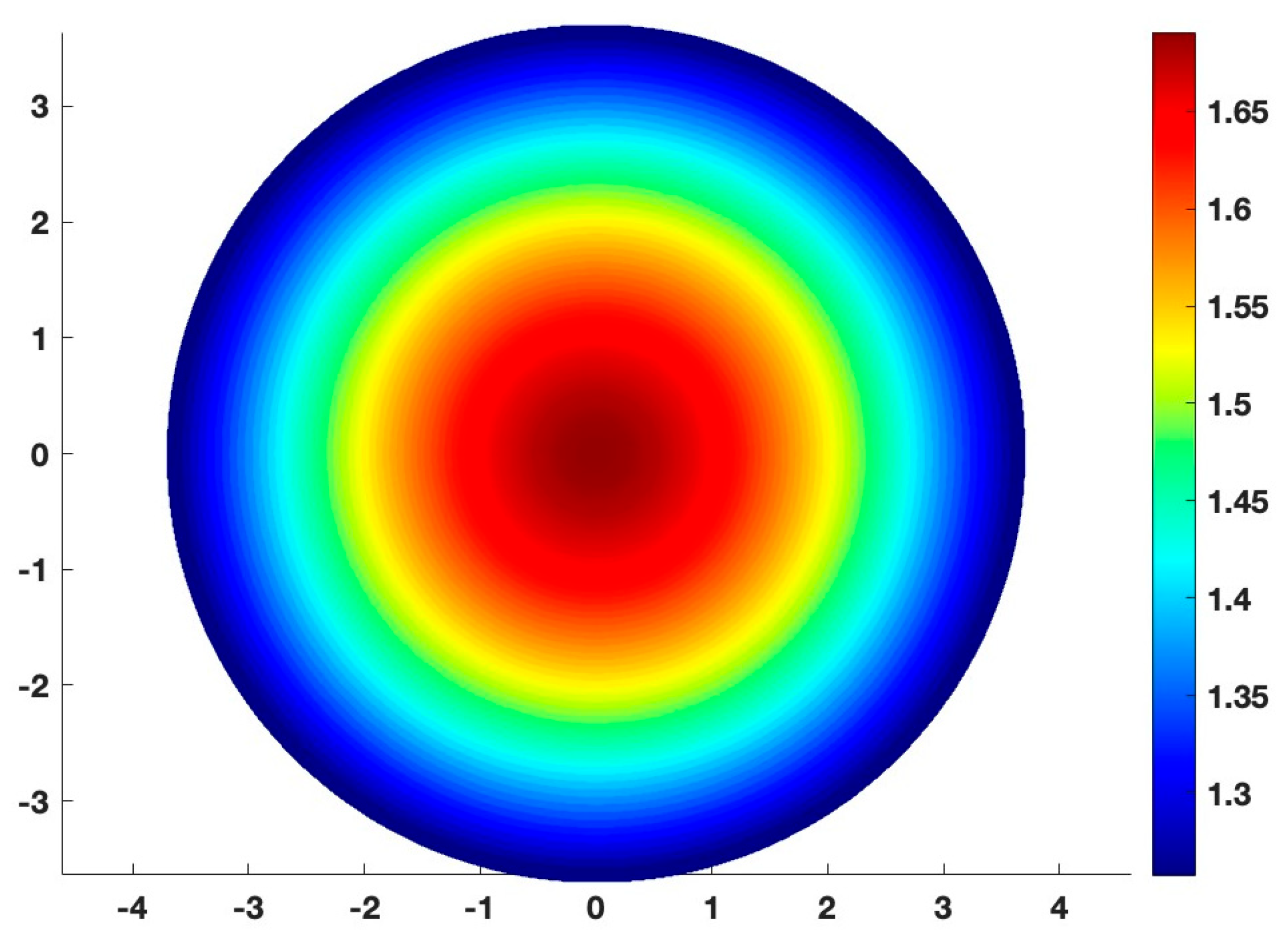
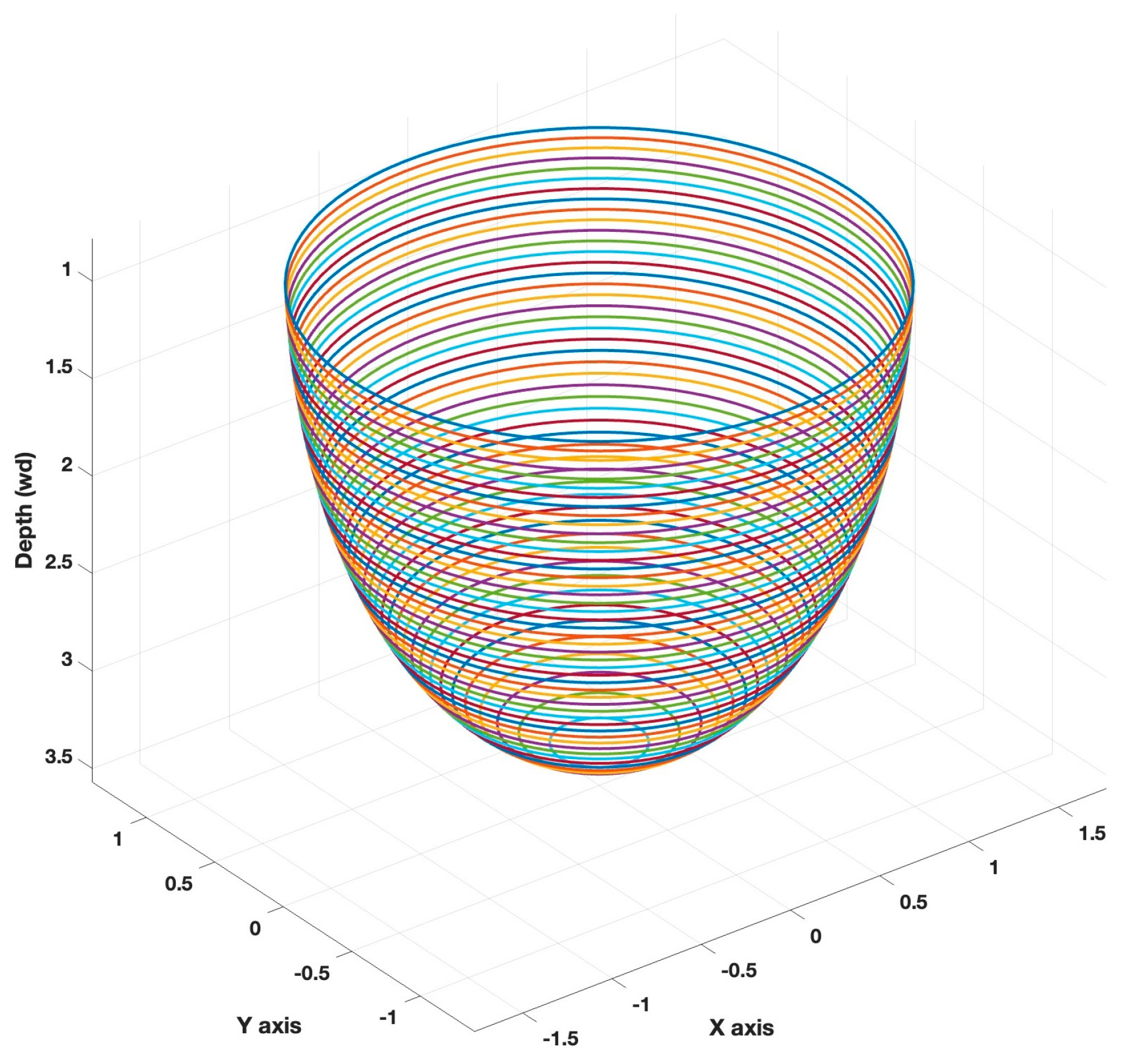
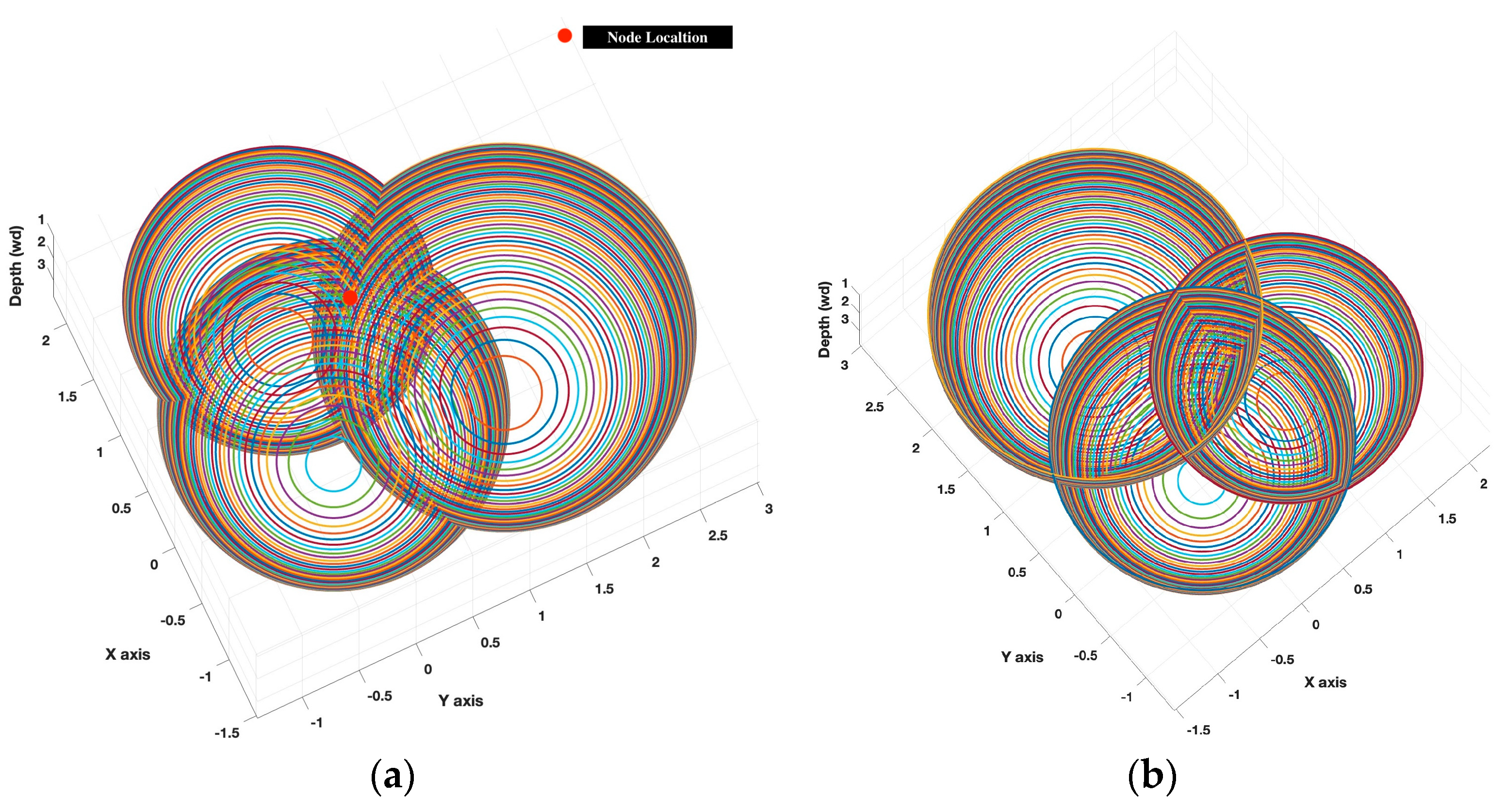
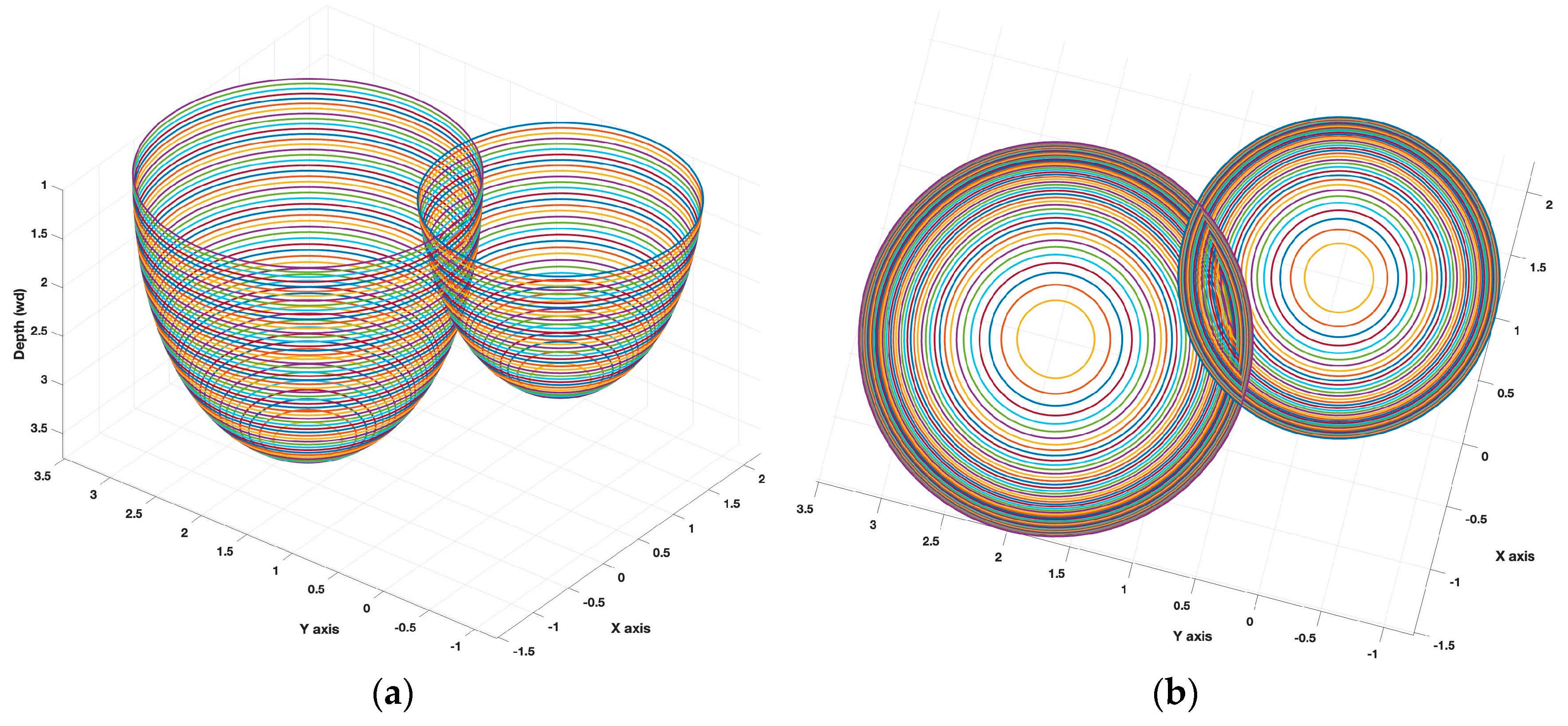
1. Introduction
The relentless advancement of communication technologies has dramatically transformed our capacity to interact with and understand the world around us. A significant contributor to this transformation is the Internet of Things (IoT), which envisions a seamlessly connected network of devices operating across diverse environments, including terrestrial, aerial, and aquatic domains. As we move towards the next generation of wireless technology with the emergence of 6G, the integration of underwater networks has become increasingly important. These networks hold the key to a multitude of critical applications such as monitoring marine life, assessing environmental pollutants, conducting oceanographic research, and executing high-priority operations like search-and-rescue missions or clandestine military surveillance.
