Trade-Off Asymmetric Profile for Extended-Depth-of-Focus Ocular Lens
Abstract
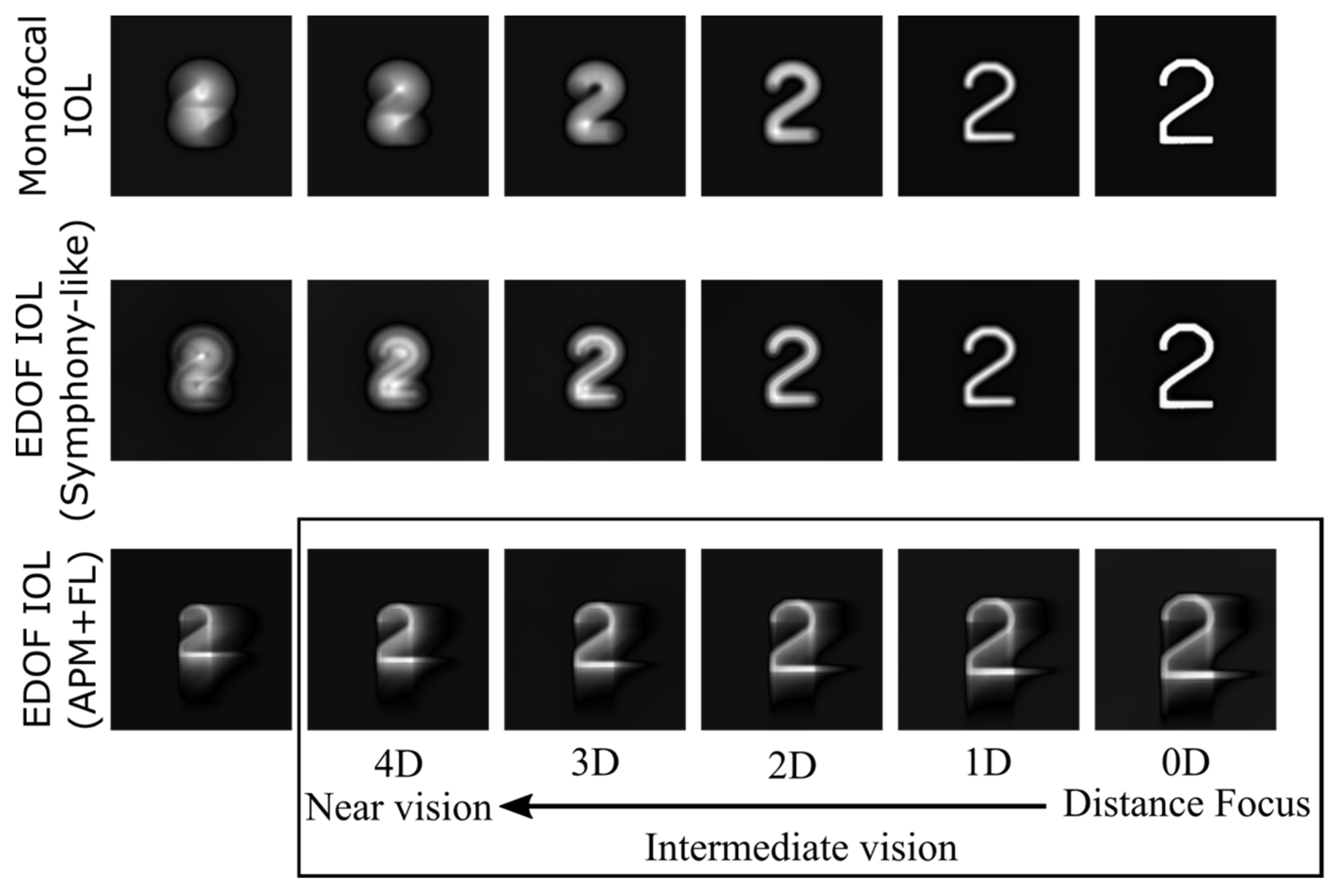
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Theoretical Background: The Generalized Pupil Function of a Thin Lens and Defocus
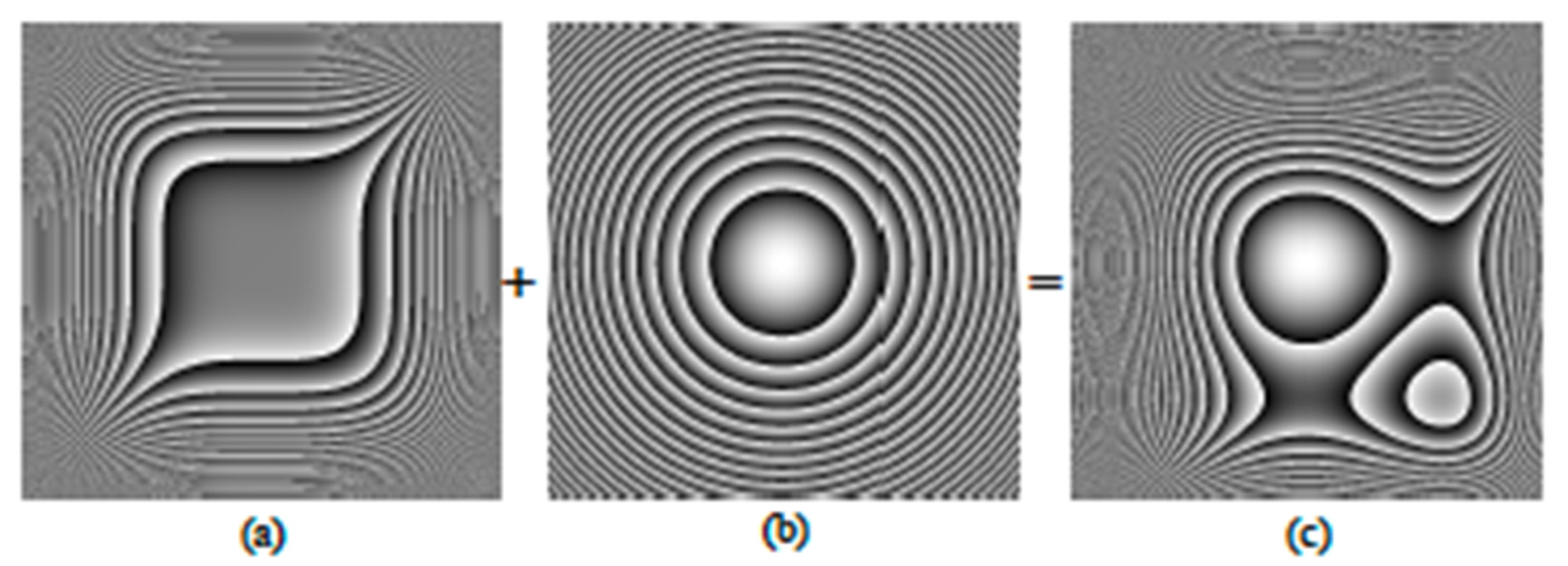
2.2. Asymmetric Phase-Mask Family to Extend the Depth of Focus
2.3. Image Quality Metrics
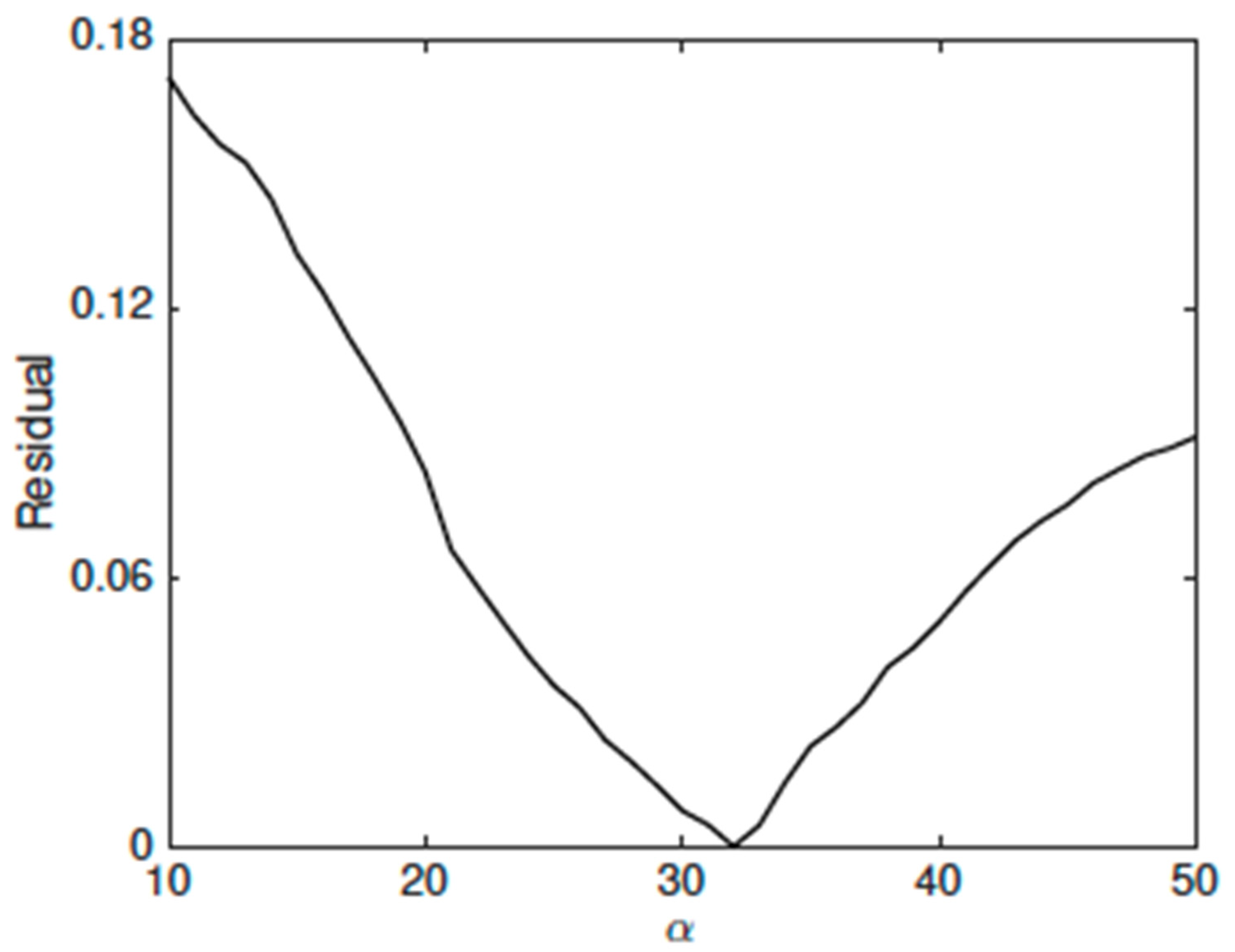
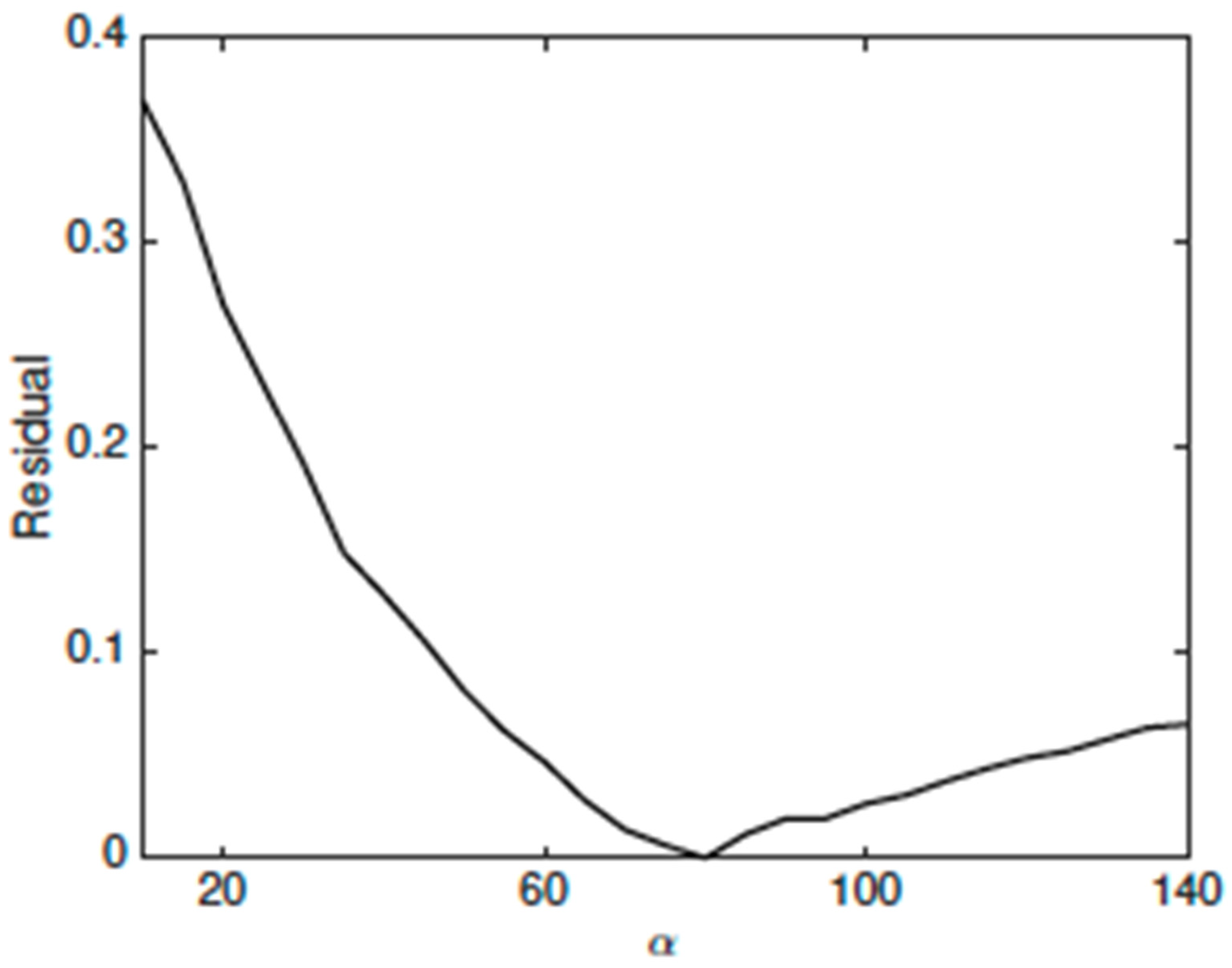
2.4. Phase Mask Trade-Off
3. Experiments and Results
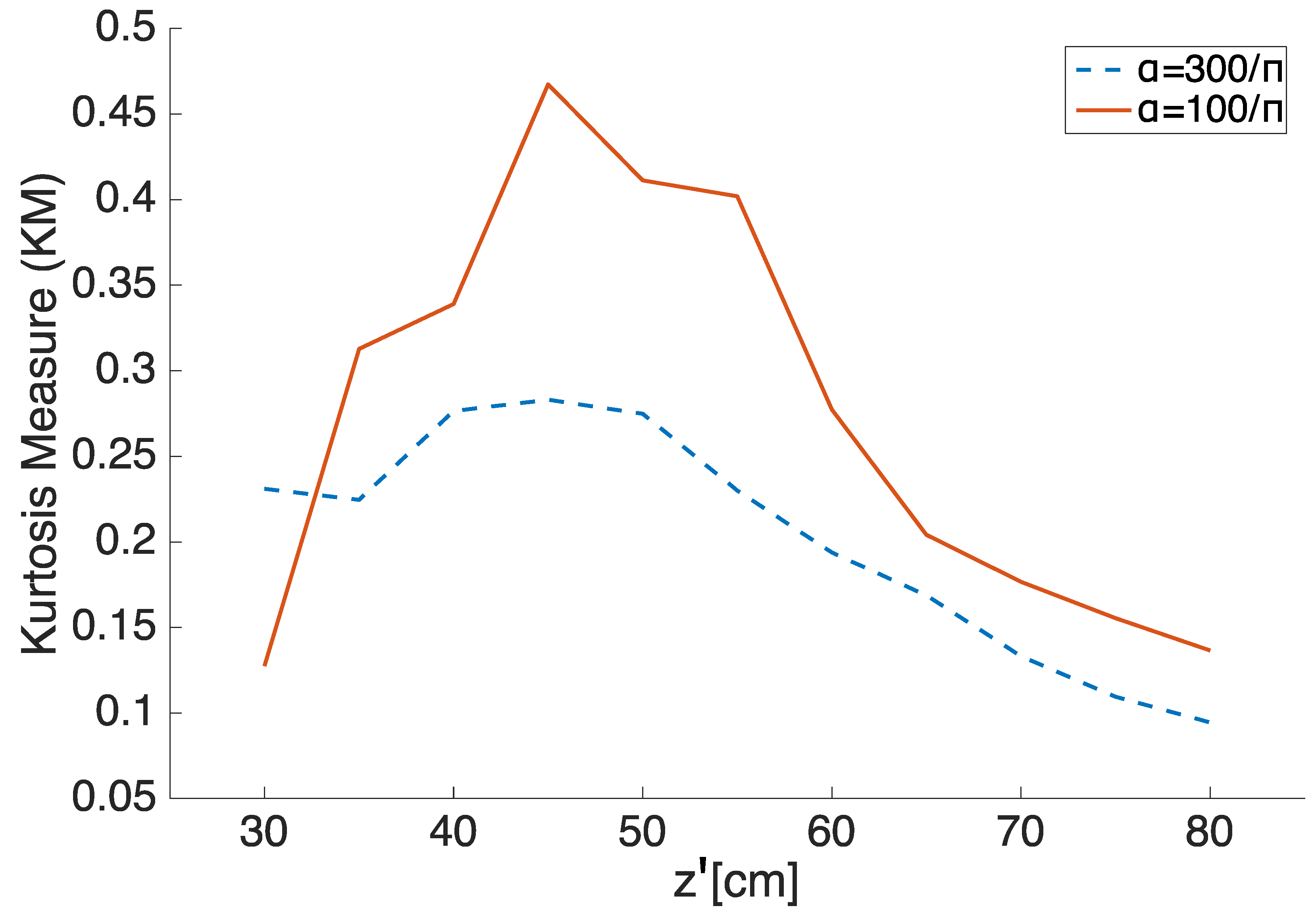
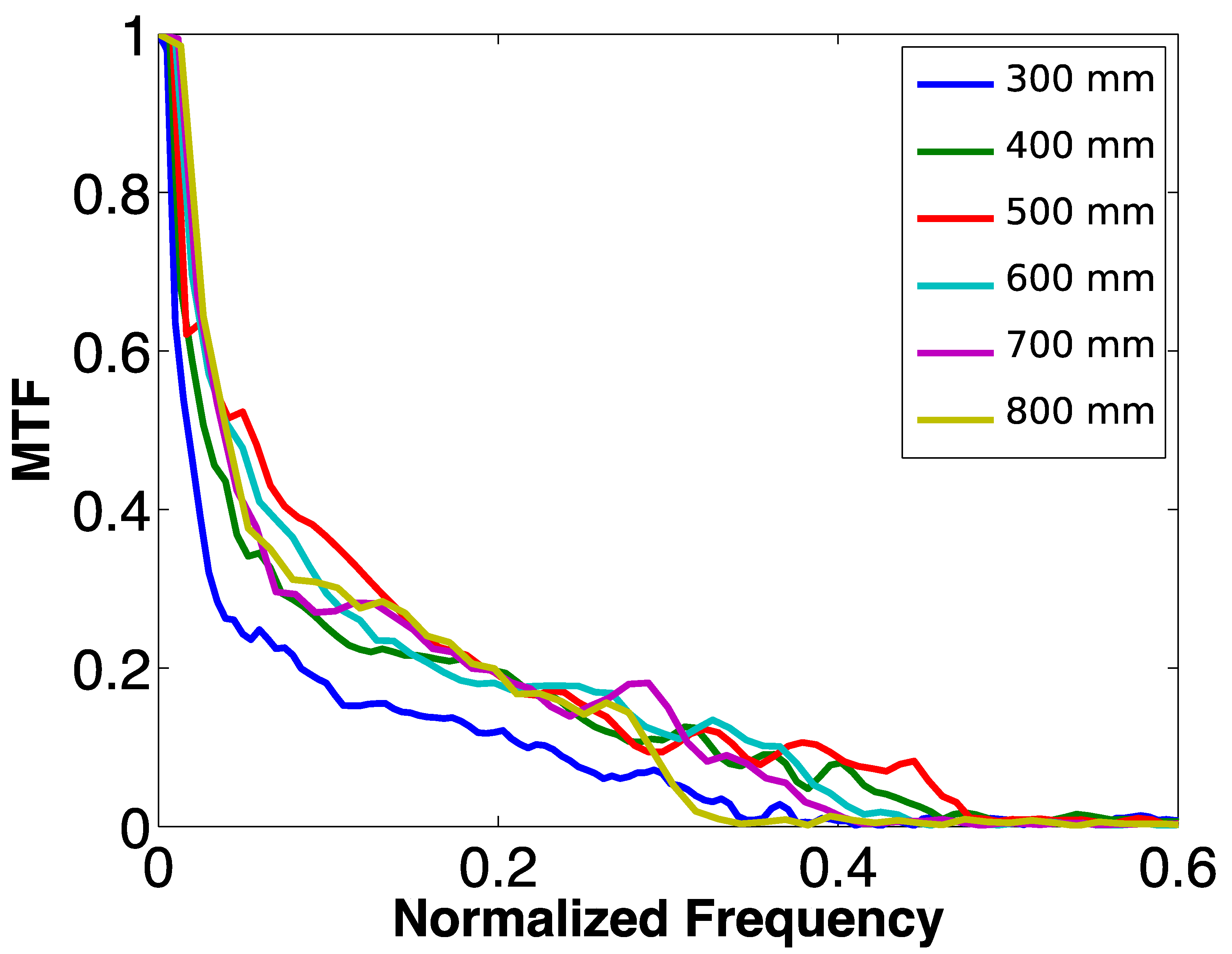
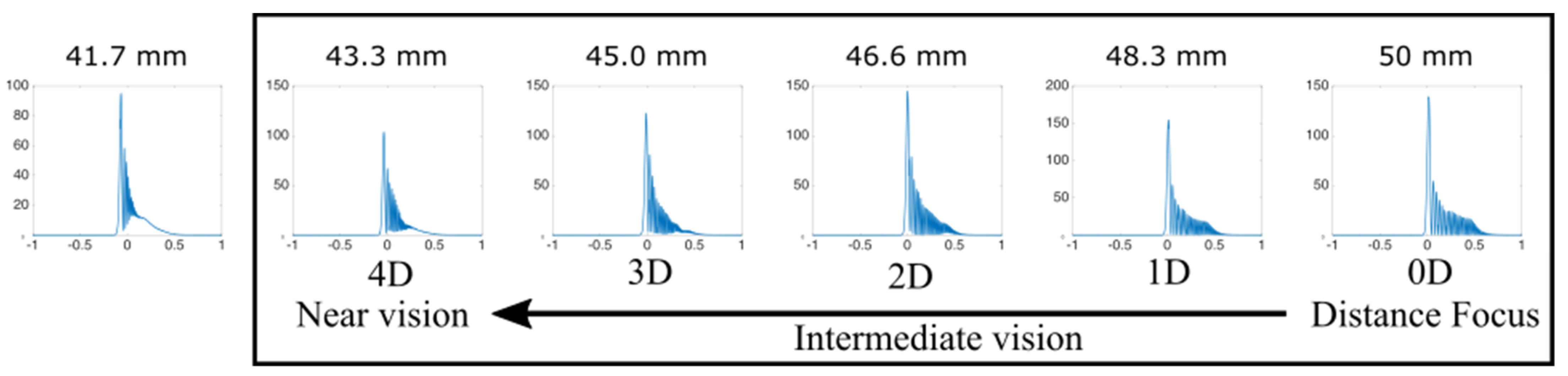
3.1. Numerical Simulation
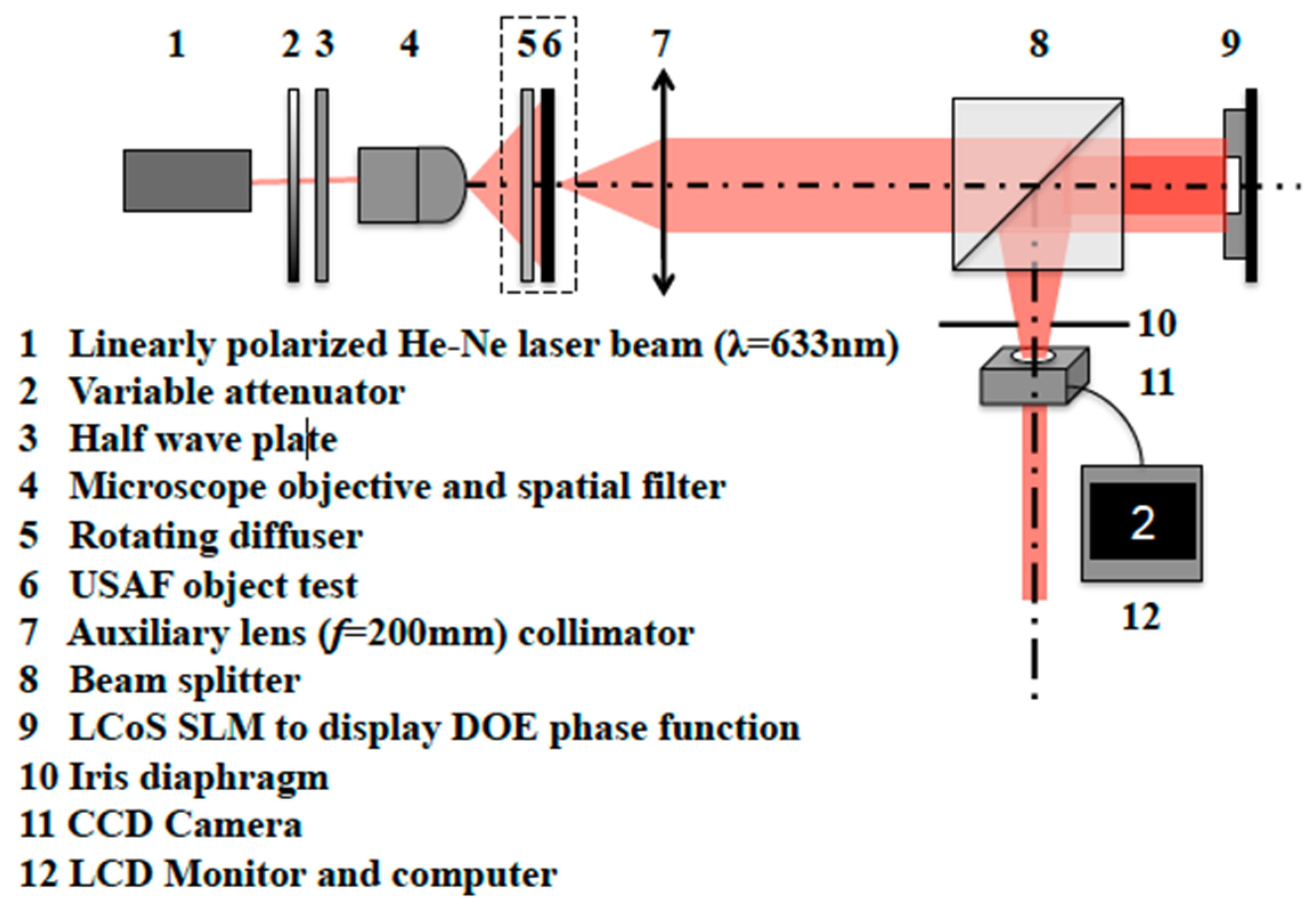
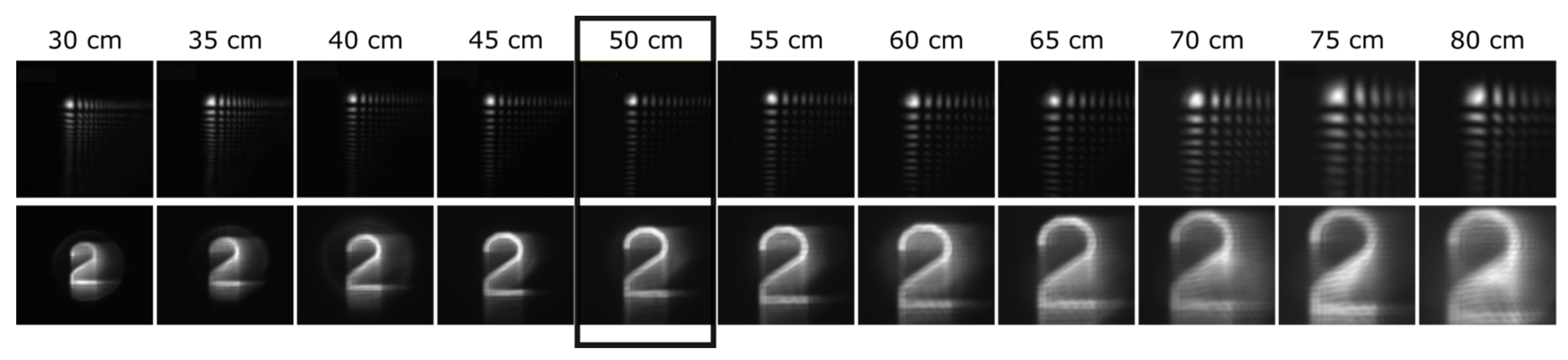
3.2. Experimental Results on Optical Bench
3.3. Exemplary Case: Optimized EDOF IOL
