Magnetic and Thermoelectric Properties of Fe2CoGa Heusler Compounds
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
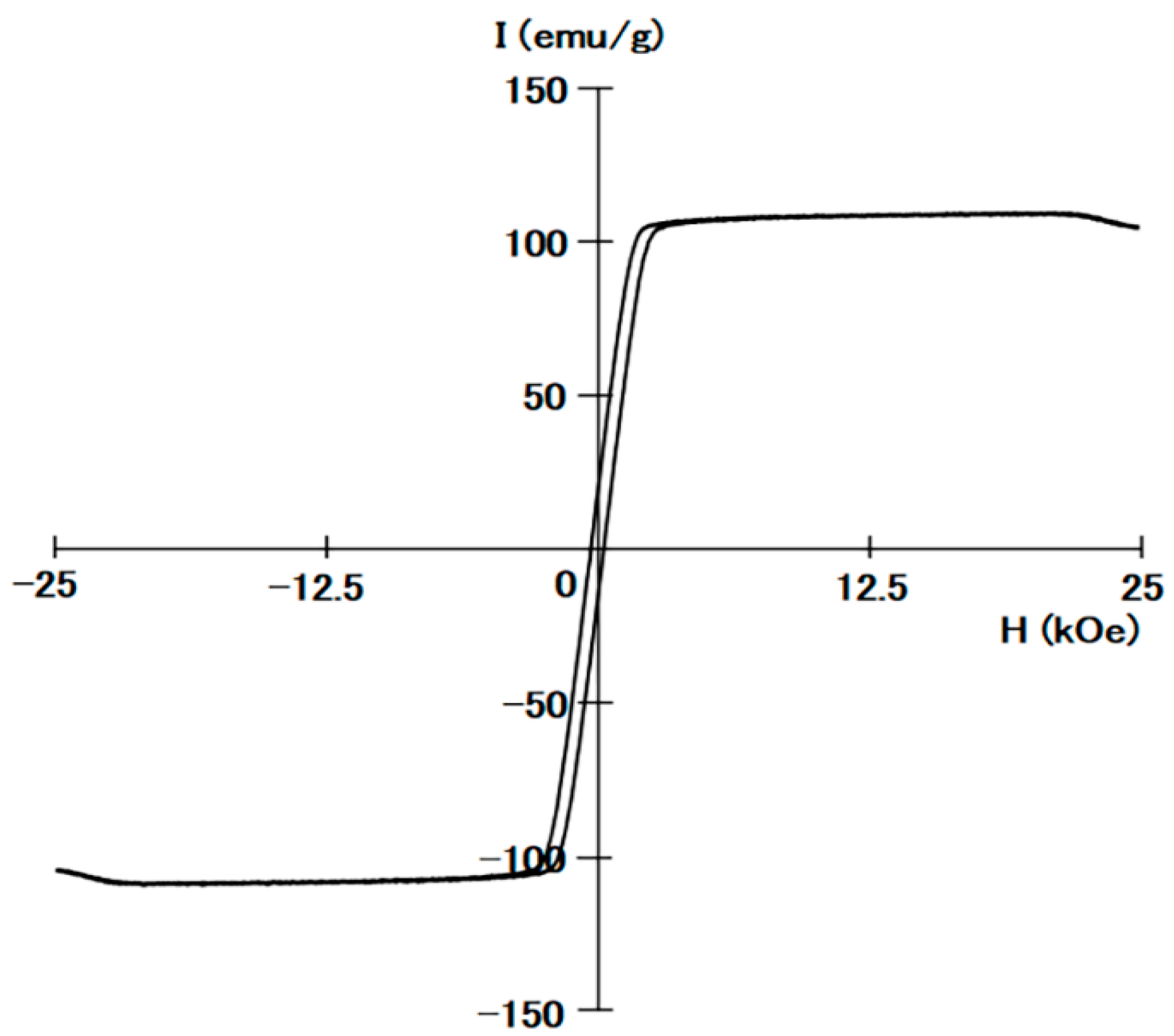
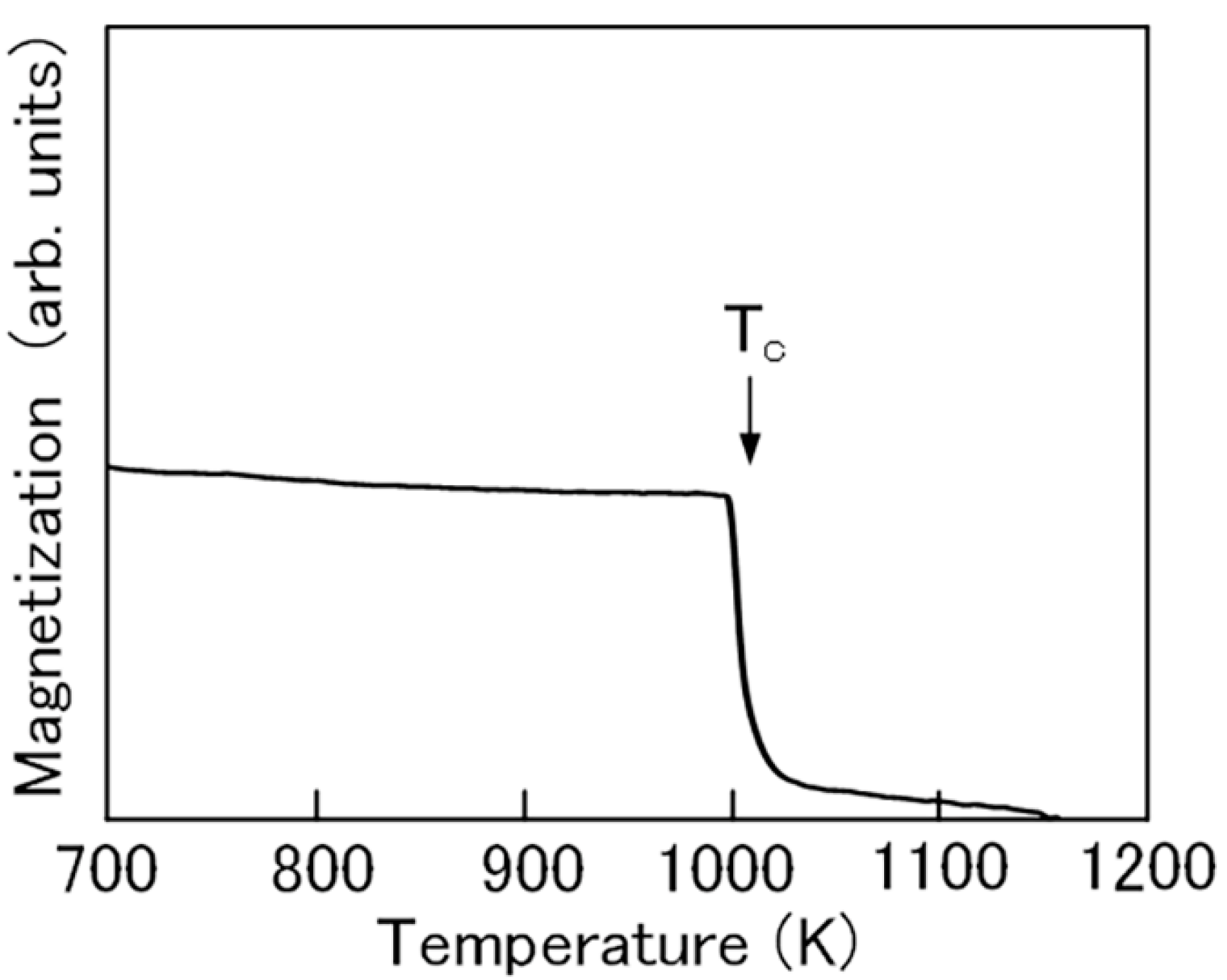
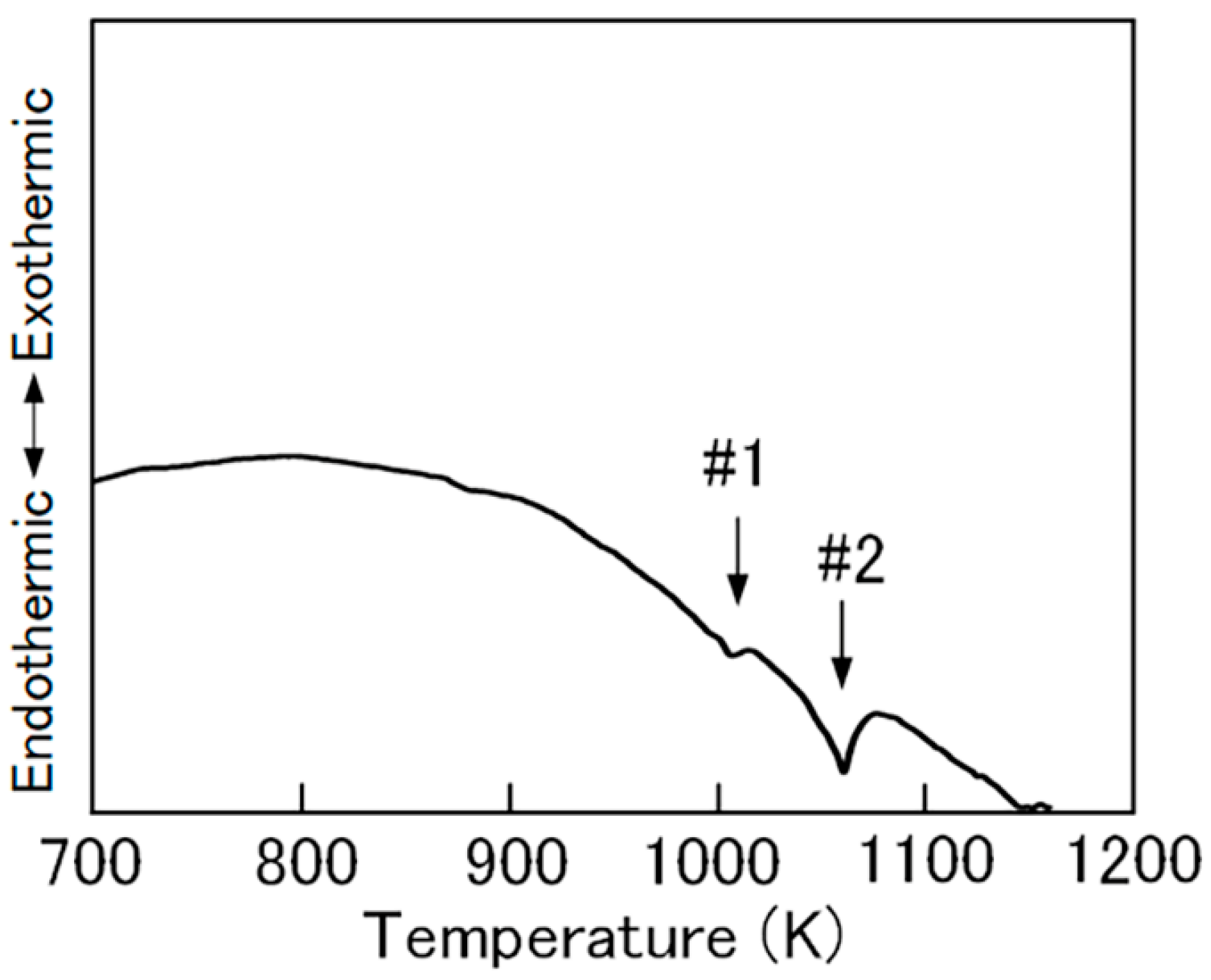
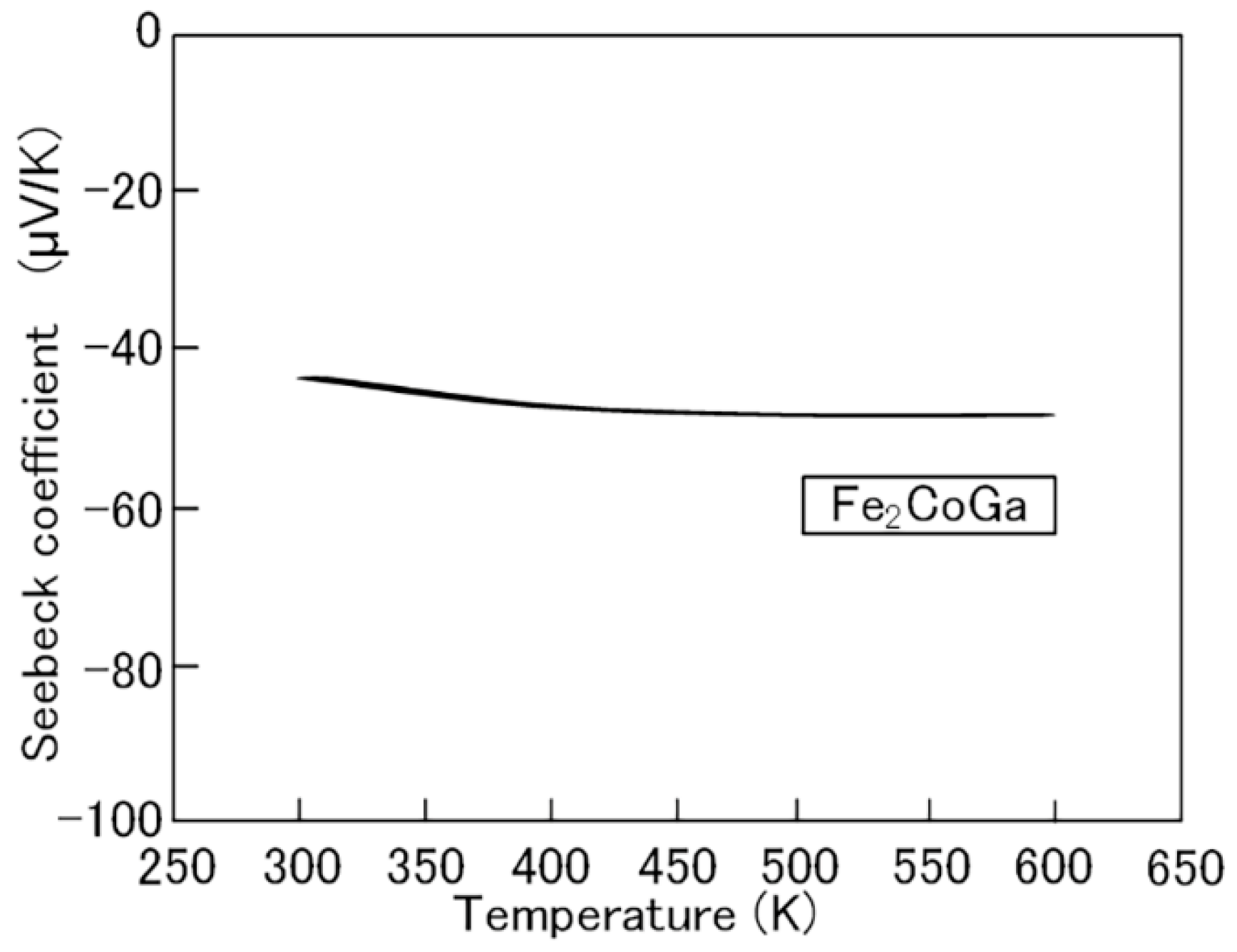
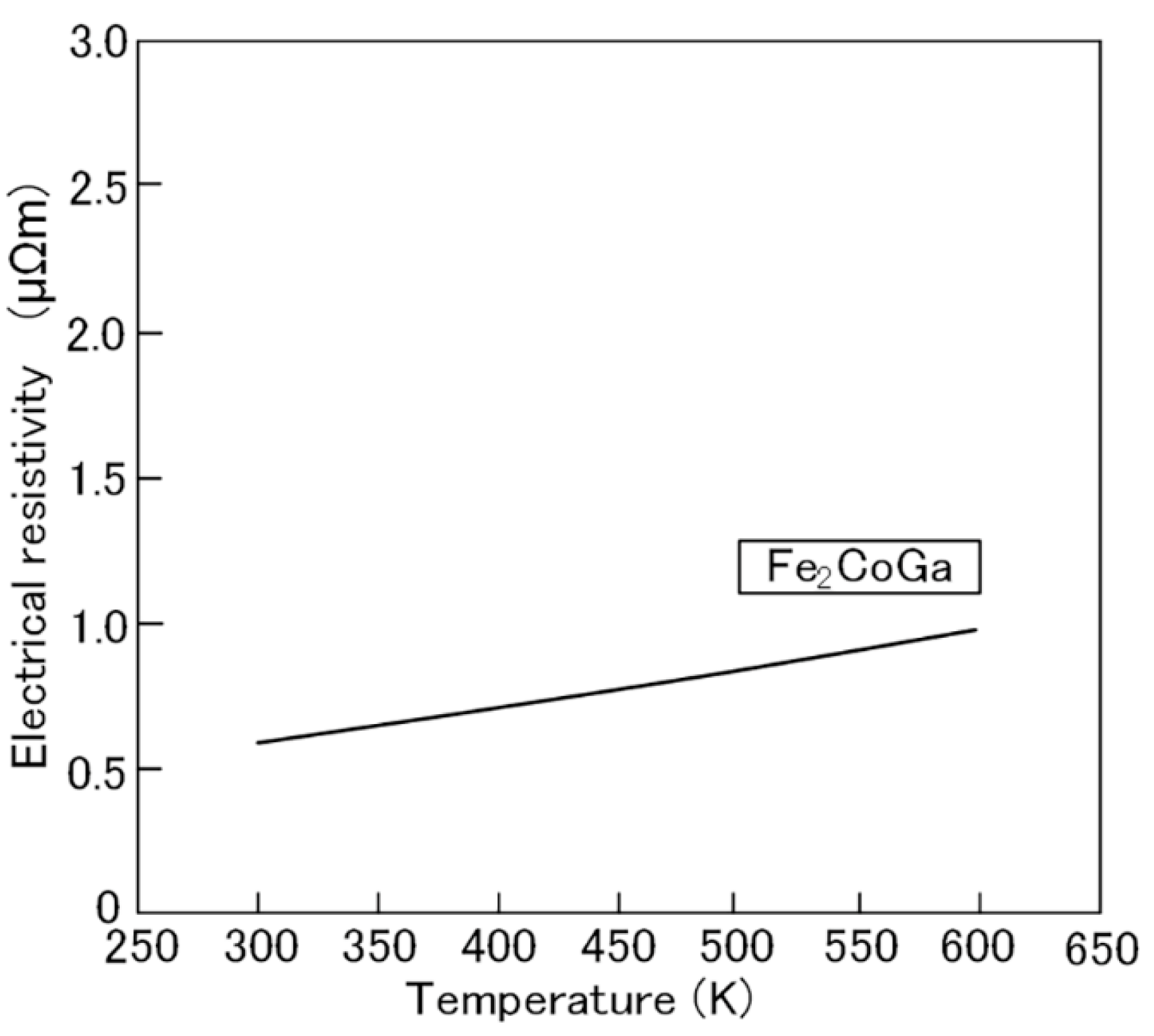
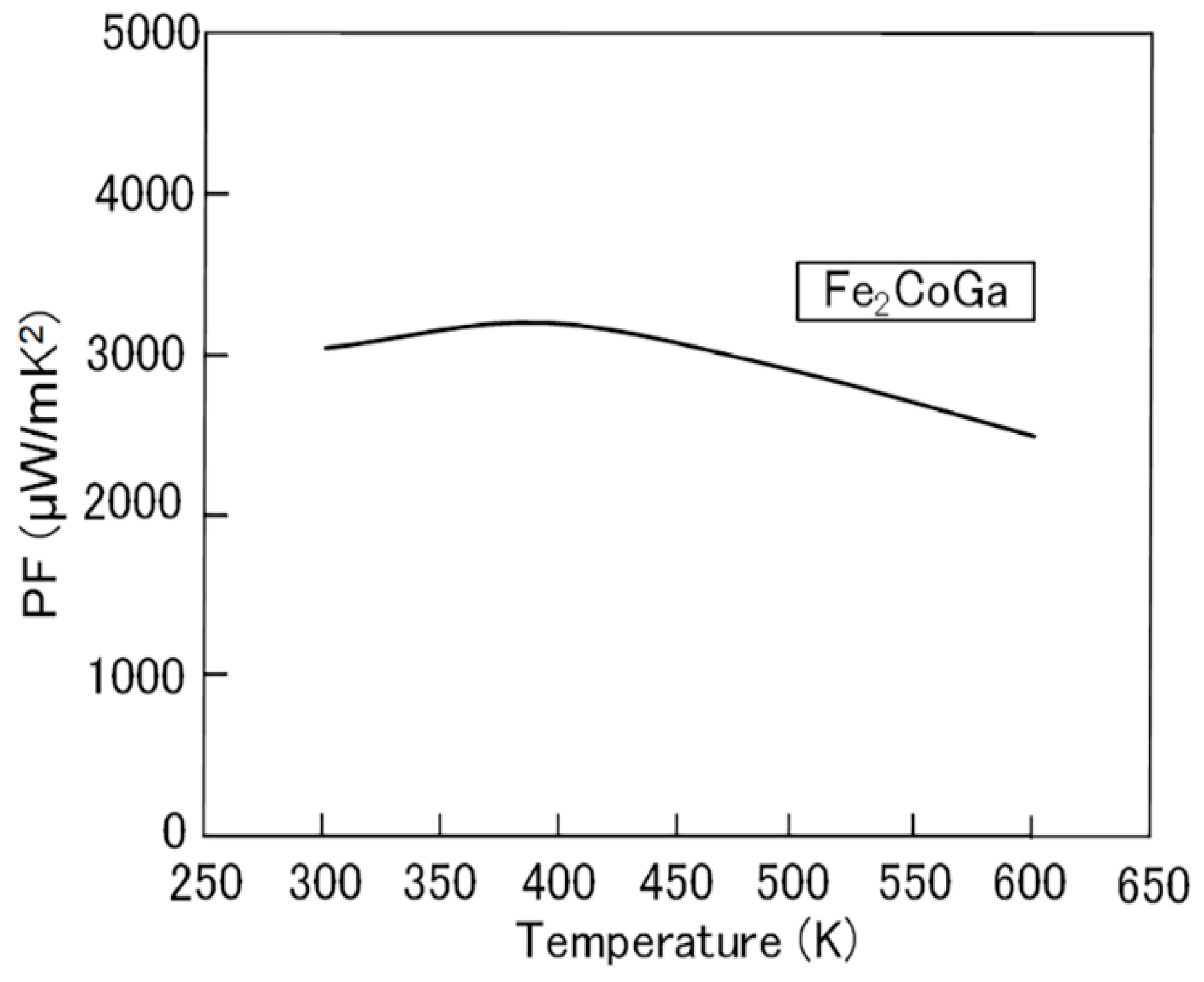
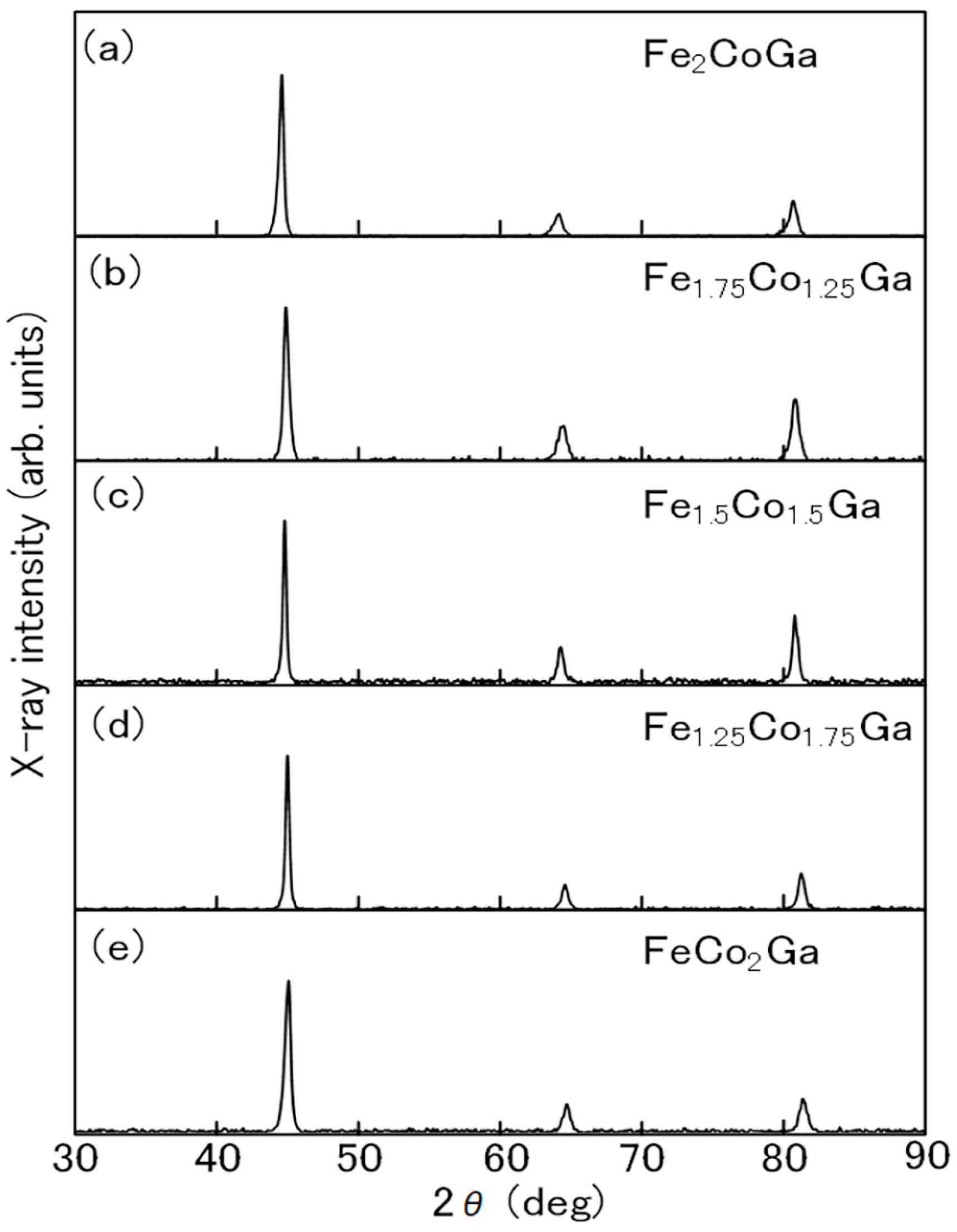
2.1. Fe2CoGa Heusler Compound
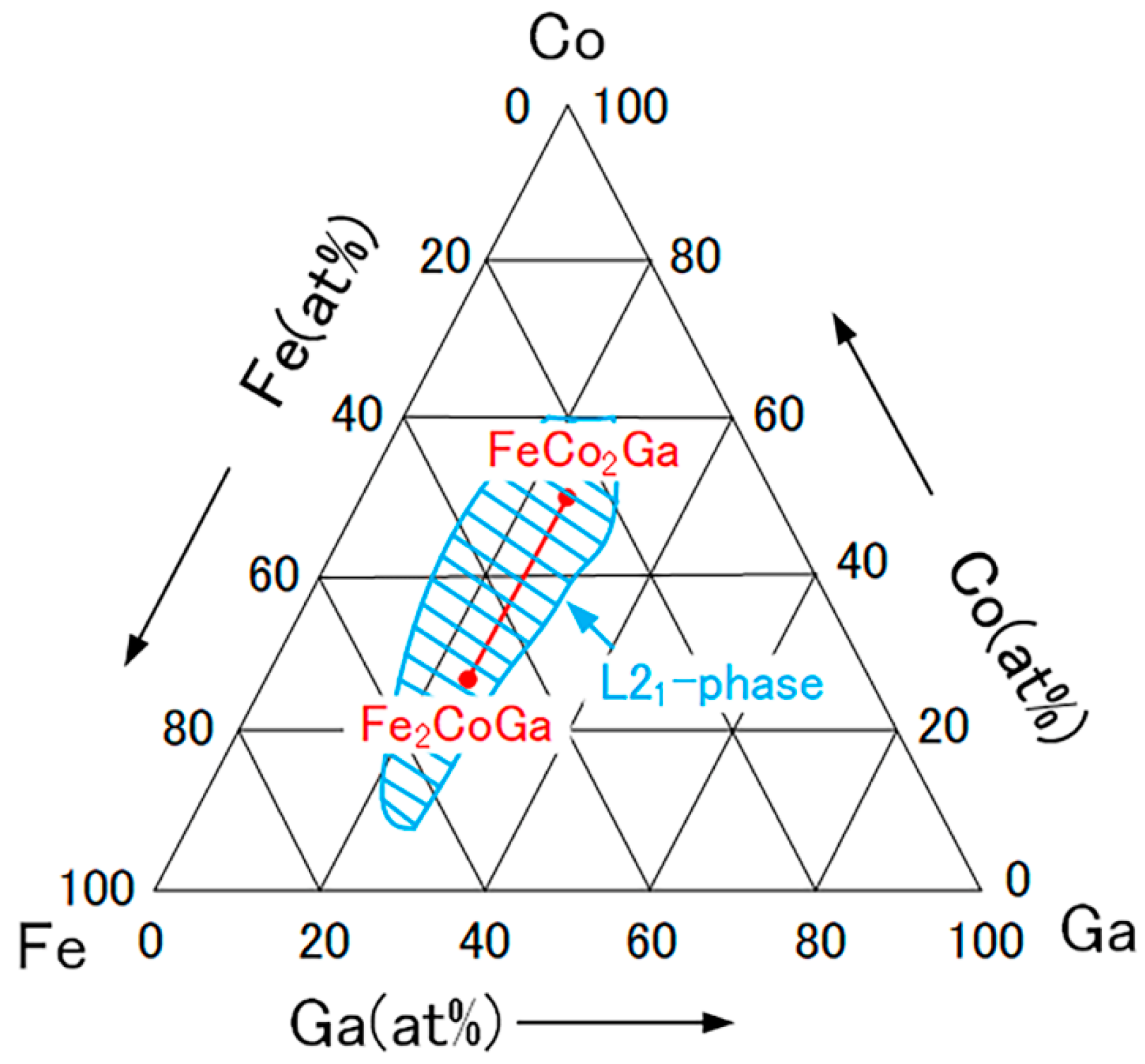
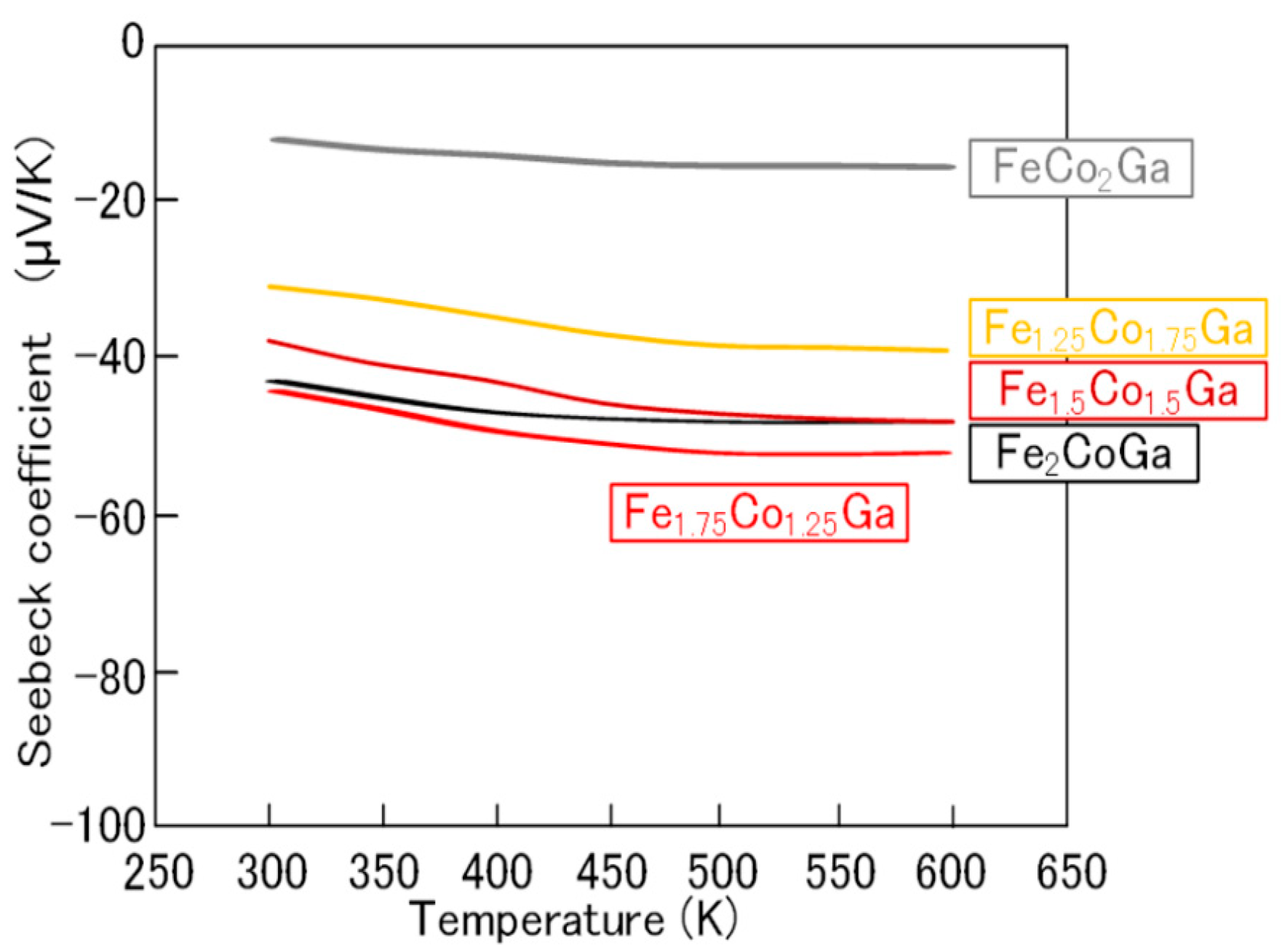
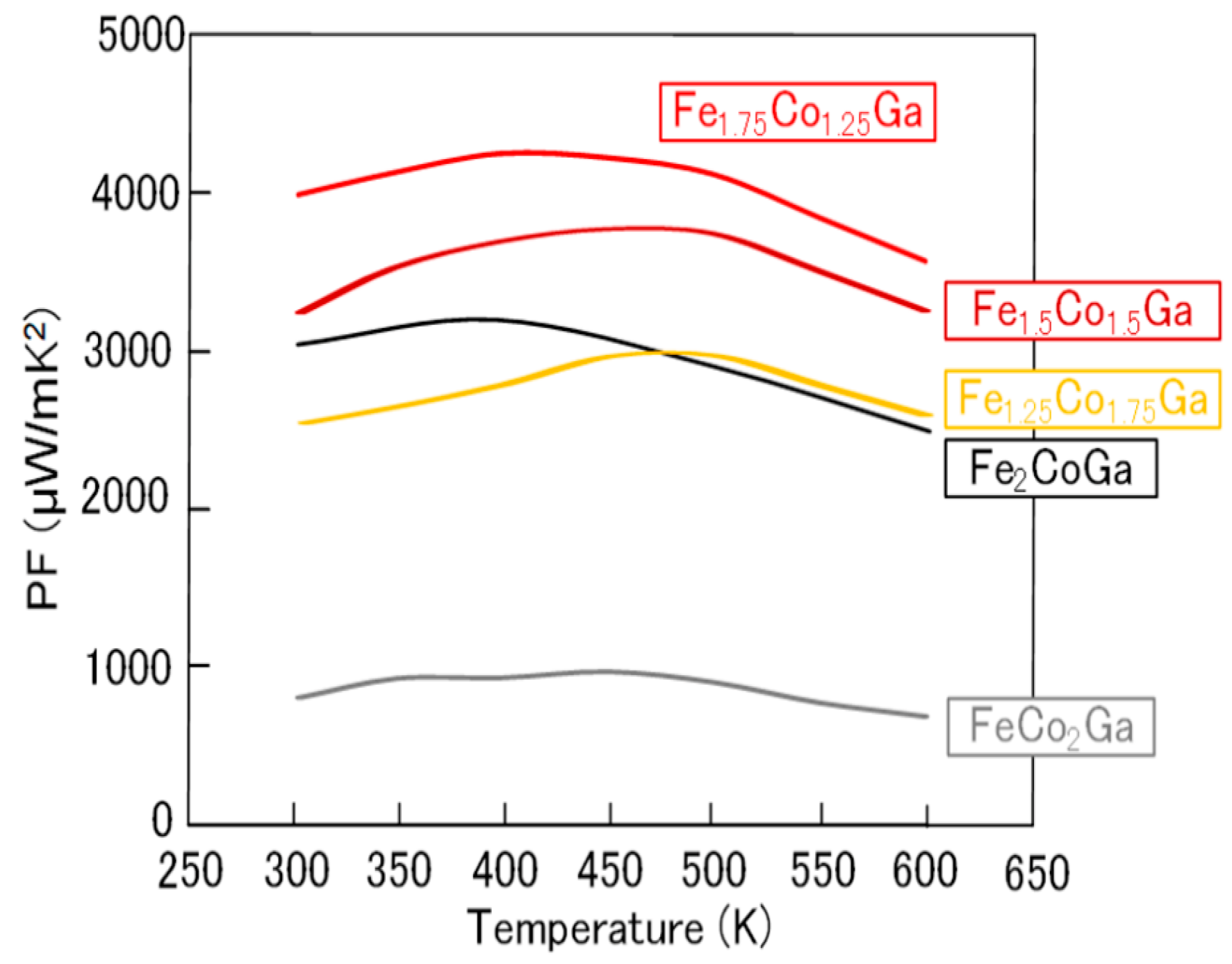
2.2. Fe2-xCo1+xGa (x = 0–1) Heusler Compounds
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sample Preparation
3.2. Characterization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, L.D. Thermoelectric materials: Energy conversion between heat and electricity. J. Materiomics 2015, 1, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouhara, H.; Olabi, A.G. Editorial: Industrial waste heat recovery. Energy 2018, 160, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brückner, S.; Liu, S.; Miró, L.; Radspieler, M.; Cabeza, L.F.; Lävemann, E. ndustrial waste heat recovery technologies: An economic analysis of heat transformation technologies. Appl. Energy 2015, 151, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, R.; Harvey, A.; Reay, D. A knowledge-based system for low-grade waste heat recovery in the process industries. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 94, 590–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Zheng, J.; Baleynaud, J.M.; Lu, J. Heat recovery potentials and technologies in industrial zones. J. Energy Inst. 2017, 90, 951–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouhara, H.; Khordehgah, N.; Almahmoud, S.; Delpech, B.; Chauhan, A.; Tassou, S.A. Waste Heat Recovery Technologies and Applications. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2018, 6, 268–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thermoelectric Devices Cool, Power Electrics. Available online: https://spinoff.nasa.gov/Spinoff2009/ip_4.html (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Savage, N. Thermoelectric coolers. Nat. Photonics 2009, 3, 541–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shehria, S.; Saberb, H.H. Experimental investigation of using thermoelectric cooling for computer chips. J. King Saud Univ.–Eng. Sci. 2019, 32, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsmid, H.J. Bismuth Telluride and Its Alloys as Materials for Thermoelectric Generation. Materials 2014, 7, 2577–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satterthwaite, C.B.; Ure, R.W., Jr. Electrical and Thermal Properties of Bi2Te3. Phys. Rev. 1957, 108, 1164–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosi, F.D.; Abeles, B.; Jensen, R.V. Materials for thermoelectric refrigeration. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1959, 10, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, H.; Sato, T.; Takahashi, K.; Nakatsukasa, K. The anisotropic powder metallurgy of n-type Bi2Te2.85Se0.15 thermoelectric material. J. Mater. Res. 1990, 5, 1052–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamur, H.; Bhuiyan, M.R.A.; Korkmaz, F.; Nil, M. A review on bismuth telluride (Bi2Te3) nanostructure for thermoelectric applications. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 4159–4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, M.P.; Stevenson, D.A.; Huggins, R.A. Self-diffusion of Pb and Te in lead telluride. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1971, 32, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ware, R.M.; McNeill, D.J. Iron disilicade as a thermoelectric generator material. Proc. Inst. Electr. Eng. 1964, 111, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaitsev, V.K.; Fedorov, M.I.; Gurieva, E.A.; Eremin, I.S.; Konstantinov, P.P.; Samunin, A.Y.; Vedernikov, M.V. Highly effective Mg2Si1−xSnx thermoelectrics. Phys. Rev. B 2006, 74, 045207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogl, G.; Rogl, P. Skutterudites, a most promising group of thermoelectric materials. Curr. Opin. Green Sustainable Chem. 2017, 4, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanada, Y.; Suzuki, R.O.; Ono, K. Seebeck coefficient of (Fe,V) Al alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2001, 329, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkholz, U.; Schelm, J. Electrical