] designed a ZP1-based photoactivatable zinc sensor to achieve spatiotemporal control of zinc response to fluorescence through the introduction of a photocleavable protecting group. The sensor restored the metal-binding ability under UV irradiation and was successfully applied to imaging zinc dynamics in living cells and brain slices with high spatiotemporal resolution, providing a novel tool for resolving the transient function of zinc in biological processes such as neural signaling. The Schiff base is a suitable metal ion ligand, its structure contains rich nitrogen oxygen and other electron-rich coordination atoms that can be easily coordinated with metal ions; rhodamine and other organic fluorescent dyes have better light stability, and unique rigid coplanar structure, etc.; it is an ideal probe material, which prepares rhodamine derivatives of fluorescent probes with a strong fluorescence signal during the reaction and good light stability/ The prepared rhodamine derivative fluorescent probe has strong fluorescent signal during reaction, good photostability, short detection time, apparent reaction phenomenon, non-toxicity, and other outstanding photophysical properties. Strianese et al. [25] investigated the coordination behavior of complexes formed by phenol-substituted bis(pyrazolyl)methane ligands (L1-H and L2-H) with zinc ions (Zn2⁺) and their potential for use in the detection of zinc ions by fluorescent probes. The fluorescence intensity of L1-H was shown to be significantly enhanced upon coordination with zinc ions, especially in dichloromethane solution (switching ratio SR = 90%) suggesting that this ligand–metal system has the potential to serve as a fluorescent probe for zinc ions. The quinoline-based macrocyclic receptors and heteroscorpionate ligands share common features in the detection of zinc ions, (1) both contain specific structures or functional groups capable of liganding with zinc ions. These structures can provide coordination sites for zinc ions, thus realizing the recognition and binding of zinc ions. (2) The formation of stable complexes: After they are combined with zinc ions, they are able to form a more stable complex structure. This stability helps maintain the capture and signal response to zinc ions during the detection process, reducing the loss of zinc ions and interference, and thus improving the accuracy and reliability of the detection. Yu et al. [26] systematically reviewed the research progress of zinc-ion fluorescent probes in the last ten years, focusing on the bioimaging properties of typical fluorophores such as naphthol, naphthalenediimide, pyrene, quinoline, coumarin, and rhodamine. The application potential of the probe in highly selective detection, real-time imaging, and disease diagnosis was analyzed, and theoretical reference was provided for the development of new zinc ion fluorescence probes with a low detection limit and high water solubility. Based on this, this paper describes some fluorescent probes for detecting zinc ions. This paper reviews the relevant literature from 2017 to the present, mentions some important findings dating back to earlier years, and aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the research vein of the field from its early development to the present, and these papers provide important support for understanding the origin of the field and its basic theory.
2. Detection Mechanism of Fluorescent Probes
Alexander Demchenko [27] systematically explained the design principle and detection mechanism of fluorescent probes in his book. The core mechanisms include the following: (1) photoinduced electron transfer (PET) (inhibition of electron transfer to restore fluorescence after the probe binds to the analyte); (2) intramolecular charge transfer (ICT) (liganding or protonation alters the distribution of electrons, resulting in spectral shifts); (3) fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) (ratiometric detection through energy transfer); and (4) aggregation-induced luminescence (AIE) (inhibition of molecular motion to enhance fluorescence). Demchenko emphasized that the probe design needs to balance selectivity with a signal dynamic range and optimize the detection sensitivity and immunity to interference through a modular strategy, providing the basis for molecular tools for disease diagnosis and environmental monitoring. The detection mechanism of fluorescent probes has a wide range of applications in the fields of bioassay, environmental monitoring and medical diagnosis due to its high sensitivity, high selectivity, and real-time monitoring capability. With the continuous development of technology, the design and application of fluorescent probes has been optimized, providing more possibilities for the detection of complex biological systems.
2.1. Light-Induced Electron Transfer
The photoinduced electron transfer (PET) process transfers electrons from an energy donor to an energy acceptor under photochemical action. This transfer occurs only when the donor and the acceptor are in proximity to one another [28,29]. The design of fluorescent probes using the PET mechanism must have the following conditions: (1) a fluorophore with high fluorescence quantum yield; (2) a recognition group with strong electron-donating or electron-acquiring ability; and (3) the highest occupied molecular orbital or the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital of the recognition group is between the highest occupied molecular orbital/lowest unoccupied molecular orbital of the fluorophore [30,31]. The PET system consists of a “fluorophore-spacer group-receptor”. The fluorophore undergoes intramolecular electron transfer with the receptor upon light excitation, resulting in a change in the fluorescence signal. In probes designed based on the PET mechanism, pesticides disrupt the original PET, leading to enhancement, bursting, or changes in the fluorescence signal, depending on the nature of the donors and acceptors involved in the PET mechanism [32,33].
2.2. Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer
Fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) is a process in which an excited fluorophore energy (energy donor) transfers its energy to a neighboring ground state acceptor (energy acceptor) through a relatively long-distance dipole–dipole interaction [34]. Loas et al. [35] synthesized ZBR4 and ZR1, two two-site zinc ion probes based on carnosine, which showed significant fluorescence enhancement in response to zinc ions, and ZBR4 could be localized to the mitochondria, while ZR1 was located in the endoplasmic reticulum. The reversible detection of zinc ions in living cells can be realized, providing a new tool for the study of organelle-specific zinc dynamics, but the solution stability problem needs to be further solved. The key to designing a fluorescent probe based on the FRET mechanism is to ensure an inevitable spectral overlap between the emission spectrum of the energy donor and the absorption spectrum of the acceptor, and that the distance between the donor and the acceptor is less than 10 nm. The practical challenge of FRET-based fluorescent probe design, however, lies in the fact that the substance to be tested may alter the distance between the donor and the acceptor or change the emission or absorption spectra of either the donor or the acceptor, leading to the possibility of observing the emission of an energy donor even in the absence of energy transfer [36,37], thus affecting the sensitivity of the assay. Pesticides usually act as FRET receptors in probes designed based on the FRET mechanism, causing a fluorescence burst when energy is efficiently transferred.
2.3. Intramolecular Charge Transfer
Intramolecular charge transfer (ICT) refers to the fact that the fluorophore backbone of a probe has electron-donating and electron-absorbing groups attached at the ends of the probe, so that the electron-donating group inside the molecule can transfer charge to the electron-absorbing group. The stronger the electron-donating or electron-absorbing ability of the electron-donating or electron-absorbing groups in the probe molecule, the stronger the ICT effect, the longer the wavelength of the ICT peak, and usually the enhanced fluorescence intensity [38]. When a probe is designed based on the ICT mechanism, the binding of a substance to be detected to the probe affects the electron-donating and electron-absorbing abilities of the moiety, resulting in a change in the fluorescence signal and a change in the quantum efficiency of the probe.
2.4. Other Mechanisms
In addition to the above three common mechanisms, the fluorescent probes work by the inner filter effect (IFE) [39], aggregation-caused quenching (ACQ) [40], aggregation-induced emission (AIE) [41], and so on. (ACQ), aggregation-induced emission (AIE), etc. Molecular IFE, like FRET, requires spectral overlap between the fluorophore and the absorber. However, unlike FRET, IFE is derived from radiative energy transfer, with no distance requirement between the energy donor and the acceptor. This process affects only the fluorescence intensity and wavelength. ACQ is a phenomenon in which a fluorophore luminesces strongly in a dilute solution but weakens or even disappears at high concentrations [42]. The mechanism of ACQ may originate from the accumulation or aggregation of fluorophores at high concentrations or bursting caused by interaction with other molecules. The process of AIE is diametrically opposite to that of ACQ. AIE is a phenomenon in which fluorophores do not emit light in dilute solution but at high concentrations or in the aggregated state. The mechanism of AIE may be because the dynamic molecular internal rotation in a dilute solution dissipates the energy of their excited states. The combined effect of molecular internal rotation limitation in the aggregated state, molecular conformation changes, and changes in electronic states due to the aggregation state give this type of probe optimal luminescence efficiency in the aggregated state [43]. In addition, Wen et al. [44] reviewed the research progress of zinc ion fluorescent probes from 2019 to 2023. The sensing systems based on the photoinduced electron transfer (PET), excited state intramolecular proton transfer (ESIPT), intramolecular charge transfer (ICT), fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET), chelate-enhanced fluorescence (CHEF) and aggregation induced luminescence (AIE) are mainly described, and their recognition performance is analyzed in combination with typical cases and theoretical calculations. It provides a reference for the development of new zinc ion detection technology.
3. Fluorescent Probe to Detect Zinc Ions
3.1. Coumarin-Based Fluorescent Probes
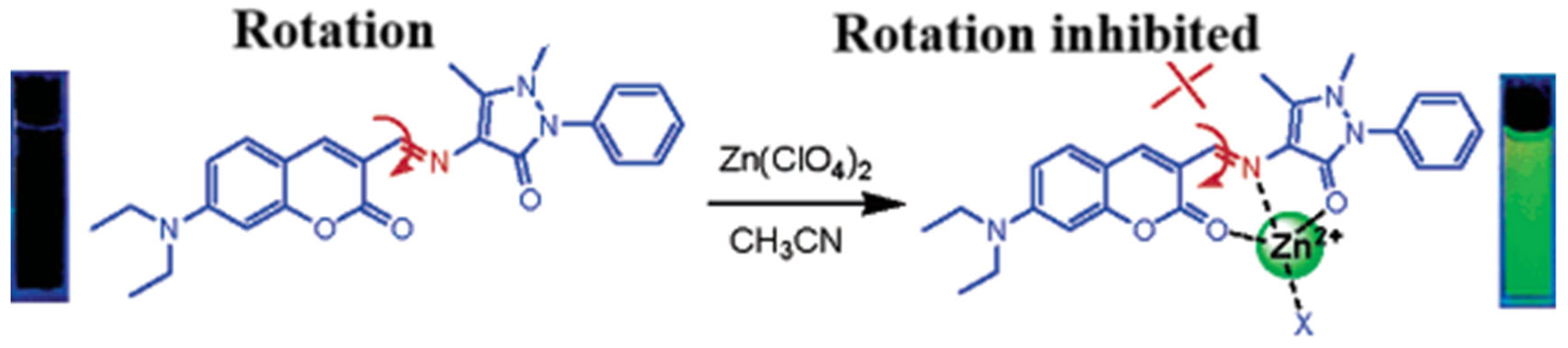
Coumarins containing the 1-benzopyran-2-one moiety are a large and widely studied family of compounds. Coumarins and their derivatives occupy an important place in the synthesis of natural products and organic chemistry. The coumarin parent ring emits weak or even no fluorescence. However, some substituted coumarin-like derivatives can produce strong fluorescence in the UV–visible range. Some novel coumarin dyes with improved and extended structures and properties have been designed and synthesized. At present, some novel coumarin dyes with improved and extended structures and properties have been designed and synthesized. Wang’s group also designed and synthesized coumarin derivatives based on the C=N rotation mechanism, as shown in Figure 1, which can selectively recognize zinc ions very well [45]. The compound itself fluoresces weakly at 480 nm before binding zinc ions. However, after binding zinc ions, the heteroatoms O, N, and O in the molecular structure are involved in coordination with Zn2+ and the C=N rotation is suppressed, resulting in strong fluorescence at 565 nm and a redshift of the emission peak by 85 nm.
