Cavity Length Sequence Matching Algorithm Based on Combined Valley Peak Positioning for Fiber-Optic Fabry-Perot Sensors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Principle of the CLSM Algorithm
2.1. Principle of Conventional P2P Algorithm
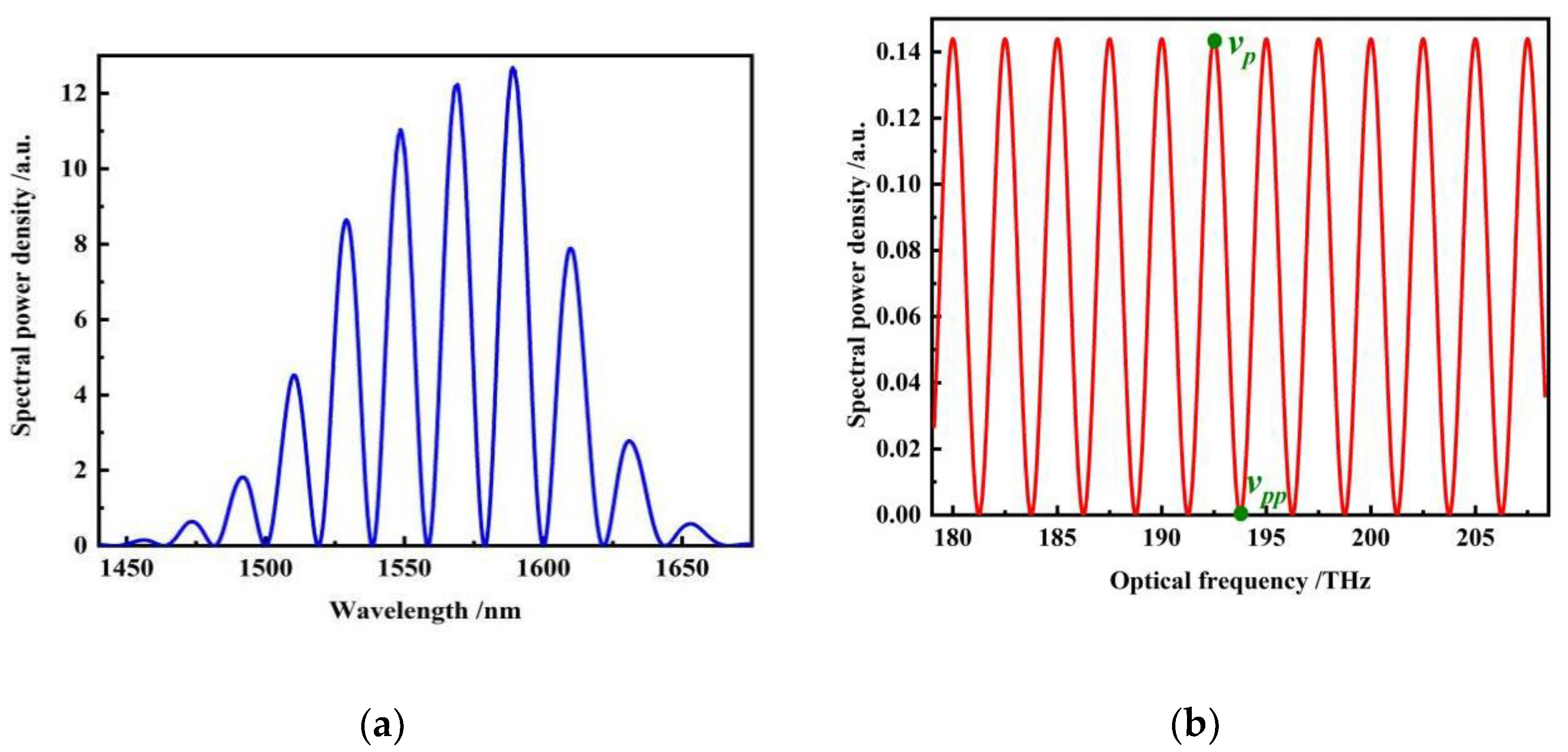
2.2. Principle of CLSM Algorithm
3. CLSM Algorithm and Simulation Analysis
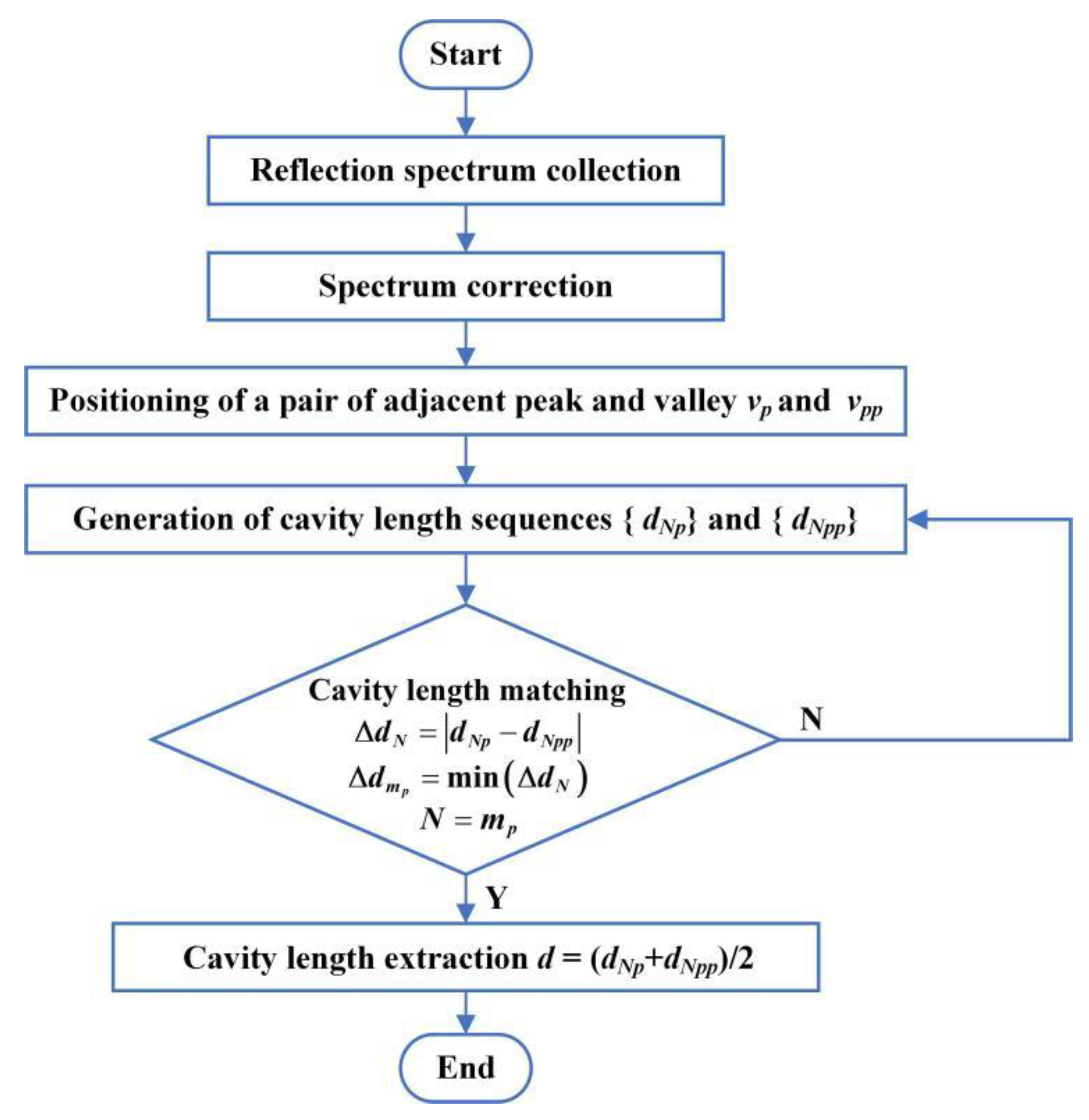
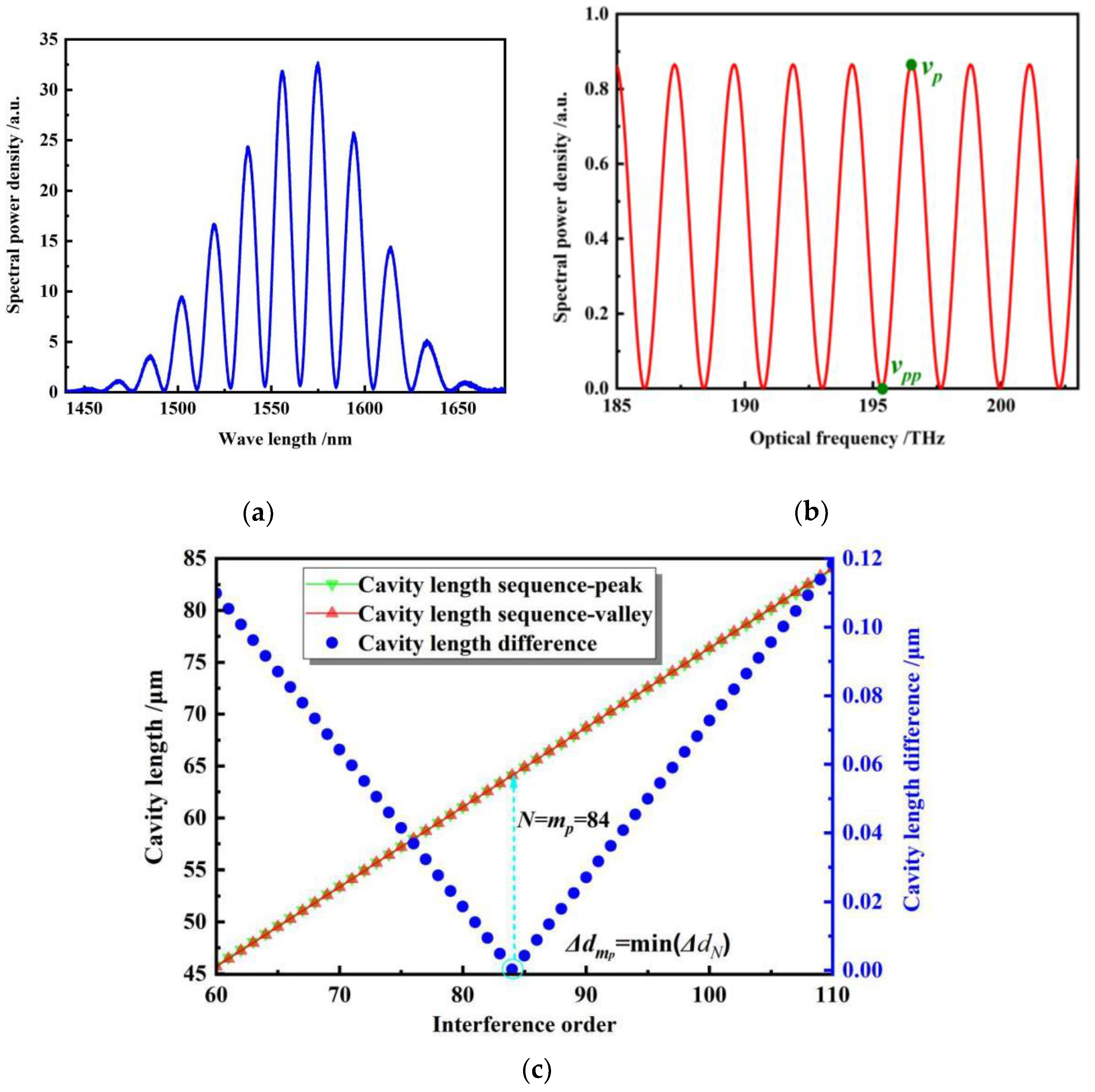
3.1. CLSM Algorithm
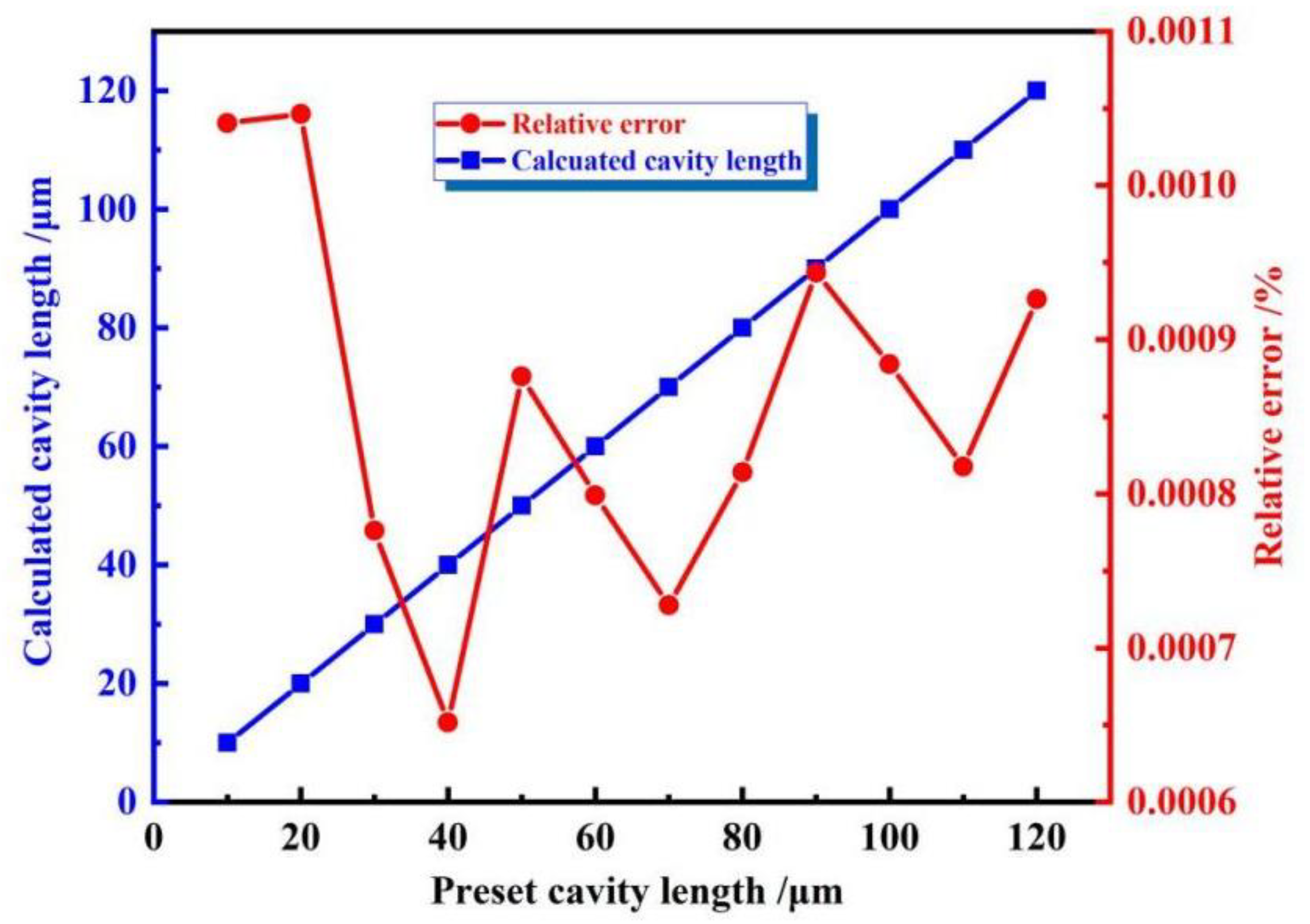
3.2. Simulation Analysis
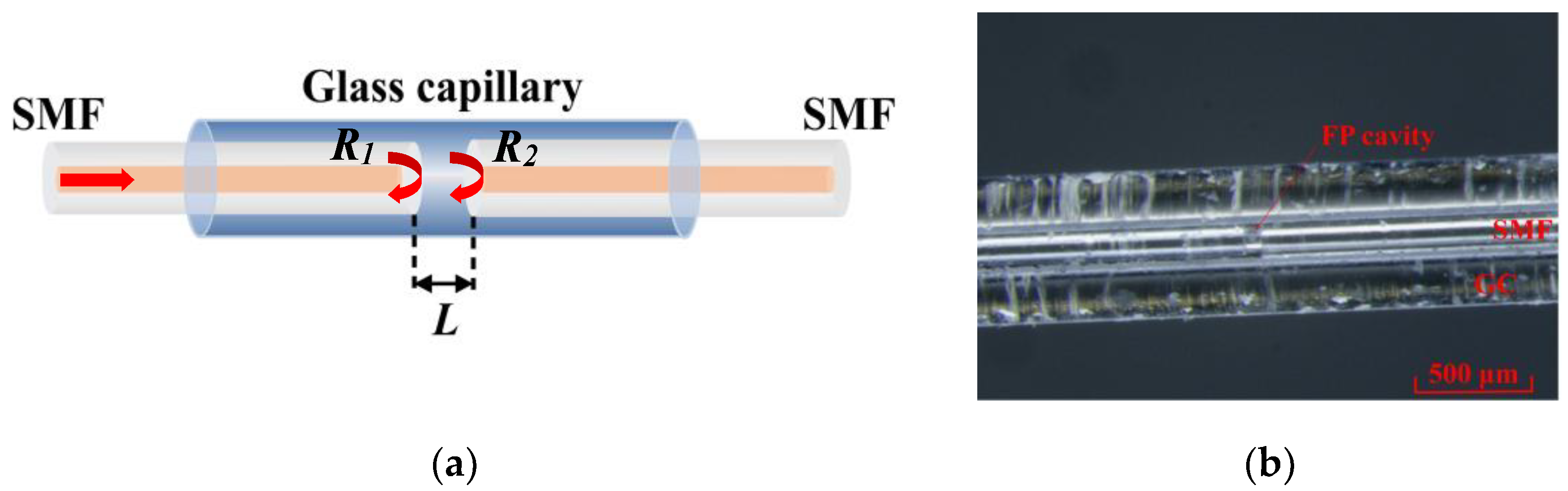
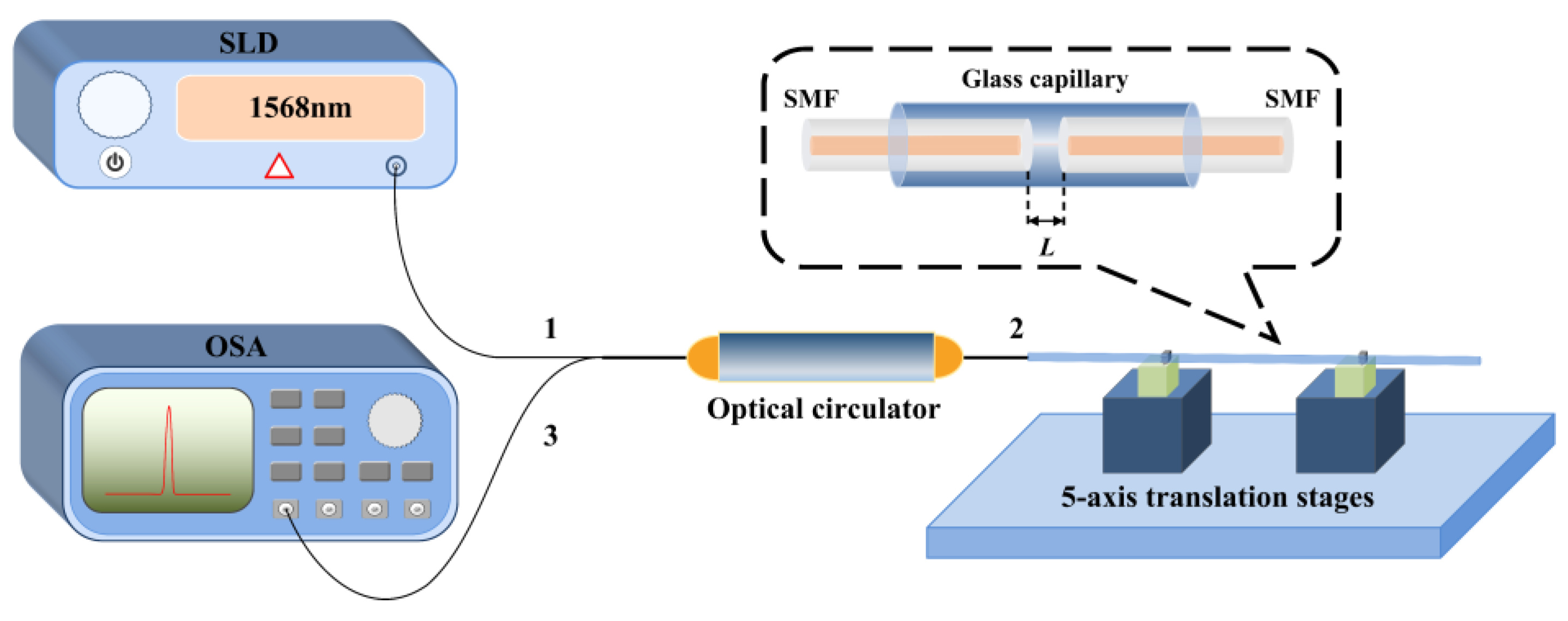
4. Experimental Verification
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gander, M.J.; Macpherson, W.N.; Barton, J.S.; Reuben, R.L.; Jones, J.D.; Stevens, R.; Chana, K.S.; Anderson, S.J.; Jones, T.V. Embedded micromachined fiber-optic Fabry-Perot pressure sensors in aerodynamics applications. IEEE Sens. J. 2003, 3, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic, O.; Digonnet, M.; Kino, G.S.; Solgaard, O. Miniature photonic-crystal