Crosstalk Reduction in Voxels for a See-Through Holographic Waveguide by Using Integral Imaging with Compensated Elemental Images
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Principles
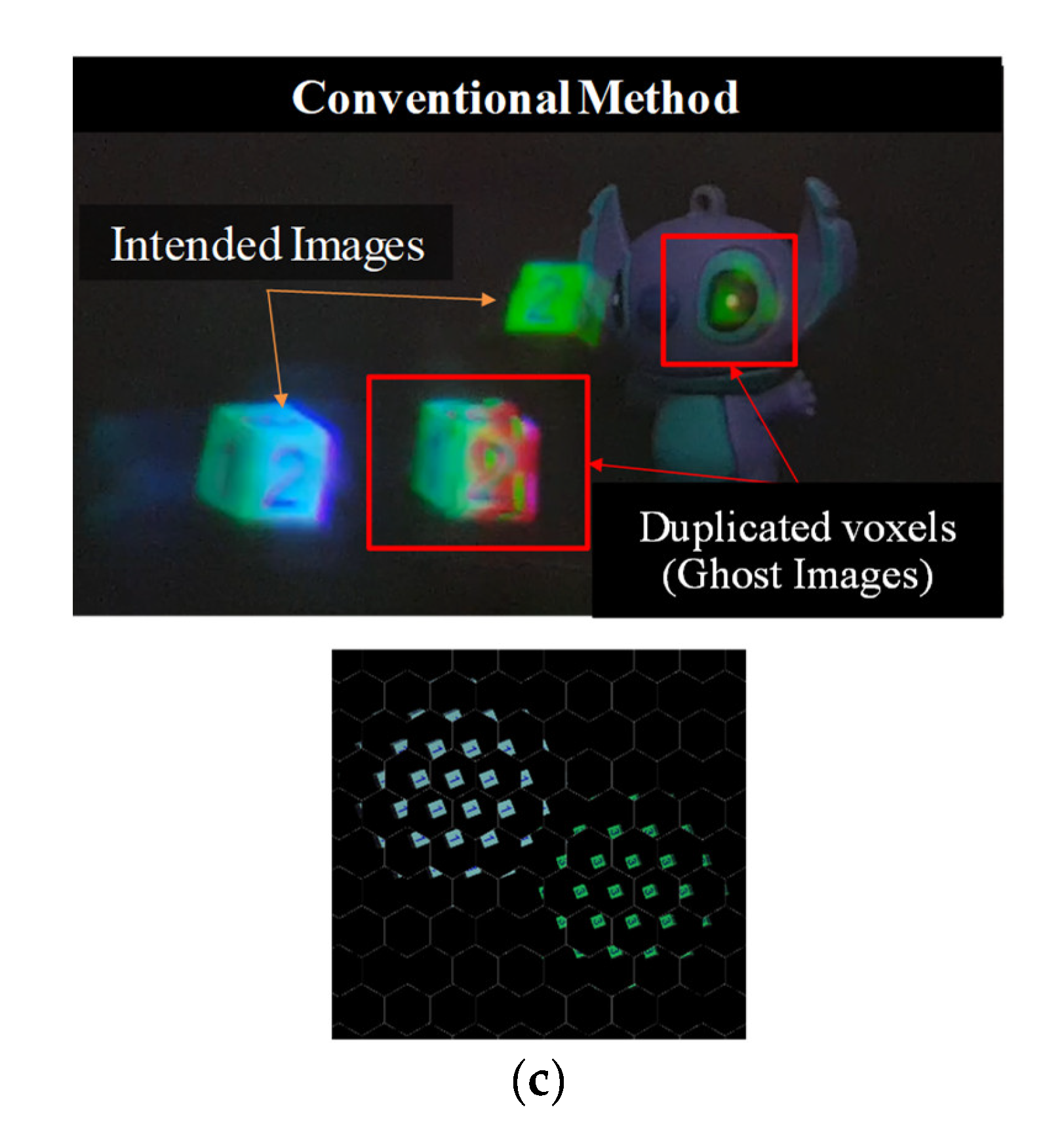
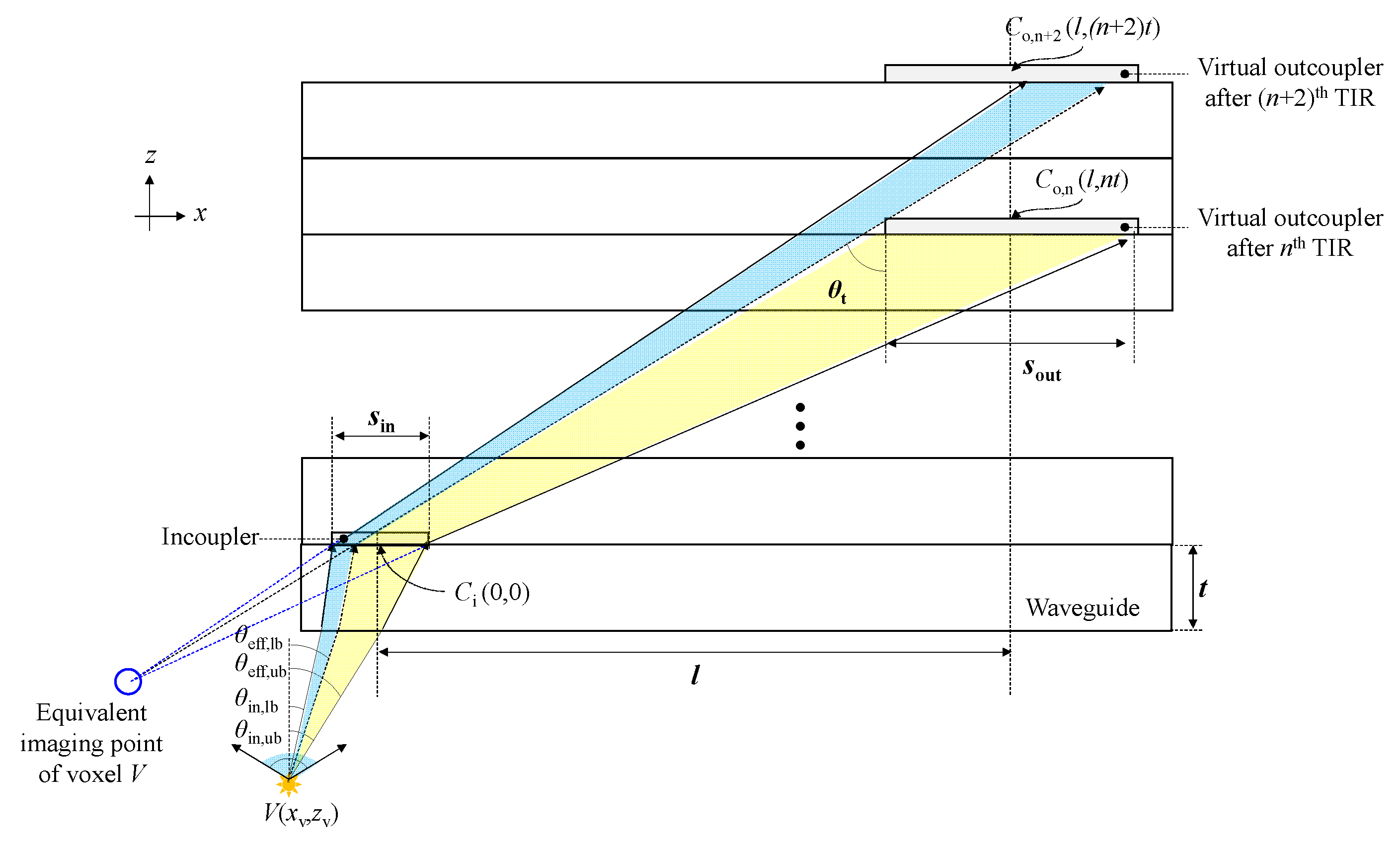
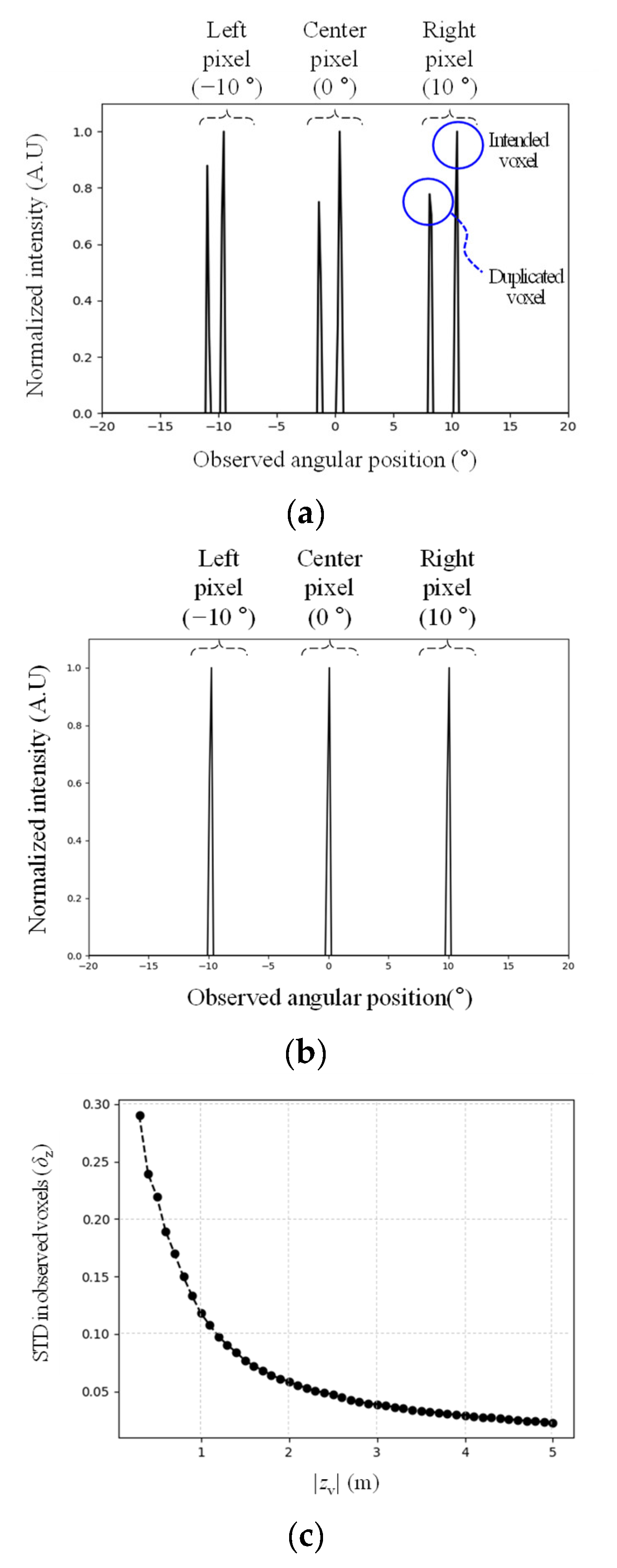
2.1. Voxel Duplication Problem in Holographic Waveguide
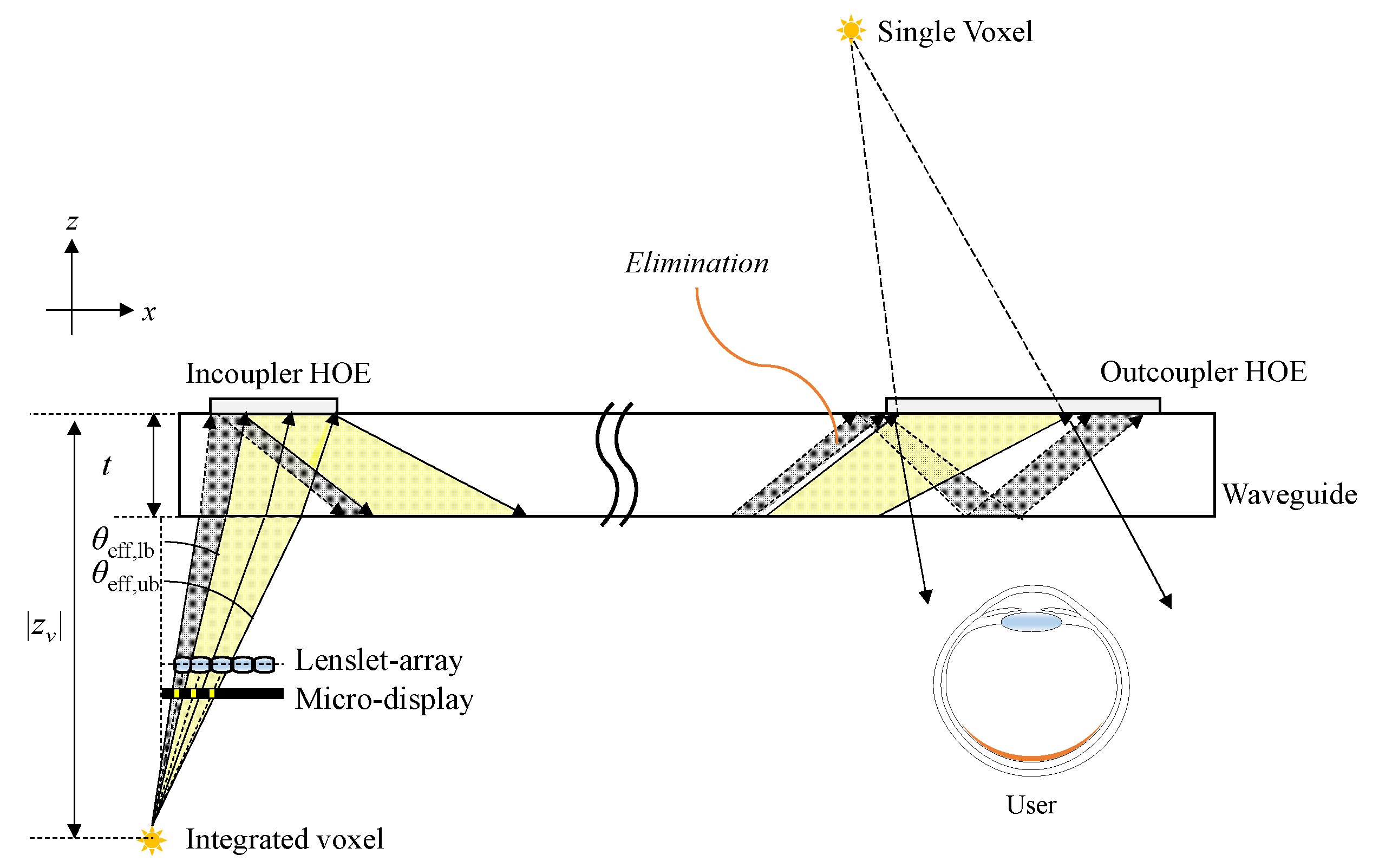
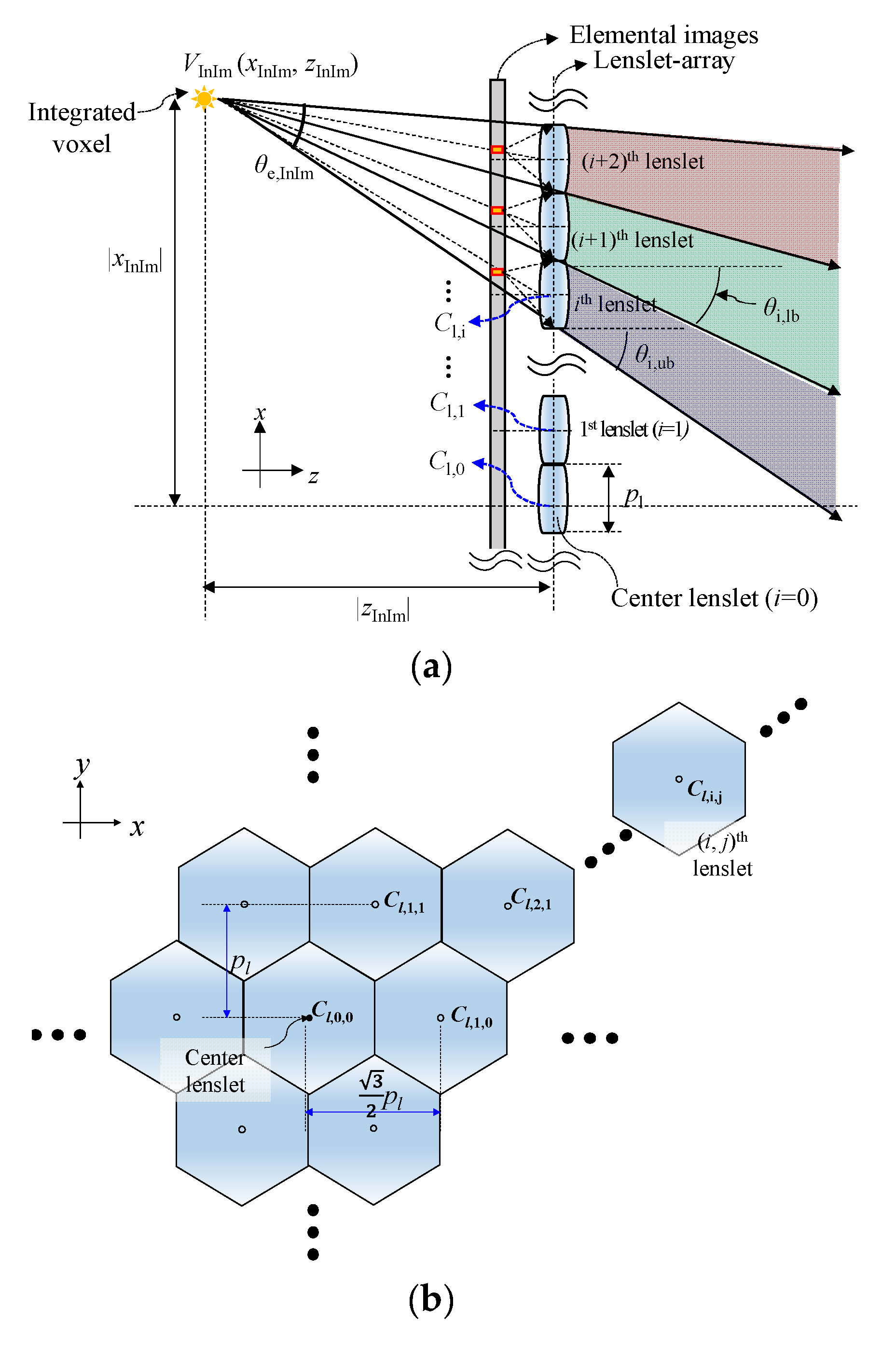
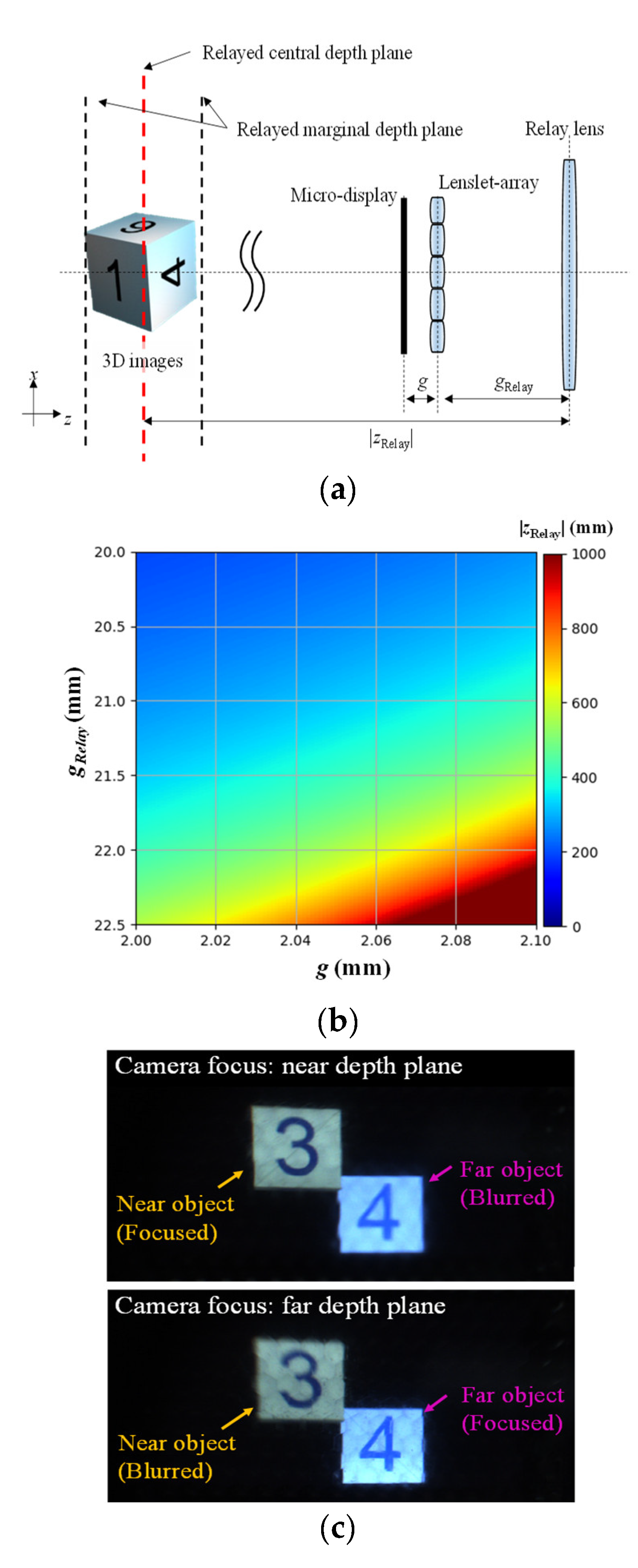
2.2. Emission Angle Adjustment for Voxels Using InIm
3. Results
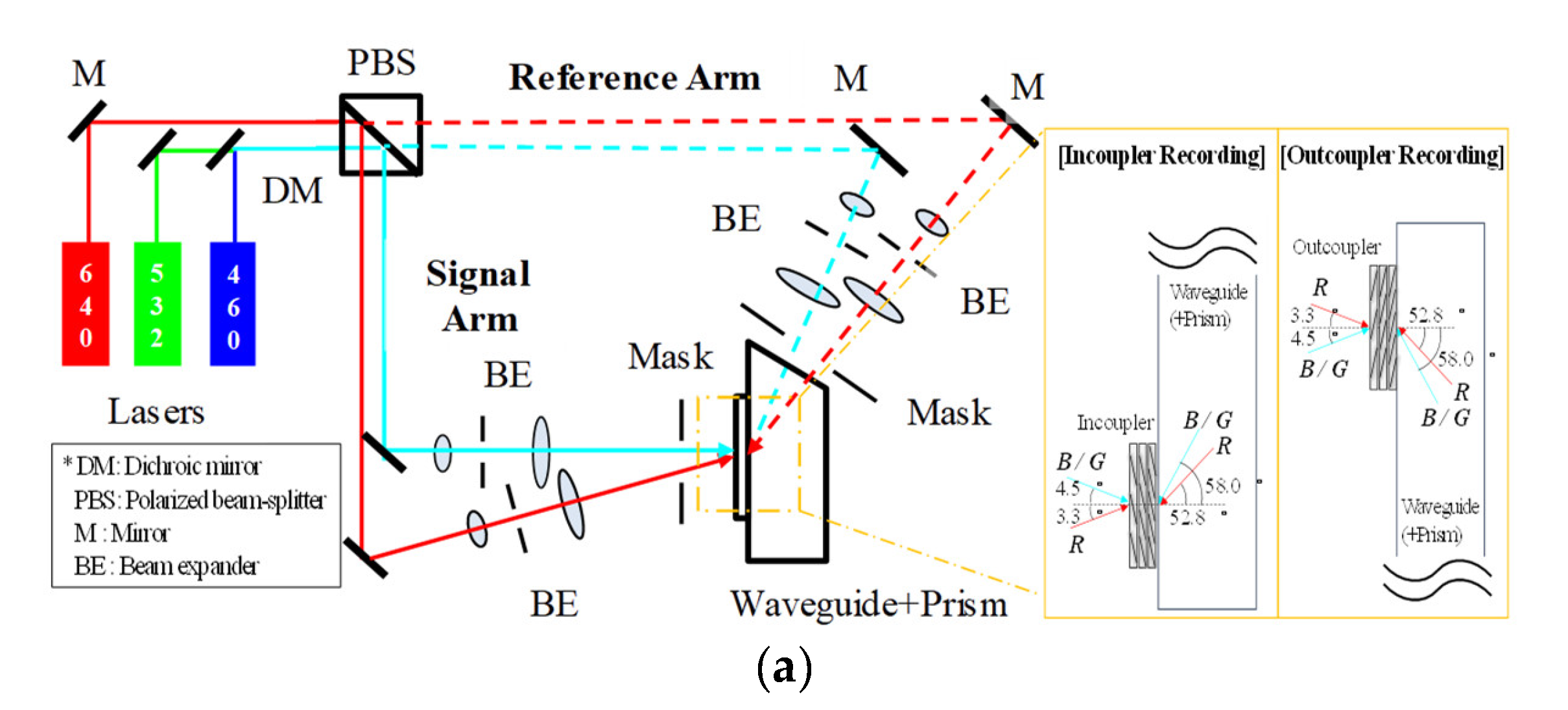
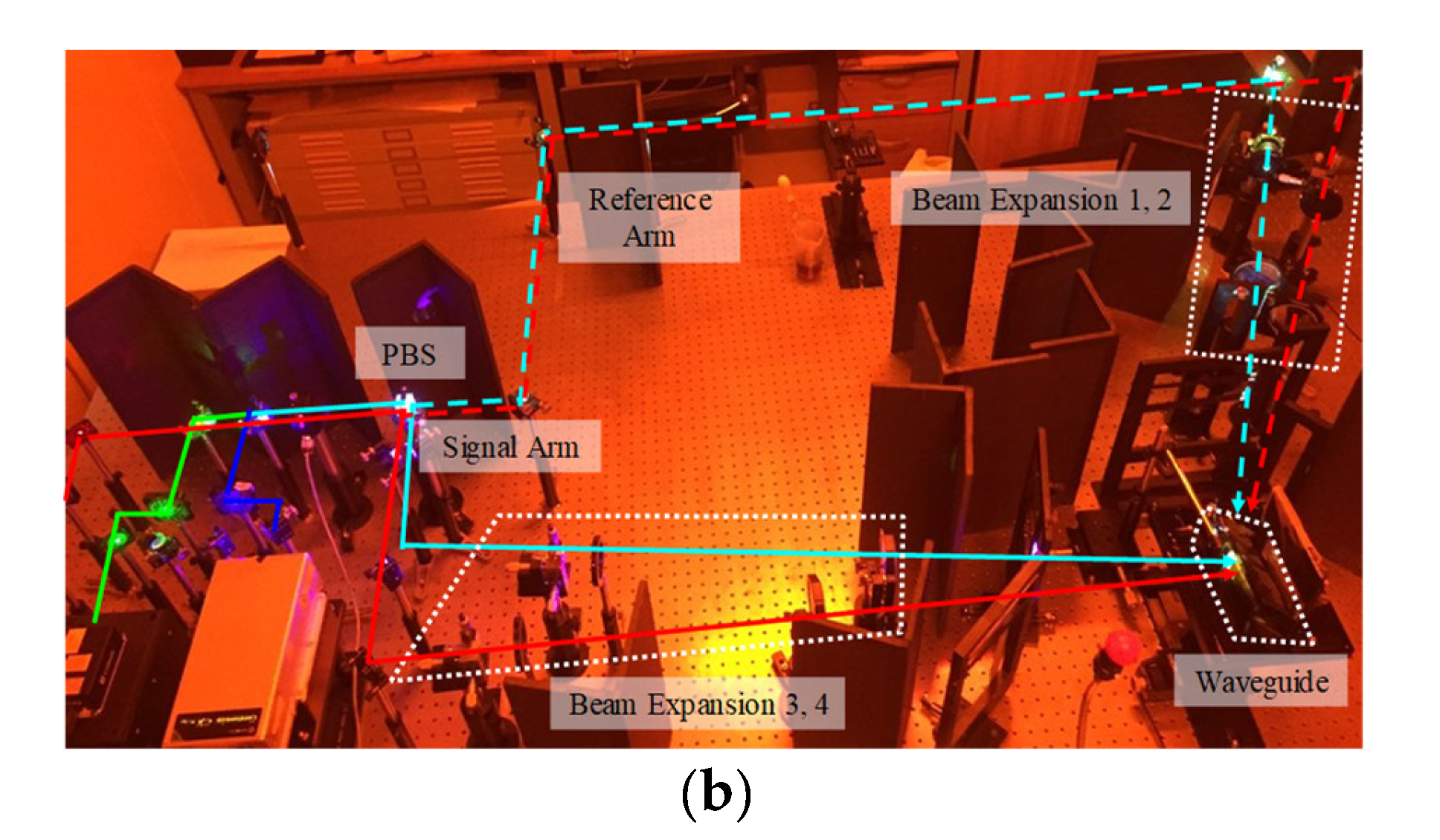
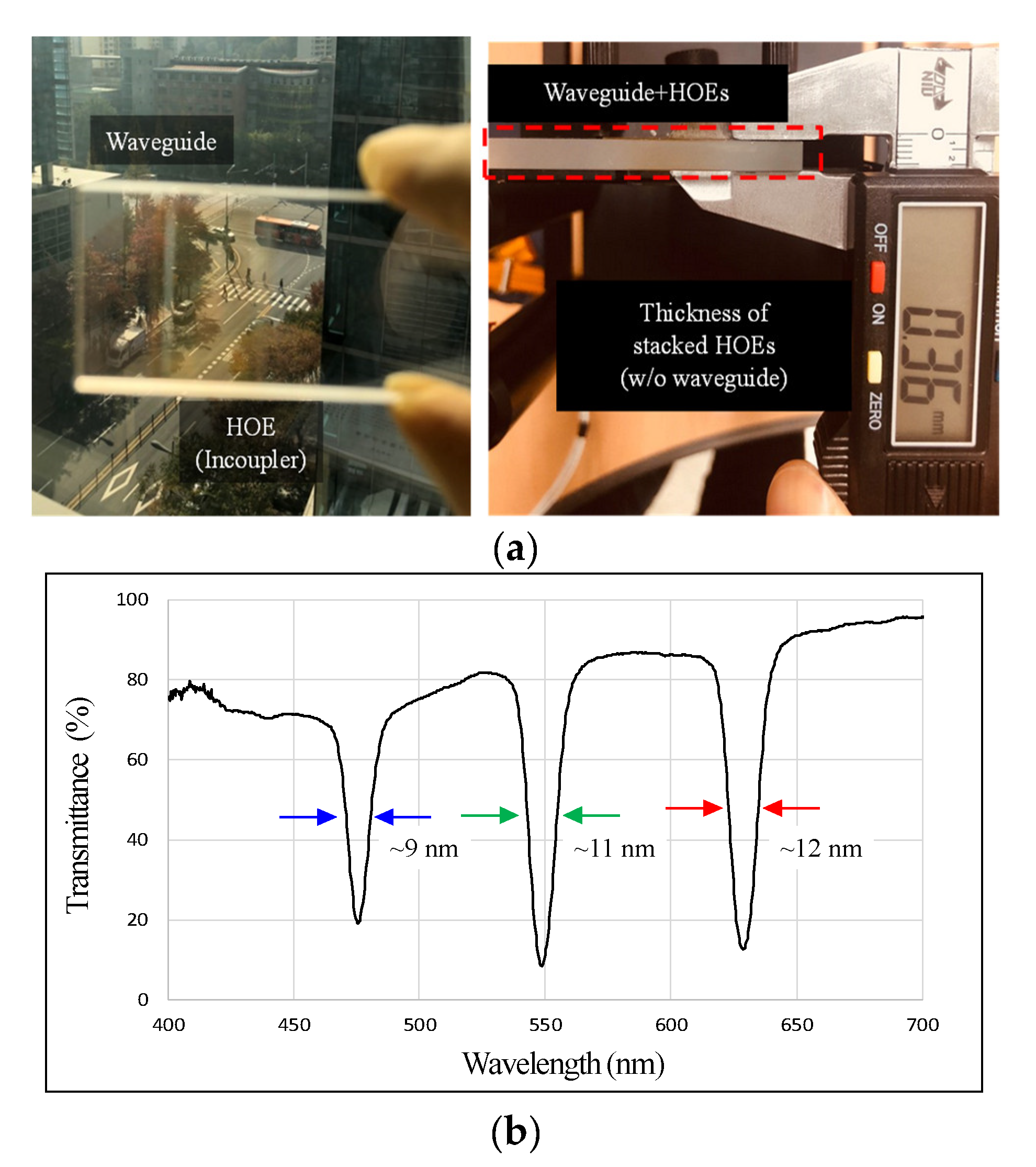
3.1. Fabrication of Full-Color Holographic Waveguide
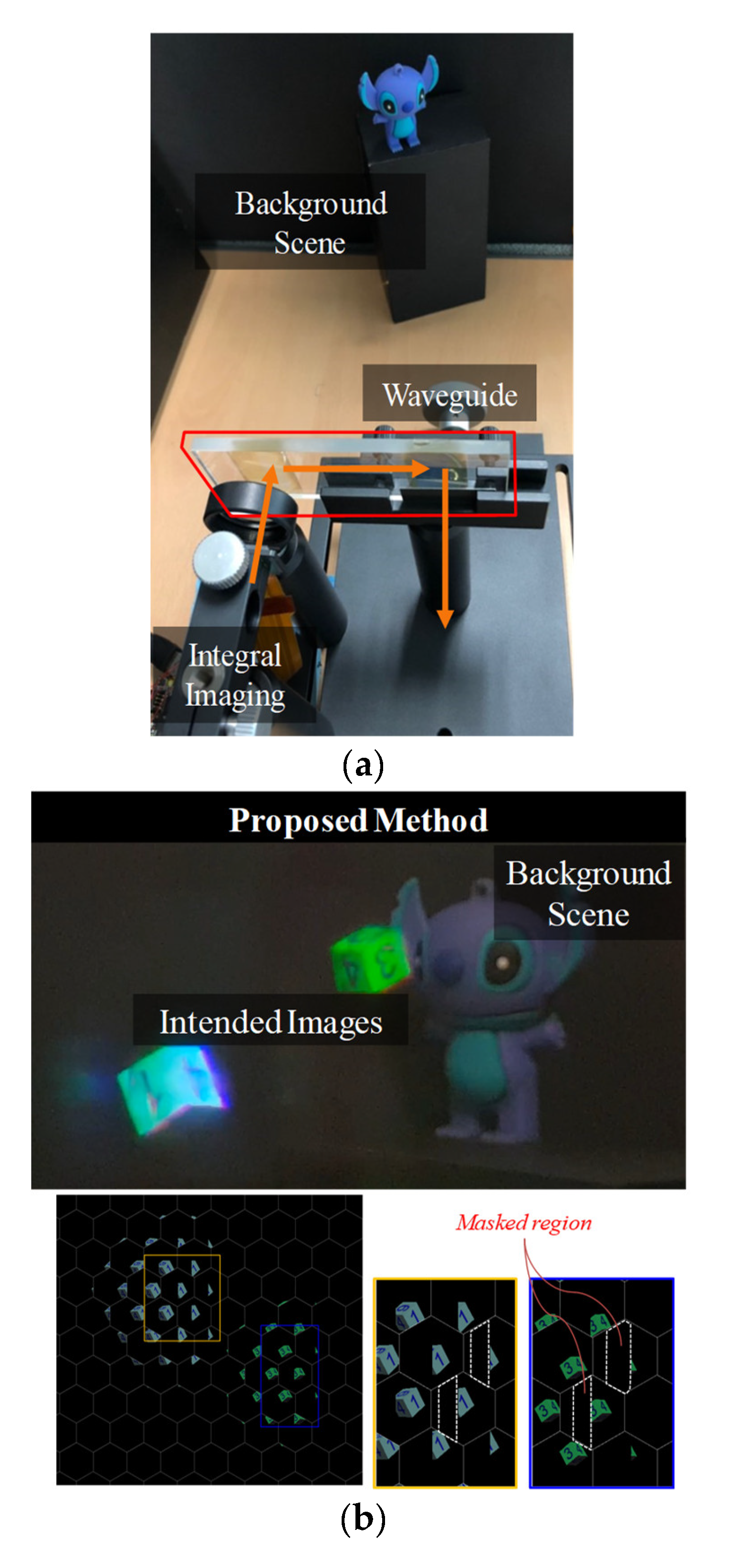
3.2. Displaying Experiments for Representing Voxels
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cakmakci, O.; Rolland, J. Head-worn displays: A review. J. Disp. Technol. 2006, 2, 199–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fang, F. Development of planar diffractive waveguides in optical see-through head-mounted displays. Precis. Eng. 2019, 60, 482–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, H.; Hu, X.; Gao, C. A high-resolution optical see-through head-mounted display with eyetracking capability. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 30993–30998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, C.; Chae, M.; Moon, S.; Lee, B. Retinal projection type lightguide-based near-eye display with switchable viewpoints. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 3116–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, C.; Bang, K.; Moon, S.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.; Lee, B. Retinal 3D: Augmented reality near-eye display via pupil-tracked light field projection on retina. ACM Trans. Graph. 2017, 36, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Wang, Y.; Xu, C.; Song, W.; Jin, G. Design of an ultra-thin near-eye display with geometrical waveguide and freeform optics. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 20705–20719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, Z.; Xu, J. Research on a surface-relief optical waveguide augmented reality display device. Appl. Opt. 2018, 57, 3720–3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Hua, H. Methods of optimizing and evaluating geometrical lightguides with microstructure mirrors for augmented reality display. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 5523–5543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kress, B.C.; Cummings, W.J. Optical Architecture of Hololens Mixed Reality Headset; SPIE: Brussels, Belgium, 2017; Volume 10335, p. 103350K. [Google Scholar]
- Piao, M.-L.; Kim, N. Achieving high levels of color uniformity and optical efficiency for a wedge-shaped waveguide headmounted display using a photopolymer. Appl. Opt. 2014, 53, 2180–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishova, M.; Zherdev, A.; Lushnikov, D.; Odinokov, S. Recording of the multiplexed Bragg diffraction gratings for waveguides using phase mask. Photonics 2020, 7, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Tokuyama, K.; Takai, Y.; Tsukuda, D.; Kaneko, T.; Suzuki, N.; Anzai, T.; Yoshikaie, A.; Akutsu, K.; Machida, A. A plastic holographic waveguide combiner for light-weight and highly-transparent augmented reality glasses. J. Soc. Inf. Disp. 2018, 26, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.-C.; Zhou, S.-K.; Lin, B.-S.; Lin, W.-K. Simplified Aberration Analysis Method of Holographic Waveguide Combiner. Photonics 2020, 7, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeom, H.