A fundamental challenge in deploying underwater networks is the precise localization of submerged nodes. Accurate positioning is essential not only for contextualizing the collected data but also for optimizing the network topology and boosting the efficiency of communication protocols. Traditional localization methods have predominantly utilized acoustic signaling [
1,
2], relying on surface vessels or anchored nodes with GPS coordinates to translate relative positions into global coordinates. However, in scenarios where operational stealth is required—such as in covert naval operations—the presence of surface or tethered markers can compromise the mission by revealing the presence of the underwater network [
3,
4]. In addition, deploying markers could constitute a logistical challenge in applications that serve emerging events such as search and rescue and naval combat.
To overcome these limitations, this paper proposes the use of VLC across the air–water interface as an innovative solution for underwater node localization. VLC stands out as an effective means due to its ability to transmit high-bandwidth data through both air and water, and hence it does not need the deployment of relaying nodes on the water surface. Unlike photoacoustic techniques [
4], which often suffer from logistical complexities and limited data rates, VLC offers a more efficient and scalable approach. VLC eliminates the need for surface-deployed infrastructure such as buoys, anchored relays, or pressure-based markers. This not only reduces logistical burden but also removes visual and physical traces of the network from the water surface. The result is a system that is inherently well-suited for covert, rapidly deployable, and infrastructure-free localization, further enhanced by the high directionality and rapid attenuation of light in water [
5], which localizes the transmission footprint and minimizes the risk of detection by unintended observers. By measuring received light intensities and applying trilateration algorithms, we demonstrate that underwater nodes can be accurately localized without the need for surface-based reference points. This method not only enhances the feasibility of deploying underwater networks in sensitive operations but also enables the introduction of new applications, e.g., studying the effect of climate change. In our preliminary investigation [
6,
7,
8], we have assumed that the underwater node is equipped with a pressure sensor to measure its depth, effectively reducing the scope of the localization problem to 2D. However, in practice, the node may not have a pressure sensor due to constraints like power consumption, node size, or cost. This paper overcomes such a limitation and proposes 3D-LUNA, a novel method for 3D localization of underwater nodes using airborne visible light beams. This novel framework enables underwater node localization using airborne VLC without relying on pressure sensors or anchored nodes. The method reconstructs 3D positions by correlating light intensity measurements with modeled beam propagation across depth layers. To address the challenge of unknown depth, we introduce an optimization approach that identifies the most likely depth by minimizing errors. The system is validated through extensive simulations, demonstrating high localization accuracy and robustness under different deployment and mobility conditions.
