Abstract
In the present study, a polarization rotation switch (PRS)-based all-optical ternary inverter circuit and ternary clocked SR flip-flop (TCSR) are proposed and discussed. The present scheme is designed by the polarization rotation of light in a waveguide coupled with a micro-ring resonator (MRR). The proposed scheme uses linear polarization-encoded light. Here, the ternary (radix = 3) logical states are expressed by the different polarized light. PRS-MRR explores the polarization-encoded methodology, which depends on polarization conversion from one state to another. All-optical ultrafast switching technology is employed to design the ternary NAND gate. We develop the ternary clocked SR flip-flop by employing the NAND gate; it produces a greater number of possible outputs as compared to the binary logic clocked SR flip-flop circuit. The performance of the proposed design is measured by the Jones parameter and Stokes parameter. The results of the polarization rotation-based ternary inverter and clocked SR flip-flop are realized using a pump–probe structure in the MRR. The numerical simulation results are confirmed by the well-known Jones vector (azimuth angle and ellipticity angle) and Stokes parameter (S1, S2, S3) using Ansys Lumerical Interconnect simulation software.
1. Introduction
The requirements for faster all-optical signal processing in an optical communication network have been increased in recent times. To fulfill these requirements, the advancement of optical communication networks shifted towards a higher bandwidth in the terahertz (THz) range. A polarization rotation-based switch can transmit data in the optical domain without using an electro-optics interface. Therefore, it is capable of achieving ultrafast switching at higher data rates. The approach has been proposed in the domain of all-optical switches and a parallel processing system [1,2]. An all-optical switch (AOS)-based conventional logic circuit can be used in the high-speed signal processing system. It can fulfill the convenient performance required due to its compact size, low power characteristic, high transmittance, and ultra-high switching speed [3,4,5]. Micro-ring resonators provide a very versatile platform for optical switching and computing, offering the advantages of ultrafast and low-power switching. The switching operation of an AOS depends on the birefringence of the material/waveguide and nonlinear refractive index change [6,7].
Many researchers have endorsed different kinds of AOSs for ultrafast operative speed using many approaches such as a micro-ring resonator (MRR), a Sagnac switch, a Mach–Zender interferometer (MZI), a terahertz optical asymmetrical demultiplexer (TOAD), an optical nonlinear material (OPNLM) and AI-based logic circuits, etc. [8,9,10,11,12,13,14]. In this study, we used a polarization-encoded light signal. The polarization-dependent phenomena in AOSs are very significant, and these can function in the “terahertz” range and require very narrow power with less circuitry [15,16].
In the last decade, the multi-valued logic (MVL) technique has been considered a potential and promising domain of research. MVL systems have some major benefits over the binary logic system, such as increased data handling capacity in the field of optical computing, increased computational processing, and reduced dynamic power dissipation. Larger numbers of logic function can be derived with MVL circuits. A large diversity of optical data can be managed in the MVL domain, which is used as a promising alternative in different practical solutions [17,18,19,20,21]. The optical MVL operation is an impressive and visionary research direction for future optical data communication [22,23,24]. But most MVL circuits constructed in the past have been complicated and faced an analogue noise dilemma. A quaternary inverter and universal quaternary inverter have been implemented by TOAD-based switches [25]. A TOAD-based switch suffers from an asymmetric switching; it could produce high crosstalk and impair the Bit Error Rate (BER). The major drawback in MZI design is that it requires a large interaction length, which leads to high insertion loss, phase instability, and large power consumption. Few other MVL circuits have been constructed using an SOA-based MZI facing phase-handling obstacles.
A performance comparison of existing all-optical MVL technologies is shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Performance comparison of existing all-optical MVL technologies.
In the present study, we propose a polarization rotation switch (PRS)-based ternary (radix, R = 3) clocked SR flip-flop using ternary NAND logic gate. The PRS using MRR-based ternary AND/NAND logic gate has already been designed and discussed in [29].
The article is organized in five sections. The ternary logic, an all-optical switch (AOS) and MVL circuits are discussed in Part 1, and the theories of the polarization rotation-based switch (PRS), ternary NAND logic gate using the MRR are discussed in Part 2. The ternary inverter using single micro-ring resonator and T-clocked SR flip-flop are discussed in Part 3. The simulation results using Ansys Lumerical Interconnect software conforming to the described design and discussion are given in Part 4. The conclusion of this study is given in Part 5.
2. Theory of Ternary Inverter Circuit and Clocked SR Flip-Flop Circuit
The polarization rotation-based ternary inverter can be designed using single MRR and applying the ternary input via the input port of the MRR to obtain the results at the through port of MRR. A ternary clocked SR flip-flop circuit can be designed using two inputs (S, R) and four ternary NAND gates. In the binary inverter, binary states are described by 0 (low logic) and 1 (high logic) according to the amplitude of the output signal. The ternary inverter includes the logic low, logic high and one intermediate state. According to the ternary inverter circuit, a large number of logic operations can be obtained for higher radix. Recently, the ternary inverter (radix, R = 3) has been used for ultrafast communication. For radix 3, a total number of possible inverter states is 27. In this proposed design, we used three different states of the polarized light to represent the ternary states (0, 1 and 2) for the logical operations, which are given below:
- (a)
- 0: Horizontally polarized light or HPL (•);
- (b)
- 1: Linearly polarized light at 45° or L45P;
- (c)
- 2: Vertically polarized light or VPL (↑).
In this study, three different logic states are used to represent the polarized light, namely the ‘Logic-0’, ‘Logic-1’, and ‘Logic-2’. The ‘Logic-0’ is used to represent the linear horizontally polarized light or HPL (•). The ‘Logic-1’ is used to represent the linearly polarized light at 45° or (L45P). The ‘Logic-2’ is used to represent the linear vertically polarized light or VPL (↑).
2.1. Modeling of MRR-Based Ternary Polarization Rotation Switch (PRS)
In this section, we designed a new method to obtain all-optical multi-valued ternary inverter using polarization rotation switching in the MRR. We investigated and evaluated the performance from the simulated result using Ansys Lumerical Interconnect software.