-J.; Kim, H.-J.; Kim, S.-B.; Zhang, H.; Li, B.; Ji, Y.-M.; Kim, S.-H.; Park, J.-H. 3D holographic head mounted display using holographic optical elements with astigmatism aberration compensation. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 32025–32034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.-K.; Matoba, O.; Lin, B.-S.; Su, W.-C. Astigmatism and deformation correction for a holographic head-mounted display with a wedge-shaped holographic waveguide. Appl. Opt. 2018, 57, 7094–7101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.; Bang, K.; Wetzstein, G.; Lee, B.; Gao, L. Toward the next-generation VR/AR optics: A review of holographic near-eye displays from a human-centric perspective. Optica 2020, 7, 1563–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Weng, Y.; Li, X. Characterization and optimization of field of view in a holographic waveguide display. IEEE Photonics J. 2017, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-K.; Lee, T.; Sung, H.; Min, S.-W. Analysis and design of wedge projection display system based on ray retracing method. Appl. Opt. 2013, 52, 3964–3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-H.; Hong, K.; Lee, B. Recent progress in three-dimensional information processing based on integral imaging. Appl. Opt. 2009, 48, H77–H94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park., S.; Yeom., J.; Jeong, Y.; Chen, N.; Hong, J.-Y.; Lee, B. Recent issues on integral imaging and its applications. J. Inf. Disp. 2014, 15, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, J.; Hong, K.; Yang, H.K.; Jung, J.-H.; Choi, H.; Min, S.-W.; Seo, J.-M.; Hwang, J.-M.; Lee, B. Accommodative response of integral imaging in near distance. J. Disp. Technol. 2012, 8, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Deng, H.; Zhong, F.-Y.; Ji, Q.-L.; Li, Q. Effect of viewpoints on the accommodation response in integral imaging 3D display. IEEE Photonics J. 2020, 12, 7000414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Yeom, J.; Jung, J.H.; Park, J.H.; Lee, B. Resolution comparison between integral-imaging-based hologram synthesis methods using rectangular and hexagonal lens arrays. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 26917–26927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.; Yan, X.; Jiang, X.; Yan, Z.; Wang, Z.; Chen, S.; Lin, M. Comparative study on light modulation characteristic between hexagonal and rectangular arranged macro lens array for integral imaging based light field display. Opt. Commun. 