Unlocking Spectral Versatility from Broadly−Tunable Quantum−Dot Lasers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
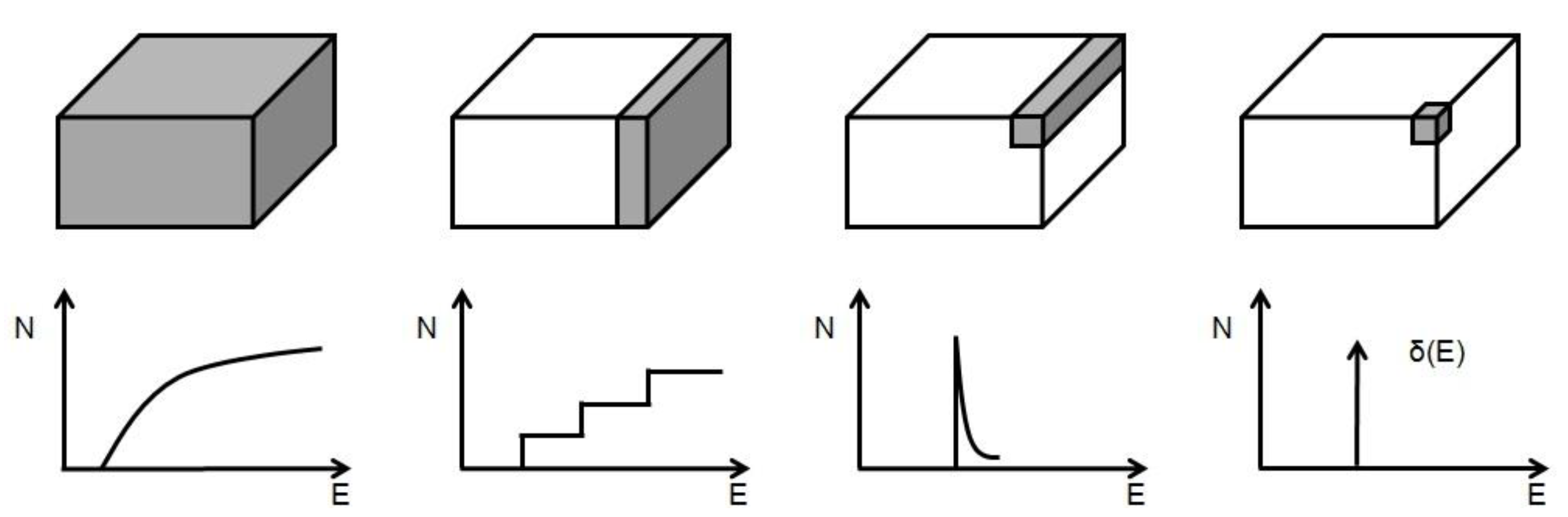
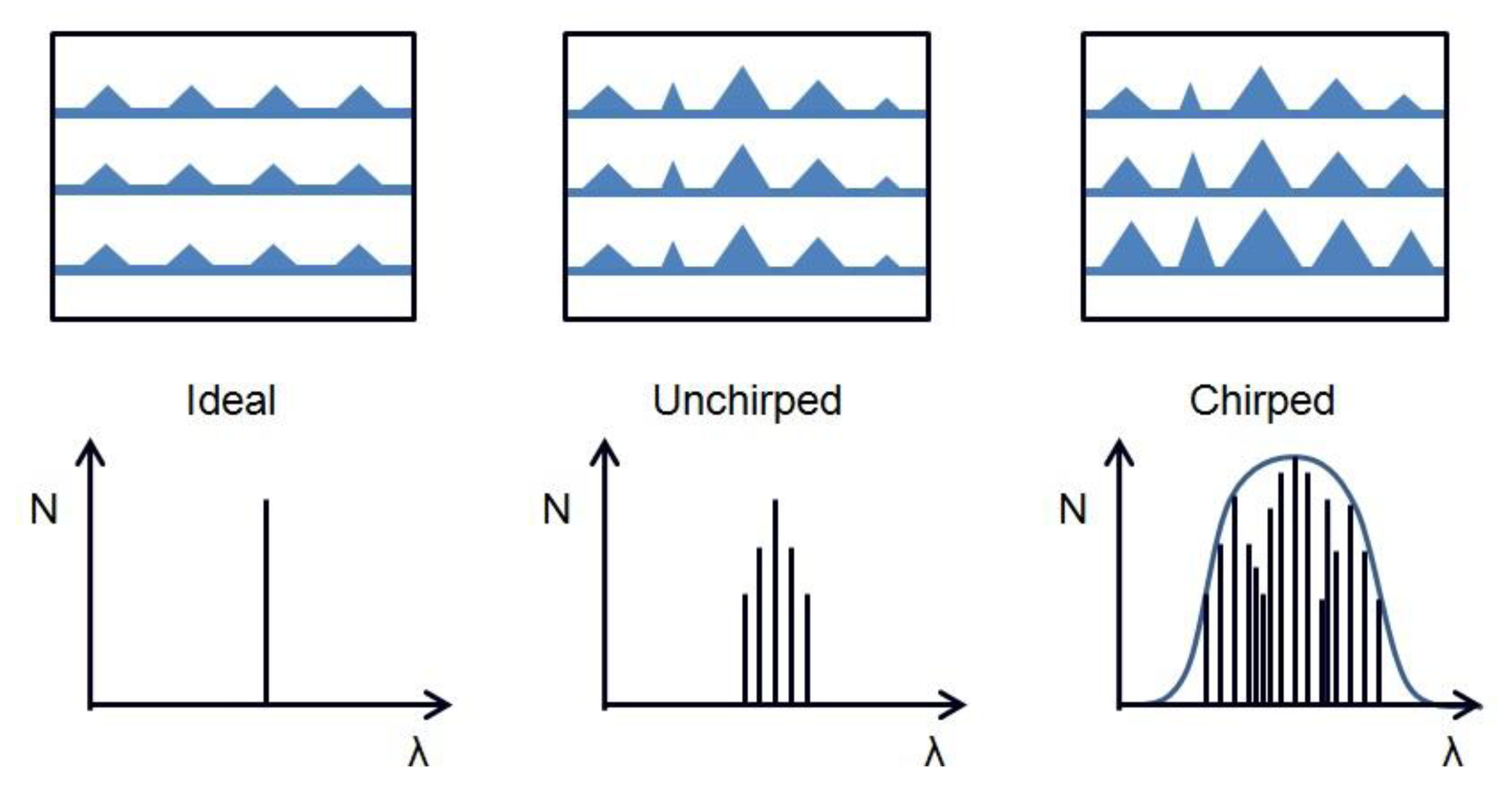
2. Quantum−Dot Lasers: Exploiting Quantum Confinement and Inhomogeneous Broadening
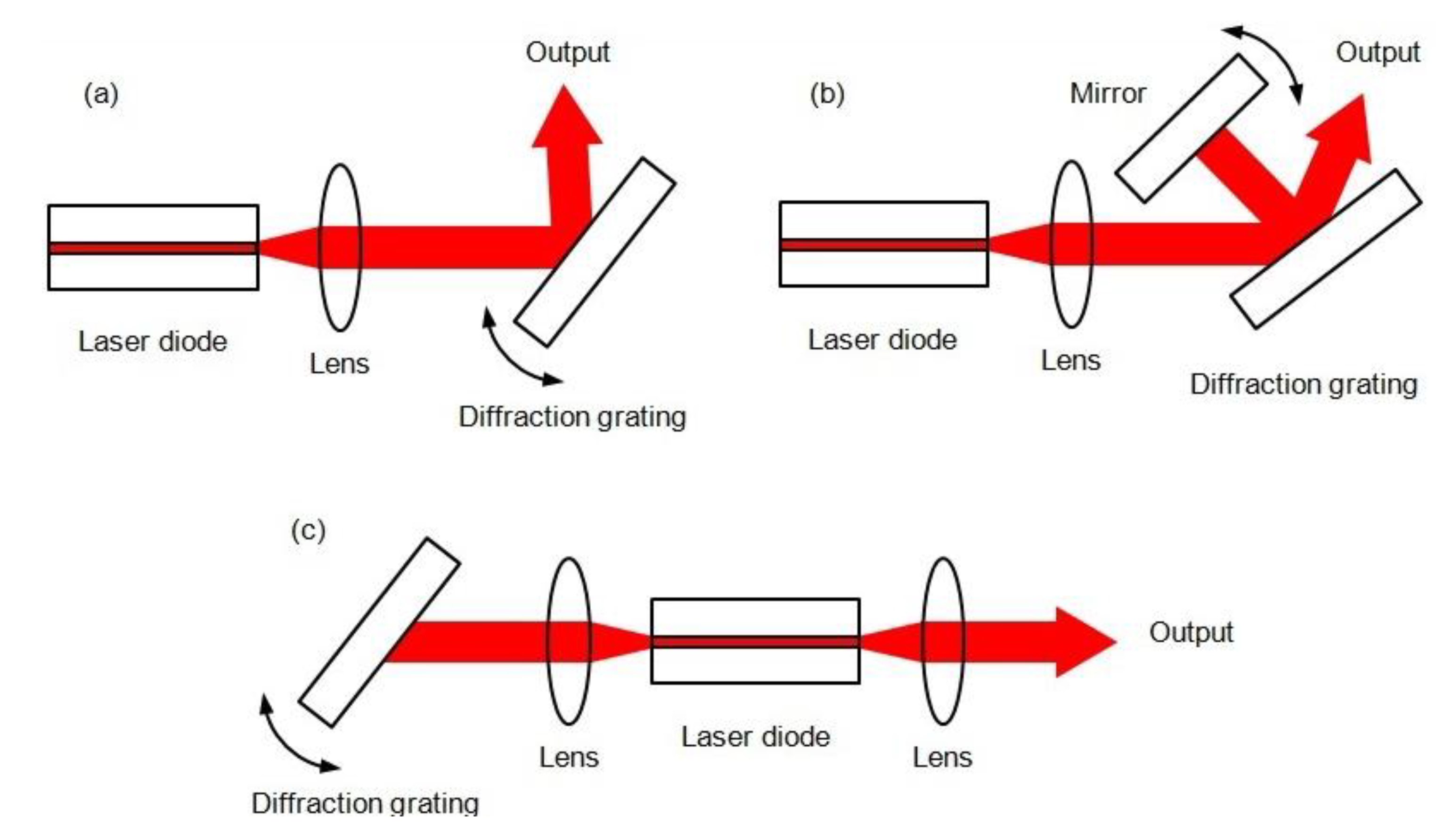
3. Broadly−Tunable Lasers: Typical Architectures
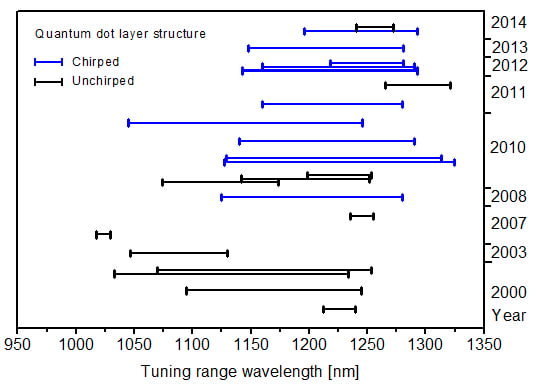
4. State of the Art in the Development of Continuous Wave Tunable QD Lasers
| Year | Laser Details | Minimum Threshold Ith/Jth | Maximum Power | Peak λ/Linewidth | λ Tuning Range | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 30 μm × 2 mm diode, 1x InAs QD layer in InGaAs QW, in a G−ECL (Littman−Metcalf) | 88 mA 0.147 kA/cm2 | 120 mW (peak power) | 1231 nm | 28 nm (1212–1240 nm) | [39] |
| 2000 | 9 μm × 2 mm RWG, 1 × InAs QD layer in InGaAs QW, in a G−ECL | 45 mA 0.25 kA/cm2 | 10 mW (peak power) | 1230 nm / < 3 nm | 150 nm (1095–1245 nm) | [40] |
| 2000 | 9 μm × 1.7 mm RWG, 1 × InAs QD layer in InGaAs QW, in a G−ECL | 0.3 kA/cm2 | 1050 nm | 201 nm (1033–1234 nm) | [41] | |
| 9 μm × 2 mm RWG, 1 × InAs QD layer in InGaAs QW, in a G−ECL | 0.25 kA/cm2 | 1090 nm | 183 nm (1070–1253 nm) | |||
| 2003 | 5 μm × 1.6 mm RWG, 7 × InAs/GaAs QD layers, in a G−ECL (Littrow) | 235 mA 2.94 kA/cm2 | ~1090 nm/ 0.8 nm | 83 nm (1047–1130 nm) | [42] | |
| 2007 | 5 μm × 750 μm RWG laser diode (two separate sections 250 μm and 500 μm long), 5 InAs/GasAs QD layers. λ tuning by current change. | 0.15 kA/cm2 | 1023 nm / < 125 pm | 11.7 nm (1017.4–1029.1 nm) | [37,43] | |
| 2007 | 100 μm × 1.5 mm diode in a Littman G−ECL | 170 mA 0.113 kA/cm2 | 140 mW | 1240 nm/ 0.07–0.1 nm | 20 nm (1235–1255 nm) | [33] |
| 2008 | 5 μm wide bent RWG, 10 non−identical InAs QD layers in a G−ECL | 630 mW | 1180 nm/ 200 kHz (0.9 fm) | 155 nm (1125–1280 nm) | [44] | |
| 2010 | 120 μm × 1 mm device, 5 layers of InAs QDs in a G−ECL | ~0.57 kA/cm2 | 65 mW | 1120 nm/ < 2 nm | 100 nm (1073.9–1173.8 nm) | |
| 120 μm × 2 mm device, 5 layers of InAs QDs in a G−ECL | ~0.22 kA/cm2 | 53 mW | 1180 nm/ < 2 nm | 110.1 nm (1141.6–1251.7 nm) | ||
| 120 μm × 3 mm device, 5 layers of InAs QDs in a G−ECL | 0.117 kA/cm2 | 54 mW | 1240 nm/ < 2 nm | 55 nm (1198.2–1253.1 nm) | ||
| 2010 | 5 μm × 4 mm gain chip based on 10 non−identical InAs QD layers in a G−ECL with 20% [or no] OC | 2.0 kA/cm2 [0.34 kA/cm2] | 138mW [480mW] | 1150 nm [1220 nm] | 197.5 nm (1127−1324.5 nm) [184.5 nm (1129–1313.5 nm)] | [22] |
| 2010 | 5μm × 4mm SOA, 10 non−identical InAs QD layers in a G−ECL with 4% R OC | not stated | 230 mW | 1213 nm/ 0.12 nm | 150 nm (1140–1290 nm) | [13] |
| 2010 | 5 μm × 2.5 mm RWG, 11 non−identical InAs QD layers in a G−ECL | ~2.15 A | 200 mW | 1200 nm/ ~1 nm | 207.7 nm (1038.3–1246 nm) | [8] |
| 2011 | 5 μm × 4 mm SOA, 10 non−identical InAs QD layers in a G−ECL | not stated | 16 mW | 1220 nm | 120 nm sweep range (~1160–1280 nm) | [14] |
| 2011 | 3.4 μm × 1.95 mm gain chip, 7 identical layers SSNS−grown InAs/InGaAs structure. ECL with narrow optical band−pass and etalon filters used for λ control. | 60 mA 0.9 kA/cm2 | 3.01 mW | 1300 nm/ 210 kHz | 56 nm (1265–1321 nm) | [34] |
| 2012 | 5 μm × 1.5 mm RWG, 10 non−identical InAs QD layers in a G−ECL | 100 mA 1.33 kA/cm2 | 27 mW | 1180 nm/ <0.5 nm | 150 nm (1143–1293 nm) | [45] |
| 5 μm × 2 mm RWG, 10 non−identical InAs QD layers in a G−ECL | 75 mA 0.75 kA/cm2 | 37 mW | 1240 nm/ <0.5 nm | 130 nm (1160–1290 nm) | ||
| 5 μm × 3 mm RWG, 10 non−identical InAs QD layers in a G−ECL | 50 mA 0.33 kA/cm2 | 40 mW | 1260 nm/ <0.5 nm | 63 nm (1218–1281 nm) | ||
| 2013 | 5 μm × 1.5 mm device, 10 non−identical QD layers in a double Littman G−ECL | 50 mA 0.66 kA/cm2 | 5.5 mW | 1180 nm | Dual−wavelength tunability within 1150–1276 nm, with max λ separation of 126 nm | [46] |
| 2014 | 6 mm long tapered SOA, width 14 μm at start, 81 μm at end, 10 chirped InAs QD layers in a G−ECL | 500 mA 0.31 kA/cm2 | 620 mW | 1230 nm/ ~0.3 nm | 96.8 nm (1195.8–1292.6 nm) | [7] |
