Abstract
Uniform luminescent films with high optical quality are promising materials for modern molecular photonics. Such film materials based on β-diketonate complexes of lanthanides have the following application problem: rapid luminescence degradation under UV radiation, low thermostability, poor mechanical properties, and aggregation propensity. An alternative approach to solving these problems is the use of anisometric analogues of β-diketonate compounds of lanthanides (III). The main advantage of such compounds is that they do not crystallize because of long hydrocarbon substituents in the structure of complexes, so they can be used to fabricate thin nano-, micro-, and macroscale uniform film materials by a melt-processing technique at relatively low temperatures, as well as by spin-coating. The method of fabrication of microscale luminescent film materials with controlled optical properties from anisometric analogues of Ln(DBM)3Phen and Ln(bzac)3Phen complexes (Ln = Eu, Tb) is proposed in this paper. Within the framework of this research, we developed original films which are highly uniform and transparent. An important advantage of these films is their high photostability and potential for applications as reusable luminescent sensors and light converters.
1. Introduction
Molecular photonics is a modern branch of science and its active areas of study are development and fabrication of highly functional luminescent materials and devices [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]. Among many different types of luminescent compounds (e.g., organic compounds, quantum dots, metal-ligand complex), lanthanide (III) coordination compounds are very promising candidates for development of luminescent molecular photonics materials and devices due to their unique photophysical properties, such as a narrow-band luminescence with a high quantum yield and a long lifetime [8]. Lanthanide (III) complexes with aromatic β-diketonate ligands are among the most interesting coordination compounds of lanthanides because they combine intensive monochromatic luminescence with attractive chemical characteristics (such as a relatively easy synthesis, good solubility in many basic solvents and a capability of incorporation into various host matrices, such as polymers and liquids crystals). Due to these properties, such compounds have a strong potential for a broad variety of applications.
Uniform luminescent films with high optical quality are promising materials for modern molecular photonics. Such film materials based on β-diketonate complexes of lanthanides have the following application problem: rapid luminescence degradation under UV radiation, low thermostability, poor mechanical properties and propensity to aggregation [9,10]. A possible solution is incorporating these compounds into host matrices (e.g., organic polymers, ionic liquids, zeolites, and etc.) [11,12,13]. There are also other methods of fabricating film materials based on these compounds, such as electro deposition and sol-gel technology [1,2,3].
Another problem of many film materials based on β-diketonate complexes of lanthanides is that their adsorption band is limited by the UV range. Therefore, UV sources are required to excite luminescence in such films, such sources are unsuitable in many applications for certain reasons (such as low brightness and high cost of such devices as compared to visible light sources). Thus, an urgent problem of molecular photonics is to broaden this adsorption band so it can include the visible light range.
The solutions for this problem offered today are known to be based on the following approaches: synthetic modification of β-diketonate ligands and coordination of complex chromophores to tris(β-diketonates) of lanthanides(III) with capabilities of efficient visible light adsorption. For example, it is challenging to select a proper solvent for both a matrix and a complex, where, in addition, this complex must not dissociate.
An alternative approach to solution of these problems is the use of anisometric analogues of β-diketonate compounds of lanthanides (III) [14,15]. The main advantage of such compounds is that they do not crystallize because of long hydrocarbon substituents in the structure of complexes and possess thermostable properties [16], so they can be used to fabricate thin nano-, micro- and macroscale uniform film materials by a melt-processing technique at relatively low temperatures, as well as by spin-coating [17]. The films produced by a melt-processing technique require a much simpler technology for fabrication of luminescent materials based on lanthanide compounds as compared to available analogues, because no solvents or photostabilizing matrices are needed in this case. Such films have the following technological advantages: intense luminescence, high optical transmittance (up to 95%) in nearly entire visible and near IR ranges, high resistance to UV light, and controllability of their photophysical properties (e.g., the absorption band width and the luminescence intensity) [18,19].
In this paper, we discuss the opportunities of application of microscale films based on anisometric europium(III) and terbium(III) β-diketonate complexes as materials for photonics and optics.
2. Materials and Methods
The synthesis of anisometric complexes was performed according to the technique developed earlier by our group. CHN elemental microanalysis was performed on a EA-1110 apparatus by CE Instruments. Europium elemental microanalysis was performed on a Bruker S8 TIGER X-ray fluorescence spectrometer (Billerica, MA, USA). The thermal behavior of complexes was studied by polarized optical microscopy (POM) on an Olympus BX51 microscope equipped with a LINKAM high-precision heating system and by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) (Olympus America, Melville, NY, USA). DSC thermograms were recorded on a Mettler-Toledo DSC 1 Star module in the heating-cooling mode at the 10 °C/min scan rate. Thin nanoscale films of complexes were prepared from toluene solution (1 × 10−3 mol/L) by spin coating on a WS-650 MZ-23NPP Laurell Spin Coater (Laurell Technologies Corporation, North Wales, PA, USA). The transmittance spectrum at room temperature was recorded on a Perkin-Elmer Lambda 35 spectrophotometer. The luminescence spectra at room temperature were measured by a Varian Cary Eclipse spectrofluorometer. The photoluminescence excitation spectra of the vitrified films were recorded at room temperature on an experimental setup consisting of a MDR-2 excitation monochromator and a MDR-12 recording monochromator. A DKSL-1000 xenon lamp was used as an excitation source. The light signal passing through the MDR-12 monochromator was detected using a FEU-79 photomultiplier tube. The input and the output slit widths of the MDR-2 monochromator were set to 10 nm. The excitation spectra were recorded in the 230–430 nm range by varying the excitation light wavelength and monitoring the photoluminescence intensity at 545 nm and 612 nm, respectively. To study the photostability of the obtained film materials, the UVGL-58 Manual UV-lamp (365 nm) with the 6 W capacity was used.
The powders of anisometric complexes were synthesized according to the procedure described in the previous papers [20,21]. A warm solution of LnCl3 · 6H2O (0.1 mmol) in ethanol was slowly added dropwise to a hot alcoholic solution containing 0.3 mmol of β-diketone [22], 0.1 mmol of Phen, and 0.3 mmol of KOH. The formed light-yellow precipitate was filtered, purified in hot alcohol and dried under vacuum. Then, the product was dissolved in toluene and the obtained solution was filtered dried under vacuum.
Tris[1-(4-(4-propylcyclohexyl)phenyl)decane-1,3-dione](1,10-phenanthroline) terbium(III) (Tb(CPDK3–7)3phen). Yield: 71% (0,107 g). Melting point: 130 °C. Elemental analysis (%): calculated for C87H119N2O6Tb: C, 72.17; H, 8.28; N, 1.93. Found: C, 71.68; H, 8.55; N, 1.95.
Tris[1-phenyl-3-(4-(4-propylcyclohexyl)phenyl)propane-1,3-dionato](1,10-phenanthroline) europium(III) (Eu(CPDk3-Ph)3Phen). Yield: 59% (0.087 g). Melting point: 142 °C. Elemental analysis (%): calculated for C84H89N2O6Eu (%): C, 73.40; H, 6.53; N, 2.04; Eu,11.06. Found (%):C, 73.01; H, 6.88; N, 2.12; Eu, 11.00.
Tris[1-(4-(4-propylcyclohexyl)phenyl)octane-1,3-dionato](1,10-phenanthroline) europium(III) (Eu(CPDK3-5)3Phen). Yield: 70% (0,105 g). Melting point: 110 °C. Elemental analysis (%): Calcd forC81H107EuN2O6: C, 71.61; H, 7.95; N, 2.06; Eu,11.20. Found: C, 71.16;H, 8.31; N, 2.02; Eu, 11.50.
