Repetition Frequency-Dependent Formation of Oxidized LIPSSs on Amorphous Silicon Films
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
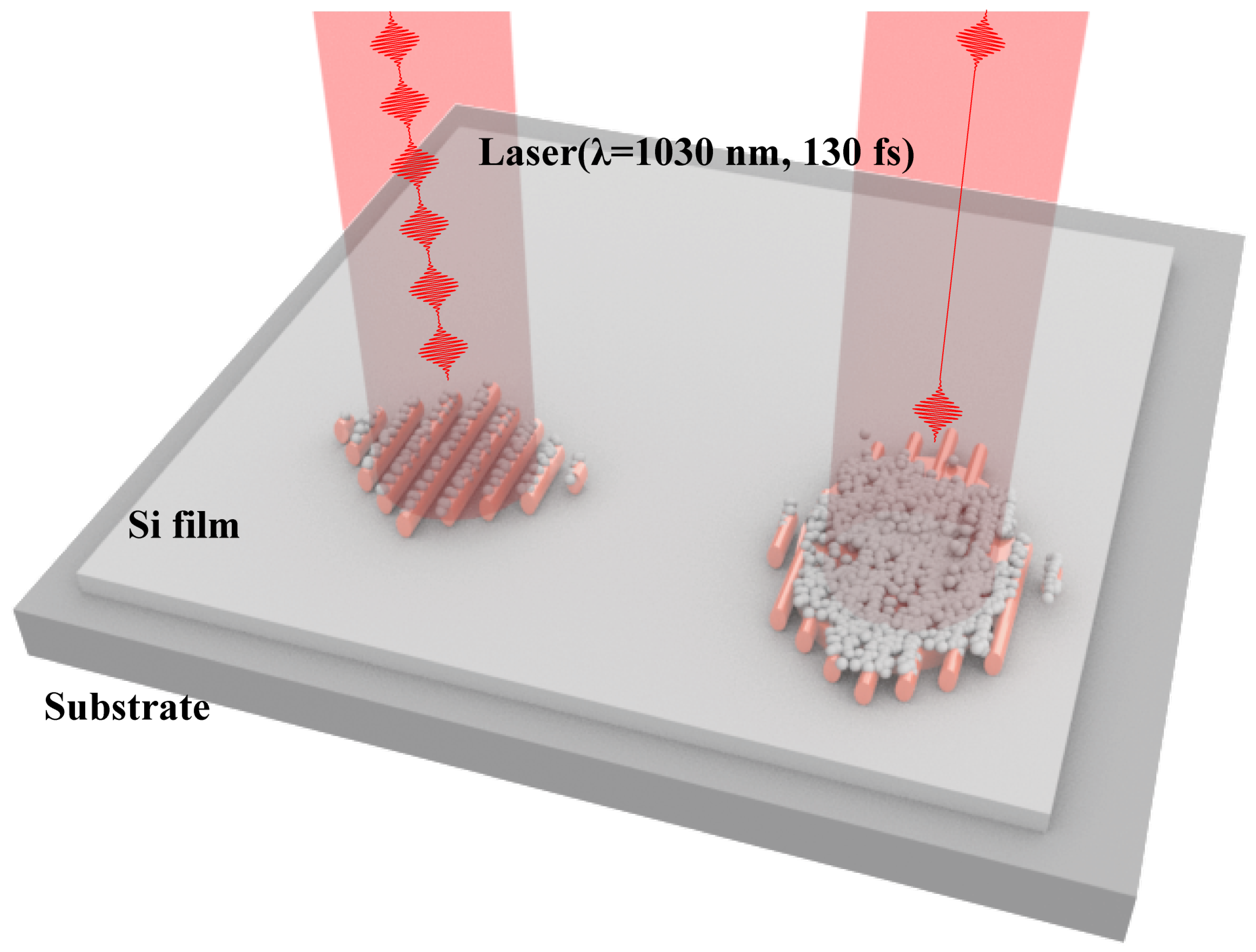
2.1. Experimental Setup
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Surface Characterization
2.4. Numerical Simulations
3. Results
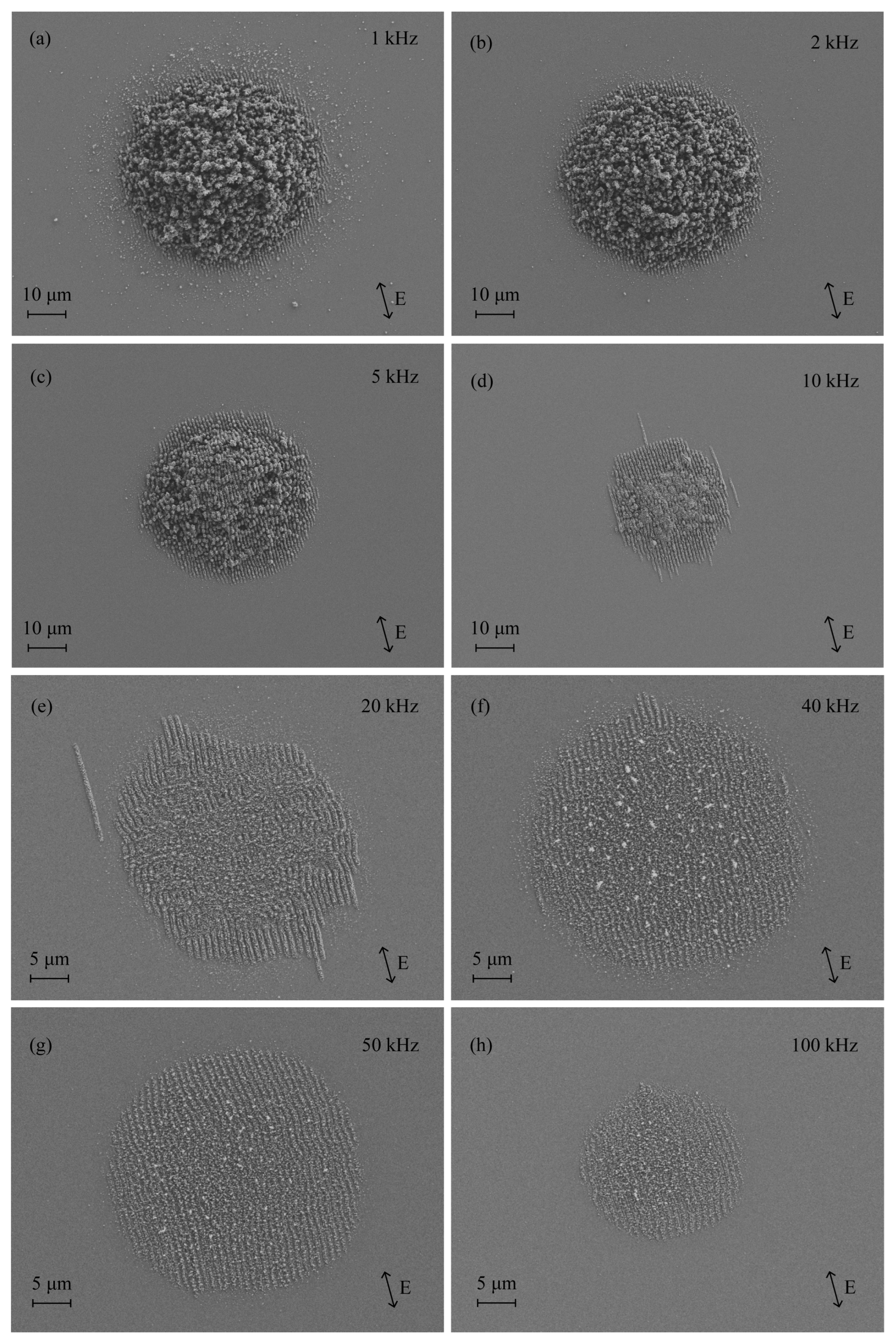
3.1. Morphology Evolution
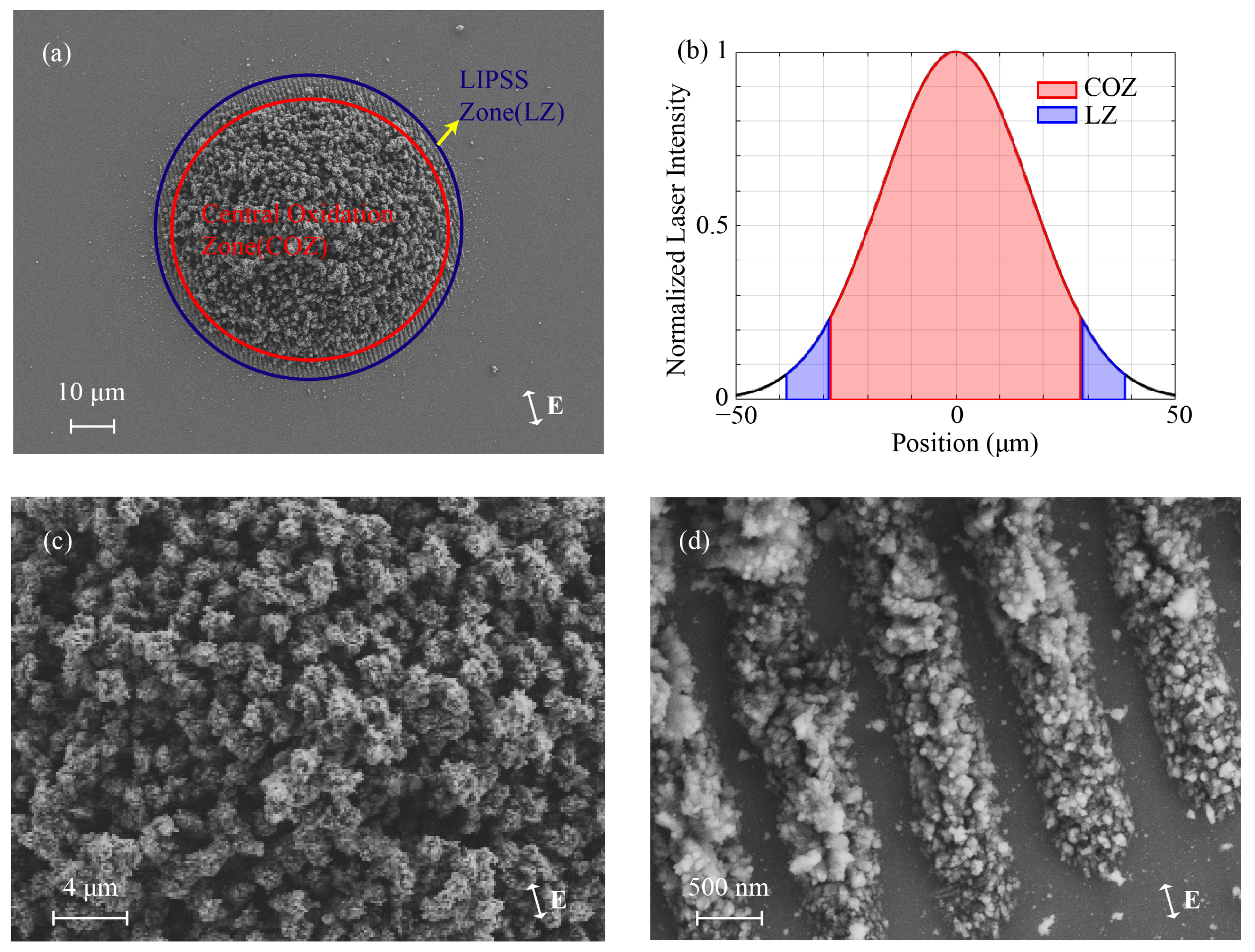
3.2. Structural Analysis
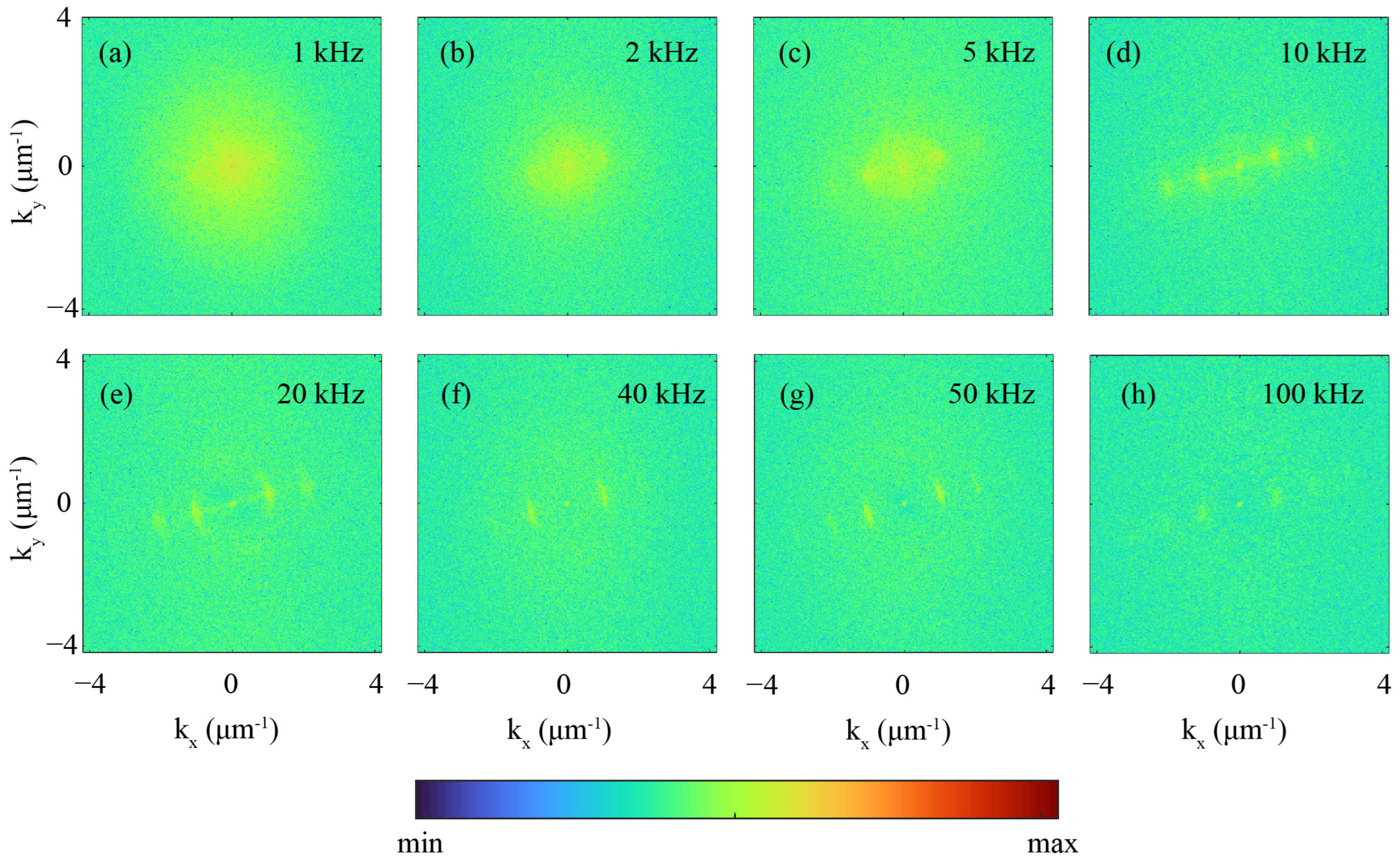
3.3. Morphological Metrics
3.4. Formation Dynamics
4. Conclusions
5. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Birnbaum, M. Semiconductor surface damage produced by ruby lasers. J. Appl. Phys. 1965, 36, 3688–3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Long, M.; Han, R.; Cao, K.; Zhang, S.; Feng, D.; Jia, T.; Sun, Z.; Qiu, J.; et al. Femtosecond laser-induced periodic structures: Mechanisms, techniques, and applications. Opto-Electron. Sci. 2022, 1, 220005-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonse, J.; Kirner, S.V.; Krüger, J. Laser-induced periodic surface structures (LIPSS). In Handbook of Laser Micro- and Nano-Engineering; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1–59. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Z.; Hong, M. Femtosecond laser precision engineering: From micron, submicron, to nanoscale. Ultrafast Sci. 2021, 2021, 9783514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Datta, A.; Nam, W.; Traverso, L.M.; Xu, X. Sub-diffraction limited writing based on laser induced periodic surface structures (LIPSS). Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dostovalov, A.V.; Derrien, T.J.Y.; Lizunov, S.A.; Přeučil, F.; Okotrub, K.A.; Mocek, T.; Korolkov, V.P.; Babin, S.A.; Bulgakova, N.M. LIPSS on thin metallic films: New insights from multiplicity of laser-excited electromagnetic modes and efficiency of metal oxidation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 491, 650–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Li, R.; Jiang, S.; Huang, M. Hybrid periodic microstructures fabricated on chromium metal surface using ns-DLIP scanning combined with LIPSS. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 153, 108261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraggelakis, F.; Lingos, P.; Cusworth, E.; Kravets, V.G.; Grigorenko, A.N.; Kabashin, A.V.; Stratakis, E. Highly ordered LIPSS on Au thin film for plasmonic sensing fabricated by double femtosecond pulses. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.03180. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, R.; Li, Z. Irregular LIPSS produced on metals by single linearly polarized femtosecond laser. Int. J. Extrem. Manuf. 2021, 4, 015102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, M.; Rebollar, E.; Ganeev, R.A.; Castillejo, M. Nanosecond laser-induced periodic surface structures on wide band-gap semiconductors. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 278, 325–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dostovalov, A.; Bronnikov, K.; Korolkov, V.; Babin, S.; Mitsai, E.; Mironenko, A.; Tutov, M.; Zhang, D.; Sugioka, K.; Maksimovic, J.; et al. Hierarchical anti-reflective laser-induced periodic surface structures (LIPSSs) on amorphous Si films for sensing applications. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 13431–13441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casquero, N.; Fuentes-Edfuf, Y.; Zazo, R.; Solis, J.; Siegel, J. Generation, control and erasure of dual LIPSS in germanium with fs and ns laser pulses. J. Phys. Appl. Phys. 2020, 53, 