| 6 mm long tapered SOA, width 14 μm at start, 81 μm at end, 15 identical InAs QD layers in a G−ECL | 300 mA 0.24 kA/cm2 | 970 mW | 1254 nm/ ~0.3 nm | 31.6 nm (1240.4–1272 nm) |
4.1. Optimization of Threshold Current
4.2. Maximising Tuning Range
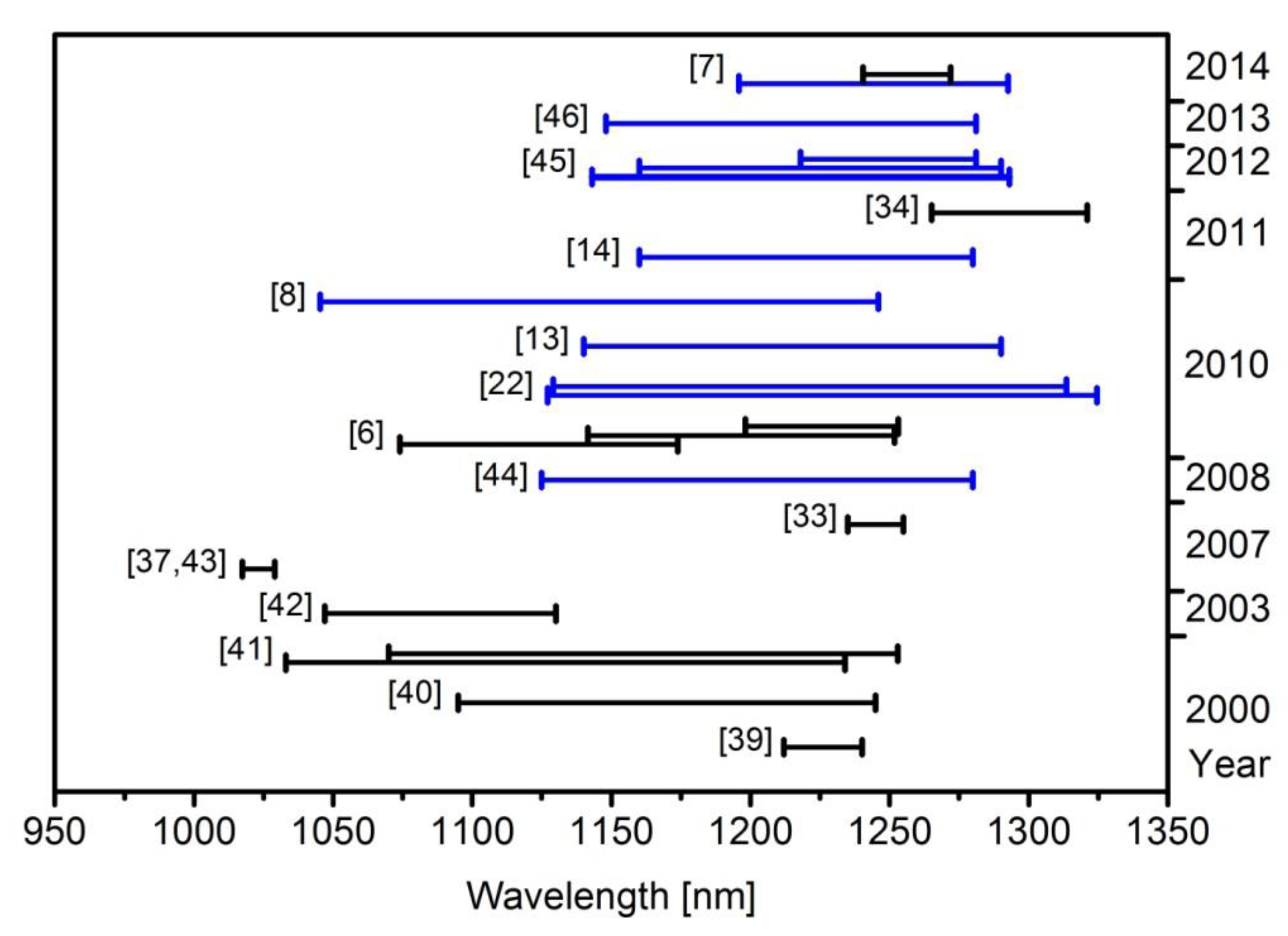
4.3. Maximising Power
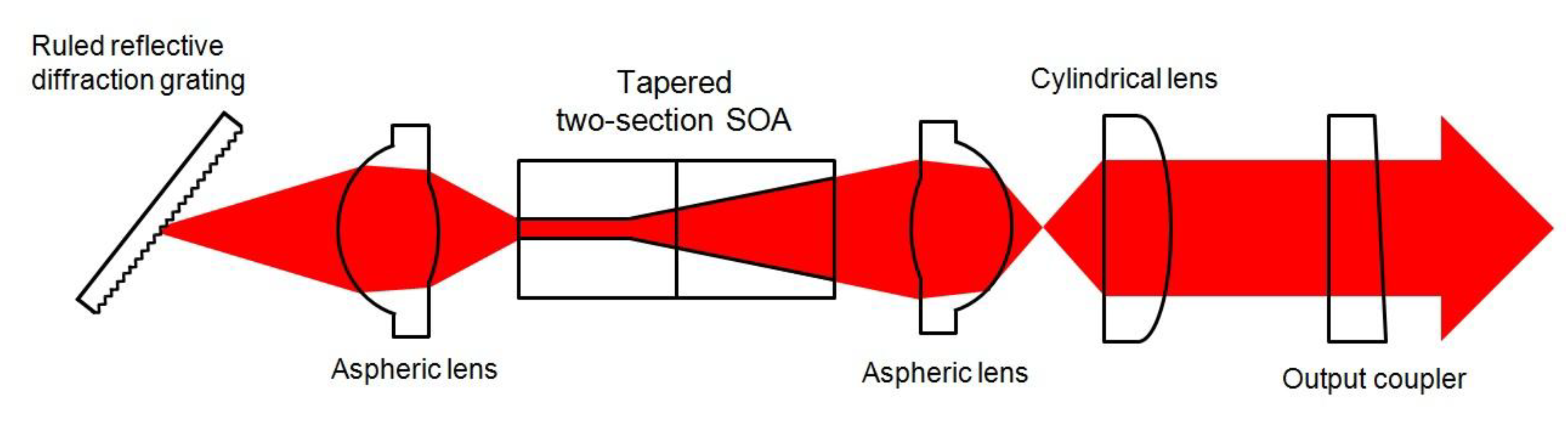
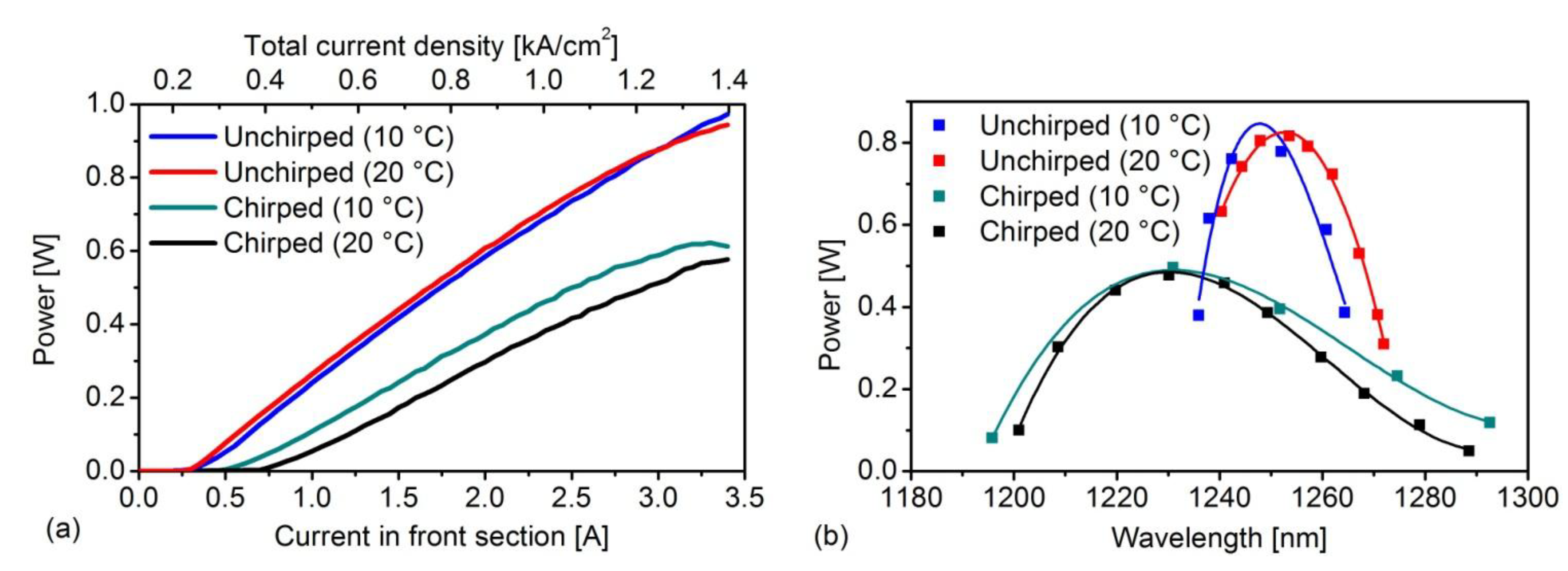
5. State of the Art in the Development of Tunable Mode−Locked QD Lasers
| Year | Laser Details | Peak λ/Spectral Bandwidth | λ Tuning Range | Maximum Power | Pulse Details | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2006 | 5 μm × 2 mm two−section device, 10 identical layers of InAs/GaAs QDs, G−ECL + 1.8 mm QD SOA | GS ~ 1274 nm ES ~ 1190 nm/ ~0.4 nm | GS: 30 nm (1265–1295 nm) ES: 50.5 nm (1170–1220 nm) | not stated | Passive ML. GS (λ = 1273 nm): Δτ = 6.6 ps. ES (λ = 1200 nm): Δτ = 12 ps. frep = 2.5 GHz. | [57] |
| 2010 | 10 GHz devices, with a saturable absorber−to−total−length ratio of either 17% or 12% | 1291–1299 nm | 8 nm (1290–1298 nm) | 1 mW average power | Passive ML + injection locking | [38] |
| 2011 | 6 μm × 4 mm multi−section RWG, 5 layers of InAs/InGaAs QDs | 1280 nm | λ separation of two GS sub−bands tunable by 2–14 nm | Passive ML, Δτ ~ 17ps, frep = 10 GHz. | [68] | |
| 2012 | 6 μm × 4 mm RWG gain chip in a G−ECL with 6 mm long tapered SOA, width 14μm at start, 81μm at end, both with 10 chirped InAs/GaAs QD layers | 1226 nm/ ~2.5 nm | 96 nm (1187–1283 nm) | 4.39 W peak power (~92 mW average power) | Passive ML, shortest Δτ = 15 ps with 1.316 GHz frep achieved within λ tuning range conditions | [58] |
| 2012 | 6μm × 4mm RWG, 10 chirped InAs QD layers in a G−ECL | 1226 nm/ ~1 nm | 136 nm (1182.5–1319 nm) | 870 mW peak power (10.5 mW average power) | Passive ML, Δτ = 12.8–39 ps, frep = 740 MHz. | [59] |
| 2012 | 3.4 μm × 3.9 mm RWG, 7 non−identical InAs QD layers in an ECL. λ tuning by band−pass filter | 1294.9 nm/ 0.25 nm | 32 nm (1262.9–1294.9 nm) | Active ML, Δτ = 10–15 ps, frep = 1 GHz. | [64] | |
| 2013 | 6 μm × 4 mm multisection RWG, 10 chirpedInAs QD layers. λ tuned by variation in reverse bias. | 1245 nm/ 4.8 nm | 45 nm (1245–1290 nm) | 27 mW average power | Passive ML, shortest Δτ = 3.3 ps, frep = 10 GHz achieved within λ tuning range | [36] |
| 2013 | 3.4 μm × 3.9 mm RWG, 7 nonidentical InAs QD layers. λ tuning by band−pass filter | 1255 nm | 100 nm (1200–1300 nm) | Active ML, Δτ ~ 14−20ps, frep = 1GHz. | [65] | |
| 2013 | Gain device comprised 10 layers InAs QDs in EC, λ tuning by prism rotation | 1183.5 nm | 35.7 nm (1147.8–1183.5 nm) | 16 mW average power | Passive ML via SESAM frep = 520 MHz | [61] |
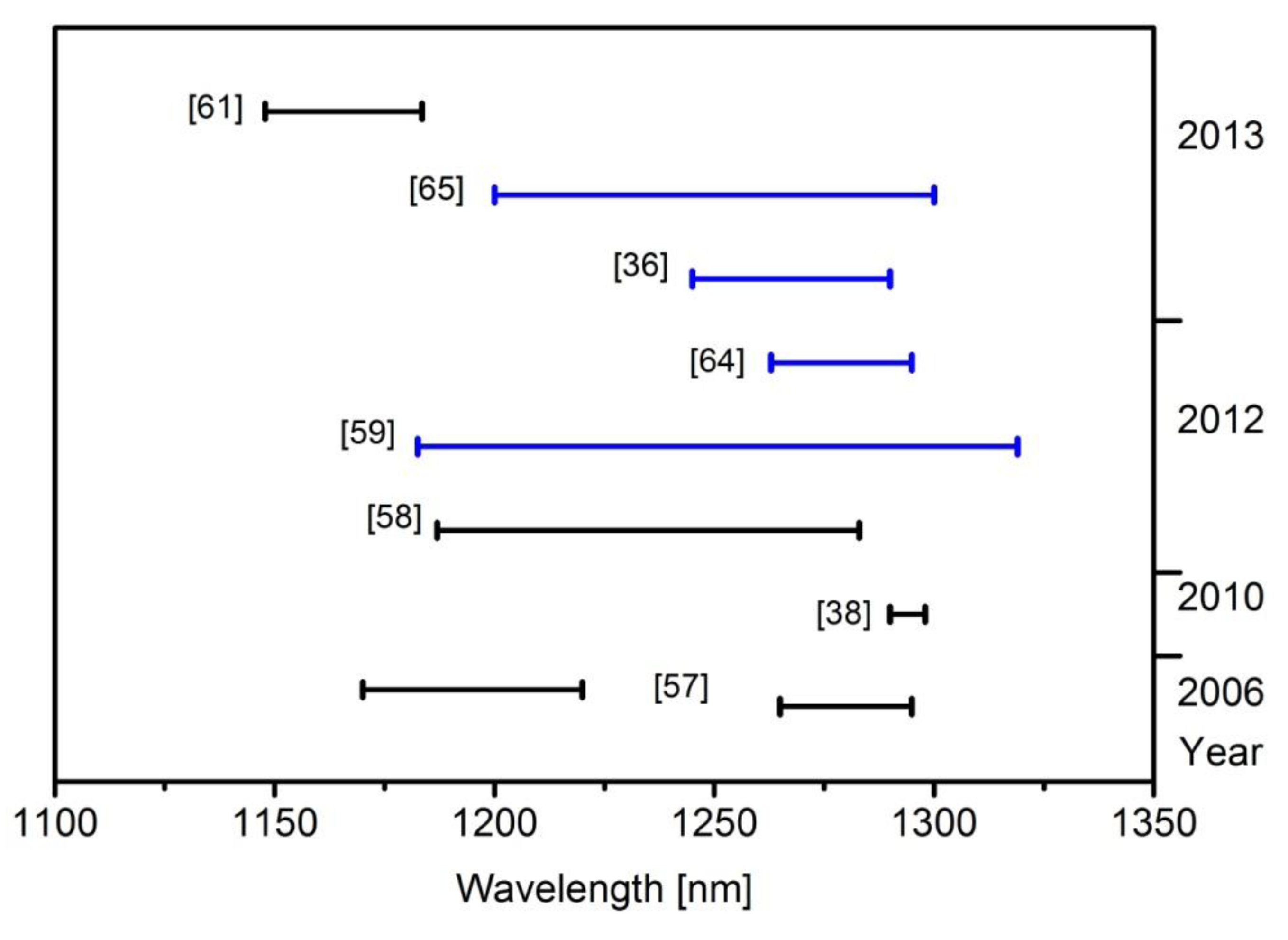
6. Applications
7. Conclusions and Outlook
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Dingle, R.; Henry, C.H. Quantum effects in heterostructure lasers. US Patent No. 3982207, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Arakawa, Y.; Sakaki, H. Multidimensional quantum well laser and temperature dependence of its threshold current. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1982, 40, 939–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, L.; Glas, F.; Marzin, J.; Charasse, M.; Le Roux, G. Growth by molecular beam epitaxy and characterization of InAs/GaAs strained-layer superlattices. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1985, 47, 1099–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledentsov, N.; Ustinov, V.; Egorov, A.Y.; Zhukov, A.; Maksimov, M.; Tabatadze, I.; Kop'ev, P. Optical properties of heterostructures with InGaAs−GaAs quantum clusters. Semiconductors 1994, 28, 832–834. [Google Scholar]
