Retinal and Choroidal Thickness in Myopic Young Adults
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
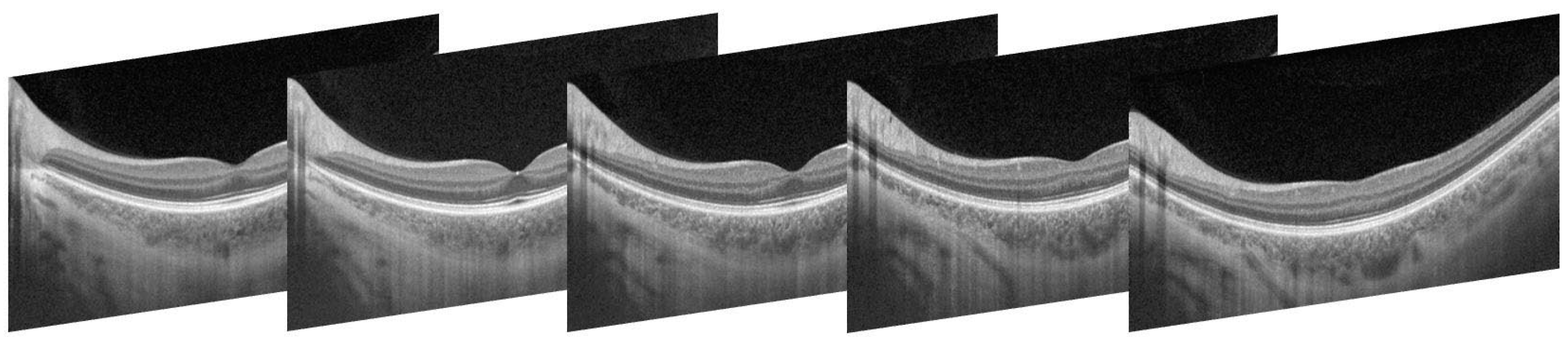
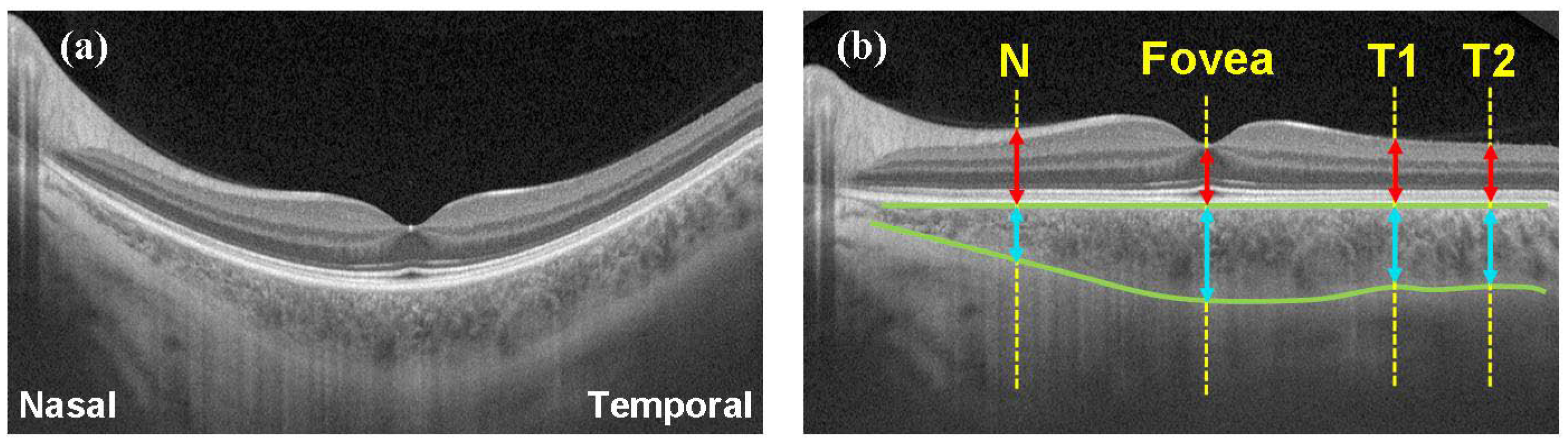
2.2. Experimental Protocol
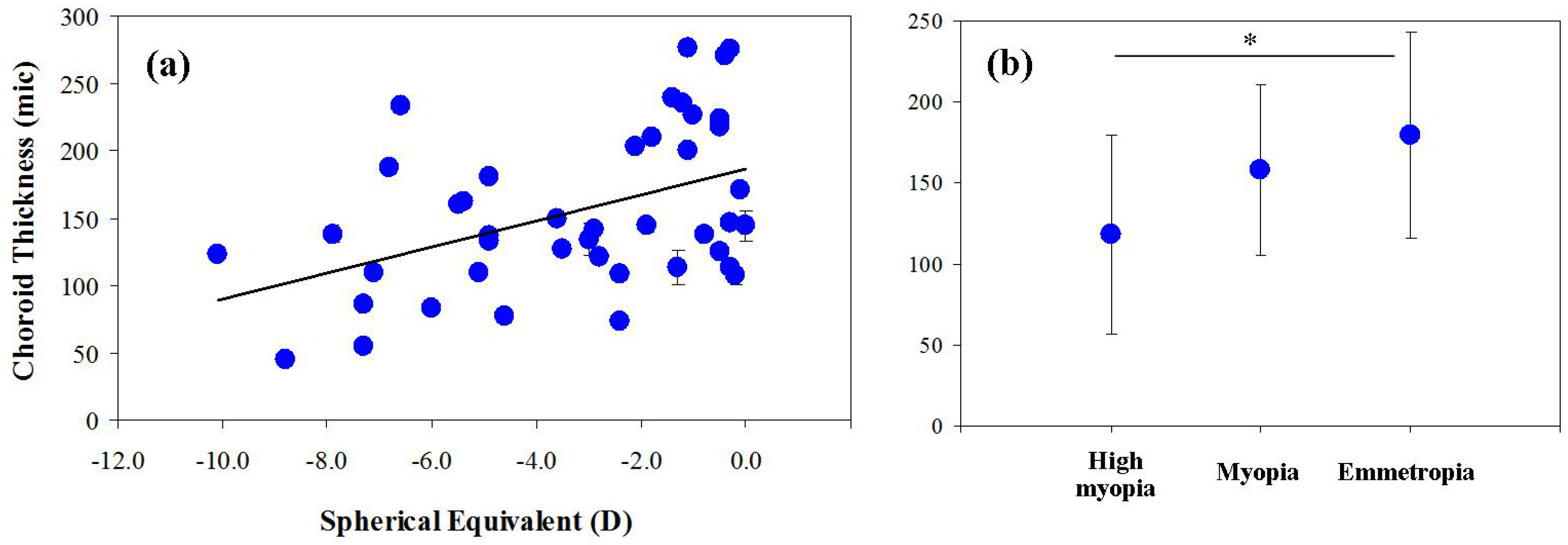
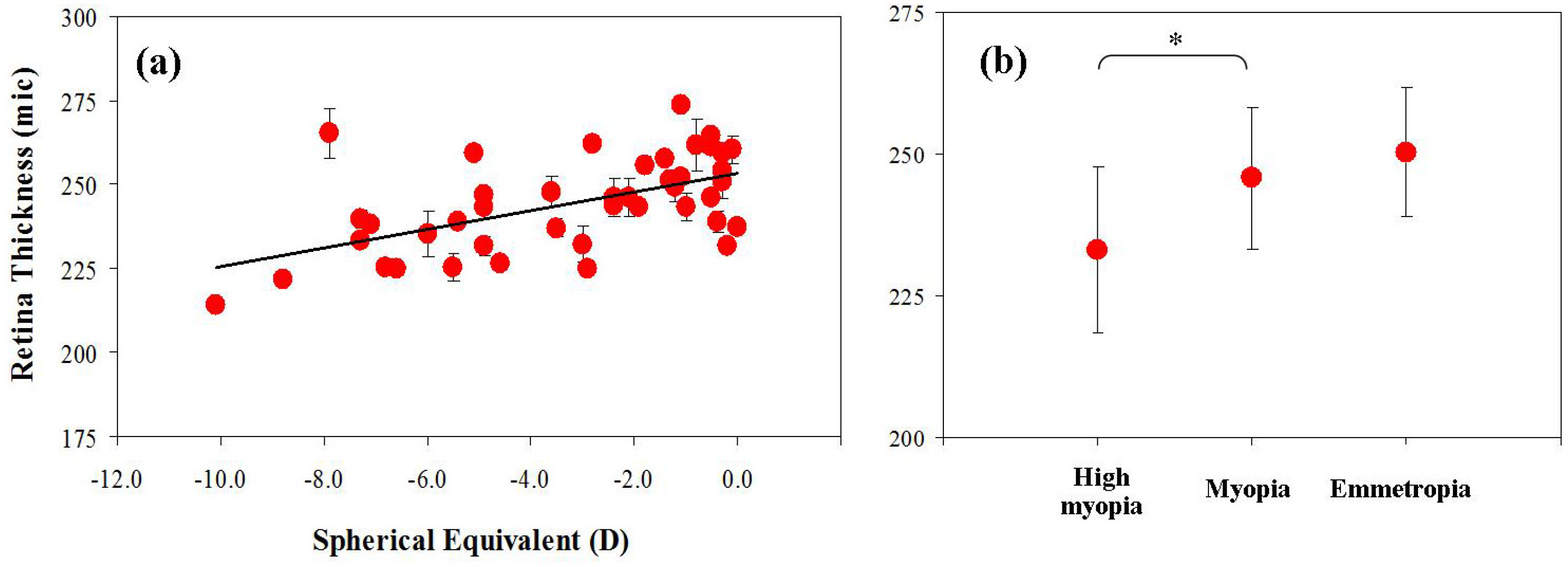
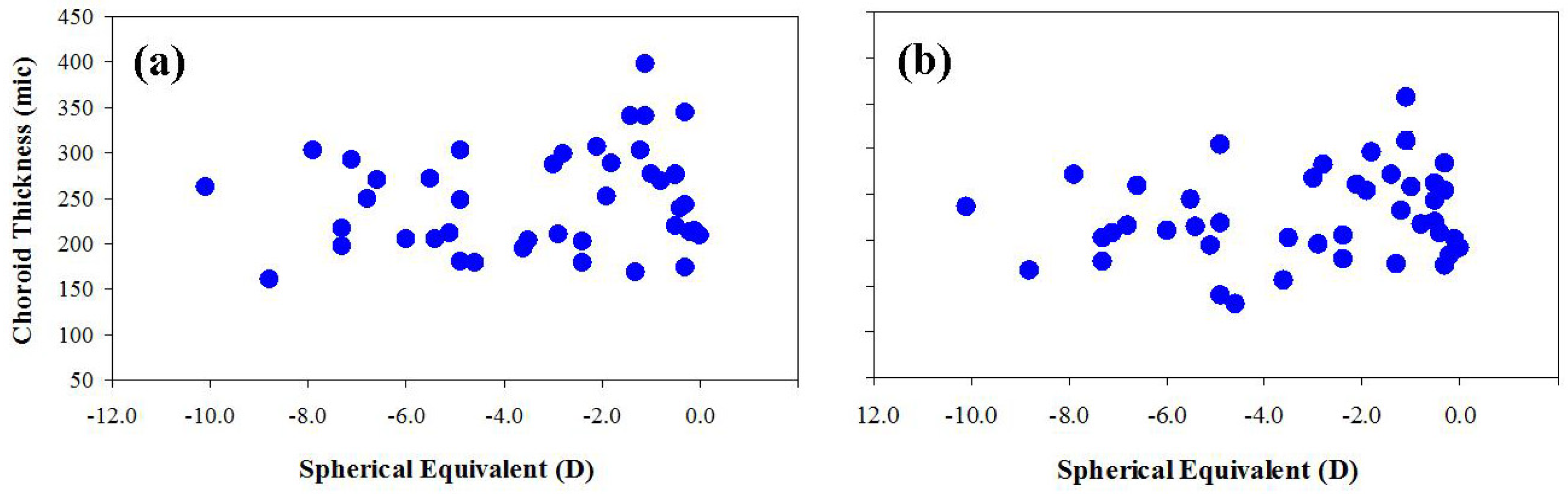
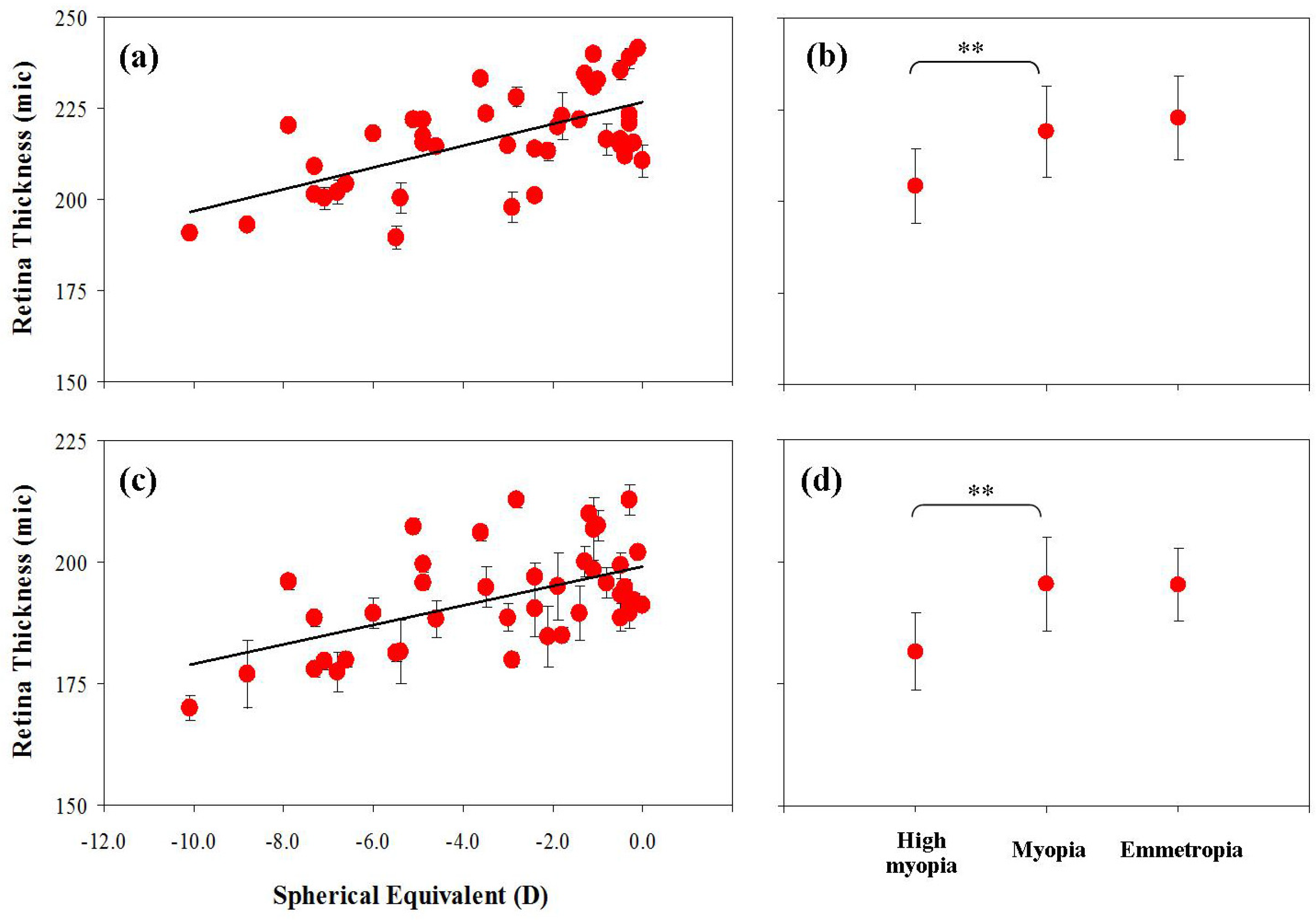
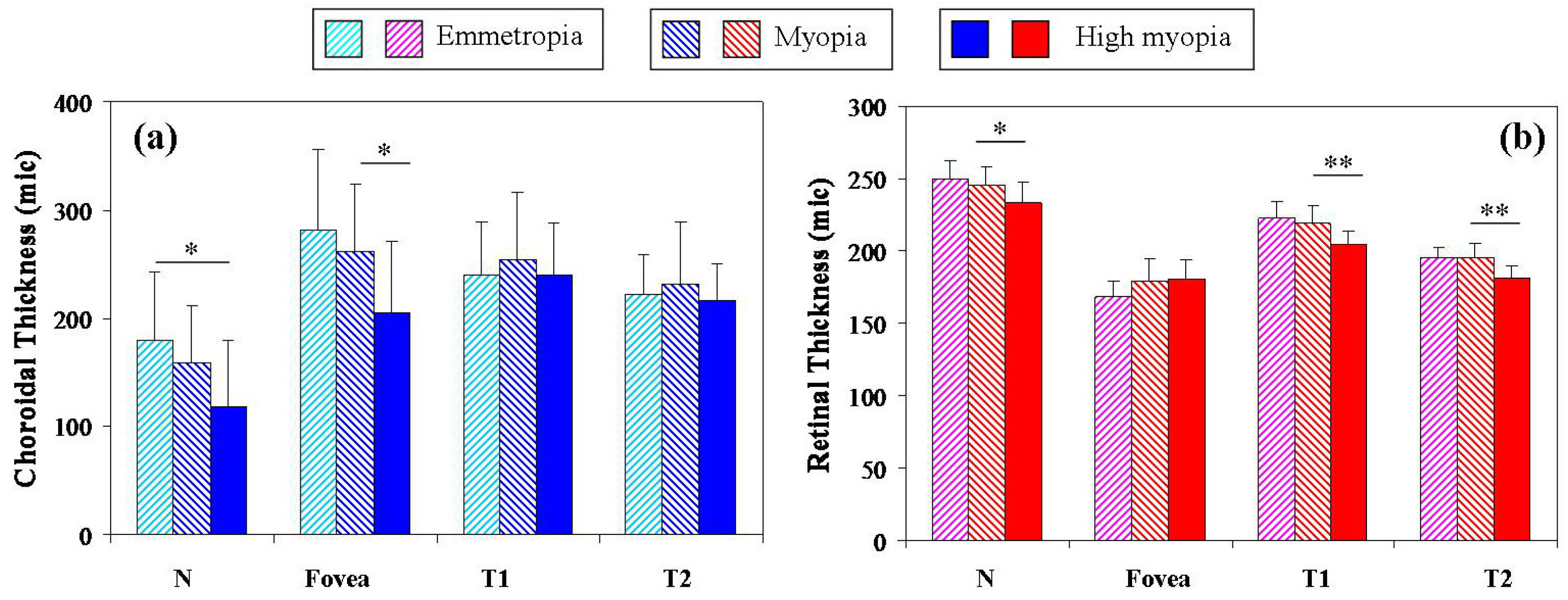
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morgan, I.G.; Ohno-Matsui, K.; Saw, S.M. Myopia. Lancet 2012, 379, 1739–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, B.A.; Fricke, T.R.; Wilson, D.A.; Jong, M.; Naidoo, K.S.; Sankaridurg, P.; Wong, T.Y.; Naduvilath, T.J.; Resnikoff, S. Global prevalence of myopia and high myopia and temporal trends from 2000 through 2050. Ophthalmology 2016, 123, 1036–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holden, B.; Sankaridurg, P.; Smith, E.; Aller, T.; Jong, M.; He, M. Myopia, an underrated global challenge to vision: Where the current data takes us on myopia control. Eye 2014, 28, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastawrous, A.; Suni, A.V. Thirty year projected magnitude (to 2050) of near and distance vision impairment and the economic impact if existing solutions are implemented globally. Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 2020, 27, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haarman, A.E.G.; Enthoven, C.A.; Tideman, J.W.L.; Tedja, M.S.; Verhoeven, V.J.M.; Klaver, C.C.W. The complications of myopia: A review and meta-analysis. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2020, 61, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, W.; Butterworth, J.; Malecaze, F.; Calvas, P. Axial length of myopia: A review of current research. Ophthalmologica 2011, 225, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Swanson, E.A.; Lin, C.P.; Schuman, J.S.; Stinson, W.G.; Chang, W.; Hee, M.R.; Flotte, T.; Gregory, K.; Puliafito, C.A.; et al. Optical coherence tomography. Science 1991, 