It is worth noting that while recent research such as the HOENN-based DoA estimation method [
9] also utilizes magnitude measurements for angular inference, its objective, methodology, and application context are fundamentally different from ours. Specifically, HOENN is designed for aerial scenarios and employs hybrid optical–electronic neural networks and diffractive metasurfaces to estimate the direction of arrival of RF signals. In contrast, our proposed 3D-LUNA framework addresses the challenge of cross-medium 3D localization of underwater nodes by modeling the propagation of visible light beams across the air–water interface. It reconstructs node coordinates based on measured light intensity without relying on learning-based architectures or angular classification. Unlike HOENN, 3D-LUNA requires no pre-training or metasurfaces and is particularly suited for infrastructure-free and covert underwater applications.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows.
Section 2 provides a review of related work, discussing existing underwater localization techniques and their limitations.
Section 3 presents the system model and the theoretical foundation of our proposed 3D-LUNA approach, including key assumptions and mathematical formulations.
Section 4 details the 3D-LUNA localization protocol, explaining how airborne VLC beams are utilized for accurate underwater node positioning.
Section 5 evaluates the proposed method through extensive simulations, analyzing its accuracy, efficiency, and robustness under various conditions. Finally,
Section 6 concludes the paper by summarizing key contributions and outcomes.
2. Related Work
Accurate localization of underwater nodes is vital for applications such as marine research, environmental monitoring, and defense operations. Traditionally, acoustic-based methods have been the primary approach, as sound waves propagate efficiently in water [
10,
11,
12]. In contrast, radio frequency (RF) and electromagnetic waves, commonly used for terrestrial and aerial localization, face significant challenges underwater [
13,
14]. The high conductivity of seawater causes severe attenuation of RF signals, drastically limiting their range. While extremely low frequency (ELF) and very low frequency (VLF) waves have been explored for deep-sea communication, their feasibility is hindered by the need for large antennas and high power consumption, making them unsuitable for compact underwater nodes [
15]. Another alternative, magnetic induction (MI) communication, has shown promise for cross-medium applications like air-to-water transmission [
16]. However, despite its ability to penetrate the water surface, MI communication suffers from substantial path loss, restricting its practical use.
Traditional underwater localization has predominantly relied on acoustic-based methods, which leverage sound waves due to their superior propagation characteristics in water. Various approaches, such as time of arrival (ToA) [
17], time difference of arrival (TDoA) [
18], and angle of arrival (AoA) [
19], have been widely employed in underwater sensor networks. Acoustic localization systems are further classified into range-based methods [
20,
21,
22], which require precise distance measurements between nodes, and range-free methods [
23,
24], which use connectivity or hop-count data to estimate positions. These techniques have been extensively studied, leading to solutions such as long baseline (LBL) [
25], short baseline (SBL) [
26], and ultra-short baseline (USBL) [
27] systems. Despite their widespread adoption, acoustic-based methods have several limitations. First, they suffer from high latency and limited bandwidth, restricting data transmission rates [
28]. Second, the presence of multipath effects, Doppler shifts, and environmental noise significantly affects accuracy [
29]. Moreover, acoustic localization often relies on surface or anchored reference nodes, which may not be viable in dynamic or covert operations.
In recent years, VLC has emerged as a promising alternative to traditional acoustic and RF-based underwater communication [
5,
30]. Recent studies have improved the understanding of VLC channel characteristics and performance, with a particular focus on light propagation across different water conditions [
31]. The behavior of light beams as they transition through air–water interfaces has been examined [
32]. VLC leverages high-bandwidth optical signals to achieve low-latency, high-data-rate transmission in underwater environments [
33,
34]. Compared to acoustic methods, VLC offers significantly higher throughput and is not affected by Doppler shifts or multipath fading. Recent research has also investigated cross-medium VLC localization, where optical signals propagate from an airborne or surface source into the underwater environment.
Some approaches rely on passive optical uplinks to improve positioning accuracy [
35]. This method typically involves placing retroreflectors or light-sensitive surfaces on underwater nodes, which reflect or modulate incoming optical signals from surface or airborne sources back to receivers. This allows for range estimation or angle-of-arrival measurements using returned light, often improving localization accuracy without requiring active transmission from the underwater node. While such systems reduce onboard power requirements and hardware complexity, they still require careful alignment between transmitters and receivers. Moreover, the optoacoustic effect has been exploited for cross-medium localization, where high-energy laser beams are used to generate underwater acoustic signals [
36,
37]. While these methods enable underwater signal transmission, they suffer from high power consumption and complex deployment requirements, making them less suitable for mobile or energy-constrained underwater networks. Xiaoyang et al. utilized polarization and deep learning techniques for underwater geolocation [
38]; however, their approach required a vast amount of data collection. Fusion of aerial image and acoustic image using neural networks has also been explored [
39], but it still relies on vast data collection and processing. Despite all the advancements, existing solutions often rely on surface nodes, pressure sensors, or passive uplinks, limiting their feasibility for real-world deployment. To the best of our knowledge, no prior study has demonstrated a fully airborne-enabled underwater localization system that transmits GPS-encoded positioning information directly to underwater nodes without relying on anchored reference points, depth sensors, or pre-collected data.
