Effect of Chelating Agents on the Structural, Optical, and Dye-Degradation Properties of Tungsten Oxide Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methods
2.1. Preparation of WO3 by Co-Precipitation Method
2.2. Characterization Techniques
2.3. Dye Degradation
3. Results and Discussions
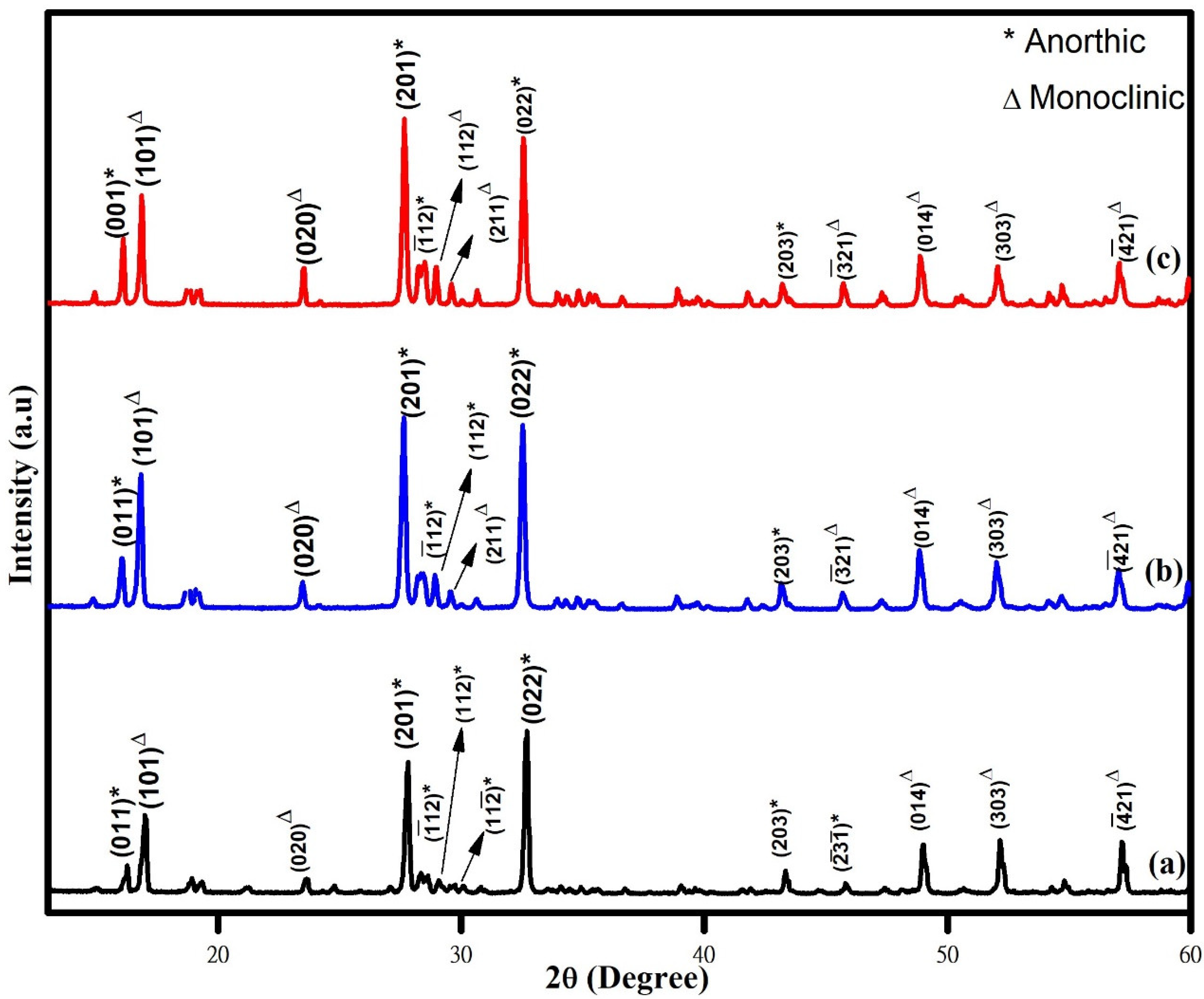
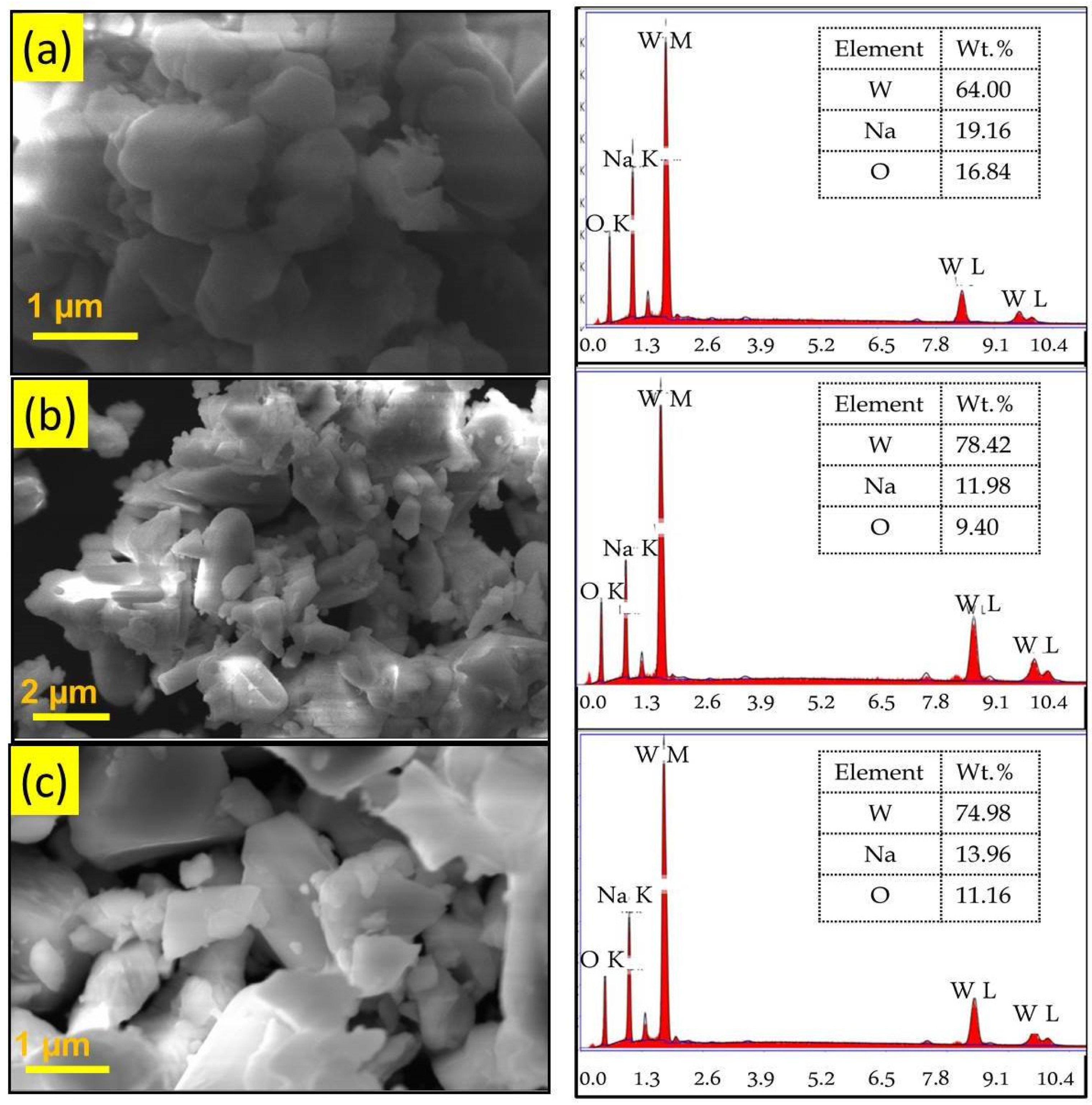
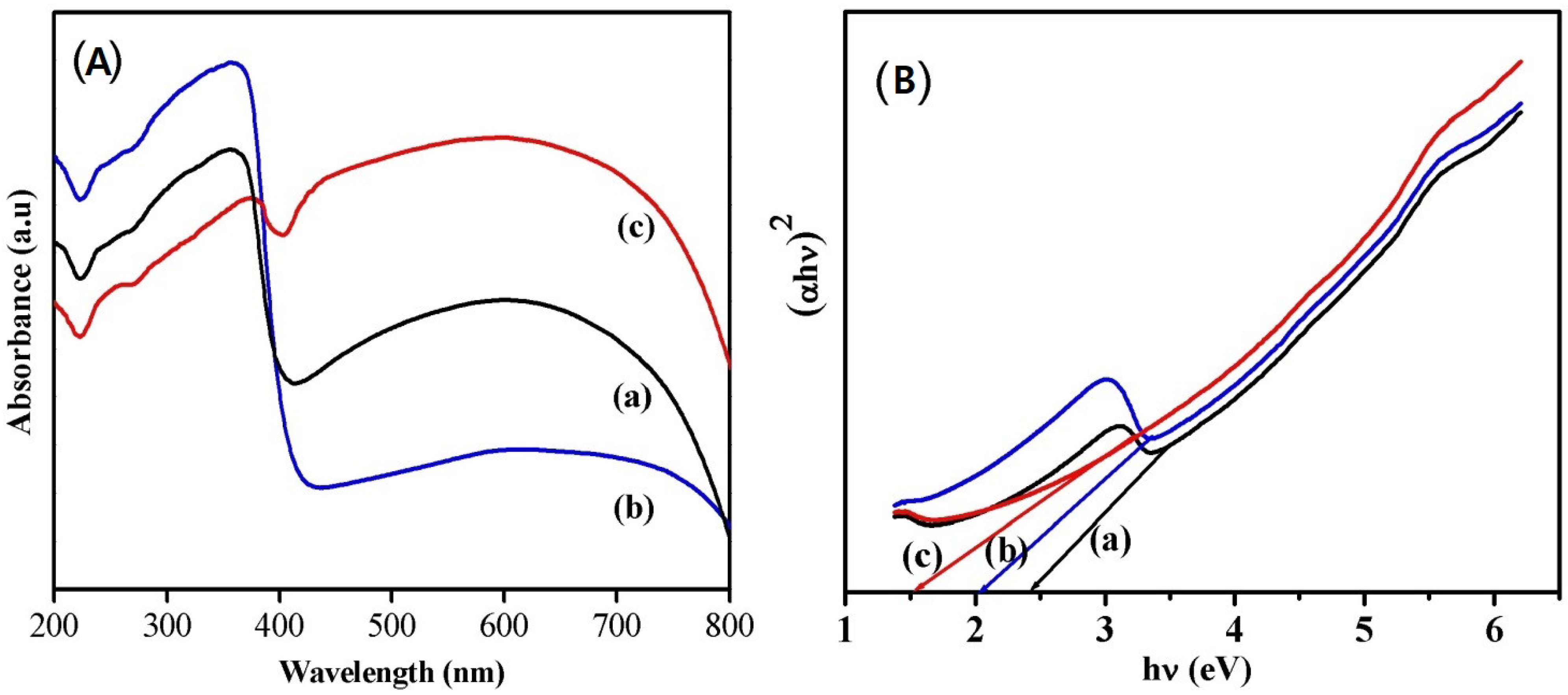
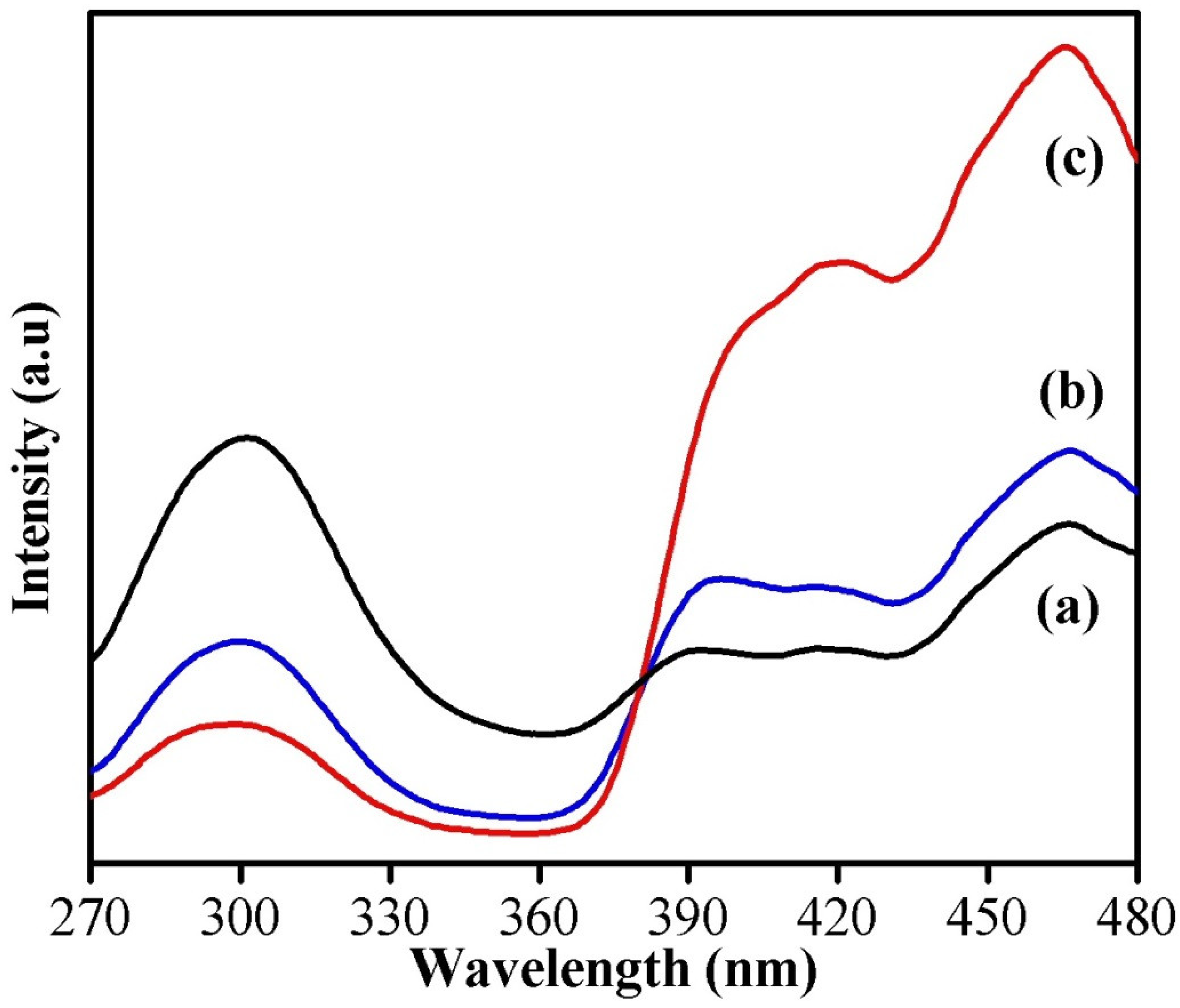
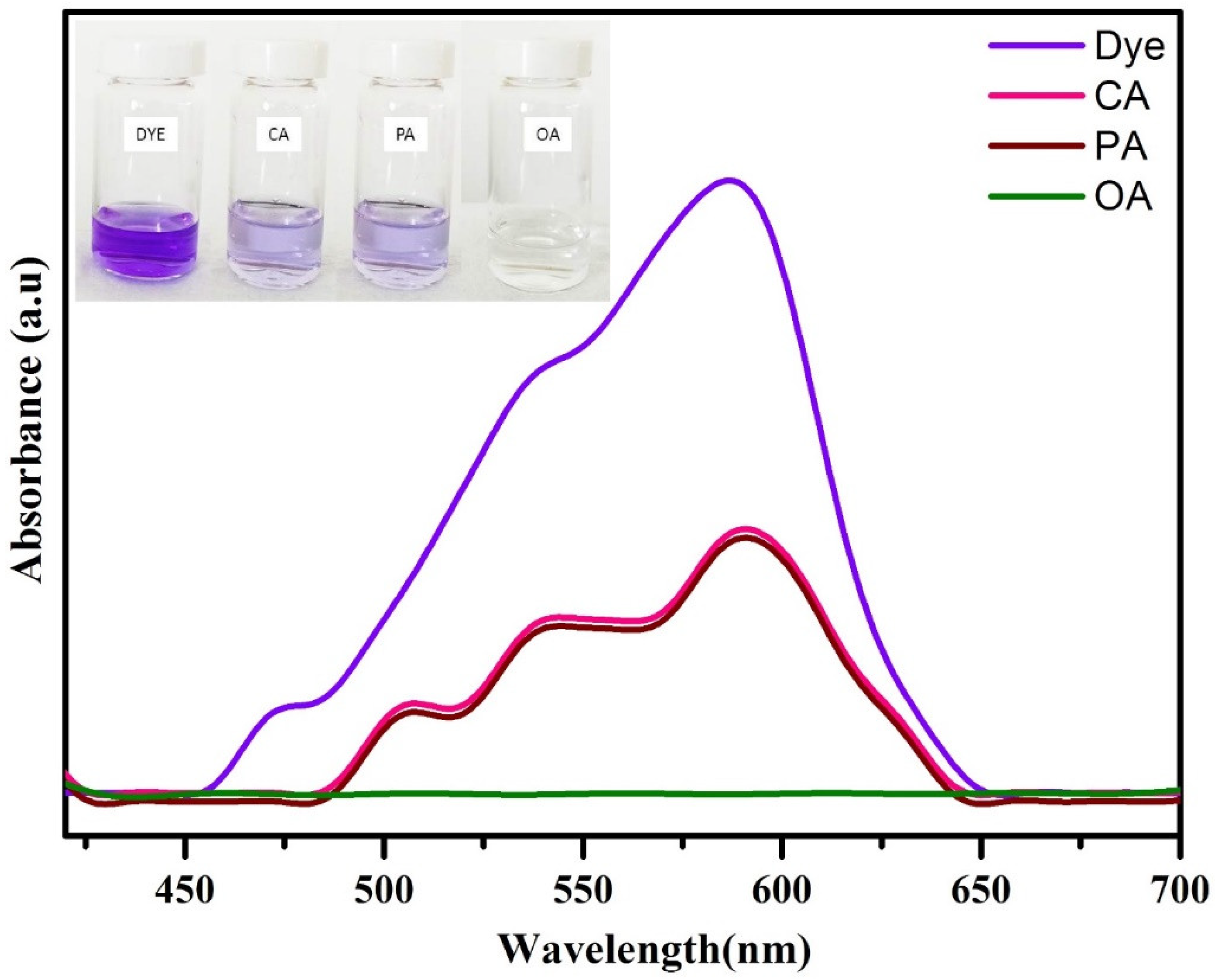
3.1. Catalyst Characterization
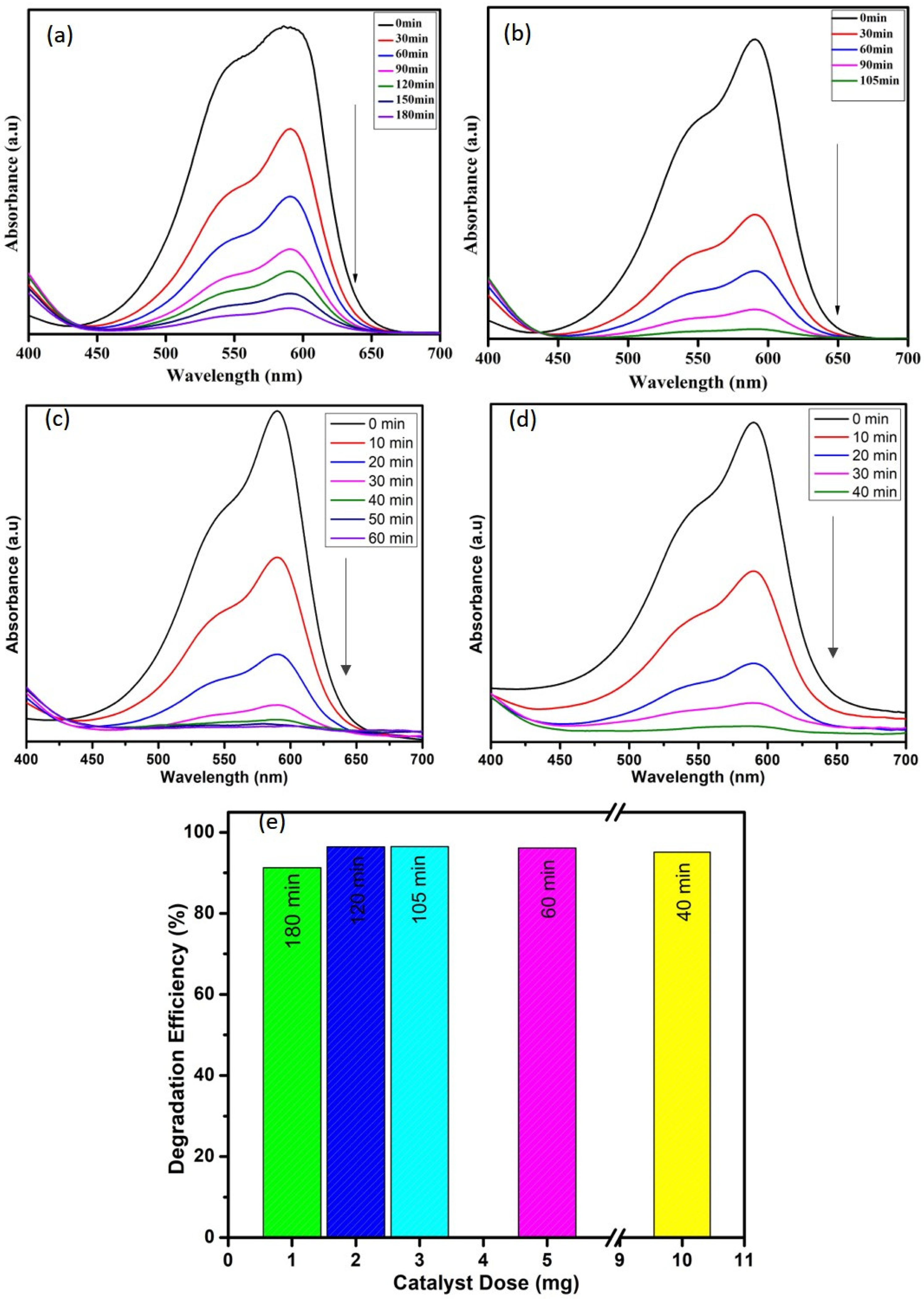
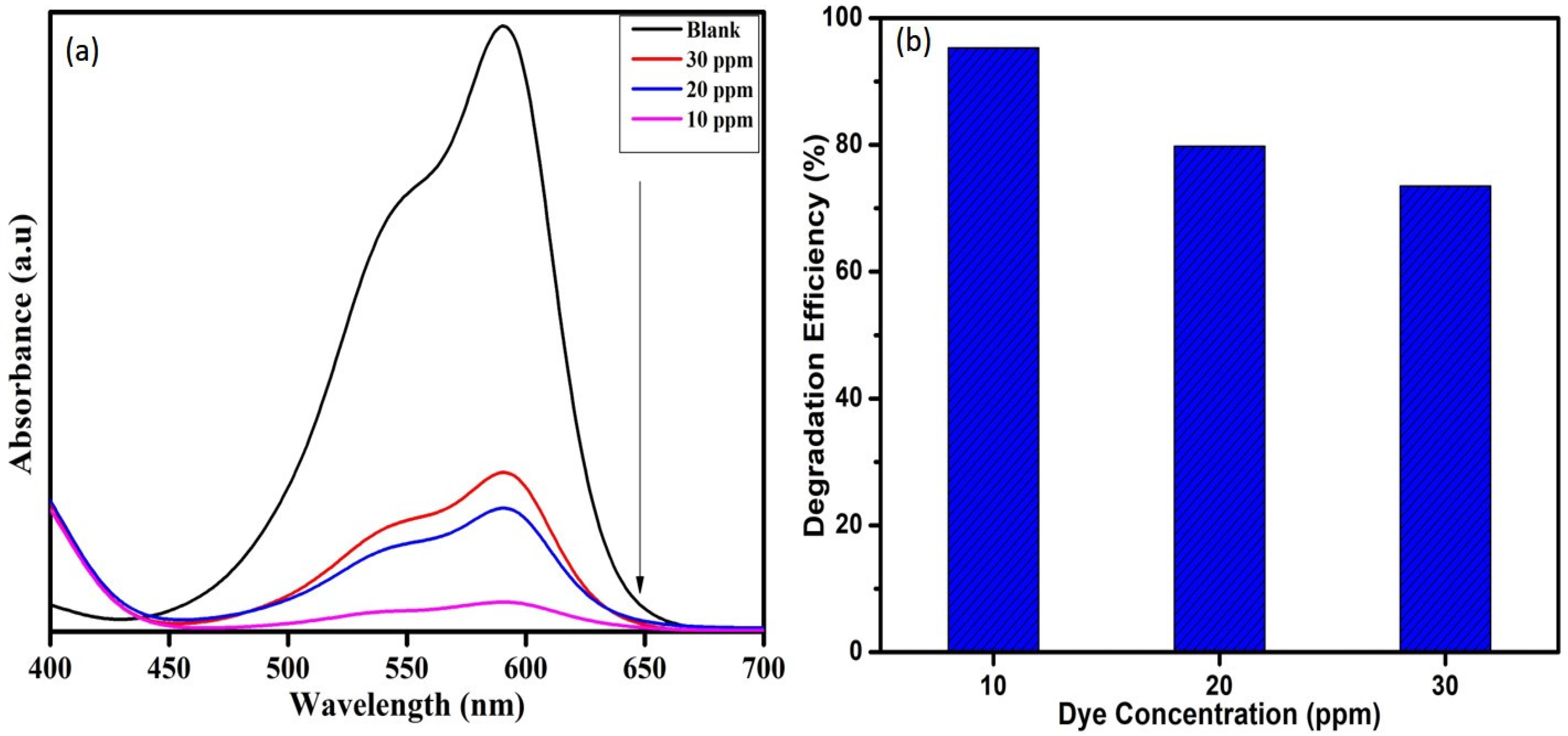
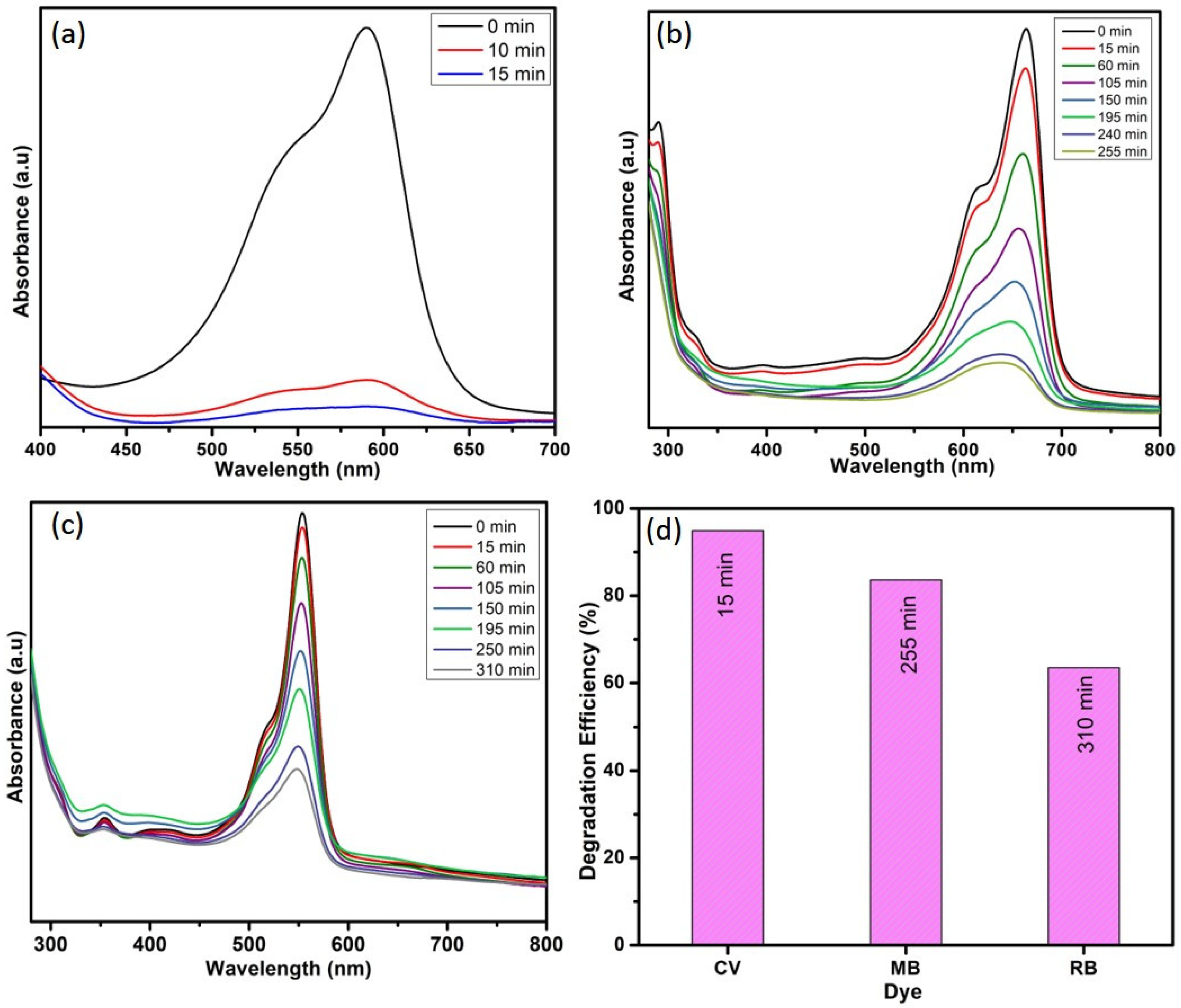
3.2. Dye-Degradation Activity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rashad, S.; Zaki, A.; Farghali, A. Morphological effect of titanate nanostructures on the photocatalytic degradation of crystal violet. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 2019, 9, 1847980418821778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmat, M.; Rehman, A.; Rahmat, S.; Bhatti, H.N.; Iqbal, M.; Khan, W.S.; Bajwa, S.Z.; Rahmat, R.; Nazir, A. Highly efficient removal of crystal violet dye from water by MnO2 based nanofibrous mesh/photocatalytic process. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 5149–5159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kim, G.; Bae, H.; Kim, E.; Moon, B.; Cheon, D.; Tarte, N.H. An Energy Independent WO3/MoCl5 Nano-Sized Catalyst for the Superior Degradation of Crystal Violet and Rhodamine B Dye. Catalysts 2019, 9, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagadevan, S.; Lett, J.A.; Weldegebrieal, G.K.; Garg, S.; Oh, W.C.; Hamizi, N.A.; Johan, M.R. Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity of rGO-CuO Nanocomposites for the Degradation of Organic Pollutants. Catalysts 2021, 11, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, H.; Ishigaki, T.; Suzuki, H.; Ota, T. Effect of Film Thickness and Air Atmosphere on Photochromic Properties of WO3-Based Composite Films. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2016, 89, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zeng, W.; Li, Y. New insight into gas sensing performance of nanorods assembled and nanosheets assembled hierarchical WO3•H2O structures. Mater. Lett. 2018, 235, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Fang, Y.; Qiao, K.; Wei, W.; Yao, Y.; Gao, Y. Printing of WO3/ITO nanocomposite electrochromic smart windows. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2019, 194, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Liu, X.; Tian, C.; Deng, H.; Wang, J.; Su, X. Oxygen defect-rich WO3-x nanostructures with high photocatalytic activity for dehydration of isopropyl alcohol to propylene. Surf. Interfaces 2018, 14, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Xu, G.-L.; Kuang, Q.; Sun, S.-G.; Yang, S. Hierarchical WO3 flowers comprising porous single-crystalline nanoplates show enhanced lithium storage and photocatalysis. Nano Res. 2012, 5, 826–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Tachibana, Y.; Kalantar-zadeh, K. Dye-sensitized solar cells based on WO3. Langmuir 2010, 26, 