The sensitive luminescent material was prepared from a powder of the Eu(CPDk3–5)3Phen, Eu(CPDk3-Ph)3Phen or Tb(CPDk3–7)3phen complexes by a melt-processing technique. Powders of complexes were melted between two quartz plates with a size of 7 × 15 × 0.5 mm placed on the stage of an Olympus BX-51 polarizing microscope. After heating up to the isotropic liquid transition temperature, the sample was quickly cooled down to room temperature to obtain vitrified films with 3 μm, 6.1 μm or 20 μm thickness, which were sandwiched between two quartz plates. To control thickness, we used 3 μm, 6.1 μm and 20 µm spacers, respectively.
3. Results and Discussion
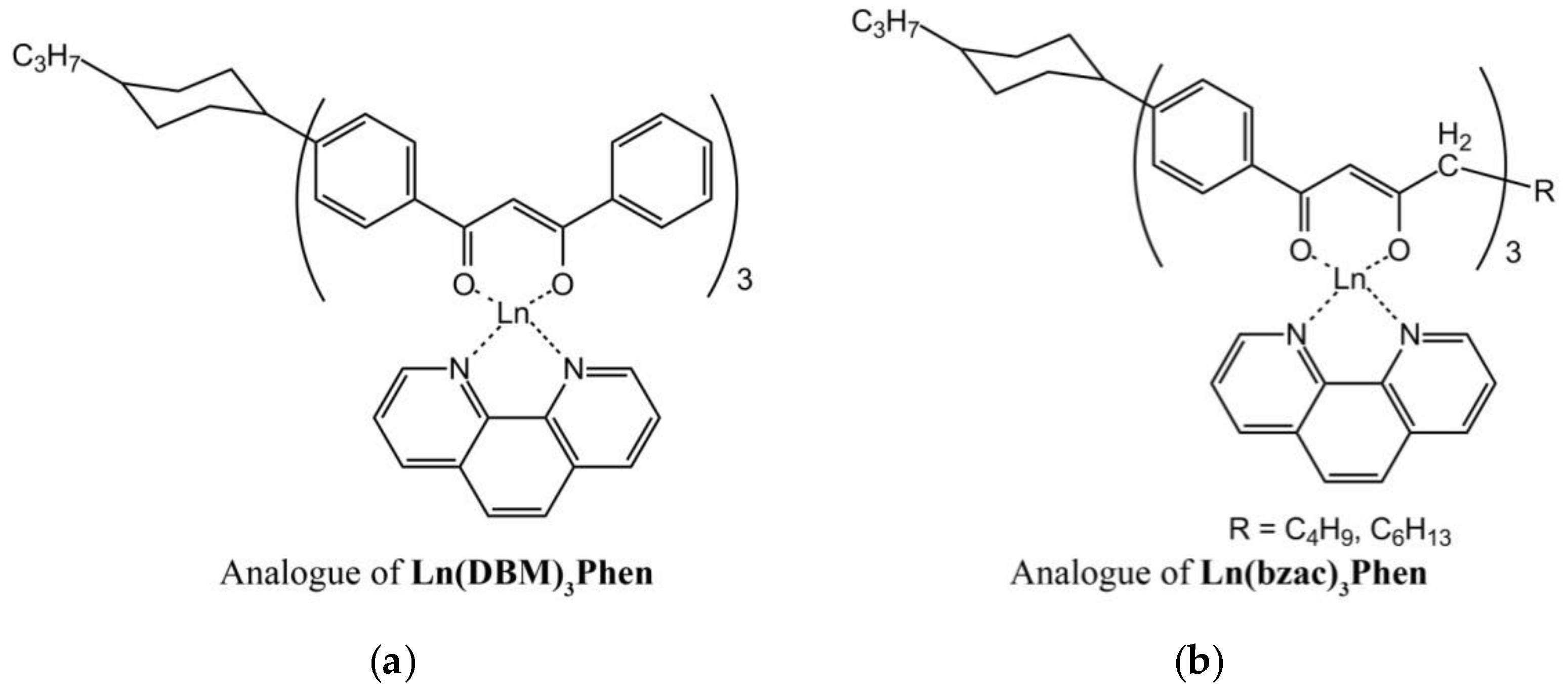
The structure of anisometric β-diketonate complexes of lanthanides(III) is demonstrated in Figure 1.
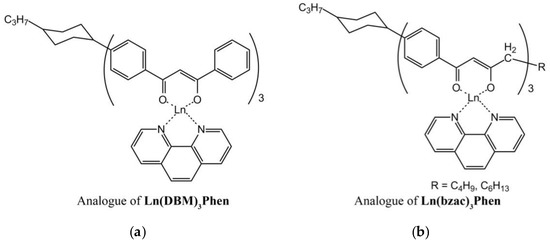
Figure 1.
The scheme of the anisometric analogues of (a) Ln(DBM)3Phen and (b) Ln(bzac)3Phen complexes (Ln = Eu, Tb).
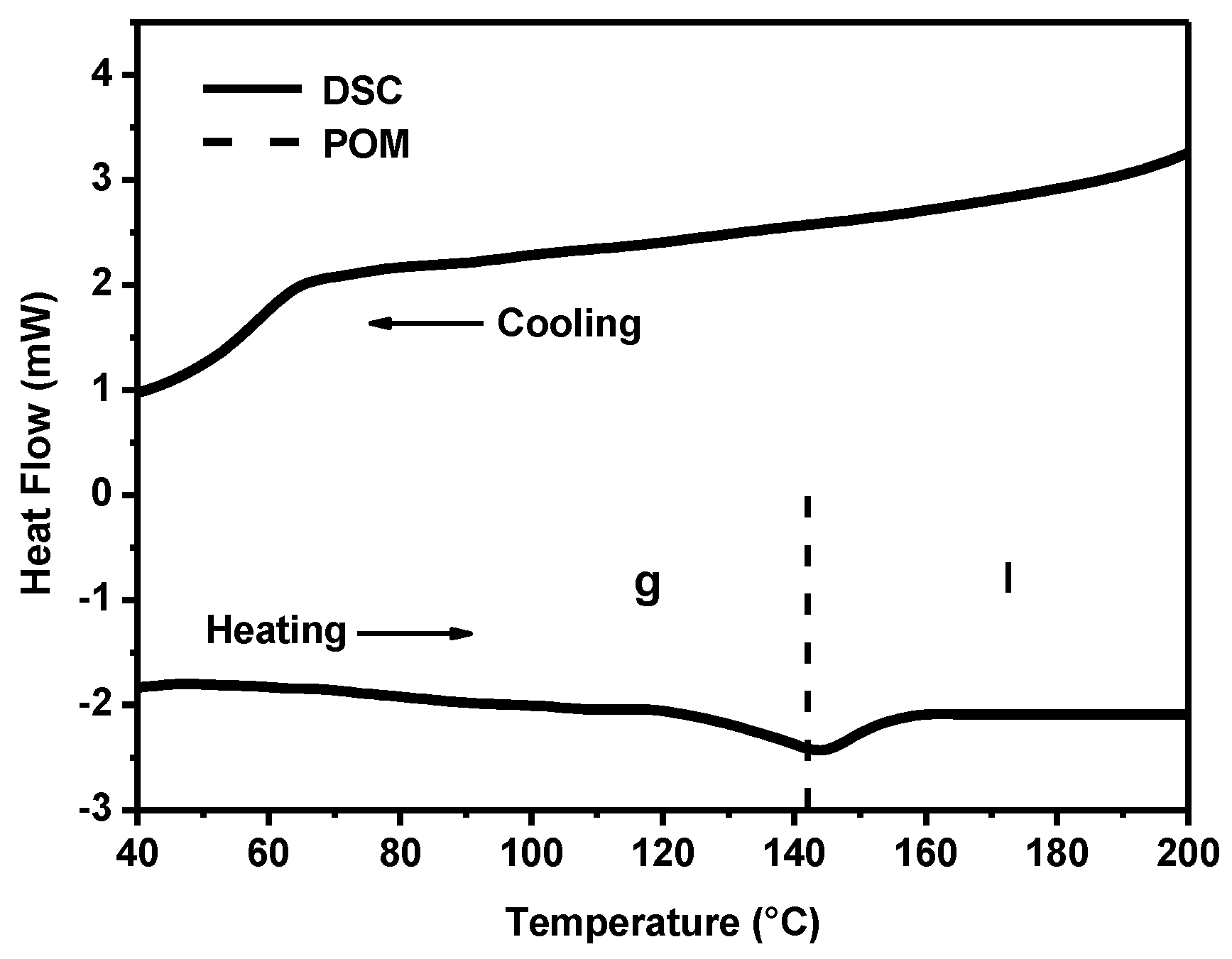
The thermal behavior of powders of anisometric complexes was studied by polarized optical microscopy (POM) and differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). The presence of alkyl and cyclohexane substituents in the chemical structure of β-diketonate ligands of anisometric β-diketonate lanthanide(III) complexes prevents them from crystallization and allows for considerable reduction of the melting temperature to avoid decomposition at melting that is typical for their non-anisometric analogues (Table 1). The phase transitions determined by the POM method have been confirmed by the DSC method, as illustrated in Figure 2 for the Eu(CPDk3–Ph)3phen complex. According to the DSC heating scan, the isotropic transition temperature was 142°C. The sample is vitrified upon cooling, as can be concluded from the absence of the exothermic crystallization peaks in the DSC cooling scan. The combination of such properties allows for fabricating vitrified luminescent films with high optical quality from melts of powders of these substances (see Figure 3 insert). These films have almost no crystalline effects, according to the polarized optical microscopy data [23]. The obtained vitrified films were stable and remained transparent at room temperature over several months. It is important to note that such films cannot be produced from non-anisometric analogues of β-diketonate lanthanide(III) complexes because of their strong aggregation propensity and high melting temperatures.