5. Results and Discussion
The validation of the 3D-LUNA model is conducted using MATLAB R2023b simulations. In these simulations, the airborne unit operates with a 60-degree beam angle and employs a blue light wavelength. Various parameters in the system are susceptible to errors, primarily due to instrumentation inaccuracies and environmental factors. Key aspects such as transmission power, the altitude of the airborne unit, and the depth of the underwater node are all influenced by measurement uncertainties, which ultimately affect light intensity, as described in Equation (1). In practice, these errors can be significantly minimized through proper calibration and the use of high-precision sensors. For the simulations, we assume that errors in measurable parameters follow a Gaussian distribution with a zero mean and a standard deviation of 1%. Additionally, the position of the underwater node is estimated using an inertial navigation system (INS), which introduces its own errors due to spatial and angular displacement. These errors are also modeled as Gaussian with a zero mean and a 1% standard deviation. The underwater environment is simulated as pure seawater with an extinction coefficient of 0.056.
In our previous work [
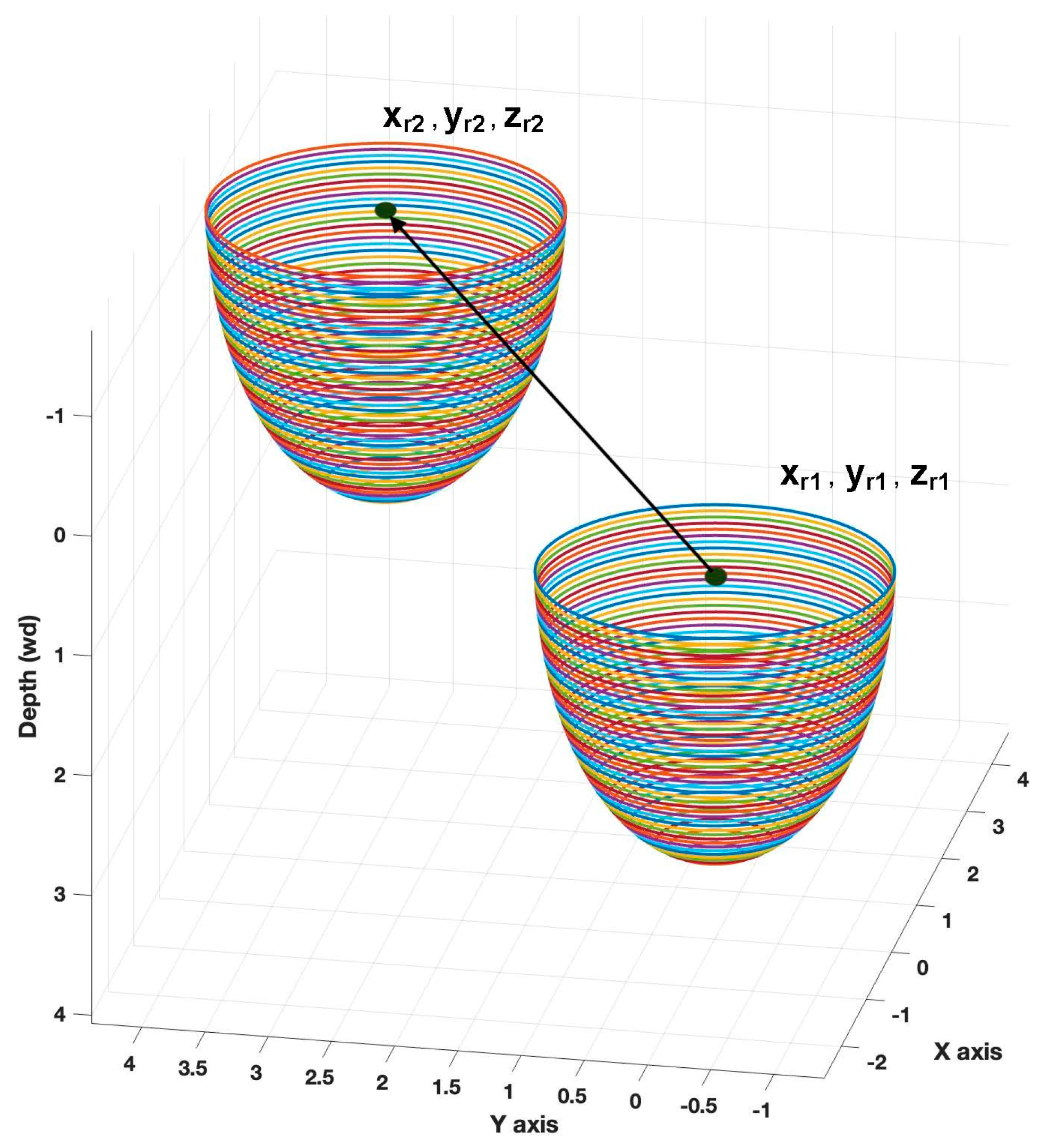
5], we investigated underwater node localizability while considering the mobility patterns of both airborne and underwater nodes. The key aspect is whether the underwater nodes receive sufficient transmissions for accurate localization. In this study, we focus on the localization error of nodes that do not know their underwater