9148–19152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanalakshmi, M.; Prabavathi, S.L.; Saravanakumar, K.; Jones, B.F.; Muthuraj, V. Iridium nanoparticles anchored WO3 nanocubes as an efficient photocatalyst for removal of refractory contaminants (crystal violet and methylene blue). Chem. Phys. Lett. 2020, 745, 137285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepa, B.; Rajendran, V. Pure and Cu metal doped WO3 prepared via co-precipitation method and studies on their structural, morphological, electrochemical and optical properties. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2018, 16, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Qu, F.; Wang, G.; Wu, X. Facile hydrothermal synthesis of WO3 nanorods for photocatalysts and supercapacitors. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 724, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarjuna, R.; Challagulla, S.; Sahu, P.; Roy, S.; Ganesan, R. Polymerizable sol–gel synthesis of nano-crystalline WO3 and its photocatalytic Cr(VI) reduction under visible light. Adv. Powder Technol. 2017, 28, 3265–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafizas, A.; Francàs, L.; Vazquez, C.S.; Ling, M.; Li, Y.; Glover, E.; Cafferty, L.M.; Blackman, C.S.; Darr, J.A.; Parkin, I.P. Optimizing the Activity of Nano-needle Structured WO3 Photoanodes for Solar Water Splitting—Direct Synthesis Via Chemical Vapor Deposition. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 5983–5993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rane, A.V.; Kanny, K.; Abitha, V.K.; Thomas, S. Methods for synthesis of nanoparticles and fabrication of nanocomposites. In Synthesis of Inorganic Nanomaterials; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2018; pp. 121–139. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Hu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, M.; He, Z.; Ngaw, C.K.; Loo, J.S.C.; Liao, D.; Tan, T.T.Y. Understanding the photoelectrochemical properties of a reduced graphene oxide–WO3 heterojunction photoanode for efficient solar-light-driven overall water splitting. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 9330–9336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Peng, T.; Ke, D.; Peng, Z.; Yan, C. Preparation and photocatalytic activity of dysprosium doped tungsten trioxide nanoparticles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2007, 104, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadian, H.; Tehrani, F.S.; Aliannezhadi, M. Hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of WO3 nanostructures: Effects of capping agent and pH. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 105024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, L.; Jafari, H. Morphological Characterization of Tungsten Trioxide Nanopowders Synthesized by Sol-Gel Modified Pechini’s Method. Mater. Res. 2017, 20, 1713–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghari, H.A.; Arabi, A.; Haratizadeh, H. A novel approach for solution combustion synthesis of tungsten oxide nanoparticles for photocatalytic and electrochromic applications. Ceram. Int. 2019, 46, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preethi, T.; Senthil, K.; Pachamuthu, M.P.; Balakrishnaraja, R.; Sundaravel, B.; Geetha, N.; Bellucci, S. Effect of Fe Doping on Photocatalytic Dye-Degradation and Antibacterial Activity of SnO2 Nanoparticles. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2022, 2022, 9334079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periasamy, P.; Krishnakumar, T.; Sathish, M.; Chavali, M.; Siril, P.F.; Devarajan, V.P. Structural and electrochemical studies of tungsten oxide (WO3) nanostructures prepared by microwave assisted wet-chemical technique for supercapacitor. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 6157–6166. [Google Scholar]
- Sadakane, M.; Sasaki, K.; Kunioku, H.; Ohtani, B.; Abe, R.; Ueda, W. Preparation of 3-D ordered macroporous tungsten oxides and nano-crystalline particulate tungsten oxides using a colloidal crystal template method, and their structural characterization and application as photocatalysts under visible light irradiation. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 1811–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.D.; Dang, D.V.; Nguyen, D.C. Hydrothermal synthesis and NH3 gas sensing property of WO3 nanorods at low temperature. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2015, 6, 035006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolhe, P.S.; Mutadak, P.; Maiti, N.; Sonawane, K.M. Synthesis of WO3 nanoflakes by hydrothermal route and its gas sensing application. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2020, 304, 111877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakarthik, P.; Thangaraj, V.; Parthibavarman, M. A facile and one-pot synthesis of pure and transition metals (M = Co & Ni) doped WO3 nanoparticles for enhanced photocatalytic performance. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2017, 28, 5990–5996. [Google Scholar]
- Baradaran, M.; Ghodsi, F.E. Highly efficient visible photocatalytic degradation of MB organic dye by heteromorphic ZnO/AZO/ZnO nanocatalysts: Effect of AZO thickness. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2019, 92, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carcel, R.A.; Andronic, L.; Duta, A. Photocatalytic Degradation of Methyl orange Using TiO2, WO3 and Mixed Thin Films Under Controlled pH and H2O2. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2011, 11, 9095–9101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshvar, N.; Salari, D.; Khataee, A. Photocatalytic degradation of azo dye acid red 14 in water: Investigation of the effect of operational parameters. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A: Chem. 2003, 157, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrokhi, M.; Hosseini, S.-C.; Yang, J.-K.; Shirzad-Siboni, M. Application of ZnO–Fe3O4 Nanocomposite on the Removal of Azo Dye from Aqueous Solutions: Kinetics and Equilibrium Studies. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2014, 225, 2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasić, M.B.; Randjelovic, M.; Momčilović, M.Z.; Matović, B.Z.; Zarubica, A.R. Degradation of crystal violet over heterogeneous TiO2-based catalysts: The effect of process parameters. Process. Appl. Ceram. 