Low-Latency Optical Wireless Data-Center Networks Using Nanoseconds Semiconductor-Based Wavelength Selectors and Arrayed Waveguide Grating Router
Abstract
1. Introduction
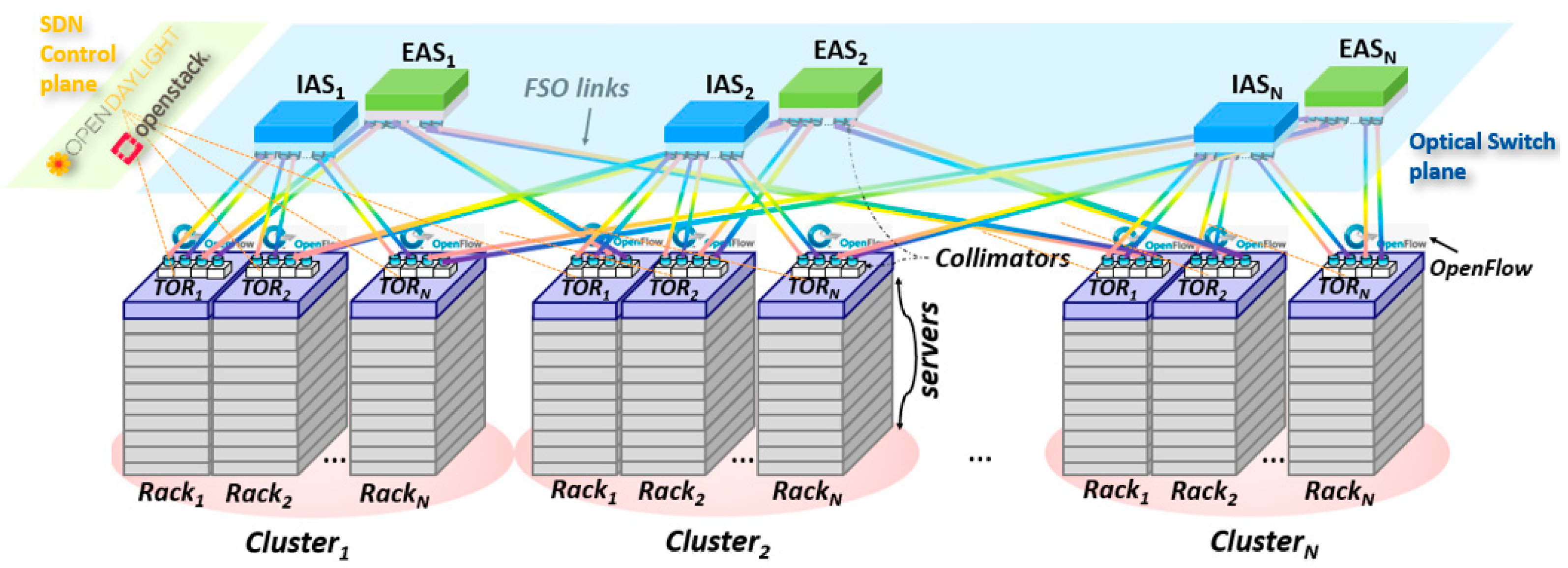
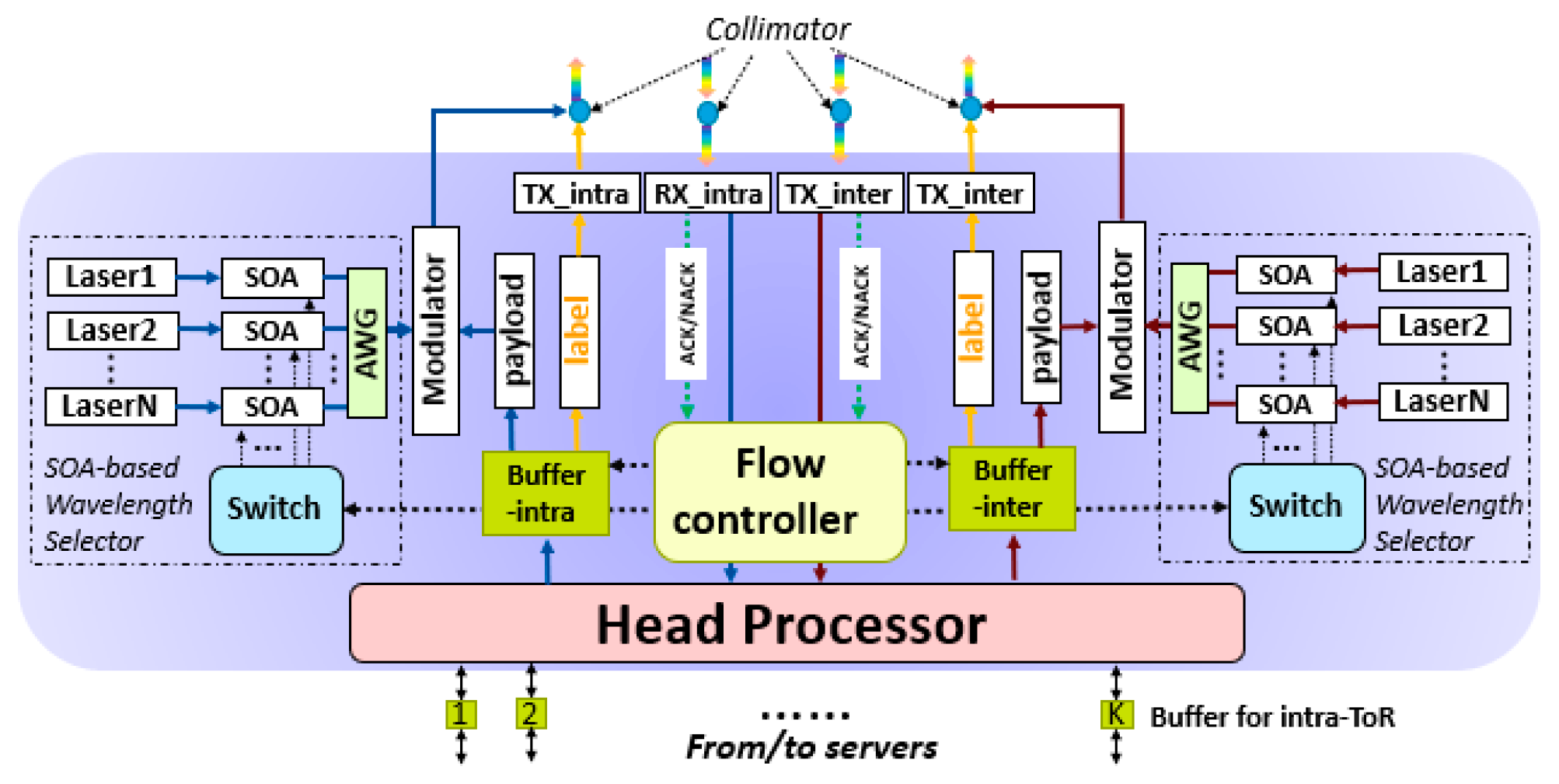