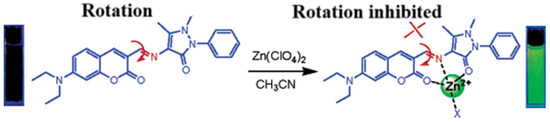
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of C=N heterogeneous fluorescent probes and their recognition of Al3+ [45].
Yang’s group [46] designed and synthesized a novel coumarin derivative fluorescent probe, FCP, based on the photo-induced electron transfer (PET) mechanism, which can be used for the quantitative detection of Zn2+. The probe FCP has the advantage of good selectivity, high sensitivity, and a broad pH response range and can be used to detect Zn2+ in aqueous solutions. Fluorescence enhancement (~13-fold) was observed upon adding Zn2+ to the solution. FCP also showed good cell penetration in the HeLa cell model and exhibited very low cytotoxicity in the HEK-293 cell model. Nam’s [47] group reported HN1, a Zn2+ ratiometric fluorescent probe with a dual fluorophore as a platform. The binding of the probe to Zn2+ inhibited the intramolecular phototransfer of the electrons mechanism and facilitated the resonance energy transfer of energy to the receptor. With good selectivity, excellent pH tolerance, and a suitable K value, probe HN1 is suitable for detecting Zn2+ in living organisms. Finally, the exogenous Zn2+ content can be detected by fluorescence colorimetry in HeLa live cells. The probe can reliably monitor the equilibrium state of zinc ions as they cross the cell membrane. Zastrow et al. [48] designed and synthesized a HaloTag-based zinc sensor, fusing ZP1 and HaloTag to achieve intracellular zinc targeting, and then combined with mCherry to achieve ratiometric sensing, which provides a powerful tool for studying the distribution and dynamic changes of zinc ions. Tong [49] group designed and synthesized a novel Zn2+ fluorescent probe, T2, using coumarin and quinoline as the detection platform. T showed high affinity for Zn2+. Its K value was 0.98 uM. The limit of detection of Zn2+ was estimated to be 48.1 nM. In addition, Probe T showed low cytotoxicity and good cell membrane permeability under physiological conditions for the quantitative determination of Zn2+ levels in actual water samples. In this study, we developed a novel Zn2+ receptor and successfully realized Zn2+ imaging in living cells, which provides a basis for the further qualitative and quantitative detection of Zn2+ in living cells. Yang’s [50] group designed and synthesized HL, a one- and two-photon probe that is simple for detecting Zn2+. This probe is highly selective for Zn2+ and shows a significant enhancement of the fluorescence intensity at 500 nm, which may be attributed to the generation of the 2:1 stoichiometric complex HL–Zn between HL and Zn2+, which results in the blocking of the isomerization of the C=N structure, thus inhibiting the light-induced electron transfer. Furthermore, the HL recognition process’s reversibility was achieved by adding the Zn2+ scavenger EDTA disodium salt. Dimethylpyridinamine (DPA) is a good zinc ion-recognizing group, and the probe [51] is composed of 7-amino-4-methylcoumarin and dimethylpyridinamine (DPA) linked by chloroacetyl chloride. Probe 1 showed almost no fluorescence in neutral aqueous solution (ΦF = 0.05) due to the transfer of a lone pair of electrons from the nitrogen atom to coumarin in the excited state (PET effect). When Cd2+ was added, the probe produced a strong violet fluorescence (Φ = 0.36) at 386 nm. With the addition of Zn2+, the probe also showed a strong fluorescence emission at 437 nm (ΦF = 0.63), while other metal ions showed no fluorescence response. IR, NMR, and potentiometric analyses confirmed that Zn2+ and Cd2+ integrated with N on pyridine, N on the amine group, and O on amide, respectively, and formed a 1:1 complex, which led to the inhibition of PET and the restoration of fluorescence. Although the coumarin probe has achieved excellent results in detecting zinc ions, the parameters of coumarin synthesis, such as reaction time and temperature, may impact on the effect of the coumarin probe on specific analytes. Therefore, the control and optimization of coumarin probe synthesis parameters may be a direction for future attention.
3.2. Schiff Base Fluorescent Probes
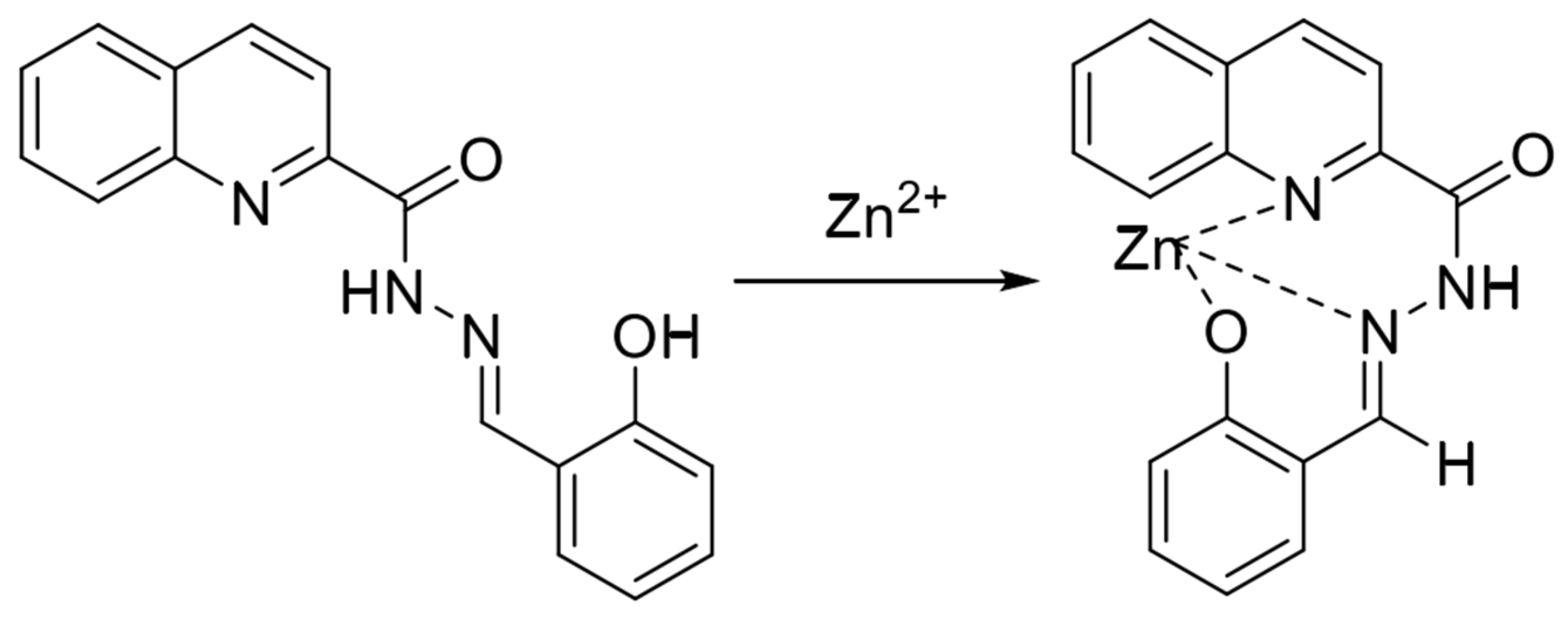
Schiff bases are excellent ligands for metal ions, and their structures contain electron-rich coordination atoms such as nitrogen and oxygen, which can be easily coordinated with metal ions. Classical Schiff bases, formed by the condensation of amine and aldehyde groups, have received attention from researchers recently because of their simple and inexpensive synthesis and the fact that they can be easily modified and remodeled. In 2016, Liu et al. [52] synthesized a quinoline fluorescent probe, QLAS, from salicylaldehyde hydrazone and quinacrine chloride, with the structure shown in Figure 2. The probe structure contains phenolic hydroxyl groups, quinoline nitrogen atoms and imine bonds, which can provide ligand sites for zinc ions. The probe triggers a fluorescence-enhanced response after forming a ligand with zinc ions, with reasonable specificity in the response process, resistance to various ionic interferences, and a low detection limit as low as 21 nM. The probe has a low cytotoxicity and a significant Stokes shift and can be used to detect zinc ions in cells. Gandin et al. [53] developed a new, sensitive, selective, and non-invasive Zn2+ fluorescence sensor. Zinpyr-1, a Zn2+ sensitive probe in a porous membrane, responds quickly and reversibly, detecting 1 µM–1 mM Zn2+ in seconds for cell-related studies. Mameli et al. [54] systematically investigated the coordination chemical behaviors of three novel quinoline derivative macrocyclic ligands (L1–L3) with Cu2⁺, Zn2⁺, Cd2⁺, Hg2⁺, and Pb2⁺, and confirmed that the quinoline-based fluorescent probe can modulate the selective recognition of Zn2⁺/Cd2⁺ through steric effect, which provides a theoretical basis for the design of highly selective zinc ion sensors.
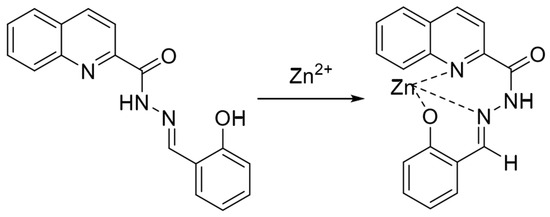
Figure 2.
Mode of action of fluorescent probe QLAS with zinc ions [52].