Table 1.
Melting temperatures of anisometric Ln(III) complexes and their commercial analogues.
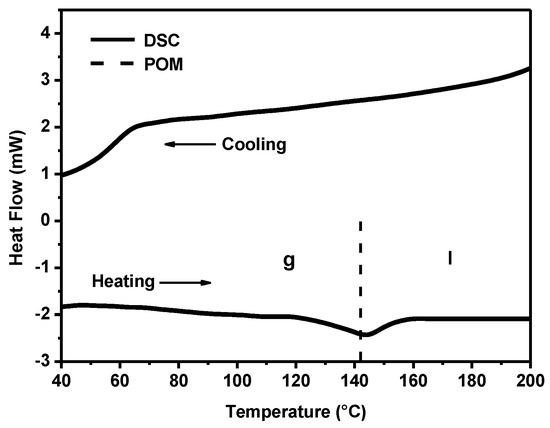
Figure 2.
Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) thermogram of Eu(CPDk3-Ph)3Phen. POM = polarized optical microscopy.
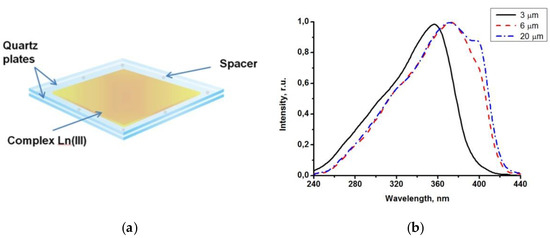
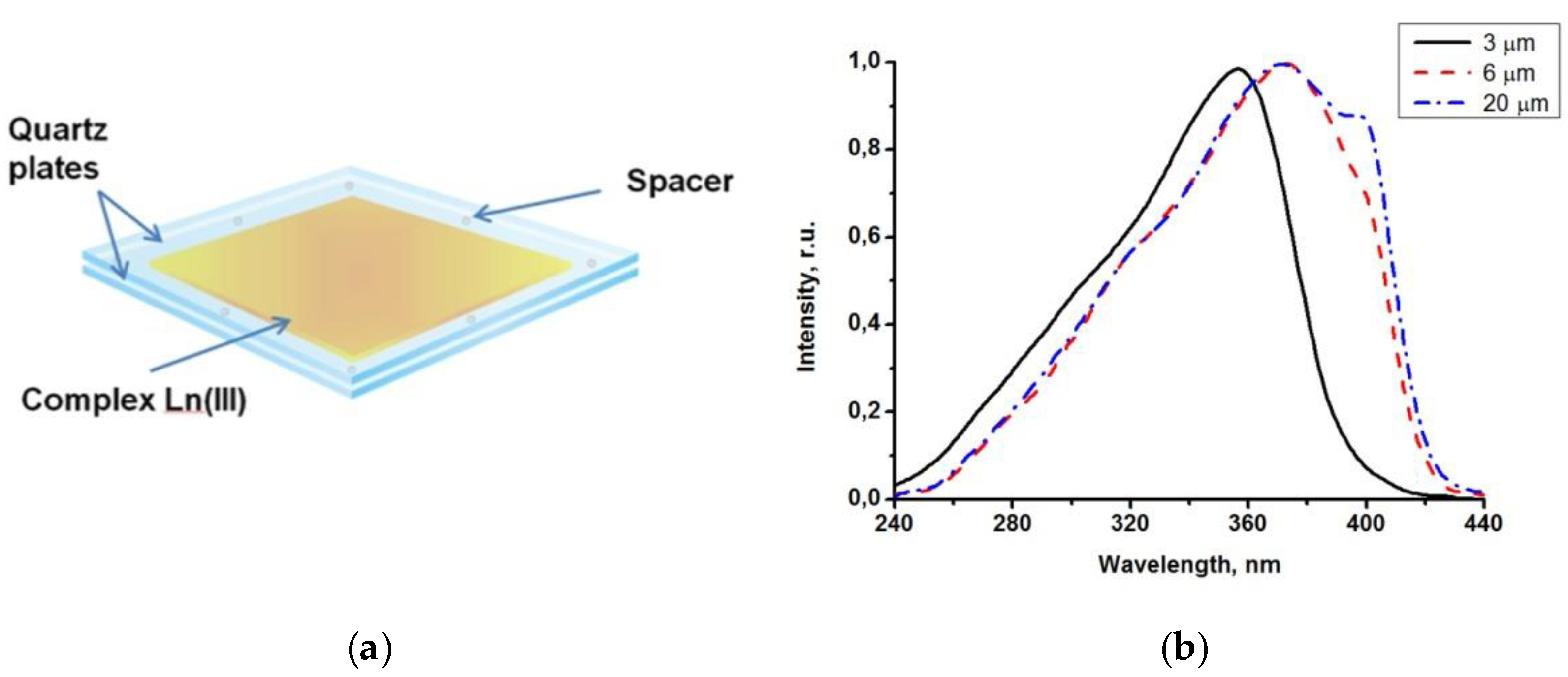
Figure 3.
A microscale film of Tb(CPDk3–7)3Phen complexes between two quartz plates (a); luminescence excitation spectra of Tb(CPDk3–7)3Phen complex films with 3, 6.1, and 20 µm thickness between quartz plates recorded at 545 nm wavelength and room temperature (b).
The technology of fabrication of microscale vitrified films from powders of anisometric β-diketonate lanthanide(III) complexes is very simple to implement because no solvents or solid matrices for photostabilization of complexes are used, as opposed to traditional approaches to fabrication of film materials based on lanthanide complexes. The following procedure was used to fabricate our films: a small amount of a powder complex was placed between two quartz plates and an isotropic melt was created by heating. Subsequent rapid cooling down to room temperature results in the glass transition of the melt and formation of a solid and uniform film. This technology allows for controlling the thickness of films by spacers, such as polystyrene microspheres with various diameter.