2. OW-DCN Architecture
3. Experimental Validation
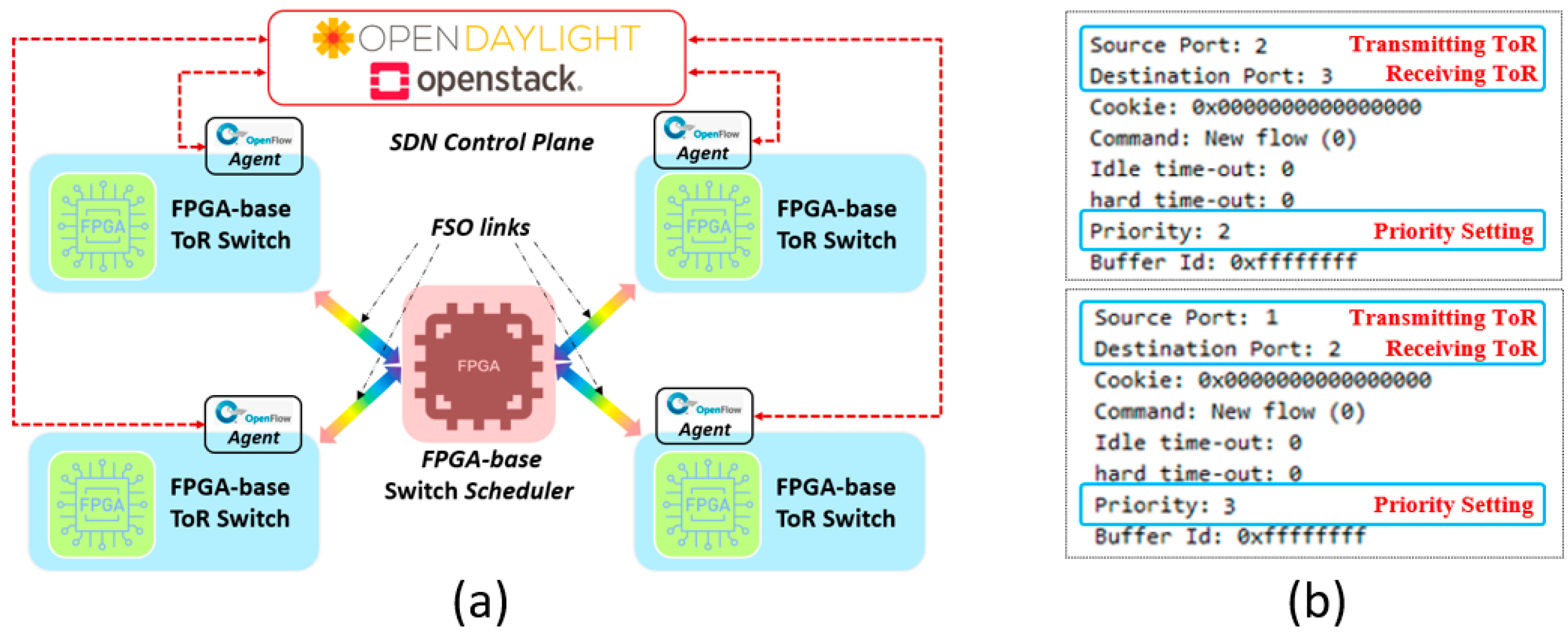
3.1. Switch Schedule and Reconfiguration of the OW-DCN
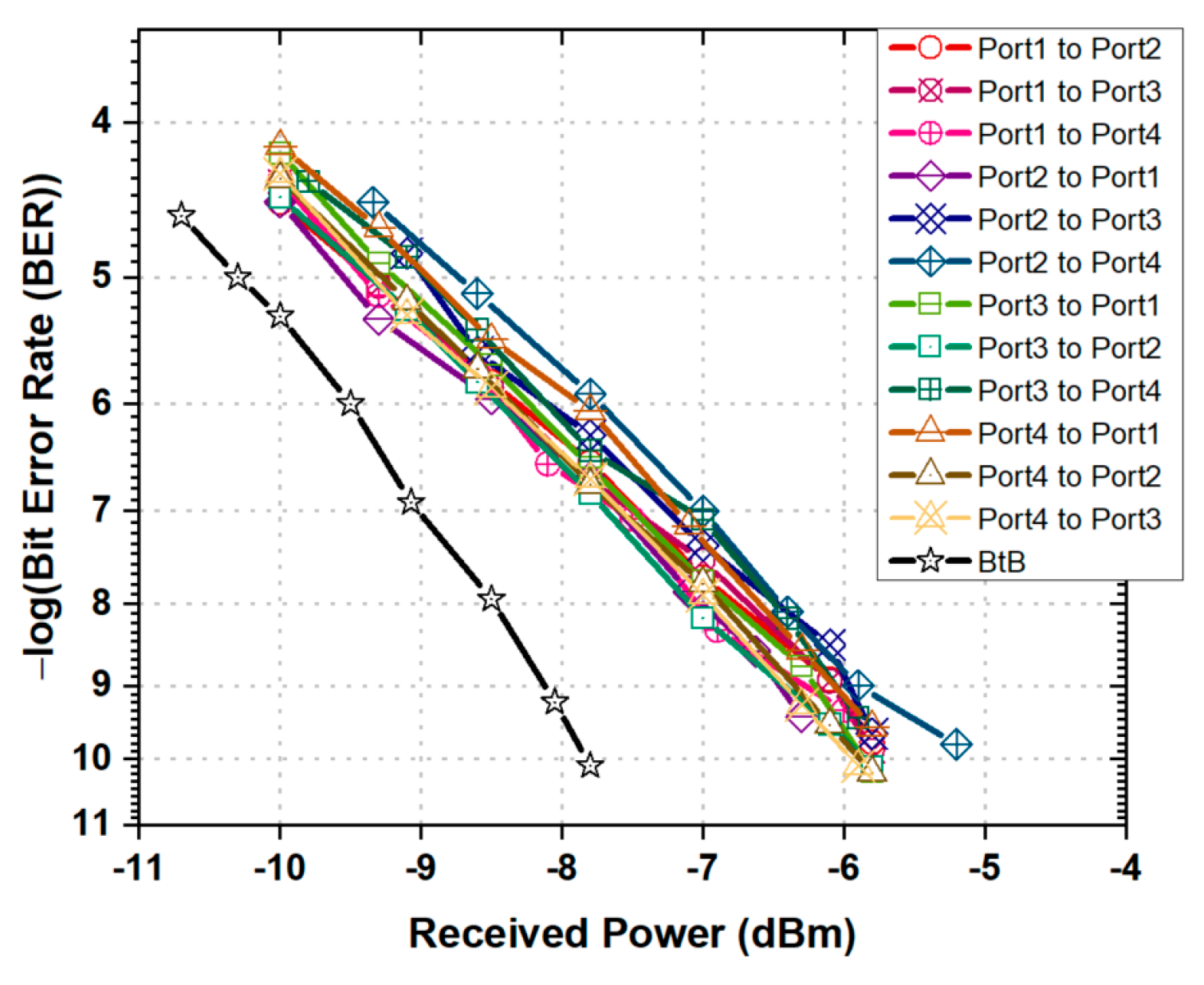
3.2. Data Plane Transmission Performance Evaluation
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meeker, M. 2018 Internet Trends; Kleiner Perkins: 2018. Available online: https://www.kleinerperkins.com/perspectives/internet-trends-report-2018/ (accessed on 15 December 2021).