- Kirstaedter, N.; Ledentsov, N.N.; Grundmann, M.; Bimberg, D.; Ustinov, V.M.; Ruvimov, S.S.; Maximov, M.V.; Kop'ev, P.S.; Alferov, Z.I.; Richter, U.; et al. Low threshold, large To injection laser emission from (InGa)As quantum dots. Electron. Lett. 1994, 30, 1416–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.Q.; Jin, P.; Wang, W.Y.; Wang, Z.G. Broadband external cavity tunable quantum dot lasers with low injection current density. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 8916–8922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haggett, S.; Krakowski, M.; Montrosset, I.; Cataluna, M.A. High−power quantum−dot tapered tunable external−cavity lasers based on chirped and unchirped structures. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 22854–22864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, X.; Jin, P.; Wang, Z. Broadly tunable grating−coupled external cavity laser with quantum−dot active region. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 2010, 22, 1799–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, W.M.; Eichfelder, M.; Roßbach, R.; Jetter, M.; Michler, P. InP/AlGaInP quantum dot laser emitting at 638 nm. J. Cryst. Growth 2011, 315, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustinov, V.M.; Zhukov, A.E.; Egorov, A.Y.; Kovsh, A.R.; Zaitsev, S.V.; Gordeev, N.Y.; Kopchatov, V.I.; Ledentsov, N.N.; Tsatsul'nikov, A.F.; Volovik, B.V.; et al. Low threshold quantum dot injection laser emitting at 1.9 μm. Electron. Lett. 1998, 34, 670–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustinov, V.M.; Zhukov, A.E.; Egorov, A.Y.; Maleev, N.A. Quantum dot lasers; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Orr, B.J.; He, Y. Rapidly swept continuous−wave cavity−ringdown spectroscopy. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2011, 512, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorova, K.; Cataluna, M.; Battle, P.; Kaleva, C.; Krestnikov, I.; Livshits, D.; Rafailov, E. Orange light generation from a PPKTP waveguide end pumped by a CW quantum−dot tunable laser diode. Appl. Phys. B 2011, 103, 41–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krstajic, N.; Childs, D.T.; Matcher, S.; Livshits, D.; Shkolnik, A.; Krestnikov, I.; Hogg, R. Swept−source laser based on quantum−dot semiconductor optical amplifier—applications in optical coherence tomography. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 2011, 23, 739–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Aviles−Espinosa, R.; Cataluna, M.; Nikitichev, D.; Ruiz, M.; Tran, M.; Robert, Y.; Kapsalis, A.; Simos, H.; Mesaritakis, C.; et al. High peak−power picosecond pulse generation at 1.26 µm using a quantum−dot−based external−cavity mode−locked laser and tapered optical amplifier. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 14308–14320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobat, D.; Durst, M.E.; Nishimura, N.; Wong, A.W.; Schaffer, C.B.; Xu, C. Deep tissue multiphoton microscopy using longer wavelength excitation. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 13354–13364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledentsov, N.N.; Grundmann, M.; Heinrichsdorff, F.; Bimberg, D.; Ustinov, V.; Zhukov, A.; Maximov, M.; Alferov, Z.I.; Lott, J. Quantum−dot heterostructure lasers. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2000, 6, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhukov, A.; Kovsh, A.; Ustinov, V. Temperature dependence of the gain of lasers based on quantum−dot arrays with an inhomogeneously broadened density of states. Semiconductors 1999, 33, 1260–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasaimeh, O. Effect of inhomogeneous line broadening on gain and differential gain of quantum dot lasers. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2003, 50, 1575–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafailov, E.U.; Cataluna, M.A.; Sibbett, W. Mode−locked quantum−dot lasers. Nat. Photon. 