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, B.; Ciureda, K.J. Depth-of-Focus of the Human Eye: Theory and Clinical Implications. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2006, 51, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zalevsky, Z. Extended depth of focus imaging: A review. SPIE Rev. 2010, 1, 018001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romero, L.A.; Millan, M.S. Programmable Diffractive Optical Elements with Applicability in Ophthalmic Optics. Opt. Pura Apl. 2017, 50, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, A.; Ojeda-Castañeda, J. Asymmetric phase masks for extended depth of field. Appl. Opt. 2004, 43, 3474–3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, A.; Frauel, Y.; Javidi, B. Integral imaging with large depth of field using an asymmetric phase mask. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 10266–10273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artal, P.; Chen, L.; Fernández, E.J.; Singer, B.; Manzanera, S.; Williams, D.R. Neural compensation for the eye’s optical aberrations. J. Vis. 2004, 4, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawides, L.; de Gracia, P.; Dorronsoro, C.; Webster, M.A.; Marcos, S. Vision is adapted to the natural level of blur present in the retinal image. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Radhakrishnan, A.; Dorronsoro, C.; Sawides, L.; Webster, M.A.; Marcos, S. A cyclopean neural mechanism compensating for optical differences between the eyes. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, 188–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petelczyc, K.; Bara, S.; Ciro López, A.; Jaroszewicz, Z.; Kakarenko, K.; Kołodziejczyk, A.; Sypek, M. Contrast transfer characteristics of the light sword optical element designed for presbyopia compensations. J. Eur. Opt. Soc. Rapid Publ. 2011, 6, 11053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romero, L.A.; Millan, M.S.; Jaroszewicz, Z.; Kolodziejczyk, A. Double peacock eye optical