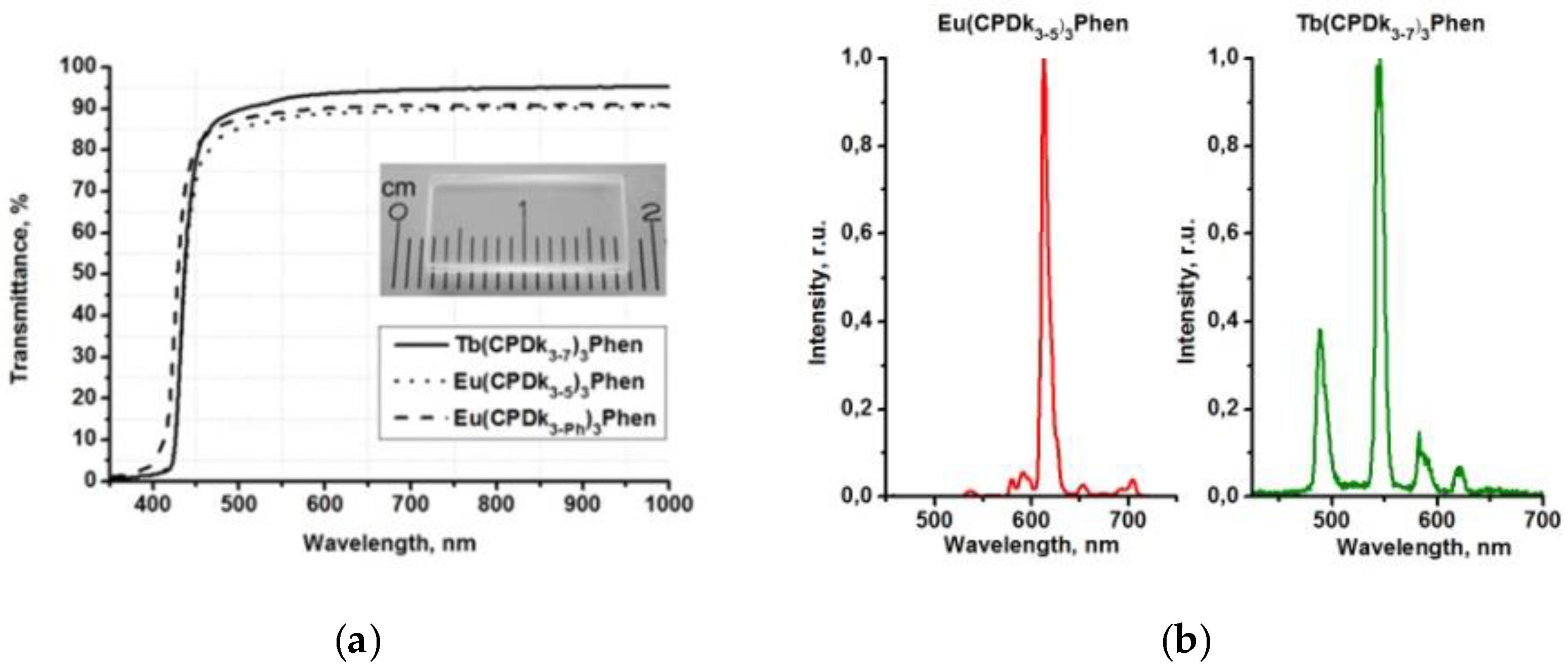
A peculiar feature of vitrified films is that their adsorption (excitation) band width can be manipulated by varying the melt thickness. Due to strong adsorption capacity of films with the thickness exceeding 3 μm in the 200−380 nm range, it was possible to detect only the long wave edge of the adsorption spectrum. Luminescence excitation spectra are more informative because they allow for detecting changes (from various thicknesses of the films) in the entire spectral range (200–450 nm). Figure 3b illustrates the influence of thicknesses of the Tb(CPDk3–7)3Phen films on their excitation spectra. The excitation spectra of a 3 μm film (monitored at 545 nm) consist of a broad band with the maximum at 356 nm corresponding to singlet-singlet transitions in ligands. The increase of the film thickness to 6 μm broadens the excitation spectrum band to the violet visible range and shifts the maximum of the spectrum. Further increase of the film thickness to 20 μm creates a distinguished shoulder of the spectrum in the 393 nm area. β-dicarbonyl compounds are known to form associates in concentrated solutions. For example, molecular associates of benzoylacetone in cyclohexane solution (C = 1 × 10−2 M) are responsible for the long-wavelength band with the maximum at 400 nm in the absorption and excitation spectra. Dimeric species in similar molecular systems were detected by NMR spectroscopy. We consider that the features mentioned above indicate clearly that the thickness of the Tb(CPDk3–7)3Phen films influences their local structure (the ratio between individual molecules and aggregates) [28]. The presence of aggregated complexes in the films with various thicknesses is the factor responsible for the long-wave “wing” of the excitation spectra of the films. Thus, variation of the ratio between individual molecules and aggregates in the local structure of films (at the stage of their fabrication) allows for manipulating the width of absorption and excitation bands and creating optically transparent luminescent materials, which are capable of absorbing light in a broad range including the visible violet light. The transmittance of the vitrified films reaches 95% in the wavelength range of 450–1000 nm. Aggregated films demonstrate complete light absorption in the entire UV range (Figure 4a). Thanks to all these properties, the films are not sensitive to sunlight or artificial illumination (such as filament lamps, halogen, and luminescent lamps) in the visible spectral range, which are intensive sources of optical disturbances. It is important to note that such films cannot be fabricated from non-anisometric analogues of β-diketonate lanthanide (III) complexes because of their strong crystallization propensity and high melting temperatures.
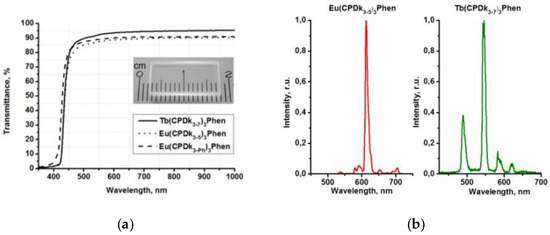
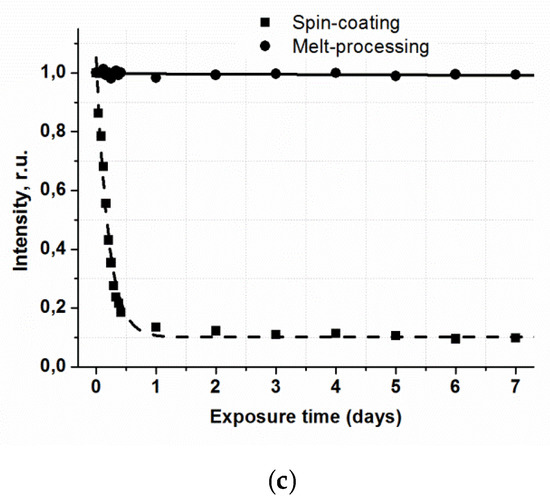
Figure 4.