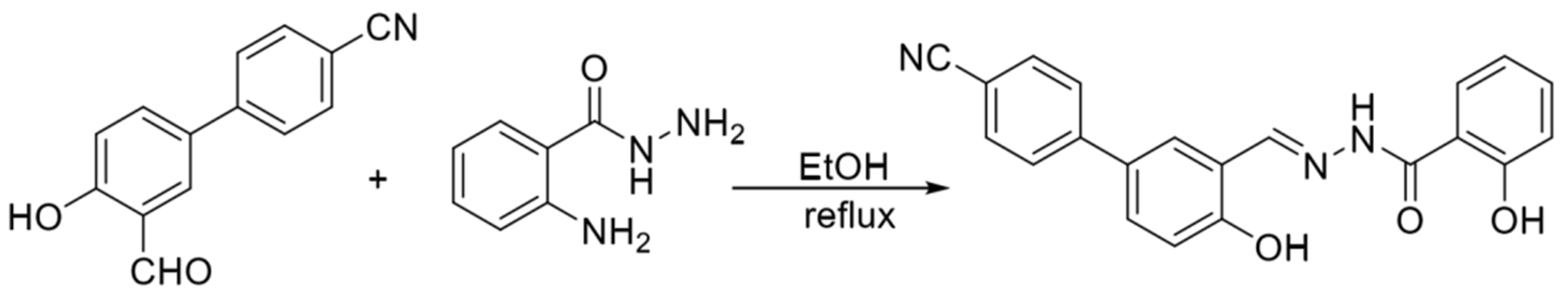
In 2019, Lu et al. [9] synthesized the fluorescent probe P-OH in a one-step process using 2-aminobenzoylhydrazine and 3′-formyl-4′-hydroxy-[1,1′-biphenyl]-4-carboni-trile, and the structure is shown in Figure 3. In the THF/HEPES (4/6, v/v) buffer system, the phenolic hydroxyl oxygen in the probe structure, the nitrogen atom in the imine structure and the oxygen atom in the hydrazide structure can be coordinated with zinc ions and the probe and zinc ions form a 2:1 ligand to realize the fluorescence-enhancement response to zinc ions, but cadmium ions also cause a fluorescence-enhancement phenomenon in the detection process. The assay process’s short response time and high sensitivity (13 nM), accompanied by visualization, can be used to detect zinc ions in cells and zebrafish.
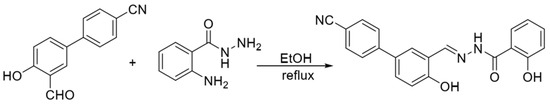
Figure 3.
Synthesis route of the probe P−OH [9].
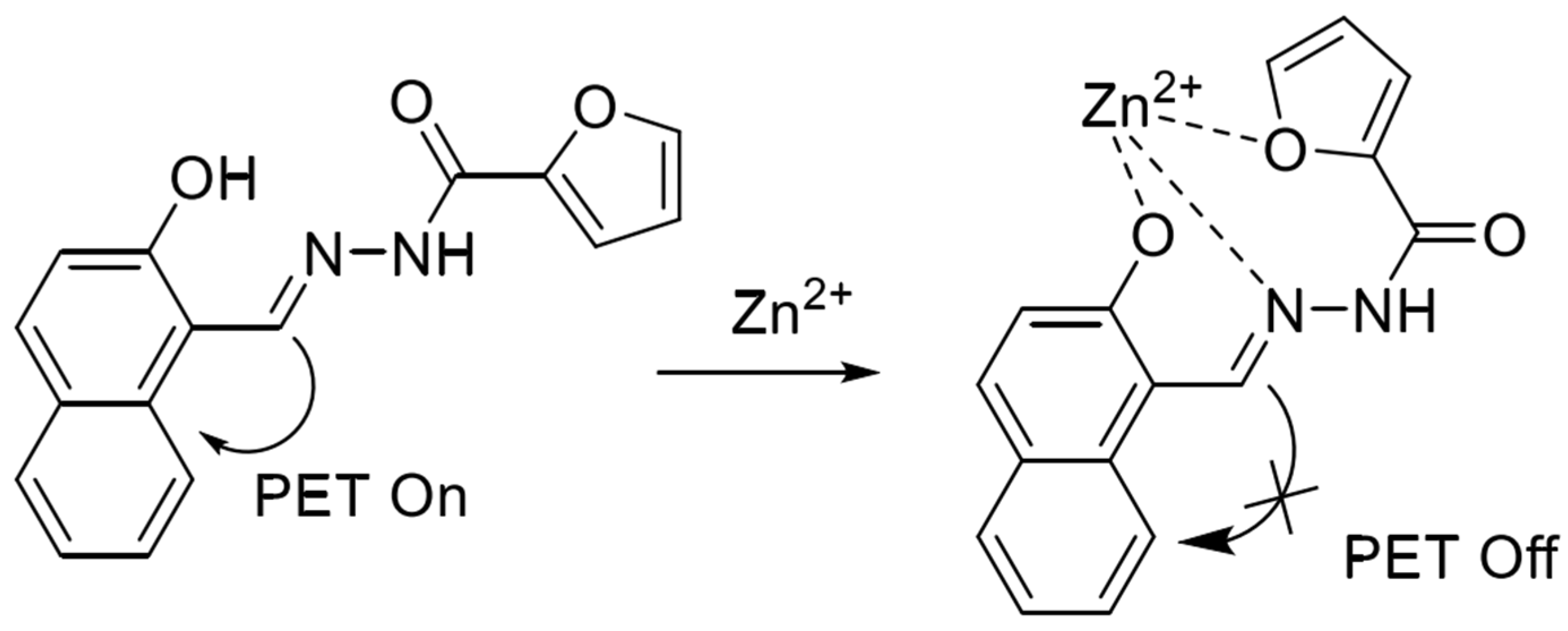
In 2020, Xiao et al. [55] synthesized a terpyridine-based fluorescent probe QTPY with 2-acetylpyridine and quinoline-2-carbaldehyde as raw materials. The probe utilizes the coordination of nitrogen atoms in the pyridine ring to form a 2:1 ligand with ions to achieve the fluorescence enhancement of zinc and cadmium ions simultaneously. However, copper ions will produce serious interference in the detection process. The probe has been applied to detect ions in water. In 2021, based on the PET detection mechanism, Mu et al. [56] synthesized a naphthalene-based Schiff base fluorescent probe based on 2-hydroxy-1-naphthaldehyde and furan-2-carbohydrazide, and the structure is shown in Figure 4. In the neutral system acetonitrile/HEPES (1/1, v/v), the phenolic hydroxyl oxygen atom, imine nitrogen atom and furan oxygen atom in the probe structure can bind to zinc ions and form a ligand in the ratio of 1:1, which leads to the inhibition of the PET process to show a strong fluorescence-enhancement effect, which can realize the real-time response to the zinc ions, high sensitivity (118 nM), and the reproducibility of the detection. However, the cadmium ions will also be part of the fluorescence-enhancement effect in the detection process. However, cadmium ions also show partial fluorescence enhancement during the detection process. The probe can be used to detect zinc ions in water and cells.
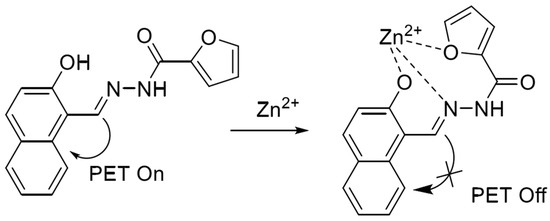
Figure 4.
Mode of action of naphthalene-based fluorescent probes with zinc ions [56].
In 2022, Wu et al. [57] synthesized a near-infrared fluorescent probe NIRF by introducing multiple nitrogen and oxygen atoms, the structure of which is shown in Figure 5. It was shown that the probe NIRF utilized the phenolic hydroxyl oxygen atoms, imine nitrogen atoms, and oxygen atoms in the acetylhydrazone in its structure to coordinate with zinc ions to form a 1:1 ligand to achieve a fluorescence-enhanced response to zinc ions. At the same time, the detection limit was 46.1 nM. The experiments also found that the ligand between the probe NIRF and zinc ions could continue to be used as a fluorescent probe to achieve a fluorescence-quenching detection of -CN, and the detection limit was reasonable, with a detection limit of 790 nM. The probe can detect zinc and cyanogen ions in organisms, with a detection limit of 790 nM. 2016 Hu et al. [58] prepared the fluorescent probe J from 2-amino benzothiazole, as shown in Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6, Figure 7, Figure 8, Figure 9, Figure 10 and Figure 11. It was found that in the neutral system DMSO/HEPES (4/1, v/v), the thiazole ring nitrogen atoms, phenol hydroxyl oxygen atoms and imine bond nitrogen atoms in the structure of the probe can be coordinated with zinc ions and form a 1:1 ligand, which leads to the fluorescence effect enhancement enabling the detection of zinc ions. The detection process has the advantages of good selectivity and reproducibility, and the detection limit is 16.4 nM. The probe can be prepared on test paper for zinc ion detection. In 2021, Wu et al. [59] designed and synthesized a benzothiazole derivative BTT with the structure shown in Figure 7. The probe HBT in Tris/MeOH (2/3, v/v) buffer can utilize the nitrogen, oxygen and sulfur atoms in the structure to form a 1:1 ligand with zinc ions, which leads to the blocked proton transfer (ESIPT) of the excited state within the molecule to produce chelated fluorescence enhancement (CHEF) to achieve the detection of zinc ions. The detection process is accompanied by an apparent color change from orange to green and the detection limit is reduced to 37.7 nM. However, mercury and copper ions can interfere with the detection process. The probe can be used to detect zinc ions in cells. Ling-Yi Shen designed a novel fluorescent probe L to enable the selective detection of Zn2+ ions [59]. Spectroscopic and single-crystal x-ray diffraction analyses revealed an asymmetric Schiff base probe structure, and the fluorescence of the probe’s fluorescence was significantly enhanced at 475 nm after adding zinc ions. The probe L can form a 1:1 complex with Zn2+ ions.
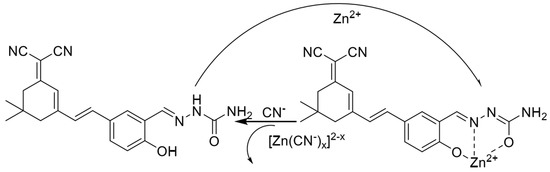
Figure 5.
The mechanisms of the probe NIRF recognizing Zn2+ and CN− [57].
Figure 5.
The mechanisms of the probe NIRF recognizing Zn2+ and CN− [57].