254, 1178–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakitani, Y.; Sasoh, M.; Sugimoto, M.; Ito, Y.; Ido, M.; Uji, Y. Macular thickness measurements in healthy subjects with different axial lengths using optical coherence tomography. Retina 2003, 23, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.C.C.; Hoh, S.T.; Foster, P.J.; Lim, T.-H.; Chew, S.-J.; Seah, S.K.L.; Aung, T. Use of optical coherence tomography to assess variations in macular retinal thickness in myopia. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2005, 46, 974–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, G.S.K.; Lee, J.W.Y.; Woo, T.T.Y.; Wong, R.L.M.; Wong, I.Y.H. Central macular thickness in children with myopia, emmetropia, and hyperopia: An optical coherence tomography study. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 847694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, D.S.C.; Leung, K.S.; Mohamed, S.; Chan, W.-M.; Palanivelu, M.S.; Cheung, C.Y.L.; Li, E.Y.M.; Lai, R.Y.K.; Leung, C.K.-S. Regional variations in the relationship between macular thickness measurements and myopia. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2007, 48, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.K.; Lee, S.C.; Lee, E.S.; Kim, C.Y.; Kim, S.S. Macular thickness variations with sex, age, and axial length in healthy subjects: A spectral domain-optical coherence tomography study. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 3913–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhi, M.; Liu, J.J.; Qavi, A.H.; Grulkowski, I.; Lu, C.D.; Mohler, K.J.; Ferrara, D.; Kraus, M.F.; Baumal, C.R.; Witkin, A.J.; et al. Choroidal analysis in healthy eyes using swept source optical coherence tomography compared to spectral domain optical coherence tomography. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2014, 157, 1272–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldstein, S.M.; Faatz, H.; Szimacsek, M.; Glodan, A.M.; Podkowinski, D.; Montuoro, A.; Simader, C.; Gerendas, B.S.; Schmidt-Erfurth, U. Comparison of penetration depth in choroidal imaging using swept source vs spectral domain optical coherence tomography. Eye 2015, 29, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, M.; Liu, D.T.; Chan, V.C.; Lam, D.S. Choroidal thickness measurement in myopic eyes by enhanced depth optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology 2013, 120, 1909–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.; Qiu, B.; Chhablani, J.; Zhang, X. Evaluation of choroidal thickness using optical coherent tomography: A review. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 783519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikuno, Y.; Tano, Y. Retinal and choroidal biometry in highly myopic eyes with spectral-domain optical coherence tomography. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2009, 50, 3876–3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teberik, K.; Kaya, M. Retinal and choroidal thickness in patients with high myopia without maculopathy. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 33, 1438–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, J.; Shen, W.; Jiang, B. Assessment of retinal and choroidal measurements in chinese school-age children with Cirrus-HD optical coherence tomography. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jin, P.; Zou, H.; Xu, X.; Chang, T.C.; Zhu, J.; Deng, J.; Lv, M.; Jin, J.; Sun, S.; Wang, L.; et al. Longitudinal changes in choroidal and retinal thicknesses in children with myopic shift. Retina 2019, 39, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach, M. The Freiburg Visual Acuity Test-Variability unchanged by post-hoc re-analysis. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2007, 245, 965–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villa-Carpes, J.A.; Bueno, J.M.; Fernández, E.J. Visual adaptation to scattering in myopes. Photonics 2021, 8, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaide, R.F.; Koizumi, H.; Pozzoni, M.C. Enhanced depth imaging spectral-domain optical coherence tomography. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2008, 146, 496–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Kim, S.S.; Koh, H.J.; Lee, S.C. Choroidal thickness, age, and refractive error in healthy Korean subjects. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2014, 91, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zou, J.; Jia, L.; Yang, J.-G.; Chen, S.-R. Spectral- and time-domain optical coherence tomography measurements of macular thickness in young myopic eyes. Diagn. Pathol. 2014, 9, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, S.F.; Sharanjeet-Kaur; Manan, F.A.; Zulkarnain, I.; Mohamad, Z.; Ariffin, A.E. Macular thickness as determined by optical coherence tomography in relation to degree of myopia, axial length and vitreous chamber depth in Malay subjects. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2012, 95, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.D.; Gazzard, G.; Fong, A.; Aung, T.; Hoh, S.T.; Loon, S.-C.; Healey, P.; Tan, D.T.H.; Wong, T.-Y.; Saw, S.-M. Myopia, axial length, and OCT characteristics of the macula in Singaporean children. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 2773–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, B.; Dong, N.; Ren, X.; Zhang, T.; Xiao, L. Macular measurements using spectral-domain optical coherence tomography in Chinese myopic children. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 7410–7416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Hanno, T.; Lade, A.C.; Mathiesen, E.B.; Peto, T.; Njølstad, I.; Bertelsen, G. Macular thickness in healthy eyes of adults (N = 4508) and relation to sex, age and refraction: The Tromsø Eye Study (2007–2008). Acta Ophthalmol. 2017, 95, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zereid, F.M.; Osuagwu, U.L. Myopia and regional variations in retinal thickness in healthy eyes. J. Ophthalmic Vis. Res. 2020, 15, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarhan, A.R.E.; Zaky, M.A.; Hassan, B.A.E. Determining the correlation