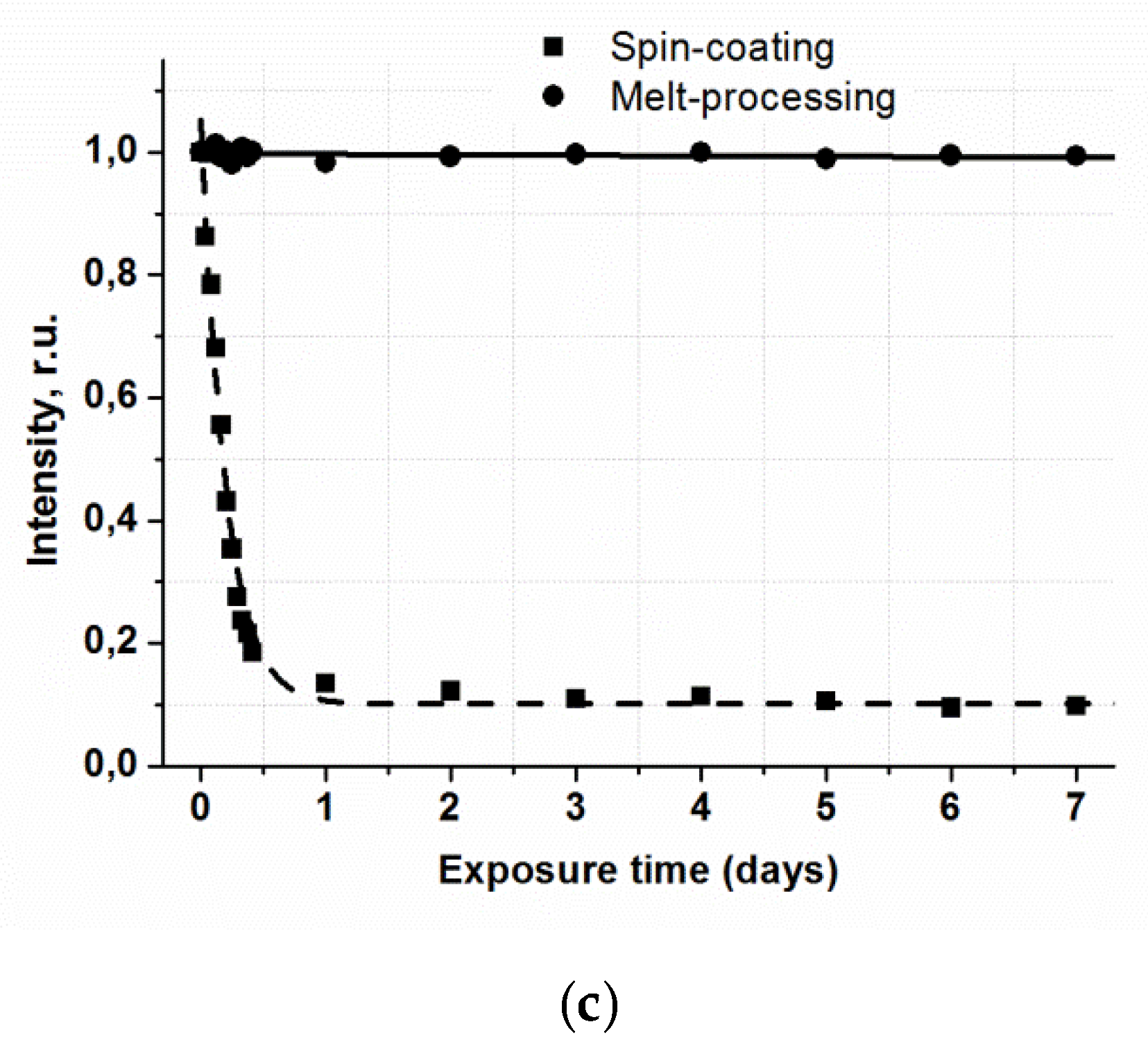
Transmittance(a) and luminescence spectra excited at 337 nm (b) of the 6.1 µm thick vitrified films at room temperature; (c) photostability of Eu(CPDk3-5)3Phen complex films fabricated by melt-processing (6.1 µm thick) and spin-coating techniques.
Aggregated films are the most promising candidates for various applications. For example, aggregated films of Tb(CPDk3–7)3Phen and Eu(CPDk3–5)3Phen complexes are characterized by broad luminescence excitation bands in the 250–420 nm range, which correspond to β-diketonate ligand-centered singlet-singlet transitions [18]. The 365 nm UV excitation of Tb(CPDk3–7)3Phen and Eu(CPDk3–5)3Phen films initiates monochromatic luminescence of Tb3+ and Eu3+ ions with 545 nm and 612 nm maximums, respectively (Figure 4b). Absence of emission from the ligands (which is expected to occur in the wavelength range of 450–670 nm) [19] suggests that the ligand-to-metal energy transfer process is very efficient in the film.
It should be noted that intensive absorption of the films in the 390–405 nm wavelength range allows for using them not only as UV light sources but also as purple LEDs.
Photostability of luminescent materials is a very important criterion for their application. A significant problem, which hinders broad application of film materials based on β-diketonate lanthanide complexes, is irreversible reduction of their luminescence intensity under UV radiation. This process is particularly intensive in the presence of atmospheric oxygen. The influence of long-time UV irradiation on the luminescence intensity of vitrified films based on anisometric β-diketonate lanthanide (III) complexes was studied. For reference, the photostability of films fabricated by spin-coating was also characterized. The results for the films of Eu(CPDk3–5)3Phen complexes are represented in Figure 4c. The UV source was the UVGL-58 Handheld UV Lamp with 365 nm wavelength and 6 W power.
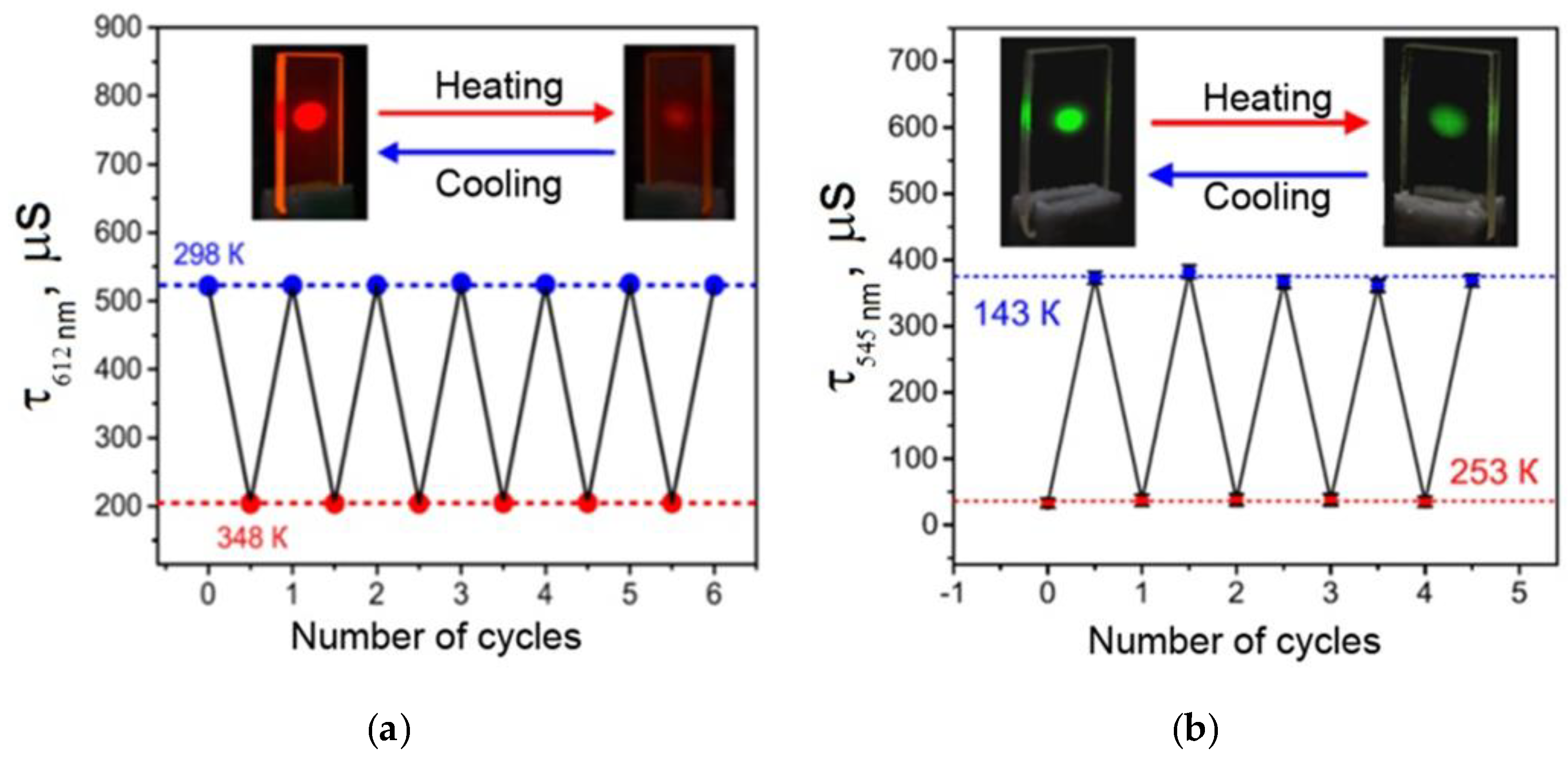
UV radiation does not change the luminescence intensity of the films fabricated from the complexes by the melt-processing technique even after the 10-h exposure, whereas the intensity of films fabricated by the spin-coating technique is reduced almost 5 times in the same exposure conditions. It may be the effect of photooxidation of the films under UV radiation. Thus, the technology of fabrication of film materials by melting between quartz glasses isolates a luminophore from atmospheric oxygen and, therefore, increases photostability of films and prevents them from photooxidation. From the application point of view, a photostable luminescent vitrified Eu(CPDk3–5)3Phen film is primarily interesting for its capability to perform multiple functions at the same time. Firstly, it completely absorbs the light energy in the entire UV range (200–385 nm) and is not destructed by the UV radiation, so it can be used as a molecular UV filter. Secondly, this material can efficiently transform the light energy in the 280–415 nm range into intensive monochromatic orange-red luminescence of Eu3+ions (the absolute quantum yield of luminescence of Eu3+ ions is ~30% [29]), so it can be an efficient light-transforming material and the source of monochromatic orange-red light. Finally, this material can reversibly change luminescence intensity and quenching time in the 298–348 K temperature range (Figure 5a), so it can become an efficient working element of multiple use luminescent thermometers. This material possesses the following technological advantages over its close