2007, 1, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovsh, A.; Krestnikov, I.; Livshits, D.; Mikhrin, S.; Weimert, J.; Zhukov, A. Quantum dot laser with 75 nm broad spectrum of emission. Opt. Lett. 2007, 32, 793–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedorova, K.A.; Cataluna, M.A.; Krestnikov, I.; Livshits, D.; Rafailov, E.U. Broadly tunable high−power InAs/GaAs quantum−dot external cavity diode lasers. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 19438–19443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.Z.; Ding, D.; Gong, Q.; Zhou, W.; Xu, B.; Wang, Z.G. Quantum−dot superluminescent diode: A proposal for an ultra−wide output spectrum. Opt. Quantum Electron. 1999, 31, 1235–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, D.C.; Song, J.D.; Choi, W.J.; Lee, J.I.; Jung, J.C.; Han, I.K. High power broadband InGaAs/GaAs quantum dot superluminescent diodes. Electron. Lett. 2003, 39, 863–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Wang, Z.G.; Xu, B.; Jin, P.; Sun, Z.Z.; Liu, F.Q. High−performance quantum−dot superluminescent diodes. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 2004, 16, 27–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Rossetti, M.; Fiore, A.; Occhi, L.; Vélez, C. Wide emission spectrum from superluminescent diodes with chirped quantum dot multilayers. Electron. Lett. 2005, 41, 41–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.K.; Groom, K.M.; Beattie, M.D.; Liu, H.Y.; Hopkinson, M.; Hogg, R.A. Broad−band superluminescent light−emitting diodes incorporating quantum dots in compositionally modulated quantum wells. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 2006, 18, 58–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossetti, M.; Li, L.; Markus, A.; Fiore, A.; Occhi, L.; Vélez, C.; Mikhrin, S.; Krestnikov, I.; Kovsh, A. Characterization and modeling of broad spectrum InAs−GaAs quantum−dot superluminescent diodes emitting at 1.2−1.3 μm. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 2007, 43, 676–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.X.; Markus, A.; Fiore, A.; Oesterle, U.; Stanley, R.P.; Carlin, J.F.; Houdré, R.; Ilegems, M.; Lazzarini, L.; Nasi, L.; et al. Tuning InAs/GaAs quantum dot properties under Stranski−Krastanov growth mode for 1.3 μm applications. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 91, 6710–6716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishi, K.; Saito, H.; Sugou, S.; Lee, J.-S. A narrow photoluminescence linewidth of 21 meV at 1.35 μm from strain−reduced InAs quantum dots covered by In0.2Ga0.8As grown on GaAs substrates. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1999, 74, 1111–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volovik, B.; Tsatsul’nikov, A.; Bedarev, D.; Egorov, A.Y.; Zhukov, A.; Kovsh, A.; Ledentsov, N.; Maksimov, M.; Maleev, N.; Musikhin, Y.G. Long−wavelength emission in structures with quantum dots formed in the stimulated decomposition of a solid solution at strained islands. Semiconductors 1999, 33, 901–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Wei, T.K. Tunable external cavity diode lasers; World Scientific: Hackensack, NJ, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Tierno, A.; Ackemann, T. Tunable, narrow−band light source in the 1.25 μm region based on broad−area quantum dot lasers with feedback. Appl. Phys. B 2007, 89, 585–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, N.; Akahane, K.; Kawanishi, T.; Omigawa, Y.; Sotobayashi, H.; Yoshioka, Y.; Takai, H. Narrow−line−width 1.31−μm wavelength tunable quantum dot laser using sandwiched sub−nano separator growth technique. Opt. Express 2011, 19, B636–B644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiser, W.; Deubert, S.; Reithmaier, J.; Forchel, A. Singlemode tapered quantum dot laser diodes with monolithically integrated feedback gratings. Electron. Lett. 2007, 43, 926–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikitichev, D.I.; Cataluna, M.A.; Fedorova, K.A.; Ding, Y.; Mikhrin, S.S.; Krestnikov, I.L.; Livshits, D.A.; Rafailov, E.U. High−power wavelength bistability and tunability in passively mode−locked quantum−dot laser. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quant. Electron. 2013, 19, 1100907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, B.; Childs, D.; Groom, K.; Hopkinson, M.; Hogg, R. All semiconductor swept laser source utilizing quantum dots. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 91, 121119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habruseva, T.; O'Donoghue, S.; Rebrova, N.; Reid, D.A.; Barry, L.P.; Rachinskii, D.; Huyet, G.; Hegarty, S.P. Quantum−dot mode−locked lasers with dual mode optical injection. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 2010, 22, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliseev, P.; Li, H.; Stintz, A.; Liu, G.; Newell, T.; Malloy, K.; Lester, L. Tunable grating−coupled laser oscillation and spectral hole burning in an InAs quantum−dot laser diode. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 2000, 36, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, G.; Varangis, P.; Newell, T.; Stintz, A.; Fuchs, B.; Malloy, K.; Lester, L. 150−nm tuning range in a grating−coupled external cavity quantum−dot laser. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 2000, 12, 759–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varangis, P.M.; Li, H.; Liu, G.T.; Newell, T.C.; Stintz, A.; Fuchs, B.; Malloy, K.J.; Lester, L.F. Low−threshold quantum dot lasers with 201 nm tuning range. Electron. Lett. 2000, 36, 1544–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biebersdorf, A.; Lingk, C.; De Giorgi, M.; Feldmann, J.; Sacher, J.; Arzberger, M.; Ulbrich, C.; Böhm, G.; Amann, M.; Abstreiter, G. Tunable single and dual mode operation of an external cavity quantum−dot injection laser. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 2003, 36, 1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, B.J.; Childs, D.T.D.; Groom, K.M.; Hopkinson, M.; Hogg, R.A. A quantum dot swept laser source based upon a multisection laser device. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 47, 2965–2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevsky, A.Y.; Bressel, U.; Ernsting, I.; Eisele, C.; Okhapkin, M.; Schiller, S.; Gubenko, A.; Livshits, D.; Mikhrin, S.; Krestnikov, I. A narrow−line−width external cavity quantum dot laser for high−resolution spectroscopy in the near−infrared and yellow spectral ranges. Appl. Phys. B 2008, 92, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Su, P.-Y.; Cheng, H.-C. Low threshold current and widely tunable external cavity lasers with chirped multilayer InAs/InGaAs/GaAs quantum−dot structure. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 3941–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pai, C.-H.; Lin, G. Tunable multiwavelength quantum dot external−cavity lasers. Proc. SPIE 2013, 8772, 87720V–87727. [Google Scholar]
- Seltzer, C.; Bagley, M.; Elton, D.; Perrin, S.; Cooper, D. 160 nm continuous tuning of an MQW laser in an external cavity across the entire 1.3 μm communications window. Electron. Lett. 1991, 27, 95–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anscombe, N. Tapered triumph. Nature Photon. 2009, 3, 24–25. [Google Scholar]
- Albrecht, A.R.; Stintz, A.; Jaeckel, F.T.; Rotter, T.J.; Ahirwar, P.; Patel, V.J.; Hains, C.P.; Lester, L.F.; Malloy, K.J.; Balakrishnan, G. 1220–1280−nm Optically Pumped InAs Quantum Dot−Based Vertical External−Cavity Surface−Emitting Laser. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2011, 17, 1787–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butkus, M.; Rautiainen, J.; Okhotnikov, O.G.; Hamilton, C.J.; Malcolm, G.; Mikhrin, S.; Krestnikov, I.L.; Livshits, D.; Rafailov, E.U. Quantum dot based semiconductor disk lasers for 1–1.3 μm. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2011, 17, 1763–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafailov, E.U.; Cataluna, M.A.; Avrutin, E.A. Ultrafast Lasers Based on Quantum Dot Structures: Physics and Devices; Wiley: Weinheim, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Cataluna, M.A.; Ding, Y.; Nikitichev, D.I.; Fedorova, K.A.; Rafailov, E.U. High−power versatile picosecond pulse generation from mode−locked quantum−dot laser diodes. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2011, 17, 1302–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, S.; Borri, P.; Langbein, W.; Woggon, U.; Sellin, R.L.; Ouyang, D.; Bimberg, D. Excited−state gain dynamics in InGaAs quantum−dot amplifiers. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 2005, 17, 2014–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piwonski, T.; Pulka, J.; Madden, G.; Huyet, G.; Houlihan, J.; Viktorov, E.A.; Erneux, T.; Mandel, P. Intradot dynamics of InAs quantum dot based electroabsorbers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 123504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataluna, M.A.; Sibbett, W.; Livshits, D.A.; Weimert, J.; Kovsh, A.R.; Rafailov, E.U. Stable mode locking via ground−or excited−state transitions in a two−section quantum−dot laser. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 081124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataluna, M.A.; Rafailov, E.U.; McRobbie, A.D.; Sibbett, W.; Livshits, D.A.; Kovsh, A.R. Ground and excited−state modelocking in a two−section quantum−dot laser. In Proceedings of the Lasers and Electro−Optics Society Annual Meeting−LEOS, Lasers and Electro−Optics Society Annual Meeting−LEOS, Sydney, Australia, 22–28 October 2005; pp. 870–871.
- Kim, J.; Choi, M.-T.; Lee, W.; Delfyett, P.J., Jr. Wavelength tunable mode−locked quantum−dot laser. Proc. SPIE 2006, 6243, 62430M–62438. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.; Alhazime, A.; Nikitichev, D.; Fedorova, K.; Ruiz, M.; Tran, M.; Robert, Y.; Kapsalis, A.; Simos, H.; Mesaritakis, C.; et al. Tunable master−oscillator power−amplifier based on chirped quantum−dot structures. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 2012, 24, 1841–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikitichev, D.; Fedorova, K.; Ding, Y.; Alhazime, A.; Able, A.; Kaenders, W.; Krestnikov, I.; Livshits, D.; Rafailov, E. Broad wavelength tunability from external cavity quantum−dot mode−locked laser. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 121107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRobbie, A.D.; Cataluna, M.A.; Zolotovskaya, S.A.; Livshits, D.A.; Sibbett, W.; Rafailov, E.U. High power all−quantum−dot−based external cavity modelocked laser. Electron. Lett. 2007, 43, 812–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Jin, P.; Li, X.-K.; Wei, H.; Wu, J.; Wang, Z.-G. Tunable mode−locked external−cavity quantum−dot laser. In Proceedings of the International Photonics and Optoelectronics Meetings (POEM), Wuhan, China, 25–26 May 2013; p. NSu2B. 3.
- Cheng, H.C.; Wu, Q.Y.; Pan, C.H.; Lee, C.P.; Lin, G. Low repetition rate and broad frequency tuning from a grating−coupled passively mode−locked quantum dot laser. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103, 211109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Cataluna, M.A.; Nikitichev, D.; Krestnikov, I.; Livshits, D.; Rafailov, E. Broad repetition−rate tunable quantum−dot external−cavity passively mode−locked laser with extremely narrow radio frequency linewidth. Appl. Phys. Express 2011, 4, 062703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, N.; Akahane, K.; Tetsuya, K.; Sotobayashi, H.; Yoshioka, Y.; Takai, H. Characterization of wavelength−tunable quantum dot external cavity laser for 1.3−μm−waveband coherent light sources. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 51, 02BG08. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, N.; Akahane, K.; Kawanishi, T.; Sotobayashi, H.; Yoshioka, Y.; Takai, H. 10−GHz high−repetition optical short pulse generation from wavelength−tunable quantum dot optical frequency comb laser. IEICE Trans. Electron. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derickson, D.J.; Helkey, R.J.; Mar, A.; Karin, J.R.; Wasserbauer, J.G.; Bowers, J.E. Short pulse generation using multisegment mode−locked semiconductor lasers. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 1992, 28, 2186–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derickson, D.J.; Morton, P.A.; Bowers, J.E.; Thornton, R.L. Comparison of timing jitter in external and monolithic cavity mode−locked semiconductor lasers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1991, 59, 3372–3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesaritakis, C.; Simos, C.; Simos, H.; Krestnikov, I.; Syvridis, D. Dual ground−state pulse generation from a passively mode−locked InAs/InGaAs quantum dot laser. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 99, 141109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataluna, M.A.; Nikitichev, D.I.; Mikroulis, S.; Simos, H.; Simos, C.; Mesaritakis, C.; Syvridis, D.; Krestnikov, I.; Livshits, D.; Rafailov, E.U. Dual−wavelength mode−locked quantum−dot laser, via ground and excited state transitions: Experimental and theoretical investigation. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 12832–12838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.-K.; Park, C.Y.; Yu, D.-H.; Park, S.E.; Lee, S.-B.; Kwon, T.Y. Generation of 578−nm yellow light over 10 mW by second harmonic generation of an 1156−nm external−cavity diode laser. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 17453–17461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedorova, K.; Sokolovskii, G.; Battle, P.; Livshits, D.; Rafailov, E. 574–647 nm wavelength tuning by second−harmonic generation from diode−pumped PPKTP waveguides. Opt. Lett. 2015, 40, 835–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedorova, K.A.; Sokolovskii, G.S.; Battle, P.R.; Livshits, D.A.; Rafailov, E.U. Green−to−red tunable SHG of a quantum−dot laser in a PPKTP waveguide. Las. Phys. Lett. 2012, 9, 790–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorova, K.; Sokolovskii, G.; Nikitichev, D.; Battle, P.; Krestnikov, I.; Livshits, D.; Rafailov, E. Orange−to−red tunable picosecond pulses by frequency doubling in a diode−pumped PPKTP waveguide. Opt. Lett. 2013, 38, 2835–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, O.B.; Hansen, A.K.; Muller, A.; Sumpf, B.; Unterhuber, A.; Drexler, W.; Petersen, P.M.; Andersen, P.E. Power scaling of nonlinear frequency converted tapered diode lasers for biophotonics. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2014, 20, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, J.M. Optical coherence tomography (OCT): A review. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 1999, 5, 1205–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, S.; Hofmann, M.R. Generation of Terahertz radiation with two color semiconductor lasers. Las. Photon. Rev. 2007, 1, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daghestani, N.; Cataluna, M.; Ross, G.; Rose, M. Compact dual−wavelength InAs/GaAs quantum−dot external−cavity laser stabilized by a single volume Bragg grating. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 2011, 23, 176–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhu, X.; Li, Q.; Guan, H.; Magill, P.; Bergman, K.; Baehr−Jones, T.; Hochberg, M. Quantum dot SOA/silicon external cavity multi−wavelength laser. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 4666–4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krakowski, M.; Resneau, P.; Calligaro, M.; Liu, H.; Hopkinson, M. High Power, Very Low Noise, CW Operation of 1.32μm Quantum−Dot Fabry−Perot Laser Diodes. In Proceedings of the IEEE 20th International Semiconductor Laser Conference, Kohala Coast, HI, USA, 17–21 September 2006; pp. 39–40.