depth and receive an adequate number of transmissions. To evaluate the localization performance of 3D-LUNA, we consider a deployment region of 100 m × 100 m × 10 m, which is divided into 100 equal-sized cells. Given the unique characteristics of this localization approach, we compare its performance against an alternative VLC-based localization model, which we refer to as OMNI. In the OMNI model, an underwater VLC transmitter is located at the center of each cell. Specifically, each cell is a 10 m cube where the transmitter is positioned at the center, emitting light omni-directionally. The underwater target node, upon receiving and measuring the light intensity, estimates its location using an inverse square law using underwater attenuation, i.e., using the following:
Though 3D-LUNA modality only deals with directional transmission, it still covers an entire cell since the VLC source is airborne. Omni-directionality is necessary for an underwater light source to cover the entire cell to ensure localizability under the OMNI method (OMNI does not have to handle cross-medium transmission since it is transmitting from underwater). This comparative analysis aims to assess the accuracy and reliability of 3D-LUNA in underwater localization scenarios.
5.1. Stationary Node
For stationary underwater nodes, 30 nodes are placed underwater in random locations. We then compare the performance of both OMNI and 3D-LUNA.
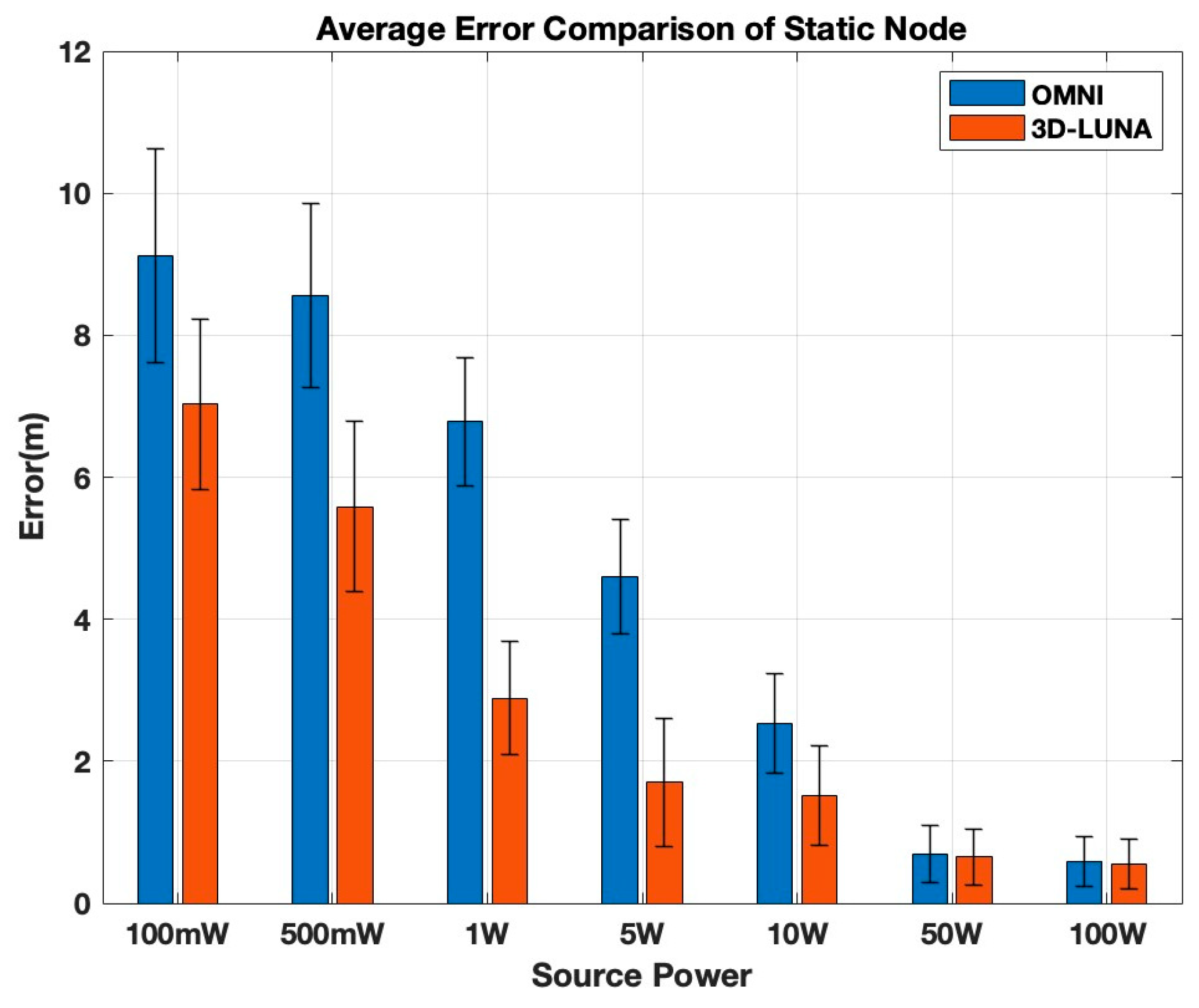
Figure 8 shows the localization error for both methods under varying transmission power. The results reflect the average of 100 iterations.