Ansys Lumerical Interconnect is a powerful photonic integrated circuit simulator in which time and frequency domain analysis are performed using a dynamic data flow simulator, allowing for more flexibility than using traditional discrete time or time-driven simulators [30]. Lumerical Interconnect simulation software primarily focuses on simulating and analyzing the behavior of optical interconnects, such as waveguides, optical fibers, photonic devices, etc. The circuits can be simulated in Lumerical Interconnect using component circuit blocks that describe the input–output behavior of the component.
The basic configuration of the racetrack MRR comprising double waveguide coupled structure is shown in Figure 1. At the resonance, maximum light is transmitted to the through port of the MRR due to the constructive interference. Accordingly, the resonance condition is expressed by mλres = 2π.R0.neff, where m denotes the mode number, R0 is the ring radius, neff is the effective refractive index (RI) of the ring, and λres is the resonance wavelength. According to the transmission curve, the through port (TP) represents the maximum transmission and the drop port (DP) represents the minimum transmittance. The pump signal of suitable power is responsible for changing the RI of the material and inducing 180° phase shift. The graph of the output transmission of this structure is shown in Figure 2.
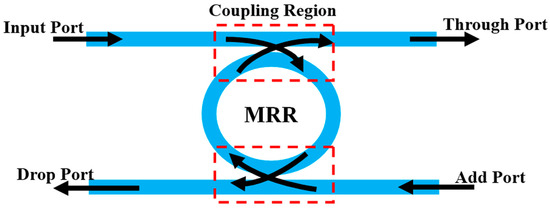
Figure 1.
Optical micro-ring resonator (MRR).
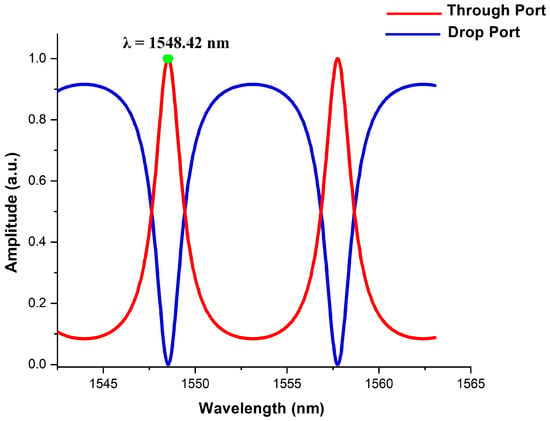
Figure 2.
Transmission curve of the optical MRR.
The polarization rotation switch is used for the realization of the ternary inverter as well as the clocked SR flip-flop circuit. The ternary clocked SR flip-flop circuit is designed with the help of MRR-PRS-based ternary NAND logic gate. The flow of operation of the MRR-based PRS is shown in Figure 3. The control signal with sufficient power is used to realize all-optical switching phenomenon. If the control signal is not present, a particular polarization state is available at the TP. When the control signal with different pump power is applied from the add port, the polarization rotation occurs at λres. The proposed configuration of PRS using MRR, consisting of nonlinear polarization maintaining (PM) fiber and a polarization rotator (PR), rotates the light polarization to a certain angle. The input polarized light enters the ring and can enhance the nonlinear birefringence dramatically due to the accumulated phase shift and the amplified intensity at the resonance wavelength. The detailed mathematical relationship between the input and output fields in terms of Jones matrix have already been discussed in [31,32,33,34,35]. The various parameters of the MRR-like coupling coefficient, waveguide height and width, ring radius and control signal power are optimized through Ansys Lumerical Interconnect simulation tool to obtain desired polarization conversion. The optimized values of these parameters are listed in Table 2. In this manuscript, horizontal axis, i.e., MRR axis, is considered as the reference axis. So, polarization angle of the MRR is considered as 0°. However, the misalignment of the polarization angle of the input light in the polarization setting may cause variation in the output of the proposed model [36,37].
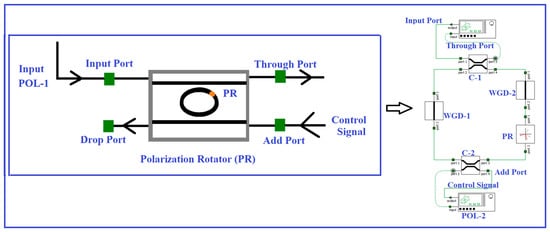
Figure 3.
Schematic diagram of the ternary MRR-PRS. C: Coupler, WGD: waveguide, PR: polarization rotator, POL: polarization analyzer.

Table 2.
List of parameters used to design ternary MRR-PRS.
If the linearly vertical polarized light is fed to the input port (IP) and no control signal is fed to the add port (AP) of the optical MRR, we obtain the same polarization state, i.e., linearly vertical polarized light at λres at the TP output. When the control signal is applied with optimized power, the MRR-PRS converts the VPL to HPL or linear 45° polarized (L45P) light.
2.2. Ternary NAND Logic Gate Using MRR-PRS
An MRR-PRS-based ternary NAND (TNAND) gate is designed in Lumerical simulation software, which is shown in Figure 4. A ternary NAND gate is realized at the TP of the proposed model and the logic levels are shown in Table 3. The polarized states of the input and control signal are used to obtain the desired output by applying the suitable pump power. Here, both the inputs A (probe signal) and B (control signal) can select any one of the three possible states (‘Logic-0’, ‘Logic-1’ and ’Logic 2’). The combinations of both the signals provide adequate phase-shift required for converting the polarization states at the output. Wavelength range and bandwidth of input signal are considered as 1547–1559 nm and 1.6 THz, respectively.
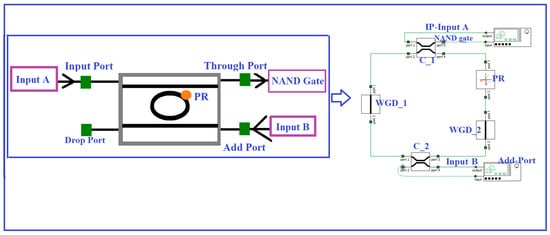
Figure 4.
Design of the MRR-PRS-based two-input ternary NAND gate.

Table 3.
Truth table of ternary NAND gate.
