Ruthenium-Based Sensors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Ruthenium-Based Sensors
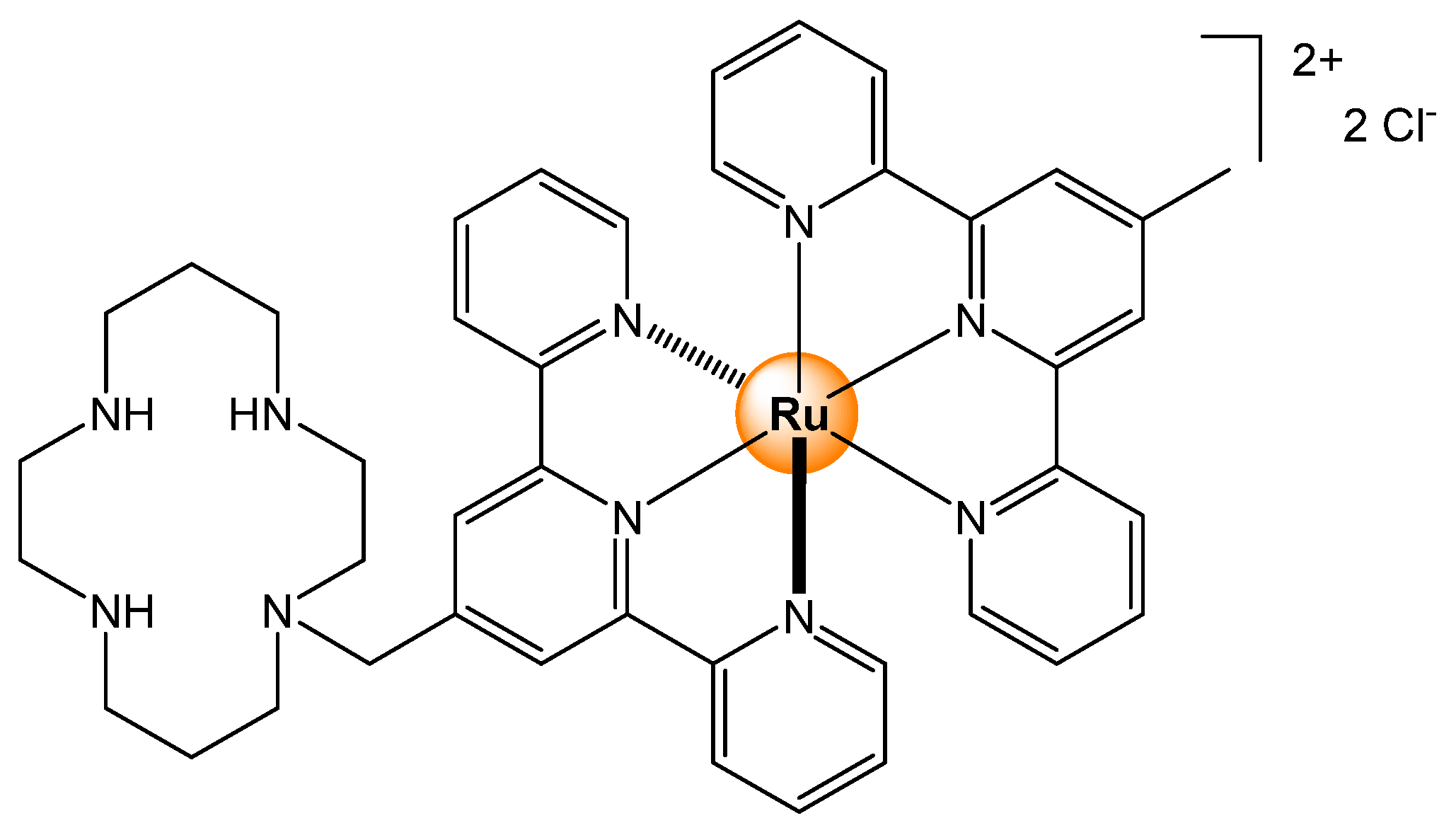
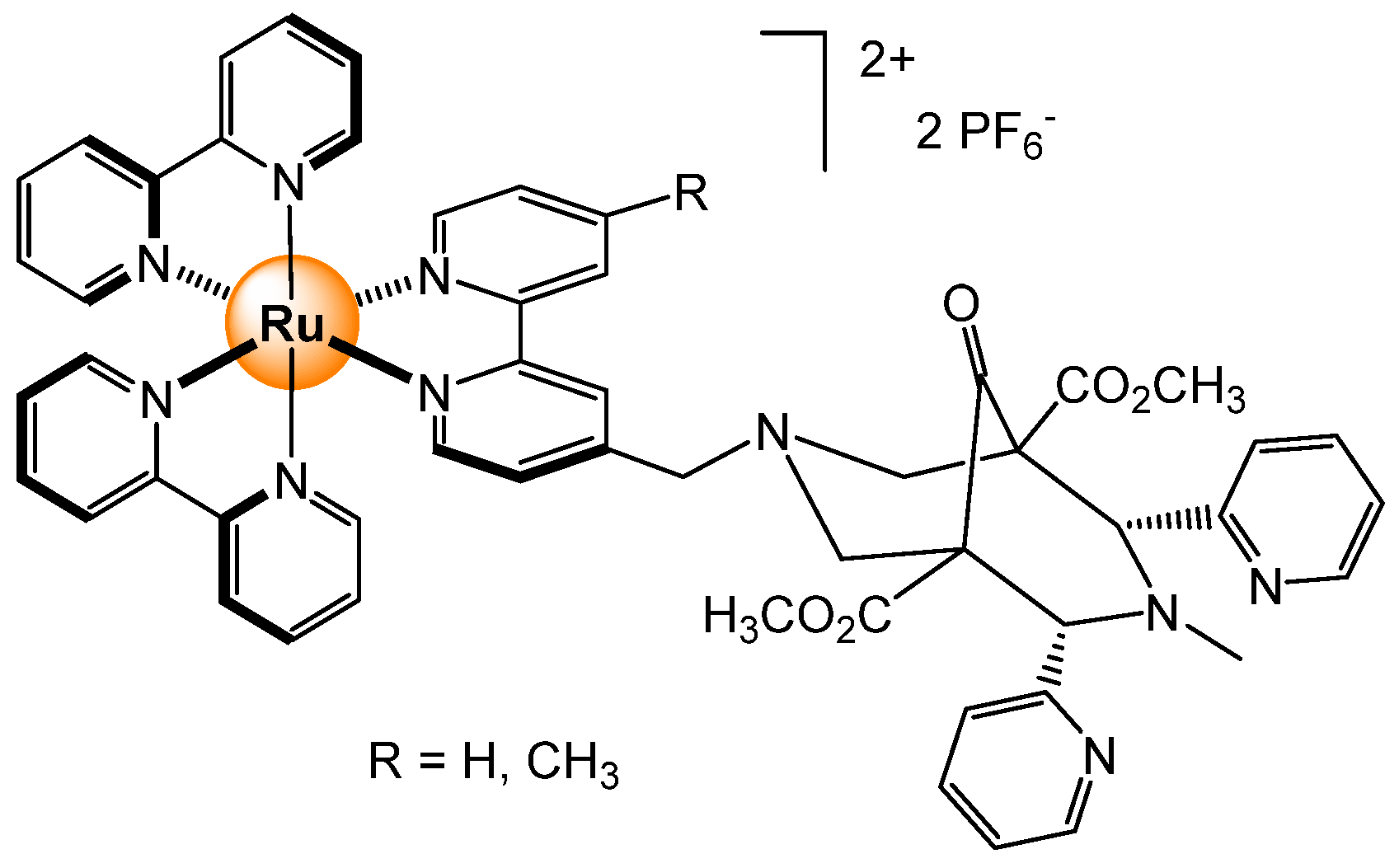
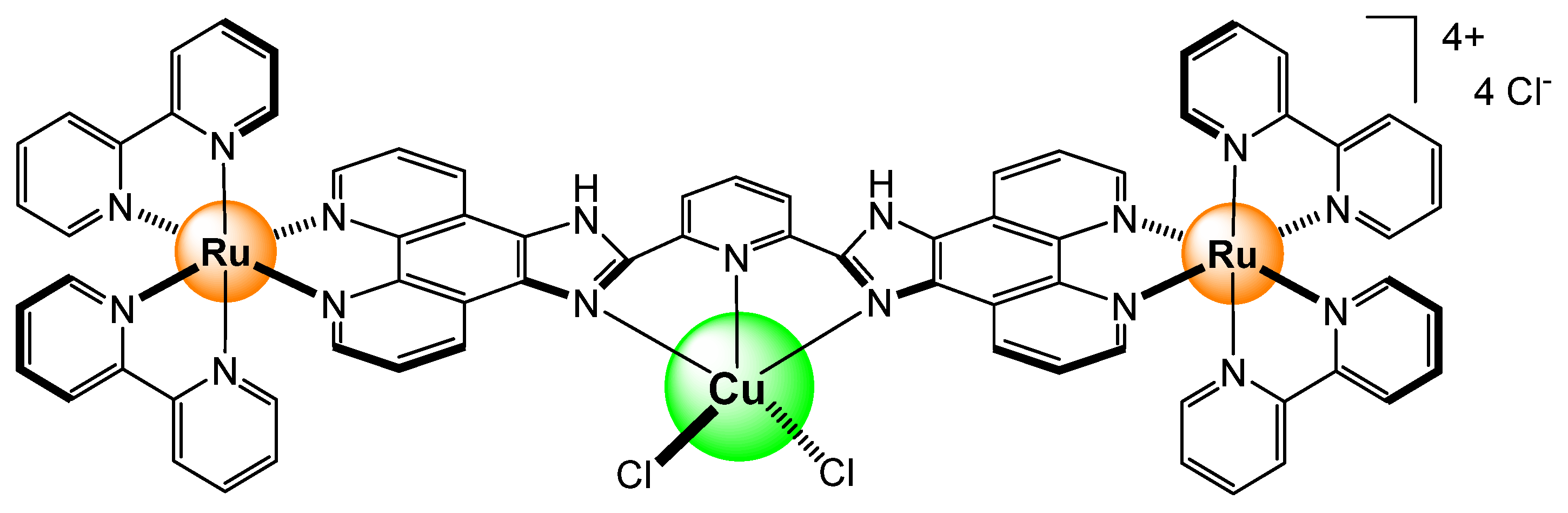
2.1. Cations
2.2. Anions
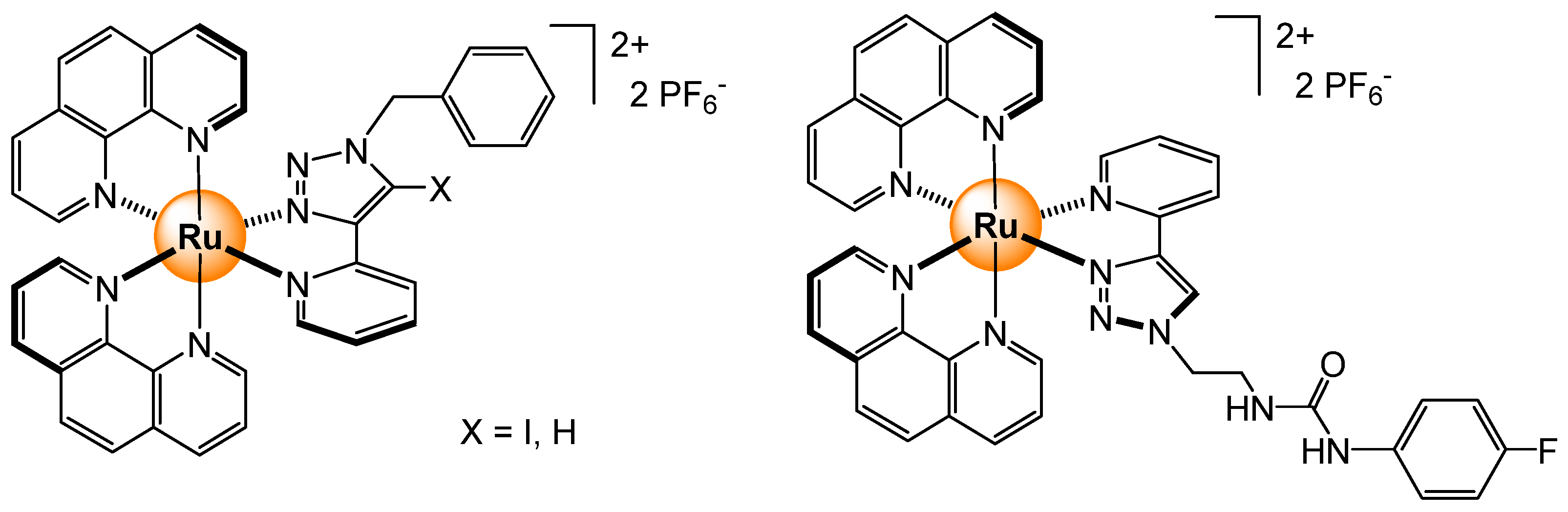
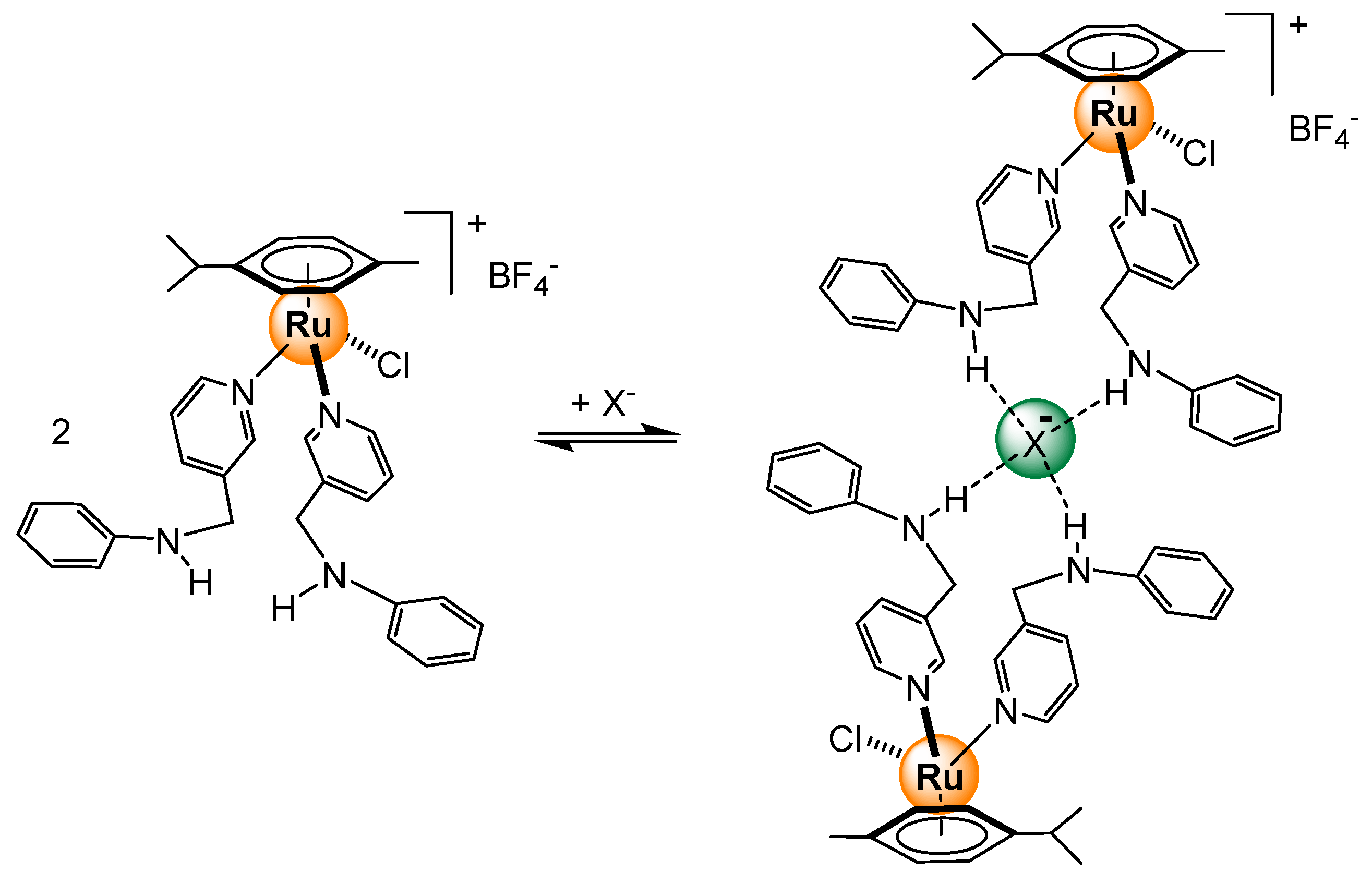
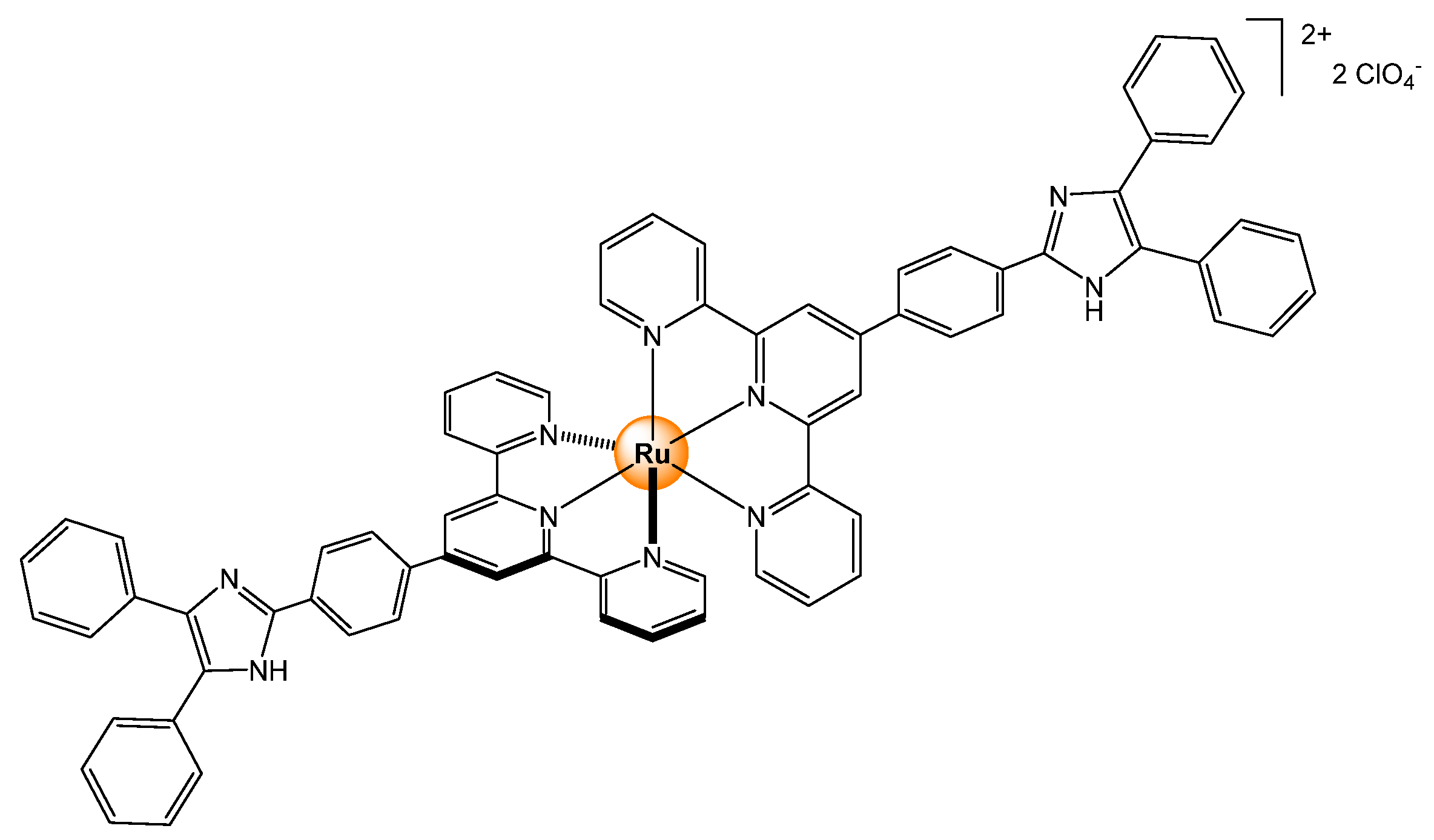
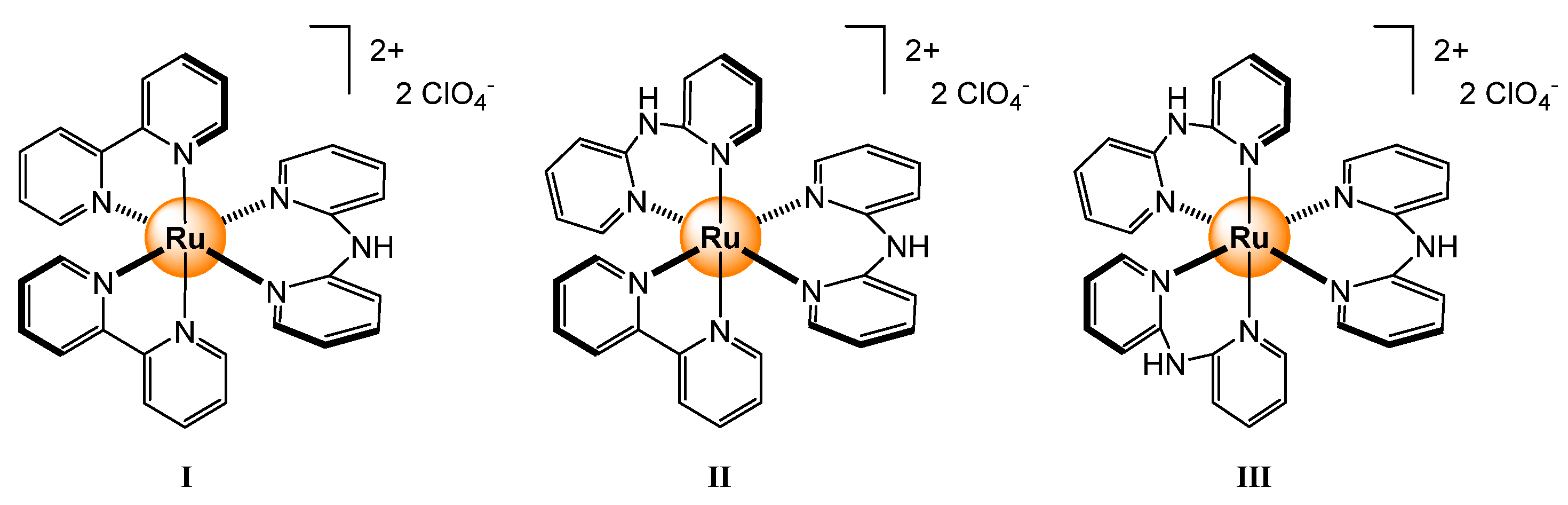
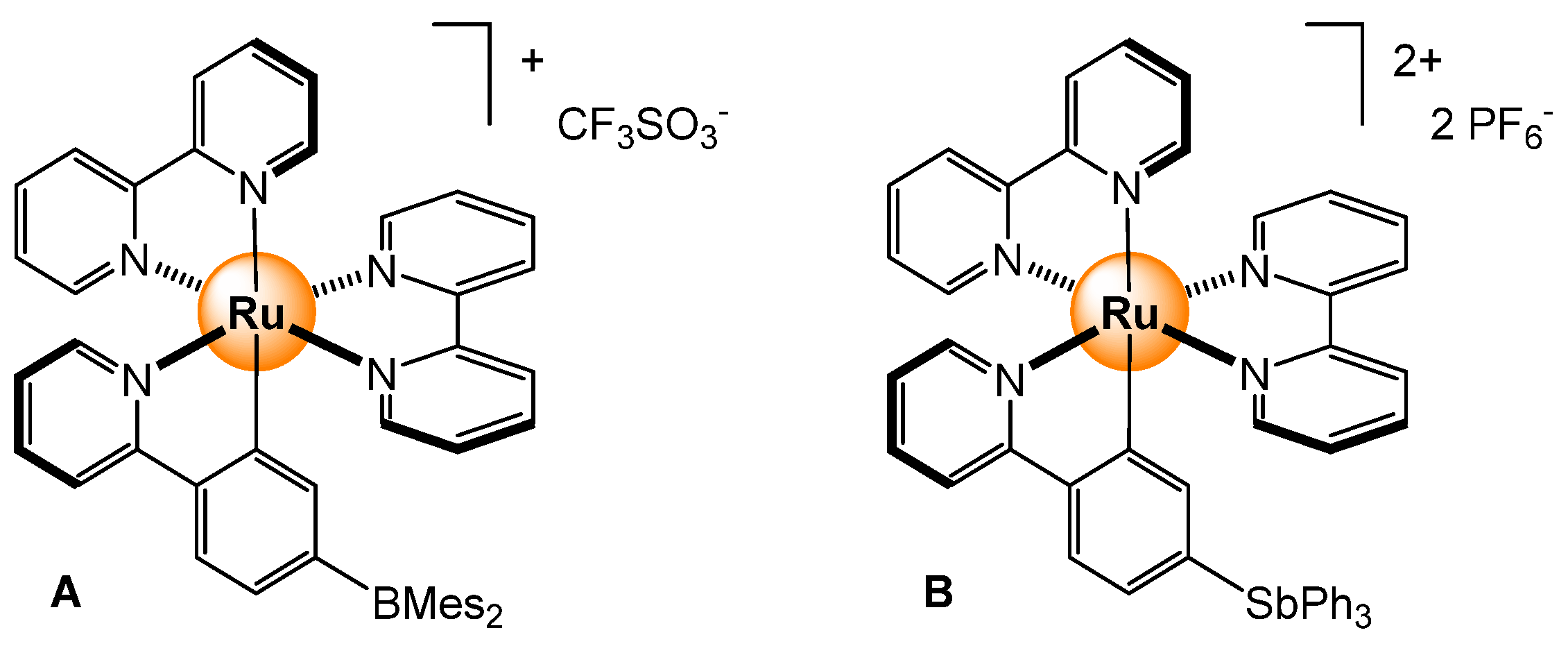
2.2.1. Halides and Small Anions
2.2.2. Phosphates
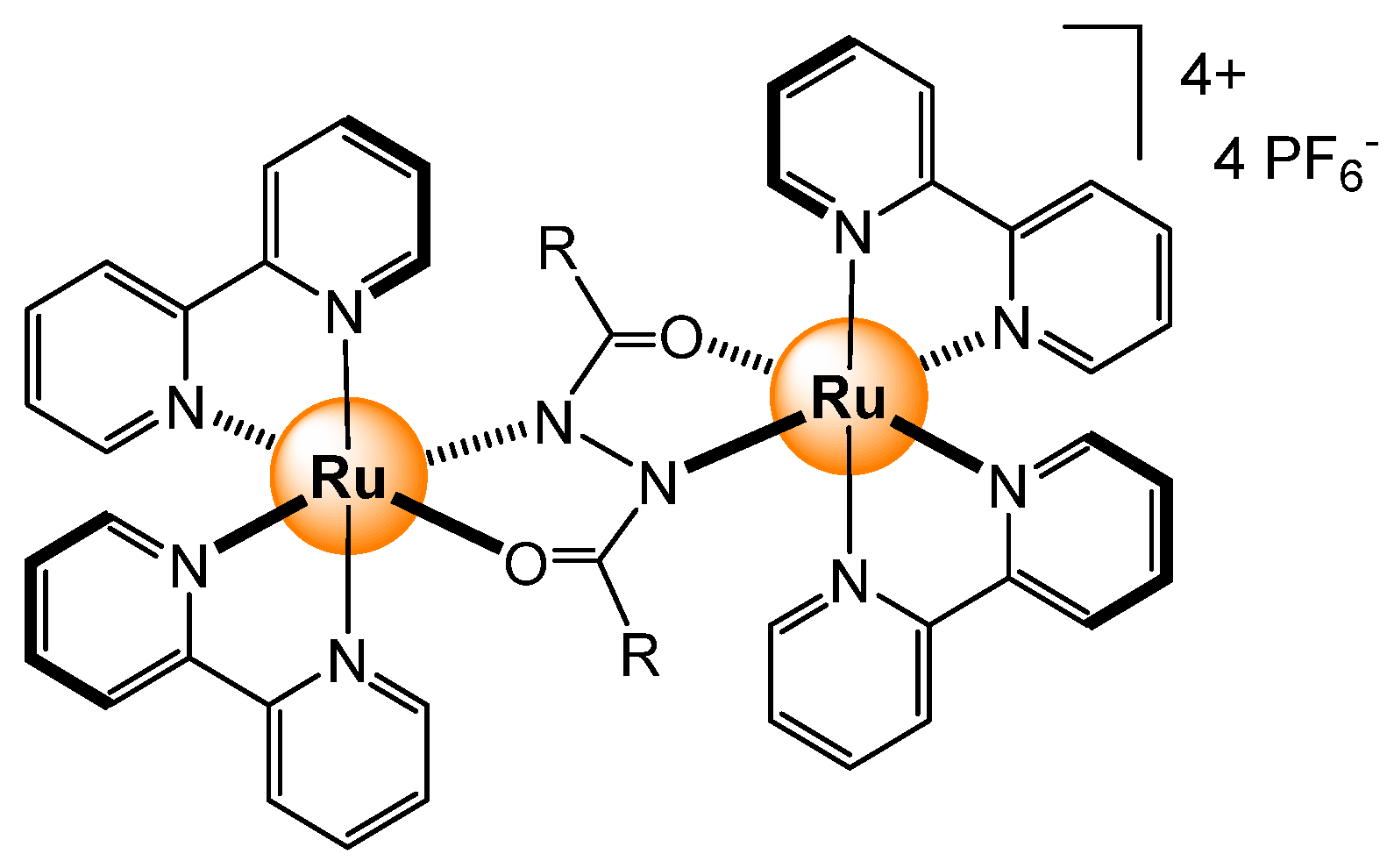
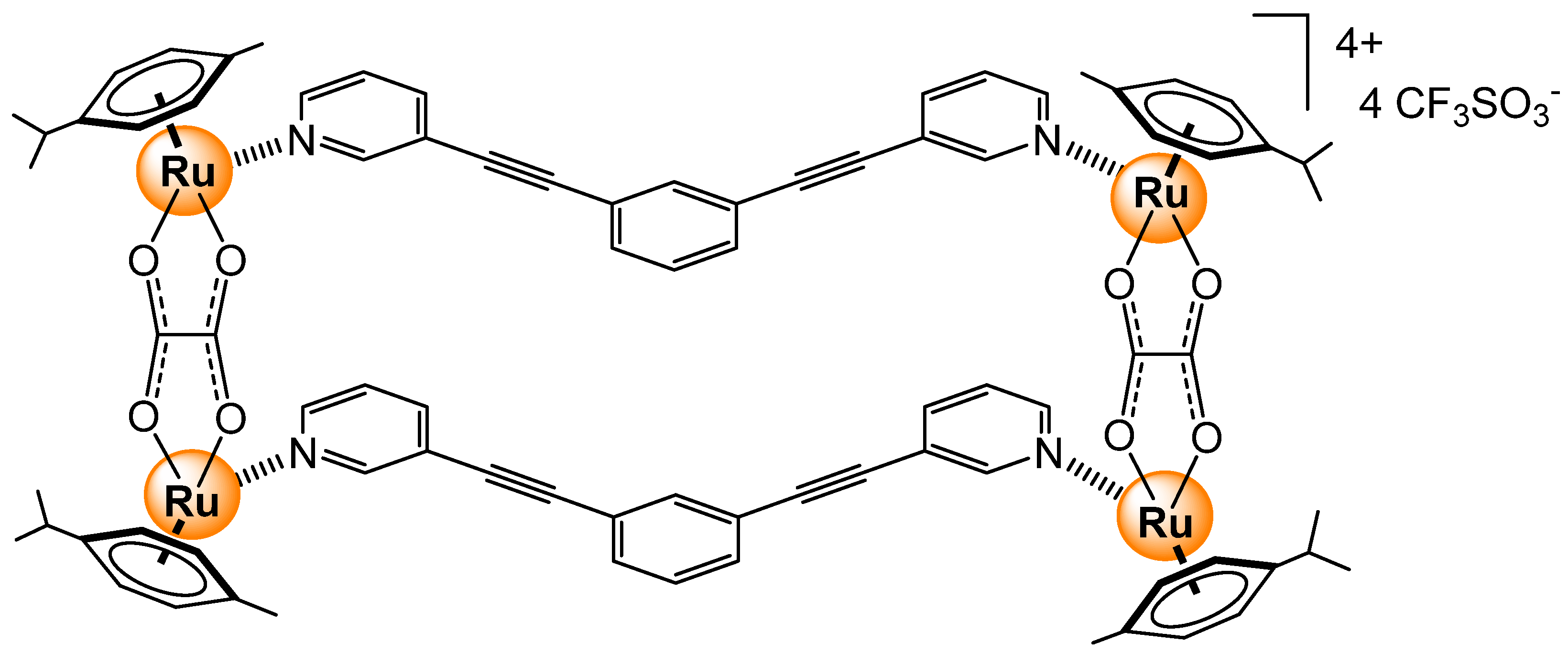
2.2.3. Carboxylates
2.2.4. Others
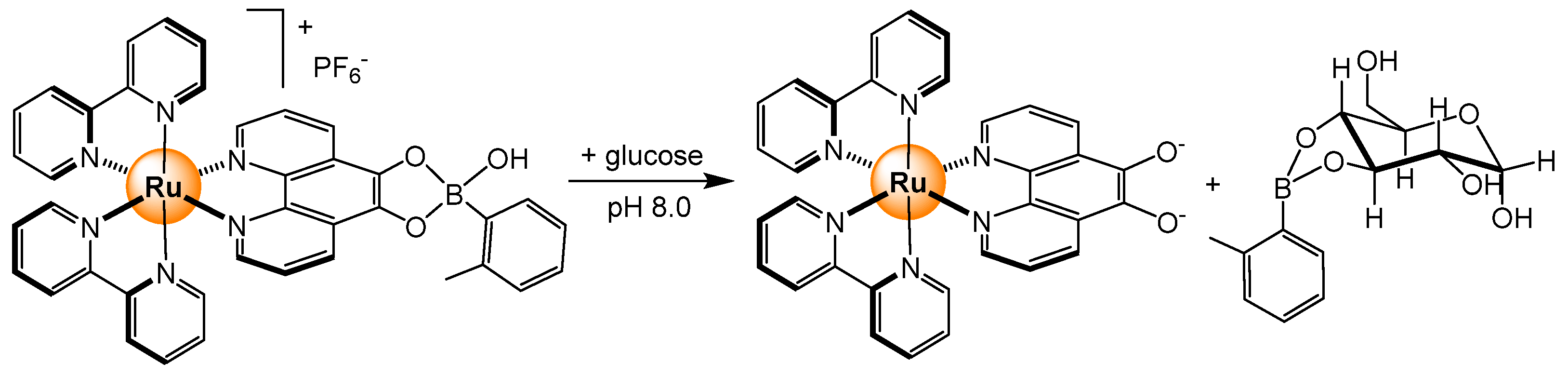
2.3. Carbohydrates
2.4. Biomolecules
2.4.1. Proteins
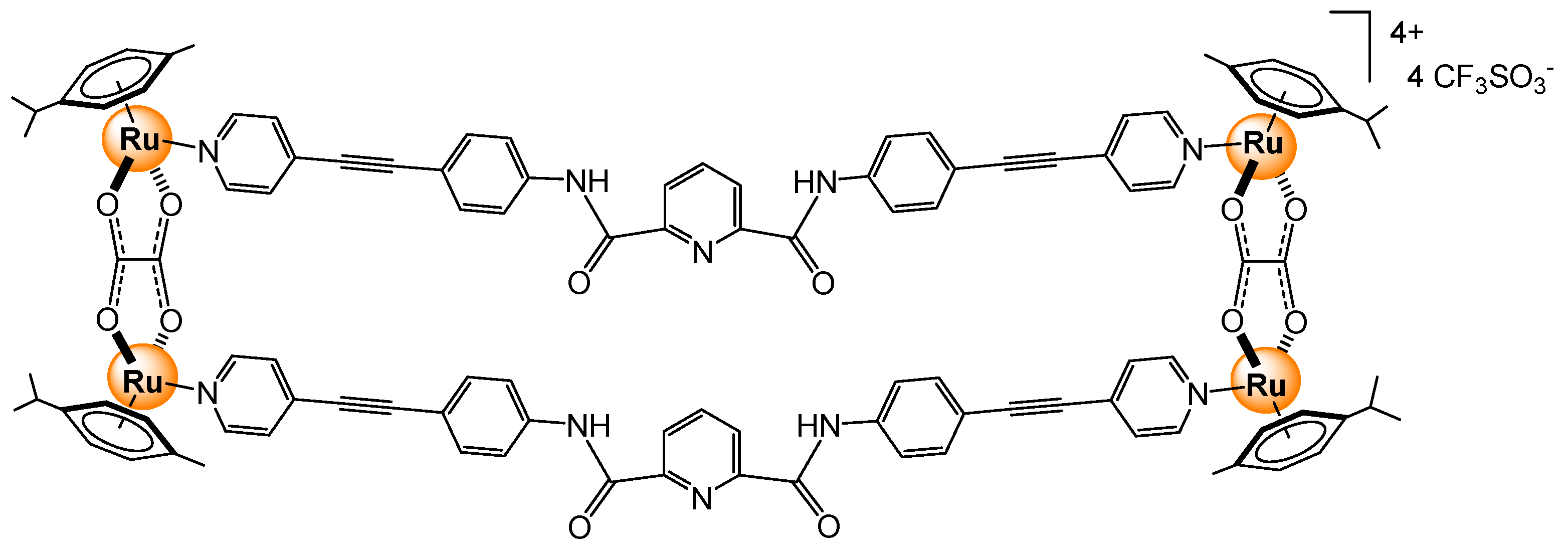
2.4.2. DNA/RNA
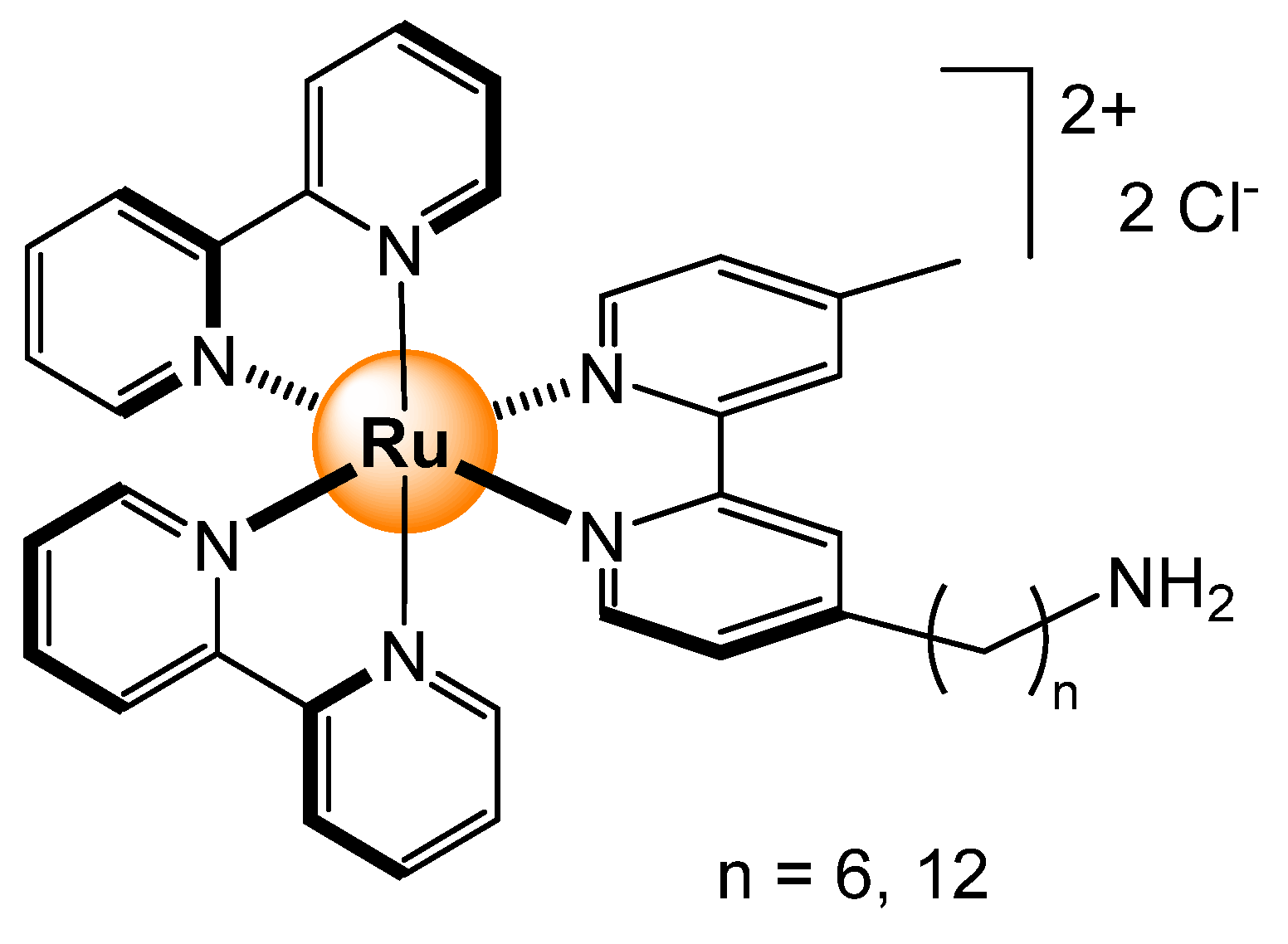
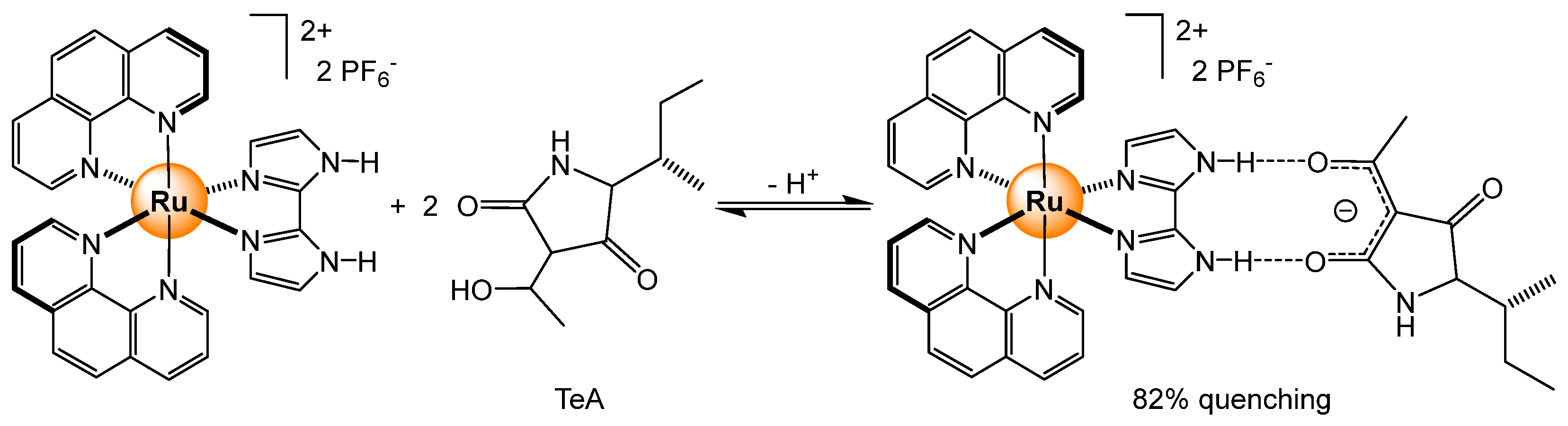
2.4.3. Primary and Secondary Metabolites
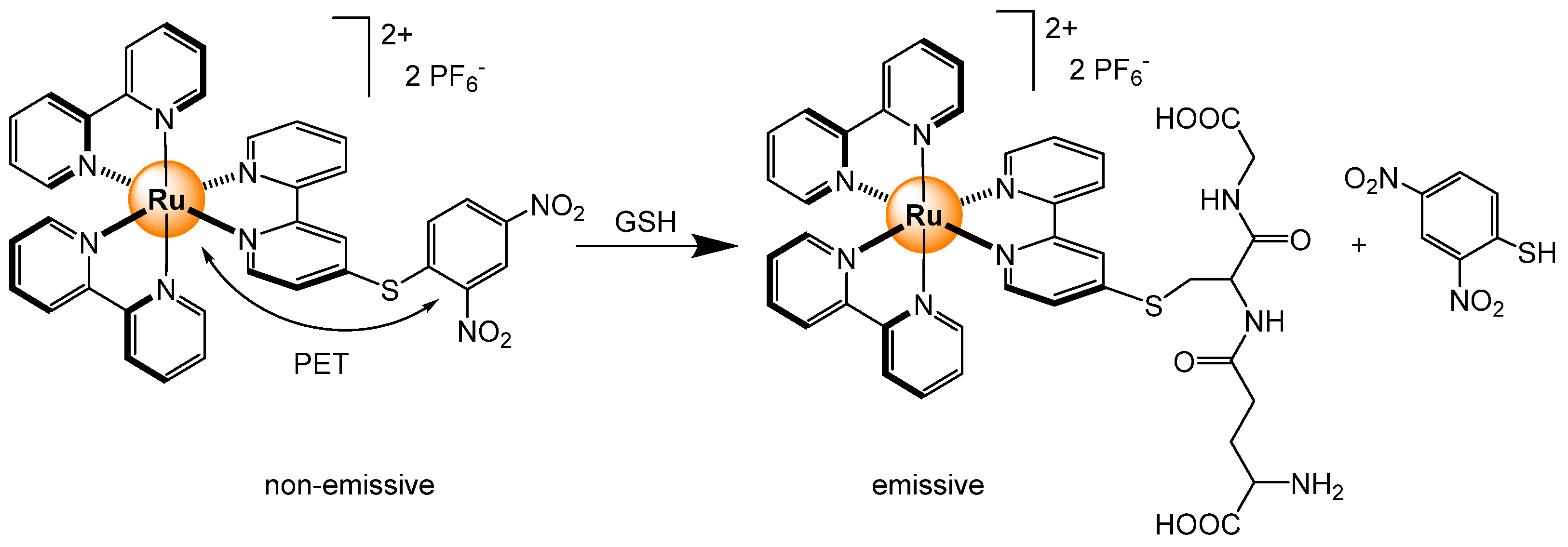
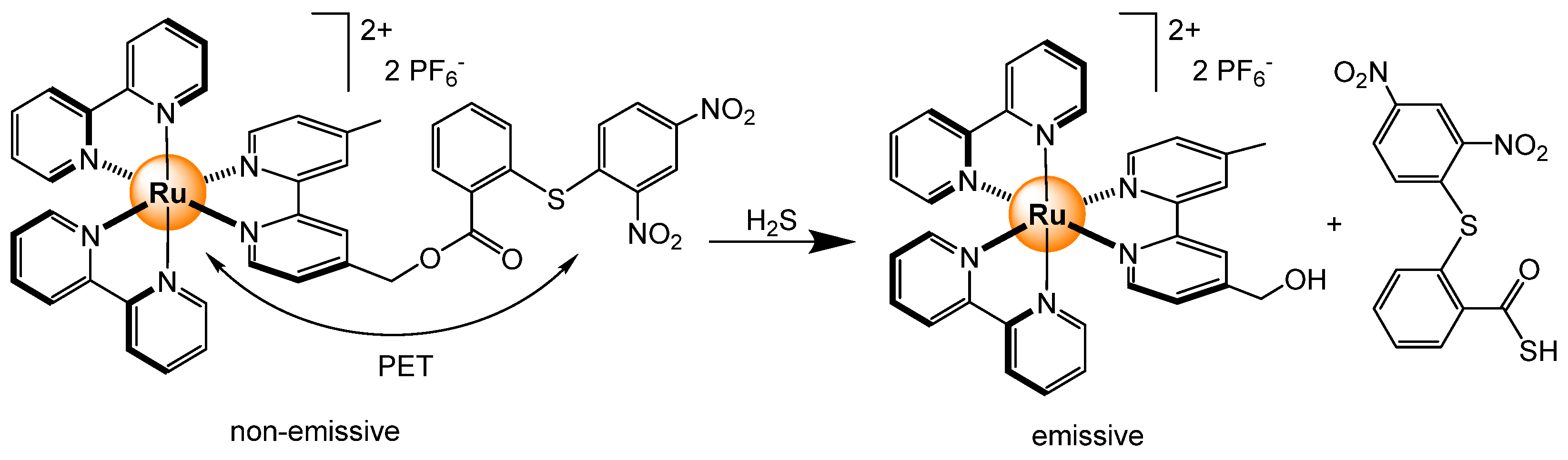
2.4.4. Biothiols
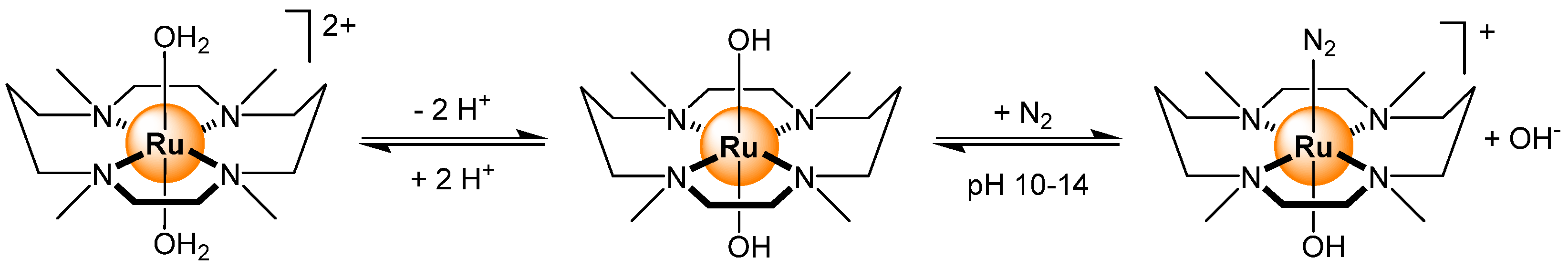
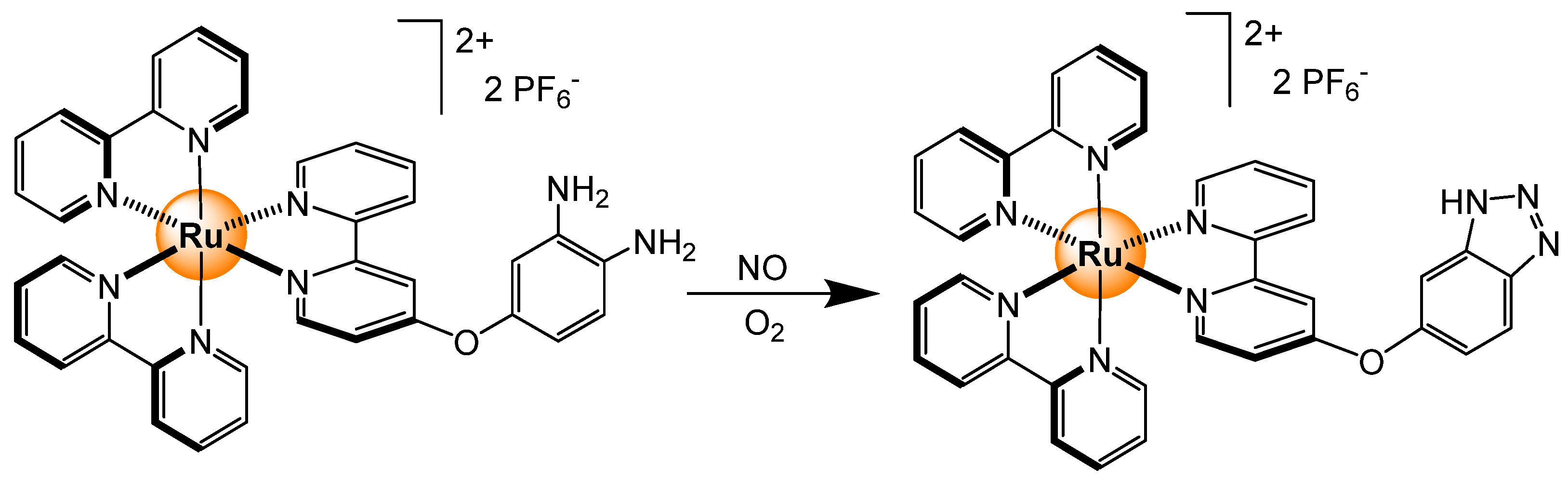
2.5. Gases
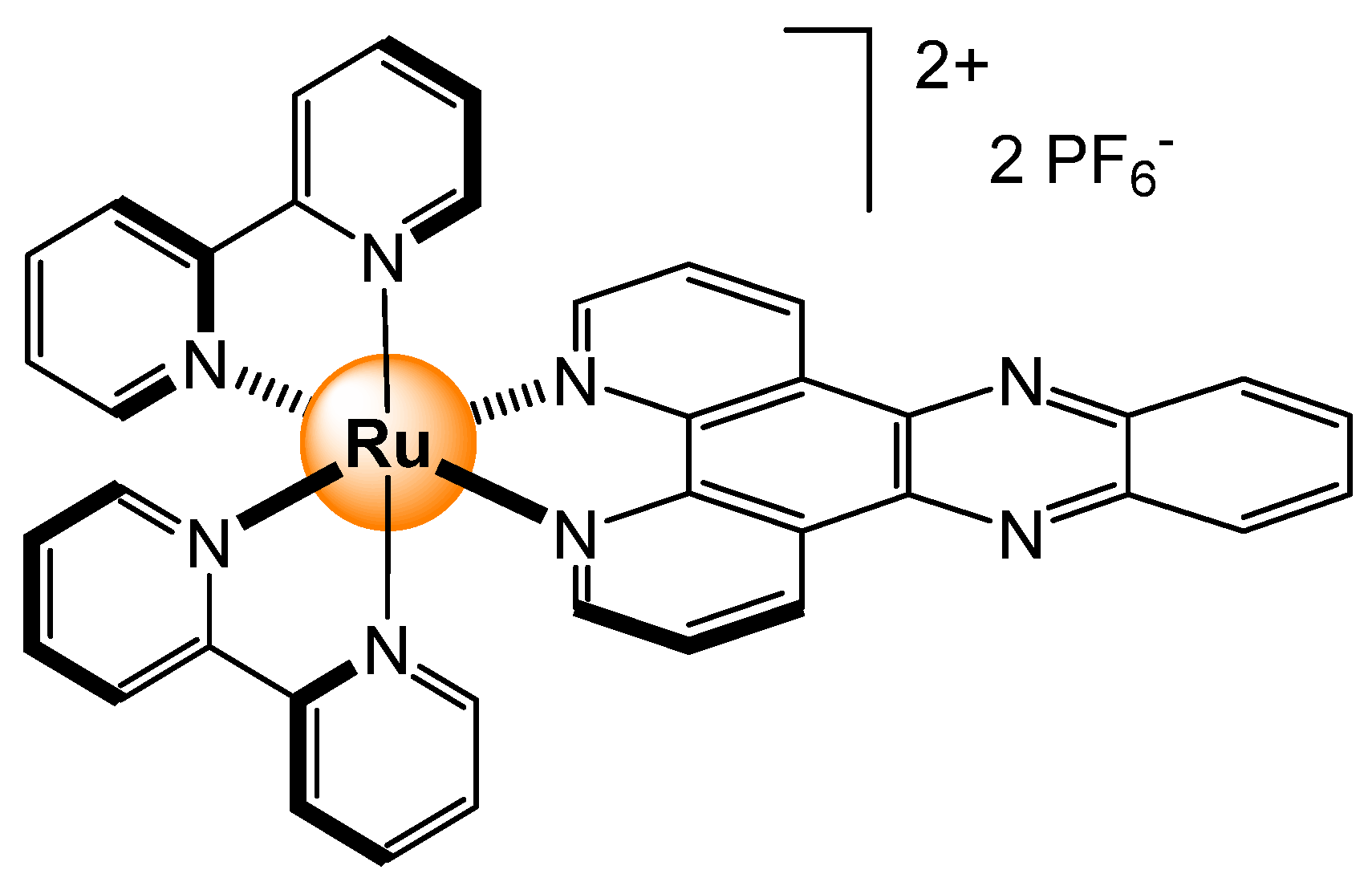
2.6. Explosives-Pollutants
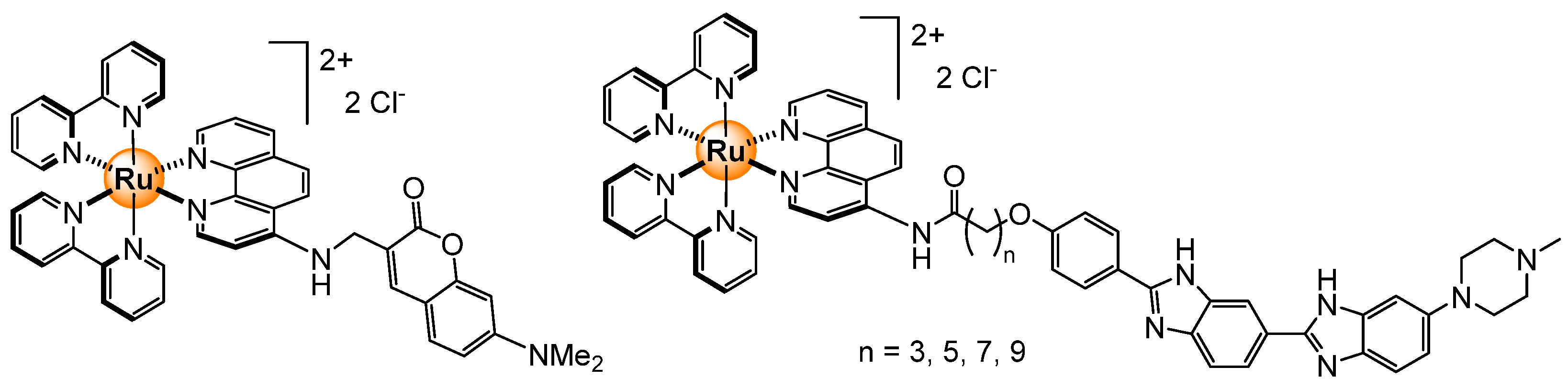
2.7. Miscellaneous
3. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Higgins, S. Regarding ruthenium. Nat. Chem. 2010, 2, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thévenot, D.R.; Toth, K.; Durst, R.A.; Wilson, G.S. Electrochemical biosensors: Recommended definitions and classification. Pure Appl. Chem. 1999, 71, 2333–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevino, K.M.; Wagner, C.R.; Tamura, E.K.; Garcia, J.; Louie, A.Y. Small molecule sensors for the colorimetric detection of Copper(II): A review of the literature from 2010–2022. Dye. Pigment. 2023, 214, 110881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
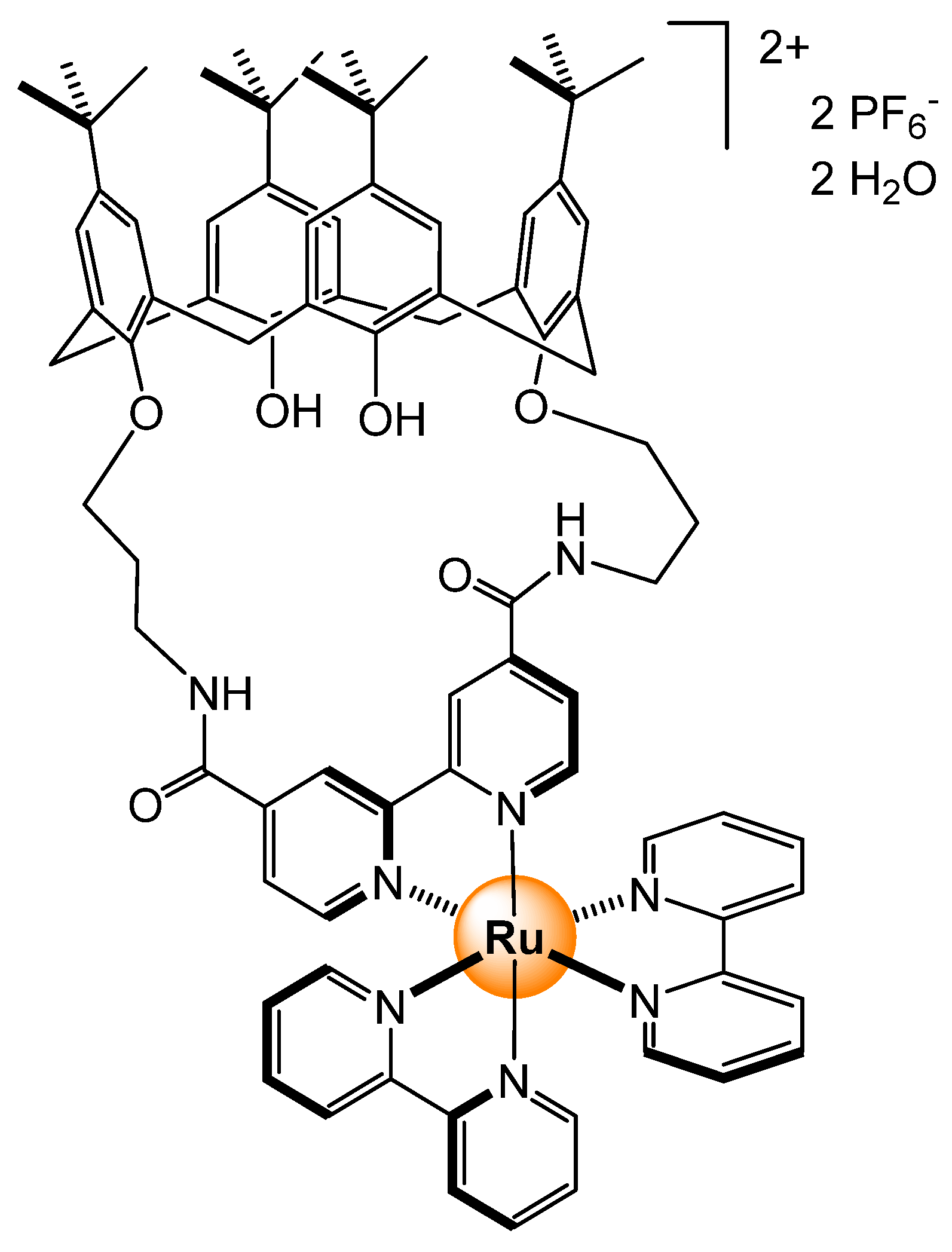
- Padilla-Tosta, M.E.; Lloris, J.M.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Benito, A.; Soto, J.; Pardo, T.; Miranda, M.A.; Marcos, M.D. Bis(terpyridyl)-Ruthenium(II) Units Attached to Polyazacycloalkanes as Sensing Fluorescent Receptors for Transition Metal Ions. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2000, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busche, C.; Comba, P.; Mayboroda, A.; Wadepohl, H. Novel RuII Complexes with Bispidine-Based Bridging Ligands: Luminescence Sensing and Photocatalytic Properties. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 1295–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Pei, L.; Chen, Y.; Xu, W.; Lin, Q.; Wang, J.; Wu, J.; Shen, Y.; Ji, L.; Chao, H. A Dinuclear Ruthenium(II) Complex as a One- and Two-Photon Luminescent Probe for Biological Cu2+ Detection. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 15494–15503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.-B.; Kang, S.-Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, N.; Yi, X.; Wang, K.-Z. pH and copper ion luminescence on/off sensing by a dipyrazinylpyridine-appended ruthenium complex. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 221, 614–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.-Y.; Yao, C.-J.; Cui, B.-B.; Gong, Z.-L.; Zhong, Y.-W. Electropolymerized films of redox-active ruthenium complexes for multistate near-infrared electrochromism, ion sensing, and information storage. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2016, 27, 1105–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, A.S.; Averin, A.D.; Cheprakov, A.V.; Beletskaya, I.P.; Meyer, M.; Bessmertnykh-Lemeune, A. Ruthenium(II) Complexes with (3-Polyamino)phenanthrolines: Synthesis and Application in Sensing of Cu(II) Ions. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronado, E.; Galán-Mascarós, J.R.; Marti-Gastaldo, C.; Palomares, E.; Durrant, J.R.; Vilar, R.; Gratzel, M.; Nazeeruddin, M.K. Reversible Colorimetric Probes for Mercury Sensing. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 12351–12356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Peng, J.; Sun, L.; Li, F. High-Efficiency Upconversion Luminescent Sensing and Bioimaging of Hg(II) by Chromophoric Ruthenium Complex-Assembled Nanophosphors. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 8040–8048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhuang, Q.; Gu, J. Zr-Based MOFs integrated with a chromophoric ruthenium complex for specific and reversible Hg2+ sensing. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 5570–5574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, X.; Sun, L.; Ma, B.; Jin, D.; Dong, L.; Shi, L.; Li, N.; Chen, H.; Huang, W. Simultaneous realization of Hg2+ sensing, magnetic resonance imaging and upconversion luminescence in vitro and in vivo bioimaging based on hollow mesoporous silica coating UCNPS and ruthenium complex. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 13877–13887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alreja, P.; Kaur, N. Modulation in Photophysical Properties of Fluorescent Imidazole Possessing 1,10-Phenanthroline on Introduction of Ru(bipy)22+ towards Cation Sensing. ChemistrySelect 2017, 2, 8638–8642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowski, H.; Hilt, G.; Schulz, A.; Mayer, P.; Polborn, K.; Severin, K. Self-Assembled Organometallic [12]Metallacrown-3 Complexes. Chem. Eur. J. 2001, 7, 3196–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratt, M.D.; Beer, P.D. Heterodinuclear ruthenium(II) bipyridyl-transition metal dithiocarbamate macrocycles for anion recognition and sensing. Tetrahedron 2004, 60, 11227–11238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, S.J.; Paterson, M.J.; Willans, C.E.; Anderson, K.M.; Steed, J.W. Anion binding and luminescent sensing using cationic ruthenium(II) aminopyridine complexes. Chem. Eur. J. 2008, 14, 7296–7305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, P.; Xu, Y.; Su, Z.; Qian, Y.; Li, S.; Yu, T.; Sadler, P.J.; Liu, H.-K. A novel strategy to construct Janus metallamacrocycles with both a Ru-arene face and an imidazolium face. Dalton Trans. 2017, 46, 16205–16215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therrien, B. The role of the second coordination sphere in the biological activity of arene ruthenium metalla-assemblies. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
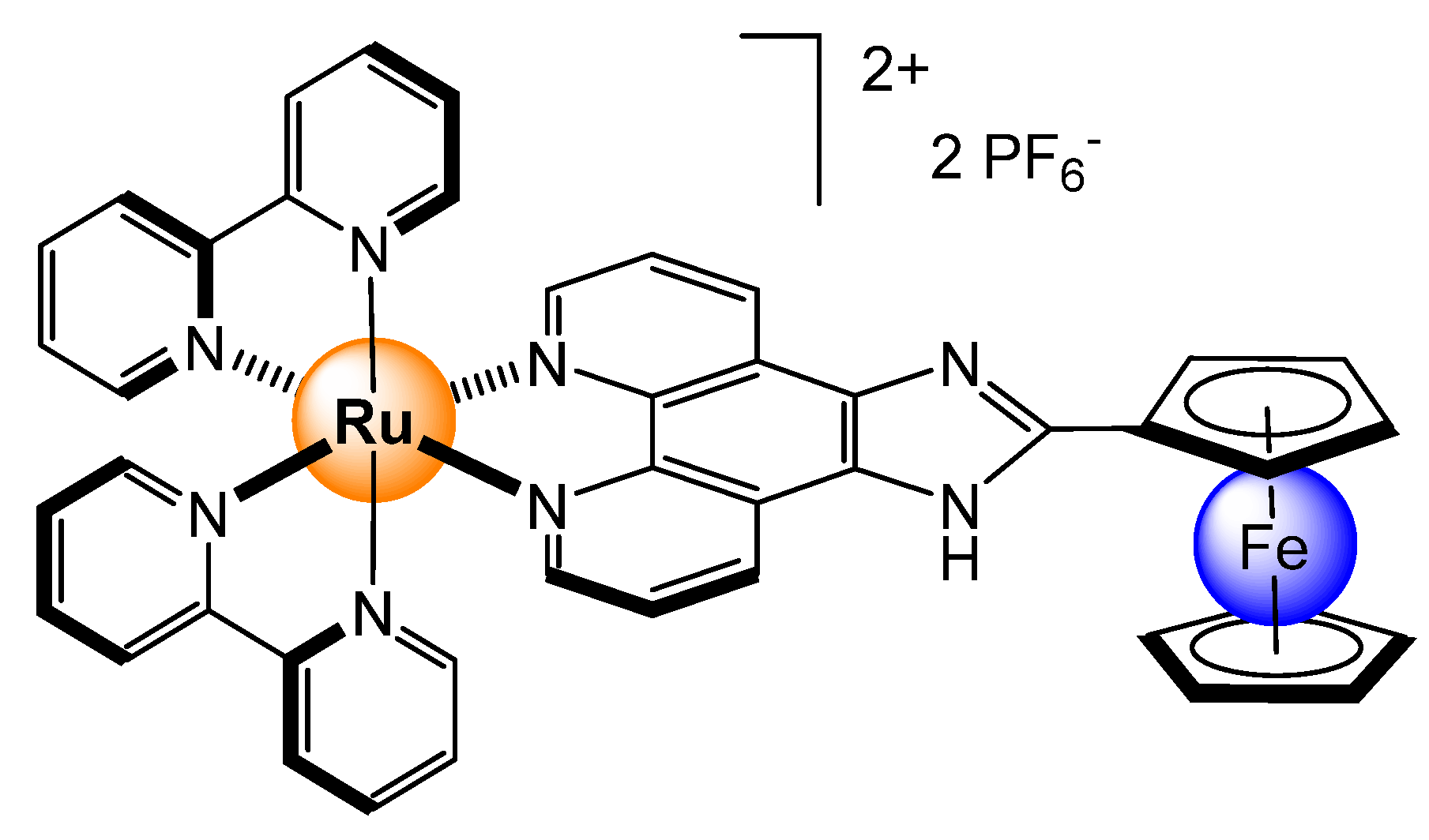
- Bhaumik, C.; Maity, D.; Das, S.; Baitalik, S. Anion sensing studies of luminescent bis-tridentate ruthenium(II) and osmium(II) complexes based on terpyridyl-imidazole ligand through different channels. Polyhedron 2013, 52, 890–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.K.; Ghosh, R.; Kennedy, P.; Mobin, S.M.; Das, D. Potential anion sensing properties by a redox and substitution series of [Ru(bpy)3-n(Hdpa)n]2+, n = 1–3; Hdpa = 2,2′-dipyridylamine: Selective recognition and stoichiometric binding with cyanide and fluoride ions. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 62310–62319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, C.R.; Gabbaï, F.P. Cyanide anion binding by a triarylborane at the outer rim of a cyclometalated ruthenium(II) cationic complex. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 49, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christianson, A.M.; Gabbaï, F.P. Fluoride and cyanide anion sensing by an Sb(V)-substituted cyclometalated Ru polypyridyl complex. J. Organomet. Chem. 2017, 847, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
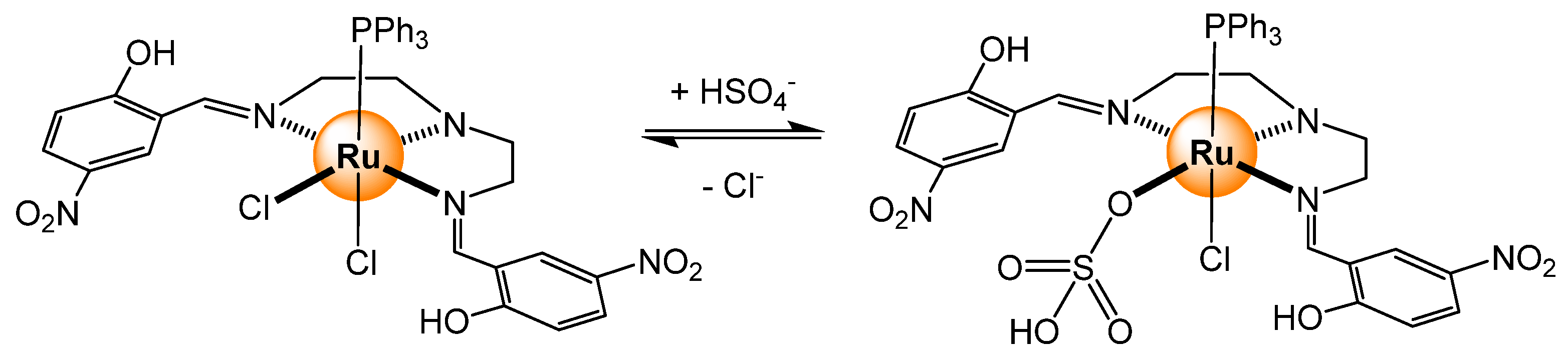
- Bazany-Rodríguez, I.J.; García-Rojas, L.M.; Hernández, J.G.; Thangarasu, P. Sequential recognition of bisulfate and acetate by a ruthenium(II) complex: Experimental and theoretical studies. ChemPhotoChem 2023, 8, e202300145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Ghosh, T.K.; Ghosh, R.; Mondal, S.; Ghosh, P. Recent advances in recognition, sensing and extraction of phosphates: 2015 onwards. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2020, 405, 213128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szemes, F.; Hesek, D.; Chen, Z.; Dent, S.W.; Drew, M.G.B.; Goulden, A.J.; Graydon, A.R.; Grieve, A.; Mortimer, R.J.; Wear, T.; et al. Synthesis and characterization of novel acyclic, macrocyclic, and calix[4]arene ruthenium(II) bipyridyl receptor molecules that recognize and sense anions. Inorg. Chem. 1996, 35, 5868–5879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickers, M.S.; Martindale, K.S.; Beer, P.D. Imidazolium functionalized acyclic ruthenium(II) bipyridyl receptors for anion recognition and luminescent sensing. J. Mater. Chem. 2005, 15, 2784–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata, F.; Caballero, A.; Espinosa, A.; Tárraga, A.; Molina, P. Cation coordination induced modulation of the anion sensing properties of a ferrocene-imidazophenanthroline dyad: Multichannel recognition from phosphate-related to chloride anions. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 73, 4034–4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, A.; Gunupuru, R.; Maity, D.; Patra, S.; Suresh, E.; Paul, P. Synthesis and anion-sensing property of a family of Ru(II)-based receptors containing functionalized polypyridine as binding site. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2010, 13, 1522–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanmohammadi, H.; Razaeian, K. A catalyst-free approach to a novel imidazo [4,5-f][1,10] phenanthroline ligand and its corresponding ruthenium(II) complex: Insights into their applications in colorimetric anion sensing. New J. Chem. 2014, 38, 5536–5543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
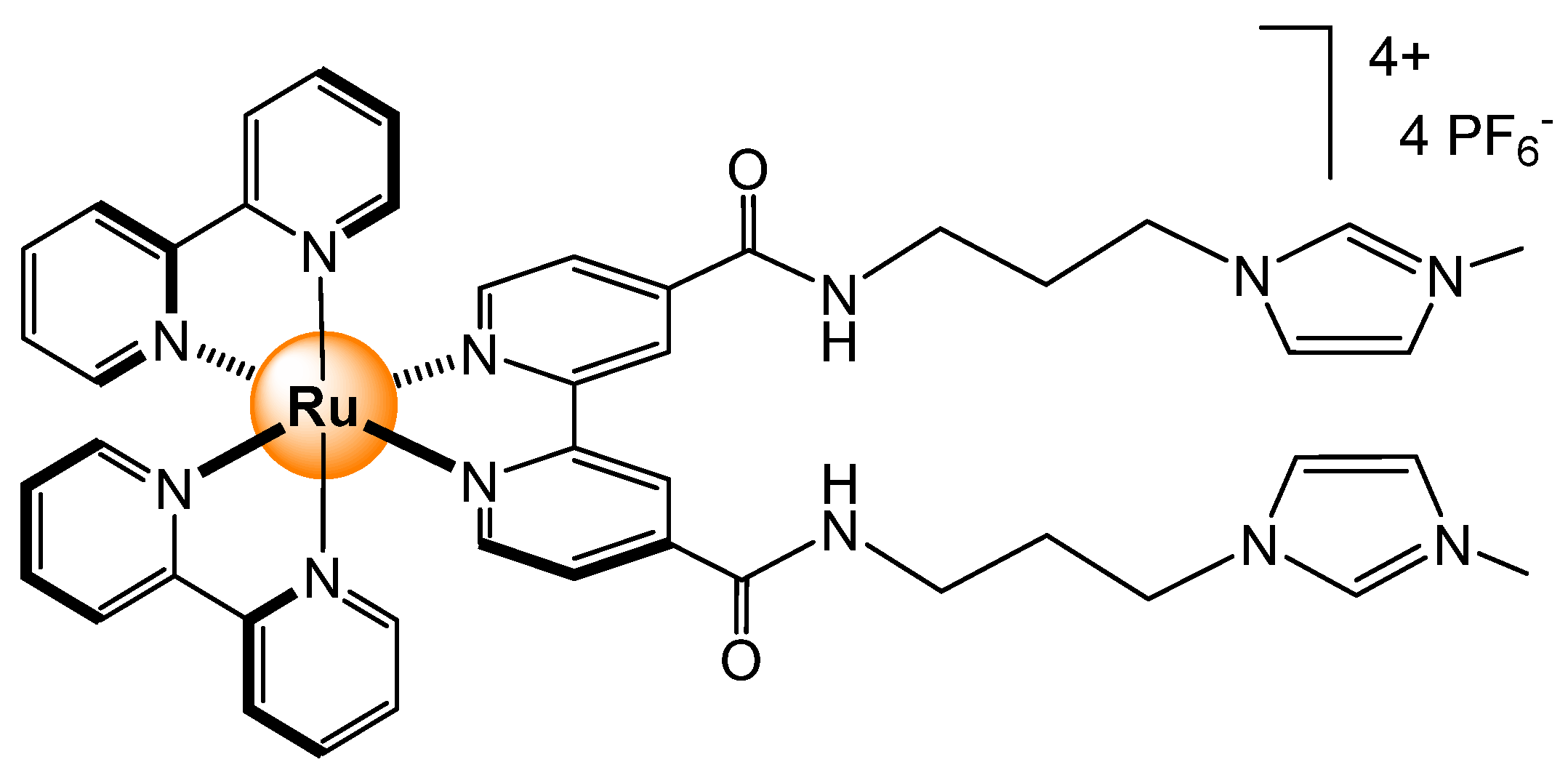
- Kitchen, J.A.; Boyle, E.M.; Gunnlaugsson, T. Synthesis, structural characterization and luminescent anion sensing studies of a Ru(II)polypyridyl complex featuring an aryl urea derivatized 2,2′-bpy auxiliary ligand. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2012, 381, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, H.; Hazel, B.W.; Meijer, A.J.H.M.; Thomas, J.A.; Wilkinson, K.A. A self-assembled luminescent host that selectively sense ATP in water. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 5081–5087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.-B.; Duan, Z.-M.; Ma, Y.-Y.; Wang, K.-Z. Highly sensitive and selective difunctional ruthenium(II) complex-based chemosensor for dihydrogen phosphate anion and ferrous cation. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 2306–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.-B.; Wu, Y.-Q.; Wang, K.-Z.; Li, F. pH luminescence switching, dihydrogen phosphate sensing, and cellular uptake of a heterobimetallic ruthenium(II)-rhenium(I) complex. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 3273–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
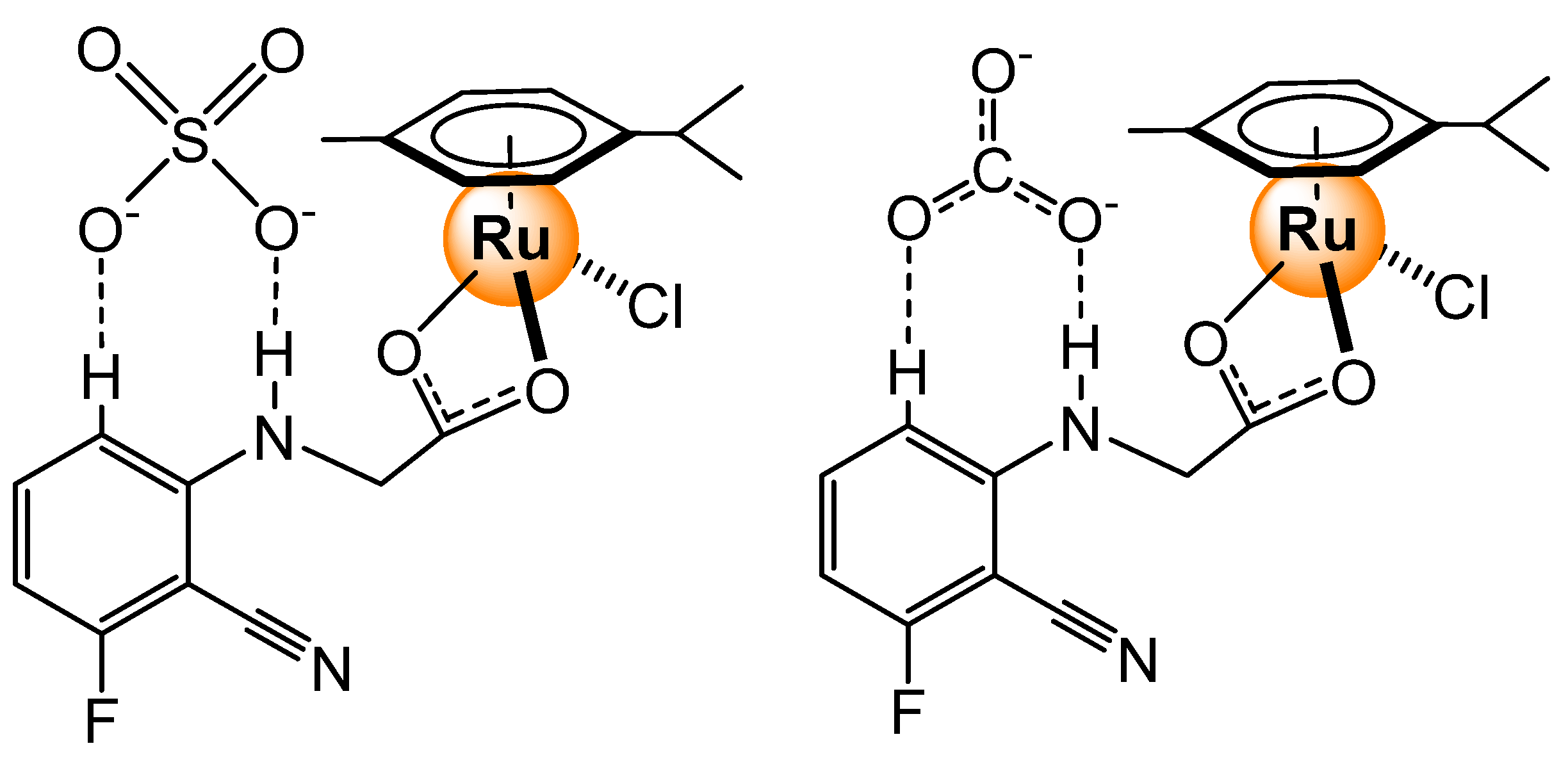
- Chowdhury, B.; Sinha, S.; Ghosh, P. Selective sensing of phosphates by a new bis-heteroleptic RuII complex through halogen bonding: A superior sensor over its hydrogen-bonding analogue. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 18051–18059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
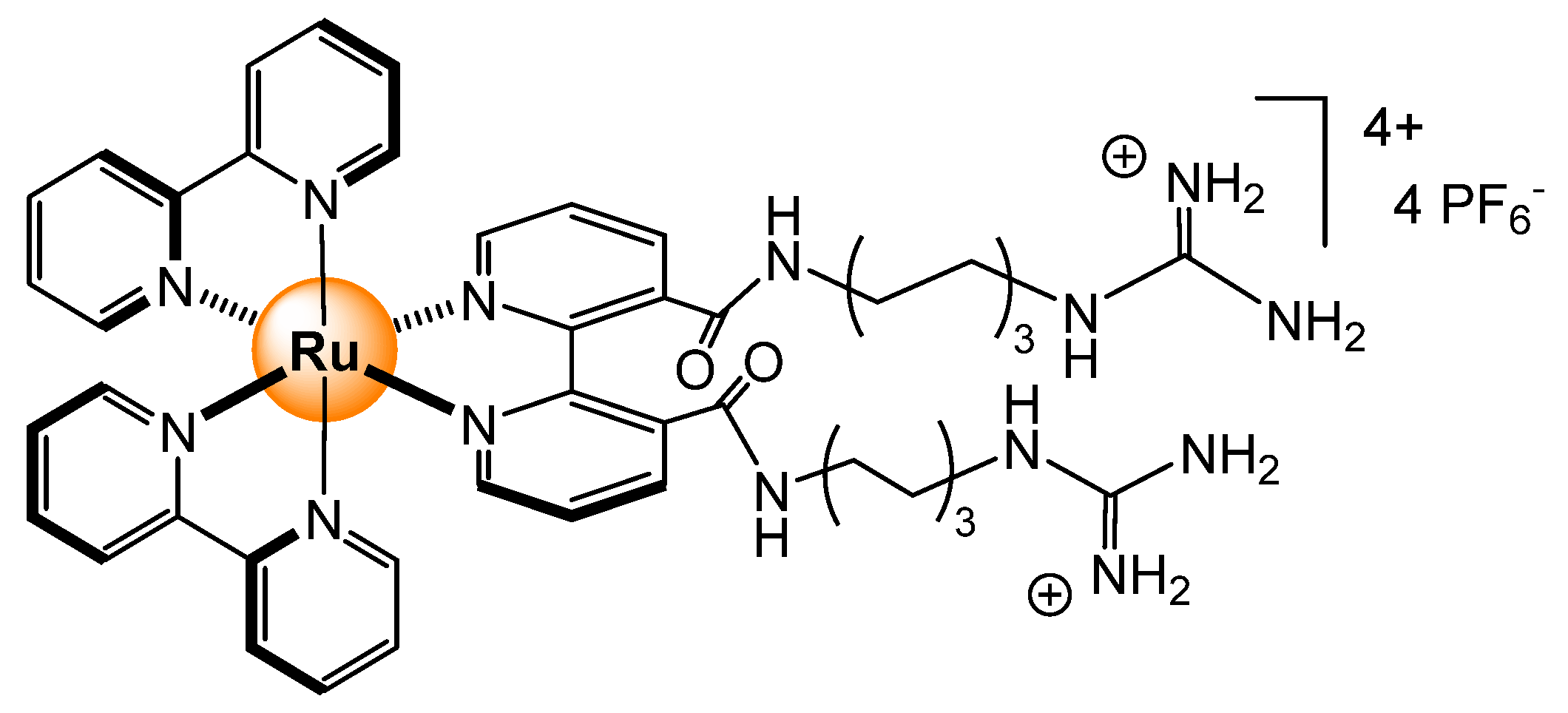
- Ghosh, T.K.; Chakraborty, S.; Chowdhury, B.; Ghosh, P. Bis-heteroleptic ruthenium(II) complex of pendent urea functionalized pyridyl triazole and phenanthroline for recognition, sensing, and extraction of oxyanions. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 5371–5382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, M.; Syed, A.; Marraiki, N.; Anandan, S. The aqueous dependent sensing of hydrazine and phosphate anions using a bis-heteroleptic Ru(II) complex with a phthalimide-anchored pyridine-triazole ligand. Analyst 2021, 146, 1430–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, M.; Anandan, S. Triazole appending ruthenium(II) polypyridine complex for selective sensing of phosphate anions through C-H---anion interaction and copper(II) ions via cancer cells. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 6186–6196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.J.; Massanet-Nicolau, J.; Guwy, A.J. A review of carboxylate production and recovery from organic wastes. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2021, 16, 100826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares, F.; Galindo, M.A.; Galli, S.; Romero, M.A.; Navarro, J.A.R.; Barea, E. Tetranuclear coordination assemblies based on half-sandwich ruthenium(II) complexes: Noncovalent binding to DNA and cytotoxicity. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 48, 7413–7420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therrien, B. Functionalised η6-arene ruthenium complexes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2009, 253, 493–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