analogues: total resistance to the UV radiation, high optical quality, total protection from the contact with atmospheric oxygen, and the highest average absolute temperature sensitivity of the luminescence decay time (6.5 μs∙K−1) among temperature-sensitive film materials based on nonmesogenic europium(III) β-diketonate complexes, which efficiently absorb light in the violet range of the visible spectrum. The value of the relative temperature sensitivity of the luminescence decay time Sτ(r) varies from −0.28%·K−1 at 298 K to −1.6%·K−1 at 348 K with τRef = 537µs. Its average value is −1.2%·K−1. It is important to note that the average Sτ(r) value is one of the largest reported for the temperature-sensitive films based on the europium(III) b-diketonate complexes, which are efficient absorbers of light in the violet region [30].
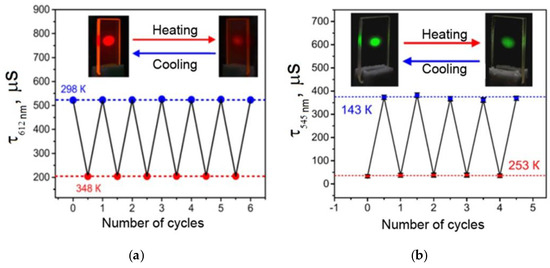
Figure 5.
Reversible changes in the luminescence decay time (monitored at 612 nm) for the Eu(CPDK3–5)3Phen film (a) and in the luminescence decay time (monitored at 545 nm) for the Tb(CPDK3–7)3Phen (b) under the excitation by the 337 nm pulsed nitrogen laser with the 0.17 mW average output power in consecutive heating-cooling cycles. Standard deviations are shown as error bars.
A luminescent material made of a vitrified Tb(CPDK3–7)3Phen 6.1 µm thick film also offers interesting properties for broad application in various areas. This film is an efficient absorber of the light energy in the broad 280−405 nm range, which is then converted into the monochromatic green luminescence of Tb3+ ions. In the 143−253 K temperature range, this material can reversibly change the luminescence quenching time (Figure 5b), so it can also become an efficient working element of multiple use luminescent thermometers [29]. A temperature sensitive material made of the Tb(CPDK3–7)3Phen film is easy to produce, insensitive to oxygen, characterized by high optical quality, and resistant to destructive effects of UV radiation. It is an efficient absorber of violet light and possesses high temperature sensitivity to a luminescence quenching time (3.3 μs∙K−1). The relative temperature sensitivity of the average luminescence decay time Sτ(r) is −0.4%·K−1 at 253 K and −1.4%·K−1 at 143 K with τRef = 373 µs. Its mean value is −0.9%·K−1. To the best of our knowledge, there are no reports describing the temperature-sensitive luminescent films (operating below room temperature) based on terbium(III) β-diketonate complexes with the similar characteristics.
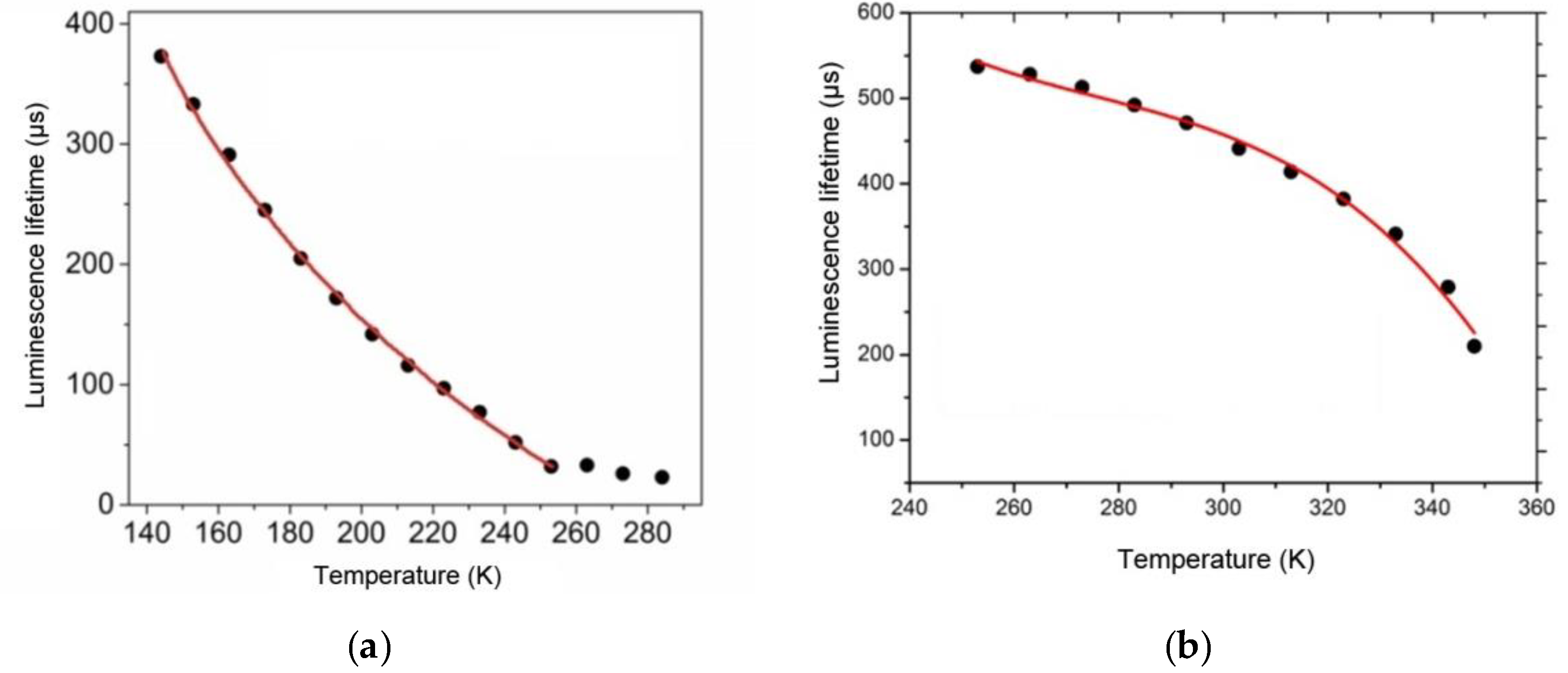
The temperature sensitivity of luminescence properties of the fabricated film materials was studied by measuring their lifetimes. As opposed to the luminescence intensity, the luminescence lifetime parameter does not depend on measurement conditions and the degradation coefficient value, so it can be used for more reliable and accurate determination of temperature. Thermally sensitive luminescent properties of the Tb(CPDk3–7)3Phen films were studied in the 143–253 K temperature range (Figure 6a) because no significant changes of the luminescence lifetime were observed in the upper range of 253–284 K, while cooling below 143 K led to irreversible changes in the local structure of films. Thermally sensitive luminescent properties of the Eu(CPDk3–5)3Phen films were studied in the 253–348 K temperature range (Figure 6b) because the luminescence lifetime was thermally irresponsive at temperatures below 253 K, while the 353 K temperature turned out to be the softening threshold of the Eu(CPDk3–5)3Phen films.
