C–H Activation via Group 8–10 Pincer Complexes: A Mechanistic Approach
Abstract
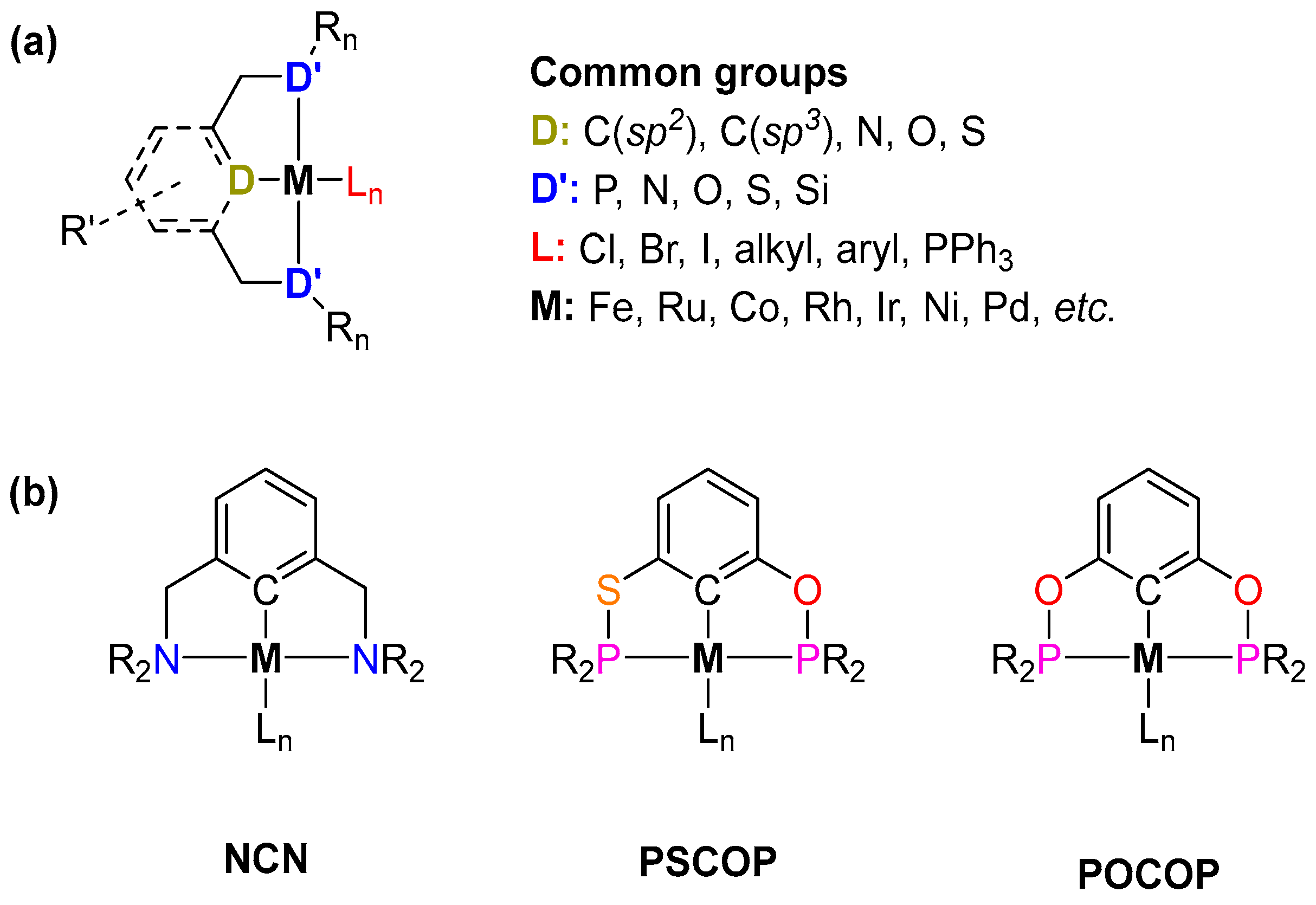
1. Introduction
2. Group 8 Pincer Complexes
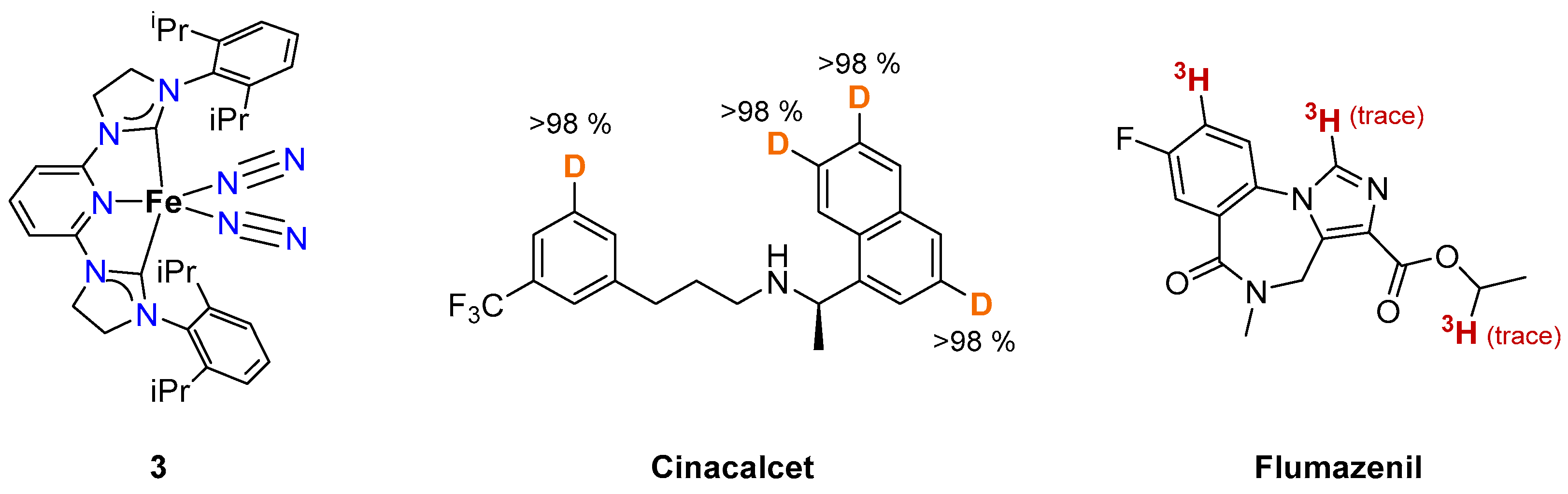
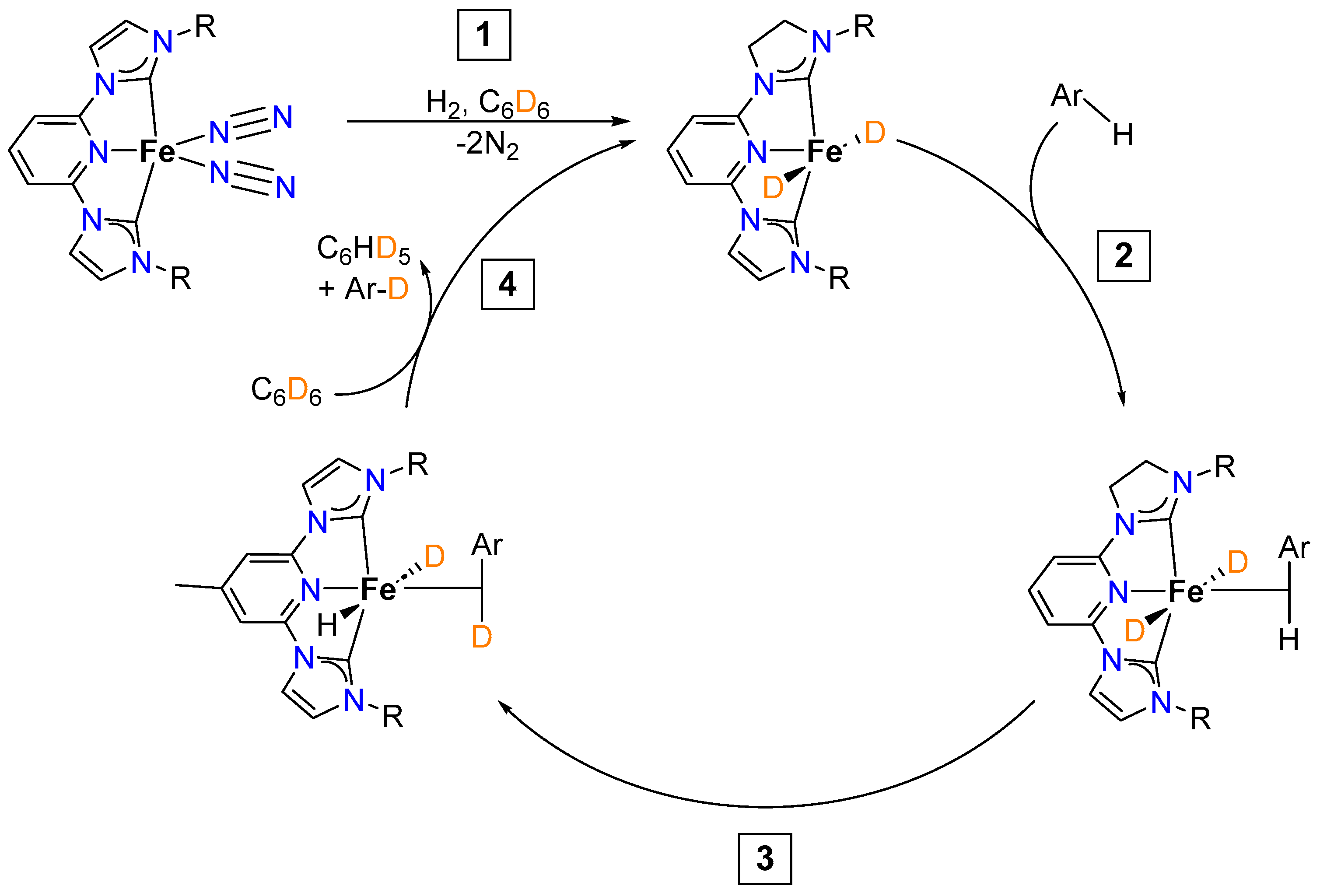
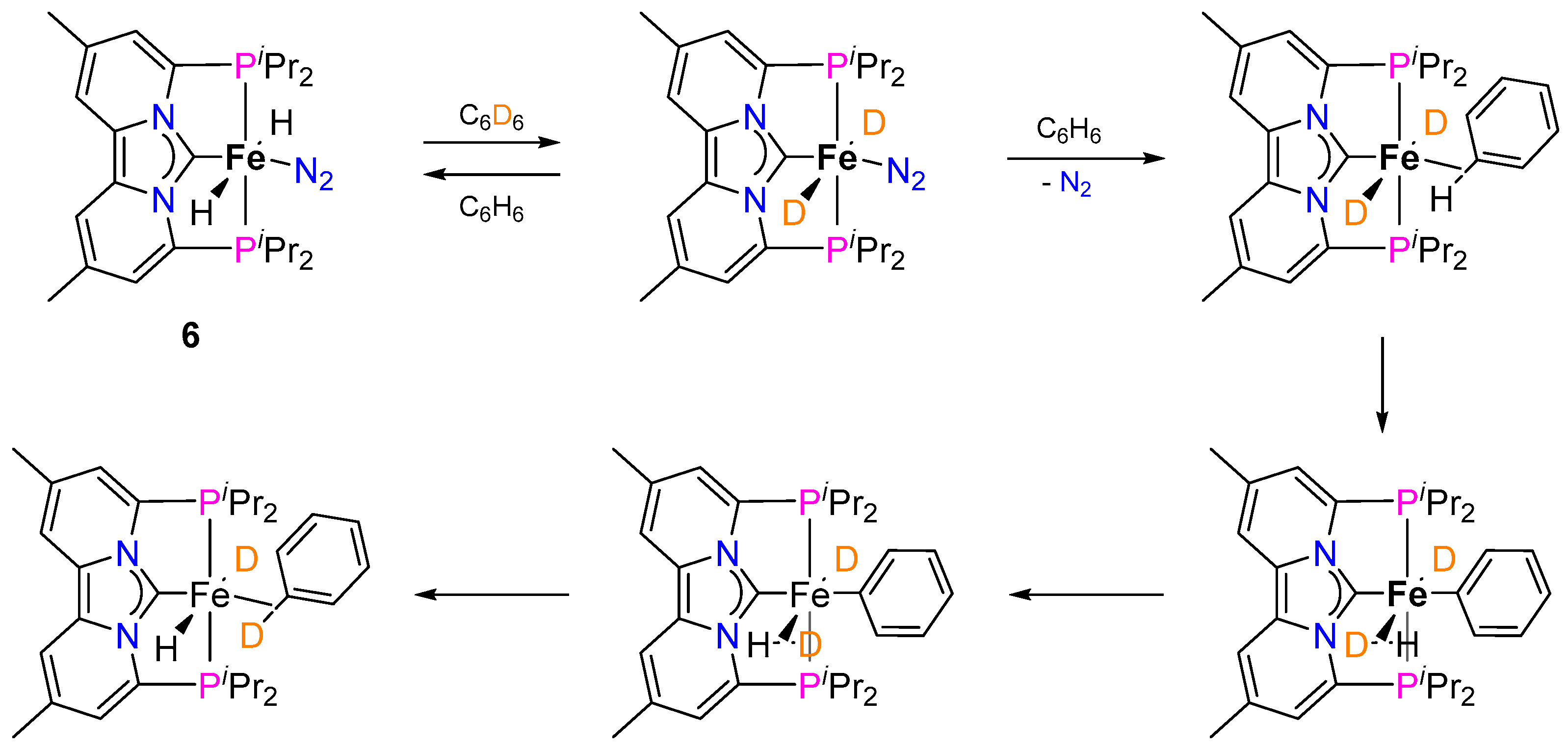
2.1. Iron
2.1.1. C–H Borylation
2.1.2. Hydrogen Isotope Exchange (HIE)
2.2. Ruthenium
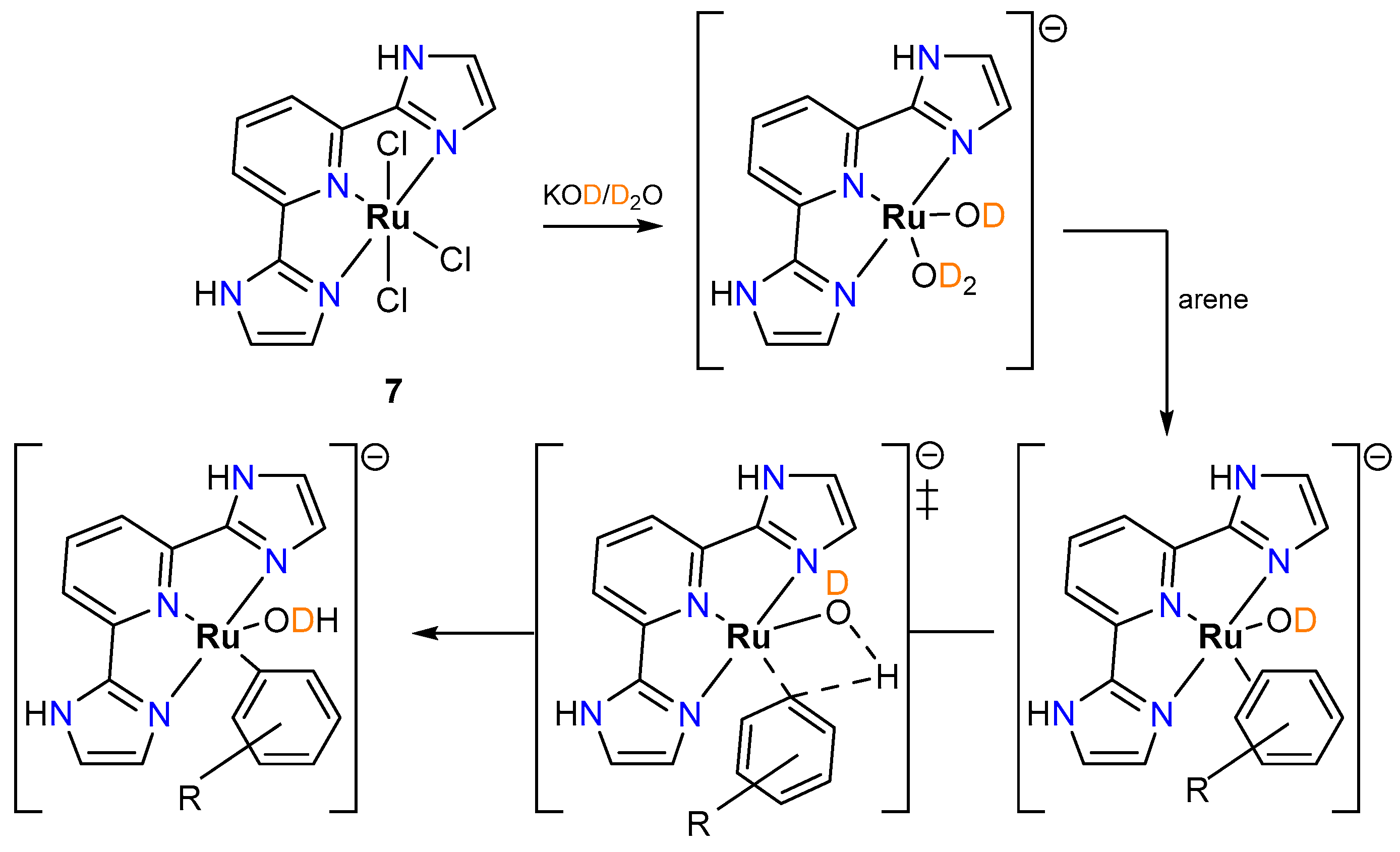
2.2.1. Hydrogen Isotope Exchange (HIE)
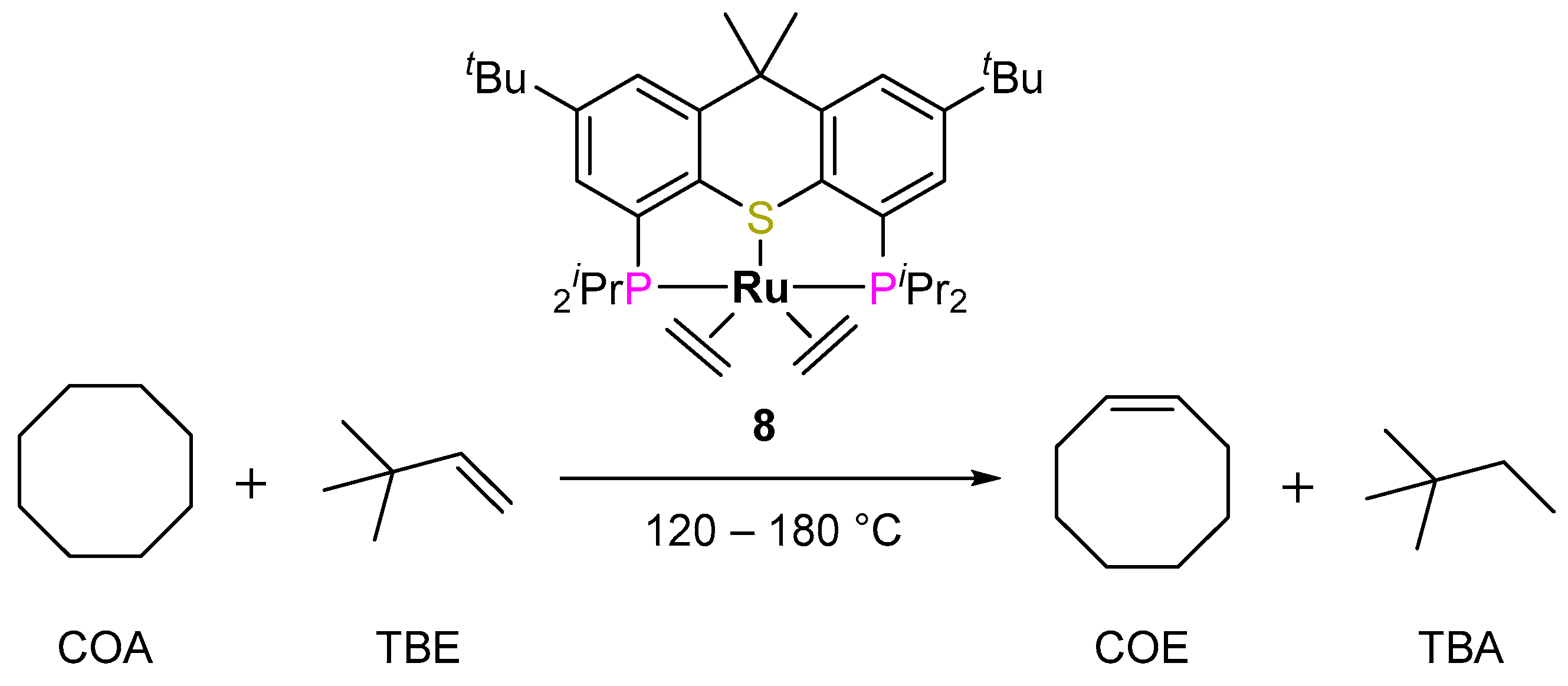
2.2.2. Alkane Dehydrogenation
2.2.3. Direct Alkenylation
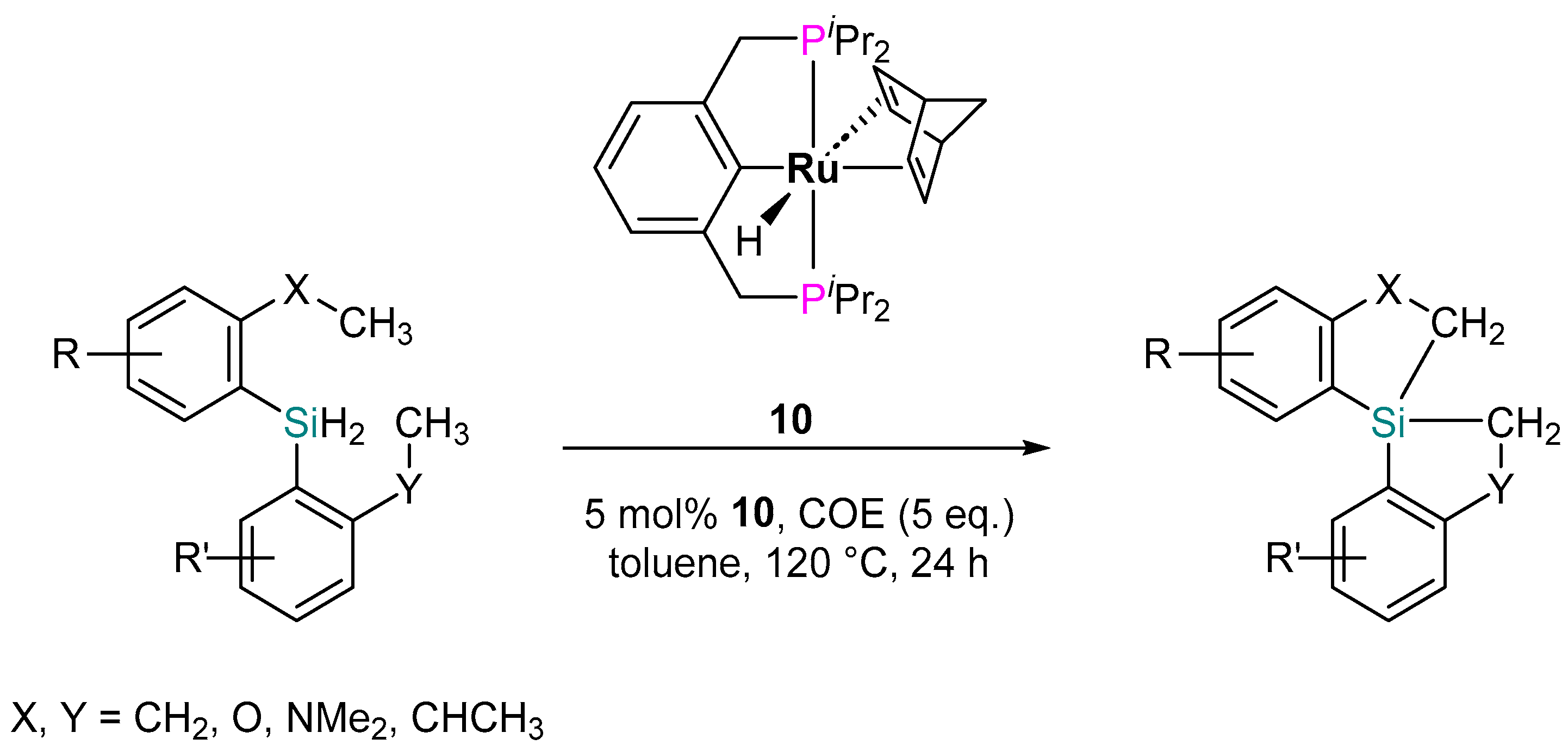
2.2.4. Dehydrogenative Silylation
2.3. Osmium
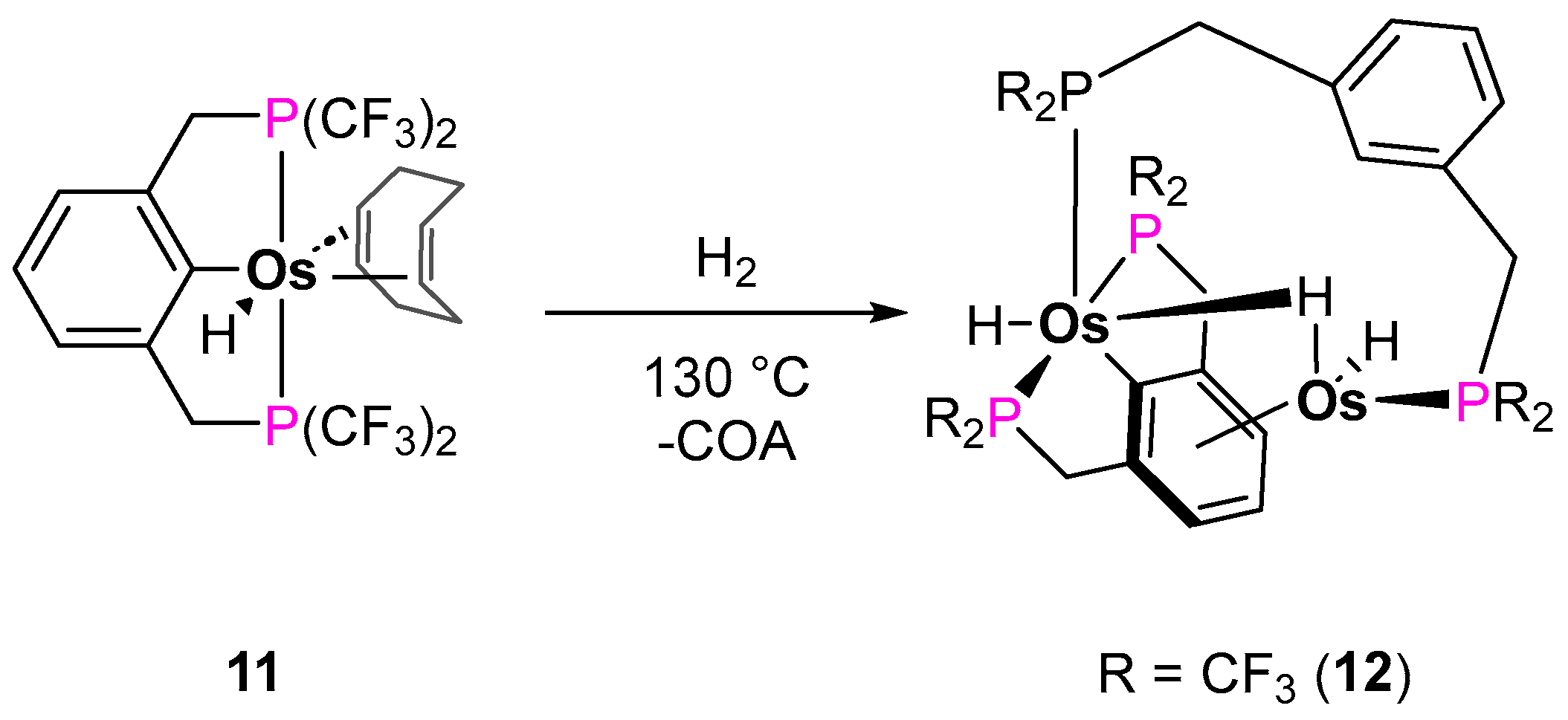
Alkane Dehydrogenation
3. Group 9 Pincer Complexes
3.1. Cobalt
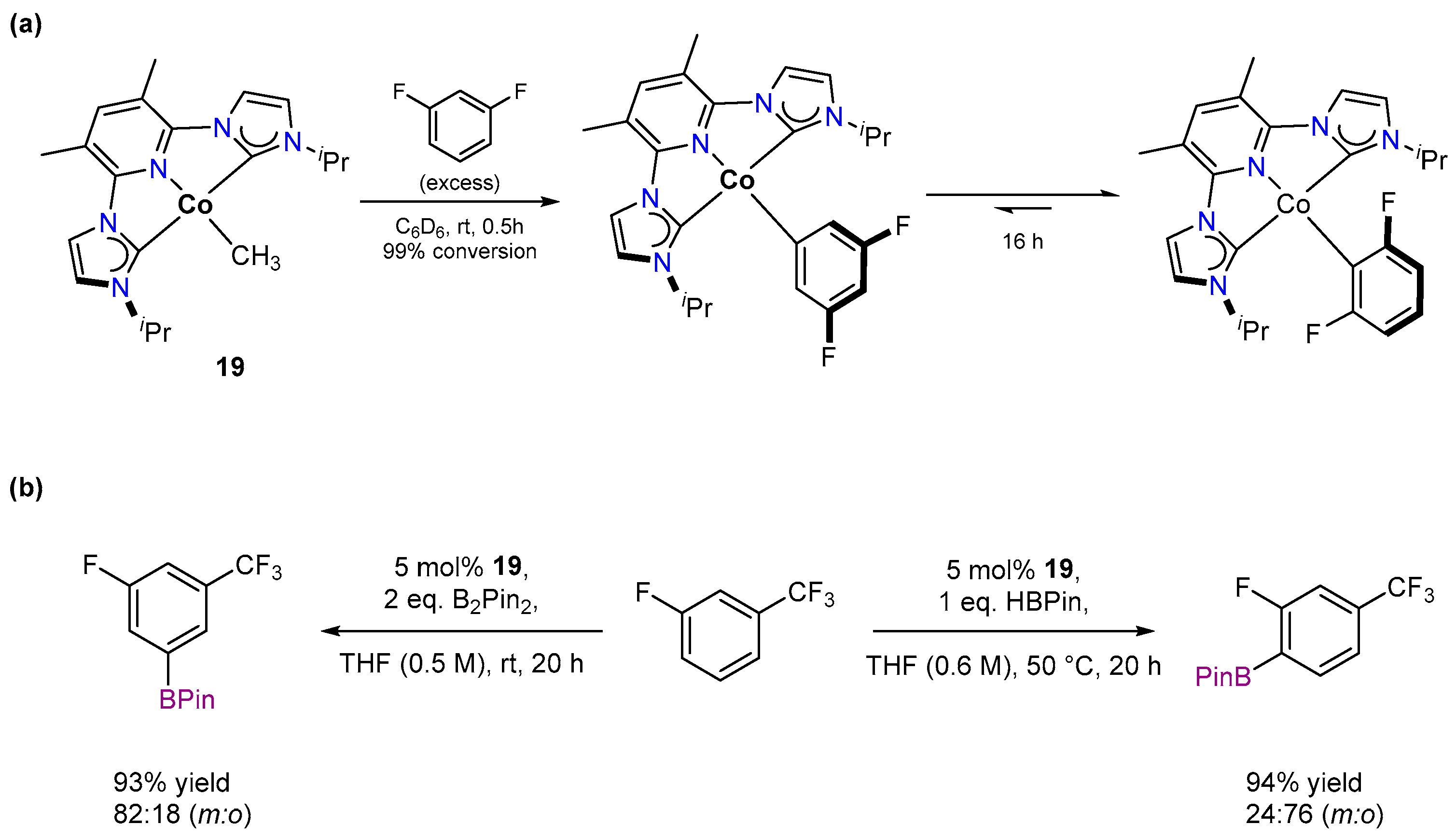
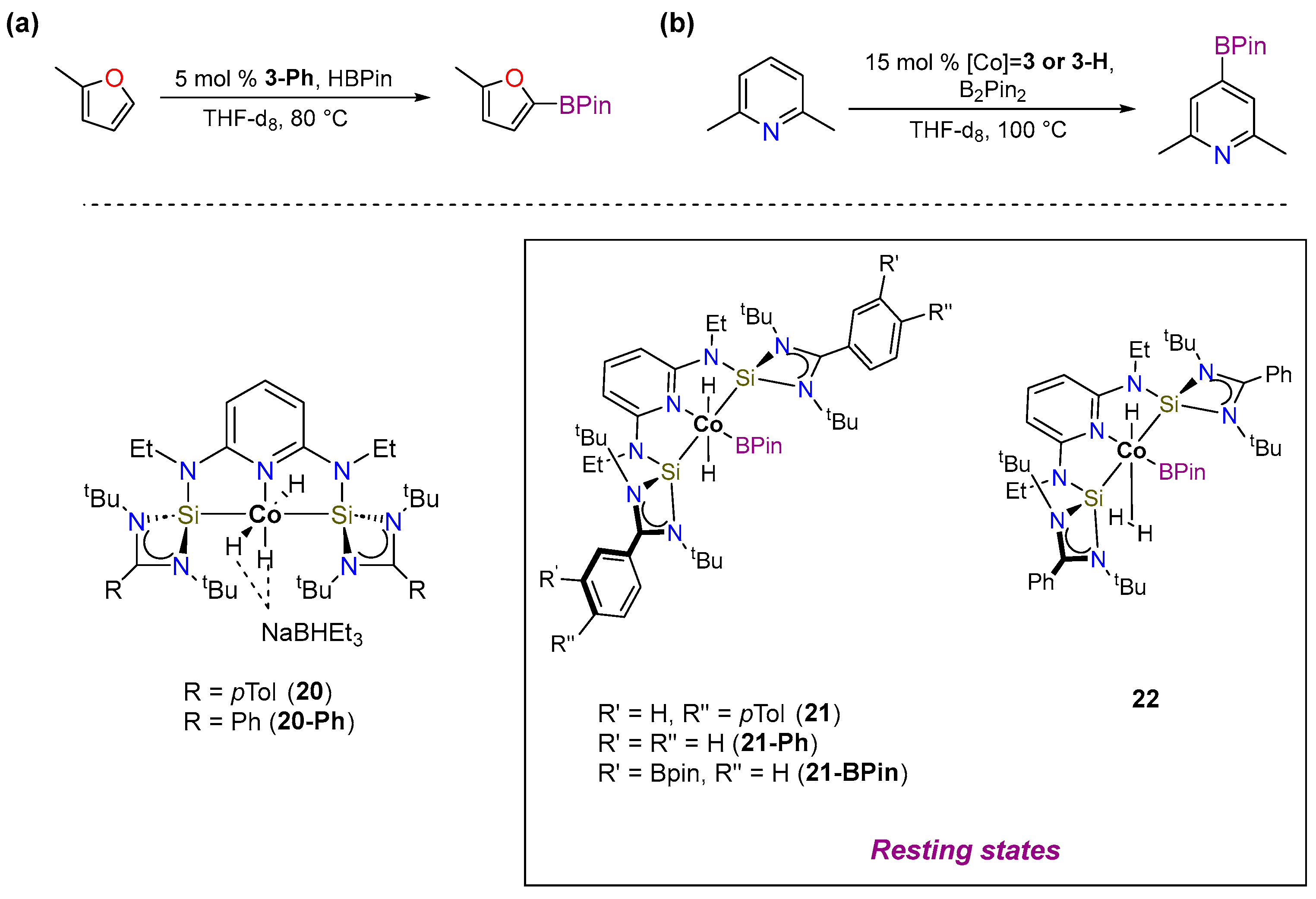
3.1.1. C–H Borylation
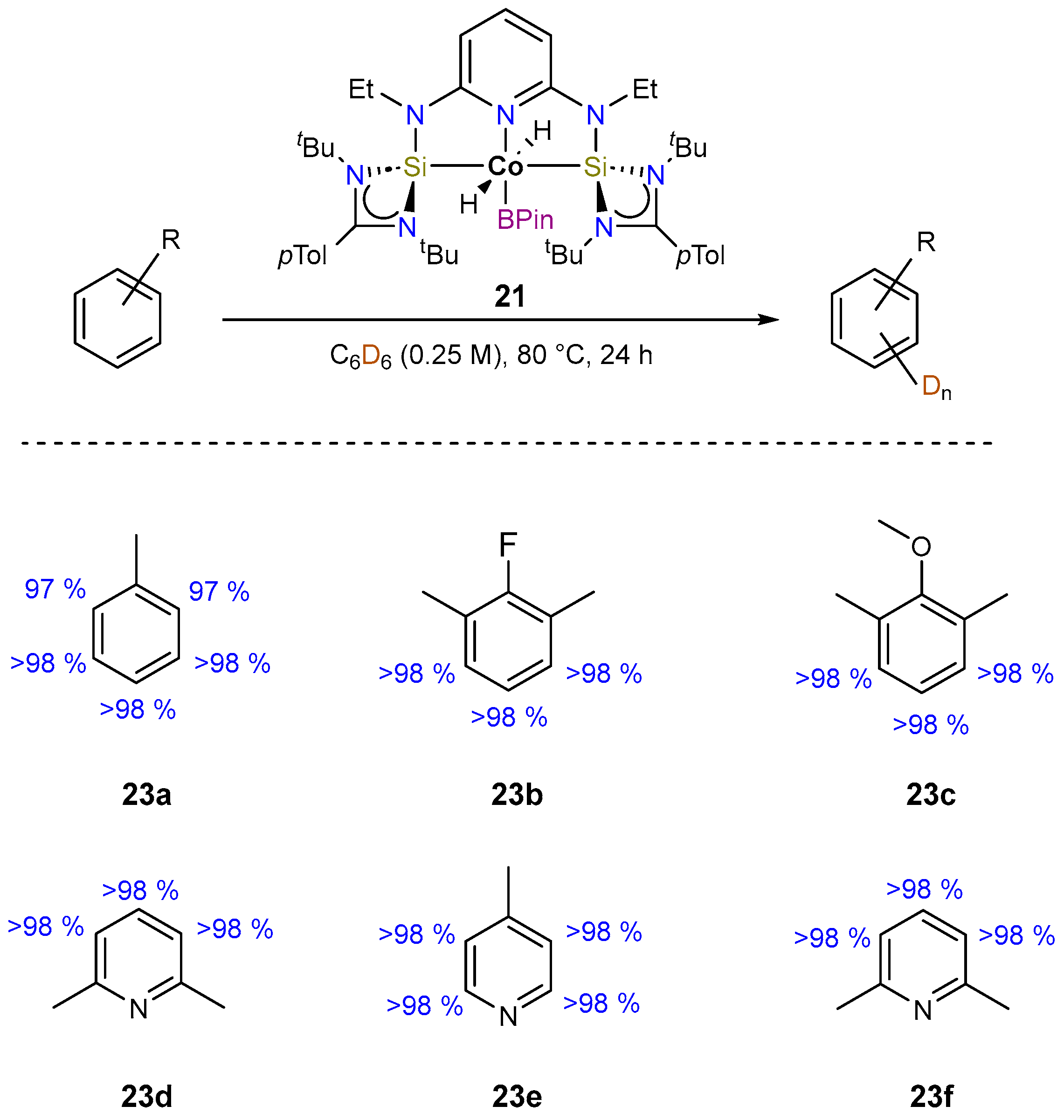
3.1.2. Hydrogen Isotope Exchange (HIE)
3.2. Rhodium
3.2.1. C–H Borylation
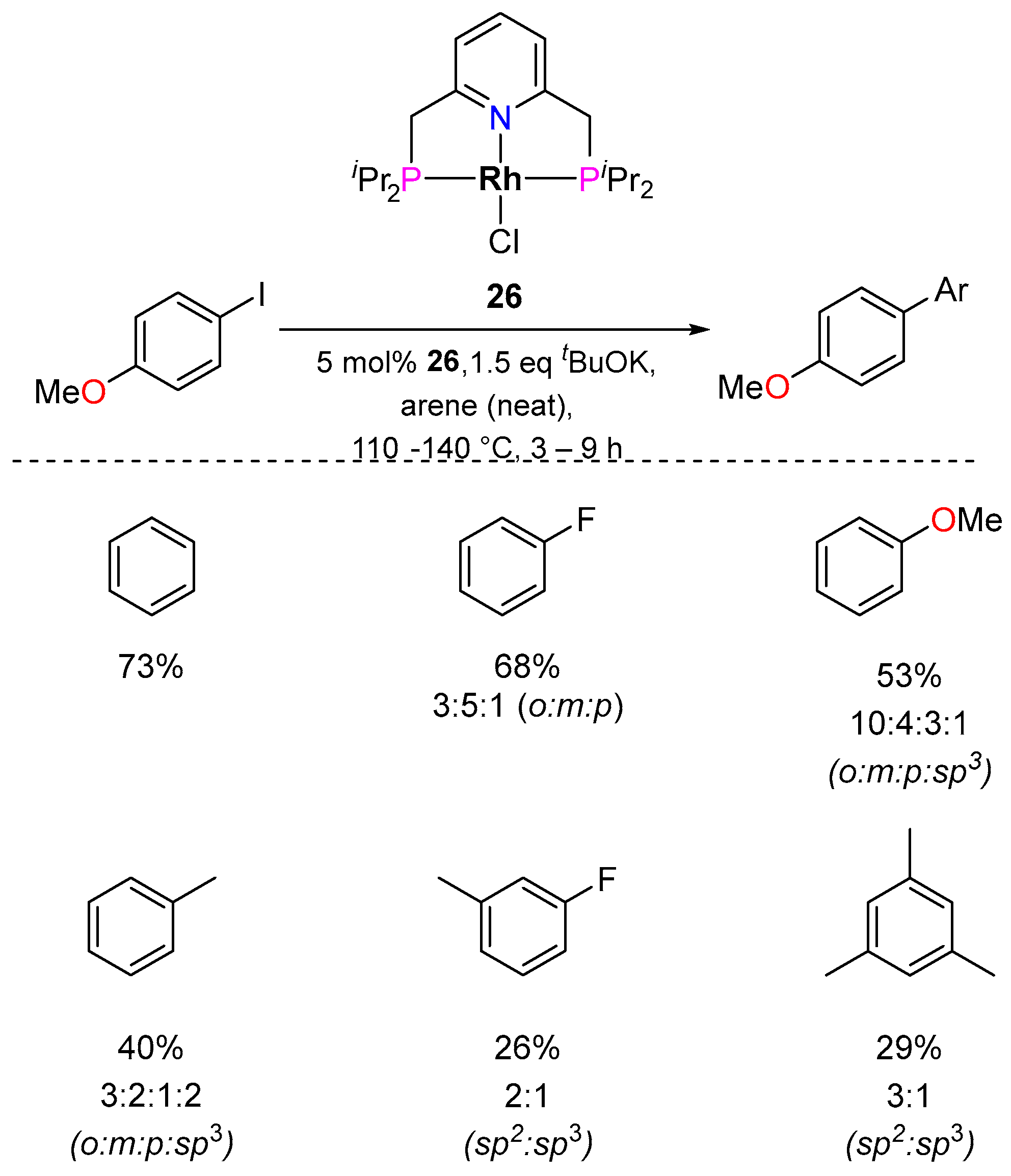
3.2.2. Direct Arylation
3.3. Iridium
3.3.1. C–H Borylation
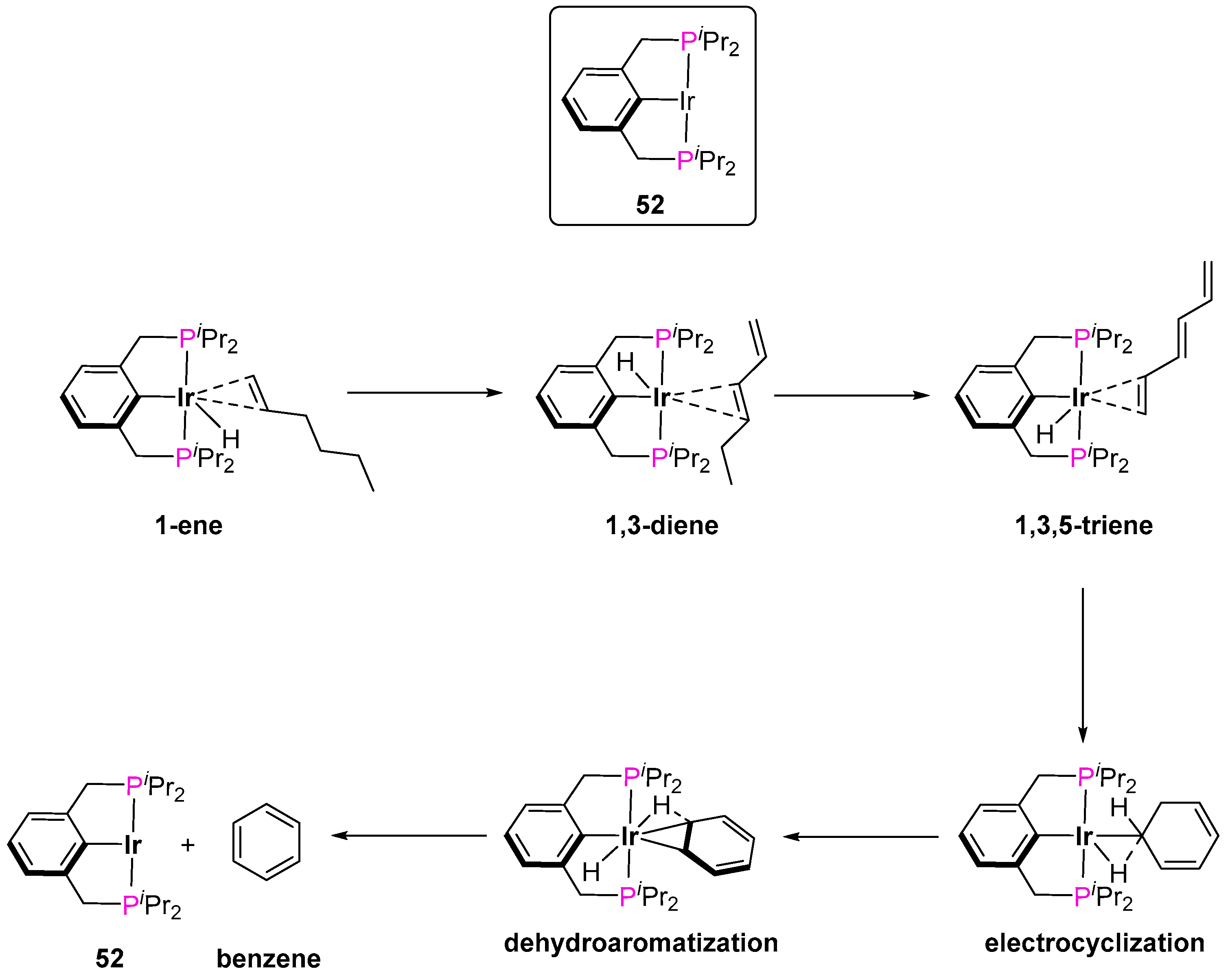
3.3.2. Alkane Dehydrogenation
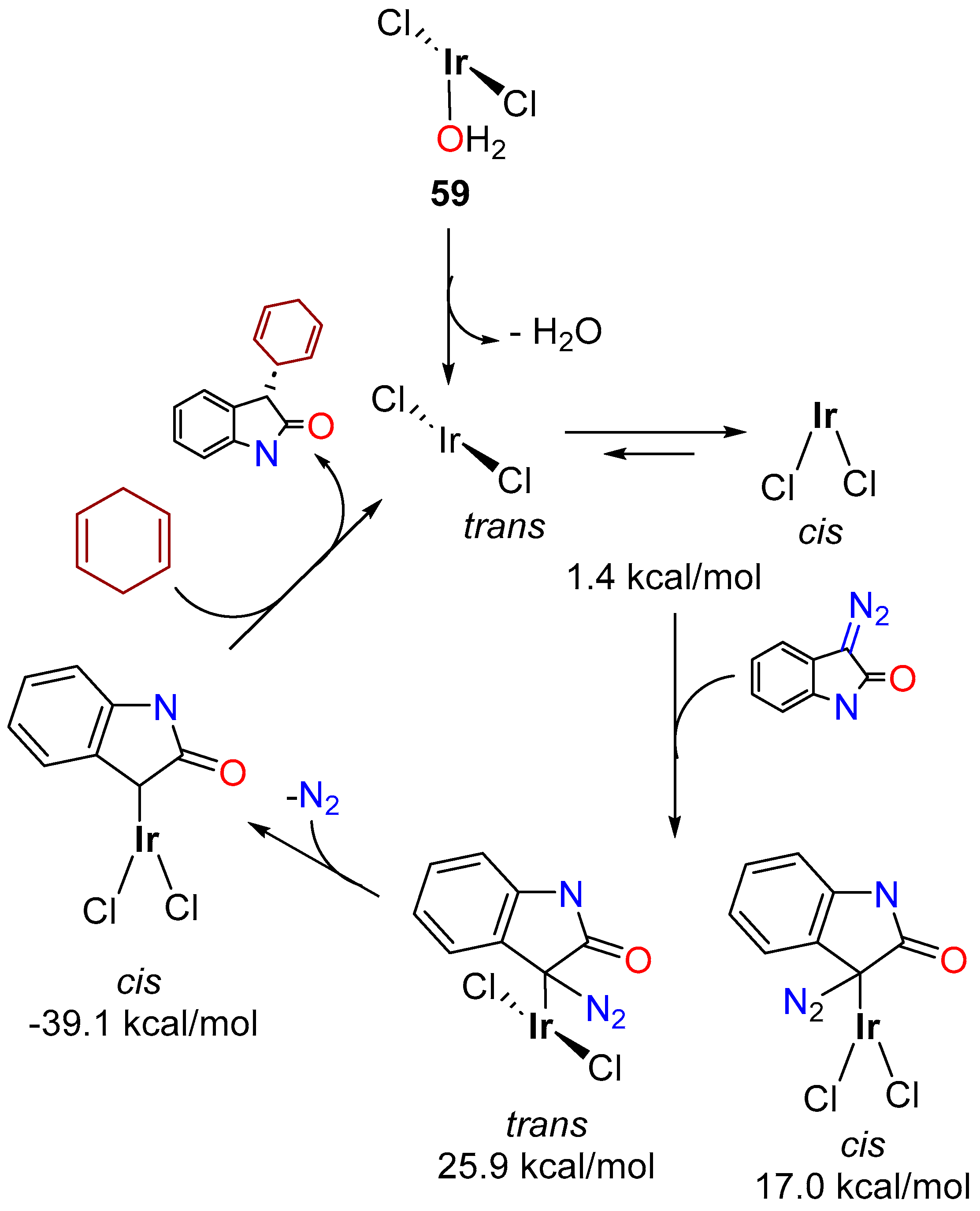
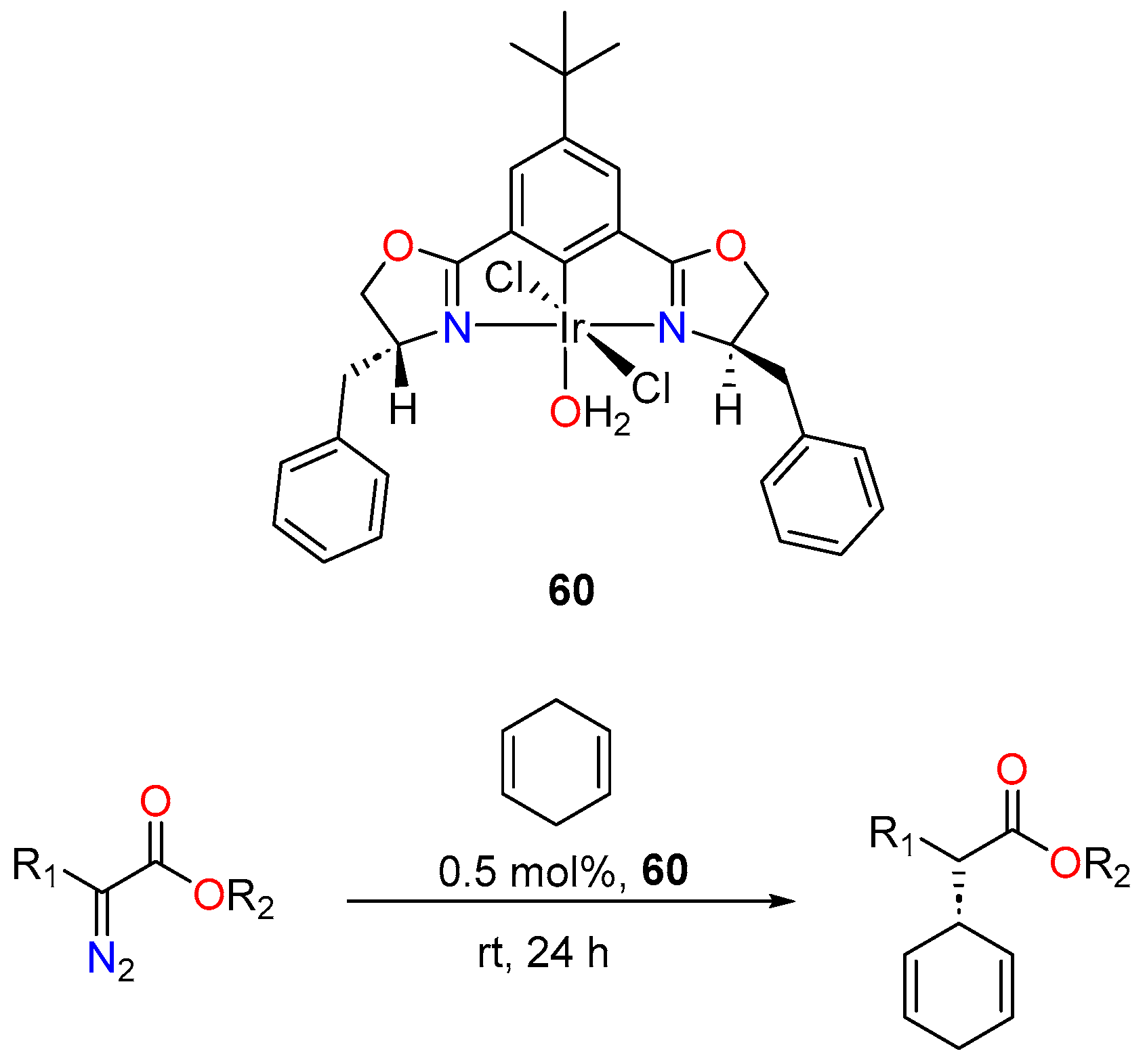
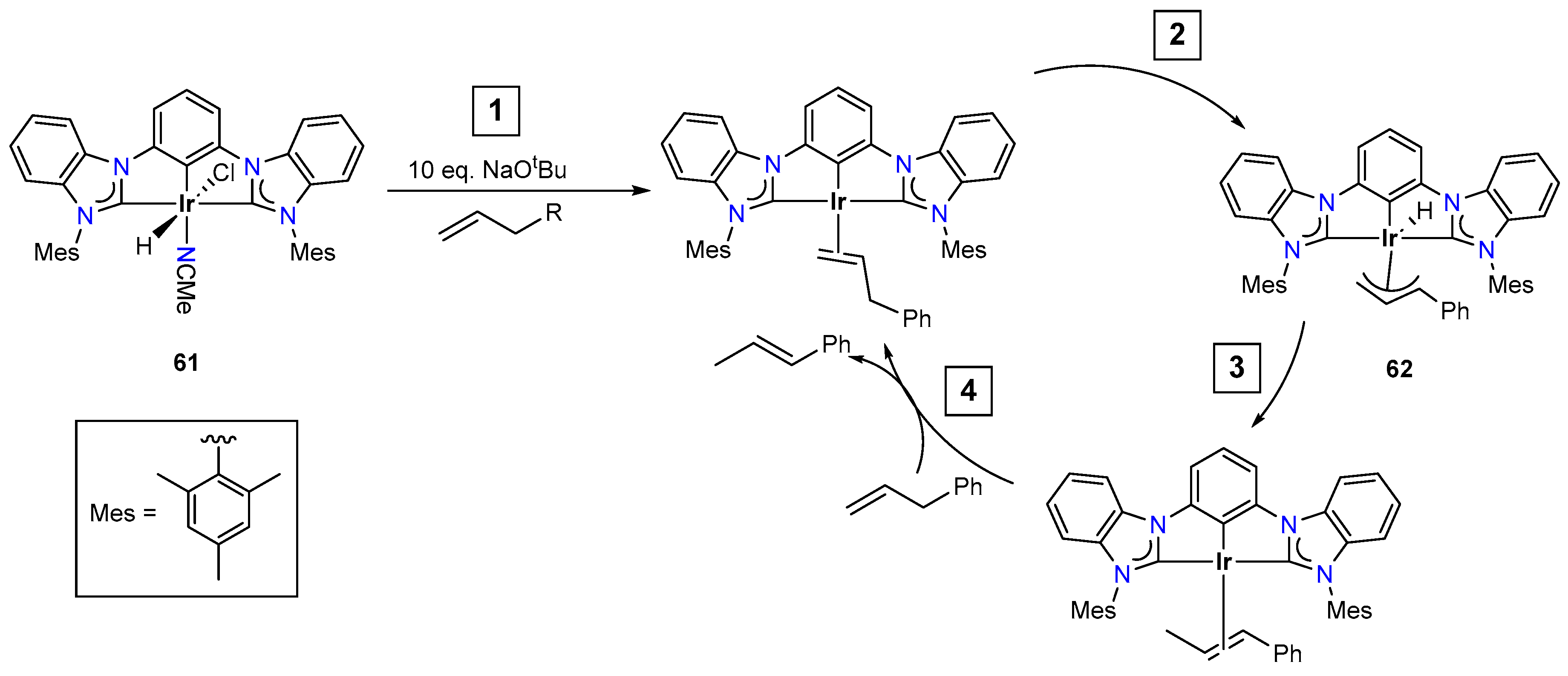
3.3.3. Direct Alkylation
3.3.4. Alkene Isomerization
4. Group 10 Pincer Complexes
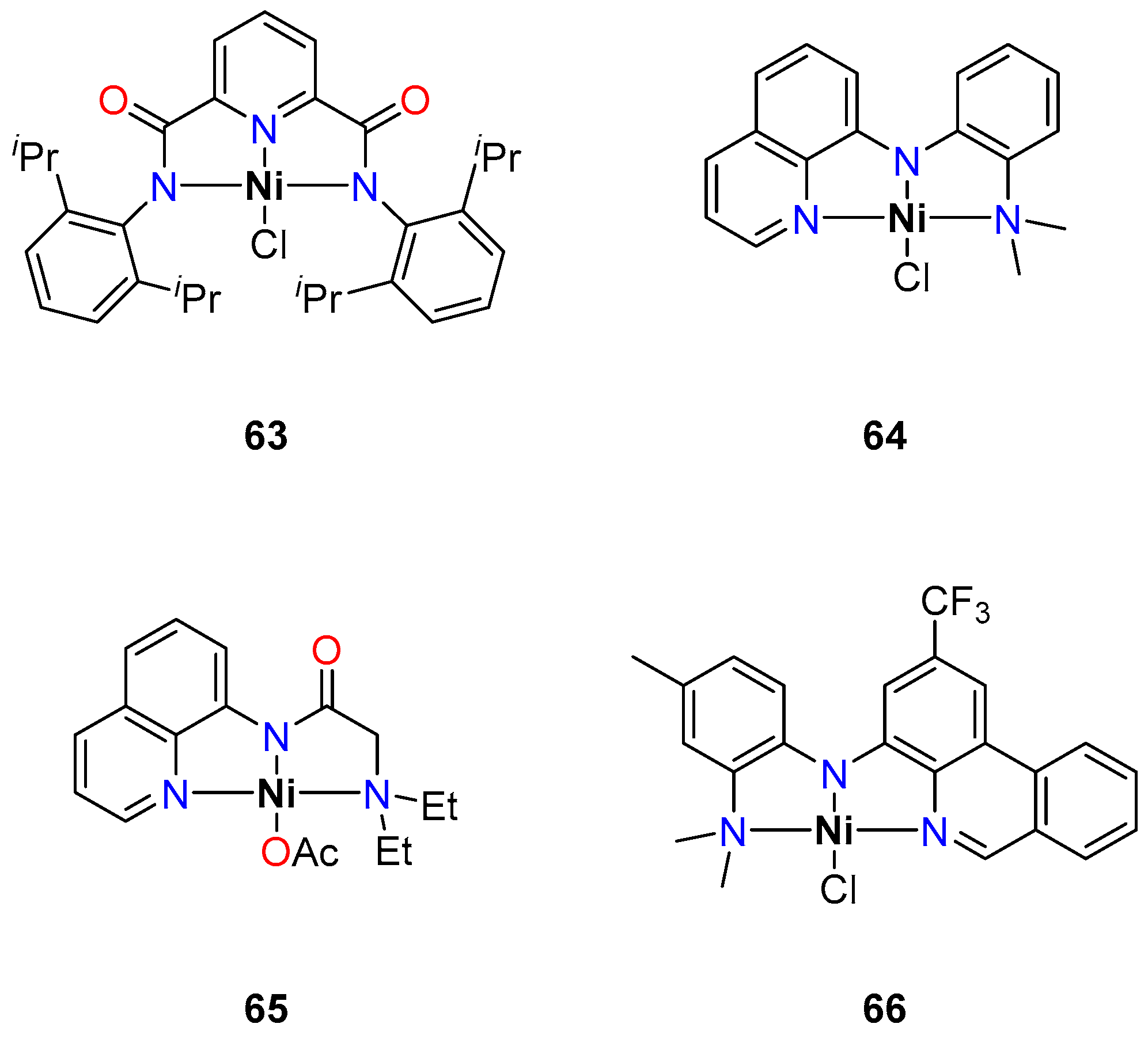
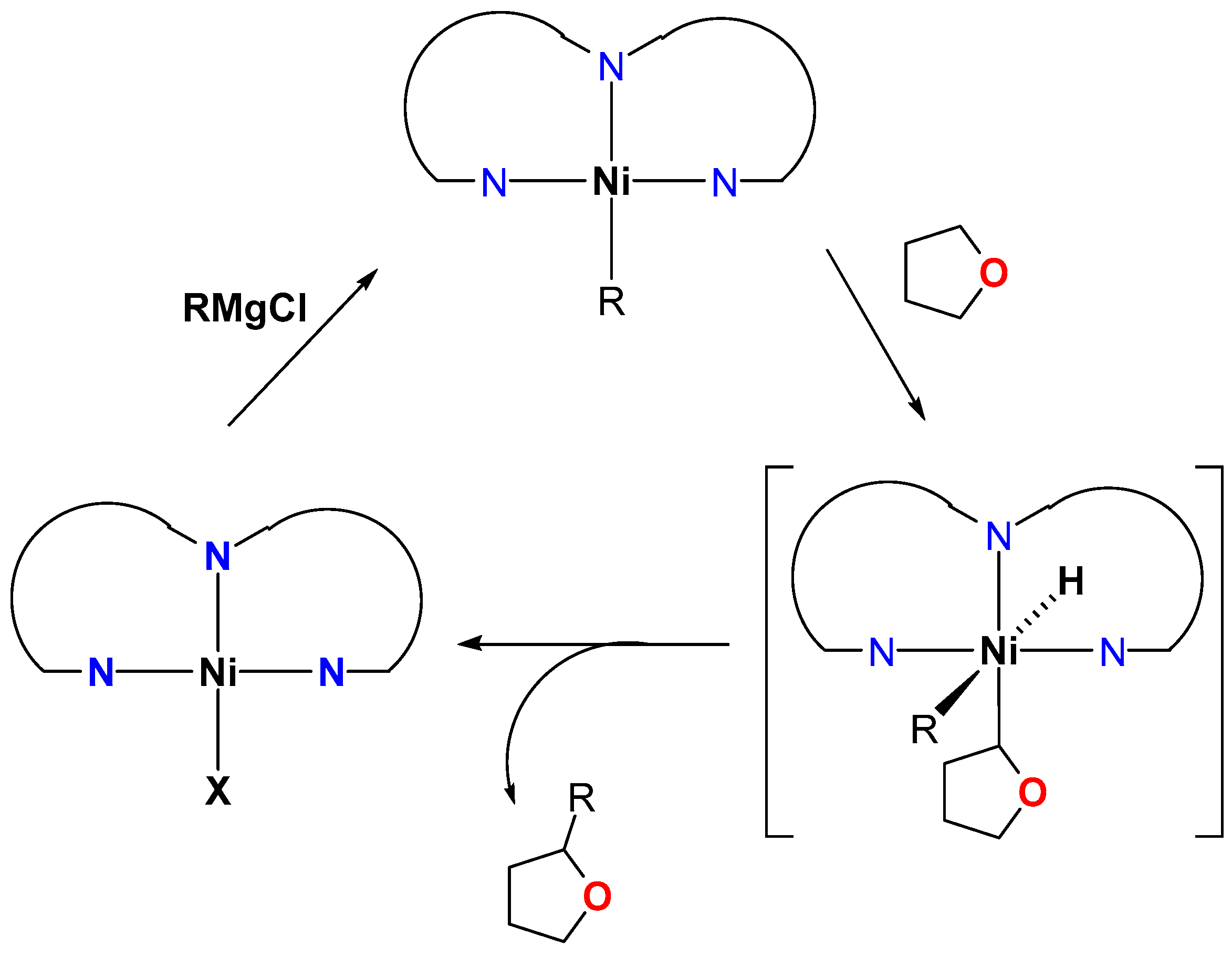
4.1. Nickel
Direct Alkylation
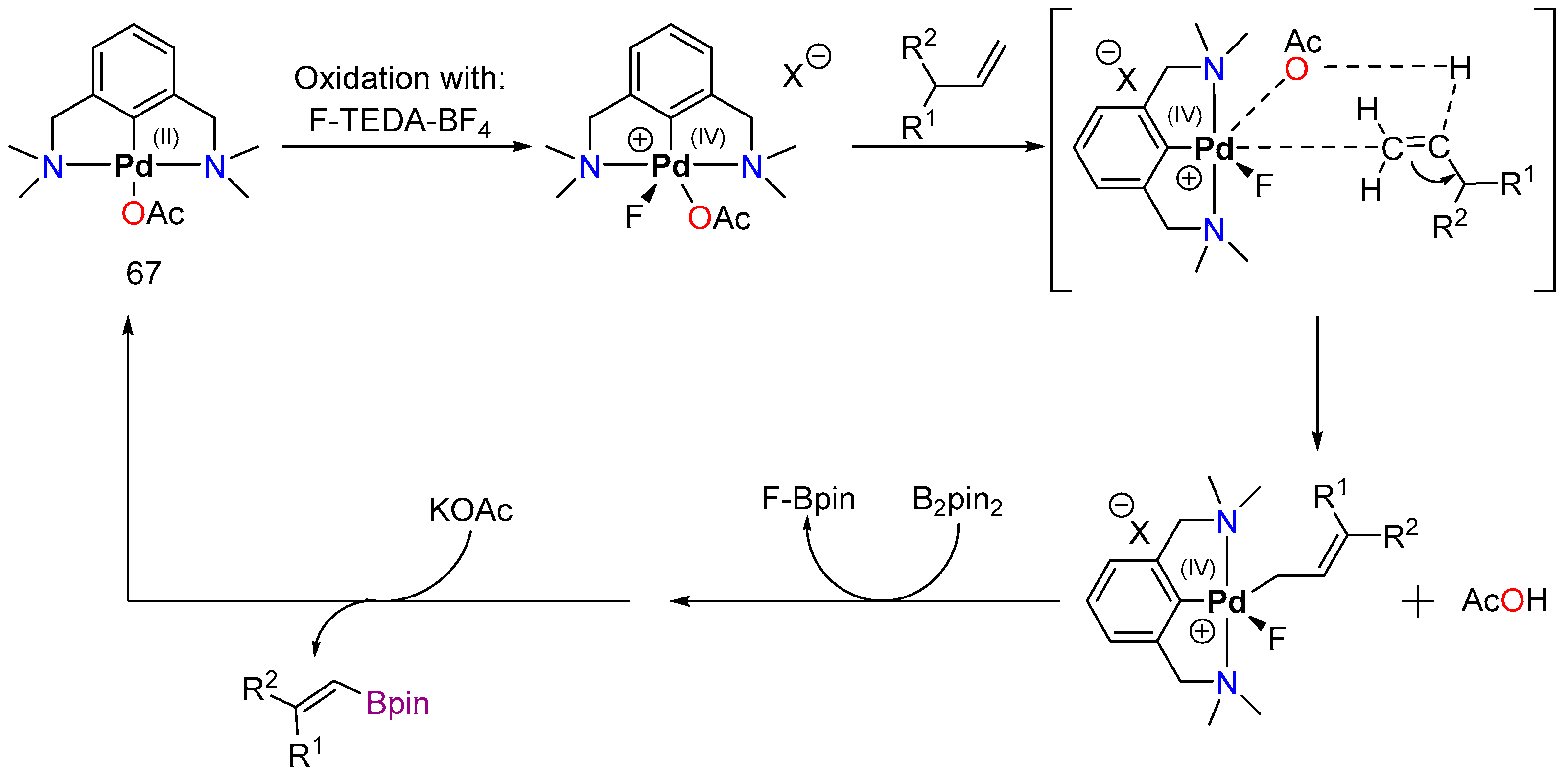
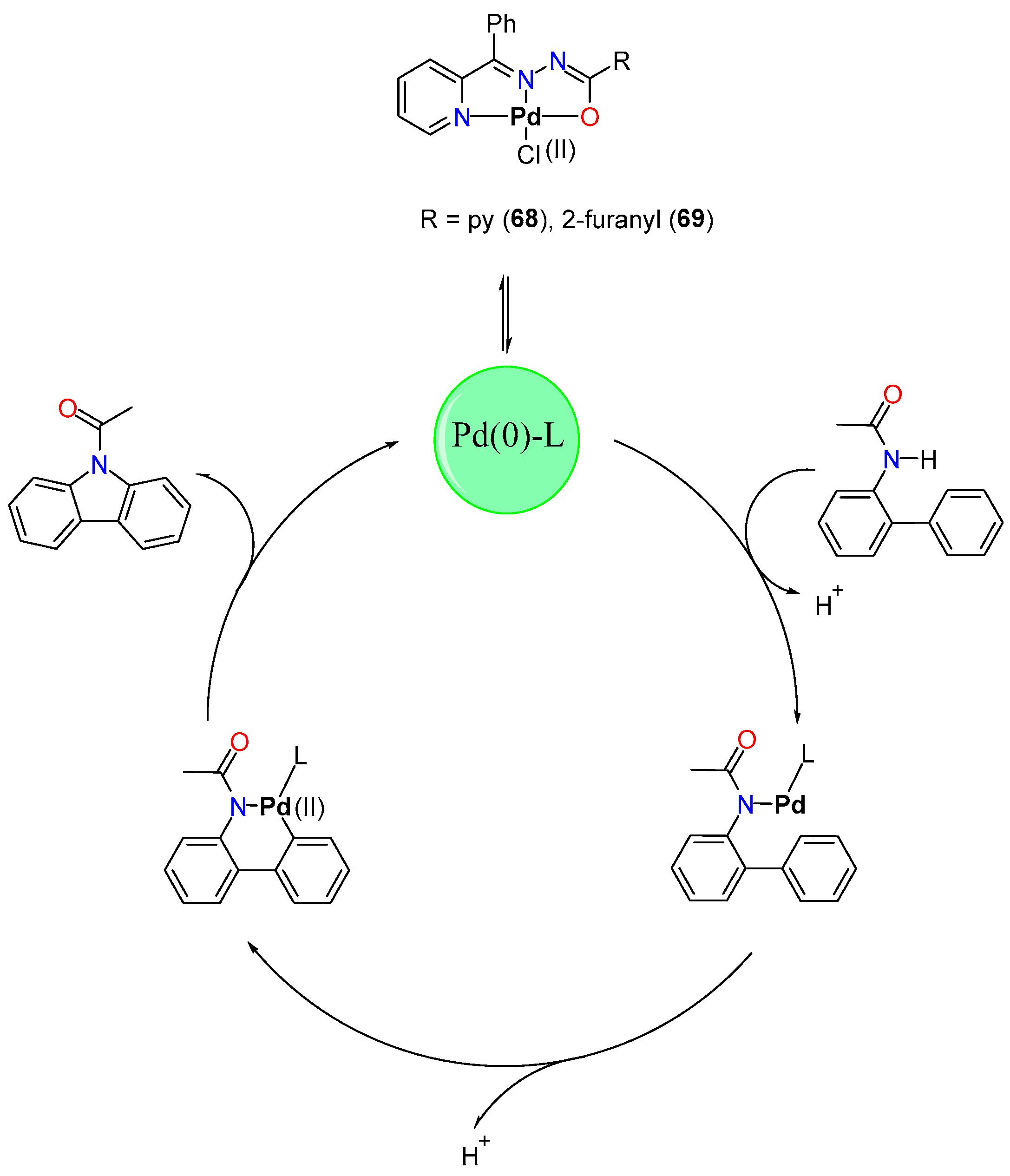
4.2. Palladium
4.2.1. C–H Borylation
4.2.2. Direct Alkylation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rogge, T.; Kaplaneris, N.; Chatani, N.; Kim, J.; Chang, S.; Punji, B.; Schafer, L.L.; Musaev, D.G.; Wencel-Delord, J.; Roberts, C.A.; et al. C–H Activation. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 2021, 1, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shul’pin, G.B. C–H Functionalization: Thoroughly Tuning Ligands at a Metal Ion, a Chemist Can Greatly Enhance Catalyst’s Activity and Selectivity. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 12794–12818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.Y.-K.; Youn, S.W. C-H activation: A Complementary Tool in the Total Synthesis of Complex Natural Products. Chem. Eur. J. 2012, 18, 9452–9474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdés, H.; Rufino-Felipe, E.; Morales-Morales, D. Pincer Complexes, Leading Characters in C–H Bond Activation Processes. Synthesis and Catalytic Applications. J. Organomet. Chem. 2019, 898, 120864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landaeta, V.R.; Rodríguez-Lugo, R.E. Insights on the C H Bond Activation by Transition Metal Complexes from Groups 8–10 Bearing (P-N) Chelates. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2017, 426, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillemard, L.; Kaplaneris, N.; Ackermann, L.; Johansson, M.J. Late-Stage C–H Functionalization Offers New Opportunities in Drug Discovery. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2021, 5, 522–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gensch, T.; Hopkinson, M.N.; Glorius, F.; Wencel-Delord, J. Mild Metal-Catalyzed C–H Activation: Examples and Concepts. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 2900–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wencel-Delord, J.; Dröge, T.; Liu, F.; Glorius, F. Towards Mild Metal-Catalyzed C–H Bond Activation. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 4740–4761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rej, S.; Das, A.; Chatani, N. Strategic Evolution in Transition Metal-Catalyzed Directed C–H Bond Activation and Future Directions. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 431, 213683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasera, A.; Biswas, J.P.; Ali Alshehri, A.; Ahmed Al-Thabaiti, S.; Mokhtar, M.; Maiti, D. Transition Metal Pincer Complexes: A Series of Potential Catalysts in C H Activation Reactions. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 475, 214915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ess, D.H.; Goddard, W.A.; Periana, R.A. Electrophilic, Ambiphilic, and Nucleophilic C−H Bond Activation: Understanding the Electronic Continuum of C−H Bond Activation Through Transition-State and Reaction Pathway Interaction Energy Decompositions. Organometallics 2010, 29, 6459–6472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakis, J.M.; Smejkal, T.; Wencel-Delord, J. Cyclometallated Complexes as Catalysts for C–H Activation and Functionalization. Chem. Commun. 