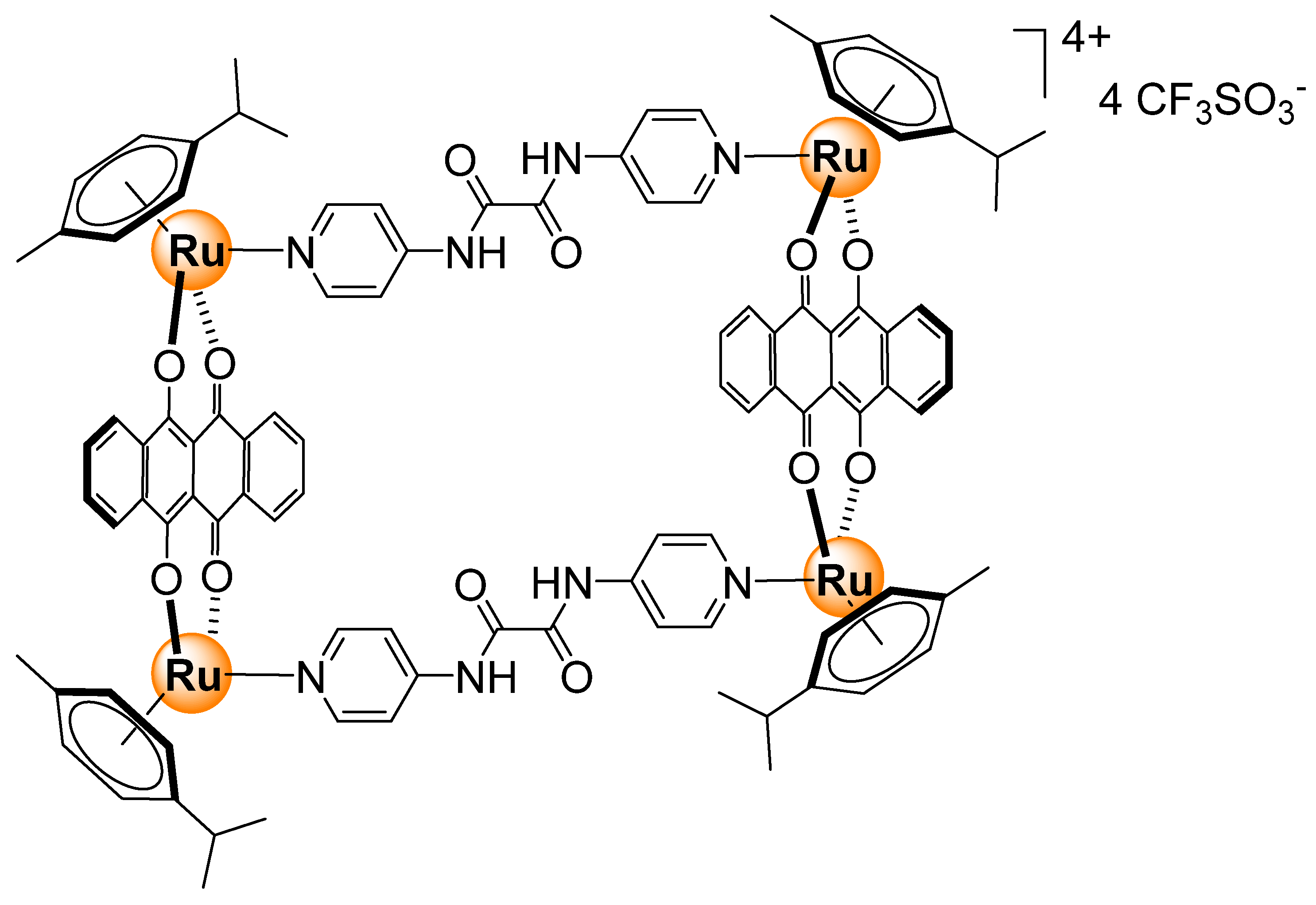
- Vajpayee, V.; Song, Y.H.; Lee, M.H.; Kim, H.; Wang, M.; Stang, P.J.; Chi, K.-W. Self-assembled arene-ruthenium-based rectangles for the selective sensing of multi-carboxylate anions. Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 7837–7844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, A.; Vajpayee, V.; Kim, H.; Lee, M.H.; Jung, H.; Wang, M.; Stang, P.J.; Chi, K.-W. Self-assembled metalla-bowls for selective sensing of multi-carboxylate anions. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 1195–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Lee, S.; Kim, H.; Cook, T.R.; Stang, P.J.; Chi, K.-W. Selective detection of multicarboxylate anions based on “Turn on” electron transfer by self-assembled molecular rectangles. Chem. Asian J. 2012, 7, 2592–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berni, E.; Gosse, I.; Badocco, D.; Pastore, P.; Sojic, N.; Pinet, S. Differential photoluminescent and electrochemiluminescent detection of anions with a modified ruthenium(II)-bipyridyl complex. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 5145–5152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonkar, C.; Sarkar, S.; Malviya, N.; Kuznetsov, M.L.; Mukhopadhyay, S. Recognition and mechanistic investigation of anion sensing by ruthenium(II) arene complexes and bio-imaging application. Dalton Trans. 2022, 51, 13071–13084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer-Sueta, G.; Campolo, N.; Trujillo, M.; Bartesaghi, S.; Carballal, S.; Romero, N.; Alvarez, B.; Radi, R. Biochemistry of peroxynitrite and protein tyrosine nitration. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 1338–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
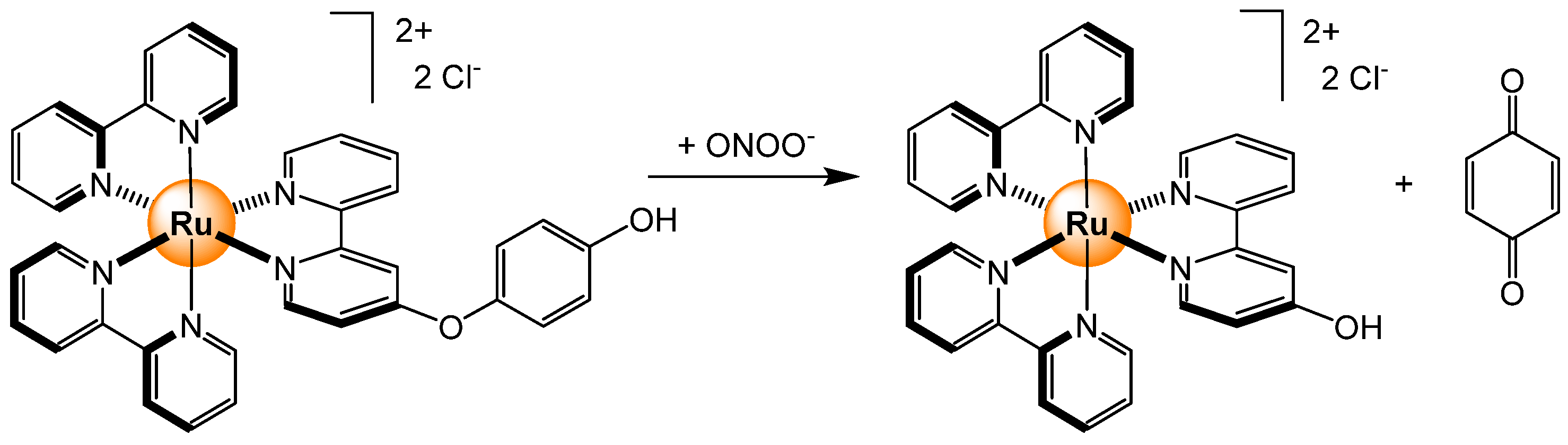
- Ma, J.; Wu, J.; Liu, W.; Wang, P.; Fan, Z. Ruthenium(II) complex-based fluorescent sensor for peroxynitrite. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2012, 94, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, G.T.; Kedge, J.L.; Fossey, J.S. Molecular boronic acid-based saccharide sensors. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 1508–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murtaza, Z.; Lakowicz, J.R. Lifetime-based sensing of glucose using luminescent ruthenium(II) metal complex. In Proceedings of the SPIE Conference on Advances in Fluorescence Sensing Technology IV, San Jose, CA, USA, 24–27 January 1999; Volume 3602, pp. 326–334. [Google Scholar]
- Murtaza, Z.; Tolosa, L.; Harms, P.; Lakowicz, J.R. On the possibility of glucose sensing using boronic acid and a luminescent ruthenium metal-ligand complex. J. Fluoresc. 2002, 12, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xun, S.; LeClair, G.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; Gao, J.P.; Wang, Z.Y. Tuning the electrical and optical properties of dinuclear ruthenium complexes for near infrared optical sensing. Org. Lett. 2006, 8, 1697–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolosa, L.; Szmacinski, H.; Rao, G.; Lakowicz, J.R. Lifetime-based sensing of glucose using energy transfer with a long lifetime donor. Anal. Biochem. 1997, 250, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Singh, R. Recent optical sensing technologies for the detection of various biomolecules: Review. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 134, 106620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, N.; Haynes, C.J.E. Supramolecular coordination complexes as optical biosensors. ChemPlusChem 2021, 86, 418–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, N.P.; Torres, V.; Jain, D.; Martí, A.A. Sensing amyloid-β aggregation using luminescent dipyridophenazine ruthenium(II) complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 1121–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, E.; Mareeswaran, P.M.; Sathish, V.; Singaravadivel, S.; Rajagopal, S. Sensing and inhibition of amyloid-β based on the simple luminescent aptamer-ruthenium complex system. Talanta 2015, 134, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yuan, Y.; Zhuo, Y.; Chai, Y.; Yuan, R. Self-enhanced electrochemiluminescence nanorods of tris(bipyridine) ruthenium(II) derivative and its sensing application for detection of N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 2258–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Liu, J.; Liu, C.; Ding, F.; Li, Y.; Tang, H.; Ma, M. Phosphate group-derivated bipyridine-ruthenium complex and titanium dioxide nanoparticles for electrochemical sensing of protein kinase activity. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 4451–4460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, M.; Dong, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhu, Z.; Li, M.; Yang, D.; Shao, Y. Fabrication of tris(bipyridine)ruthenium(II)-functionalized metal-organic framework thin films by electrochemically assisted self-assembly technique for electrochemiluminescent immunoassay. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 11622–11628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Ravikumar, S.; Song, Y.H.; Prabhu, N.S.; Kim, H.; Hong, S.H.; Cheon, S.; Noh, J.; Chi, K.-W. A new arene-Ru based supramolecular coordination complex for efficient binding and selective sensing of green fluorescent protein. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 6032–6040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, L.E.H.; Therrien, B.; Furrer, J. Interactions of arene ruthenium metallaprisms with human proteins. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2015, 13, 946–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therrien, B. Unmasking arene ruthenium building blocks. Chem. Rec. 2021, 21, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Liang, Z.; Xie, B.-P.; Li, R.-T.; Li, L.-Z.; Jiang, Z.-H.; Bai, L.-P.; Chen, J.-X. Fluorescence sensing platform based on ruthenium(II) complexes as high 3S (sensitivity, specificity, speed) and “on-off-on” sensors for the miR-185 detection. Talanta 2018, 179, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.-T.; Liang, Z.; Li, M.-C.; Tan, Y.; Xie, B.-P.; Duan, W.-J.; Ning, C.-T.; Chen, J.-X.; Sun, B. Speedy, specific, synchronous sensing platforms with ruthenium complexes for multiplexed microRNA detection. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 58, 15126–15137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Liu, G.; Yan, M.; Zhu, Q.; Zhu, L.; Huang, J.; Yang, X. Highly luminescent and self-enhanced electrochemiluminescence of tris(bipyridine) ruthenium(II) nanohybrid and its sensing application for label-free detection of microRNA. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 13237–13243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, T.; Casero, E.; Revenga-Parra, M.; Martín-Benito, J.; Pariente, F.; Vázquez, L.; Lorenzo, E. Architectures based on the use of gold nanoparticles and ruthenium complexes as a new route to improve genosensor sensitivity. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 24, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.-J.; Zhan, C.-Q.; Zheng, Y.-M.; Chen, G.-N.; Chen, X. Simple and selective sensing of cysteine using gold nanoparticles modified by ruthenium(II) complexes. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2011, 11, 3578–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazloum-Ardakani, M.; Sheikh-Mohseni, M.A.; Salavati-Niasari, M. A ruthenium complex/carbon nanotube based electrode as the first electrochemical sensor for simultaneous sensing D-penicillamine, 6-thioguanine and catecholamines. Electroanalysis 2016, 28, 1370–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, K.C.F.; Bonacin, J.A. Preferential coordination of ruthenium complex as an electroactive self-assembled monolayer on gold substrate and its application in sensing of dopamine. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2019, 99, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Chen, T.; Xu, Y.; Wei, S.; Huang, W.; Liu, R.; Liu, J. A versatile signal-enhanced ECL sensing platform based on molecular imprinting technique via PET-RAF cross-linking polymerization using bifunctional ruthenium complex as both catalyst and sensing probes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 124–125, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Zhao, Q.; Yang, L.; Ma, H.; Wu, D.; Liu, L.; Ren, X.; Ju, H.; Wei, Q. Dual-mode sensing platform guided by intramolecular electrochemiluminescence of a ruthenium complex and cationic N,N-bis(2-(trimethylammonium iodide)propylene) perylene-3,4,9,10-tetracarboxydiimide for estradiol assay. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 6088–6093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quílez-Alburquerque, J.; García-Iriepa, C.; Marazzi, M.; Descalzo, A.B.; Orellana, G. Interaction of a 1,3-dicarbonyl toxin with Ru(II)-biimidazole complexes for luminescence sensing: A spectroscopic and photochemical experimental study rationalized by time-dependent density functional theory calculations. Inorg. Chem. 2022, 61, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Z.; Gao, Q.; An, X.; Song, B.; Yuan, J. A functional ruthenium(II) complex for imaging biothiols in living bodies. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 8278–8283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Liu, J.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.-L.; Liu, Q.; Song, B.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, R. “Two birds with one stone” ruthenium(II) complex probe for biothiols discrimination and detection in vitro and in vivo. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 2000458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Ye, Z.; Yin, Y.; Wang, G.; Jin, D.; Yuan, J.; Piper, J.A. Developing red-emissive ruthenium(II) complex-based luminescent probes for cellular imaging. Bioconjug. Chem. 2012, 23, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.-B.; Han, Y.-F.; Ge, Y.-Q.; Cui, J.-C.; Zuo, J.; Nie, K. Rapid and selective detection of biothiols by novel ruthenium(II) complex-based phosphorescence probes. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 216, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramamoorthy, R.; Dutta, P.K.; Akbar, S.A. Oxygen sensors: Materials, methods, designs and applications. J. Mat. Sci. 2003, 38, 4271–4282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimant, I.; Belser, P.; Wolfbeis, O.S. Novel metal-organic ruthenium(II) diimin complexes for use as longwave excitable luminescent oxygen probes. Talanta 1994, 41, 985–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, M.P.; Garcia-Fresnadillo, D.; Moreno-Bondi, M.C.; Orellana, G. Oxygen sensing in nonaqueous media using porous glass with covalently bound luminescent Ru(II) complexes. Anal. Chem. 1998, 70, 5184–5189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Fresnadillo, D.; Marazuela, M.D.; Moreno-Bondi, M.C.; Orellana, G. Luminescent Nafion membranes dyed with ruthenium(II) complexes as sensing materials for dissolved oxygen. Langmuir 1999, 15, 6451–6459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McShane, M.J.; Brown, J.Q.; Guice, K.B.; Lvov, Y.M. Polyelectrolyte microshells as carriers for fluorescent sensors: Loading and sensing properties of a ruthenium-based oxygen indicator. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2002, 2, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Guo, J.; Wang, Y.; Pang, W. Incorporation of luminescent tris(pyridine)ruthenium(II) complex in mesoporous silica spheres and their spectroscopic and oxygen-sensing properties. Mat. Lett. 2002, 53, 400–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, D.; Komatsu, H.; Son, A.; Nishimoto, S.-I.; Tanabe, K. Water-soluble phosphorescent ruthenium complex with a fluorescent coumarin unit for ratiometric sensing of oxygen levels in living cells. Bioconjug. Chem. 2015, 26, 645–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, D.; Umehara, Y.; Son, A.; Asahi, W.; Misu, S.; Kurihara, R.; Kondo, T.; Tanabe, K. Tracking the oxygen status in the cell nucleus with a Hoechst-tagged phosphorescent ruthenium complex. ChemBioChem 2018, 19, 956–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertekin, K.; Kocak, S.; Ozer, M.S.; Aycan, S.; Cetinkaya, B. Enhanced optical oxygen sensing using a newly synthesized ruthenium complex together with oxygen carriers. Talanta 2003, 61, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oter, O.; Ertekin, K.; Dayan, O.; Cetinkaya, B. Photocharacterization of novel ruthenium dyes and their utilities as oxygen sensing materials in presence of perfluorochemicals. J. Fluoresc. 