2016, 10, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Rashid, J.; Barakat, M. Zero valent Ag deposited TiO2 for the efficient photocatalysis of methylene blue under UV-C light irradiation. Colloids Interface Sci. Commun. 2015, 5, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindaraj, T.; Mahendran, C.; Marnadu, R.; Shkir, M.; Manikandan, V. The remarkably enhanced visible-light-photocatalytic activity of hydrothermally synthesized WO3 nanorods: An effect of Gd doping. Ceram. Int. 2020, 47, 4267–4278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warsi, A.-Z.; Ahmad, T.; Aziz, F.; Warsi, M.F.; Munir, S.; Agboola, P.O.; Shakir, I. Synthesis and characterisation of WO3 and Ag2O nanoparticles and their nanocomposite for photocatalytic degradation of dyes. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antony, A.J.; Kala, S.M.J.; Joel, C.; Bennie, R.B.; Praveendaniel, S. Enhancing the visible light induced photocatalytic properties of WO3 nanoparticles by doping with vanadium. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2021, 157, 110169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eroi, S.N.; Ello, A.S.; Diabate, D.; Ossonon, D.B. Heterogeneous WO3/H2O2 system for degradation of Indigo Carmin dye from aqueous solution. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 37, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| S. No | Catalyst | Dye | Light Source | Efficiency (%) | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | WO3 Gd@WO3 | Rhodamine B | Visible light | 75 94 | [34] |