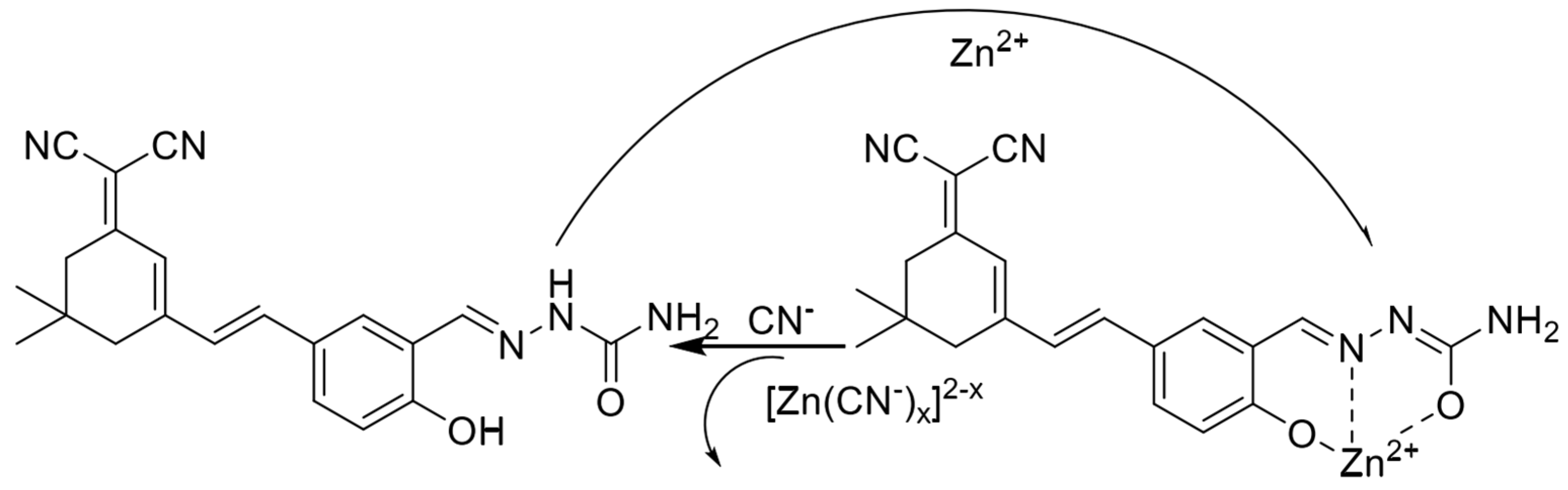
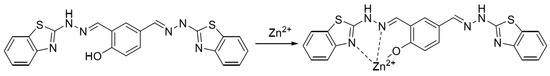
Figure 6.
Mechanism of interaction of fluorescent probes with zinc ions [58].
Figure 6.
Mechanism of interaction of fluorescent probes with zinc ions [58].
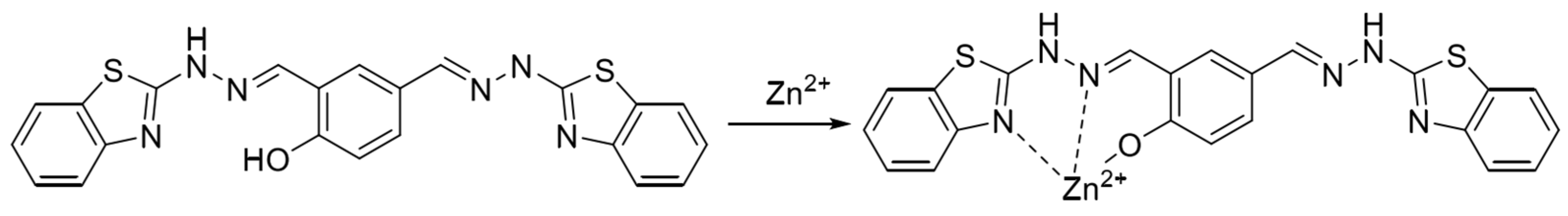
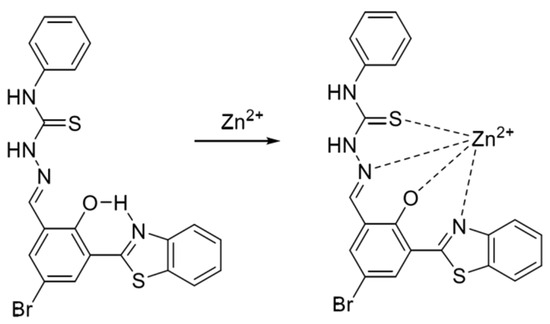
Figure 7.
Formulation of benzazole derivative BTT with zinc ions [59].
Figure 7.
Formulation of benzazole derivative BTT with zinc ions [59].
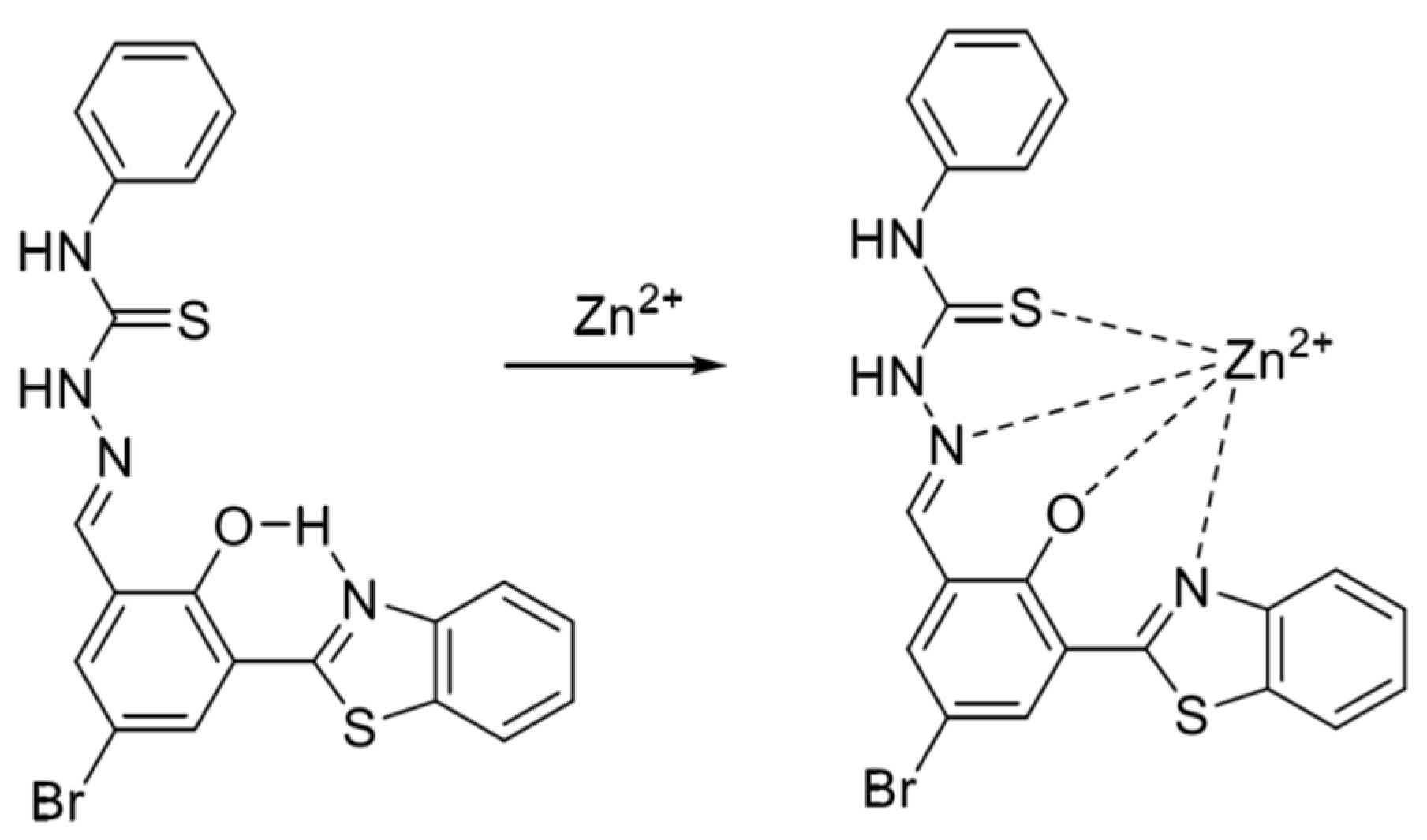
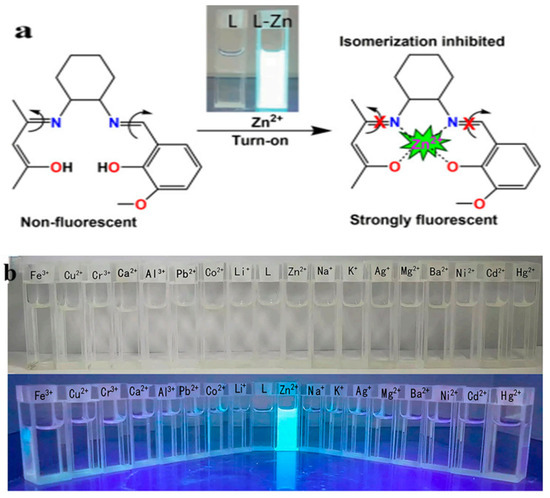
Figure 8.
(a) Schematic representation of the response of probe L to zinc ions. (b) Fluorescence response of probe L with the addition of different metal ions [60].
Figure 8.
(a) Schematic representation of the response of probe L to zinc ions. (b) Fluorescence response of probe L with the addition of different metal ions [60].