element for extended focal depth imaging with ophthalmic applications. J. Biomed. Opt. 2012, 17, 046013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Charman, W.N.; Liu, Y.; Atchison, D.A. Small-aperture optics for the presbyope: Do comparable designs of corneal inlays and intraocular lenses provide similar transmittances to the retina? J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2019, 36, B7–B14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benard, Y.; Lopez-Gil, N.; Legras, R. Subjective depth of field in presence of 4th-order and 6th-order Zernike spherical aberration using adaptive optics technology. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2010, 36, 2129–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbero, S. Smooth multifocal wavefronts with a prescribed mean curvature for visual optics applications. Appl. Opt. 2021, 60, 6147–6154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, J.W. Introduction to Fourier Optics, 2nd ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1996; Chapter 5. [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins, H.H. The frequency response of a defocused optical system. Proc. R. Soc. London Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1955, 231, 91–103. [Google Scholar]
- Boreman, G.D. Modulation Transfer Function in Optical and Electro-Optical Systems, Volume TT 52; SPIE Press: Bellingham, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Marsack, J.D.; Thibos, L.N.; Applegate, R.A. Metrics of optical quality derived from wave aberrations predict visual performance. J. Vis. 2004, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thibos, L.N.; Hong, X.; Bradley, A.; Applegate, R.A. Accuracy and precision of objective refraction from wavefront aberrations. J. Vis. 2004, 4, 329–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Demenikov, M. Optimization of hybrid imaging systems