Optical Properties of Black Carbon Aerosols with Different Coating Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. The Modeling of Black Carbon (BC) Aerosols
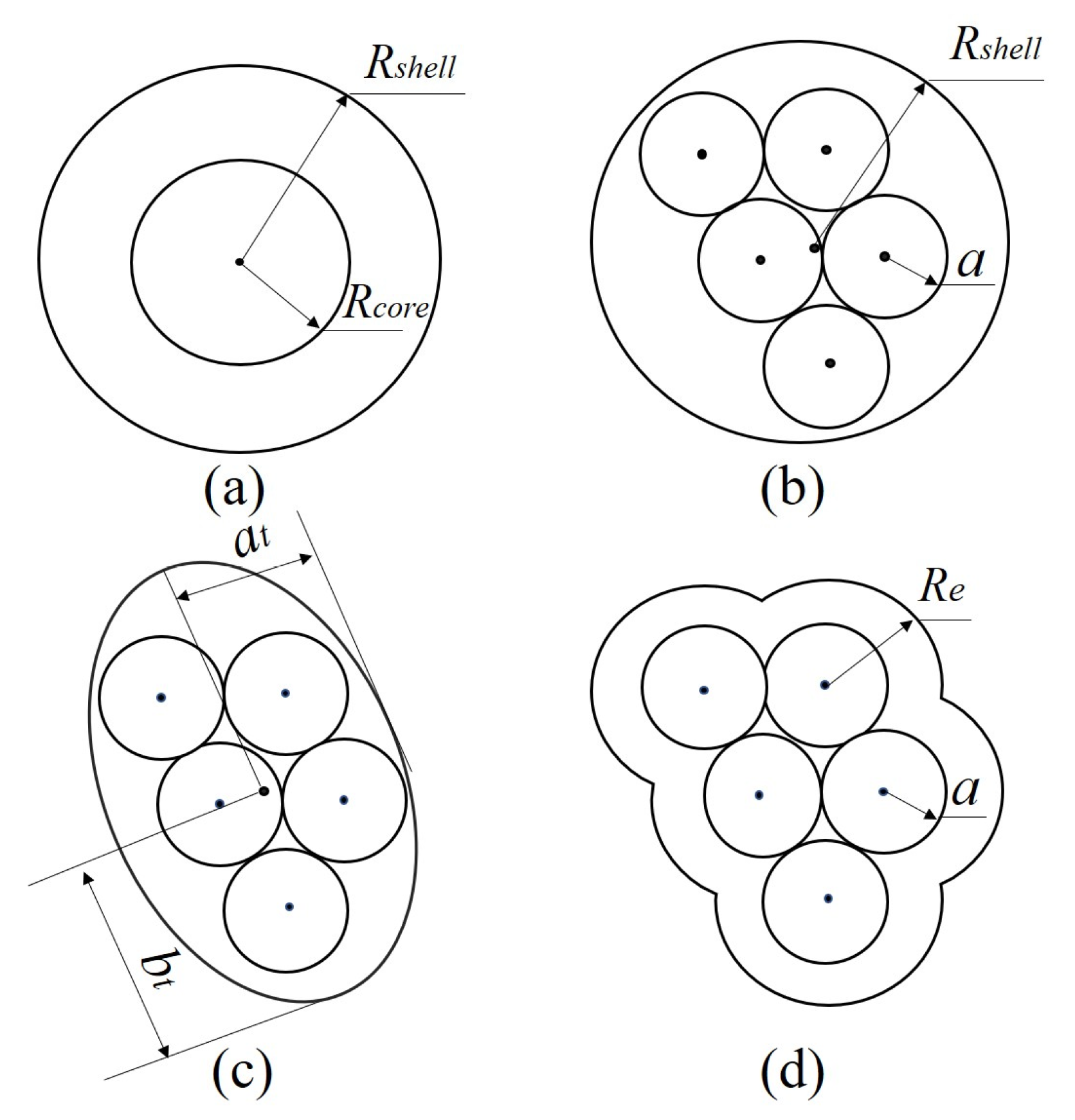
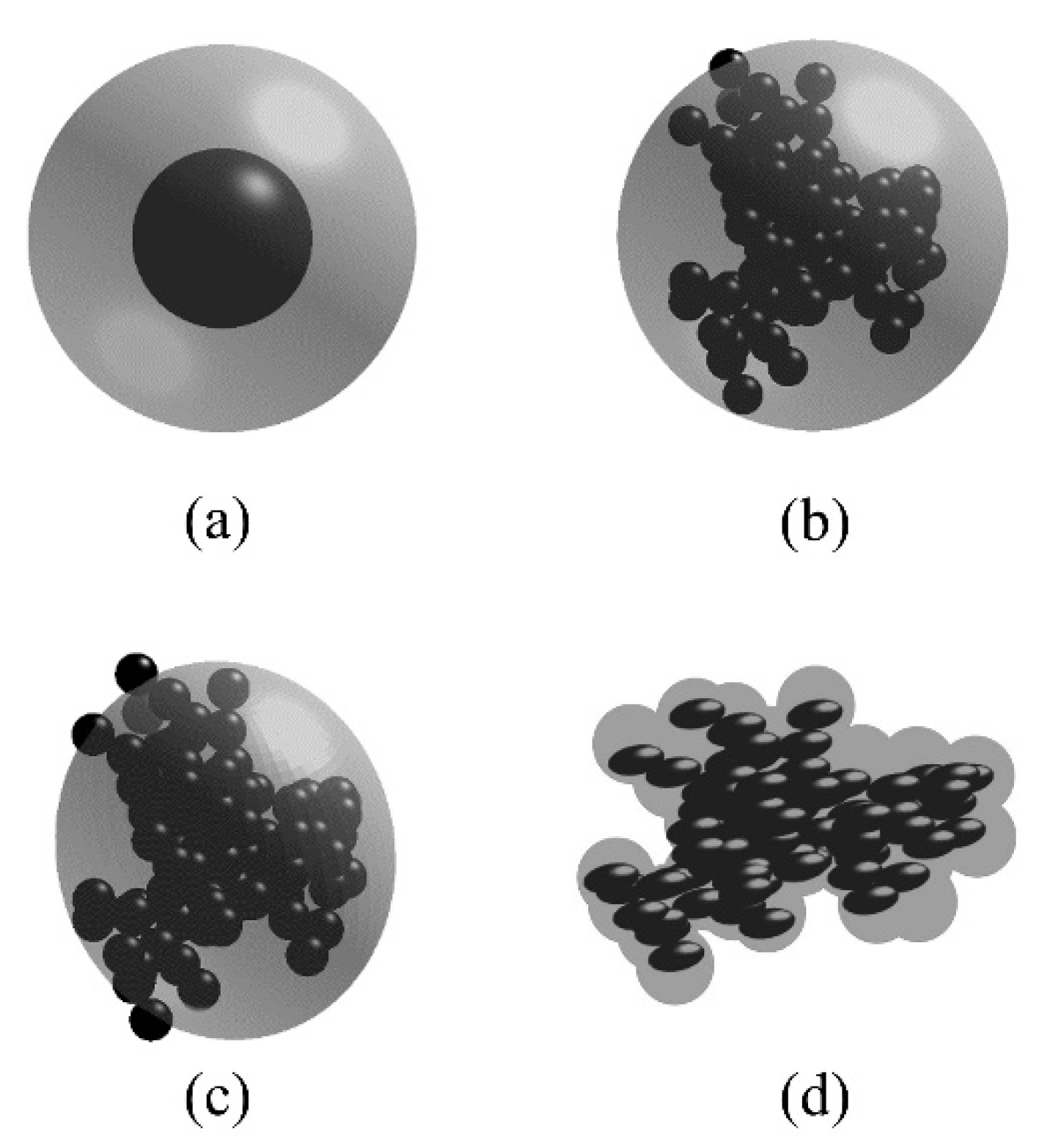
- the core-shell model: The BC aggregate is simplified as a homogeneous sphere core with radius , and the spherical coating is assumed to be a concentric shell with radius Rshell.
- the spherical coating model: First, BC aggregates with the radius of monomer a, and the monomer number of are constructed according to Section 2.1. Next, we create the spherical coating with the same center position of aggregates. The radius of spherical coating is Rshell. Finally, we remove the part occupied by BC aggregates in the spherical coating.