hydrophone optimized for ocean acoustics. JASA 2011, 129, 1837–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Min, R.; Liu, Z.; Pereira, L.; Yang, C.; Marques, C. Optical fiber sensing for marine environment and marine structural health monitoring: A review. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 140, 107082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Wang, S.; Jiang, J.; Liu, K.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Liu, T. Fiber optic Fabry-Perot pressure sensor with embedded MEMS micro-cavity for ultra-high pressure detection. J. Lightwave Technol. 2018, 37, 2719–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choquet, P.; Juneau, F.; Bessette, J.; Claus, R.O.; Spillman, W.B. New generation of Fabry-Perot fiber optic sensors for monitoring of structures. Proc. SPIE 2000, 3986, 418–426. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Yu, Q.; Peng, W. Fiber-optic Fabry-Perot pressure sensor for down-hole application. Opt. Laser Eng. 2019, 121, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal-Junior, A.G.; Avellar, L.M.; Diaz, C.; Frizera, A.; Marques, C.; Pontes, M.J. Fabry-Perot curvature sensor with cavities Based on UV-curable resins: Design, analysis, and data integration approach. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 9798–9805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, C.A.R.; Marques, C.; Domingues, M.; Ribeiro, M.; Frizera, A.; Pontes, M.J.; André, P.S.; Antunesal, P.F.C. A cost-effective ddge-filter based FBG interrogator using catastrophic fuse effect micro-cavity interferometers. Measurement 2018, 124, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y. Fourier transform white-light interferometry for the measurement of fiber-optic extrinsic Fabry-PÉrot interferometric sensors. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2008, 20, 75–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Ding, W.; Gao, R. Fourier transform white-light interferometry based on nonlinear wavelength sampling. Opt. Eng. 2013, 52, 104102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Wang, Z.; Guo, M.; Liu, B.; Yu, Q. Single-mode