based on maximization of kurtosis of the restored point spread function. Opt. Lett. 2011, 36, 4740–4742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carles, G.; Carnicer, A.; Bosch, S. Phase mask selection in wavefront coding systems: A design approach. Opt. Laser Eng. 2010, 48, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voelz, D.G. Computational Fourier Optics: A MATLAB Tutorial; SPIE Press: Bellingham, DC, USA, 2011; Chapter 7. [Google Scholar]
- Otón, J.; Ambs, P.; Millán, M.S.; Pérez-Cabré, E. Multipoint phase calibration for improved compensation of inherent wavefront distortion in parallel aligned liquid crystal on silicon displays. Appl. Opt. 2007, 46, 5667–5679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samei, E.; Flynn, M.; Reimann, D. A method for measuring the presampled MTF of digital radiographic systems using an edge test device. Med. Phys. 1998, 25, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mikuła, G.; Kolodziejczyk, A.; Makowski, M.; Prokopowicz, C.; Sypek, M. Diffractive elements for imaging with extended depth of focus. Opt. Eng. 2005, 44, 058001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, L. Programmable Diffractive Optical Elements with Applicability in Ophthalmic Optics. Ph.D. Dissertation, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya-BarcelonaTech, Barcelona, Spain, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 11979-2; Ophthalmic Implants, Intraocular Lenses—Part 2: Optical Properties and Test Methods. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014.
- Millán, M.S.; Vega, F. Extended depth of focus intraocular lens: Chromatic performance. Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 4294–4309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- ANSI Z80.35-2018; American National Standard Institute, Ophthalmics. Extended Depth of Focus Intraocular Lenses. The Vision Council: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2018.



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Romero, L.A.; Marrugo, A.G.; Millán, M.S. Trade-Off Asymmetric Profile for Extended-Depth-of-Focus Ocular Lens. Photonics 2022, 9, 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9020119
Romero LA, Marrugo AG, Millán MS. Trade-Off Asymmetric Profile for Extended-Depth-of-Focus Ocular Lens. Photonics. 2022; 9(2):119. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9020119
Chicago/Turabian StyleRomero, Lenny A., Andrés G. Marrugo, and María S. Millán. 2022. "Trade-Off Asymmetric Profile for Extended-Depth-of-Focus Ocular Lens" Photonics 9, no. 2: 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9020119
APA StyleRomero, L. A., Marrugo, A. G., & Millán, M. S. (2022). Trade-Off Asymmetric Profile for Extended-Depth-of-Focus Ocular Lens. Photonics, 9(2), 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9020119