For example, if input ‘A’ = L45P or (‘Logic-1’), and ‘B’ = HPL (•) or (‘Logic-0’), VPL (↑) comes out from the TP at λres of 1548.42 nm. The obtained results are analyzed in terms of Jones parameters and Stokes parameters. For example, simulation results for inputs A and B in terms of Jones and Stokes parameters for ‘Logic-1’ and ‘Logic-0’, respectively, are shown in Figure 5. Figure 5a shows that the ellipticity angle is 0° and the azimuth angle is 90°. Figure 5b shows that Stokes parameters are [S1, S2, S3] = [−1, 0, 0] at the TP of MRR, which indicates that the TP output is VPL (‘Logic-2’). The simulation results of the different combinations are given in Table 4.
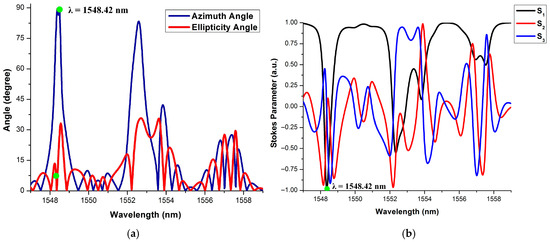
Figure 5.
‘Logic-2’ output at TP when both inputs are ‘Logic-1’ and ‘Logic-0’. (a): Jones parameters, (b) Stokes parameters.

Table 4.
Truth table and polarization states of ternary NAND gate.
3. Design of the Ternary Inverter and Clocked SR Flip-Flop Circuit
Many researchers have explained the binary coded ternary logic to implement different kinds of ternary arithmetic and logical functions. In the study, intensity-encoded light signal is also investigated to represent the different types of logic states for the implementation of Boolean logic functions, which require apparent specific intensity level of light for individual state [16,20] and the intensity-encoded signal may also be altered due to many reasons. This problem can be avoided in the polarization-based encoding and decoding method.
The binary inverter is expressed by [0 1] [x y], which indicates the transmission of the incoming signal of state 0 (low) into an outgoing signal x and the transmission of an incoming signal of state 1 into an outgoing signal y accordingly. For multi-valued, the total numbers of possible logical operations are for a system of radix = R, and the number of input variables is n. According to binary logic system (n = 1, R = 2), we obtain four possible numbers of inverter states [0 1] [0 0], [0 1] [1 0], [0 1] [0 1] and [0 1] [1 1], respectively. Similarly, we can explain the ternary logic inverter in ternary logic system (radix, R = 3). We can obtain the total of 27 inverter states [0 0 0], [1 0 0], [2 0 0], [0 1 0], … and [2 2 2], which are shown in Table 5.

Table 5.
Truth table and polarization properties of Ternary inverter.
A polarization-encoded all-optical ternary inverter uses polarization states of the light to represent and manipulate three-logic levels (ternary logic: 0, 1, 2). The polarization inversion operation is performed using polarization-selective elements that transform the polarization state to its logical inverse.
The PRS-based ternary logic circuit is implemented using double waveguide coupled MRR in Ansys Lumerical Interconnect simulation software, which is shown in Figure 6. It consists of symmetrical couplers, i.e., k1 = k2 = k = 0.45, and the refractive index of the waveguide is nearly 3.38. The polarization-based all-optical switching depends on the pump power of the optical signal.
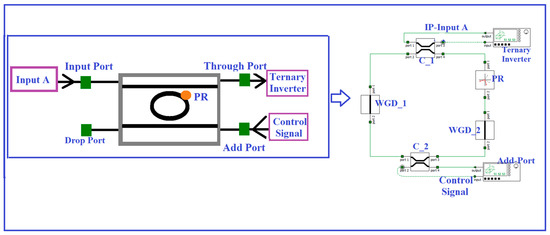
Figure 6.
Representation of the ternary inverter circuit.
The design of clocked S-R ternary flip-flop is described by ternary NAND gate. NAND gate-based clocked S-R flip-flop is shown in Figure 7. The corresponding Interconnect simulation model is shown in Figure 8 and its truth table is shown in Table 6.
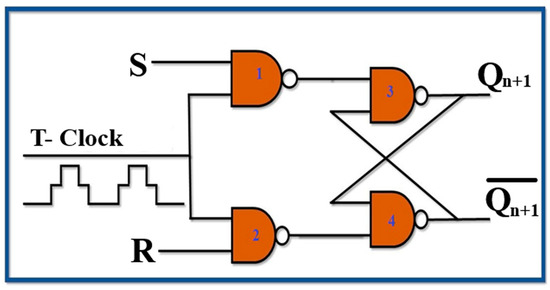
Figure 7.
Schematic diagram of MRR-PRS-based ternary (T-) clocked SR flip-flop.
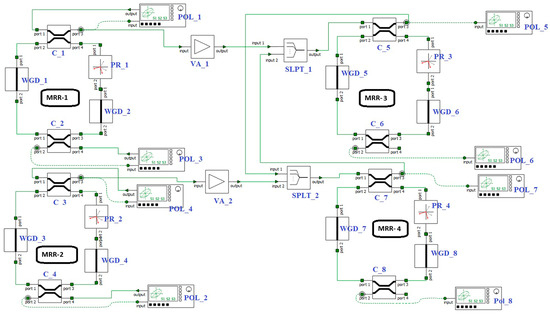
Figure 8.
Design of the MRR-PRS-based ternary clocked SR flip-flop using in Interconnect simulation software.

Table 6.
Truth table of ternary clocked SR flip-flop circuit.
As per the definition of the ternary inverter, output is 2, when 0 is input and vice versa. But the output remains 1, when input is 1, i.e., 1’s complement is 1. Now for the SR flip-flop, states are referred to as “Set” when = 2 and = 0 for any combination of S and R. Inversely, states are referred to as “Reset” when = 0 and = 2 for any combination of S and R. But when = 1, then is also 1. So = 1 and = 1 is also valid output state in ternary flip-flop unlike binary flip-flops and is called ‘intermediate state’. All other output combinations are not valid as per flip-flop definition. So, these states are called ‘forbidden state’.
The signal flow graph (SFG) diagram for a particular case of Table 6 of the proposed SR flip-flop is shown in Figure 9. In the diagram, for an instant, let us consider Clock = HPL (‘Logic-0’), S = HPL (‘Logic-0’), R = L45P (‘Logic-1’) and previous output () = VPL (‘Logic-2’). So, as per truth Table 6, the output, = 2, then = 0, i.e., ‘Set’ condition is achieved.