- Capua, A.; Rozenfeld, L.; Mikhelashvili, V.; Eisenstein, G.; Kuntz, M.; Laemmlin, M.; Bimberg, D. Direct correlation between a highly damped modulation response and ultra low relative intensity noise in an InAs/GaAs quantum dot laser. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 5388–5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gubenko, A.; Krestnikov, I.; Livshtis, D.; Mikhrin, S.; Kovsh, A.; West, L.; Bornholdt, C.; Grote, N.; Zhukov, A. Error−free 10 Gbit/s transmission using individual Fabry−Perot modes of low−noise quantum−dot laser. Electron. Lett. 2007, 43, 1430–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovsh, A.; Gubenko, A.; Krestnikov, I.; Livshits, D.; Mikhrin, S.; Weimert, J.; West, L.; Wojcik, G.; Yin, D.; Bornholdt, C.; et al. Quantum dot comb−laser as efficient light source for silicon photonics. Proc. SPIE 2008, 6996, 69960V. [Google Scholar]
- Livshits, D.; Yin, D.; Gubenko, A.; Krestnikov, I.; Mikhrin, S.; Kovsh, A.; Wojcik, G. Cost−effective WDM optical interconnects enabled by quantum dot comb lasers. Proc. SPIE 2010, 7607, 76070W. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.S.; Guo, W.; Basu, D.; Bhattacharya, P. High performance tunnel injection quantum dot comb laser. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 96, 101107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yausoka, N.; Ishida, M.; Takada, K.; Yamaguchi, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Arakawa, Y. Low−noise four−wavelength simultaneous oscillation of a 1.3−μm external−cavity quantum−dot laser. Proc. SPIE 2015, 9373, 937304. [Google Scholar]
- Yasuoka, N.; Ishida, M.; Yamaguchi, M.; Uetake, A.; Yamamoto, T.; Arakawa, Y. 1.3 μm External−Cavity Quantum−Dot Comb Laser for Temperature Control Free Operation. In Proceedings of the Optical Fiber Communication Conference, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 22–26 March 2015; p. Tu3I.3.
- Smowton, P.M.; Pearce, E.J.; Schneider, H.C.; Chow, W.W.; Hopkinson, M. Filamentation and linewidth enhancement factor in InGaAs quantum dot lasers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 81, 3251–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribbat, C.; Sellin, R.L.; Kaiander, I.; Hopfer, F.; Ledentsov, N.N.; Bimberg, D.; Kovsh, A.R.; Ustinov, V.M.; Zhukov, A.E.; Maximov, M.V. Complete suppression of filamentation and superior beam quality in quantum−dot lasers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 82, 952–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, S.A.; O'Faolain, L.; Cataluna, M.A.; Flynn, M.B.; Kotlyar, M.V.; Krauss, T.F. Reduced surface sidewall recombination and diffusion in quantum−dot lasers. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 2006, 18, 1861–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, K.; Zhang, Z.; Childs, D.; Hugues, M.; Ramsay, A.; Hogg, R. Ultra−broad spontaneous emission and modal gain spectrum from a hybrid quantum well/quantum dot laser structure. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 041118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, K.; Zhang, Z.; Wada, O.; Childs, D.; Hugues, M.; Jin, X.; Hogg, R. Room temperature simultaneous three−state lasing in hybrid quantum well/quantum dot laser. Electron. Lett. 2012, 48, 644–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyvast, N.; Chen, S.; Zhou, K.; Babazadeh, N.; Khozim, A.; Zhang, Z.; Childs, D.; Wada, O.; Hugues, M.; Hogg, R. Development of broad spectral bandwidth hybrid QW/QD structures from 1000−1400 nm. Proc. SPIE 2014, 9002, 900204. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, K.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, S.; Liu, H.; Lu, Z.; Kennedy, K.; Matcher, S.; Hogg, R. Quantum dot selective area intermixing for broadband light sources. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 26950–26957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Liu, H.; Lee, A.; Pozzi, F.; Seeds, A. 1.3−μm InAs/GaAs quantum−dot lasers monolithically grown on Si substrates. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 11381–11386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Tang, M.; Jiang, Q.; Wu, J.; Dorogan, V.G.; Benamara, M.; Mazur, Y.I.; Salamo, G.J.; Smowton, P.; Seeds, A. InAs/GaAs quantum−dot superluminescent light−emitting diode monolithically grown on a Si substrate. ACS Photon. 2014, 1, 638–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Tang, M.; Chen, S.; Wu, J.; Seeds, A.; Liu, H. InAs/GaAs quantum−dot superluminescent diodes monolithically grown on a Ge substrate. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 23242–23248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fafard, S.; Hinzer, K.; Raymond, S.; Dion, M.; McCaffrey, J.; Feng, Y.; Charbonneau, S. Red−emitting semiconductor quantum dot lasers. Science 1996, 274, 1350–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smowton, P.M.; Lutti, J.; Lewis, G.M.; Krysa, A.B.; Roberts, J.S.; Houston, P.A. InP−GaInP quantum−dot lasers emitting between 690−750 nm. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2005, 11, 1035–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlereth, T.W.; Schneider, C.; Gerhard, S.; Höfling, S.; Forchel, A. Short−wavelength (760−920 nm) AlGaInAs quantum dot lasers. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2009, 15, 792–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilma, B.W.; Jiao, Y.; Kotani, J.; Smalbrugge, B.; Ambrosius, H.P.M.M.; Thijs, P.J.; Leijtens, X.J.M.; Nötzel, R.; Smit, M.K.; Bente, E.A.J.M. Integrated tunable quantum−dot laser for optical coherence tomography in the 1.7 μm wavelength region. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 2012, 48, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
White, S.E.; Cataluna, M.A. Unlocking Spectral Versatility from Broadly−Tunable Quantum−Dot Lasers. Photonics 2015, 2, 719-744. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics2020719
White SE, Cataluna MA. Unlocking Spectral Versatility from Broadly−Tunable Quantum−Dot Lasers. Photonics. 2015; 2(2):719-744. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics2020719
Chicago/Turabian StyleWhite, Stephanie E., and Maria Ana Cataluna. 2015. "Unlocking Spectral Versatility from Broadly−Tunable Quantum−Dot Lasers" Photonics 2, no. 2: 719-744. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics2020719
APA StyleWhite, S. E., & Cataluna, M. A. (2015). Unlocking Spectral Versatility from Broadly−Tunable Quantum−Dot Lasers. Photonics, 2(2), 719-744. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics2020719