- Cisco Global Cloud Index: Forecast and Methodology, 2016–2021. Available online: https://virtualization.network/Resources/Whitepapers/0b75cf2e-0c53-4891-918e-b542a5d364c5_white-paper-c11-738085.pdf (accessed on 15 December 2021).
- Xia, W.; Zhao, P.; Wen, Y.; Xie, H. A Survey on Data Center Networking (DCN): Infrastructure and Operations. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2017, 19, 640–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; Haleem, S. Optical interconnects for cloud computing data centers: Recent advances and future challenges. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Grids and Clouds, Taipei, Taiwan, 16–23 March 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Quttoum, A.N. Interconnection Structures, Management and Routing Challenges in Cloud-Service Data Center Networks: A Survey. Int. J. Interact. Mob. Technol. 2018, 12, 36–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yan, F.; Xue, X.; Calabretta, N. HiFOST: A Scalable and Low-Latency Hybrid Data Center Network Architecture Based on Flow-Controlled Fast Optical Switches. J. Opt. Commun. Netw. 2018, 10, B1–B14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Nakamura, F.; Prifti, K.; Pan, B.; Yan, F.; Wang, F.; Guo, X.; Tsuda, H.; Calabretta, N. SDN enabled flexible optical data center network with dynamic bandwidth allocation based on photonic integrated wavelength selective switch. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 8949–8958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popoola, O.; Pranggono, B. On energy consumption of switch-centric data center networks. J. Supercomput. 2018, 74, 334–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, K.; Khan, S.U.; Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Hayat, K.; Madani, S.A.; Min-Allah, N.; Wang, L.; Chen, D.; Iqbal, M.; et al. Quantitative comparisons of the state-of-the-art data center architectures. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2013, 25, 1771–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnon, S. Optical wireless communication in data centers. Broadband Access Commun. Technol. XII 2018, 10559, 105590. [Google Scholar]