Investigation of the Semiconductor-to-Metal Transition in FeSi2. Phys. Stat. Sol. B 1969, 34, K177–K180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, I. Study of Semiconductor-to-Metal Transition in Mn-Doped FeSi2. Phys. Rev. B 1973, 7, 2710–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piton, J.P.; Fay, M.F. Phase changes in iron–silicon alloys around the composition FeSi2. Acad. C. R. Sci. 1968, C266, 514–516. [Google Scholar]
- Kojima, T. Semiconducting and Thermoelectric Properties of Sintered Iron Disilicide. Phys. Stat. Sol. A 1989, 111, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, Y.; Miura, S.; Mishima, Y. Thermoelectric semiconductor iron disilicides produced by sintering elemental powders. Intermetallics 1999, 7, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dąbrowski, F.; Ciupiński, Ł.; Zdunek, J.; Kruszewski, J.; Zybała, R.; Michalski, A.; Kurzydłowski, K.J. Microstructure and thermoelectric properties of p and n type doped β-FeSi2 fabricated by mechanical alloying and pulse plasma sintering. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 8, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Asakawa, R. Production of (Fe,Co)Si2 and (Fe.Mn)Si2 thermoelectric materials by spark plasma sintering. Crystals 2023, 14, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buschow, K.H.J.; van Engen, P.G. Magnetic and magneto-optical properties of heusler alloys based on aluminum and gallium. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1981, 25, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuszýnski, M.; Zarek, W.; Popiel, E.S. Magnetic properties of atomically disordered Fe3-xVxAl alloys with x≦0. Hyperfine Interact. 1990, 59, 369–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graf, T.; Felser, C.; Parkin, S.S.P. Simple rules for the understanding of Heusler compounds. Prog. Solid State Chem. 2011, 39, 1–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmstrøm, C.J. Heusler compounds and spintronics. Prog. Cryst. Growth Charact. Mater. 2016, 62, 371–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullakko, K.; Huang, J.K.; Kantner, C.; O’Handley, R.C. Large magnetic-field-induced strains in Ni2MnGa single crystals. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1996, 69, 1966–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kainuma, R.; Imano, Y.; Ito, W.; Sutou, Y.; Morito, H.; Okamoto, S.; Kitakami, O.; Oikawa, K.; Fujita, A.; Kanomata, T.; et al. Magnetic-field-induced shape recovery by reverse phase transformation. Nature 2006, 439, 957–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishino, Y.; Kato, M.; Asano, S.; Soda, K.; Hayasaki, M.; Miuztani, U. Semiconductorlike Behavior of Electrical Resistivity in Heusler-type Fe2VAl Compound. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 79, 1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Hamane, D.N. Magnetic and thermoelectric properties of melt-spun ribbons of Fe2XAl (X = Co, Ni) Heusler compounds. J. Appl. Phys. 2018, 124, 075105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, R.O.; Kyono, T. Thermoelectric properties of Fe2TiAl Heusler alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2004, 377, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabuuchi, S.; Okamoto, M.; Nishide, A.; Kurosaki, Y.; Hayakawa, J. Large Seebeck coefficients of Fe2TiSn and Fe2TiSi: Fisrt-Principles study. Appl. Phys. Express 2013, 6, 022504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, T.; Kamishima, S. Magnetic and thermoelectric properties of Fe-Ti-Sn Heusler alloys. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2019, 55, 2900104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, K.; Mori, A.; Yamada, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Miyazaki, H.; Nishino, Y. Thermoelectric properties of the Heusler-type Fe2VTaxAl1-x. J. Appl. Phys. 2014, 115, 033707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Cao, Y.; Tao, Q.; Yan, Y.; Su, X.; Tang, X. Distinct role of Sn and Ge doping on thermoelectric properties in p-type (Bi, Sb)2Te3-alloys. J. Solid State Chem. 2020, 292, 121722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaggi, N.K.; Rao, K.R.P.M.; Grover, A.K.; Gupta, L.C.; Vijayaraghanvan, R.; Khoi, L.D. Mössbauer and NMR study of site preference and local environment effects in Co2FeGa & Fe2CoGa. Hyperfine Interact 1978, 4, 402–406. [Google Scholar]
