Objectivisation In Simplified Quantum Brownian Motion Models
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The General Mechanism
2.2. Model of Quantum Brownian Motion
2.3. Full Quantum Measurement Limit And Exact Timescales
2.4. Partial Quantum Measurement Limit And Time Averages
2.5. Squeezed Thermal States in The Full Model
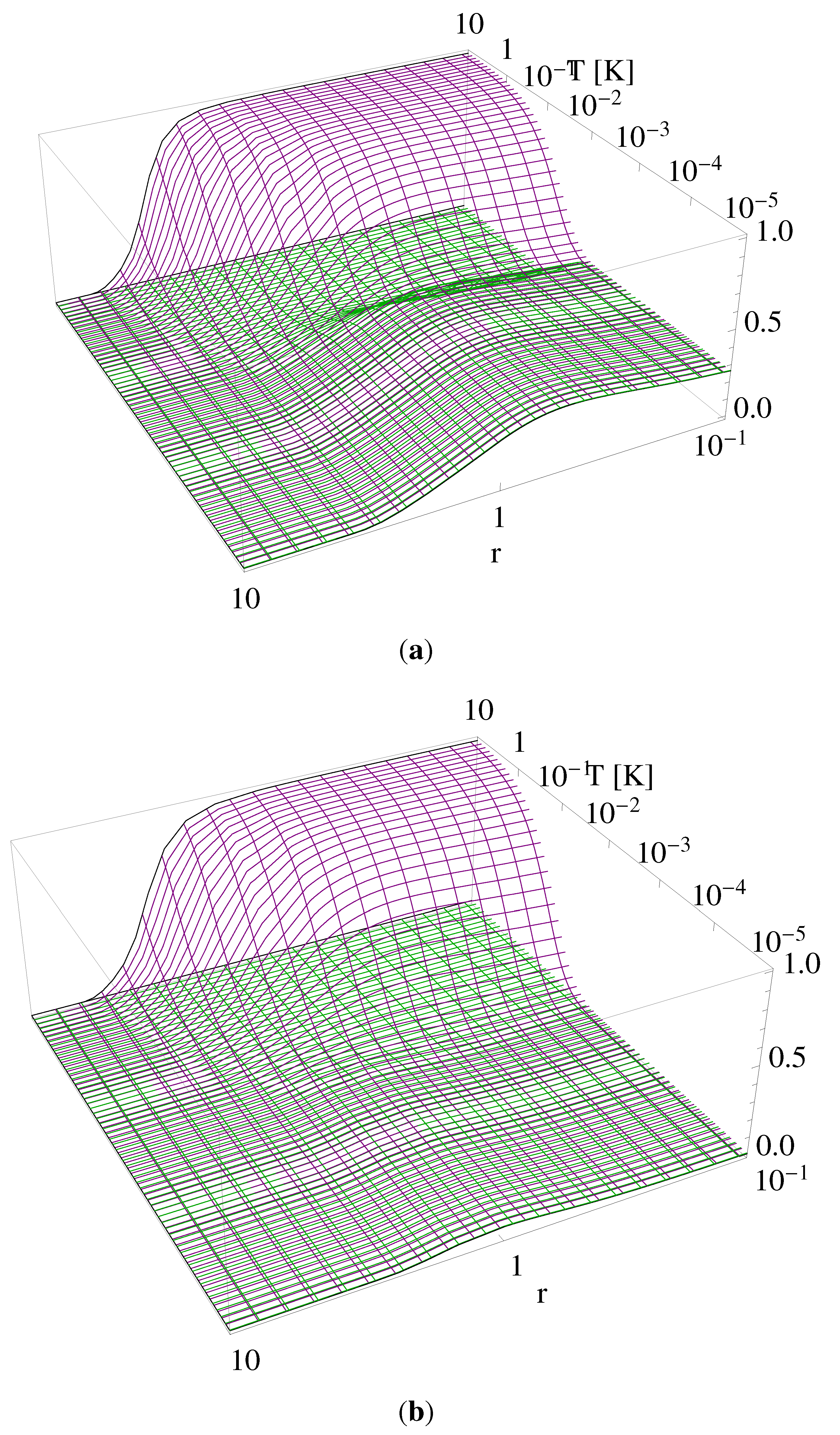
3. Discussion
4. Methods
4.1. Time Averages of Almost Periodic Functions with Positive Coefficients
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Von Neumann, J. Mathematical Foundations of Quantum Mechanics; Beyer, R.T., Translator; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1955. [Google Scholar]
- Zurek, W.H. Quantum Darwinism. Nat. Phys. 2009, 5, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlosshauer, M. Decoherence and the Quantum-to-Classical Transition; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Blume-Kohout, R.; Zurek, W.H. Quantum Darwinism in Quantum Brownian Motion. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 101, 240405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwolak, M.; Quan, H.T.; Zurek, W.H. Quantum Darwinism in non-ideal environments. Phys. Rev. A 2010, 81, 062110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel, C.J.; Zurek, W.H. Quantum Darwinism in an everyday environment: Huge redundancy in scattered photons. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 020404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horodecki, R.; Korbicz, J.K.; Horodecki, P. Objectivity From Quanta Via State Information Broadcasting. 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Brandao, F.G.S.L.; Piani, M.; Horodecki, P. Quantum Darwinism is Generic. 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bohr, N. Can Quantum-Mechanical Description of Physical Reality be Considered Complete? Phys. Rev. 1935, 47, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnum, H.; Caves, C.M.; Fuchs, C.A.; Jozsa, R.; Schumacher, B. Noncommuting Mixed States Cannot Be Broadcast. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 76, 2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korbicz, J.K.; Horodecki, P.; Horodecki, R. Quantum-correlation breaking channels, broadcasting scenarios, and finite Markov chains. Phys. Rev. A 2012, 86, 042319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korbicz, J.K.; Horodecki, P.; Horodecki, R. Objectivity in a Noisy Photonic Environment through Quantum State Information Broadcasting. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 112, 120402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Objectivity in Spin Systems. In preparation.
- Tuziemski, J.; Korbicz, J.K. Dynamical Objectivity in Quantum Brownian Motion. 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Breuer, H.-P.; Petruccione, F. The Theory of Open Quantum Systems; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs, C.A.; van de Graaf, J. Cryptographic distinguishability measures for quantum-mechanical states. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theor. 1999, 45, 1216–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sewell, G. On the mathematical structure of quantum measurement theory. Rep. Math. Phys. 2005, 56, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurek, W.H. Environment-induced superselection rules. Phys. Rev. D 1982, 26, 1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wintner, A. Upon a Statistical Method in the Theory of Diophantine Approximations. Am. J. Math. 1933, 55, 309–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tuziemski, J.; Korbicz, J.K. Objectivisation In Simplified Quantum Brownian Motion Models. Photonics 2015, 2, 228-240. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics2010228
Tuziemski J, Korbicz JK. Objectivisation In Simplified Quantum Brownian Motion Models. Photonics. 2015; 2(1):228-240. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics2010228
Chicago/Turabian StyleTuziemski, Jan, and Jarek K. Korbicz. 2015. "Objectivisation In Simplified Quantum Brownian Motion Models" Photonics 2, no. 1: 228-240. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics2010228
APA StyleTuziemski, J., & Korbicz, J. K. (2015). Objectivisation In Simplified Quantum Brownian Motion Models. Photonics, 2(1), 228-240. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics2010228