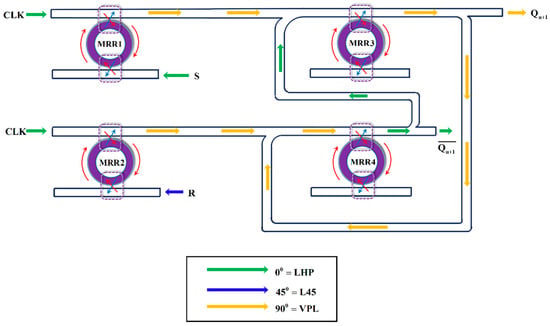
Figure 9.
Signal flow graph for SR flip-flop.
4. Simulation Results and Discussion
The simulation results of ternary states are analyzed by the Jones matrix, which defines azimuth angle and ellipticity angle of the polarized light. The pump signal is injected from the AP and the polarization rotation-based ternary inverter operation is observed at the TP of the MRR at the resonance wavelength of 1548.428 nm. The simulation results of the Jones matrix method are also verified by Stokes parameters. The Stokes parameters, in general, are often combined into a vector, and are discussed below:
where = is the phase difference between x and y components of the polarized light.
4.1. Inverter
MVL system (radix, R = 3) is represented as non-binary logic and performs the polarization switching between the three polarization states. In the ternary logic, a particular logic state is changed to the desired states at the resonant wavelength of 1548.42 nm. The polarization rotation of the signal depends upon the nature of the polarization and the power level of the control signal. In the design of Figure 6, the light source (LS) of the ternary input ‘A’ with any one of the polarization states (HPL/L45P/VPL) is applied at the IP of the MRR. An optical control signal (B) is applied to the AP of the MRR that changes the polarization state of the output. We realized the ternary inverter at the TP of the MRR.
Case 1: When input ‘A’ = HPL (•) or Logic-0’ and control signal B = HPL (•) or ‘Logic-0”, depending on the power of the control signal, we can deduce the ternary output as follows:
(i) The azimuth angle is 0°, the ellipticity angle is 0° and the Stokes parameters are S1 = 1, S2 = 0, and S3 = 0 and we get the ‘Logic-0’ (HPL) at the output when control signal is 10 µW.
(ii) The azimuth angle is 45°, the ellipticity angle is 0° and Stokes parameters are S1 = 0, S2 = 1, and S3 = 0 and we get the ‘Logic-1’ (L45P) at the output when control signal is 90 µW.
(iii) The azimuth angle is 90°, the ellipticity angle is 0° and Stokes parameters are S1 = −1, S2 = 0, and S3 = 0 and we get the ‘Logic-2’ (VPL) at the output when control signal is 180 µW.
The simulation results of one of the above combinations (case 1(i)) are depicted in Figure 10. The output of the ternary inverter for the above-specified combination is shown in the first row of Table 7.
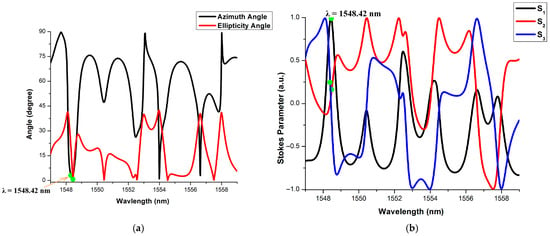
Figure 10.
Output Y is ‘Logic-0’ when input A is HPL (•) or ‘Logic-0’. (a): Jones parameters, (b) Stokes parameters.

Table 7.
Truth table of ternary Inverter with control power.
Case 2: When input A = L45P or “Logic-1” and control signal B = HPL (•) or ‘Logic-0’, depending on the power of the control signal, we can deduce the ternary output at a resonant wavelength of 1548.42 nm as follows:
(i) The azimuth angle = 0°, the ellipticity angle is 0° and the Stokes parameters are S1 = 1, S2 = 0, and S3 = 0 and we get the ‘Logic-0’ (HPL) at the output when control signal is 165 µW.
(ii) The azimuth angle is 45°, the ellipticity angle is 0° and the Stokes parameters are S1 = 0, S2 = 1, and S3 = 0 and we get the ‘Logic-1’ (L45P) at the output when control signal is 15 µW.
(iii) The azimuth angle is 90°, the ellipticity angle is 0° and the Stokes parameters are S1 = −1, S2 = 0, and S3 = 0 and we get the VPL (↑) or ‘Logic-2’ at the output when control signal is 922 μW, which is shown in Figure 11. The output of the ternary inverter for the above-specified combination is shown in the twelfth row of Table 7.
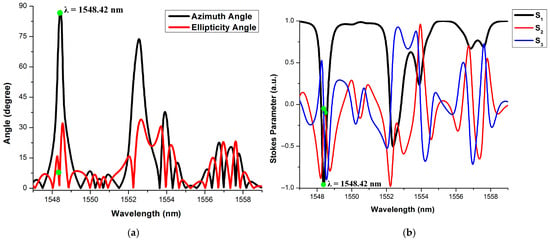
Figure 11.
Output Y is ‘Logic-2’ when input A is L45P or ‘Logic-1’. (a): Jones parameters, (b) Stokes parameters.
Case 3: When input A is VPL (↑) or “Logic-2” and control signal B is also HPL (•) or ‘Logic-0’, depending on the power of the control signal, we can conclude the ternary output at the resonant wavelength of 1548.42 nm as the following:
(i) The azimuth angle is 0°, the ellipticity angle is 0° and the Stokes parameters are S1 = 1, S2 = 0, and S3 = 0 and we get the ‘Logic-0’ (HPL) at the output when control signal is 915 µW.
(ii) The azimuth angle is 90°, the ellipticity angle is 0° and the Stokes parameters are S1 = −1, S2 = 0, and S3 = 0 and we get the ‘Logic-2’ (VPL) at the output when control signal is 14 µW.
(iii) The azimuth angle is 45°, the ellipticity angle is 0° and the Stokes parameters are S1 = 0, S2 = 1, and S3 = 0 and we get the ‘Logic-1’ (L45P) at the output when control signal is 650 µW. This combination is shown in Figure 12. The output of the ternary inverter for the above-specified combination is shown in the twelfth row of Table 7. Similarly, all the remaining possible logic combinations are mentioned in Table 7.