485106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Chi, Z.; Pan, R.; Qin, F.; Qiu, P.; Huang, J.; Xu, S. Materials removal mechanism of single crystalline SiC with laser-induced periodic surface structures (LIPSS). J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2023, 321, 118108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labbe, W.; Aspe, B.; Stolz, A.; Cachoncinlle, C.; Semmar, N. Formation of decorated LIPSS on GaN thin film by UV picosecond laser beam in air and under vacuum. Appl. Phys. A 2024, 130, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaković, B.; Zamfirescu, M.; Panjan, P.; Luculescu, C.; Albu, C.; Petrović, S. Laser ablation and LIPSS formation at static and dynamic multi-pulse regime on protective Al2O3/TiAlN coating. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2024, 56, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz, C.; Bonse, J.; Spaltmann, D.; Neumann, C.; Turchanin, A.; Bartolomé, J.F.; Müller, F.A.; Gräf, S. Tribological performance of metal-reinforced ceramic composites selectively structured with femtosecond laser-induced periodic surface structures. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 499, 143917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldera, M.M.; Fortuna, F.; Teutoburg Weiss, S.; Milles, S.; Taretto, K.R.; Lasag, A.F. Comparison of structural colors achieved by laser-induced periodic surface structures and direct laser interference patterning. 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Arthanari, S.; Park, J.E.; Bose, S.; Kang, H.W.; Kim, S.; Yang, M.; Lee, H.; Hwang, J.S. Structural color generation on transparent and flexible substrates by nanosecond laser induced periodic surface structures. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2023, 8, 2201725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalek, A.; Jwad, T.; Penchev, P.; See, T.L.; Dimov, S. Inline LIPSS monitoring method employing light diffraction. J. Micro Nano-Manuf. 2020, 8, 011002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arul, R.; Dong, J.; Simpson, M.C.; Gao, W. LIPSS-Sticks: Laser Induced Double Self Organization Enhances the Broadband Light Absorption of TiO2 Nanotube Arrays. Adv. Photonics Res. 2021, 2, 2000133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echarri, D.T.; San-Blas, A.; Martinez-Calderon, M.; Olaizola, S.M.; Granados, E. Propagation of broadband coherent light through LIPSS-based metasurfaces in diamond. Opt. Mater. Express 2022, 12, 2415–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonse, J.; Kirner, S.; Koter, R.; Pentzien, S.; Spaltmann, D.; Krüger, J. Femtosecond laser-induced periodic surface structures on titanium nitride coatings for tribological applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 418, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathmann, L.; Rusche, T.; Hasselbruch, H.; Mehner, A.; Radel, T. Friction and wear characterization of LIPSS and TiN/DLC variants. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 584, 152654. [Google Scholar]
- Onufrijevs, P.; Grase, L.; Padgurskas, J.; Rukanskis, M.; Durena, R.; Willer, D.; Iesalnieks, M.; Lungevics, J.; Kaupuzs, J.; Rukuiža, R.; et al. Anisotropy of the tribological performance of periodically oxidated laser-induced periodic surface structures. Coatings 2023, 13, 1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, F.A.; Kunz, C.; Gräf, S. Bio-inspired functional surfaces based on laser-induced periodic surface structures. Materials 2016, 9, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrikson, W.; Masman-Bakker, W.; van Bochove, B.; Skolski, J.; Eichstädt, J.; Koopman, B.; van Blitterswijk, C.; Grijpma, D.; Römer, G.w.; Moroni, L.; et al. Mold-Based Application of Laser-Induced Periodic Surface Structures (LIPSS) on Biomaterials for Nanoscale Patterning. Macromol. Biosci. 