2020, 466, 125613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeom, J.; Son, Y.; Choi, K.-S. Pre-compensation method for optimizing recording process of holographic optical element lenses with spherical wave reconstruction. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 33318–33333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Yeom, J.; Lee, B. Enhancing angular sampling rate of integral floating display using dynamically variable apertures. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 10242–10255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.-G.; Xiao, X.; Martínez-Corral, M.; Chen, C.-W.; Javidi, B.; Wang, Q.-H. Analysis of the depth of field of integral imaging displays based on wave optics. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 31263–31273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.; Kim, C.; Koo, G.; Won, W.H. Depth plane adaptive integral imaging system using a vari-focal liquid lens array for realizing augmented reality. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 5602–5616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Hua, H. High-performance integral-imaging-based light field augmented reality display using freeform optics. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 17578–17590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Items | Specifications | |
|---|---|---|
| Waveguide | Dimension | 105.0 mm × 34.0 mm × 5.0 mm |
| Material | BK7 | |
| HOEs | Dosage | 31.0 mJ/cm2 (460 nm) 21.4 mJ/cm2 (532 nm) 17.2 mJ/cm2 (640 nm) |
| DE 1 (in-coupler) | 72.3% (460 nm) 78.0% (532 nm) 72.0% (640 nm) | |
| DE (out-coupler) | 73.3% (460 nm) 75.1% (532 nm) 72.9% (640 nm) | |
| Size | 25.0 mm × 16.0 mm | |
| Distance between in-coupler and out-coupler | 62.5 mm | |
| Thickness | 0.36 mm | |
| Items | Specifications | |
|---|---|---|
| Micro-display | Resolution | 1920 × 1080 |
| Pixel pitch | 8.3 μm | |
| Size | 15.8 mm × 8.99 mm | |
| Lenslet-array (Hexagonal) | Pitch | 1 mm |
| Focal length | 3 mm | |
| Relay Lens | Diameter | 1 inch |
| Focal length | 30 mm | |
| Method | Display Source | Color | Voxel Representation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Proposed method | OLED + lenslet-array (Broad-band source) | Full-color | Supported |
| Virtual images at optical infinity (Refs. [10,12]) | Flat-panel display + Collimation optics (Broad-band source) | Full-color | Not supported |
| Holographic display (Refs. [14,15]) | Phase modulator + Collimated laser | Monochrome | Supported |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yeom, J.; Son, Y.; Choi, K. Crosstalk Reduction in Voxels for a See-Through Holographic Waveguide by Using Integral Imaging with Compensated Elemental Images. Photonics 2021, 8, 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics8060217
Yeom J, Son Y, Choi K. Crosstalk Reduction in Voxels for a See-Through Holographic Waveguide by Using Integral Imaging with Compensated Elemental Images. Photonics. 2021; 8(6):217. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics8060217
Chicago/Turabian StyleYeom, Jiwoon, Yeseul Son, and Kwangsoon Choi. 2021. "Crosstalk Reduction in Voxels for a See-Through Holographic Waveguide by Using Integral Imaging with Compensated Elemental Images" Photonics 8, no. 6: 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics8060217
APA StyleYeom, J., Son, Y., & Choi, K. (2021). Crosstalk Reduction in Voxels for a See-Through Holographic Waveguide by Using Integral Imaging with Compensated Elemental Images. Photonics, 8(6), 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics8060217