- the ellipsoidal coating model: The establishment process of this model is similar to that of the spherical coating model, except that the shape of coating is ellipsoid. The length of each axis of the ellipsoid is determined by the ratio t which is the ratio of the length of x, y and z in aggregates, i.e.,
- the irregular coating model: First, BC aggregates which are the same as the aggregates in the spherical and ellipsoidal coating model are generated. Next, we create the overlapping coating aggregates with the same monomer center as BC aggregates. The monomer radius of coating aggregates Re is larger than the radius of BC monomer a. Finally, we remove the part occupied by BC aggregates in the overlapping coating aggregates.
2.2. Computational Method
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sensitivity Studies of the Numbers of Target Orientations
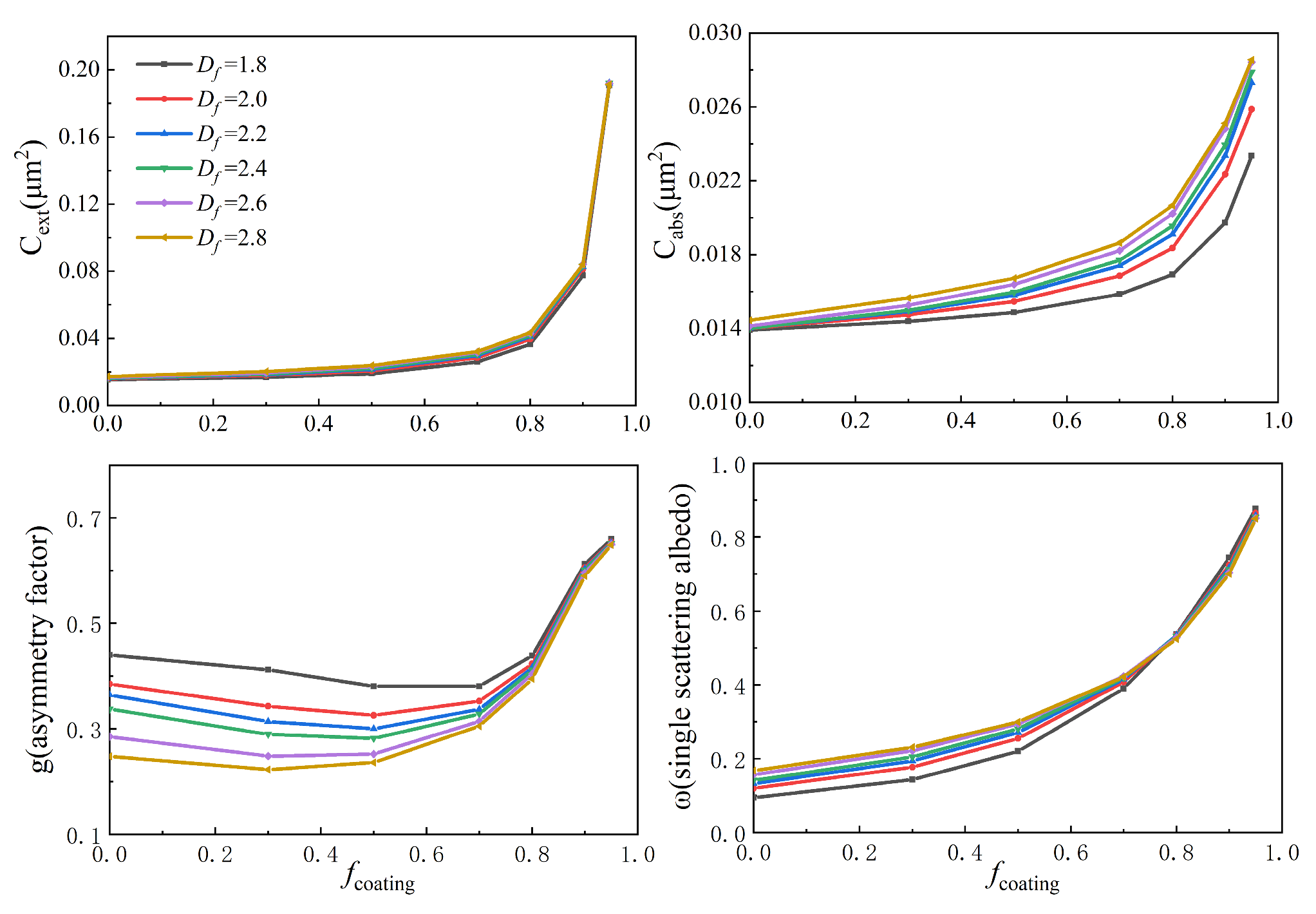
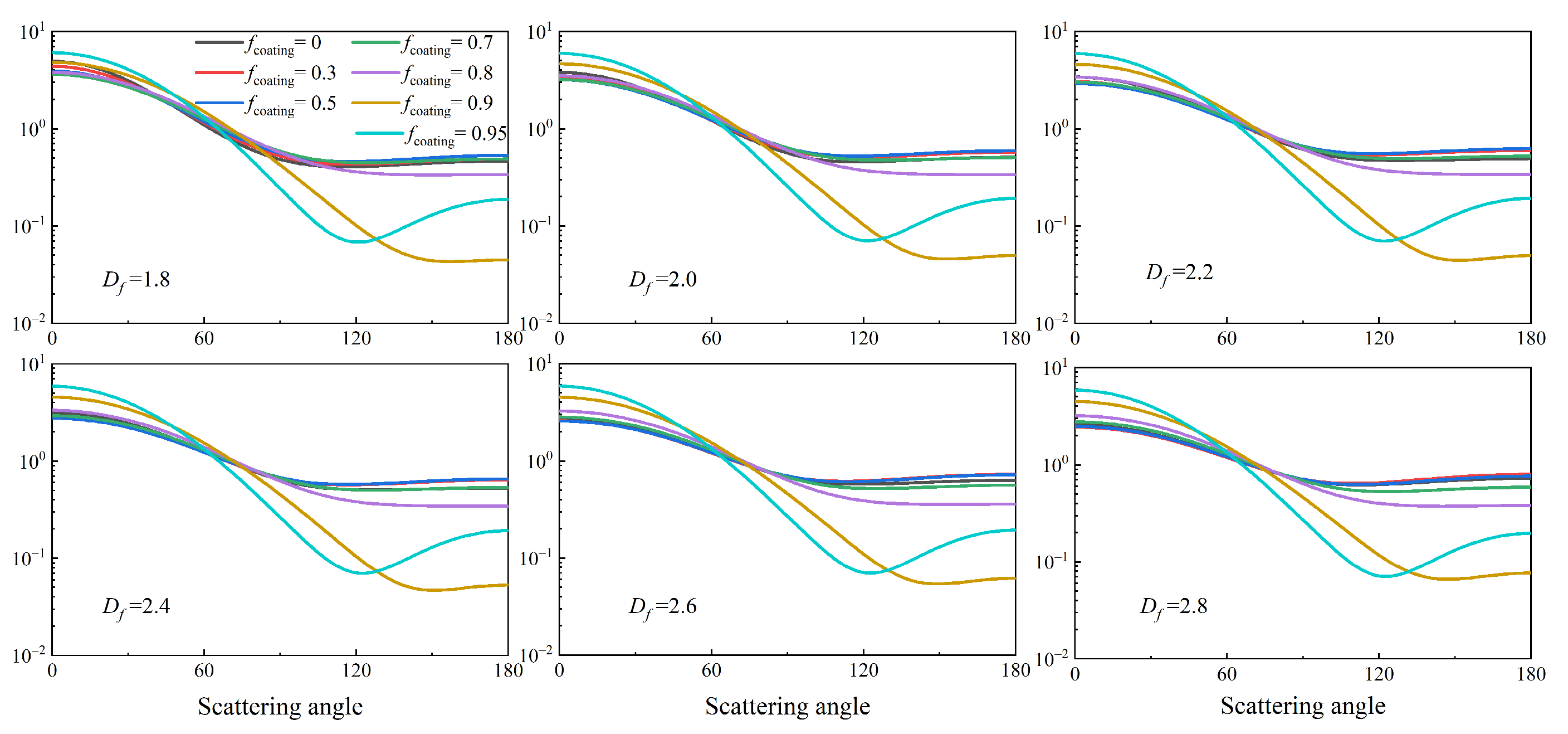
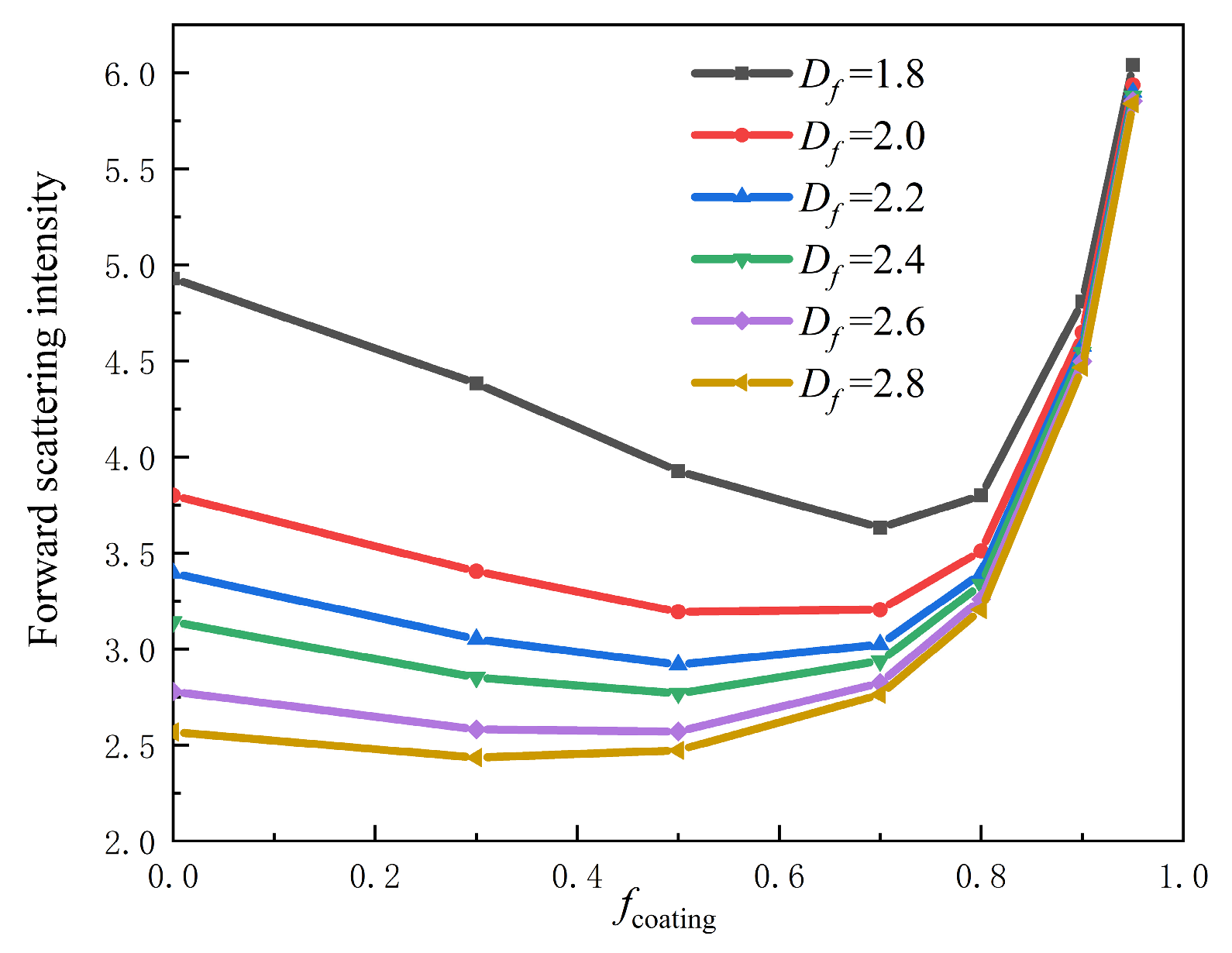
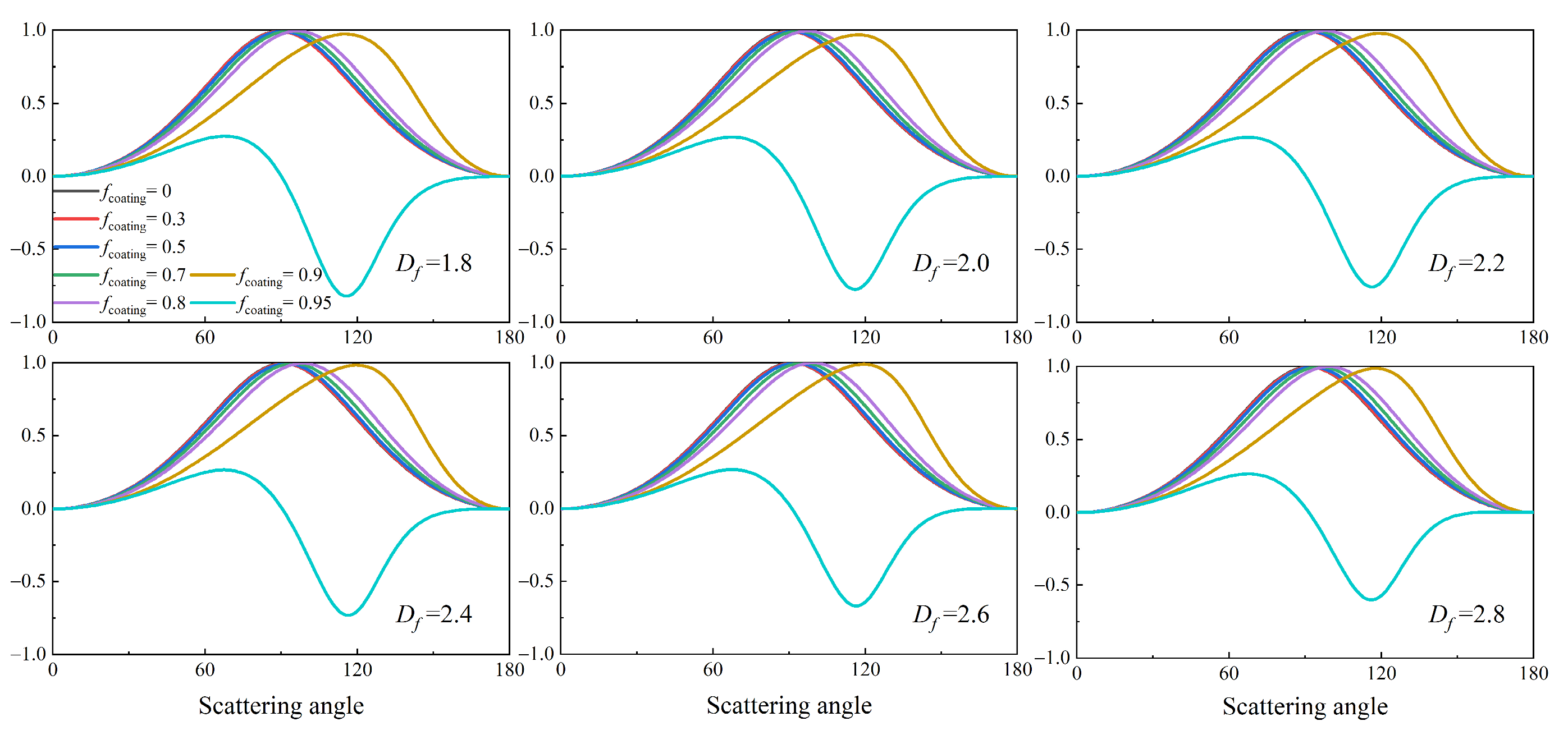
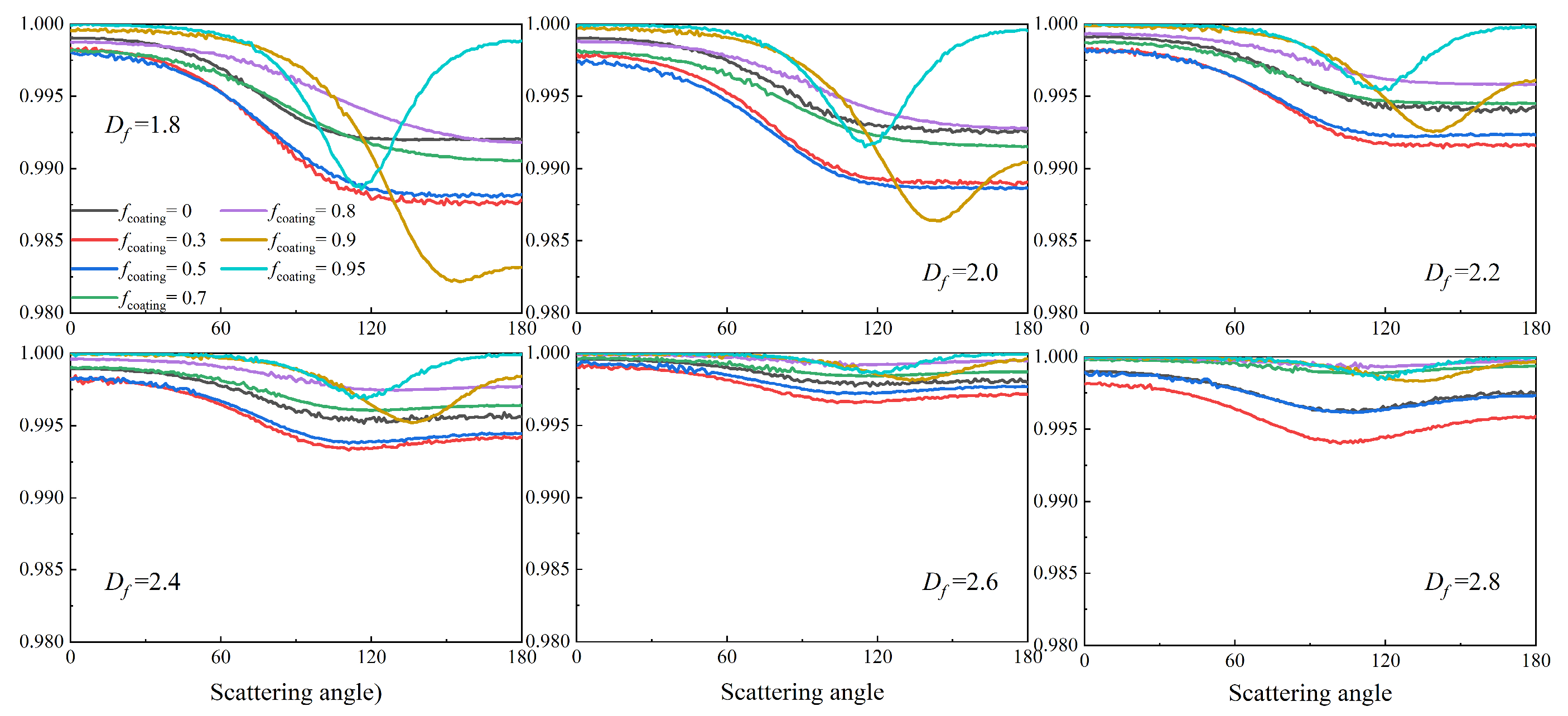
3.2. Spherical Coating Model for BC Aerosols with Different Coating Volumes
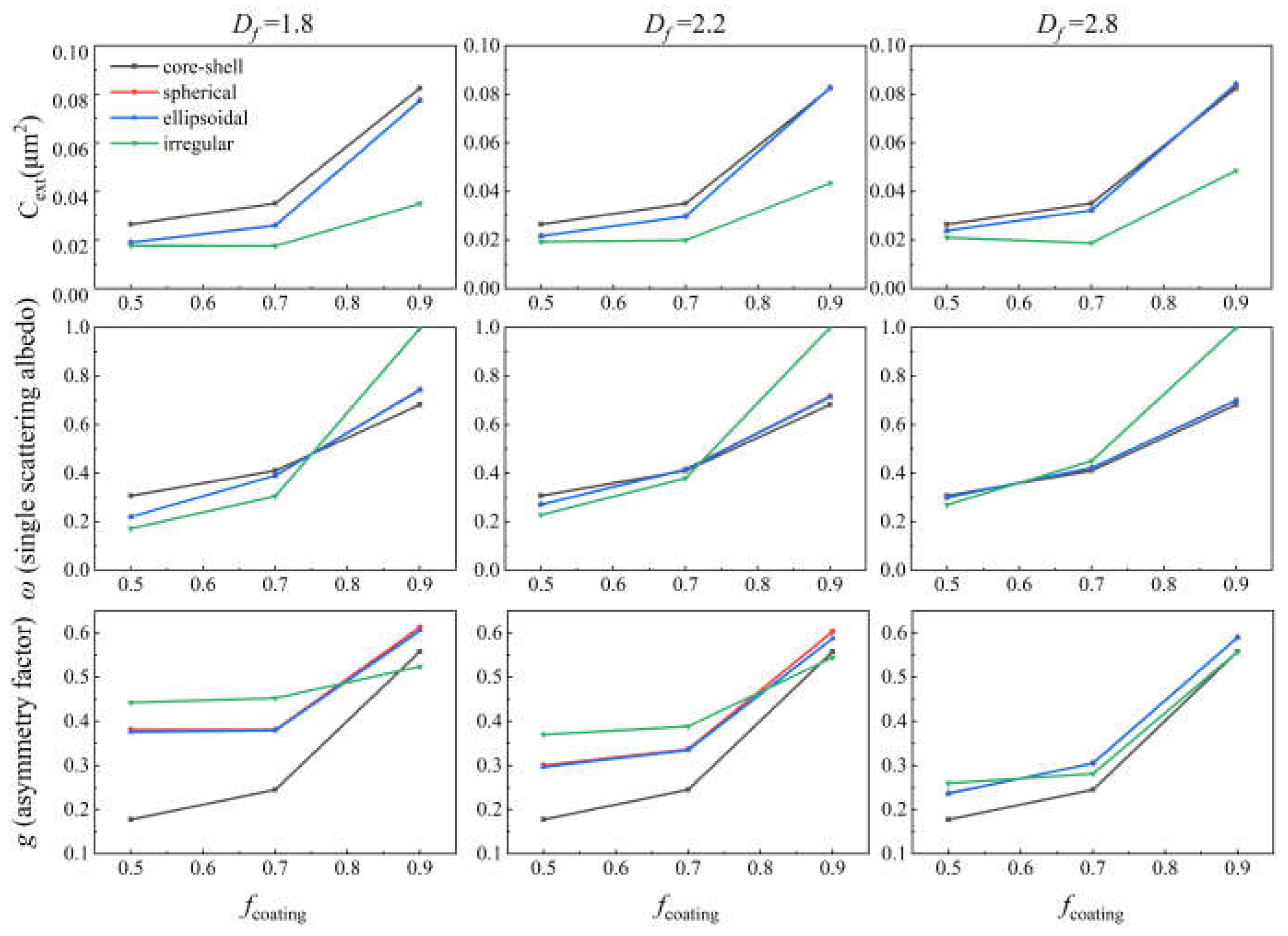
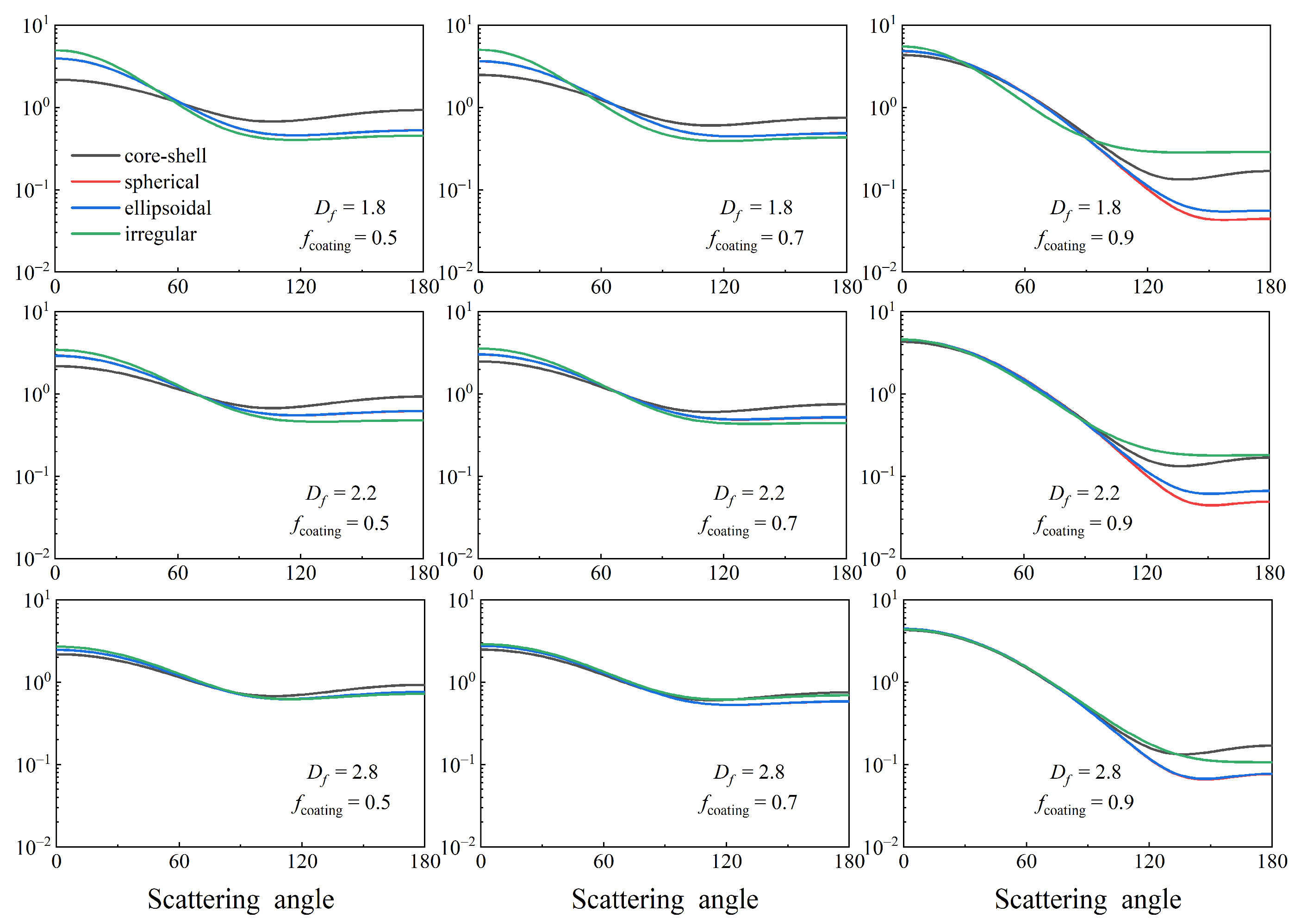
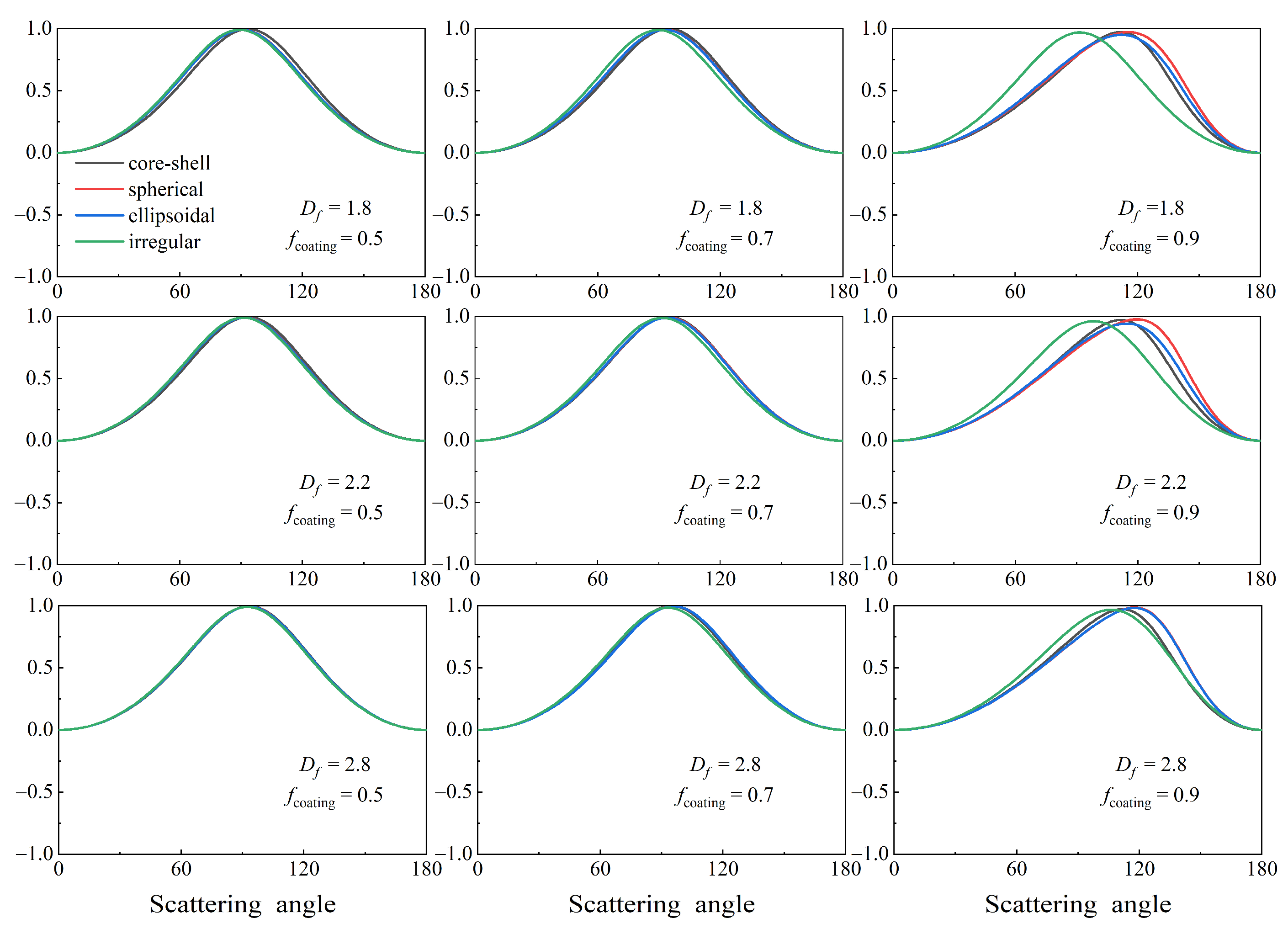
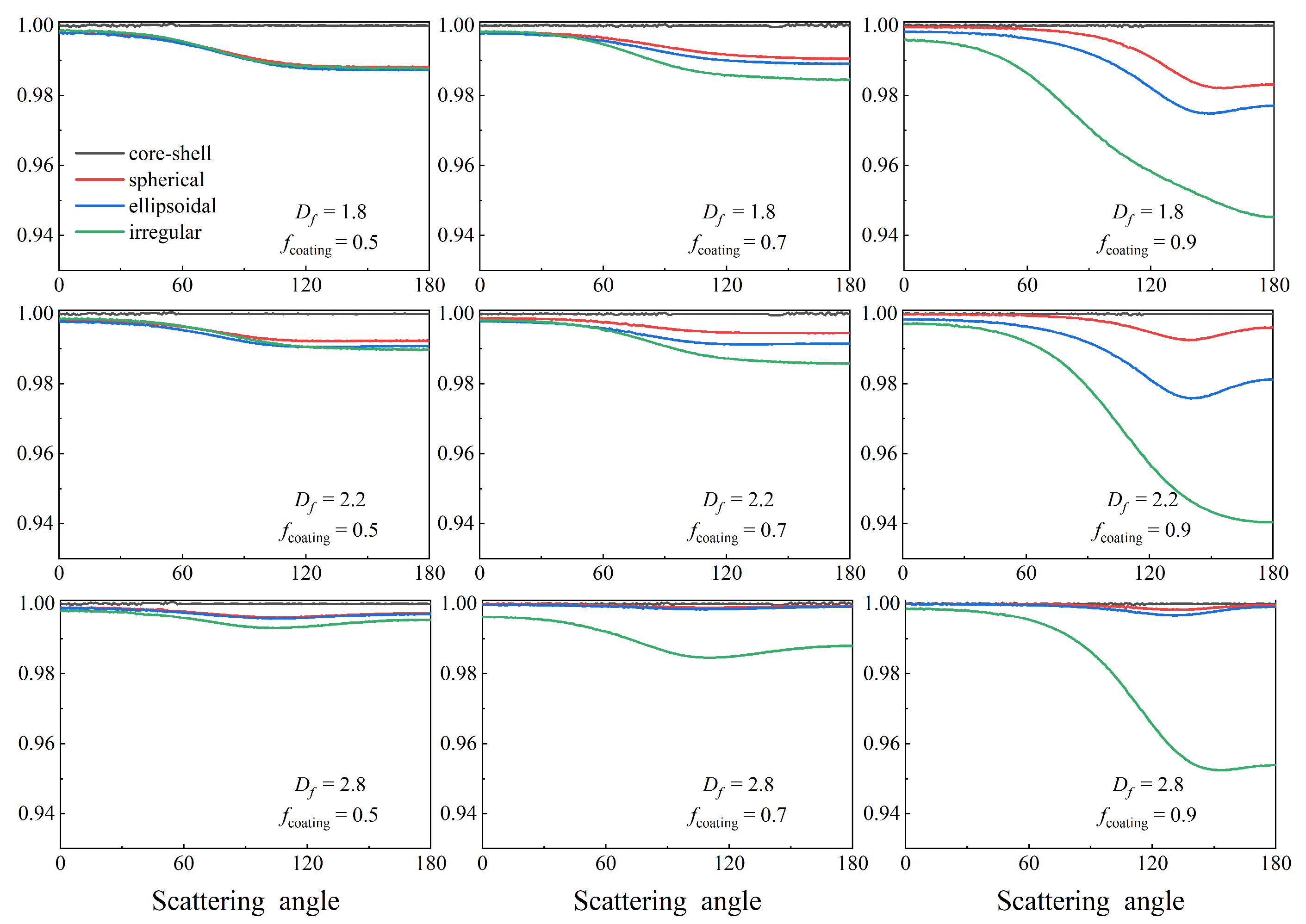
3.3. BC Aerosols with Different Coating Models
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bond, T.C.; Sun, H. Can Reducing Black Carbon Emissions Counteract Global Warming? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 5921–5926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Wong, C.; Snelling, D.R.; Smallwood, G.J. Investigation of Absorption and Scattering Properties of Soot Aggregates of Different Fractal Dimension at 532 nm Using RDG and GMM. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 1393–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, V.; Carmichael, G. Global and regional climate changes due to black carbon. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC 2013; Stocker, T.; Qin, D.; Plattner, G.-K.; Tignor, M.; Allen, S.K.; Boschung, J.; Nauels, A.; Xia, Y.; Bex, V.; et al. Climate Change 2013. The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013; 1535p. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, M.Z. Strong radiative heating due to the mixing state of black carbon in atmospheric aerosols. Nature 2001, 409, 695–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraiwa, M.; Kondo, Y.; Iwamoto, T.; Kita, K. Amplification of Light Absorption of Black Carbon by Organic Coating. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wentzel, M.; Gorzawski, H.; Naumann, K.H.; Saathoff, H.; Weinbruch, S. Transmission electron microscopical and aerosol dynamical characterization of soot aerosols. J. Aerosol Sci. 2003, 34, 1347–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Pósfai, M.; Hobbs, P.V.; Buseck, P.R. Individual aerosol particles from biomass burning in southern Africa: 2, Compositions and aging of inorganic particles. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, 8484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China, S.; Mazzoleni, C.; Gorkowski, K.; Aiken, A.C.; Dubey, M.K. Morphology and mixing state of individual freshly emitted wildfire carbonaceous particles. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, J.V.; Artaxo, P.; Liousse, C.; Reid, J.S.; Hobbs, P.V.; Kaufman, Y.J. Effects of black carbon content, particle size, and mixing on light absorption by aerosols from biomass burning in Brazil. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1998, 103, 32041–32050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.J.A.; Grainger, R.G. Simplifying the calculation of light scattering properties for black carbon fractal aggregates. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 7825–7836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Khalizov, A.F.; Pagels, J.; Zhang, D.; Xue, H.; McMurry, P.H. Variability in morphology, hygroscopicity, and optical properties of soot aerosols during atmospheric processing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10291–10296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bond, T.C.; Habib, G.; Bergstrom, R.W. Limitations in the enhancement of visible light absorption due to mixing state. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111, D20211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappa, C.D.; Onasch, T.B.; Massoli, P.; Worsnop, D.R.; Bates, T.S.; Cross, E.S.; Davidovits, P.; Hakala, J.; Hayden, K.L.; Jobson, B.T.; et al. Radiative Absorption Enhancements Due to the Mixing State of Atmospheric Black Carbon. Science 2012, 337, 1078–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, J.P.; Gao, R.S.; Spackman, J.R.; Watts, L.A.; Thomson, D.S.; Fahey, D.W.; Ryerson, T.B.; Peischl, J.; Holloway, J.S.; Trainer, M.; et al. Measurement of the mixing state, mass, and optical size of