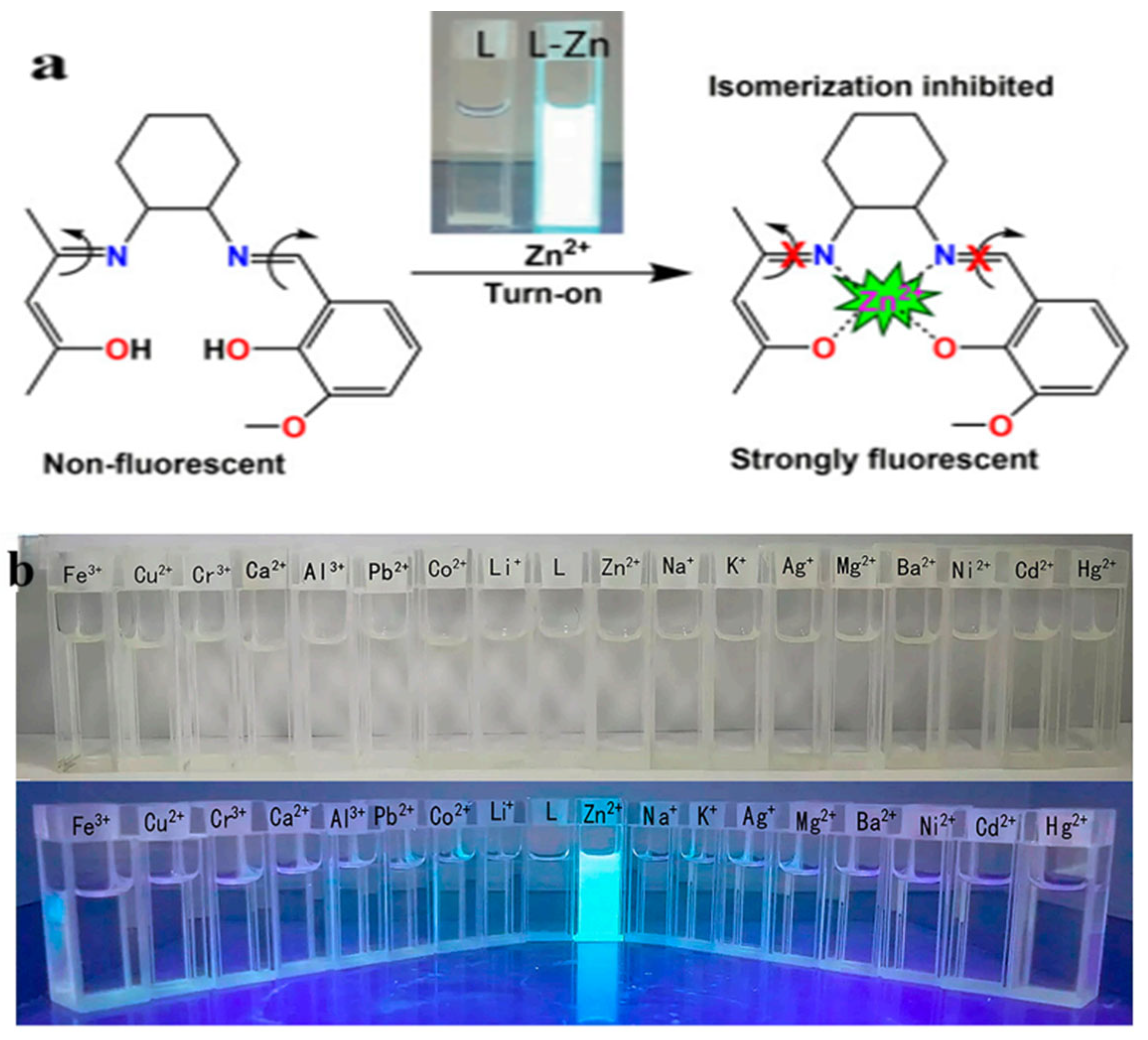
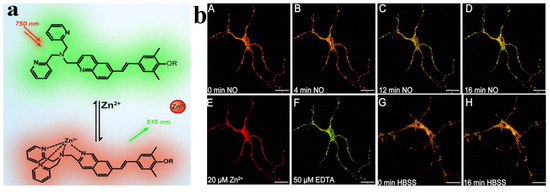
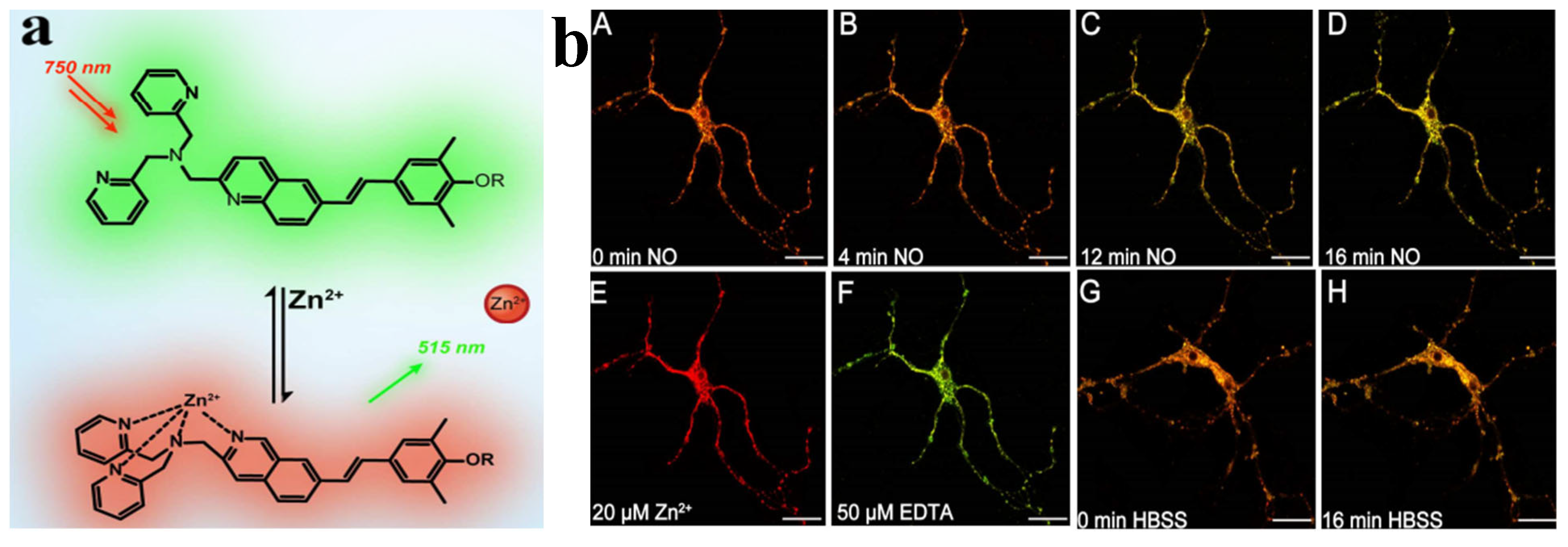
Figure 9.
(a) Schematic of the response mechanism of probe TEO-MPVQ to Zn2+; (b) The fluorescence changes of 5µM TEO−MPVQ in NO-induced neurons. In TEO−MPVQ, the fluorescence images of NO at different time points before incubation (A) and after incubation were: (B) 4 min, (C) 12 min, (D) 16 min. The image after 10µM Zn2+/pyrithione (1:2) processing is (E), and the image after 20 µM EDTA processing is (F). HBSS processed fluorescence images of neurons at 0 min (G) and 16 min (H) [61].
Figure 9.
(a) Schematic of the response mechanism of probe TEO-MPVQ to Zn2+; (b) The fluorescence changes of 5µM TEO−MPVQ in NO-induced neurons. In TEO−MPVQ, the fluorescence images of NO at different time points before incubation (A) and after incubation were: (B) 4 min, (C) 12 min, (D) 16 min. The image after 10µM Zn2+/pyrithione (1:2) processing is (E), and the image after 20 µM EDTA processing is (F). HBSS processed fluorescence images of neurons at 0 min (G) and 16 min (H) [61].
Wanying Li et al. reported that a two-photon probe TEO-MPVQ based on intramolecular charge transfer can be used for scale imaging and biosensing of Zn2+ ions. The chelation of the probe TEO-MPVQ with Zn2+ ions resulted in a redshift of the fluorescence emission peak by about 60 nm and an increase in the spectral emission intensity [61], which enabled the fluorescence ratiometric recognition of Zn2+ ions. The probe has high sensitivity, selectivity, good biocompatibility, high spatial resolution, and profound tissue penetration ability to tracer endogenous Zn2+ ions in neuronal cells. It has been applied to imaging Zn2+ ions in zebrafish. The probe [62] is a three-legged fluorescent probe synthesized based on terpyridine, which has a strong fluorescence emission at 412 nm in DMSO. With increasing water content in the solvent, the fluorescence intensity decreases and redshifts to 479 nm, which is attributed to the H-aggregation of the ligand with the increase of undesirable solvents, which leads to fluorescence bursts. In contrast, by adding Zn2+, the tertiary pyridyl group forms a coordination bond with Zn2+, which induces the complexes to come together to inhibit the rotation of the intramolecular chemical bonds of the tripyridine, which reduces the loss of energy due to the non-radiative mode of the probe 53, resulting in a robust fluorescence. It was also shown that the detection limit of this probe for Zn2+ was up to 1.1 nM. The probe [63] is a Schiff base obtained by a simple condensation reaction of a diamine with salicylaldehyde, whose mechanism of aggregation-induced luminescence (AIE) is thought to be related to restricted intramolecular rotation (RIR). The ligand has irreversible mechanoluminescent (ML) properties, and upon milling, the solid color changes from blue to green (445 nm–512 nm). However, applying pressure axially (using a hydraulic press) underwent a reversible transformation with the exact color change (blue–-green). The probe also showed the good recognition of Zn2+ due to the coordination of Zn2+ with the ligand to form a 1:1 complex. The complex’s aggregation effect restricts the rotation of the intramolecular bonds, resulting in strong fluorescence emission. In addition, the detection limit of the probe was 0.064 ppm for Zn2+. Although the Schiff base fluorescent probe has strong specificity and high sensitivity for the detection of zinc ions, the specific binding of the probe to the target ions needs to be solved in the complex detection environment, especially in the presence of substances with the same functional group as that of the target zinc ions.
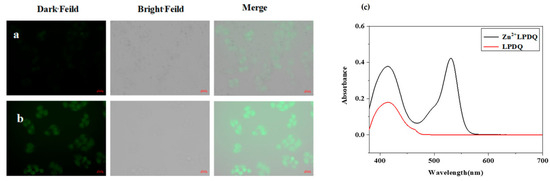
Figure 10.
LPDQ cell imaging. (a) Hela cells incubated with the LPDQ probe. (b) Hela cells incubated with the LPDQ probe and Zn2+. (c) LPDQ cell imaging, UV−Vis absorption spectrum after the reaction of LPDQ and Zn2+ [64].
Figure 10.
LPDQ cell imaging. (a) Hela cells incubated with the LPDQ probe. (b) Hela cells incubated with the LPDQ probe and Zn2+. (c) LPDQ cell imaging, UV−Vis absorption spectrum after the reaction of LPDQ and Zn2+ [64].