- Hamza, A.S.; Deogun, J.S.; Alexander, D.R. Wireless Communication in Data Centers: A Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2016, 18, 1572–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koonen, T.; Mekonnen, K.; Cao, Z.; Huijskens, F.; Pham, N.Q.; Tangdiongga, E. Ultra-high-capacity wireless communication by means of steered narrow optical beams. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2020, 378, 20190192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghassemlooy, Z.; Member, S.; Arnon, S.; Member, S.; Uysal, M.; Member, S.; Xu, Z.; Member, S.; Cheng, J.; Member, S. Emerging Optical Wireless Communications-Advances and Challenges. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2015, 33, 1738–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koonen, T.; Mekonnen, K.A.; Cao, Z.; Huijskens, F.; Pham, N.Q.; Tangdiongga, E. Beam-Steered Optical Wireless Communication for Industry 4.0. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2021, 27, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, A.S.; Yadav, S.; Ketan, S.; Deogun, J.S.; Alexander, D.R. OWCell: Optical wireless cellular data center network architecture. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Communications, Paris, France, 21–25 May 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Chaintoutis, C.; Shariati, B.; Bogris, A.; Dijk, P.V.; Roeloffzen, C.G.H.; Bourderionnet, J.; Tomkos, I.; Syvridis, D. Free Space Intra-Datacenter Interconnects Based on 2D Optical Beam Steering Enabled by Photonic Integrated Circuits. Photonics 2018, 5, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alteri, A.S.; Alsulami, O.Z.; El-Gorashi, T.E.H.; Alresheedi, M.T.; Elmirghani, J.M.H. Data