2008, 18, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, M.B.; McLaurin, E.J.; Reece, S.Y.; Olea, C., Jr.; Nocera, D.G.; Marletta, M.A. Ru-porphyrin protein scaffolds for sensing O2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 5582–5583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Liu, Y.; Li, B.; Yue, S.; Li, W. Optical oxygen sensing materials based on trinuclear starburst ruthenium(II) complexes assembled in mesoporous silica. J. Lumin. 2008, 128, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Song, L.; Li, B.; Liu, Y. Synthesis, characterization, and oxygen sensing properties of Ru(II) complex covalently grafted to mesoporous MCM-41. J. Lumin. 2010, 130, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Zhang, L.; Song, H. Multifunctional mesoporous nanocomposites with magnetic, optical, and sensing features: Synthesis, characterization, and their oxygen-sensing performance. Langmuir 2013, 29, 1273–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, B.; Zhang, L.; Liu, L.; Wang, Y. Photoluminescent and oxygen sensing properties of core-shell nanospheres based on a covalently grafted ruthenium(II) complex. Appl. Organometal. Chem. 2011, 25, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, B.; Qin, R.; Zhao, H.; Ren, X.; Su, Z. Synthesis and characterization of new bifunctional nanocomposites possessing upconversion and oxygen-sensing properties. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 285701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Yu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, B. Mesoporous silica coating NaYF4:Yb,Er@NaYF4 upconversion nanoparticles loaded with ruthenium(II) complex nanoparticles: Fluorometric sensing and cellular imaging of temperature by upconversion and oxygen by downconversion. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, B.W.-K.; Yam, V.W.-W. Sensitive single-layered oxygen-sensing systems: Polypyridyl ruthenium(II) complexes covalently attached or deposited as Langmuir-Blodgett monolayer on glass surfaces. Langmuir 2006, 22, 7437–7443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge, P.A.S.; Maule, C.; Silva, A.J.; Benrashid, R.; Santos, J.L.; Farahi, F. Dual sensing of oxagen and temperature using quantum dots and a ruthenium complex. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 606, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ruda-Eberenz, T.A.; Nagy, A.; Waldman, W.J.; Dutta, P.K. Entrapment of ionic tris(2,2′-bipyridyl) ruthenium(II) in hydrophobic siliceous zeolite: O2 sensing in biological environments. Langmuir 2008, 24, 9140–9147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.-L.; Liu, S.-Y.; Lin, R.-B.; Liao, P.-Q.; Ye, J.-W.; Lai, Z.; Guan, Y.; Cheng, X.-N.; Zhang, J.-P.; Chen, X.-M. Phosphorescence doping in a flexible ultramicroporous framework for high and tunable oxygen sensing efficiency. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 6864–6866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizaki, T.; Matsumoto, T.; Ogo, S. Dissolved N2 sensing by pH-dependent Ru Complexes. Dalton Trans. 2010, 39, 1339–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellana, G.; Moreno-Bondi, M.C.; Segovia, E.; Marazuela, M.D. Fiber-optic sensing of carbon dioxide based on excited-state proton transfer to a luminescent ruthenium(II) complex. Anal. Chem. 1992, 64, 2210–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toscani, A.; Marín-Hernández, C.; Moragues, M.E.; Sancenón, F.; Dingwall, P.; Brown, N.J.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; White, A.J.P.; Wilton-Ely, J.D.E.T. Ruthenium(II) and osmium(II) vinyl complexes as highly sensitive and selective chromogenic and fluorogenic probes for the sensing of carbon monoxide in air. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 14529–14538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toscani, A.; Marín-Hernández, C.; Robson, J.A.; Chua, E.; Dingwall, P.; White, A.J.P.; Sancenón, F.; de la Torre, C.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Wilton-Ely, J.D.E.T. Highly sensitive and selective molecular probes for chromo-fluorogenic sensing of carbon monoxide in air, aqueous solution and cells. Chem. Eur. J. 2019, 25, 2069–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Ye, Z.; Wang, G.; Zhang, W.; Yuan, J. Development of a ruthenium(II) complex based luminescent probe for imaging nitric oxide production in living cells. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 6884–6891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Y.; Han, F.; Zhang, Q.; Xie, T.; Lu, L.; Li, S.; Xia, H. Off/On fluorescent chemosensors for organotin halides based on binuclear ruthenium complexes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 5599–5603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanmugaraju, S.; Bar, A.K.; Joshi, S.A.; Patil, Y.P.; Mukherjee, P.S. Constructions of 2D-metallamacrocycles using half-sandwich RuII2 precursors: Synthesis, molecular structures, and self-selection for a single linkage isomer. Organometallics 2011, 30, 1951–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugaraju, S.; Jadhav, H.; Mukherjee, P.S. Self-assembly of chloro-bridged arene-ruthenium based rectangle: Synthesis, structural characterization and sensing study. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. India Sect. A Phys. Sci. 2014, 84, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vajpayee, V.; Bivaud, S.; Goeb, S.; Croué, V.; Allain, M.; Popp, B.V.; Garci, A.; Therrien, B.; Sallé, M. Electron-rich arene-ruthenium metalla-architectures incorporating tetrapyridyl-tetrathiafulvene donor moieties. Organometallics 2014, 33, 1651–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Ni, J.; Zhang, J.-J.; Liu, S.-Q.; Sun, Y.-J.; Zhou, H.; Li, Y.-Q.; Duan, C.-Y. A trichromatic MOF composite for multidimensional ratiometric luminescent sensing. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 2918–2926. [Google Scholar]
- Bedoya, M.; Díez, M.T.; Moreno-Bondi, M.C.; Orellana, G. Humidity sensing with a luminescent Ru(II) complex and phase-sensitive detection. Sens. Actuators B 2006, 113, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocakoglu, K.; Okur, S. Humidity sensing properties of novel ruthenium polypyridyl complex. Sens. Actuators B 2010, 151, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, S.S.; Nadargi, D.Y.; Tamboli, M.S.; Chaudhary, L.S.; Patil, P.S.; Mulla, I.S.; Suryavanshi, S.S. Ru-loaded mesoporous WO3 microflowers for dual applications: Enhanced H2S sensing and sunlight-driven photocatalysis. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 16840–16845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.-S.; Li, X.-H.; You, F.-T.; Teng, F.; Huang, S.-H. Sensing water in organic solvent using a polyurethane-silica hybrid membrane doped with a luminescent ruthenium complex. Microchim. Acta 2013, 180, 807–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Song, B.; Zhang, W.; Duan, C.; Wang, Y.-L.; Liu, C.; Zhang, R.; Yuan, J. Quantitative monitoring and visualization of hydrogen sulfide in vivo using a lumiscent probe based on a ruthenium(II) complex. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 3999–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bustamante, N.; Ielasi, G.; Bedoya, M.; Orellana, G. Optimization of temperature sensing with polymer-embedded luminescent Ru(II) complexes. Polymers 2018, 10, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, M.C.-L.; Yam, V.W.-W. Luminescent cation sensors: From host-guest chemistry, supramolecular chemistry to reaction-based mechanisms. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 4192–4202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
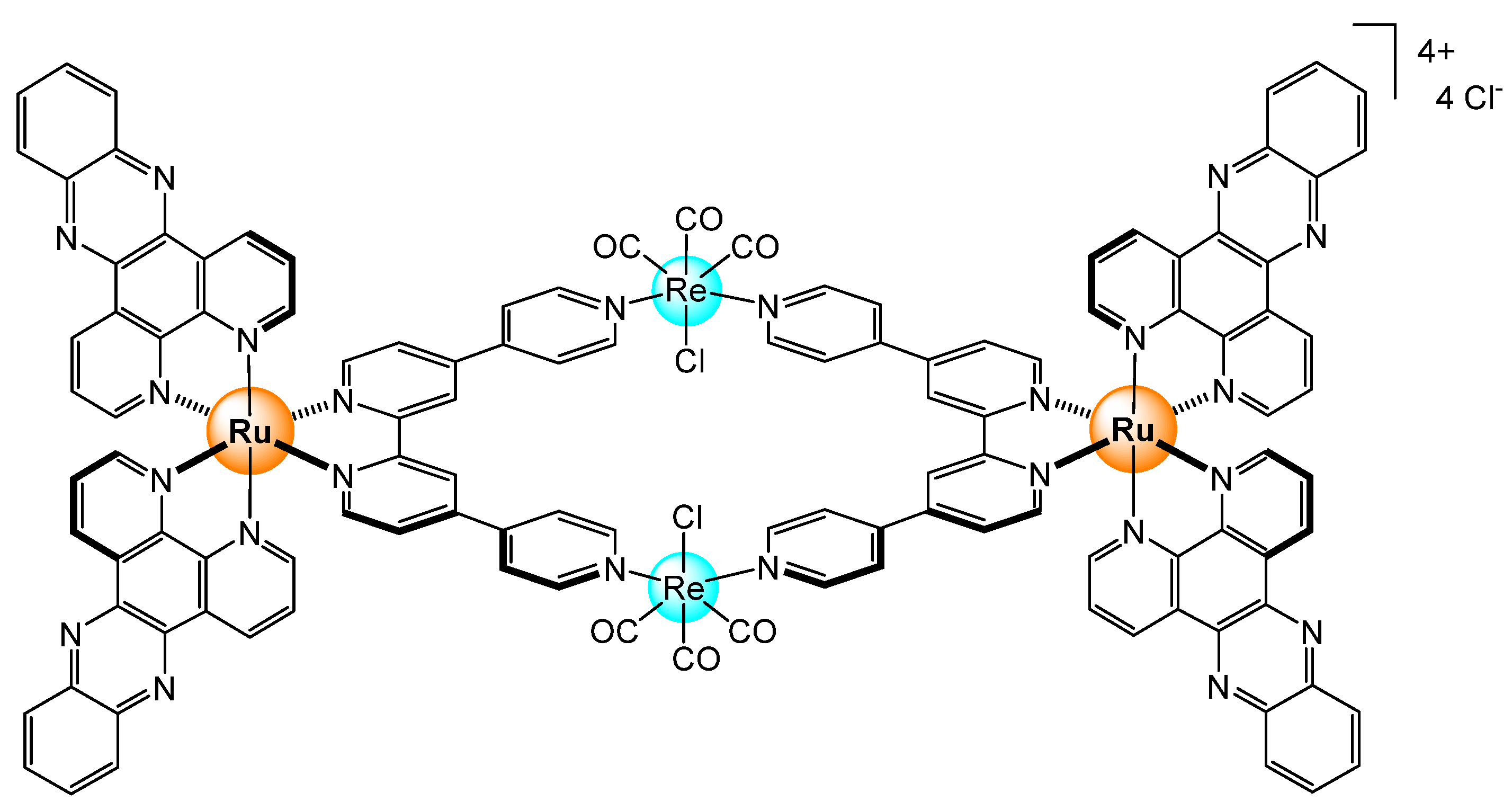
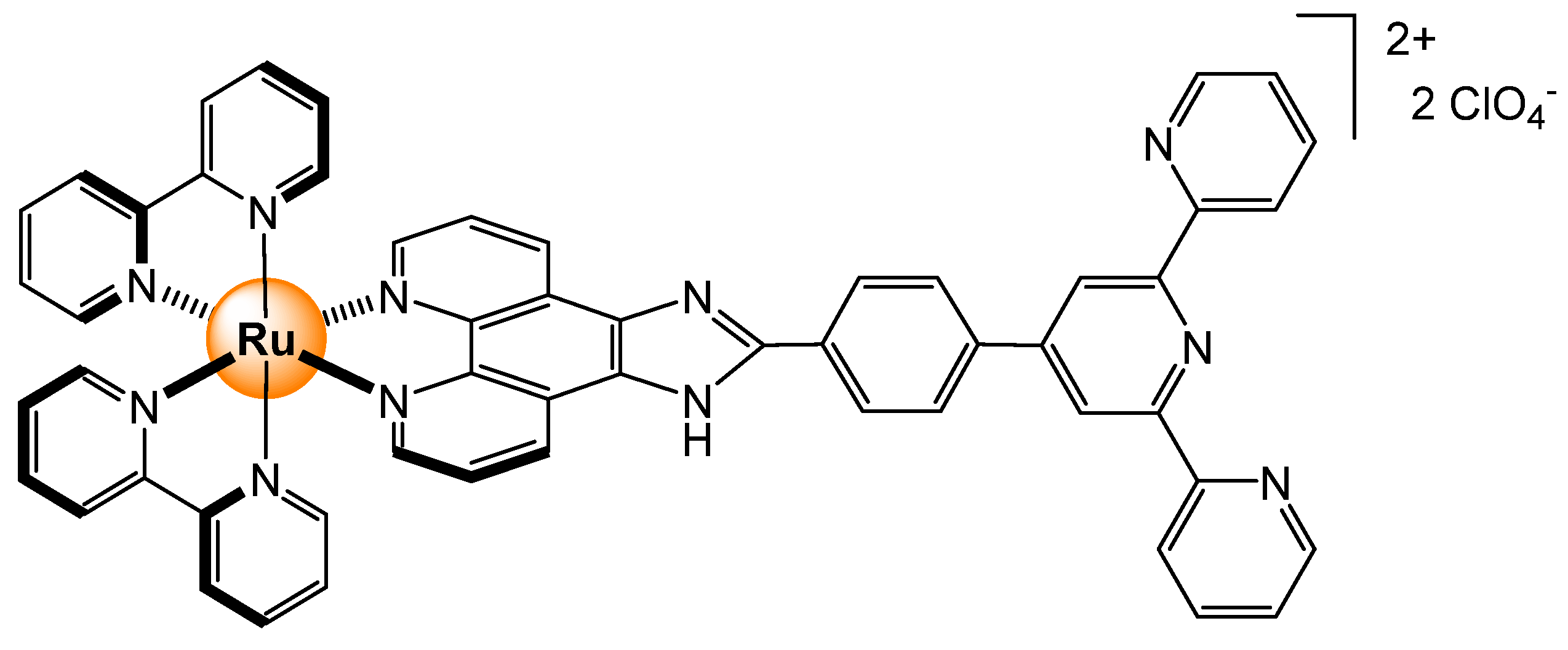
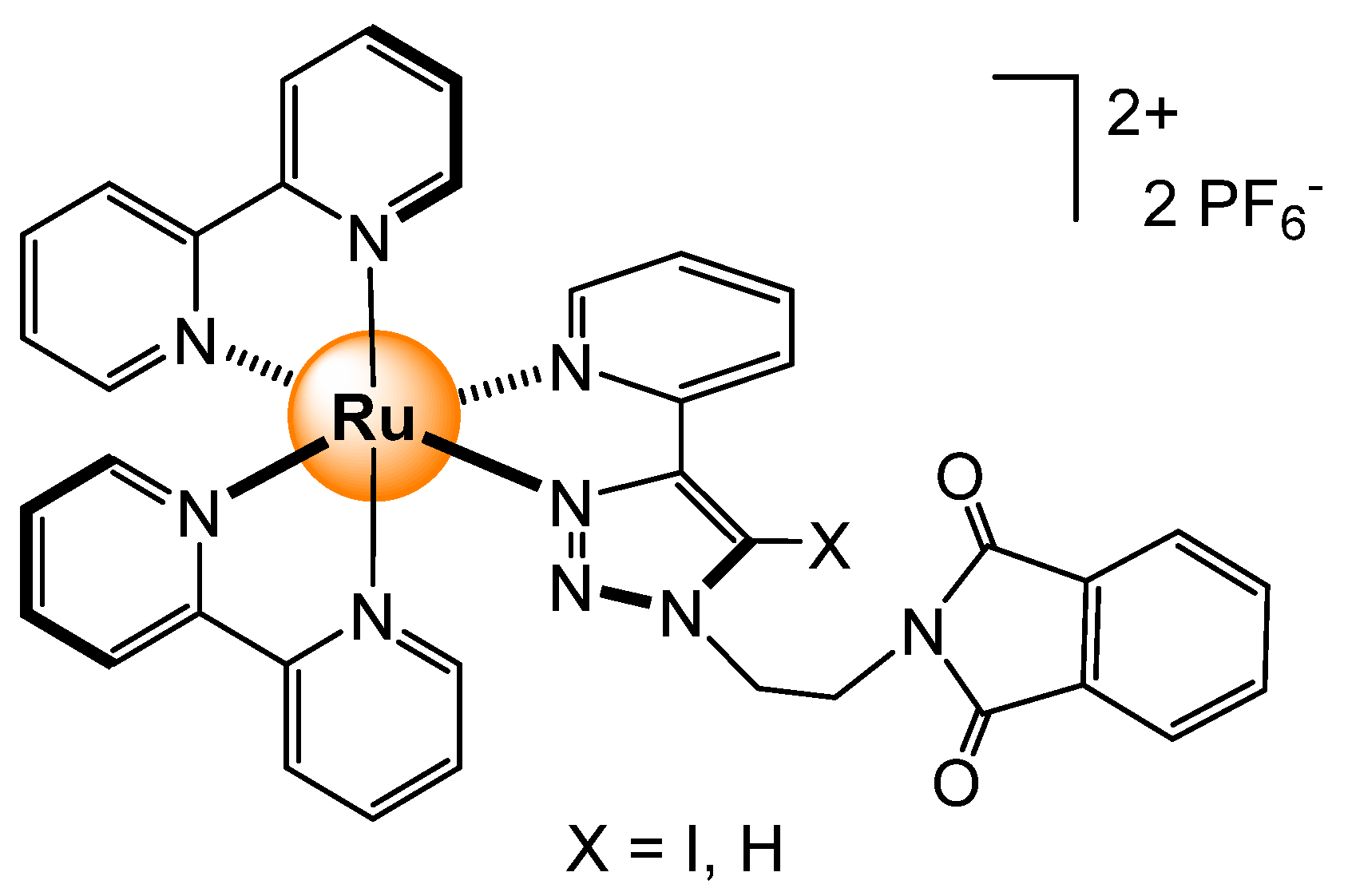
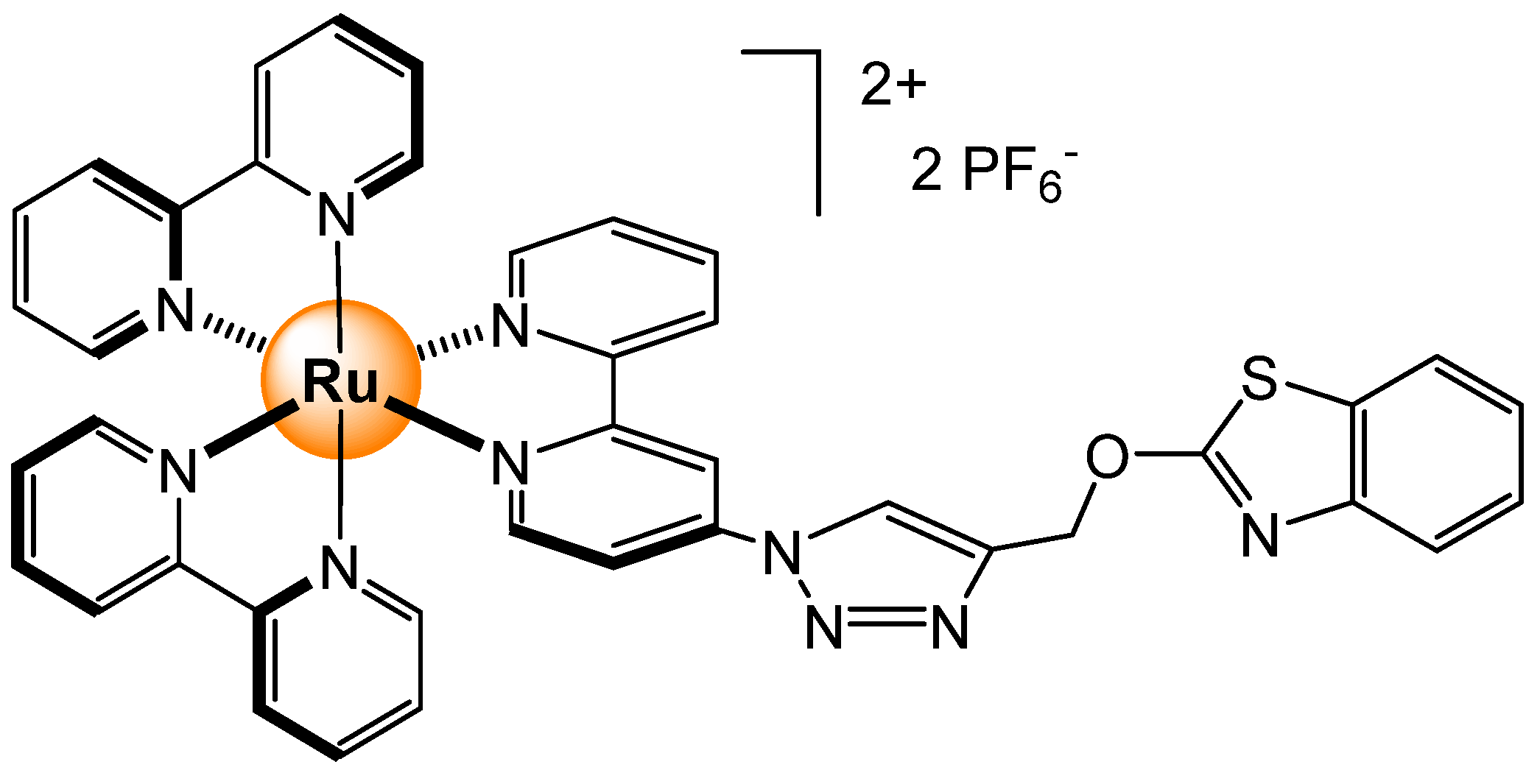


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Therrien, B. Ruthenium-Based Sensors. Inorganics 2024, 12, 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics12090239
Therrien B. Ruthenium-Based Sensors. Inorganics. 2024; 12(9):239. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics12090239
Chicago/Turabian StyleTherrien, Bruno. 2024. "Ruthenium-Based Sensors" Inorganics 12, no. 9: 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics12090239
APA StyleTherrien, B. (2024). Ruthenium-Based Sensors. Inorganics, 12(9), 239. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics12090239