2022, 58, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najafian, A.; Cundari, T.R. Methane C–H Activation via 3d Metal Methoxide Complexes with Potentially Redox-Noninnocent Pincer Ligands: A Density Functional Theory Study. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 12282–12290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Wang, C.; Fan, H. Theoretical Studies on the Intra- and Intermolecular C–H Activation by T-Shaped Pincer Complexes. J. Organomet. Chem. 2011, 696, 4064–4069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Koten, G. Tuning the Reactivity of Metals Held in a Rigid Ligand Environment. Pure Appl. Chem. 1989, 61, 1681–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Morales, D. Pincer Compounds: Chemistry and Applications, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; ISBN 0128129328. [Google Scholar]
- Morales-Morales, D.; Cruz Almanza, R. Pincer Complexes. Applications in Catalysis. J. Mex. Chem. Soc. 2004, 48, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asay, M.; Morales-Morales, D. Non-Symmetric Pincer Ligands: Complexes and Applications in Catalysis. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 17432–17447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omae, I. Organometallic Intramolecular-Coordination Compounds Containing a Phosphorus Donor Ligand. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1980, 32, 235–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parshall, G.W. Intramolecular Aromatic Substitution in Transition Metal Complexes. Acc. Chem. Res. 1970, 3, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peris, E.; Crabtree, R.H. Key Factors in Pincer Ligand Design. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 1959–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Morales, D.; Jensen, C.G.M. The Chemistry of Pincer Compounds; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; ISBN 0080545157. [Google Scholar]
- van Koten, G. Organometallic Pincer Chemistry. Top Organomet. Chem. 2013, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulton, C.J.; Shaw, B.L. Transition Metal–Carbon Bonds. Part XLII. Complexes of Nickel, Palladium, Platinum, Rhodium and Iridium with the Tridentate Ligand 2,6-Bis[(Di-t-Butylphosphino) Methyl] Phenyl. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1976, 1020–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Empsall, H.D.; Hyde, E.M.; Shaw, B.L. Some Unusual Iridium-(I), -(II), and -(III) Complexes Formed from 2-Methoxyphenyl- or 2-Hydroxyphenyl-Di-t-Butylphosphine. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1975, 1690–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, B.L.; Uttley, M.F. Dihydro-Platinum(II) and Related Complexes. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1974, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Morales, D. Recent Applications of Phosphinite POCOP Pincer Complexes Towards Organic Transformations. Mini Rev. Org. Chem. 2008, 5, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asay, M.; Morales-Morales, D. Recent Advances on the Chemistry of POCOP–Nickel Pincer Compounds. In The Privileged Pincer-Metal Platform: Coordination Chemistry & Applications, 1st ed.; van Koten, G., Gosagge, R.A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 54, pp. 239–268. [Google Scholar]
- Serrano-Becerra, J.M.; Morales-Morales, D. Applications in Catalysis and Organic Transformations Mediated by Platinum Group PCP and PNP Aromatic-Based Pincer Complexes: Recent Advances. Curr. Org. Synth. 2009, 6, 169–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés, H.; González-Sebastián, L.; Morales-Morales, D. Aromatic Para-Functionalized NCN Pincer Compounds. J. Organomet. Chem. 2017, 845, 229–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Navarro, J.A.; Sánchez-Mora, A.; Serrano-García, J.S.; Amaya-Flórez, A.; Colorado-Peralta, R.; Reyes-Márquez, V.; Morales-Morales, D. Advances in Cross-Coupling Reactions Catalyzed by Aromatic Pincer Complexes Based on Earth-Abundant 3d Metals (Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu). Catalysts 2024, 14, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Morales, D.; Redón, R.; Yung, C.; Jensen, C.M. Dehydrogenation of Alkanes Catalyzed by an Iridium Phosphinito PCP Pincer Complex. Inorganica Chim. Acta 2004, 357, 2953–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés, H.; García-Eleno, M.A.; Canseco-Gonzalez, D.; Morales-Morales, D. Recent Advances in Catalysis with Transition-Metal Pincer Compounds. ChemCatChem 2018, 10, 3136–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gensch, T.; James, M.J.; Dalton, T.; Glorius, F. Increasing Catalyst Efficiency in C−H Activation Catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 2296–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, I.F.; Wilson, J.W.; Hartwig, J.F. Transition-Metal-Catalyzed Silylation and Borylation of C–H Bonds for the Synthesis and Functionalization of Complex Molecules. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 11619–11663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartwig, J.F. Borylation and Silylation of C–H Bonds: A Platform for Diverse C–H Bond Functionalizations. Acc. Chem. Res. 2012, 45, 864–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arevalo, R.; Chirik, P.J. Enabling Two-Electron Pathways with Iron and Cobalt: From Ligand Design to Catalytic Applications. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 9106–9123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T.; Kuriyama, S.; Nakajima, K.; Nishibayashi, Y. Catalytic C−H Borylation Using Iron Complexes Bearing 4,5,6,7-Tetrahydroisoindol-2-ide-Based PNP-Type Pincer Ligand. Chem. Asian J. 2019, 14, 2097–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamitani, M.; Kusaka, H.; Yuge, H. Iron-Catalyzed Versatile and Efficient C(sp2)-H Borylation. Chem. Lett. 2019, 48, 898–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzrodt, J.; Derdau, V.; Kerr, W.J.; Reid, M. Deuterium- and Tritium-Labelled Compounds: Applications in the Life Sciences. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 1758–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Q.-K.; Shi, H. Catalytic Hydrogen Isotope Exchange Reactions in Late-Stage Functionalization. Synlett 2022, 33, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, G.; Paul, N.; Oliver, G.A.; Werz, D.B.; Maiti, D. C–H Deuteration of Organic Compounds and Potential Drug Candidates. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 3123–3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzrodt, J.; Derdau, V.; Kerr, W.J.; Reid, M. C−H Functionalisation for Hydrogen Isotope Exchange. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 3022–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Hesk, D. Base Metal-catalyzed Hydrogen Isotope Exchange. J. Label. Comp. Radiopharm. 2020, 63, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopf, S.; Bourriquen, F.; Li, W.; Neumann, H.; Junge, K.; Beller, M. Recent Developments for the Deuterium and Tritium Labeling of Organic Molecules. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 6634–6718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattler, A. Hydrogen/Deuterium (H/D) Exchange Catalysis in Alkanes. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 2296–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pony Yu, R.; Hesk, D.; Rivera, N.; Pelczer, I.; Chirik, P.J. Iron-Catalysed Tritiation of Pharmaceuticals. Nature 2016, 529, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.P.; Darmon, J.M.; Semproni, S.P.; Turner, Z.R.; Chirik, P.J. Synthesis of Iron Hydride Complexes Relevant to Hydrogen Isotope Exchange in Pharmaceuticals. Organometallics 2017, 36, 4341–4343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corpas, J.; Viereck, P.; Chirik, P.J. C(sp2)–H Activation with Pyridine Dicarbene Iron Dialkyl Complexes: Hydrogen Isotope Exchange of Arenes Using Benzene-d6 as a Deuterium Source. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 8640–8647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garhwal, S.; Kaushansky, A.; Fridman, N.; Shimon, L.J.W.; Ruiter, G. De Facile H/D Exchange at (Hetero)Aromatic Hydrocarbons Catalyzed by a Stable Trans-Dihydride N-Heterocyclic Carbene (NHC) Iron Complex. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 17131–17139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashiguchi, B.G.; Young, K.J.H.; Yousufuddin, M.; Goddard, W.A.; Periana, R.A. Acceleration of Nucleophilic CH Activation by Strongly Basic Solvents. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 12542–12545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yao, W.; Fang, H.; Hu, A.; Huang, Z. Catalytic Alkane Dehydrogenations. Sci. Bull. 2015, 60, 1316–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Bhatti, T.M.; Goldman, A.S. Dehydrogenation of Alkanes and Aliphatic Groups by Pincer-Ligated Metal Complexes. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 12357–12384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Zhou, T.; Emge, T.J.; Mironov, O.; Saxton, R.J.; Krogh-Jespersen, K.; Goldman, A.S. Dehydrogenation of n-Alkanes by Solid-Phase Molecular Pincer-Iridium Catalysts. High Yields of α-Olefin Product. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 9894–9911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shada, A.D.R.; Miller, A.J.M.; Emge, T.J.; Goldman, A.S. Catalytic Dehydrogenation of Alkanes by PCP-Pincer Iridium Complexes Using Proton and Electron Acceptors. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 3009–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalenko, O.O.; Wendt, O.F. An Electron Poor Iridium Pincer Complex for Catalytic Alkane Dehydrogenation. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 15963–15969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Malakar, S.; Zhou, T.; Murugesan, S.; Huang, C.; Emge, T.J.; Krogh-Jespersen, K.; Goldman, A.S. Catalytic Alkane Transfer Dehydrogenation by PSP-Pincer-Ligated Ruthenium. Deactivation of an Extremely Reactive Fragment by Formation of Allyl Hydride Complexes. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 4072–4083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherney, A.H.; Kadunce, N.T.; Reisman, S.E. Enantioselective and Enantiospecific Transition-Metal-Catalyzed Cross-Coupling Reactions of Organometallic Reagents to Construct C–C Bonds. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 9587–9652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, R.; Bellina, F.; Lessi, M. Alkenylation Reactions of Heteroarenes by Transition-Metal Catalysts. Synthesis 2010, 24, 4131–4153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messaoudi, S.; Brion, J.; Alami, M. Transition-Metal-Catalyzed Direct C–H Alkenylation, Alkynylation, Benzylation, and Alkylation of (Hetero)Arenes. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2010, 2010, 6495–6516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Tu, Y.-Q.; Lu, K.; Chen, Q.-L.; Zhang, F.-M.; Zhang, X.-M.; Pan, Y.-J.; Yan, Z.-B. Aromatic and Olefinic C-H Alkenylation by Catalysis with Spirocyclic NHC Ru(IV) Pincer Complex. Sci. China Chem. 2023, 66, 2791–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sarkar, S.; Liu, W.; Kozhushkov, S.I.; Ackermann, L. Weakly Coordinating Directing Groups for Ruthenium(II)-Catalyzed C-H Activation. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2014, 356, 1461–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Fang, H.; Liu, G.; Huang, Z. Ruthenium-Catalyzed Dual Dehydrogenative Silylation of C(sp3)–H Bonds: Access to Diverse Silicon-Centered Spirocycles. Org. Lett. 2021, 23, 7603–7607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Huang, W.-S.; Zhang, J.; Xu, L.-W. Recent Advances in Transition-Metal-Catalyzed Silylations of Arenes with Hydrosilanes: C–X Bond Cleavage or C–H Bond Activation Synchronized with Si–H Bond Activation. Synthesis 2015, 47, 3645–3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruver, B.C.; Adams, J.J.; Arulsamy, N.; Roddick, D.M. Acceptor Pincer Chemistry of Osmium: Catalytic Alkane Dehydrogenation by (CF3PCP)Os(Cod)(H). Organometallics 2013, 32, 6468–6475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obligacion, J.V.; Semproni, S.P.; Chirik, P.J. Cobalt-Catalyzed C–H Borylation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 4133–4136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obligacion, J.V.; Semproni, S.P.; Pappas, I.; Chirik, P.J. Cobalt-Catalyzed C(sp2)-H Borylation: Mechanistic Insights Inspire Catalyst Design. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 10645–10653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obligacion, J.V.; Chirik, P.J. Mechanistic Studies of Cobalt-Catalyzed C(sp2)–H Borylation of Five-Membered Heteroarenes with Pinacolborane. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 4366–4371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabst, T.P.; Obligacion, J.V.; Rochette, É.; Pappas, I.; Chirik, P.J. Cobalt-Catalyzed Borylation of Fluorinated Arenes: Thermodynamic Control of C(sp2)-H Oxidative Addition Results in Ortho-to-Fluorine Selectivity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 15378–15389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Obligacion, J.V.; Chirik, P.J.; Hall, M.B. Cobalt Pincer Complexes in Catalytic C–H Borylation: The Pincer Ligand Flips Rather Than Dearomatizes. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 10606–10618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabst, T.P.; Chirik, P.J. A Tutorial on Selectivity Determination in C(sp2)–H Oxidative Addition of Arenes by Transition Metal Complexes. Organometallics 2021, 40, 813–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obligacion, J.V.; Bezdek, M.J.; Chirik, P.J. C(sp2)–H Borylation of Fluorinated Arenes Using an Air-Stable Cobalt Precatalyst: Electronically Enhanced Site Selectivity Enables Synthetic Opportunities. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 2825–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.; Pabst, T.P.; Hierlmeier, G.; Chirik, P.J. Exploring the Effect of Pincer Rigidity on Oxidative Addition Reactions with Cobalt(I) Complexes. Organometallics 2023, 42, 708–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Pabst, T.P.; Chirik, P.J. Effect of Pincer Methylation on the Selectivity and Activity in (PNP)Cobalt-Catalyzed C(sp2)–H Borylation. Organometallics 2021, 40, 3766–3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obligacion, J.V.; Zhong, H.; Chirik, P.J. Insights into Activation of Cobalt Pre-Catalysts for C(sp2)−H Functionalization. Isr. J. Chem. 2017, 57, 1032–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Léonard, N.G.; Bezdek, M.J.; Chirik, P.J. Cobalt-Catalyzed C(sp2)–H Borylation with an Air-Stable, Readily Prepared Terpyridine Cobalt(II) Bis(Acetate) Precatalyst. Organometallics 2017, 36, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabst, T.P.; Chirik, P.J. Development of Cobalt Catalysts for the Meta-Selective C(sp2)–H Borylation of Fluorinated Arenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 6465–6474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roque, J.B.; Shimozono, A.M.; Pabst, T.P.; Hierlmeier, G.; Peterson, P.O.; Chirik, P.J. Kinetic and Thermodynamic Control of C(sp2)–H Activation Enables Site-Selective Borylation. Science 2023, 382, 1165–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, H.; Zhou, Y.; Bai, Y.; Cui, C.; Driess, M. Cobalt-Catalyzed Regioselective Borylation of Arenes: N-Heterocyclic Silylene as an Electron Donor in the Metal-Mediated Activation of C−H Bonds. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 5663–5667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arevalo, R.; Pabst, T.P.; Chirik, P.J. C(sp2)–H Borylation of Heterocycles by Well-Defined Bis(Silylene)Pyridine Cobalt(III) Precatalysts: Pincer Modification, C(sp2)–H Activation, and Catalytically Relevant Intermediates. Organometallics 2020, 39, 2763–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roque, J.B.; Pabst, T.P.; Chirik, P.J. C(sp2)–H Activation with Bis(Silylene)Pyridine Cobalt(III) Complexes: Catalytic Hydrogen Isotope Exchange of Sterically Hindered C–H Bonds. ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 8877–8885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semproni, S.P.; Hojilla Atienza, C.C.; Chirik, P.J. Oxidative Addition and C–H Activation Chemistry with a PNP Pincer-Ligated Cobalt Complex. Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 1956–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteruelas, M.A.; Oliván, M.; Vélez, A. POP–Rhodium-Promoted C–H and B–H Bond Activation and C–B Bond Formation. Organometallics 2015, 34, 1911–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, T.; Brennessel, W.W.; Clot, E.; Eisenstein, O.; Jones, W.D. Synthesis, Structure, and Reductive Elimination in the Series Tp′Rh(PR3)(ArF)H.; Determination of Rhodium–Carbon Bond Energies of Fluoroaryl Substituents. Dalton Trans. 2010, 39, 10495–10509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budiman, Y.P.; Perutz, R.N.; Steel, P.G.; Radius, U.; Marder, T.B. Applications of Transition Metal-Catalyzed Ortho-Fluorine-Directed C–H Functionalization of (Poly)Fluoroarenes in Organic Synthesis. Chem. Rev. 2024, 124, 4822–4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalläne, S.I.; Teltewskoi, M.; Braun, T.; Braun, B. C–H and C–F Bond Activations at a Rhodium(I) Boryl Complex: Reaction Steps for the Catalytic Borylation of Fluorinated Aromatics. Organometallics 2015, 34, 1156–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gair, J.J.; Qiu, Y.; Chan, N.H.; Filatov, A.S.; Lewis, J.C. Rhodium Complexes of 2,6-Bis(Dialkylphosphinomethyl)Pyridines: Improved C–H Activation, Expanded Reaction Scope, and Catalytic Direct Arylation. Organometallics 2017, 36, 4699–4706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.H.; Pérez-Torrente, J.J.; Jiménez, M.V.; Modrego, F.J.; Gómez-Bautista, D.; Lahoz, F.J.; Oro, L.A. Unsaturated Iridium(III) Complexes Supported by a Quinolato–Carboxylato ONO Pincer-Type Ligand: Synthesis, Reactivity, and Catalytic C–H Functionalization. Organometallics 2013, 32, 6918–6930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Press, L.P.; Kosanovich, A.J.; McCulloch, B.J.; Ozerov, O.V. High-Turnover Aromatic C-H Borylation Catalyzed by POCOP-Type Pincer Complexes of Iridium. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 9487–9497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, M.U.; Press, L.P.; Bhuvanesh, N.; Ozerov, O.V. Examination of a Series of Ir and Rh PXL Pincer Complexes as (Pre)Catalysts for Aromatic C-H Borylation. Organometallics 2021, 40, 1004–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-I.; Zhou, J.; Reinbenspies, J.H.; Ozerov, O.V. Synthesis of Triborylalkenes from Terminal Alkynes by Iridium-Catalyzed Tandem C-H Borylation and Diboration. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 14003–14007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; MacArthur, A.H.R.; Brookhart, M.; Goldman, A.S. Dehydrogenation and Related Reactions Catalyzed by Iridium Pincer Complexes. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 1761–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Suguri, T.; Dohi, C.; Yamada, H.; Kojima, S.; Yamamoto, Y. Highly Active Catalysts for the Transfer Dehydrogenation of Alkanes: Synthesis and Application of Novel 7-6-7 Ring-Based Pincer Iridium Complexes. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 10672–10689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, W.; Braunstein, P. N-Heterocyclic Dicarbene Iridium(III) Pincer Complexes Featuring Mixed NHC/Abnormal NHC Ligands and Their Applications in the Transfer Dehydrogenation of Cyclooctane. Organometallics 2012, 31, 2606–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, D.Y.; Emge, T.J.; Goldman, A.S. Dehydrogenation of Ketones by Pincer-Ligated Iridium: Formation and Reactivity of Novel Enone Complexes. Inorganica Chim. Acta 2011, 369, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Liu, G.; Huang, Z. A New Paradigm in Pincer Iridium Chemistry: PCN Complexes for (De)Hydrogenation Catalysis and Beyond. Acc. Chem. Res. 2022, 55, 2148–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, S.-B.; Leng, X.; Chung, L.W.; Liu, G.; Huang, Z. N-Bridged Pincer Iridium Complexes for Highly Efficient Alkane Dehydrogenation and the Relevant Linker Effects. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 6475–6487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, X.; Huang, Z. Selective Catalytic Transfer Dehydrogenation of Alkanes and Heterocycles by an Iridium Pincer Complex. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 1390–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, W.; Jia, X.; Leng, X.; Goldman, A.S.; Brookhart, M.; Huang, Z. Catalytic Alkane Transfer-Dehydrogenation by PSCOP Iridium Pincer Complexes. Polyhedron 2016, 116, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göttker-Schnetmann, I.; Brookhart, M. Mechanistic Studies of the Transfer Dehydrogenation of Cyclooctane Catalyzed by Iridium Bis(Phosphinite) p-XPCP Pincer Complexes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 9330–9338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Göttker-Schnetmann, I.; White, P.S.; Brookhart, M. Synthesis and Properties of Iridium Bis(Phosphinite) Pincer Complexes (p-XPCP)IrH2, (p-XPCP)Ir(CO), (p-XPCP)Ir(H)(Aryl), and {(p-XPCP)Ir}2{μ-N2} and Their Relevance in Alkane Transfer Dehydrogenation. Organometallics 2004, 23, 1766–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.; Blessent, M.J.; Gordon, B.M.; Zhou, T.; Malakar, S.; Wang, D.Y.; Krogh-Jespersen, K.; Goldman, A.S. Origin of Regioselectivity in the Dehydrogenation of Alkanes by Pincer-Iridium Complexes: A Combined Experimental and Computational Study. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 12038–12051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.J.; Zhang, X.; Malakar, S.; Krogh-Jespersen, K.; Hasanayn, F.; Goldman, A.S. Formation of Enamines via Catalytic Dehydrogenation by Pincer-Iridium Complexes. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 85, 3020–3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, R.; Punji, B.; Findlater, M.; Supplee, C.; Schinski, W.; Brookhart, M.; Goldman, A.S. Catalytic Dehydroaromatization of N-Alkanes by Pincer-Ligated Iridium Complexes. Nat. Chem. 2011, 3, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thawani, A.; Rajeev, R.; Sunoj, R.B. On the Mechanism of the Dehydroaromatization of Hexane to Benzene by an Iridium Pincer Catalyst. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 4069–4077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laviska, D.A.; Guan, C.; Emge, T.J.; Wilklow-Marnell, M.; Brennessel, W.W.; Jones, W.D.; Krogh-Jespersen, K.; Goldman, A.S. Addition of C-C and C-H Bonds by Pincer-Iridium Complexes: A Combined Experimental and Computational Study. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 16354–16365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubashkin, S.B.; Chu, W.Y.; Goldberg, K.I. Lowering the Barrier to C−H Activation at Ir(III) through Pincer Ligand Design. Organometallics 2021, 40, 1296–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilklow-Marnell, M.; Li, B.; Zhou, T.; Krogh-Jespersen, K.; Brennessel, W.W.; Emge, T.J.; Goldman, A.S.; Jones, W.D. Catalytic Dehydrogenative C-C Coupling by a Pincer-Ligated Iridium Complex. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 8977–8989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahlstrand, D.A.; Polukeev, A.V.; Marcos, R.; Ahlquist, M.S.G.; Wendt, O.F. Csp3−H Activation without Chelation Assistance in an Iridium Pincer Complex Forming Cyclometallated Products. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 1748–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Yang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, F.; Gong, J.; Song, M. Pincer Iridium(III)-Catalyzed Enantioselective C(sp3)-H Functionalization via Carbenoid C-H Insertion of 3-Diazooxindoles with 1,4-Cyclohexadiene. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 2437–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Zhu, W.J.; Huang, J.J.; Hao, X.Q.; Gong, J.F.; Song, M.P. Chiral NCN Pincer Iridium(III) Complexes with Bis(Imidazolinyl)Phenyl Ligands: Synthesis and Application in Enantioselective C-H Functionalization of Indoles with α-Aryl-α-Diazoacetates. Organometallics 2020, 39, 2222–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, C.P.; Varela-Álvarez, A.; Boyarskikh, V.; Musaev, D.G.; Davies, H.M.L.; Blakey, S.B. Iridium(III)-Bis(Oxazolinyl)Phenyl Catalysts for Enantioselective C-H Functionalization. Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 2590–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Delolo, F.G.; Spannenberg, A.; Jackstell, R.; Beller, M. A Selective and General Cobalt-Catalyzed Hydroaminomethylation of Olefins to Amines. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202112597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migliorini, F.; Monciatti, E.; Romagnoli, G.; Parisi, M.L.; Taubert, J.; Vogt, M.; Langer, R.; Petricci, E. Switching Mechanistic Pathways by Micellar Catalysis: A Highly Selective Rhodium Catalyst for the Hydroaminomethylation of Olefins with Anilines in Water. ACS Catal. 2023, 13, 2702–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rätze, K.H.G.; Kortuz, W.; Kirschtowski, S.; Jokiel, M.; Hamel, C.; Sundmacher, K. Optimal Experimental Design for the Identification of a Reaction Kinetic Model for the Hydroaminomethylation of 1-Decene in a Thermomorphic Multiphase System. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 469, 143713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delolo, F.G.; Vieira, G.M.; Avendaño-Villarreal, J.A.; de Oliveira Dias, A.; dos Santos, E.N.; Gusevskaya, E.V. Working Together to Avoid Unwanted Reactions: Hydroformylation/O-Acylation of Terpene-Based Hydroxyolefins. J. Catal. 2023, 421, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vemuri, G.N.; Hughes, J.R.; Iovine, P.M. Synthesis and Characterization of Terpene-Derived Cationic Bolaamphiphiles. Tetrahedron 2022, 124, 133008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, S.M.M.; Shaner, S.E.; Kim, D.; Shopov, D.Y.; Tendler, J.A.; Pudalov, D.M.; Chianese, A.R. Mechanistic Studies of Alkene Isomerization Catalyzed by CCC-Pincer Complexes of Iridium. Organometallics 2014, 33, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, V.; Narjinari, H.; Nandi, P.G.; Kumar, A. Recent Advances in Pincer–Nickel Catalyzed Reactions. Dalton Trans. 