between axial length/spherical equivalent and macular thickness in myopia. Menoufia Med. J. 2020, 33, 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, E.J.; Bermann, B.; Považay, B.; Unterhuber, A.; Sattmann, H.; Hofer, B.; Ahnelt, P.K.; Drexler, W. Ultrahigh resolution optical coherence tomography and pancorrection for cellular imaging of the living human retina. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 11083–11094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, W.; Zhao, M.; Tsai, S.H.; Burkes, W.L.; Potts, L.B.; Xu, W.; Payne, H.R.; Hein, T.W.; Kuo, L.; Rosa, R.H., Jr. Correlation of spectral domain optical coherence tomography with histology and electron microscopy in the porcine retina. Exp. Eye Res. 2018, 177, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, X.; Son, T.; Kim, T.H.; Le, D. Interpretation of anatomic correlates of outer retinal bands in optical coherence tomography. Exp. Biol. Med. 2021, 246, 2140–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, T.; Imamura, Y.; Margolis, R.; Slakter, J.S.; Spaide, R.F. Enhanced depth imaging optical coherence tomography of the choroid in highly myopic eyes. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2009, 148, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldenberg, D.; Moisseiev, E.; Goldstein, M.; Loewenstein, A.; Barak, A. Enhanced depth imaging optical coherence tomography: Choroidal thickness and correlations with age, refractive error, and axial length. Ophthalmic Surg. Lasers Imaging. 2012, 43, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, S.A.; Collins, M.J.; Vincent, S.J.; Alonso-Caneiro, D. Choroidal thickness in myopic and nonmyopic children assessed with enhanced depth imaging optical coherence tomography. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 7578–7586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harb, E.; Hyman, L.; Gwiazda, J.; Marsh-Tootle, W.; Zhang, Q.; Hou, W.; Norton, T.T.; Weise, K.; Dirkes, K.; Zangwill, L.M. Choroidal thickness profiles in myopic eyes of young adults in the correction of myopia evaluation trial cohort. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 160, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhayana, A.A.; Kumar, V.; Tayade, A.; Chandra, M.; Chandra, P.; Kumar, A. Choroidal thickness in normal Indian eyes using swept-source optical coherence tomography. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 67, 252–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, Y.; Fujiwara, T.; Imamura, Y.; Lima, L.H.; Kurosaka, D.; Spaide, R.F. Choroidal thickness and visual acuity in highly myopic eyes. Retina 2012, 32, 1229–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, P.; Zou, H.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, J.; Xu, X.; Jin, J.; Chang, T.C.; Lu, L.; Yuan, H.; Sun, S.; et al. Choroidal and retinal thickness in children with different refractive status measured by swept-source optical coherence tomography. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 168, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Li, J.; Zeng, J.; Ma, W.; Liu, R.; Li, T.; Yu, S.; Tang, S. Choroidal thickness in healthy Chinese subjects. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 9555–9560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.W.; Shin, Y.U.; Cho, H.Y.; Lee, B.R. Measurement of choroidal thickness in normal eyes using 3D OCT-1000 spectral domain optical coherence tomography. Korean J. Ophthalmol. 2012, 26, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuncer, I.; Karahan, E.; Zengin, M.O.; Atalay, E.; Polat, N. Choroidal thickness in relation to sex, age, refractive error, and axial length in healthy Turkish subjects. Int. Ophthalmol. 2015, 35, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, N.; Ehsaei, A.; Hoseini-Yazdi, H.; Shoeibi, N.; Alonso-Caneiro, D.; Collins, M.J. Wide-field choroidal thickness and vascularity index in myopes and emmetropes. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2021, 41, 1308–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoseini-Yazdi, H.; Vincent, S.J.; Collins, M.J.; Read, S.A.; Alonso-Caneiro, D. Wide-field choroidal thickness in myopes and emmetropes. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.S.; Cheong, K.X.; Lim, L.W.; Li, K.Z. Topographic variation of choroidal and retinal thicknesses at the macula in healthy adults. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2014, 98, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, Z.; Rishi, P.; Srikanth, R.; Rishi, E.; Bhende, M.; Raman, R. Choroidal thickness in normal Indian subjects using Swept source optical coherence tomography. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, S.A.; Fuss, J.A.; Vincent, S.J.; Collins, M.J.; Alonso-Caneiro, D. Choroidal changes in human myopia: Insights from optical coherence tomography imaging. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2019, 102, 270–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margolis, R.; Spaide, R.F. A pilot study of enhanced depth imaging optical coherence tomography of the choroid in normal eyes. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2009, 147, 811–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-S.; Lim, H.-B.; Lee, W.-H.; Kim, K.-M.; Nam, K.Y.; Kim, J.-Y. Wide-field swept-source optical coherence tomography analysis of interocular symmetry of choroidal thickness in healthy young individuals. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2021, 62, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, R.; Read, S.A.; Collins, M.J. Diurnal variations in axial length, choroidal thickness, intraocular pressure, and ocular biometrics. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 5121–5129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verkicharla, P.K.; Kammari, P.; Das, A.V. Myopia progression varies with age and severity of myopia. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0241759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charman, W.N. The eye in focus: Accommodation and presbyopia. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2008, 91, 207–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunders, H. Age-dependence of human refractive errors. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 1981, 1, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders, H. A longitudinal study of the age-dependence of human ocular refraction—I. Age-dependent changes in the equivalent sphere. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 1986, 6, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheil, C.J.; Goncharov, A.V. Crystalline lens paradoxes revisited: Significance of age-related restructuring of the GRIN. Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 4172–4180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flitcroft, D.I.; He, M.; Jonas, J.B.; Jong, M.; Naidoo, K.; Ohno-Matsui, K.; Rahi, J.; Resnikoff, S.; Vitale, S.; Yannuzzi, L. IMI-defining and classifying myopia: A proposed set of standards for clinical and epidemiologic studies. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2019, 60, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernández, E.J.; Villa-Carpes, J.A.; Martínez-Ojeda, R.M.; Ávila, F.J.; Bueno, J.M. Retinal and Choroidal Thickness in Myopic Young Adults. Photonics 2022, 9, 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9050328
Fernández EJ, Villa-Carpes JA, Martínez-Ojeda RM, Ávila FJ, Bueno JM. Retinal and Choroidal Thickness in Myopic Young Adults. Photonics. 2022; 9(5):328. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9050328
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernández, Enrique J., José A. Villa-Carpes, Rosa M. Martínez-Ojeda, Francisco J. Ávila, and Juan M. Bueno. 2022. "Retinal and Choroidal Thickness in Myopic Young Adults" Photonics 9, no. 5: 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9050328
APA StyleFernández, E. J., Villa-Carpes, J. A., Martínez-Ojeda, R. M., Ávila, F. J., & Bueno, J. M. (2022). Retinal and Choroidal Thickness in Myopic Young Adults. Photonics, 9(5), 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9050328