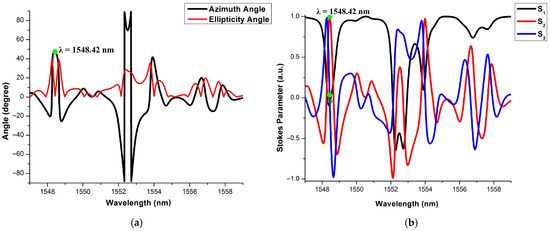
Figure 12.
Output Y is ‘Logic-1’ when input A is VPL or ‘Logic-2’. (a): Jones parameters, (b) Stokes parameters.
4.2. Clocked SR Flip-Flop Circuit
The clocked SR ternary flip-flop comprises of four identical MRRs (MRR-1, MRR-2, MRR-3 and MRR-4), as shown in Figure 7. The output TP-3 of MRR-3 represents Qn+1 and TP-4 of MRR-4 represents . It fulfills all the conditions similarly to the conventional clocked binary flip-flop. In the binary SR flip-flop, only four possible conditions occur. Like binary, all four conditions (SET, RESET, Unchanged and Forbidden) of the SR flip-flop have been taken into consideration in our proposed design along with intermediate states, as shown in Table 6. The simulation model of the proposed ternary clocked SR flip-flop circuit is shown in Figure 8. The simulation results are validated by the Jones matrix (azimuth and ellipticity angle) and Stokes parameters (S1 S2 S3). According to the truth table of the ternary clocked SR flip flop, the first three rows of Table 6 show unchanged condition, when T-Clock is ‘Logic-0’ and inputs, S = 0, R = 0.
Case 1: The clock is ‘Logic-0’, input S is ‘Logic-0’ or HPL (•) and R is ‘Logic-0’ or HPL (•). According to the simulation model, the ternary clocked SR flip-flop is realized using MRR-based ternary NAND gates. The polarization rotation switching occurs at the resonant wavelength of 1548.42 nm due to the MRR-PRS property. Three different outputs are obtained for different combinations of the previous output states. When the previous outputs are Qn = 0 and = 2, the next output Qn+1 is obtained at the TP-3 of MRR-3, which receives the ‘Logic-0’ or HPL. The output is obtained at the TP-4 of MRR-4, which receives the ‘Logic-2’ or VPL. The Jones parameters’ representation of Qn+1 and is shown in Figure 13a and Figure 14a, respectively. According to Figure 13a, it is observed that both the azimuth and ellipticity angles are almost 0°, which signifies that the output is ‘Logic-0’ or HPL (•). From Figure 14a, it is observed that the azimuth angle is 90° and the ellipticity angle is almost 0°, which signifies that the output is “Logic-2 or VPL (↑).
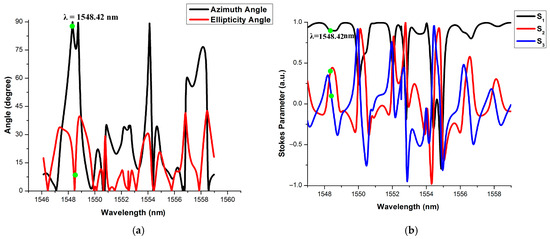
Figure 13.
Output Qn+1 is ‘Logic-0’ when Input S is ‘Logic-0’ or HPL (•) and R is ‘Logic-1’ or L45P. (a): Jones parameters, (b) Stokes parameters.
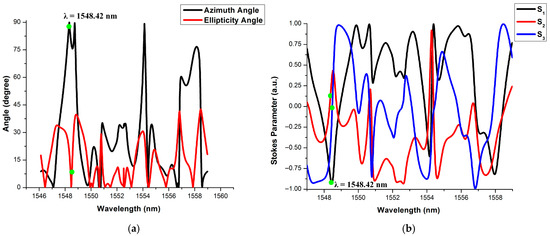
Figure 14.
Output is ‘Logic-2’ when input S is ‘Logic-0’ or HPL (•) and R is ‘Logic-1’ or L45P. (a): Jones parameters, (b) Stokes parameters.
The Stokes parameters for Qn+1 and are illustrated in Figure 13b and Figure 14b, respectively. From Figure 13b and Figure 14b it is observed that the Stokes parameters are [S1 = 1, S2 = 0, S3 = 0] and [S1 = −1, S2 = 0, S3 = 0], respectively. It is shown that Qn+1 and outputs are ‘Logic-0’ or HPL (•) and ‘Logic-2’ or VPL (↑), respectively. The outputs of the TP-3 and TP-4 for the above-mentioned combination are (0, 2), which implies the RESET condition. Like this case, the present state remains the same in the other two cases when S = R = ‘Logic-0’. All the three cases are shown in the first three rows of Table 8.

Table 8.
Truth table of ternary clocked SR flip-flop circuit with control power.
Case 2: The clock is “Logic-1”, Input S is ‘Logic-1’ or L45P and R is ‘Logic-1’ or L45P. The polarization rotation switching occurs at the resonant wavelength of 1548.42 nm due to the MRR-PRS property. Three different outputs are obtained for different combinations of the previous output states. When the previous outputs Qn = 1 and = 1, the next output Qn+1 is obtained as ‘Logic-1’ or L45P at the TP-3 of the MRR-3. The output is also obtained as ‘Logic-1’ or L45P at the TP-4 of the MRR-4. The Jones parameter representations of Qn+1 and are shown in Figure 15a and Figure 16a, respectively. According to the simulation results in Figure 15a and Figure 16a, it is observed that the azimuth angle is 45° and the ellipticity angle is almost 0°, which implies that the output is ‘Logic-1’ or L45P.
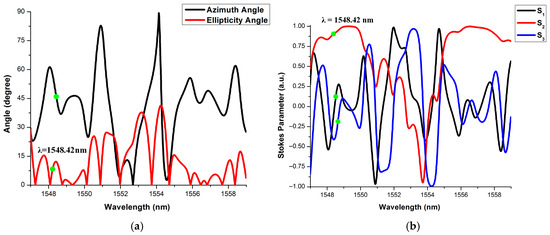
Figure 15.
