Continuous and Intermittent Planetary Ball Milling Effects on the Alloying of a Bismuth Antimony Telluride Powder Mixture
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
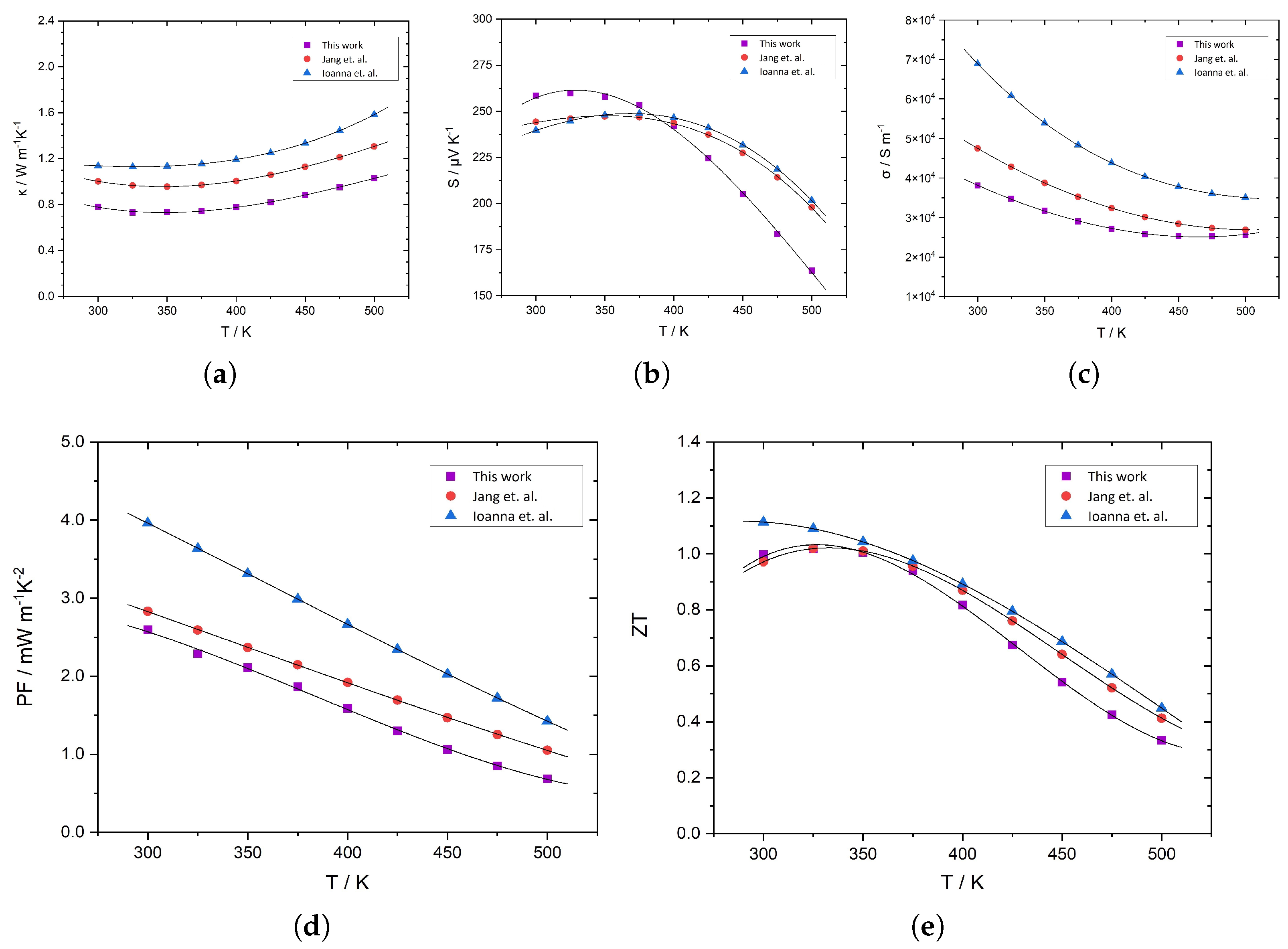
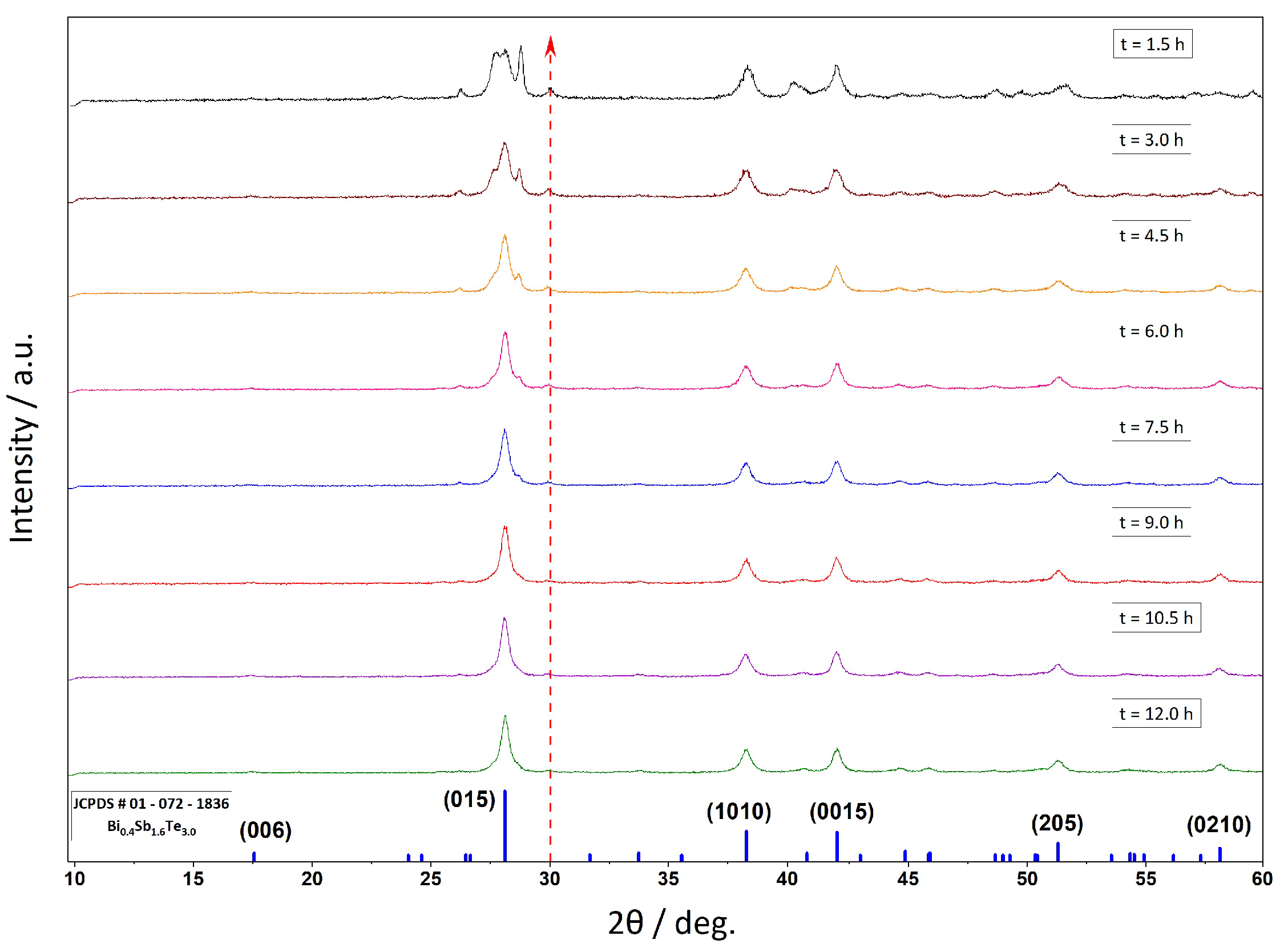
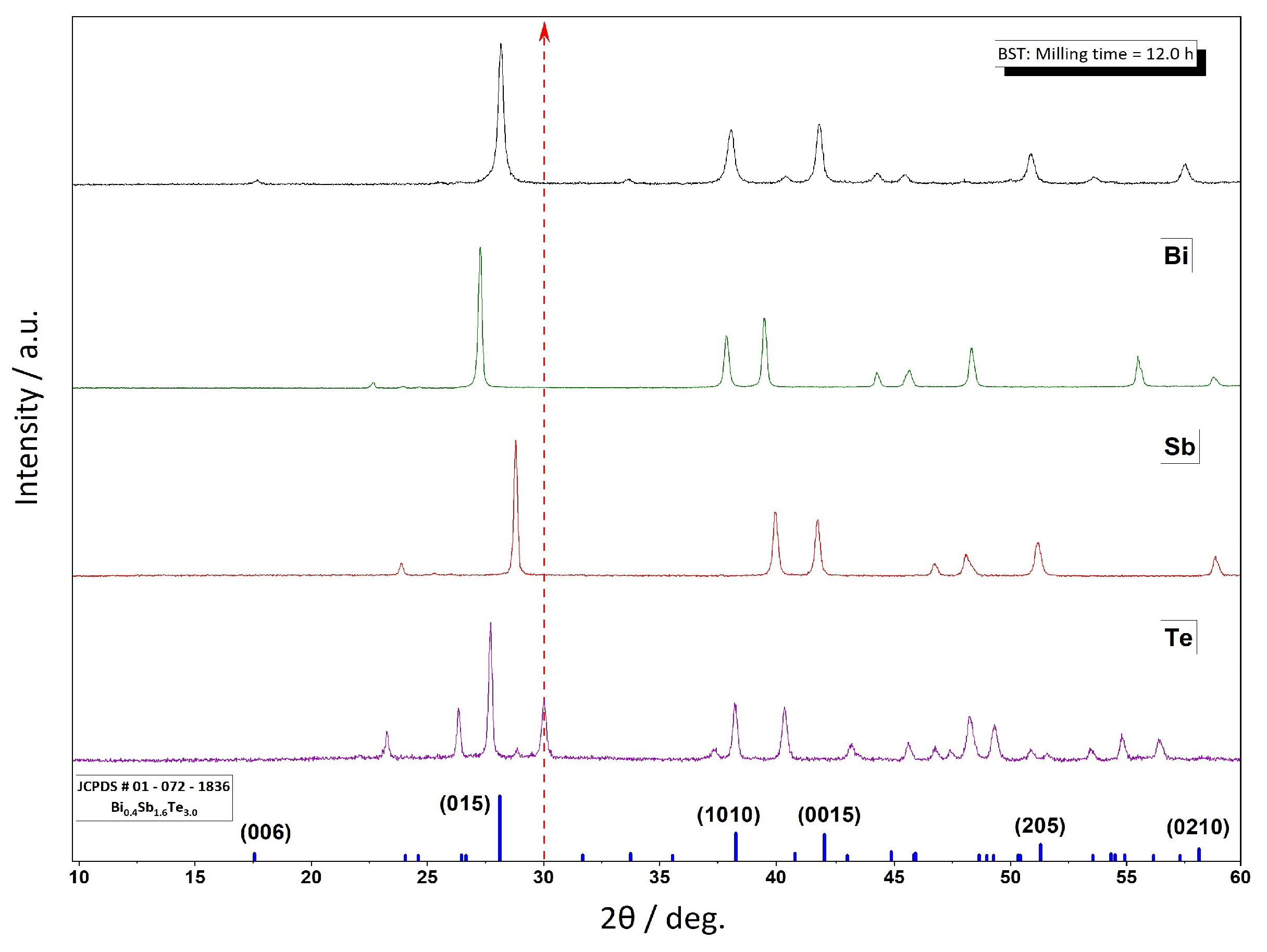
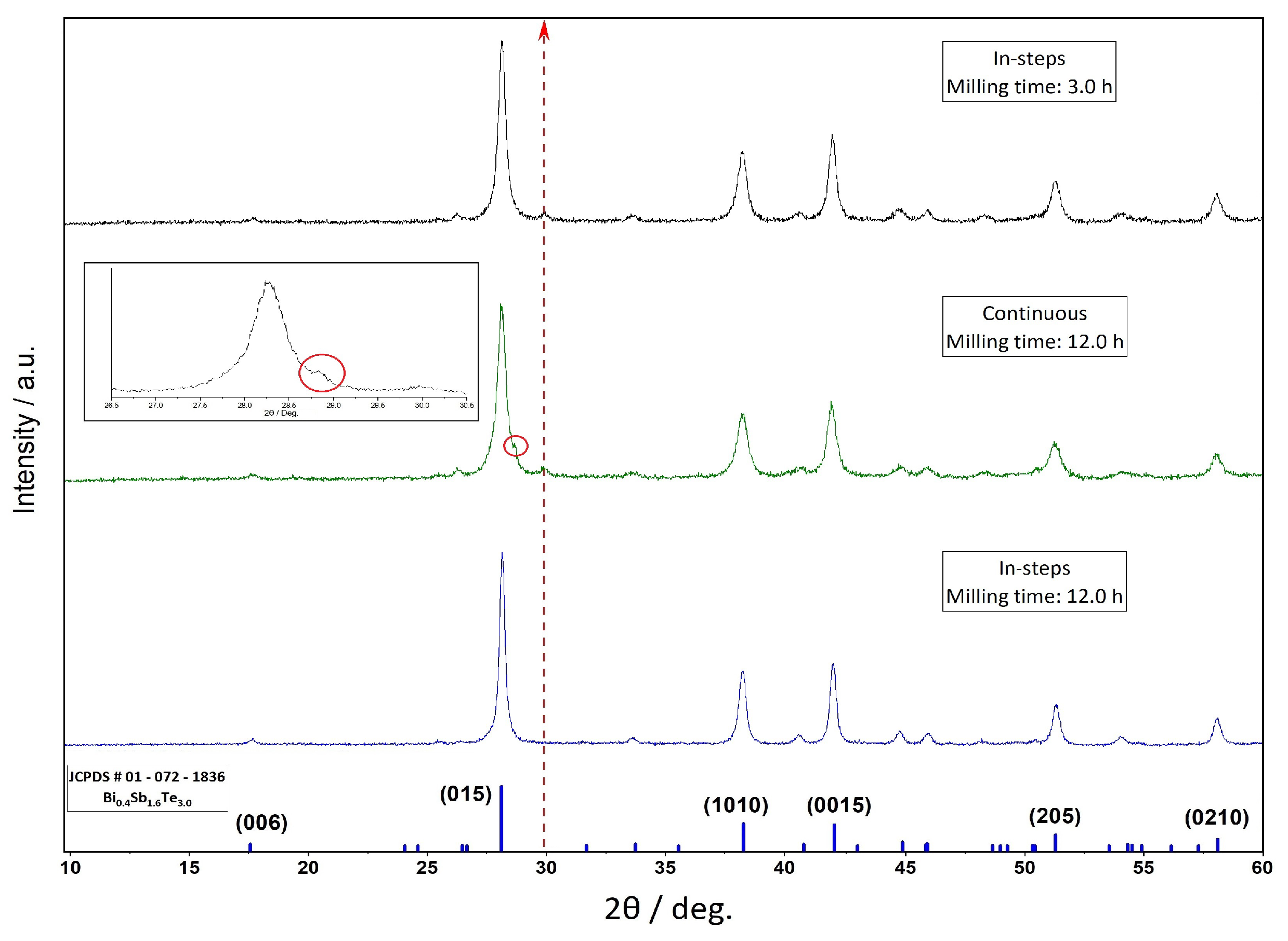
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hasezaki, K.; Nishimura, M.; Umata, M.; Tsukuda, H.; Araoka, M. Mechanical alloying of BiTe and BiSbTe thermoelectric materials. Mater. Trans. JIM 1994, 35, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunderlich, W.; Pixius, K.; Schilz, J. Microstructure of mechanical alloyed Si76Ge23.95P0.05. Nanostruct. Mater. 1995, 6, 441–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokiai, T.; Uesugi, T.; Eton, Y.; Tamura, S.; Yoneyama, Y.; Koumoto, K. Thermoelectric properties of p-type bismuth telluride material fabricated by plasma sintering of metal powder mixture. J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn. 1996, 104, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, A.; Kobayashi, K.; Ozaki, K.; Nishio, T.; Matsumoto, A. Preparation of functionally graded Mg2Si-FeSi2 thermoelectric material by mechanical alloying-pulsed current sintering process. Nippon Kinzoku Gakkaishi (1952) 1998, 62, 1082–1087. [Google Scholar]
- Suryanarayana, C. Mechanical alloying and milling. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2001, 46, 1–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Eskandarany, M.S. Mechanical Alloying: For Fabrication of Advanced Engineering Materials; William Andrew: Norwich, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Burmeister, C.F.; Kwade, A. Process engineering with planetary ball mills. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 7660–7667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Liu, C.; Miao, L.; Lin, H.; Gao, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Wu, S.; Li, X.; Cai, H. Cost effective synthesis of p-type Zn-doped MgAgSb by planetary ball-milling with enhanced thermoelectric properties. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 35353–35359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bumrungpon, M.; Hirota, K.; Takagi, K.; Hanasaku, K.; Hirai, T.; Morioka, I.; Yasufuku, R.; Kitamura, M.; Hasezaki, K. Synthesis and thermoelectric properties of bismuth antimony telluride thermoelectric materials fabricated at various ball-milling speeds with yttria-stabilized zirconia ceramic vessel and balls. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 13869–13876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, P.; Battabyal, M.; Bose, A.C.; Gopalan, R. Effect of ball-milling on the phase formation and enhanced thermoelectric properties in zinc antimonides. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2021, 271, 115274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, H.J.; Koo, B.; Kim, M.S.; Lee, J.E. Optimization of high-energy ball milling process for uniform p-type Bi-Sb-Te thermoelectric material powder. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 39, 1227–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokina, E.; Budim, N.; Kochnev, V.; Chernik, G. Planetary mills of periodic and continuous action. J. Mater. Sci. 2004, 39, 5217–5221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mio, H.; Kano, J.; Saito, F.; Kaneko, K. Optimum revolution and rotational directions and their speeds in planetary ball milling. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2004, 74, S85–S92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruckmann, A.; Krebs, A.; Bolm, C. Organocatalytic reactions: Effects of ball milling, microwave and ultrasound irradiation. Green Chem. 2008, 10, 1131–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolle, A.; Szuppa, T.; Leonhardt, S.E.; Ondruschka, B. Ball milling in organic synthesis: Solutions and challenges. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 2317–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, F.; Stolle, A.; Ondruschka, B.; Hopf, H. The Suzuki- Miyaura reaction under mechanochemical conditions. Org. Process. Res. Dev. 2009, 13, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szuppa, T.; Stolle, A.; Ondruschka, B.; Hopfe, W. Solvent-free dehydrogenation of γ-terpinene in a ball mill: Investigation of reaction parameters. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 1288–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, K.; Masuda, T.; Ishida, H.; Mitsuda, T. Structural degradation of tobermorite during vibratory milling. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1996, 79, 1569–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balema, V.P.; Wiench, J.W.; Pruski, M.; Pecharsky, V.K. Solvent-free mechanochemical synthesis of phosphonium salts. Chem. Commun. 2002, 7, 724–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, B.; Bruckmann, A.; Bolm, C. A highly efficient asymmetric organocatalytic aldol reaction in a ball mill. Chem.–Eur. J. 2007, 13, 4710–4722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, P.R.; Kartha, K.R. Solvent-free synthesis of thioglycosides by ball milling. Green Chem. 2009, 11, 953–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadier, S.; Le Bolay, N.; Rey, C.; Combes, C. Co-grinding significance for calcium carbonate–calcium phosphate mixed cement. Part I: Effect of particle size and mixing on solid phase reactivity. Acta Biomater. 2011, 7, 1817–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gayner, C.; Kar, K.K. Recent advances in thermoelectric materials. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2016, 83, 330–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Hu, J.; Zhang, S.; Deng, M.; Han, C.G.; Liu, Y. New trends, strategies and opportunities in thermoelectric materials: A perspective. Mater. Today Phys. 2017, 1, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chasmar, R.; Stratton, R. The thermoelectric figure of merit and its relation to thermoelectric generators. Int. J. Electron. 1959, 7, 52–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, D.; Min, G. Evaluation of thermoelectric modules for power generation. J. Power Sources 1998, 73, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, D.M. CRC Handbook of Thermoelectrics: Macro to Nano; CRC Taylor & Francis: Boca Ratcon, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, B.I.; Ahmed, W.H. Thermoelectric power generation using waste-heat energy as an alternative green technology. Recent Patents Electr. Electron. Eng. (Former. Recent Patents Electr. Eng.) 2009, 2, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleurial, J.P. Thermoelectric power generation materials: Technology and application opportunities. JOM 2009, 61, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, O.; Tomiyoshi, S.; Makita, K. Bismuth telluride compounds with high thermoelectric figures of merit. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 93, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.J.; Chun, B.S. Microstructure and thermoelectric properties of extruded n-type 95% Bi2Te2–5% Bi2Se3 alloy along bar length. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2003, 356, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, D.Y.; Hogan, T.P.; Rocci-Lane, M.; Brazis, P.; Ireland, J.R.; Kannewurf, C.R.; Bastea, M.; Uher, C.; Kanatzidis, M.G. A new thermoelectric material: CsBi4Te6. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 6414–6428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanatzia, A.; Papageorgiou, C.; Lioutas, C.; Kyratsi, T. Design of ball-milling experiments on Bi2Te3 thermoelectric material. J. Electron. Mater. 2013, 42, 1652–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symeou, E.; Nicolaou, C.; Delimitis, A.; Androulakis, J.; Kyratsi, T.; Giapintzakis, J. High thermoelectric performance of Bi2-xSbxTe3 bulk alloys prepared from non-nanostructured starting powders. J. Solid State Chem. 2019, 270, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symeou, E.; Nicolaou, C.; Kyratsi, T.; Giapintzakis, J. Enhanced thermoelectric properties in vacuum-annealed Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3 thin films fabricated using pulsed laser deposition. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 125, 215308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, K.W.; Kim, H.J.; Jung, W.J.; Kim, I.H. Charge transport and thermoelectric properties of p-type Bi2-xSbxTe3 prepared by mechanical alloying and hot pressing. Korean J. Met. Mater. 2018, 56, 66–71. [Google Scholar]
- Ioannou, I.; Ioannou, P.S.; Kyratsi, T.; Giapintzakis, J. Low-cost preparation of highly-efficient thermoelectric BixSb2-xTe3 nanostructured powders via mechanical alloying. J. Solid State Chem. 2023, 319, 123823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakeri, M.; Allahkarami, M.; Kavei, G.; Khanmohammadian, A.; Rahimipour, M. Synthesis of nanocrystalline Bi2Te3 via mechanical alloying. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2009, 209, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, S.; Perez, J.G.; Tritt, T.M.; Zhu, S.; Sosa-Sanchez, J.L.; Martinez-Juarez, J.; López, O. Synthesis and thermoelectric performance of a p-type Bi0.4Sb1.6Te3 material developed via mechanical alloying. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 87, 868–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Chen, H.; Jia, S.; Wang, W. 3D printing fabrication of porous bismuth antimony telluride and study of the thermoelectric properties. J. Manuf. Process. 2019, 37, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Ke, H.; Yang, J.; Uher, C.; Tang, X. Fabrication and thermoelectric properties of n-type CoSb2.85Te0.15 using selective laser melting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 13669–13674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Yan, Y.; Luo, T.; Tang, K.; Yao, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, M.; Su, X.; Tan, G.; Xie, H.; et al. 3D Printing of highly textured bulk thermoelectric materials: Mechanically robust BiSbTe alloys with superior performance. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 3106–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Samourgkanidis, G.; Kyratsi, T. Continuous and Intermittent Planetary Ball Milling Effects on the Alloying of a Bismuth Antimony Telluride Powder Mixture. Inorganics 2023, 11, 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11050221
Samourgkanidis G, Kyratsi T. Continuous and Intermittent Planetary Ball Milling Effects on the Alloying of a Bismuth Antimony Telluride Powder Mixture. Inorganics. 2023; 11(5):221. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11050221
Chicago/Turabian StyleSamourgkanidis, Georgios, and Theodora Kyratsi. 2023. "Continuous and Intermittent Planetary Ball Milling Effects on the Alloying of a Bismuth Antimony Telluride Powder Mixture" Inorganics 11, no. 5: 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11050221
APA StyleSamourgkanidis, G., & Kyratsi, T. (2023). Continuous and Intermittent Planetary Ball Milling Effects on the Alloying of a Bismuth Antimony Telluride Powder Mixture. Inorganics, 11(5), 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics11050221