2016, 16, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasálková, N.S.; Juřicová, V.; Rimpelová, S.; Fajstavr, D.; Frỳdlová, B.; Kolská, Z.; Švorčík, V.; Slepička, P. LIPSS pattern induced by polymer surface instability for myoblast cell guidance. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2024, 221, 110667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutey, A.H.; Gemini, L.; Romoli, L.; Lazzini, G.; Fuso, F.; Faucon, M.; Kling, R. Towards laser-textured antibacterial surfaces. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schell, F.; Helbig, R.; Bouchard, F.; Zwahr, C.; Renner, L.D.; Lasagni, A.F. Embossed sub-micron DLIP and LIPSS textures on polypropylene delay surface colonization of Staphylococcus aureus. Mater. Lett. 2025, 379, 137722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Quan, Y.; Wackerow, S.; Abdolvand, A.; Zolotovskaya, S.A.; Zhao, Q. Hybrid Antibacterial Surfaces: Combining Laser-Induced Periodic Surface Structures with Polydopamine-Chitosan-Silver Nanoparticle Nanocomposite Coating. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2025, 12, 2400660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsibidis, G.D.; Barberoglou, M.; Loukakos, P.A.; Stratakis, E.; Fotakis, C. Dynamics of ripple formation on silicon surfaces by ultrashort laser pulses in subablation conditions. Phys. Rev. Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 2012, 86, 115316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Cao, K.; Chen, T.; Cheng, K.; Zhang, S.; Feng, D.; Jia, T.; Sun, Z.; Qiu, J. Extremely regular periodic surface structures in a large area efficiently induced on silicon by temporally shaped femtosecond laser. Photonics Res. 2021, 9, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öktem, B.; Pavlov, I.; Ilday, S.; Kalaycıoğlu, H.; Rybak, A.; Yavaş, S.; Erdoğan, M.; Ilday, F.Ö. Nonlinear laser lithography for indefinitely large-area nanostructuring with femtosecond pulses. Nat. Photonics 2013, 7, 897–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Geng, J.; Shi, L.; Cui, W.; Qiu, M. Impact of film thickness in laser-induced periodic structures on amorphous Si films. Front. Optoelectron. 2023, 16, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Geng, J.; Shi, L.; Cui, W.; Qiu, M. Oxidation-driven 2D LIPSS on amorphous Si films atop metal layers: The interplay of near-field and far-field effects. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2024, 649, 159100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Fang, X.; Zhang, L.; Yao, G.; Xu, L.; Liu, F.; Tang, W.; Shi, L.; Qiu, M. Controllable generation of large-scale highly regular gratings on Si films. Light. Adv. Manuf. 2021, 2, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Shi, L.; Liu, J.; Xu, L.; Yan, W.; Qiu, M. Laser-induced deep-subwavelength periodic nanostructures with large-scale uniformity. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2023, 122, 021104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Yan, W.; Shi, L.; Qiu, M. Quasicylindrical waves for ordered nanostructuring. Nano Lett. 2022, 22, 9658–9663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinev, D.A.; Yuzhakova, D.S.; Moskvin, M.K.; Veiko, V.P. Formation of the submicron oxidative LIPSS on thin titanium films during nanosecond laser recording. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraggelakis, F.; Mincuzzi, G.; Lopez, J.; Manek-Hönninger, I.; Kling, R. Controlling 2D laser nano structuring over large area with double femtosecond pulses. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 470, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Yan, W.; Shi, L.; Qiu, M. Surface plasmons interference nanogratings: Wafer-scale laser direct structuring in seconds. Light. Sci. Appl. 2022, 11, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florian, C.; Fuentes-Edfuf, Y.; Skoulas, E.; Stratakis, E.; Sanchez-Cortes, S.; Solis, J.; Siegel, J. Influence of heat accumulation on morphology debris deposition and wetting of LIPSS on steel upon high repetition rate femtosecond pulses irradiation. Materials 2022, 15, 7468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, H.; Deng, G.; Feng, G.; Chen, L.; Li, J.; Yang, C.; Zhou, S. Role of nanoparticles generation in the formation of femtosecond laser-induced periodic surface structures on silicon. Opt. Lett. 2017, 42, 3315–3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnilitskyi, I.; Derrien, T.J.Y.; Levy, Y.; Bulgakova, N.M.; Mocek, T.; Orazi, L. High-speed manufacturing of highly regular femtosecond laser-induced periodic surface structures: Physical origin of regularity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.T.; Rodak, D.; Wong, C.; Hayden, C. Effects of micro-and nano-structures on the self-cleaning behaviour of lotus leaves. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, G.S.; Watson, J.A. Natural nano-structures on insects—possible functions of ordered arrays characterized by atomic force microscopy. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2004, 235, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonse, J. Quo vadis LIPSS?—recent and future trends on laser-induced periodic surface structures. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Zhang, D.; Li, Z. Femtosecond laser subtractive/additive-integrated biomimetic manufacturing for visible/infrared encryption and stimuli-responsive infrared decryption. Int. J. Extrem. Manuf. 2025, 7, 045009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
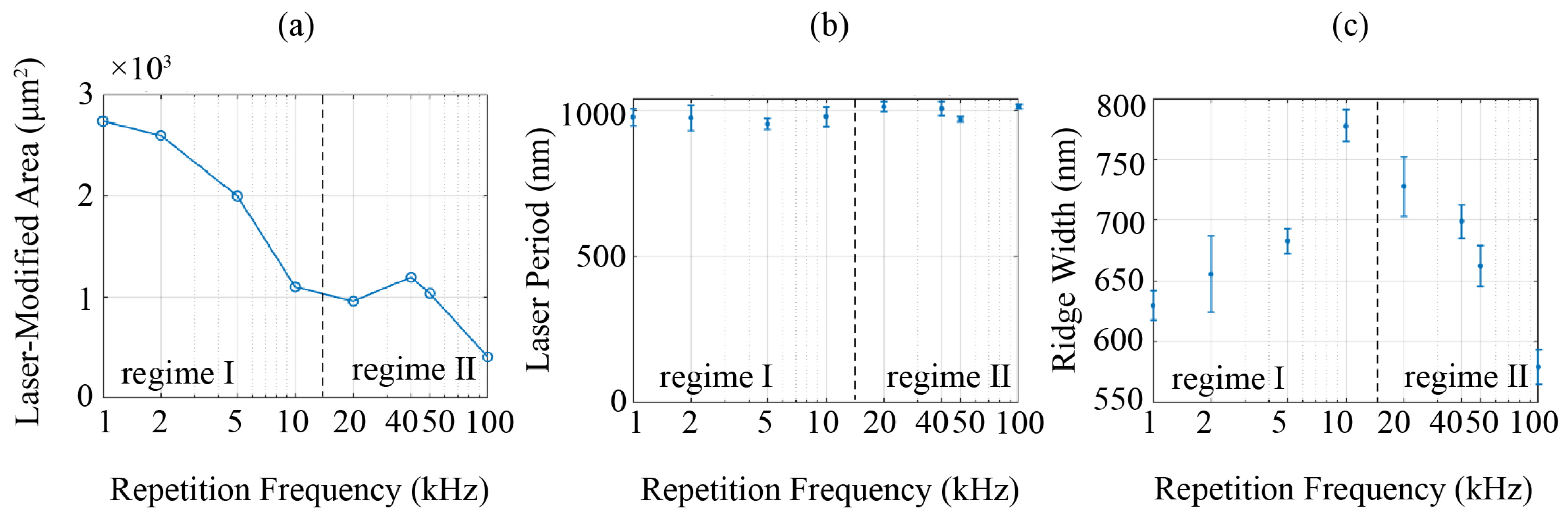
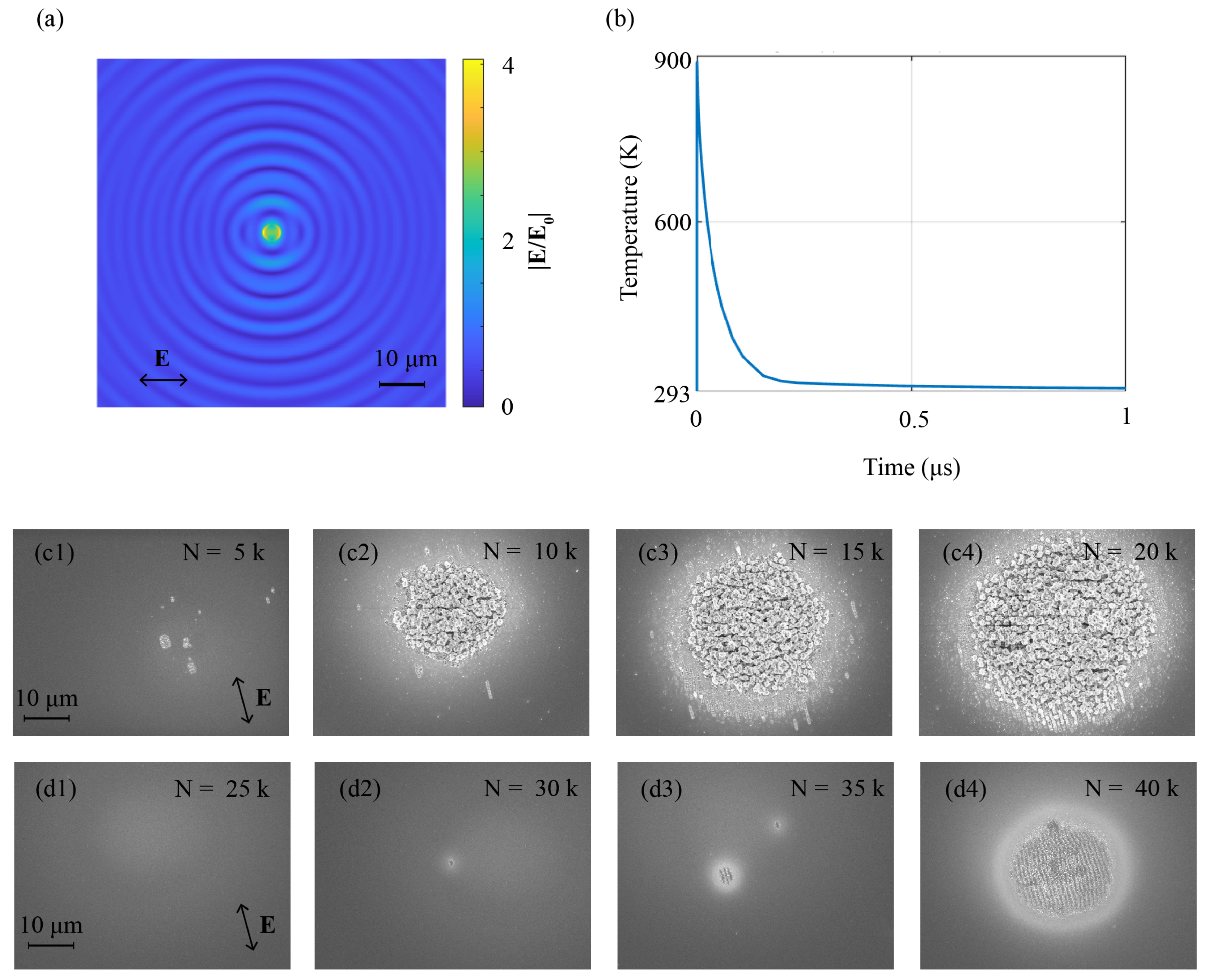
| Repetition Frequency (kHz) | DLOA (°) | Morphological Regime |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | N/A | Disordered oxidation-dominated |
| 2 | N/A | Disordered oxidation-dominated |
| 5 | N/A | Disordered oxidation-dominated |
| 10 | 9.43 | Disordered oxidation-dominated (transition point) |
| 20 | 25.17 | LIPSS-dominated |
| 40 | 18.38 | LIPSS-dominated |
| 50 | 17.15 | LIPSS-dominated |
| 100 | 4.90 | LIPSS-dominated |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, L.; Yan, W.; Cui, W.; Qiu, M. Repetition Frequency-Dependent Formation of Oxidized LIPSSs on Amorphous Silicon Films. Photonics 2025, 12, 667. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12070667
Xu L, Yan W, Cui W, Qiu M. Repetition Frequency-Dependent Formation of Oxidized LIPSSs on Amorphous Silicon Films. Photonics. 2025; 12(7):667. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12070667
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Liye, Wei Yan, Weicheng Cui, and Min Qiu. 2025. "Repetition Frequency-Dependent Formation of Oxidized LIPSSs on Amorphous Silicon Films" Photonics 12, no. 7: 667. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12070667
APA StyleXu, L., Yan, W., Cui, W., & Qiu, M. (2025). Repetition Frequency-Dependent Formation of Oxidized LIPSSs on Amorphous Silicon Films. Photonics, 12(7), 667. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12070667