| 2. | WO3 Ag2O Ag2O/WO3 | Methylene blue and Rhodamine B | Sunlight | 79.6 and 70.9 86.1 and 80.7 90.8 and 87.3 | [35] |
| 3. | WO3 V@WO3 | Rhodamine B | Visible light | 68 93 | [36] |
| 4. | WO3/H2O2 | Indigo carmine | - | 90 | [37] |
| 5. | WO3 | Crystal violet | Normal light + H2O2 | 95 | This work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thangavel, P.; Karuppanan, S.; Muthusamy Poomalai, P.; Sakthivel, A.; Nandagopalan, G.; Bellucci, S. Effect of Chelating Agents on the Structural, Optical, and Dye-Degradation Properties of Tungsten Oxide Nanoparticles. Photonics 2022, 9, 849. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9110849
Thangavel P, Karuppanan S, Muthusamy Poomalai P, Sakthivel A, Nandagopalan G, Bellucci S. Effect of Chelating Agents on the Structural, Optical, and Dye-Degradation Properties of Tungsten Oxide Nanoparticles. Photonics. 2022; 9(11):849. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9110849
Chicago/Turabian StyleThangavel, Preethi, Senthil Karuppanan, Pachamuthu Muthusamy Poomalai, Ashokan Sakthivel, Geetha Nandagopalan, and Stefano Bellucci. 2022. "Effect of Chelating Agents on the Structural, Optical, and Dye-Degradation Properties of Tungsten Oxide Nanoparticles" Photonics 9, no. 11: 849. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9110849
APA StyleThangavel, P., Karuppanan, S., Muthusamy Poomalai, P., Sakthivel, A., Nandagopalan, G., & Bellucci, S. (2022). Effect of Chelating Agents on the Structural, Optical, and Dye-Degradation Properties of Tungsten Oxide Nanoparticles. Photonics, 9(11), 849. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics9110849