Output Qn+1 is ‘Logic-1’ when input S is ‘Logic-1’ or L45P and R is ‘Logic-1’ or L45P. (a): Jones parameters, (b) Stokes parameters.
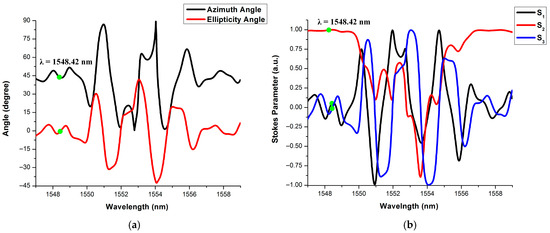
Figure 16.
Output is ‘Logic-1’ when input S is ‘Logic-1’ or L45P and R is ‘Logic-1’ or L45P. (a): Jones parameters, (b) Stokes parameters.
The Stokes parameters for Qn+1 and are illustrated in Figure 15b and Figure 16b, respectively. From Figure 15b and Figure 16b, the Stokes parameters are [S1 = 0, S2 = 1, S3 = 0]. It is shown that the Qn+1 and outputs are ‘Logic-1’ or L45P. The outputs of the TP-3 and TP-4 for the above-mentioned combinations are (1, 1), which implies the intermediate condition. All three cases are shown in the thirteenth to fifteenth rows of Table 8.
Case 3: The clock is “Logic -2”, input S is ‘Logic-2’ or VPL (↑) and R is ‘Logic-0’ or HPL (•). Three different outputs are obtained for the different combinations of the previous output states. When the previous outputs are Qn = 2 and = 0, the next output Qn+1 is obtained at the TP-3 of the MRR-3, which receives the ‘Logic-2’ or VPL (↑). The output is obtained at the TP-4 of the MRR-4, which receives the ‘Logic-0’ or HPL (•). The Jones parameters’ representation of Qn+1 and is shown in Figure 17a and Figure 18a, respectively. According to the simulation results in Figure 17a, it is observed that the azimuth angle is 90° and the ellipticity angle is almost 0°, which implies that the output is ‘Logic-2’ or VPL (↑). Similarly, from the simulation results in Figure 18a, it is observed that both the azimuth angle and the ellipticity angle are almost 0°, which implies that the output is ‘Logic-0’ or HPL (•).
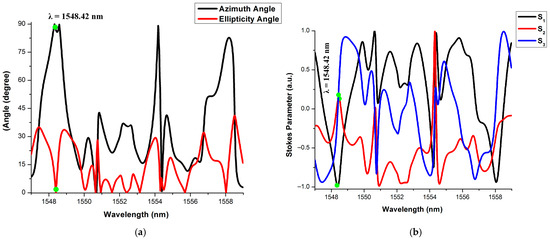
Figure 17.
Output Qn+1 is ‘Logic-2’ when Input S = ‘Logic-2’ or VPL and R is ‘Logic-0’ or HPL (•). (a): Jones parameters, (b) Stokes Parameters.
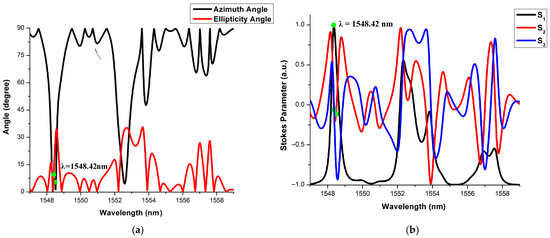
Figure 18.
Output is ‘Logic-1’ when Input S = ‘Logic-2’ or VPL and R is ‘Logic-0’ or HPL (•). (a): Jones parameters, (b) Stokes parameters.
The Stokes parameters for Qn+1 and are depicted in Figure 17b and Figure 18b, respectively. From Figure 17b and Figure 18b, the Stokes parameters are [S1 = −1, S2 = 0, S3 = 0] and [S1 = 1, S2 = 0, S3 = 0], respectively. It is validated that outputs Qn+1 and are ‘Logic-2’ or VPL (↑) and ‘Logic-0’ or HPL (•), respectively. The outputs of the TP-3 and TP-4 for the above-mentioned combinations are (2, 0), which satisfies the SET condition. All three cases are shown in the nineteenth to twenty-first rows of Table 8.
4.3. Discussion
The performance improvement of all optical ternary flip-flop in MRR is reflected through several key metrics, such as on-off ratio, free spectral range (FSR), switching speed, compactness, power efficiency, and attenuation loss.
We calculated the on-off ratio and free spectral range (FSR) from the transmission curve as shown in Figure 19. The on-off ratio is an important parameter of the micro-ring resonator-based ternary inverter and T-clock SR flip-flop. It can be quantified by calculating the ration of the “ON resonance” signal to the “OFF resonance” signal:
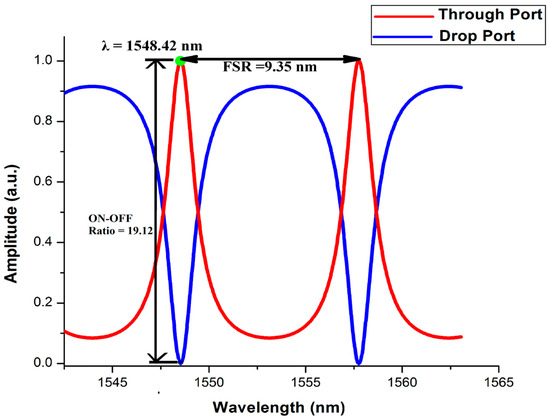
Figure 19.
Transmission characteristics of MRR.
For high performance, the value of the on-off ratio of micro-ring resonator-based devices should be greater than 20 dB [38] and the obtained value from the simulation of our proposed design is 19.12 dB, which is slightly less than the desired value. There is a scope to improve on-off ratio by optimizing more preciously the ring parameters, like ring radius, coupling coefficient. The output FSR is defined as the wavelength range between two successive resonance peaks and the calculated value from the simulation is nearly 9.35 nm. The other performance parameters of the model are switching speed and attenuation loss. The simulation results for switching speed and overall attenuation loss of the proposed model are shown in Figure 20. The switching speed and overall attenuation loss of the proposed circuit are 0.14 ps, 0.52 dB, respectively. The proposed ternary circuit reduces the total number of logic elements, which translates to lower overall power consumption. In the proposed model the required power varies from µW to a few mW only. The ternary flip-flops store three discrete logic levels (0, 1, 2) unlike binary flip-flops. This reduces the required number of components and interconnect complexity in multi-valued logic (MVL) systems, which leads to higher integration density in photonic circuits, which is another important improvement of the proposed design.