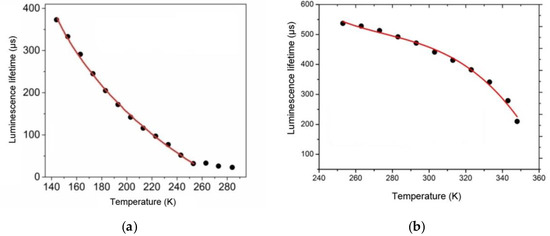
Figure 6.
Temperature dependence of the luminescence lifetime of the Tb (CPDk3–7)3Phen films (a) and the Eu(CPDk3–5)3Phen (b) complexes.
We previously demonstrated [29] that the major quenching route of luminescence of Tb3+ ions in the Tb(CPDK3–7)3Phen film is the energy back transfer from the 5D4 level of the Tb3+ ion to the T1 state of the ligands and the subsequent non-radiative relaxation. The paper [30] shows that the low-lying ligand-to-metal charge transfer (LMCT) states are responsible for the strong luminescence quenching from the 5D0 level in the Eu(CPDK3–5)3Phen film at high temperatures.
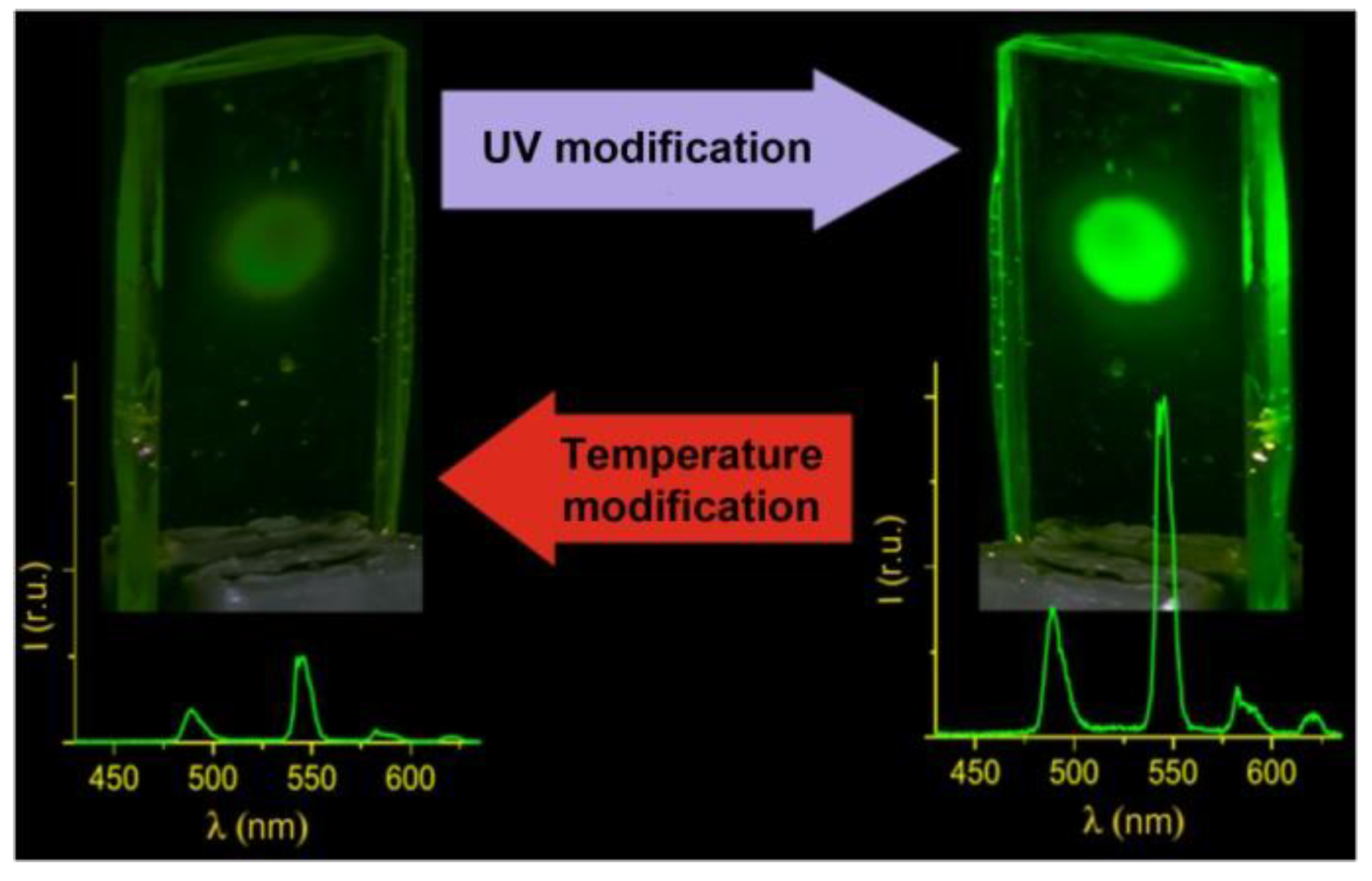
At room temperature, the vitrified Tb(CPDK3–7)3Phen film demonstrates substantial increase of the luminescence intensity of the Tb3+ ions under UV laser radiation (Figure 7) that is untypical for classical β-diketonate complexes [18]. In the context of potential applications, it is interesting that the modified luminescence brightness of the films is sustainable for several months, while the films return to their initial state after thermal processing. Experiments confirmed that it is possible to perform multiple switching of the luminescence brightness. The films with such characteristics provide potential solutions for creating brand-new molecular photonics devices, such as multiple use luminescent UV sensors, which can “remember” their modified state for several months.
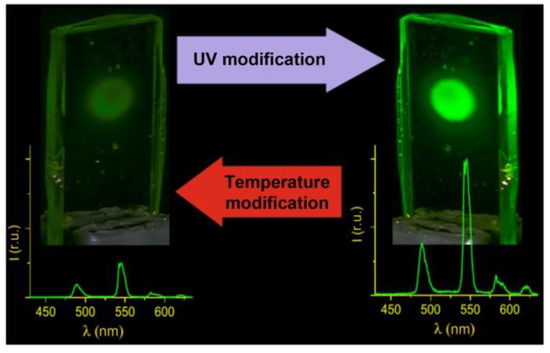
Figure 7.
Laser control and temperature switching of luminescence intensity in photostable transparent film based on the terbium(III) β-diketonate complex.
4. Conclusions
In this paper, we proposed a simple method for creating microscale luminescent film materials with controlled optical properties based on anisometric compounds of Tb(III) and Eu(III) for applications in optics and photonics. The presence of long alkyl substituents in the structure of ligands prevents them from destruction by melting, reduces melting and glass transition temperatures, and minimizes conditions that favor formation of crystalline defects. The anisometric complexes synthesized within the framework of this research are capable of transforming UV radiation into visible light. Thus, this research resulted in fabrication of highly photostable and uniform transparent films with possible application as reusable sensors and light converters.