Center Top of Rack Switch to Multiple Spine Switches Optical Wireless Uplinks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Transparent Optical Networks, Bari, Italy, 19–23 July 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riza, N.A. The camceiver: Empowering robust agile indoor optical wireless for massive data centres. In Proceedings of the 42nd International Conference on Telecommunications and Signal Processing, Budapest, Hungary, 1–3 July 2019; pp. 445–448. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, W.; Cossu, G.; Gilli, L.; Ertunc, E.; Messa, A.; Sturniolo, A.; Ciaramella, E. 10 Gbit/s OWC System for Intra-Data Centers Links. IEEE Photon-Technol. Lett. 2019, 31, 805–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, P.; Kane, T.; Alharbi, O. Reconfigurable free space optical data center network using gimbal-less MEMS retroreflective acquisition and tracking. In Proceedings of the Free-Space Laser Communication and Atmospheric Propagation XXX, San Francisco, CA, USA, 29–30 January 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobadi, M.; Mahajan, R.; Phanishayee, A.; Devanur, N.; Kulkarni, J.; Ranade, G.; Blanche, P.A.; Rastegarfar, H.; Glick, M.; Kilper, D. ProjecToR: Agile reconfigurable data center interconnect. In Proceedings of the PACM SIGCOMM Conference, Florianopolis, Brazil, 22–26 August 2016; pp. 216–229. [Google Scholar]
- Hamedazimi, N.; Qazi, Z.; Gupta, H.; Sekar, V.; Das, S.R.; Longtin, J.P.; Shah, H.; Tanwery, A. FireFly: A reconfigurable wireless data center fabric using free-space optics. In Proceedings of the ACM Conference on SIGCOMM, Chicago, IL, USA, 18 August 2014; pp. 319–330. [Google Scholar]