fiber-optic Fabry-Perot interferometry sensor based on optical cross-correlation demodulation. Opt. Eng. 2019, 58, 026106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W.; Ma, Z.; Lv, W.; Guo, Z. High-order harmonic-frequency cross-correlation algorithm for absolute cavity length interrogation of white-light fiber-optic Fabry-Perot sensors. J. Lightwave Technol. 2020, 38, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, B. Novel data processing techniques for dispersive white light interferometer. Opt. Eng. 2003, 42, 3165–3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Q.; Uddin, N.; Han, M. Spurious jumps in wavelength tracking of fiber-optic Fabry-Perot interferometric sensor. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2021, 38, 3039–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, J.S.; Asundi, A. Real-time cure monitoring of smart composite materials using extrinsic Fabry-Perot interferometer and fiber Bragg grating sensors. Smart Mater. Struct. 2002, 11, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Tang, C. High-finesse micro-lens fiber-optic extrinsic Fabry-Perot interferometric sensors. Smart Mater. Struct. 2008, 17, 055013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y. High-resolution interrogation technique for fiber optic extrinsic Fabry-Perot interferometric sensors by the peak-to-peak method. Appl. Opt. 2008, 47, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Jing, X.; Guo, Q.; Yuan, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, R.; Guo, Q. Squared peak-to-peak algorithm for the spectral interrogation of short-cavity fiber-optic Fabry-Perot sensors. Appl. Opt. 2020, 59, 1198–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Predetermined Cavity Length (μm) | Demodulated Cavity Length (μm) | Demodulation Error (nm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLSM | P2P | CLSM | P2P | |
| 10.0000 | 9.9999 | 10.0010 | 0.1 | 1.0 |
| 20.0000 | 19.9998 | 20.0033 | 0.2 | 3.3 |
| 30.0000 | 29.9998 | 30.0049 | 0.2 | 4.9 |
| 40.0000 | 39.9997 | 40.0108 | 0.3 | 10.8 |
| 50.0000 | 49.9996 | 50.0267 | 0.4 | 26.7 |