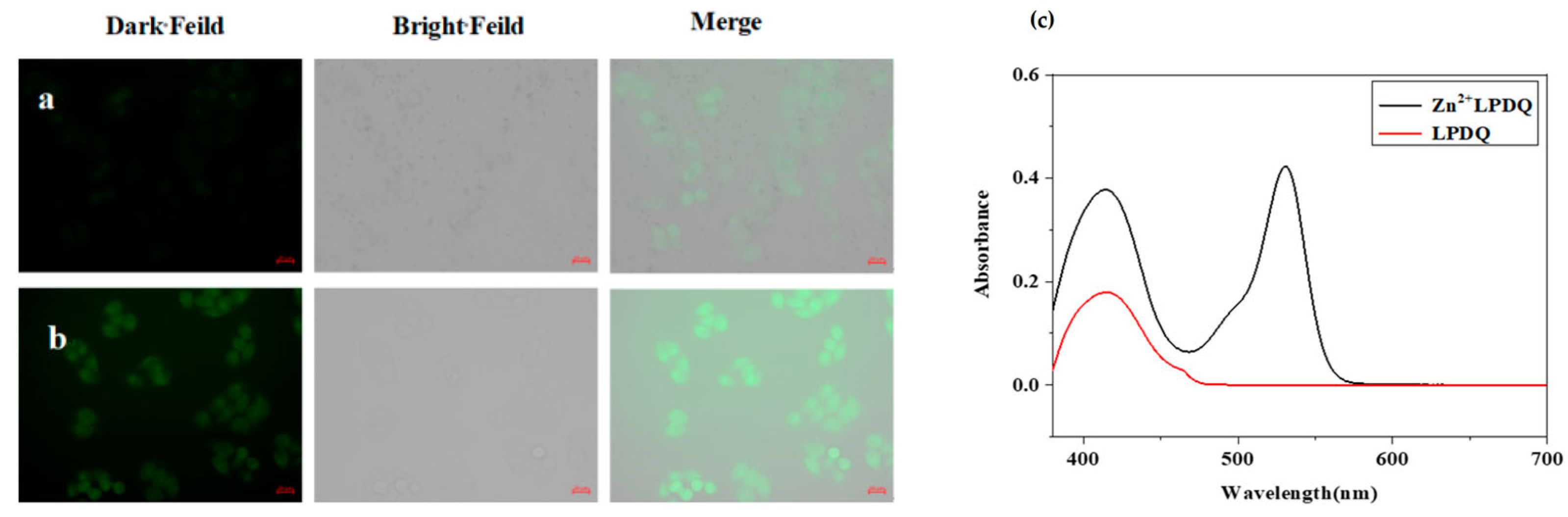
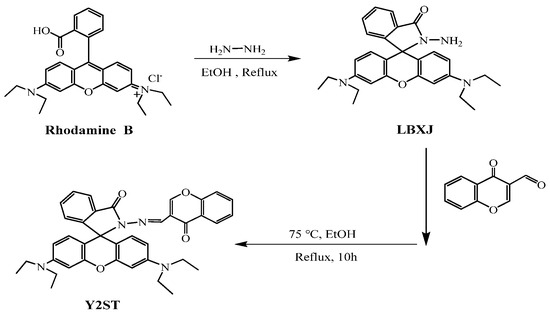
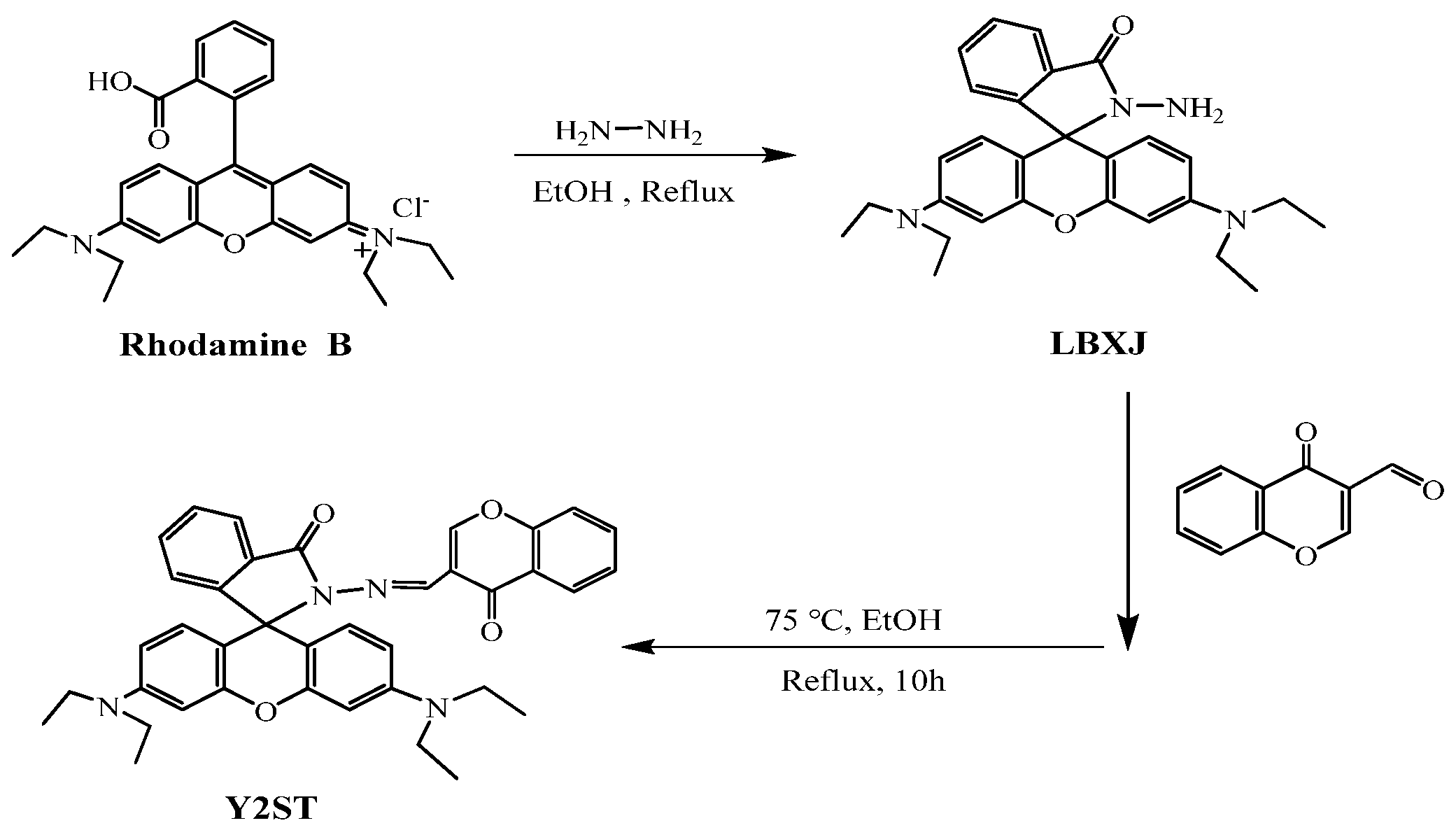
Figure 11.
Structure of LBXJ and Y2ST [65].
Figure 11.
Structure of LBXJ and Y2ST [65].
3.3. Rhodamine Fluorescent Probes
Rhodamine fluorescein-like derivatives belong to the xanthene class of basic dyes and represent a typical organic fluorescent dye with a xanthene structure. The fluorescent material exists an oxygen bridge between benzene rings, which makes this class of molecular materials characterized by rigid coplanarity, manifesting itself as a significant enhancement of the stability of the molecular structure. The material’s structure will be transformed into an open ring state, and through the action of excitation light, it will emit strong fluorescence. Its maximum emission wavelength range is between 500 and 700 nm, which is located in the red visible region, and the fluorescence in this range can effectively avoid the background fluorescence range of the biological system, which significantly improves the probe’s sensitivity and the fluorescent probe with rhodamine fluorescent derivative as the material has attracted the attention of many researchers and scholars. The fluorescent probes using rhodamine fluorescent derivatives as materials have attracted the attention of many scientific research scholars. They are often used in the design of fluorescent probes in biological analysis and have high application value and research prospects. Wang et al. [64] synthesized an “on–off” rhodamine fluorescent probe LPDQ with a new structure by modifying the structure of pyridoxal phosphate, which can be used for the detection of Zn2+ in water and oil paintings, and the probe LPDQ can be applied to cellular imaging studies of Zn2+. Jin et al. [65] prepared the intermediate LBXJ from rhodamine B, hydrazine hydrate, and HCl, and then prepared a Y2ST probe using LBXJ, chromone-3-carbaldehyde, and anhydrous ethanol. It was used for the detection of Zn2+ in zinc gluconate. Serkan et al. successfully designed and synthesized a novel dual-channel probe based on bisphenol A-rhodamine (BAR) with high selectivity and sensitivity to Zn2+ ions. In pure MeCN and MeCN-H2O (v/v = 8/2, 5 mM, HEPES, pH 7.0), BAR showed adequate selectivity and sensitivity to Zn2+ ions through two different mechanisms (i.e., ESIPT and FRET). The detection limit of Zn2+ was 2.21 μM, which provides a good reference for synthesizing such probe derivatives [66]. Yang et al. synthesized a novel molecular probe for detecting Zn by modifying the intermediate of rhodamine and hydrazine hydrate with chlorsalicylaldehyde. The probe can detect changes in Zn with the naked eye and has a detection sensitivity limit of 3.6 μ mol/L. When the concentration range of Zn is 10–250 μ mol/L, there is a good linear relationship, which can be used for detecting trace amounts of zinc [67]. Tomat E. et al. used the condensation reaction of rhodamine with xanthene to produce a fluorescent probe that can be coordinated with Zn, which is an “on–off” type probe that can be coordinated with Zn in neutral aqueous solution for the detection of Zn [68]. The probe [69] was composed of acridine–dione as a fluorophore. In acetonitrile and aqueous solution (80:20, v/v), the fluorescence of the probe was burst due to the lone-pair electron transfer of N on the DPA, and the fluorescence of the probe at 426 nm was enhanced by a factor of 4.5 when Zn2+ was added. The probe [70], which uses a fluorescein backbone as a fluorophore, showed no fluorescence emission or weak fluorescence under physiological conditions (pH = 7.0), also due to the PET process caused by the lone pair of electrons of N on DPA, which was inhibited by the addition of Zn2+ coordinated to DPA, thus showing a strong fluorescence emission. The probe [71] was based on BODIPY as a fluorophore, and again the ligand did not fluoresce due to the presence of the PET effect, and the addition of Zn2+ increased its fluorescence intensity by a factor of 7, with a quantum yield of 0.857. The Zn2+ fluorescent probes are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Names of zinc ion fluorescent probes, wavelengths of incidence and excitation, detection limits, etc.
4. Conclusions
Compared with non-detection problems, fast detection, and the inaccuracy of traditional zinc ion residue detection methods, fluorescent probes have achieved good zinc ion residue detection results. This paper reviewed the mechanism of zinc ion detection by fluorescent probes. This paper refers to the relevant literature since 2017, and cites several earlier studies, which is of great value in building basic knowledge in this field. The characteristics, detection strategies, and applications of different probes were introduced. The fluorescent probe methods have the advantages of rapidity, sensitivity, and easy operation. In summary, given the characteristics of various types of fluorescent materials, attempts can be made to synthesize the advantages of each to achieve accurate detection, multiple detection, and anti-interference detection to meet the realistic needs of ion detection. This review will provide a valuable reference for developing more cost-effective and widely applicable methods for detecting zinc ions in the future.
Author Contributions
Z.W.: Formal analysis, data curation and writing—original draft; Z.R.: Investigation, methodology and writing—review and editing; X.C. and Y.N.: Methodology and writing—original draft; Y.L.: Resources and writing—review and editing; Y.N. and X.C.: Investigation and data curation; Y.L.: Resources, funding acquisition and writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Department of Scientific Research project in Heilong jiang province (No. LH2022B022), and the 2023 Jiamusi University National Foundation Incubation Program (JMSUGPZR2023-006). This work was financially supported by Basic business expenses of Heilongiiang Provincial Department of Education (No. 2023-KYYWF-0594).