- Calabretta, N.; Prifti, K.; Xue, X.; Yan, F.; Pan, B.; Guo, X. Nanoseconds photonic integrated switches for optical data center interconnect systems. In Proceedings of the Optical Interconnects XX, San Francisco, CA, USA, 1–6 February 2020; Volume 11286, p. 1128605. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.; Oxenløwe, L.K. Chip-based optical frequency combs for high-capacity optical communications. Nanophotonics 2021, 10, 1367–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.; Lee, J.K.; Kim, K. Suppression of thermal wavelength drift in widely tunable DS-DBR laser for fast channel-to-channel switching. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 30406–30417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
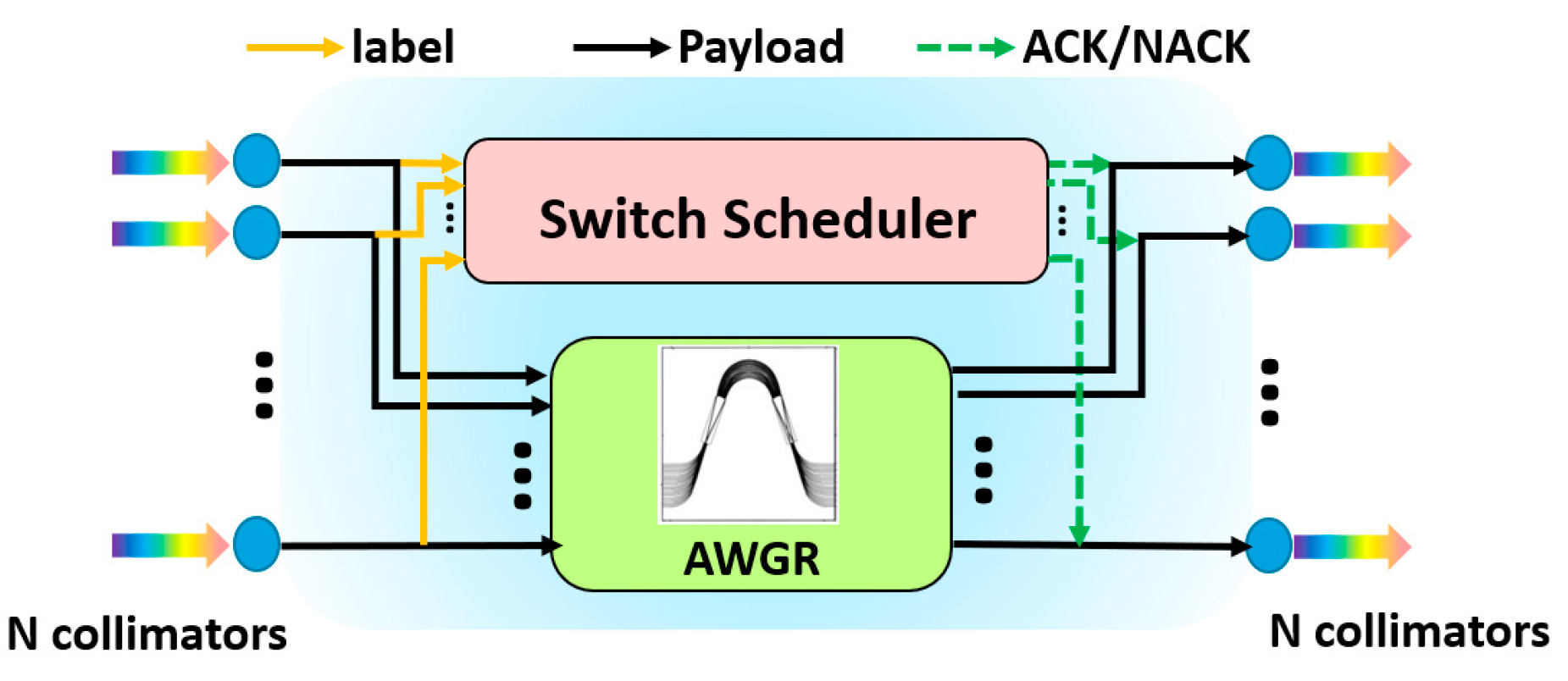
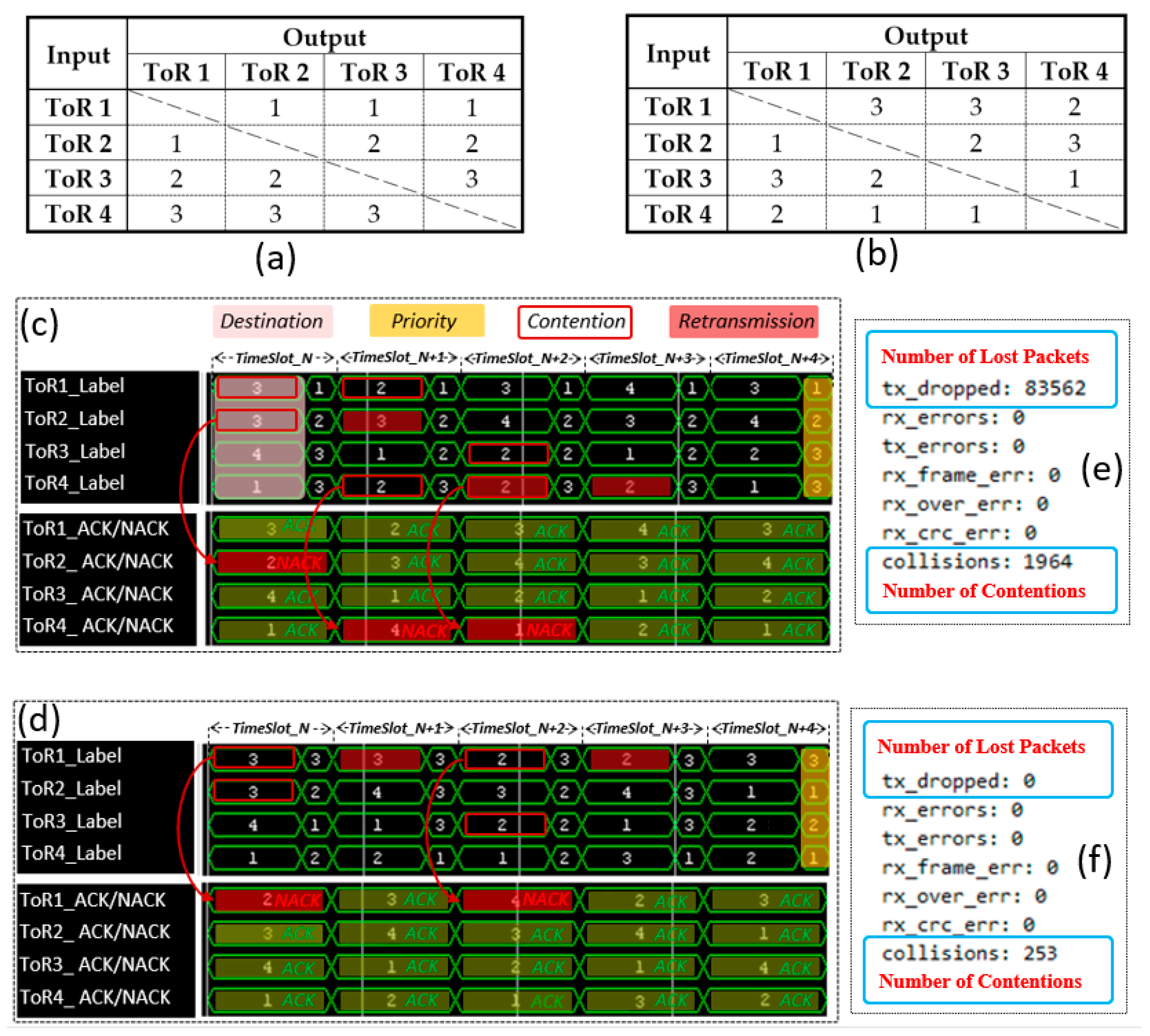
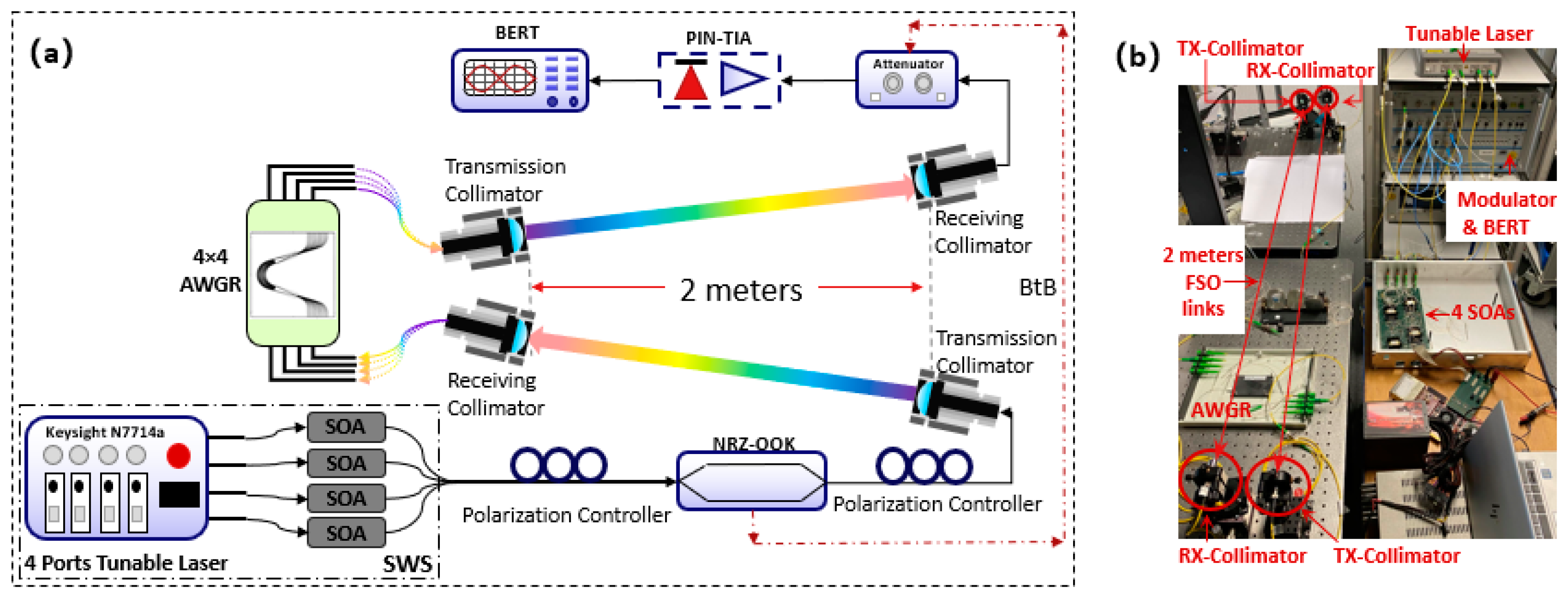
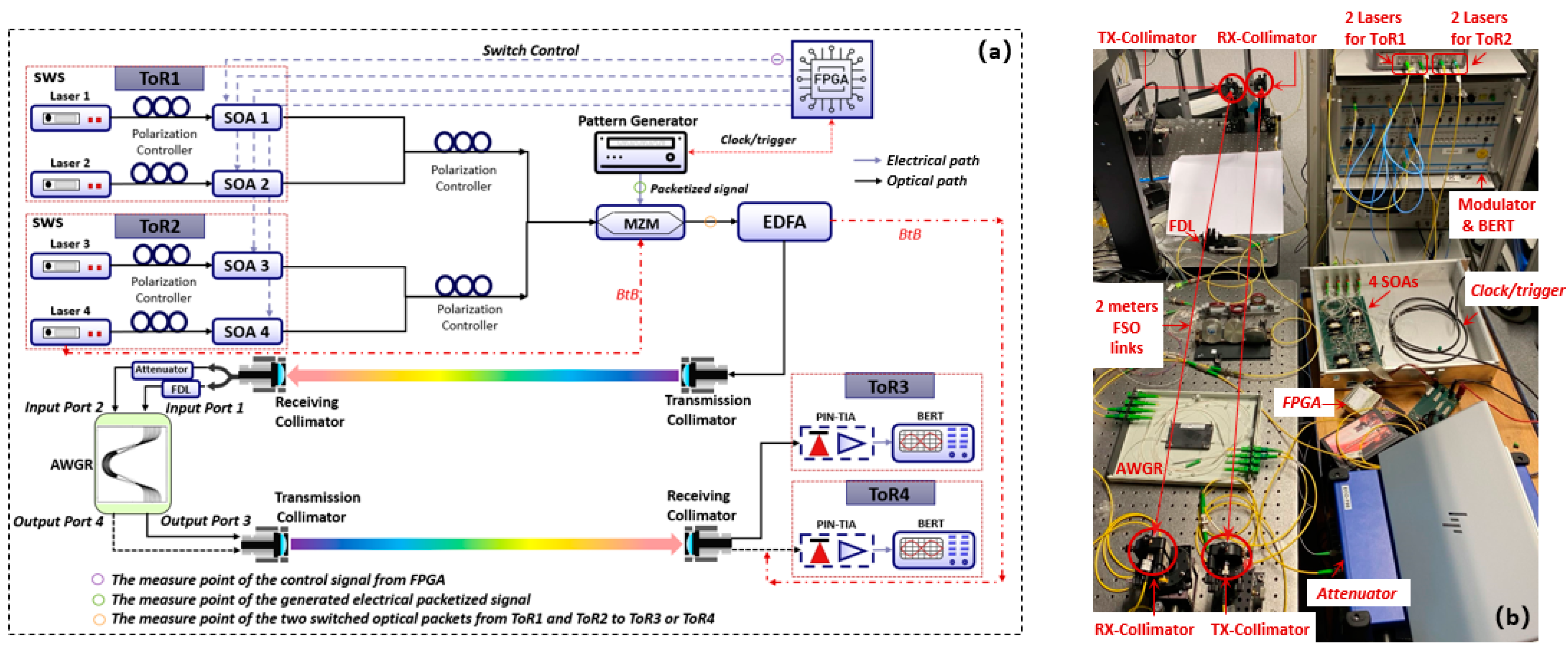


| AWGR | O1 (ToR1) | O2 (ToR2) | O3 (ToR3) | … | ON (ToRN) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I1 (ToR1) | λ0 | λ1 | λ2 | … | λN |
| I2 (ToR1) | λ1 | λ2 | λ3 | … | λ0 |
| ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ |
| IN (ToR1) | λN | λ0 | λ1 | … | λ(N − 1) |
| Processing Blocks | Latency (ns) |
|---|---|
| Label generation (ToR) | 25.6 |
| Label packet received (Switch Scheduler) | 25.6 |
| ACK/NACK generation (Switch Scheduler) | 19.2 |
| ACK/NACK received and processing (ToR) | 73.5 |
| Optical wireless transmission (4 m) | 13.3 |
| 10G GTH (IP from Xinlinx Ultrascale XCVU095) (ToR)—TX path | 79.2 |
| 10G GTH (IP from Xinlinx Ultrascale XCVU095) (ToR)—RX path | 87.8 |
| 10G GTH (IP from Xinlinx Virtex VC709) (Switch Scheduler)—TX path | 145.6 |
| 10G GTH (IP from Xinlinx Virtex VC709) (Switch Scheduler)—RX path | 207.8 |
| Total | 677.6 |
| Input | Output | |
|---|---|---|
| ToR3 | ToR4 | |
| ToR1 | 1560.70 nm | 1559.08 nm |
| ToR2 | 1562.26 nm | 1560.64 nm |
| Authors | Enabled Tech | Switching Time | Switching System | Switching Complexity | Full Architecture | Experiment (Single Link/Network) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arnon, S. [10] | MEMS or optical phased array | ms or μs | × | NA | √ | × |