| 60.0000 | 59.9995 | 60.0236 | 0.5 | 23.6 |
| 70.0000 | 69.9995 | 69.9754 | 0.5 | 24.6 |
| 80.0000 | 79.9993 | 79.9645 | 0.7 | 35.5 |
| 90.0000 | 89.9992 | 90.0382 | 0.8 | 38.2 |
| 100.0000 | 99.9991 | 100.0385 | 0.9 | 38.5 |
| 110.0000 | 109.9991 | 110.0383 | 0.9 | 38.3 |
| 120.0000 | 119.9989 | 119.9603 | 1.1 | 39.7 |
| Predetermined Cavity Length (μm) | Demodulated Cavity Length | Demodulation Error | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLSM (μm) | P2P (μm) | CLSM(nm) | P2P(μm) | |
| 16.4698 | 16.4656 | 18.7605 | 4.2 | 2.3 |
| 29.3783 | 29.3735 | 32.0028 | 4.8 | 2.6 |
| 41.0298 | 41.0245 | 43.8287 | 5.3 | 2.8 |
| 53.2906 | 53.2961 | 56.8075 | 5.5 | 3.5 |
| 64.1130 | 64.1191 | 68.1084 | 6.1 | 4.0 |
| 76.3849 | 76.3916 | 80.9057 | 6.7 | 4.5 |
| 88.1071 | 88.0998 | 92.9886 | 7.3 | 4.9 |
| 102.0809 | 102.0893 | 107.3067 | 8.4 | 5.2 |
| 113.5901 | 113.5813 | 108.0648 | 8.8 | 5.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nie, L.; Li, X.; Chen, H.; Zhang, J.; Chen, H.; Zhao, X.; Wang, S.; Liu, G. Cavity Length Sequence Matching Algorithm Based on Combined Valley Peak Positioning for Fiber-Optic Fabry-Perot Sensors. Photonics 2022, 9, 451. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9070451
Nie L, Li X, Chen H, Zhang J, Chen H, Zhao X, Wang S, Liu G. Cavity Length Sequence Matching Algorithm Based on Combined Valley Peak Positioning for Fiber-Optic Fabry-Perot Sensors. Photonics. 2022; 9(7):451. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9070451
Chicago/Turabian StyleNie, Liang, Xiaonan Li, Hongwei Chen, Junying Zhang, Haibin Chen, Xueqing Zhao, Sheng Wang, and Guanghai Liu. 2022. "Cavity Length Sequence Matching Algorithm Based on Combined Valley Peak Positioning for Fiber-Optic Fabry-Perot Sensors" Photonics 9, no. 7: 451. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9070451
APA StyleNie, L., Li, X., Chen, H., Zhang, J., Chen, H., Zhao, X., Wang, S., & Liu, G. (2022). Cavity Length Sequence Matching Algorithm Based on Combined Valley Peak Positioning for Fiber-Optic Fabry-Perot Sensors. Photonics, 9(7), 451. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9070451