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Shi, L.; Zhang, S.; Fan, M.; Wang, D.; Li, N. Environmental pollution analysis based on the luminescent metal organic frameworks: A review. J. TRAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2021, 134, 116131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luca, B.; Erica, C.; Fabio, M.D.; Paolo, P. Metal Nanostructures for Environmental Pollutant Detection Based on Fluorescence. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, J.; Hu, S. Preparation of LiLu(MoO4)2: Eu3+ and Its Fluorescence Detection for Fe3+ Ions. J. Liaocheng Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2024, 37, 64–69. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.y.; Wang, D.; Hu, S.; Yang, J. Hydrothermal Synthesis of SrF2:Tb3+ for Selective Detection of Fe3+ Ions. J. Liaocheng Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2023, 36, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, P.; Wang, X.; Hao, Q.; Zhou, J.; Xu, C. Preparation of 3D Hierarchical Molybdenum-Polydopamine Microflowers as Cathode for Aqueous Zinc-Ion Batteries with Large Voltage Range. J. Liaocheng Univ. 2023, 36, 85–92. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Lao, S.; Ding, W.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, S. A novel ratiometric fluorescent probe for detection of iron ions and zinc ions based on dual-emission carbon dots. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 284, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Liu, Y.R.; Dong, C.; Han, X.E. Novel ratio fluorescence probes for selectively detecting zinc ion based on Y-type quinoxaline framework. J. Lumin. 2017, 183, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devender, S.; Sarika, T.; Sweta, S.; Garima, C.; Amit, P.S.; Rajeev, G. A fluorescent pH switch probe for the ‘turn-on’ dual-channel discriminative detection of magnesium and zinc ions. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2023, 435, 114334. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z.; Lu, Y.; Fan, W.; Fan, C.; Li, Y. Ultra-fast zinc ion detection in living cells and zebrafish by a light-up fluorescent probe. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 206, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markovich, J.R.; Margarita, K.; Maksim, S.; Marianna, Z.; Elena, K.; Kristina, K.; Alexander, G.; Anton, B.; Nicolas, B. The Role of the Metabolism of Zinc and Manganese Ions in Human Cancerogenesis. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeun, Y.; Hyunbeom, L.; Geonhee, L.; Eun, H.; Kim, E.H.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, J.-O.; Yunseon, S.; Jinyoung, P.; So-Dam, K.; et al. A Metabolomics Investigation of the Metabolic Changes of Raji B Lymphoma Cells Undergoing Apoptosis Induced by Zinc Ions. Metabolites 2021, 11, 689. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.Y.; Azrad, M.; Demark-Wahnefried, W.; Frederickson, C.J.; Lippard, S.J.; Radford, S.J. Peptide-based, two-fluorophore, ratiometric probe for quantifying mobile zinc in biological solutions. ACS Chem. Biol. 2015, 10, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.y.; Xe, X.; Wan, S.; Jin, C.; Zhao, L.; Yan, B. Covalent Organic Framework Modified Polyaniline Electrospun Nanofiber Membrane for Electrochemical Detecting of Pb2+. J. Liaocheng Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.), 2023; 36, 74–81. [Google Scholar]
- Long, T.; Wang, Z.; He, Y.; Fang, J.; Feng, J.; Sun, Q. Synergistic Effects of Pollutant Purification and Heavy Metal Reduction in Photocatalytic Fuel Cells. J. Liaocheng Univ. 2023, 36, 45–56. [Google Scholar]
- Nasar, A.; Rizwan, A.A.Z.U.; Baig, M.A. Laser ionization time of flight mass spectrometer for isotope mass detection and elemental analysis of materials. Laser Phys. 2017, 27, 086001. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, C.; Guo, D.; Wang, N.; Wu, S.; Zhang, P.; Zhu, Y. Detection of trace fluoride in serum and urine by online membrane-based distillation coupled with ion chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1500, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Yang, J.; Hu, S. Upconversion luminescence and Temperature Sensing Properties of Yb3+/Ho3+ Co-Doped Sc2W3O12 Phosphors. J. Liaocheng Univ. 2024, 37, 42–49. [Google Scholar]
- Han, M.; Cao, M.; Duan, W.; Gong, S. Two Birds with One Stone: Quantitative and Enantioselective Recognition of Amino Acids Using One Molecule with Dual-Wavelength Emission. J. Liaocheng Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2023, 36, 96–110. [Google Scholar]
- Panicker, R.R.; Joseph, S.; Dharani, S.; John, M.L.; Kuriappan, A.T.; Abraham, J.T.; Majeed, S.A.; Pavankumar, B.B.; Kumar, S.A.; Sivaramakrishna, A. A highly lipophilic terpyridine ligand as an efficient fluorescent probe for the selective detection of zinc(II) ions under biological conditions. Anal. Methods 2024, 17, 232–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera-Fuentes, P.; Wrobel, A.T.; Zastrow, M.L.; Khan, M.; Georgiou, J.; Luyben, T.T.; Roder, J.C.; Okamoto, K.; Lippard, S.J. A far-red emitting probe for unambiguous detection of mobile zinc in acidic vesicles and deep tissue. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 1944–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsi, M.; Hehua, L.; Jianhua, G.; Arun, R.C.; Jia, S. Fluorescent Aptaswitch for Detection of Lead Ions. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2022, 5, 5089–5093. [Google Scholar]
- Caiping, D.; Tianbing, R. Near infrared fluorescent probes for detecting and imaging active small molecules. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 482, 215080. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Liu, K.; Tian, M.; Lin, W. A ratiometric fluorescent probe for hydrazine detection with large fluorescence change ratio and its application for fluorescence imaging in living cells. Spectrochim Acta Part A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2018, 212, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, J.M.; Wang, F.; Sessler, C.D.; Vogler, N.W.; Zhang, D.Y.; Loucks, W.H.; Tzounopoulos, T.; Lippard, S.J. Photoactivatable sensors for detecting mobile zinc. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 2020–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strianese, M.; Milione, S.; Bertolasi, V.; Pellecchia, C.; Grassi, A. Heteroscorpionate-based Co2+, Zn2+, and Cu2+ complexes: Coordination behavior, aerobic oxidation, and hydrogen sulfide detection. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 900–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Yu, H.; Wang, S.; Qi, Y. Progress in research of zinc ion fluorescent probes for biological imaging. J. Lumin. 2024, 266, 120318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demchenko, A.P. Introduction to Fluorescence Sensing: Volume 2: Target Recognition and Imaging; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Rather, S.R.; Scholes, G.D. From fundamental theories to quantum coherences in electron transfer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 141, 708–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Choi, H.S.; Eom, J.B.; Choi, Y. Mini-platform for off–on near-infrared fluorescence imaging using peptide-targeting ligands. Bioconjugate Chem. 2020, 31, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Liu, J.; O’Connor, H.M.; Gunnlaugsson, T.; James, T.D.; Zhang, H. Photoinduced electron transfer (PeT) based fluorescent probes for cellular imaging and disease therapy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2023, 52, 2322–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, S.; Daga, P.; Dey, N. Exploring various photochemical processes in optical sensing of pesticides by luminescent nanomaterials: A Concise discussion on challenges and recent advancements. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 44395–44423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.Q.; Wang, D.; Meng, L.Y.; Wang, Y.Q.; Chen, J. Glutathione-modified graphene quantum dots as fluorescent probes for detecting organophosphorus pesticide residues in radix angelica sinensis. Spectrochim Acta A 2023, 286, 122021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garimell, L.; Dhiman, T.K.; Kumar, R.; Singh, A.K.; Solanki, P.R. One-step synthesized ZnO np-based optical sensors for detection of aldicarb via a photoinduced electron transfer route. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 2552–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saini, S.; Srinivas, G.; Bagchi, B. Distance and orientation dependence of excitation energy transfer: From molecular systems to metal nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 1817–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loas, A.; Radford, R.J.; Lippard, S.J. Addition of a second binding site increases the dynamic range but alters the cellular localization of a red fluorescent probe for mobile zinc. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 6491–6493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, A.C.M.; Barbieri, M.V.; Chino, M.; Manco, G.; Febbraio, F. A FRET approach to detect paraoxon among organophosphate pesticides using a fluorescent biosensor. Sensors 2022, 22, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Ye, S.; Sun, Z.; You, J.; Li, W.; Song, Y.; Zhang, H. A fluorescent aptasensor based on gold nanoparticles quenching the fluorescence of rhodamine B to detect acetamiprid. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 35260–35269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, W.; Huang, G.; Jiang, G.; Jiang, G.; Dauda, S.A.A.; Pi, F. Direct phoxim sensing based on fluorescent metal-organic framework of Nu-1000 induced FRET. Food Biosci. 2023, 55, 102967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Luo, L.; Chen, C.; Li, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Mari, G.M.; Xing, C.; Xia, X.F.; Shen, J.Z.; Yu, X.Z.; et al. Environment-friendly dual-mode immunoassay based on the inner filter effect of polydopamine-polyethylenimine copolymer nanoparticles for the highly sensitive detection of norfloxacin. Food Chem. 2025, 480, 143928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Jia, Y.; Feng, Z.; Liu, F. A highly sensitive and selective fluorescent probe without quencher for detection of Pb2+ ions based on aggregation-caused quenching phenomenon. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 38929–38934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.J.; Zheng, P.; Xia, Y.X.; Li, F.; Zhang, M. A simple AIE probe to pesticide trifluralin residues in aqueous phase: Ultra-fast response, high sensitivity, and quantitative detection utilizing a portable platform. Talanta 2024, 269, 125352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhong, K.; Tang, L.; Yan, X. A triphenylamine derived fluorescent probe for efficient detection of H2S based on aggregation-induced emission. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 13399–13405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, M.D.; Kocak, H.S.; Kara, H.K. A BODIPY-based ICT probe for ratiometric and chromo-fluorogenic detection of hazardous oxalyl chloride. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol Biomol. Spectrosc. 2023, 284, 121828. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, J.; Hua, Q.; Ding, S.; Sun, A.; Xia, Y. Recent advances in fluorescent probes for zinc ions based on various response mechanisms. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2024, 54, 3313–3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Liu, W.; Zhuang, X.Q.; Wang, F.; Wang, P.F.; Tao, S.L.; Zhang, X.H.; Wu, S.K.; Lee, S.T. Fluorescence turn on of coumarin derivatives by metal cations: A new signaling mechanism based on C=N isomerization. Org. Lett. 2007, 9, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, C.; Ming, Z.Z.; Hao, G.F.; Yang, W.C.; Yang, G.F. Coumarin-based novel fluorescent zinc ion probe in aqueous solution. Tetrahedron 2013, 69, 4743–4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, H.; You, Y.; Kim, T.; Jhon, G.J.; Nam, W. Fluorescence ratiometric zinc sensors based oncontrolled energy transfer. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 17100–17112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zastrow, M.L.; Huang, Z.; Lippard, S.J. HaloTag-based hybrid targetable and ratiometric sensors for intracellular zinc. ACS Chem. Biol. 2020, 15, 396–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Gao, O.; Li, M.; Tang, X.; Lai, K.W.C.; Tong, Q. A Ratiometric Probe Based on Coumarin-Quinolinefor Highly Selective and Sensitive Detection of Zn2+ lons in Living Cells. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2017, 355, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Fan, L.; Yang, Z.Y. A small-molecule and resumable two-photon fluorescent probe for Zn2+ based on a coumarin Schiff-base. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 228, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuhiro, S.S.; Takayuki, H. Mechanism for Different Fluorescence Response of a Coumarin-Amide-Dipicolylamine Linkage to Zn(II) and Cd(II) in Water. J. Phys. Chem. A 2013, 117, 1474–1482. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.Y.; Dong, Y.S.; Zhang, B.B.; Liu, F.; Tan, C.; Tan, Y.; Jiang, Y. An Efficient Quinoline-based Fluorescence Sensor for Zinc(II) and Its Application in Live-cell Imaging. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 234, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandin, A.; Brigo, L.; Giacomazzo, S.; Torresan, V.; Brusatin, G.; Franco, A. Reversible fluorescent solid porous films for detection of zinc ions in biological media. J. Biol. Eng. 2025, 19, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mameli, M.; Aragoni, M.C.; Arca, M.; Atzori, M.; Bencini, A.; Bazzicalupi, C.; Blake, A.J.; Caltagirone, C.; Devillanova, F.A.; Garau, A.; et al. Synthesis and coordination properties of quinoline pendant arm derivatives of [9] aneN3 and [9] aneN2S as fluorescent zinc sensors. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 48, 9236–9249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Ma, J.; Li, D.H.; Liu, L.; Wang, H. Preparation 4′-Quinolin-2-yl-[2, 2′; 6′, 2”] Terpyridine as a Ratiometric Fluorescent Probe for Cadmium Ions and Zinc Ions in Aqueous. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2020, 399, 112613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.Y.; Shi, L.P.; Yan, L.Q.; Tang, N. A 2-Hydroxy-1-naphthaldehyde Schiff Base for turn-on Fluorescence Detection of Zn2+ Based on PET Mechanism. J. Fluoresc. 2021, 31, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.Q.; Liu, Y.; Wu, X.D.; Li, Y.; Du, J.; Qi, S.; Yang, Q.; Xu, H.; Li, Y. A Novel Near-infrared Fluorescent Probe for Zn2+ and CN– Double Detection Based on Dicyanoisfluorone Derivatives with Highly Sensitive and Selective, and Its Application in Bioimaging. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2022, 267, 120621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.H.; Qi, J.; Sun, Y.; Pei, P.X. A New Fluorescence Chemosensor Based on Benzothiazole Derivative for Zn2+ and Its Logic Gate Behavior. Phosphorus Sulfur Silicon Relat. Elem. 2017, 192, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Feng, L.H.; Chao, J.B.; Wang, Y.; Shuang, S. Ratiometric Sensing of Zn2+ with A New Benzothiazole-based Fluorescent Sensor and Living Cell Imaging. Analyst 2021, 146, 4348–4356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.Y.; Chen, X.L.; Yang, X.J.; Xu, H.; Huang, Y.L.; Zhang, X.; Redshaw, C.; Zhang, Q.L. A highly selective turn-on fluorescent probe for the detection of zinc. Molecules. 2021, 26, 3825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.Y.; Liu, Z.C.; Fang, B.Q.; Jin, M.; Tian, Y. Two-photon fluorescent Zn2+ probe for ratiometric imaging and biosensing of Zn2+ in living cells and larval zebrafish. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 148, 111666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.H.; Kwona, K.Y.; Jung, J. HA turn-on fluorogenic Zn(II) chemoprobe based on a terpyridine derivative with aggregation-induced emission (AIE) effects through nanofiber aggregation into spherical aggregates. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 952–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasha, S.S.; Hare, R.Y.; Choudhury, A.R.; Laskar, I.R. Synthesis of an aggregation-induced emission(AIE) active salicylaldehyde based Schiff base: Study of mechanoluminescence and sensitive Zn(II) sensing. J. Mater. Chem. C. 2017, 5, 9651–9658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Ren, Z.; Lv, Y. Application of the rhodamine derivative LPDQ fluorescent probe for the detection of zinc white in oil paints. AIP Adv. 2024, 14, 035022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Liu, H.; Wang, Z. Study on the Properties of rhodamine B fluorescent probe Y2ST. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2024, 101, 101420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Tian, L.; Yang, Z. A novel rhodamine-chromone Schiff-base as turn-on fluorescent probe for the detection of Zn (II) and Fe (Ⅲ) in different solutions. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2019, 369, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wechakorn, K.; Suksen, K.; Piyachaturawat, P.; Kongsaeree, P. Rhodamine-based fluorescent and colorimetric sensor for zinc and its application in bioimaging. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 228, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Jiang, X.J.; Zhu, Y.Y.; Zhou, B.J.; Zang, S.Q.; Tang, M.S.; Zhang, H.Y.; Mak, T.C. A new fluorescent probe for Al3+ based on rhodamine 6G and its application to bioimaging. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 12624–12632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashokkumar, P.; Ramakrishnan, V.T.; Ramamurthy, P. Photoinduced Electron Transfer (PET) Based Zn2+ Fluorescent Probe: Transformation of Turn-On Sensors into Ratiometric Ones with Dual Emission in Acetonitrile. J. Phys. Chem. A. 2011, 115, 14292–14299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burdette, S.C.; Walkup, G.K.; Spingler, B.; Tsien, R.Y.; Lippard, S.J. Fluorescent Sensors for Zn2+ Based on a Fluorescein Platform: Synthesis, Properties and Intracellular Distribution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 7831–7841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Peng, X.; Guo, B.; Fan, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Cui, A.; Gao, Y. Boron dipyrromethene fluorophore based fluorescence sensor for the selective imaging of Zn (II) in living cells. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2005, 3, 1387–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.q.; Yang, H.; Li, J.; Zhou, C.; Li, L.; Wu, X.; Lei, C. A near infrared fluorescent probe for detection and bioimaging of zinc ions and hypochlorous acid. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2022, 1206, 339750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.T.; Pei, Y.Y.; Yan, M.Y.; Li, Y.G.; Yang, G.G.; Qu, C.H.; Luo, W.; Wang, J.; Li, Q.F. A fast-response turn-on quinoline-based fluorescent probe for selective and sensitive detection of zinc (II) and its application. Microchem. J. 2021, 160, 105776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Zhou, C.; Li, J.; Yang, H.; Wu, X.; Li, L. A near-infrared fluorescent probe based on Dicyanisophorone for the detection of zinc ions (Zn2+) in Water and living cells. J. Fluoresc. 2023, 33, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, B.; Rong, X.; Qiu, X.; Sun, L.; Cheng, Y. Development of a novel near-infrared fluorescent probe for selective detection of zinc ions in environmental and food samples. Tetrahedron Lett. 2023, 129, 154713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Pan, S.; Sivaram, S.; De, P. Naphthalimide-based fluorescent polymeric probe: A dual-phase sensor for formaldehyde detection. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2025, 26, 2469493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Chen, J.; Tang, J.; Ma, Y.; Sang, W.; Feng, S.; Yang, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, X. Quantitative Detection of Zn2+ in Infant Formula and Living Cells Using Quinoline-Based Fluorescent Probes. Food Anal. Methods 2025, 18, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Chang, D.; Luo, Y.; Yu, H.; Li, J.; Liu, K. Synthesis of an Antipyrine-Based Fluorescent Probe with Synergistic Effects for the Selective Recognition of Zinc Ion. Minerals 2024, 14, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhou, C.; Yang, H.; Wu, X.; Yan, L. Two near-infrared fluorescent probes based on dicyanoisfluorone for rapid monitoring of Zn2+ and Pb2+. Methods Appl. Fluoresc. 2022, 10, 035010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Jiang, T.; Lin, Z.; Yu, H.; Wang, S.; Qi, Y. Two novel pyrene-based Schiff base fluorescent probes for the turn-on detection of Zn2+ and their application in bioimaging. Microchem. J. 2025, 209, 112715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Ga, L.; Ai, J. Synthesis of fluorescent BSA templated silver nanomaterials and it’s application of detection of Zn2+ and Co2+. Mater. Res. Express 2018, 5, 105703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, X.; Sun, P.; Li, H.; Tian, X.; Zhang, B.; Wu, J.; Tian, Y.; Zhou, H. A conveniently prepared and hypersensitized small molecular fluorescent probe: Rapidly detecting free zinc ion in HepG2 cells and Arabidopsis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 86, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jović, M.; Marković, O.; Newhouse, T.R.; Opsenica, I.M.; Selaković, Ž. A highly selective ESIPT-mechanism-based, ratiometric fluorescent sensor for zinc ions. Dye. Pigment. 2025, 234, 112547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Kumar, A.; Singh, M.K.; Sahu, S.K.; John, R.P. A novel benzidine based Schiff base “turn-on” fluorescent chemosensor for selective recognition of Zn2+. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 241, 1218–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdemir, S.; Malkondu, S.; Kocyigit, O. A reversible calix [4] arene armed phenolphthalein based fluorescent probe for the detection of Zn2+ and an application in living cells. Luminescence 2019, 34, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zou, Y.; Liu, J. A single 8-hydroxyquinoline-appended bile acid fluorescent probe obtained by click chemistry for solvent-dependent and distinguishable sensing of zinc (II) and cadmium (II). Luminescence 2024, 39, e4610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, C.; Huang, J.; Sun, Q. A thiazolo [4, 5-b] pyridine-based fluorescent probe for detection of zinc ions and application for in vitro and in vivo bioimaging. Talanta 2018, 185, 396–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.X.; Chen, W.; Jiang, C.; Lu, H. A turn-on near-infrared fluorescent probe with rapid response and large Stokes shift for the selective and sensitive detection of zinc (II) and its application in living cells. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 2396–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wu, J. Highly selective and sensitive detection of Zn (II) and Cu (II) ions using a novel peptide fluorescent probe by two different mechanisms and its application in live cell imaging. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 208, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Gong, F.; Chen, X.; Cao, Z.; Xia, J.; Gu, T.; Li, Z. Intrinsically fluorescent and highly functionalized polymer nanoparticles as probes for the detection of zinc and pyrophosphate ions in rabbit serum samples. Talanta 2018, 188, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).