| Hamza, A.S. [15] | Multipoint system | NA | √ | Complex | × | × |
| Chaintoutis, C. [16] | Photonic chip based 2D beam steering | ns | √ | Complex | √ | × |
| Alhazmi, A.S. [17] | Angle diversity transmitter | NA | × | NA | √ | × |
| Hamedazimi, N. [22] | Switchable mirror | ms | √ | Complex | √ | Single link (10 Gb/s) |
| Riza, N.A. [18] | Mechanically steerable links | NA | × | NA | √ | × |
| Ali, W. [19] | VCSEL and lens | NA | × | NA | × | Single link (10 Gb/s) |
| Deng, P. [20] | MEMS | ms | × | NA | × | Single link (10 Gb/s) |
| Ghobadi, M. [21] | Digital micro-mirror device | μs | × | NA | × | Three links (9.3 Gb/s) |
| This Work | SOA and AWGR | ns | √ | Simple | √ | Network (50 Gb/s) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Xue, X.; Tangdiongga, E.; Calabretta, N. Low-Latency Optical Wireless Data-Center Networks Using Nanoseconds Semiconductor-Based Wavelength Selectors and Arrayed Waveguide Grating Router. Photonics 2022, 9, 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9030203
Zhang S, Xue X, Tangdiongga E, Calabretta N. Low-Latency Optical Wireless Data-Center Networks Using Nanoseconds Semiconductor-Based Wavelength Selectors and Arrayed Waveguide Grating Router. Photonics. 2022; 9(3):203. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9030203
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shaojuan, Xuwei Xue, Eduward Tangdiongga, and Nicola Calabretta. 2022. "Low-Latency Optical Wireless Data-Center Networks Using Nanoseconds Semiconductor-Based Wavelength Selectors and Arrayed Waveguide Grating Router" Photonics 9, no. 3: 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9030203
APA StyleZhang, S., Xue, X., Tangdiongga, E., & Calabretta, N. (2022). Low-Latency Optical Wireless Data-Center Networks Using Nanoseconds Semiconductor-Based Wavelength Selectors and Arrayed Waveguide Grating Router. Photonics, 9(3), 203. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9030203