individual black carbon particles in urban and biomass burning emissions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L13810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, T.C.; Doherty, S.J.; Fahey, D.W.; Forster, P.M.; Berntsen, T.; DeAngelo, B.J.; Flanner, M.G.; Ghan, S.; Kärcher, B.; Koch, D.; et al. Bounding the role of black carbon in the climate system: A scientific assessment. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 5380–5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; Sinyuk, A.; Lapyonok, T.; Holben, B.N.; Mishchenko, M.; Yang, P.; Eck, T.F.; Volten, H.; Muñoz, O.; Veihelmann, B.; et al. Application of spheroid models to account for aerosol particle nonsphericity in remote sensing of desert dust. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, D11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Videen, G.; Chylek, P.J.O.C. Scattering by a composite sphere with an absorbing inclusion and effective medium approximations. Optis Commun. 1998, 158, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahnert, M.; Nousiainen, T.; Lindqvist, H. Review: Model particles in atmospheric optics. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2014, 146, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerman, T.P.; Toon, O.B. Absorption of visible radiation in atmosphere containing mixtures of absorbing and nonabsorbing particles. Appl. Opt. 1981, 20, 3661–3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.Y.; Liu, L.H. Influence of complex component and particle polydispersity on radiative properties of soot aggregate in atmosphere. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2010, 111, 2115–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Chen, L.; Li, S.; Zou, M.; Su, L.; Tao, J. The Effects of Morphology and Water Coating on the Optical Properties of Soot Aggregates. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2016, 16, 1315–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Zhao, J.M.; Liu, L.H. Morphological effects on the radiative properties of soot aerosols in different internally mixing states with sulfate. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2015, 165, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, J.; Yin, Y.; Zhu, B.; Feng, Q. Optical properties of black carbon aggregates with non-absorptive coating. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2017, 187, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahnert, M.; Nousiainen, T.; Lindqvist, H. Models for integrated and differential scattering optical properties of encapsulated light absorbing carbon aggregates. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 7974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahnert, M. Optical properties of black carbon aerosols encapsulated in a shell of sulfate: Comparison of the closed cell model with a coated aggregate model. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 24579–24593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahnert, M.; Kanngiesser, F. Aerosol optics model for black carbon applicable to remote sensing, chemical data assimilation, and climate modelling. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 10639–10658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuqiang, W.; Hao, W.; Dayang, G.; Ziming, C.; Lanxin, M. Radiative transfer analysis of semitransparent medium with particles having non-uniform size distribution by differential-integration method. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2019, 130, 342–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Wang, C.; Liu, L. Polarized radiative transfer in dense dispersed media containing optically soft sticky particles. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 28252–28268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyu, Z.; Fuqiang, W.; Ziming, C.; Huaxu, L.; Xuhang, S. Radiative property investigation of dispersed particulate medium with the consideration of non-uniform particle size distribution and dependent scattering effects. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2022, 186, 122488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C. Optical Properties of Black Carbon Aggregates. In Springer Series in Light Scattering. Volume 3: Radiative Transfer and Light Scattering; Springer Series in Light Scattering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 167–218. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Li, W.; Zhu, K. Comparison of the scattering properties between TiO2 and ITO clusters based on the particle superposition model. Opt. Mater. Express 2019, 9, 562–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witten, T.A.; Sander, L.M. Diffusion-Limited Aggregation in Three Dimensions. Phys. Rev. B Condens. Matter 1983, 27, 5686–5697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasanna, S.; Rivière, P.; Soufiani, A. Effect of fractal parameters on absorption properties of soot in the infrared region. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2014, 148, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Cheng, T.; Zheng, L.; Chen, H. Effect of morphology on the optical properties of soot aggregated with spheroidal monomers. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2016, 168, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tianhai Cheng, X.G.; Yu, W.; Hao, C. Effects of atmospheric water on the optical properties of soot aerosols with different mixing states. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2014, 147, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.-T.; Liu, D.; Duan, Y.-Y.; Wang, X.-D. Theoretical model of radiative transfer in opacified aerogel based on realistic microstructures. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2014, 70, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopher, M.; Sorensen, G.C.R. The Prefactor of Fractal Aggregates. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1997, 186, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrest, S.R.; Witten, T.A. Long-range correlations in smoke-particle aggregates. J. Phys. A Math. Gen. 1979, 12, L109–L117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorensen, C.M. Light Scattering by Fractal Aggregates: A Review. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 648–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, T.C.; Bergstrom, R.W. Light Absorption by Carbonaceous Particles: An Investigative Review. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 27–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Q. Effects of brown coatings on the absorption enhancement of black carbon: A numerical investigation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 16897–16914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahnert, M.; Nousiainen, T.; Lindqvist, H.; Ebert, M. Optical properties of light absorbing carbon aggregates mixed with sulfate: Assessment of different model geometries for climate forcing calculations. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 10042–10058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Zhao, R.; Li, W. Radiative characteristics of nonspherical particles based on a particle superposition model. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 11–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Jin, C.; Bao, Y. Effects of bump/pit on the radiative properties of small particles. Opt. Lett. 2016, 41, 1455–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.; Zhu, K.; Huang, Y. Radiative properties of porous fly ash particles based on the particle superposition model. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2022, 277, 107977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, E.M.; Pennypacker, C.R. Scattering and Absorption of Light by Nonspherical Dielectric Grains. Astrophys. J. 1973, 186, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draine, B.T. The Discrete-Dipole Approximation and Its Application to Interstellar Graphite Grains. Astrophys. J. 1988, 333, 848–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draine, B.T.; Flatau, P.J. Discrete-Dipole Approximation for Scattering Calculations. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1994, 11, 1491–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draine, B.T.; Flatau, P.J. User guide for the discrete dipole approximation code DDSCAT 7.3. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1305.6497. [Google Scholar]
- Draine, B.T.; Flatau, P.J. Discrete-dipole approximation for periodic targets: Theory and tests. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2008, 25, 1491–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flatau, P.; Draine, B. Fast near field calculations in the discrete dipole approximation for regular rectilinear grids. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 1247–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flatau, P.; Draine, B. Light scattering by hexagonal columns in the discrete dipole approximation. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 21834–21846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Draine, B.; Goodman, J. Beyond Clausius-Mossotti—Wave propagation on a polarizable point lattice and the discrete dipole approximation. Astrophys. J. 1993, 405, 685–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travis, L.; Lacis, A. Scattering, Absorption, and Emission of Light by Small Particles; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2002; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Kandilian, R.; Heng, R.-L.; Pilon, L. Absorption and scattering by fractal aggregates and by their equivalent coated spheres. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2015, 151, 310–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishchenko, M.I. Light scattering by randomly oriented axially symmetric particles. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1991, 8, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nousiainen, T.; Kahnert, M.; Lindqvist, H. Can particle shape information be retrieved from light-scattering observations using spheroidal model particles? J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2011, 112, 2213–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, C.; Yin, Y.; Kumar, K.R. Numerical investigation on the Ångström exponent of black carbon aerosol. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 3506–3518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
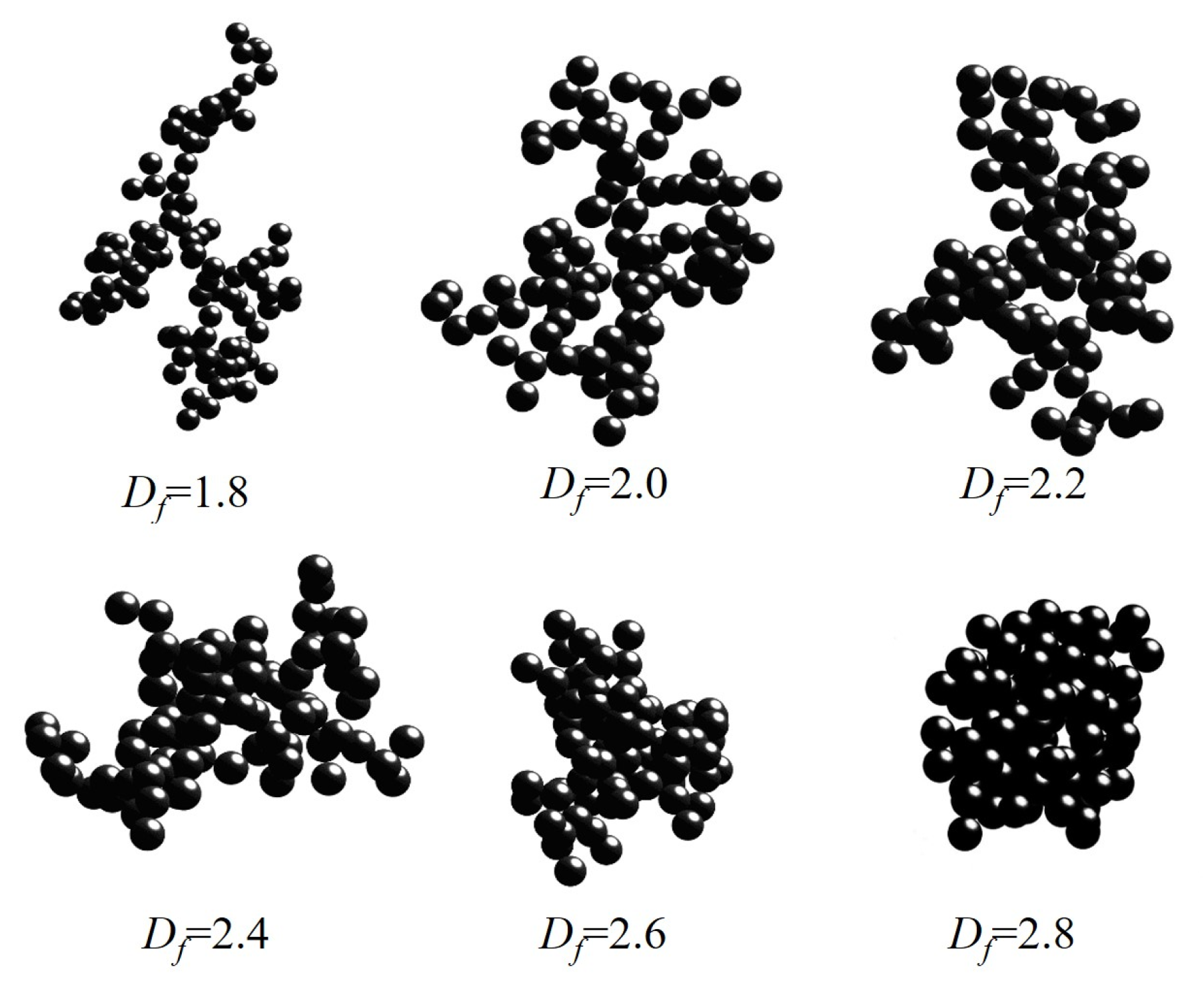
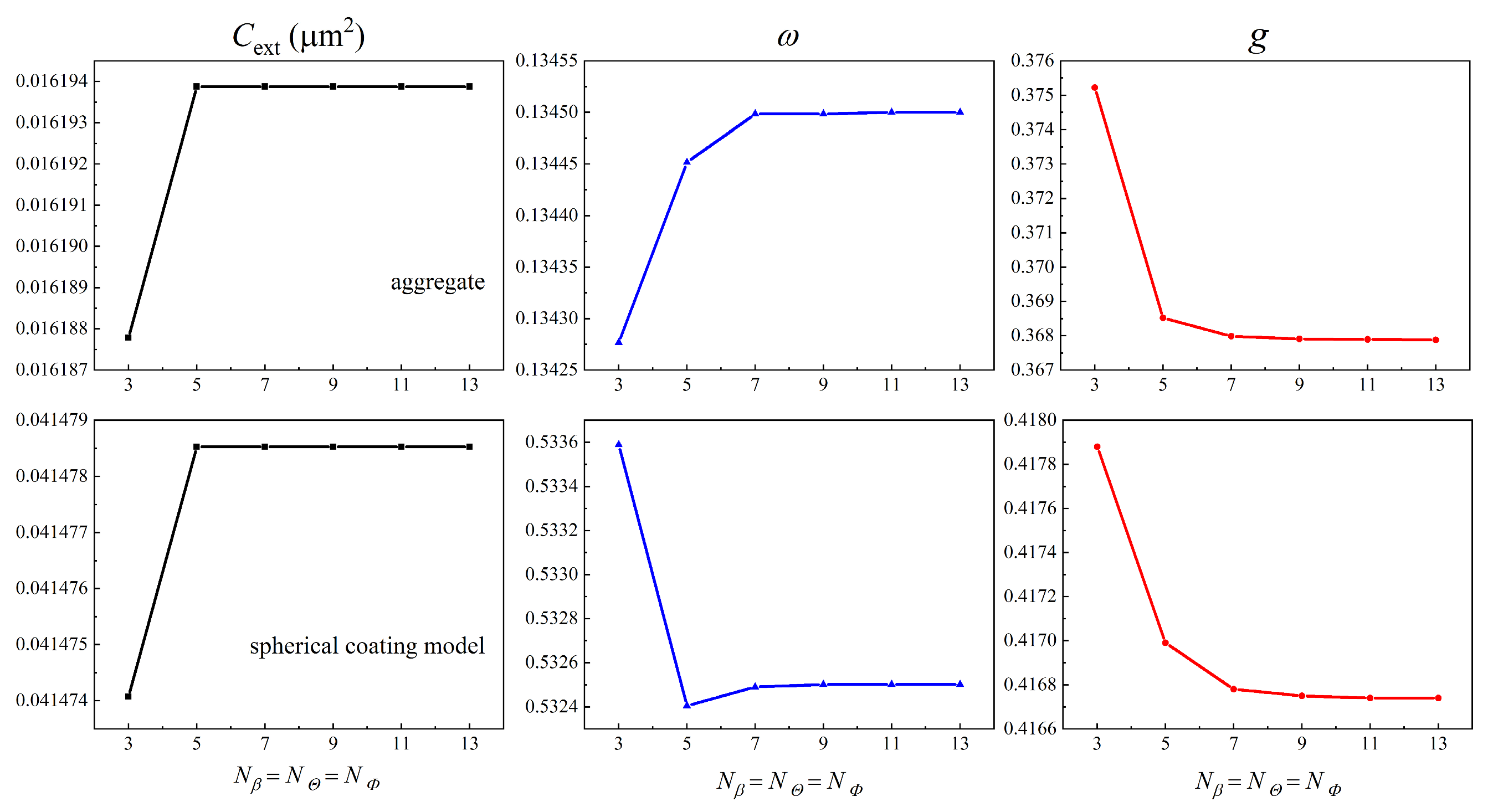
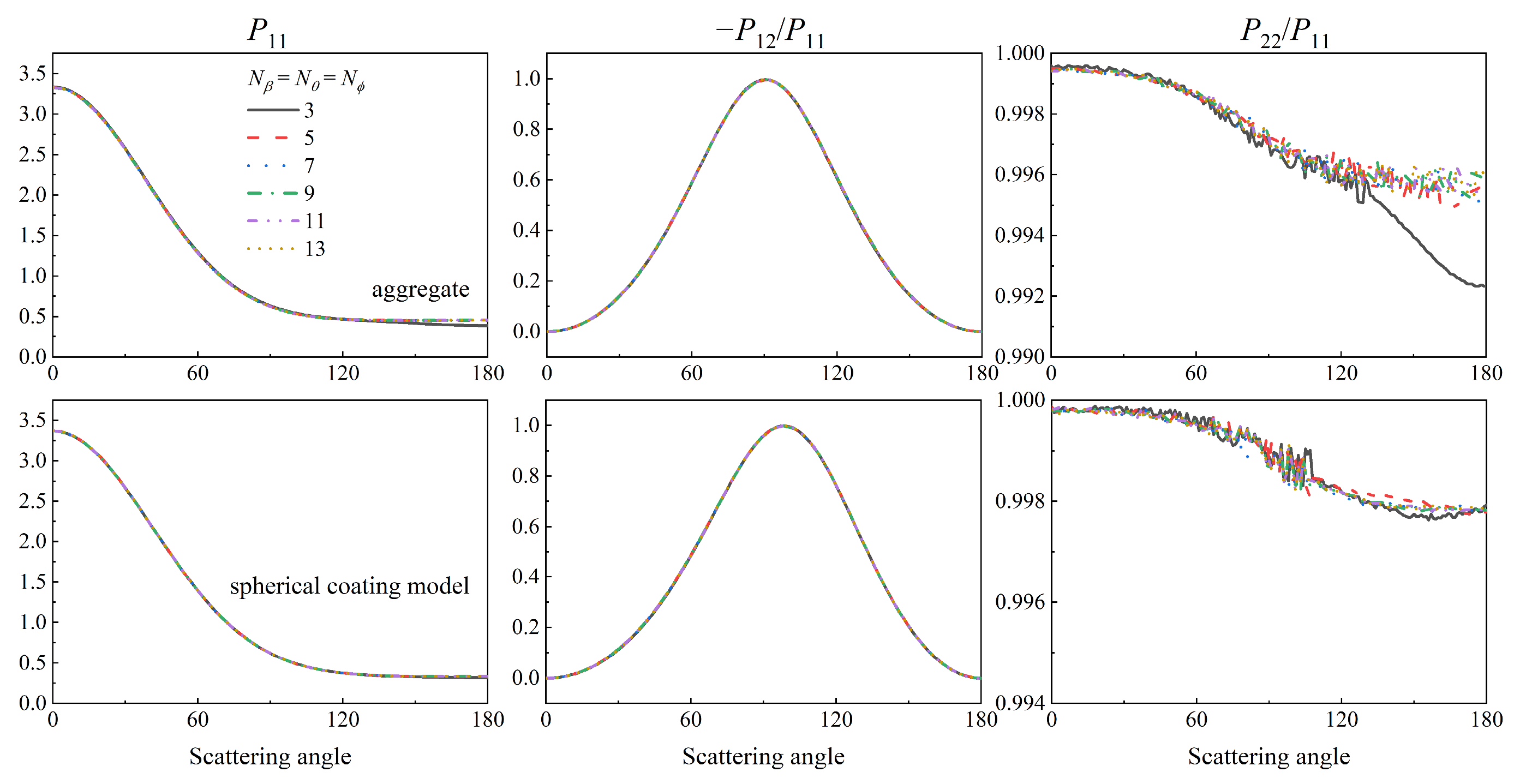
| Numbers | Cext × 10−2 μm2 | g | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 × 3 × 3 | 1.61878 | - | 0.13428 | - | 0.37522 | - |
| 5 × 5 × 5 | 1.61939 | 0.0376 | 0.13445 | 0.13038 | 0.36852 | −1.7856 |
| 7 × 7 × 7 | 1.61939 | 0 | 0.13450 | 0.03495 | 0.36799 | −0.1438 |
| 9 × 9 × 9 | 1.61939 | 0 | 0.13450 | 0 | 0.36790 | −0.0245 |
| 11 × 11 × 11 | 1.61939 | 0 | 0.13451 | 0.00699 | 0.36790 | 0 |
| 13 × 13 × 13 | 1.61939 | 0 | 0.13451 | 0 | 0.36790 | 0 |
| Numbers | Cext × 10−2 μm2 | g | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 × 3 × 3 | 4.14741 | - | 0.53359 | - | 0.41788 | - |
| 5 × 5 × 5 | 4.14785 | 0.01074 | 0.53241 | −0.22200 | 0.41699 | −0.21298 |
| 7 × 7 × 7 | 4.14785 | 0 | 0.53249 | 0.01613 | 0.41678 | −0.05036 |
| 9 × 9 × 9 | 4.14785 | 0 | 0.53250 | 0.00202 | 0.41675 | −0.00960 |
| 11 × 11 × 11 | 4.14785 | 0 | 0.53250 | 0 | 0.41674 | 0 |
| 13 × 13 × 13 | 4.14785 | 0 | 0.53250 | 0 | 0.41674 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, K. Optical Properties of Black Carbon Aerosols with Different Coating Models. Photonics 2022, 9, 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9050359
Tang Y, Huang Y, Zhu K. Optical Properties of Black Carbon Aerosols with Different Coating Models. Photonics. 2022; 9(5):359. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9050359
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Yanxia, Yong Huang, and Keyong Zhu. 2022. "Optical Properties of Black Carbon Aerosols with Different Coating Models" Photonics 9, no. 5: 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9050359
APA StyleTang, Y., Huang, Y., & Zhu, K. (2022). Optical Properties of Black Carbon Aerosols with Different Coating Models. Photonics, 9(5), 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9050359