- Ducher, R.; Kainuma, R.; Ohnuma, I.; Ishida, K. Phase equilibria and stability of B2 and L21 ordered phases in the Co-Fe-Ga Hequsler alloy system. J. Alloys Compd. 2007, 437, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Gasper, F.; Gasi, T.; Ksenofontov, V.; Balke, B.; Fecher, G.H.; Felser, C.; Hwu, Y.K.; Lee, J.J. Structural and magnetic properties of Fe2CoGa Heusler nanoparticles. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2012, 45, 295001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastave, M.; Sahariah, M.B.; Srinivasan, A. Size-dependent properties of single domain Fe2CoGa nanoparticles prepared by a facile template-less chemical route. J. Mater. Chem. C 2022, 10, 11946–11958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mende, F.; Noky, J.; Guin, S.N.; Fecher, G.H.; Manna, K.; Adler, P.; Schnelle, W.; Sun, Y.; Fu, C.; Felser, C. Large anomalous Hall and Nernst effects in high curie temperature iron-based Heusler compounds. Adv. Sci. 2021, 2, 100782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, H.; Ide, N.; Nishino, Y. Thermoelectric Properties of P-Type Heusler Compounds (Fe2-xCox)(V1-yTiy)Al. Mater. Trans. 2008, 49, 1858–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Zhang, W.; Chen, L. Thermoelectric properties of (Fe1−xCox)2VAl Heusler-type compounds. J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 484, 812–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, V. Co-Fe-Ga(Cobalt-Iron-Gallium). J. Phase Equilibria Diffus. 2008, 29, 438–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikazumi, S.; Charap, S.H. Physics of Magnetism; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1964; pp. 72–73. [Google Scholar]
- Cullity, B.D.; Graham, C.D. Introduction to Magnetic Materials; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; p. 466. [Google Scholar]
- Shibata, T.; Arai, S. Magnetic properties and crystal structures of Nd-Fe-Co-B system permanent magnets. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1985, TJMJ-1, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saito, T.; Watanabe, H. Magnetic and Thermoelectric Properties of Fe2CoGa Heusler Compounds. Inorganics 2025, 13, 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13020033
Saito T, Watanabe H. Magnetic and Thermoelectric Properties of Fe2CoGa Heusler Compounds. Inorganics. 2025; 13(2):33. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13020033
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaito, Tetsuji, and Hayai Watanabe. 2025. "Magnetic and Thermoelectric Properties of Fe2CoGa Heusler Compounds" Inorganics 13, no. 2: 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13020033
APA StyleSaito, T., & Watanabe, H. (2025). Magnetic and Thermoelectric Properties of Fe2CoGa Heusler Compounds. Inorganics, 13(2), 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics13020033