Author Contributions
The work described in this article is the collaborative development of all authors. Conceptualization, A.K. and Y.G.; Methodology, A.K. and Y.G.; Software, M.K.; Validation, A.K., M.K. and Y.G.; Formal Analysis, M.K.; Investigation, A.K., M.K. and Y.G.; Resources, Y.G.; Data Curation, A.K. and Y.G.; Writing-Original Draft Preparation, A.K. and M.K.; Writing-Review & Editing, Y.G.; Supervision, A.K. and Y.G.
Funding
This research was funded by Russian Science Foundation (grant No. 18-13-00112).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thanks the Russian Science Foundation (grant No. 18-13-00112) for funding this research work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chu, T.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Ng, S.W. A novel electrophoretic deposited coordination supramolecular network film for detecting phosphate and biophosphate. Chem. A Eur. J. 2017, 23, 7748–7754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, H.; Wang, S.; Rao, Z.; Yang, Y. A luminescent Terbium-Succinate MOF thin film fabricated by electrodeposition for sensing of Cu2+ in aqueous environment. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 2015, 220, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; Gao, J.; Deng, S.; Zhang, R.; Zheng, Y. Dual-target optical sensors assembled by lanthanide complex incorporated sol–gel-derived polymeric films. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2016, 78, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, H.; Kuyama, M.; Seo, J.; Goto, T.; Matsumoto, T.; Ogo, S. Luminescent Tb (III) and Sm (III) complexes with a 1, 4, 7-triazacyclononane-based tris-aryloxide ligand for high-performance oxygen sensors. Dalt. Trans. 2017, 46, 9126–9130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, C.; Ma, L.; Wei, H.; Liu, Z.; Bian, Z.; Huang, C. Advances in luminescent lanthanide complexes and applications. Sci. Chin. Technol. Sci. 2018, 61, 1265–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Liu, D.; Tian, C.; Wang, S.; Li, H. Flexible and transparent films consisting of lanthanide complexes for ratiometric luminescence thermometry. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 519, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Xie, J.; Yin, X.; Silver, M.A.; Cai, Y.; Chai, Z. Monitoring ultraviolet radiation dosage based on a luminescent lanthanide metal–organic framework. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 8714–8717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SeethaLekshmi, S.; Ramya, A.R.; Reddy, M.L.P.; Varughese, S. Lanthanide complex-derived white-light emitting solids: A survey on design strategies. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2017, 33, 109–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Zhao, Z.; Wei, C.; Yu, G.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, B.; Huang, C. Antiphotobleaching: A type of structurally rigid chromophore ready for constructing highly luminescent and highly photostable europium complexes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 2085–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.D.; Wolfbeis, O.S.; Meier, R.J. Luminescent probes and sensors for temperature. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 7834–7869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brites, C.D.S.; Millán, A.; Carlos, L.D. Lanthanides in luminescent thermometry. In Handbook on the Physics and Chemistry of Rare Earths; Bünzli, J.-C., Pecharsky, V.K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 49, pp. 339–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, H. Luminescent materials of zeolite functionalized with lanthanides. CrystEngComm 2014, 16, 9764–9778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Zhang, H. Hybrid materials based on lanthanide organic complexes: A review. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 387–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knyazev, A.A.; Krupin, A.S.; Heinrich, B.; Donnio, B.; Galyametdinov, Y.G. Controlled polarized luminescence of smectic lanthanide complexes. Dyes Pigment. 2018, 148, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knyazev, A.A.; Krupin, A.S.; Molostova, E.Y.; Romanova, K.A.; Galyametdinov, Y.G. Influence of structural anisotropy on mesogenity of Eu (III) adducts and optical properties of vitrified films formed on their base. Inorg.Chem. 2015, 54, 8987–8993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knyazev, A.A.; Karyakin, M.E.; Romanova, K.A.; Heinrich, B.; Donnio, B.; Galyametdinov, Y.G. Influence of Lewis bases on the mesogenic and luminescent properties of homogeneous films of europium(III) tris (β-diketonate) adducts. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 2017, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapaev, D.V.; Nikiforov, V.G.; Lobkov, V.S.; Knyazev, A.A.; Galyametdinov, Y.G.; Shukhina, K.L. Effect of photochemical and photophysical processes with the participation of oxygen on the luminescent properties of a film of a terbium(III) β-diketonate complex. Bull. Russ. Acad. Sci. Phys. 2018, 82, 1022–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapaev, D.V.; Nikiforov, V.G.; Safiullin, G.M.; Lobkov, V.S.; Salikhov, K.M.; Knyazev, A.A.; Galyametdinov, Y.G. Laser control and temperature switching of luminescence intensity in photostable transparent film based on terbium (III) β-diketonate complex. Opt. Mater. 2014, 37, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapaev, D.V.; Nikiforov, V.G.; Safiullin, G.M.; Lobkov, V.S.; Knyazev, A.A.; Krupin, A.S.; Galyametdinov, Y.G. Changes in luminescent properties of vitrified films of terbium (III) β-diketonate complex upon UV laser irradiation. J. Lumin. 2016, 175, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knyazev, A.A.; Karyakin, M.E.; Krupin, A.S.; Romanova, K.A.; Galyametdinov, Y.G. Influence of Eu(III) complexes structural anisotropy on luminescence of doped conjugated polymer blends. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 6067–6075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galyametdinov, Y.G.; Knyazev, A.A.; Dzhabarov, V.I.; Cardinaels, T.; Driesen, K.; Görller-Walrand, C.; Binnemans, K. Polarized luminescence from aligned samples of nematogenic lanthanide complexes. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knyazev, A.A.; Dzhabarov, V.I.; Lapaev, D.V.; Lobkov, V.S.; Haase, W.; Galyametdinov, Y.G. New nematogenic β-diketones for synthesis of lanthanidomesogens. Russ. J. Gen. Chem. 2010, 80, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapaev, D.V.; Nikiforov, V.G.; Safiullin, G.M.; Lobkov, V.S.; Knyazev, A.A.; Krupin, A.S.; Galyametdinov, Y.G. UV laser-induced enhancement of photoluminescence intensity in vitrified terbium(III) β-diketonate complex film in air. J. Lumin. 2018, 194, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnemans, K. Rare-earth beta-diketonates. In Handbook on the Physics and chemistry of Rare Earths; Gschneidner, K.A., Bünzli, J.-C., Pecharsky, V.K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; Volume 35, pp. 107–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nockemann, P.; Beurer, E.; Driesen, K.; Van Deun, R.; Van Hecke, K.; Van Meervelt, L.; Binnemans, K. Photostability of a highly luminescent europium β-diketonate complex in imidazolium ionic liquids. Chem. Commun. 2005, 134, 4354–4356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faustino, W.M.; Junior, S.A.; Thompson, L.C.; De Sá, G.F.; Malta, O.L.; Simas, A.M. Theoretical and experimental luminescence quantum yields of coordination compounds of trivalent europium. Internat. J. Quant. Chem. 2005, 103, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanova, K.A.; Datskevich, N.P.; Taidakov, I.V.; Vitukhnovskii, A.G.; Galyametdinov, Y.G. Luminescent characteristics of some mesogenic tris(β-diketonate) europium(III) complexes with Lewis bases. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. A 2013, 87, 2108–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolov, P.; Fratev, F.; Petkov, I.; Markov, P. Dimer fluorescence of some β-dicarbonyl compounds. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1981, 83, 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapaev, D.V.; Nikiforov, V.G.; Lobkov, V.S.; Knyazev, A.A.; Galyametdinov, Y.G. A photostable vitrified film based on a terbium (III) β-diketonate complex as a sensing element for reusable luminescent thermometers. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 9475–9481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapaev, D.V.; Nikiforov, V.G.; Lobkov, V.S.; Knyazev, A.A.; Galyametdinov, Y.G. Reusable temperature-sensitive luminescent material based on vitrified film of europium(III) b-diketonate complex. Opt. Mater. 2018, 75, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).