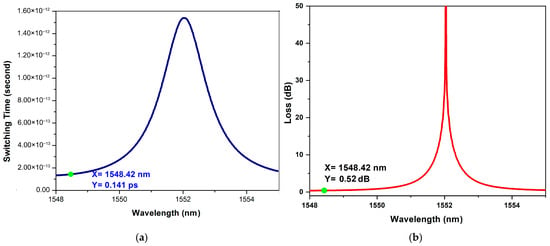
Figure 20.
Simulated (a) switching time, (b) output for attenuation loss in logarithmic scale.
The device performance is affected by fabrication tolerances, such as variations in ring radius, and coupling coefficient. So, the proposed model is analyzed by considering variation of coupling coefficient (k). The variations of azimuth angle with k1 = 0.45(±0.05), i.e., 0.4 and 0.5 with constant k2 = 0.45 and constant ring radius R0 = 12 µm are observed and shown in Figure 21a and Figure 21b, respectively. From Figure 21 it is observed that the azimuth angle varies less than 10% for the above variation of coupling coefficient.
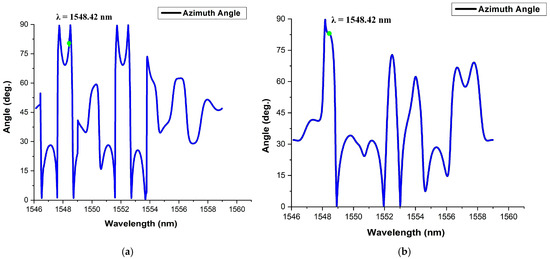
Figure 21.
Variation of azimuth angle for (a) k1 = 0.40 and (b) k1 = 0.5.
Similarly, variation of the MRR radius is analyzed. In the proposed model radius of the MRR is considered as 12 µm. The variations of azimuth angle with radius, R0 = (12 ± 1) µm with constant k1 = k2 = 0.45 are observed and shown in Figure 22a and Figure 22b, respectively. From Figure 22 it is observed that the tolerance level of the radius may be considered as 10%.
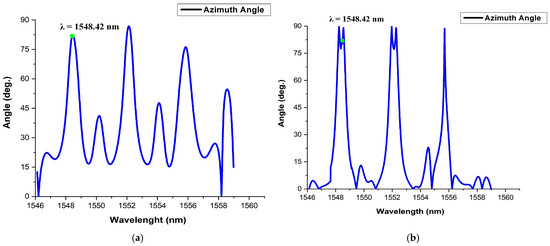
Figure 22.
Variation of azimuth angle for (a) r = 11 µm and (b) r = 13 µm.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we have designed ternary inverter and SR flip-flop by exploiting PRS-MRR-based ternary NAND logic gates using Interconnect simulation software. The obtained simulation results for the ternary inverter and the clocked SR flip-flop are confirmed by both the Stokes parameters and the Jones matrix. The PRS-MRR-based design is compact, simple and requires very small power with very high switching speed of 0.141 ps. The control signal power is very low and it is in the range of micro-watts to a few milli-watts. The parameters are optimized in such a way that proper polarization conversion occurs. So, these methods can be successfully implemented for higher-order MVL logic and counter circuits. Furthermore, AI-based modeling might be a future option for studying more complex, cascaded systems, demonstrating a forward-looking perspective and broader awareness of the field.
Author Contributions
M.P.S.: methodology, software, investigation, writing-original draft preparation; J.K.R.: conceptualization, resources, data curation, writing—review and editing, supervision; K.E.Z.: conceptualization, writing- review and editing, M.H.: conceptualization, writing—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| PRS | polarization rotation switch |
| TCSR | ternary clocked SR flip-flop |
| MRR | micro-ring resonator |
| AOS | All-optical switch |
| MZI | Mach-Zender Interferometer |
| TOAD | Terahertz Optical Asymmetrical Demultiplexer |
| OPNLM | Optical Nonlinear Material |
| MVL | multi-valued logic |
| DP | Drop Port |
| TP | Through Port |
| WGD | Waveguide |
| PR | polarization rotator |
| POL | polarization analyzer |
| TNAND | ternary NAND gate |
| HPL | Horizontally polarized light |
| L45P | Linearly polarized light at 45° |
| VPL | Vertically polarized light |
References
- Li, Z.; Chen, Z.; Li, B. Optical pulse controlled all-optical logic gates in SiGe/Si multimode interference. Opt. Express 2005, 13, 1033–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.; Rakshit, J.K.; Singh, M.P. Numerical analysis of all-optical silicon microring resonator-based cyclic redundancy check encoder. J. Nanophoton. 2022, 16, 036007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizou, Z.V.; Zoiros, K.E. Performance analysis and improvement of semiconductor optical amplifier direct modulation with assistance of microring resonator notch filter. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2017, 49, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, D.G.S.; Swarnakar, S.; Palacharla, V.; Raju, K.S.R.; Kumar, S. Design of all-optical AND, OR, and XOR logic gates using photonic crystals for switching applications. Photonic Netw. Commun. 2021, 41, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.; Zoiros, K.E.; Chattopadhyay, T.; Rakshit, J.K. Speed enhancement of all-optical pseudo random binary sequence (PRBS) generator using microring resonator. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2021, 53, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakshit, J.K.; Zoiros, K.E.; Bharti, G.K. Proposal for ultrafast all-optical pseudo random binary sequence generator using microring resonator-based switches. J. Comput. Electron. 2021, 20, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Ou, H.; Xu, J.; Xiong, M.; An, Y.; Hu, H.; Galili, M.; Riesgo, A.L.; Seoane, J.; Yvind, K.; et al. Linear all-optical signal processing using silicon micro-ring resonators. Front. Optoelectron. 2016, 9, 362–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awwal, A.A.S.; Karim, M.A.; Cherri, A.K. Polarization-encoded optical shadow-casting scheme: Design of multioutput trinary combinational logic units. Appl. Opt. 1987, 26, 4814–4818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Mandal, D.; Mandal, M.K.; Garai, S.K. Design of optical quaternary adder and subtractor using polarization switching. J. Opt. 2018, 47, 332–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Jin, Y.; Zuo, K. Decrease-radix design principle for carrying/borrowing free multi-valued and application in ternary optical computer. Sci. China Ser. F Inf. Sci. 2008, 51, 1415–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakshit, J.K.; Singh, M.P.; Hossain, M.; Roy, J.N. Polarization rotation based all-optical ternary half-adder and full-adder: Design and analysis using micro-ring resonator. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2022, 54, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahromi, H.D.; Binaie, A.; Zarifkar, A.; Sheikhi, M.H. A new structure for all-optical three-input XOR logic gate based on semiconductor optical amplifier mach–zehnder interferometer. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 2014, 28, 1450052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamedi, S.; Jahromi, H.D. Performance analysis of all-optical logical gate using artificial neural network. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 178, 115029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parandin, F.; Yahya, S.I.; Rezaeenia, M.; Askarian, A.; Roshani, S.; Roshani, S.; Ghadi, Y.Y.; Jamshidi, M.; Rezaee, S. A neural networks approach for designing compact all-optical photonic crystal based AND logic gate. J. Opt. Commun. 2025, 45, s2627–s2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.P.; Hossain, M.; Rakshit, J.K.; Bharti, G.K.; Roy, J.N. Proposal for Polarization Rotation–Based Ultrafast All Optical Switch in Ring Resonator. Braz. J. Phys. 2021, 51, 1763–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, A.; Mukherjee, K.; Roy, J.N. Ultra-high-speed all-optical multivalued inverter using nonlinear polarization rotation in semiconductor optical amplifier. J. Opt. 2022, 51, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, S.L. Multiple-valued logic—It’s status and it’s future. IEEE Trans. Comput. C 1984, 33, 1160–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.C. Multiple-valued logic—A tutorial and appreciation. IEEE Comput. 1988, 8, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, R.; Boudinov, H.; Carro, L. Quaternary look-up tables using voltage mode CMOS logic design. In Proceedings of the 37th International Symposium of multiple-valued logic (ISMVL’07), Oslo, Norway, 13–16 May 2007; p. 56. [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay, T.; Roy, J.N. Polarization encoded all optical quaternary successor with the help of SOA assisted Sagnac switch. Opt. Commun. 2011, 284, 2755–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuda, Y.; Tokuda, Y.; Zaima, S.; Pak, K.; Nakamura, T.; Yoshida, A. Realization of quaternary logic circuits by n-channel MOS devices. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 1986, 21, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, T.; Roy, J.N. Polarization-encoded all-optical quaternary universal inverter and design of multivalued flip-flop. Opt. Eng. 2010, 49, 035201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, Y.; Ohtsuka, Y. Optical multiple-output and multiplevalued logic operation based on fringe shifting techniques using a spatial light modulator. Appl. Opt. 1987, 26, 274–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizvi, R.A.; Zaheer, K.; Zubairy, M.S. Implementation of trinary logic in polarization encoded shadow-casting scheme. Appl. Opt. 1991, 30, 936–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chattopadhyay, T.; Bhowmik, P.; Roy, J.N. Polarization encoded optical N-valued inverter. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2012, 29, 2852–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, A.; Mukherjee, K.; Roy, J.N. Design of dual semiconductor optical amplifier structure based all-optical standard quaternary inverter and quaternary clocked SR flip-flop. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2022, 54, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, T. All-optical symmetric ternary logic gate. Opt. Laser Technol. 2010, 42, 1014–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.P.; Rakshit, J.K.; Hossain, M. Implantation of polarization rotation based ternary 3:1 multiplexer and 1:3 demultiplexer using optical micro ring resonator. Opt. Commun. 2022, 522, 128646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.P.; Rakshit, J.K.; Hossain, M. Design of polarization conversion and rotation based ternary logic AND/NAND, OR/NOR, Ex-OR/Ex-NOR gates using ring resonator. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2021, 53, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrostowski, L.; Lu, Z.; Flueckiger, J.; Wang, X.; Klein, J.; Liu, A.; Jhoja, J.; Pond, J.; Vivien, L.; Pavesi, L.; et al. Design and simulation of silicon photonic schematics and layouts. Silicon Photonics Photonic Integr. Circuits V 2016, 9891, 185–195. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Li, L.; Jin, L.; Li, C. All-optical switch and limiter based on nonlinear polarization in Mach–Zehnder interferometer coupled with a polarization-maintaining fiber-ring resonator. Opt. Commun. 2006, 260, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.P.; Rakshit, J.K.; Hossain, M. Modeling of Polarization-Conversion and Rotation-Based Ultrafast All-Optical Ternary Logic Switch Using Microring Resonator. Braz. J. Phys. 2023, 53, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahrom, H.D. Germanium-incorporated Si-Ge-Si heterojunction phototransistors for a high-limit of detection and wide linear dynamic range near-infrared light detection. Opt. Express 2024, 32, 43475–43489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahromi, H.D.; Mahmoodi, A.; Sheikhi, M.H.; Zarifkar, A. Spectral response, dark current, and noise analyses in resonant tunneling quantum dot infrared photodetectors. Appl. Opt. 2016, 55, 8494–8499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahromi, H.D.; Zarifkar, A. A physical model for quantum wire infrared photodetectors under illumination condition. Opt. Commun. 2021, 493, 127043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Liu, X.; Li, H.; Wang, C.; Sun, J.; Zhou, J. THz polarization conversion metamaterial based on bianisotropic response of split-ring resonators. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2020, 53, 345102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokhari, S.H.A.; Cheema, H.M. Broadband asymmetric transmission via angle-induced chirality enhancement in split ring resonators. J. Appl. Phys. 2020, 128, 063102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabus, D.; Hamacher, M.; Troppenz, U.; Heidrich, H. Optical filters based on ring resonators with integrated semiconductor optical amplifiers in GaInAsP-InP. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2003, 8, 1405–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).