2021, 50, 3394–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, U.N.; Pandey, D.K.; Gonnade, R.G.; Punji, B. Synthesis of Quinoline-Based NNN-Pincer Nickel(II) Complexes: A Robust and Improved Catalyst System for C–H Bond Alkylation of Azoles with Alkyl Halides. Organometallics 2016, 35, 1785–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, U.N.; Jain, S.; Pandey, D.K.; Gonnade, R.G.; Vanka, K.; Punji, B. Mechanistic Aspects of Pincer Nickel(II)-Catalyzed C–H Bond Alkylation of Azoles with Alkyl Halides. Organometallics 2018, 37, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, V.; Jagtap, R.A.; Gonnade, R.G.; Punji, B. Unified Strategy for Nickel-Catalyzed C-2 Alkylation of Indoles through Chelation Assistance. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 5666–5672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagtap, R.A.; Soni, V.; Punji, B. Expeditious and Solvent-Free Nickel-Catalyzed C−H Arylation of Arenes and Indoles. ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 2242–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartia, Y.; Ramidi, P.; Jones, D.E.; Pulla, S.; Ghosh, A. Nickel Complex Catalyzed Efficient Activation of Sp3 and Sp2 C–H Bonds for Alkylation and Arylation of Oxygen Containing Heterocyclic Molecules. Catal. Lett. 2014, 144, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandapati, P.; Braun, J.D.; Sidhu, B.K.; Wilson, G.; Herbert, D.E. Catalytic C–H Bond Alkylation of Azoles with Alkyl Halides Mediated by Nickel(II) Complexes of Phenanthridine-Based N^N^-N Pincer Ligands. Organometallics 2020, 39, 1989–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Bertermann, R.; Rachor, S.G.; Szabó, K.J.; Marder, T.B. Palladium-Catalyzed Oxidative Borylation of Allylic C–H Bonds in Alkenes. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 6590–6593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arumugam, V.; Kaminsky, W.; Nallasamy, D. Pd(II) Pincer Type Complex Catalyzed Tandem C–H and N–H Activation of Acetanilide in Aqueous Media: A Concise Access to Functionalized Carbazoles in a Single Step. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 3295–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




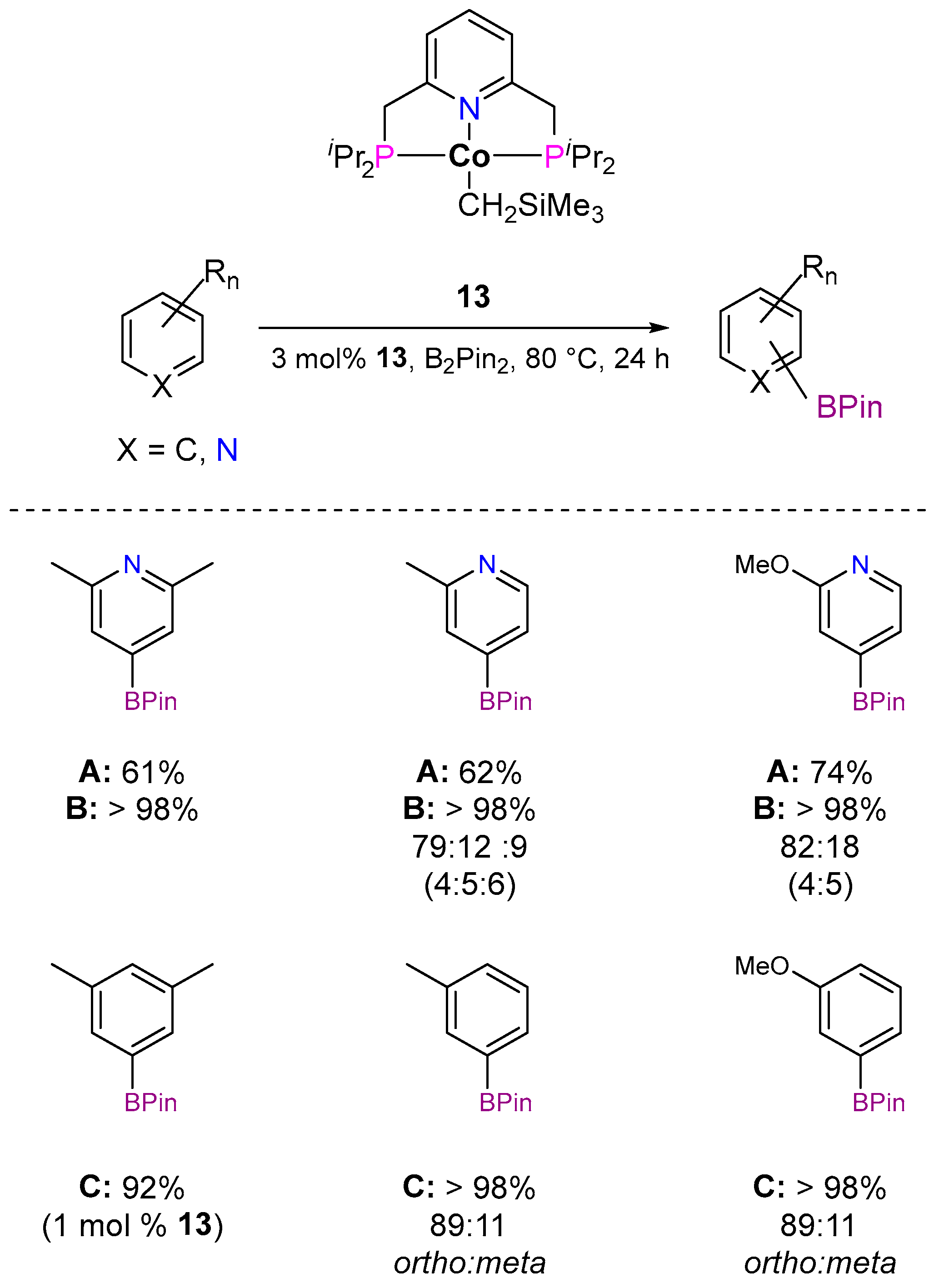
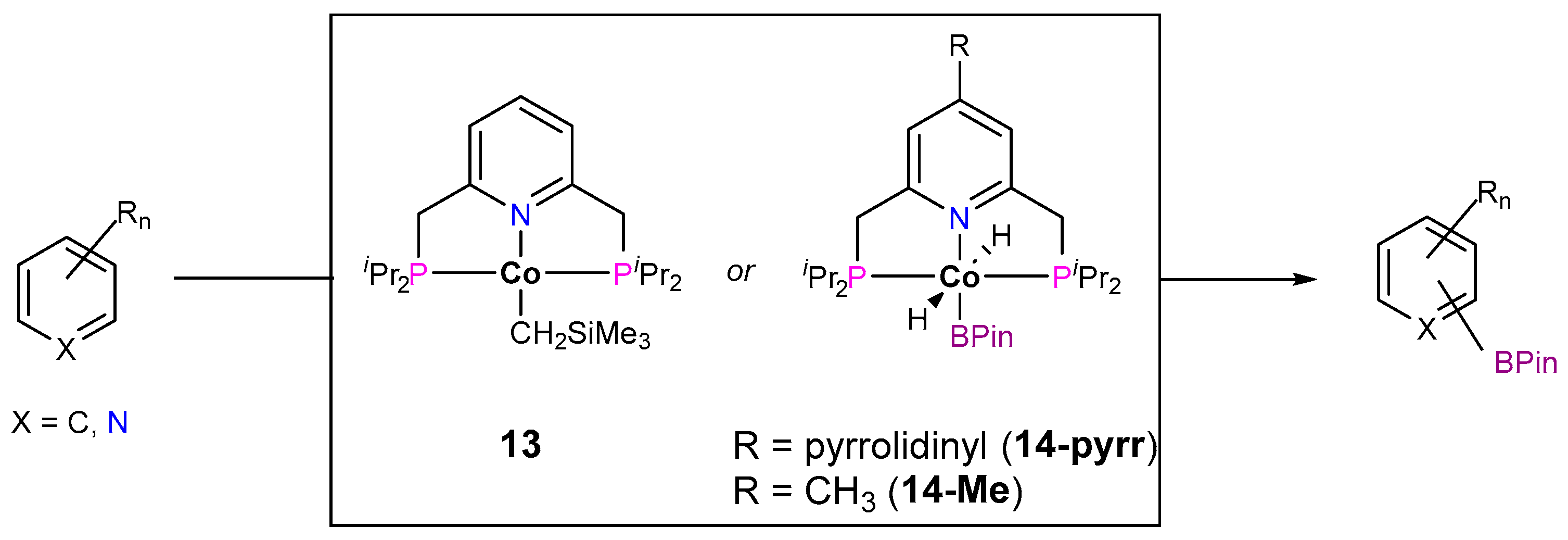


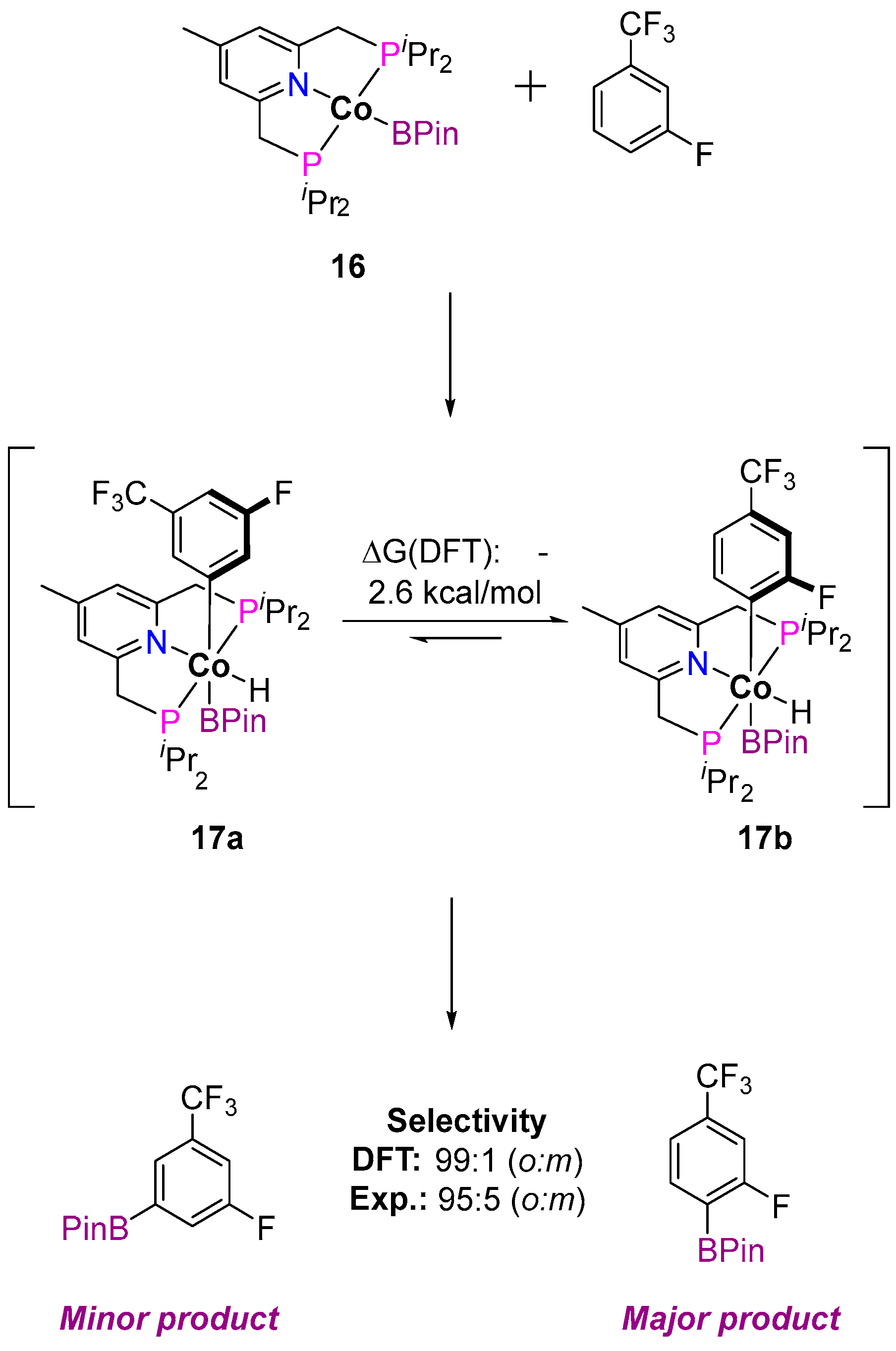
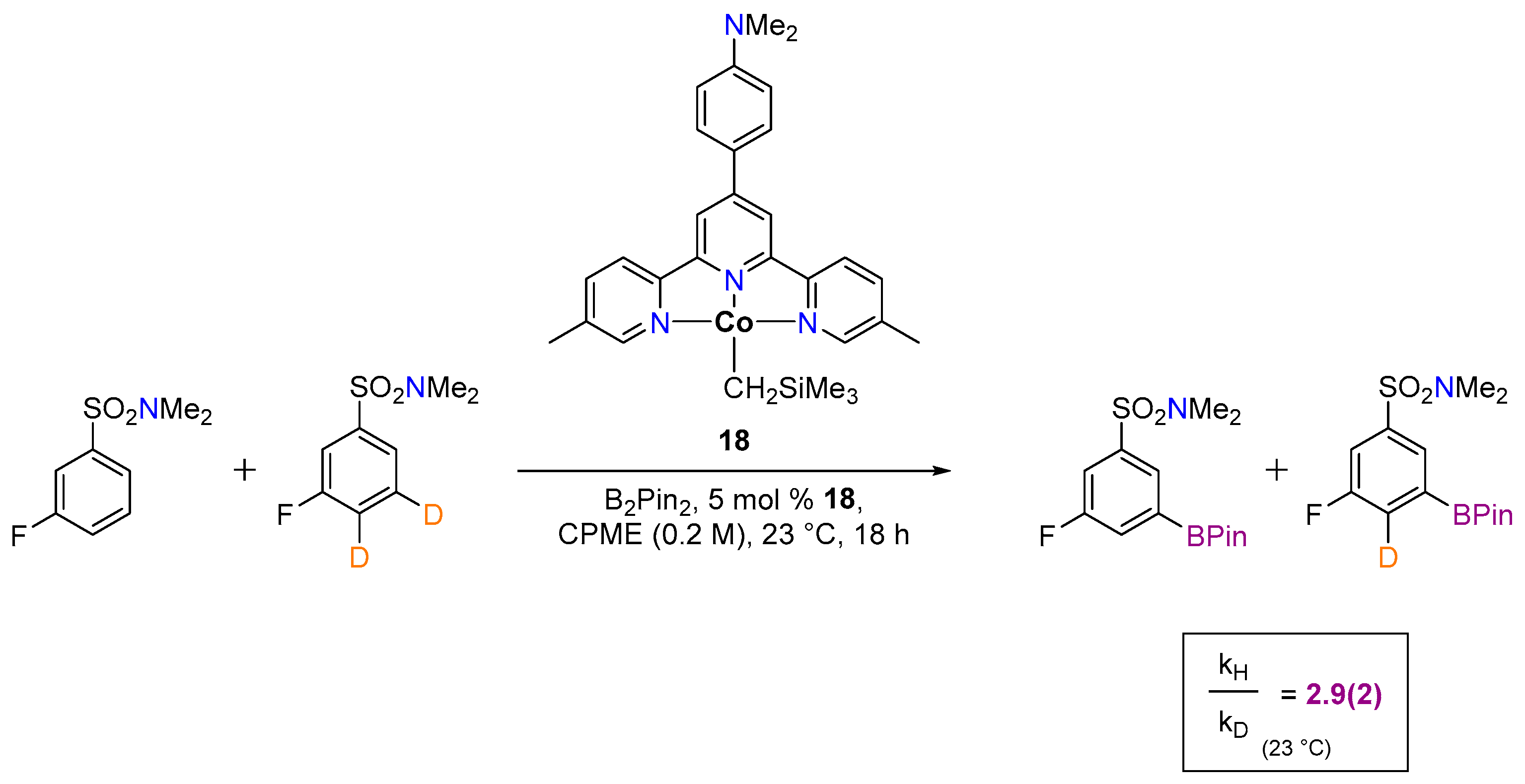



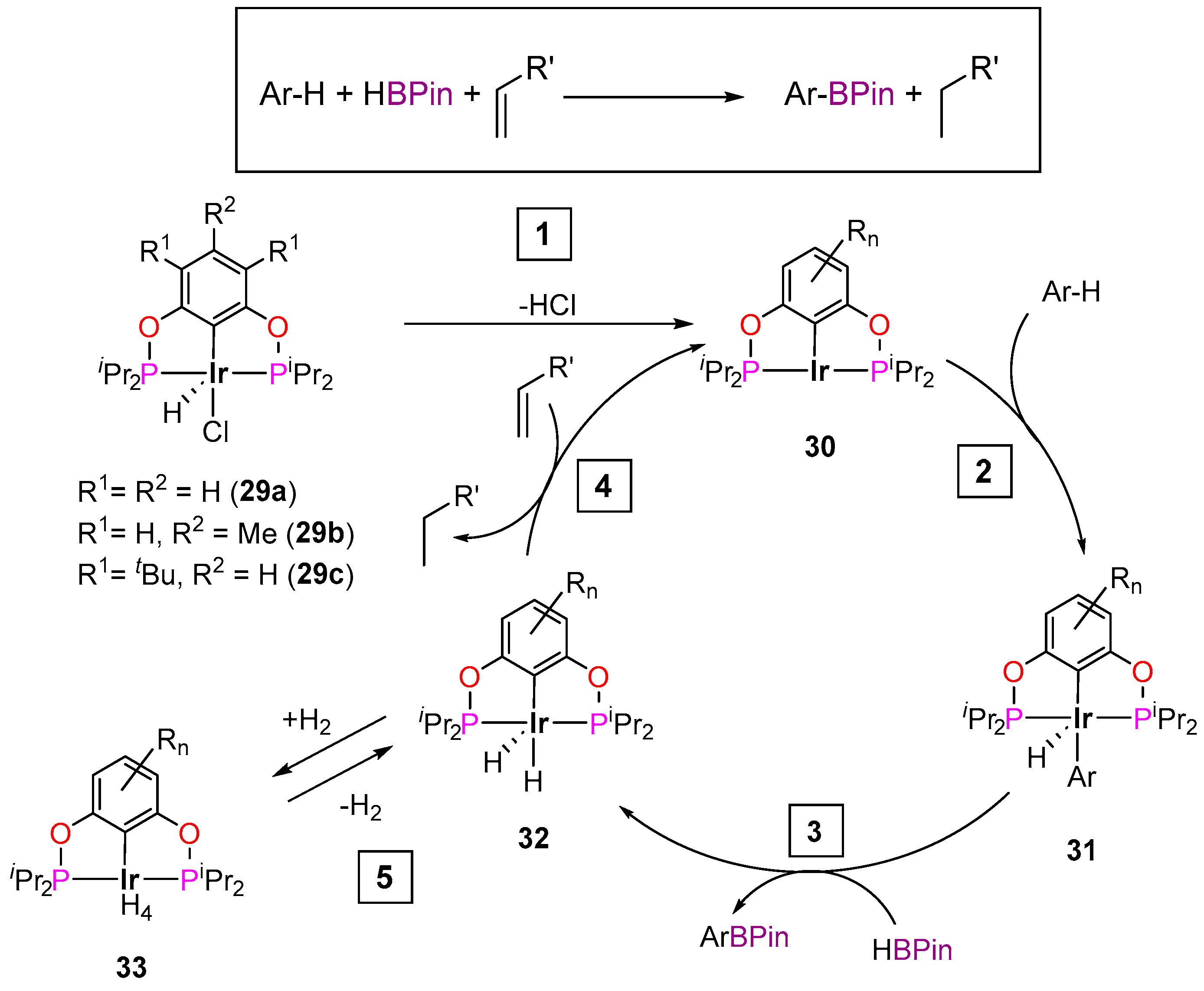


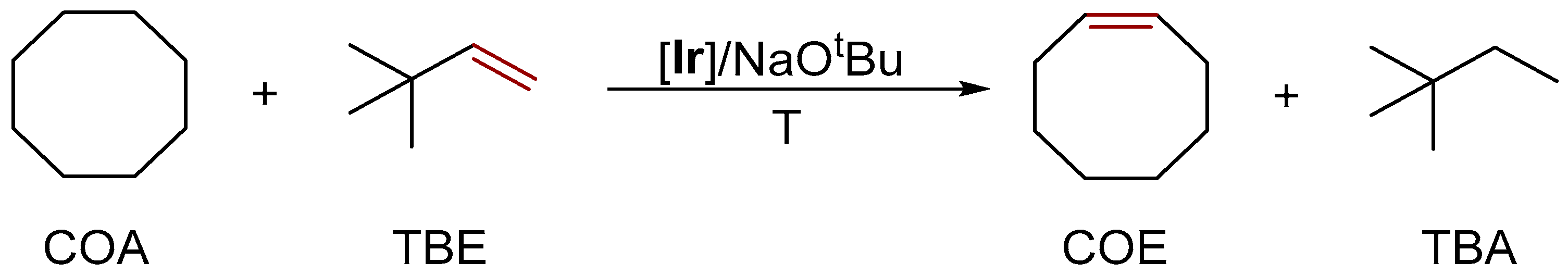

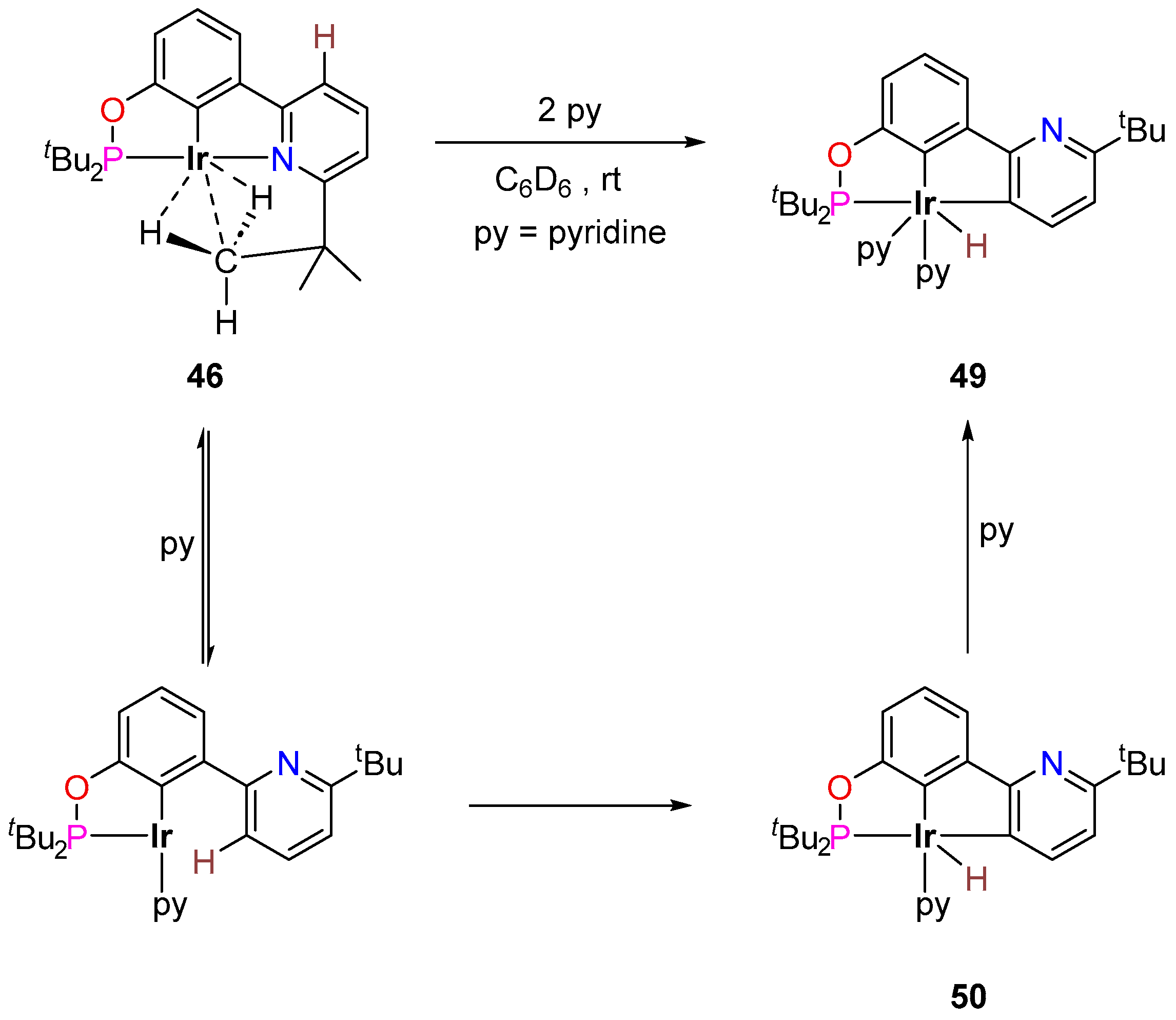

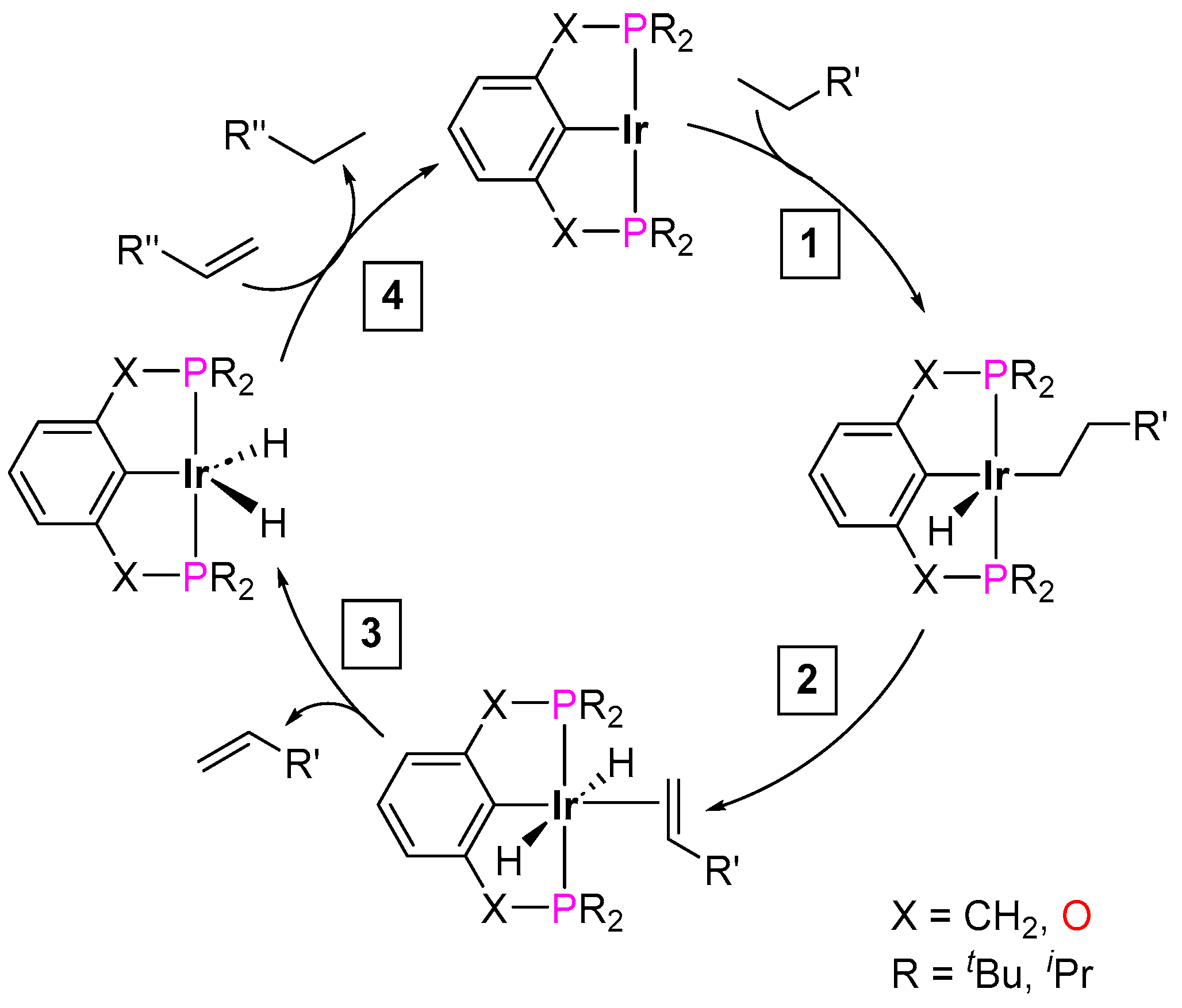


| Cat. | Substrate | Experimental Conditions | KIE | Rate Law | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13 | 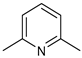 | 3 mol%, B2Pin2, 80 °C | 2.9(1) | rate=kobs[13][substrate]1[B2Pin2]0 | [67] |
| 14-pyrr |  | 3 mol%, B2Pin2, 80 °C | 1.6(1) | rate=kobs[14-pyrr][substrate]1[B2Pin2]0 | [67] |
| 13 |  | 1 mol%, HBPin, 80 °C | 1.9(1) | rate=kobs[13][substrate]0[HBPin]0 | [68] |
| 14-Me |  | 10 mol%, B2Pin2, 50 °C | 1.1(1), 0.9(1) * | rate=kobs[14-Me][substrate]0[B2Pin2]0 [HBPin]0.5 | [69] |
| Entry | Cat. | Cat. Loading (mol%) | T (°C) | TOF (h−1) 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 35 | 0.2 | 150 | 26 |
| 2 | 36 | 0.2 | 150 | 3 |
| 3 | 37 | 0.2 | 150 | 2 |
| 4 | 38 | 0.2 | 150 | 333 |
| 5 | 39 | 0.2 | 150 | 6 |
| 6 | 40 | 0.2 | 150 | 6 |
| 7 | 41 | 0.025 | 200 | 191 |
| 8 | 47 2 | 0.033 | 200 | 448 |
| 9 | 48 2 | 0.017 | 200 | 328 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Serrano-García, J.S.; Amaya-Flórez, A.; R.-Galindo, J.; González-Sebastián, L.; Delgado-Rangel, L.H.; Morales-Morales, D. C–H Activation via Group 8–10 Pincer Complexes: A Mechanistic Approach. Inorganics 2024, 12, 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics12080221
Serrano-García JS, Amaya-Flórez A, R.-Galindo J, González-Sebastián L, Delgado-Rangel LH, Morales-Morales D. C–H Activation via Group 8–10 Pincer Complexes: A Mechanistic Approach. Inorganics. 2024; 12(8):221. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics12080221
Chicago/Turabian StyleSerrano-García, Juan S., Andrés Amaya-Flórez, Jordi R.-Galindo, Lucero González-Sebastián, Luis Humberto Delgado-Rangel, and David Morales-Morales. 2024. "C–H Activation via Group 8–10 Pincer Complexes: A Mechanistic Approach" Inorganics 12, no. 8: 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics12080221
APA StyleSerrano-García, J. S., Amaya-Flórez, A., R.-Galindo, J., González-Sebastián, L., Delgado-Rangel, L. H., & Morales-Morales, D. (2024). C–H Activation via Group 8–10 Pincer Complexes: A Mechanistic Approach. Inorganics, 12(8), 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics12080221