As indicated by the results, 3D-LUNA consistently outperforms Omni by maintaining a lower localization error across all power levels. At low power levels (100 mW–1 W), Omni’s error is significantly higher compared to 3D-LUNA, with the gap remaining noticeable at 500 mW and 1 W. In the mid-power range (5 W–10 W), Omni still exhibits nearly double the error of 3D-LUNA at 5 W, though the difference starts to shrink at 10 W. However, at higher power levels (50 W and 100 W), both methods achieve similar accuracy, with error becoming minimal, indicating that at very high power, transmission strength dominates over method choice. When analyzing the error rate change relative to power levels, 3D-LUNA clearly stands out as it consistently demonstrates a higher reduction rate at lower power levels, particularly between 100 mW and 5 W. Initially, between 100 mW and 500 mW, 3D-LUNA achieves an error reduction rate of approximately 15–20%, whereas OMNI reduces error by only 10–15%. As power increases to 1 W, the gap widens, with 3D-LUNA achieving up to 30–35% reduction compared to OMNI’s 20–25%. The most significant divergence occurs between 1 W and 5 W, where 3D-LUNA reaches a peak reduction of 50–55%, nearly 10–15% higher than OMNI’s 30–40%. This indicates that 3D-LUNA adapts more efficiently in the mid-power range. However, beyond 10 W, both methods experience a sharp decline in rate change, with OMNI dropping to 25–30% and 3D-LUNA maintaining a slight lead at 35–40%. At 50 W and 100 W, both methods exhibit minimal rate change, converging at 5–10%, showing diminishing returns. Overall, the gap in rate change between the two methods is most prominent in the lower-to-mid power range, whereas at high power levels, their performance stabilizes, indicating that 3D-LUNA is most beneficial in power-constrained environments, while both methods perform similarly at high power.
Both OMNI and 3D-LUNA are highly dependent on the transmission power and how the signal intensity is distributed. At lower power levels (100 mW to 5 W), the error is significantly higher for both methods due to weaker signals, which are more susceptible to attenuation and environmental noise. However, the error in OMNI remains consistently larger compared to 3D-LUNA because OMNI distributes power uniformly in all directions, leading to greater signal dispersion and reduced signal strength at the receiver. In contrast, 3D-LUNA appears to use a more concentrated and efficient power distribution, ensuring stronger signal reception and reduced localization error. When power increases beyond 5 W, the stronger transmission mitigates attenuation effects. However, beyond 10 W, both methods approach a point where increasing power has minimal impact on localization error. By 50 W and 100 W, both OMNI and 3D-LUNA reach similar low-error performance, indicating that at these high power levels, the effectiveness of signal distribution becomes less critical as the primary constraints shift to environmental factors. This suggests that while transmission power plays a key role in reducing localization error, the way the power is distributed is crucial at lower power levels, where a more focused transmission like 3D-LUNA provides a significant advantage.
Overall, 3D-LUNA proves to be the superior approach, especially at lower and mid-power levels, offering better accuracy without requiring excessive power, making it a more efficient option in scenarios where power consumption matters.
5.2. Mobile Node
To evaluate the localization performance for mobile underwater nodes, we have implemented the random waypoint (RWP) mobility model [
40] to simulate the relatively complex movement of the mobile underwater node. In this mobility model, the underwater node moves at a constant speed, beginning its journey from a randomly chosen point within a 3D space. It then travels in a randomly selected direction within the defined region. After a randomly determined duration in the range of 10 to 30 s, the mobile underwater node changes direction, selecting a new random path. Notably, there is no pause time when the mobile underwater node alters its direction.
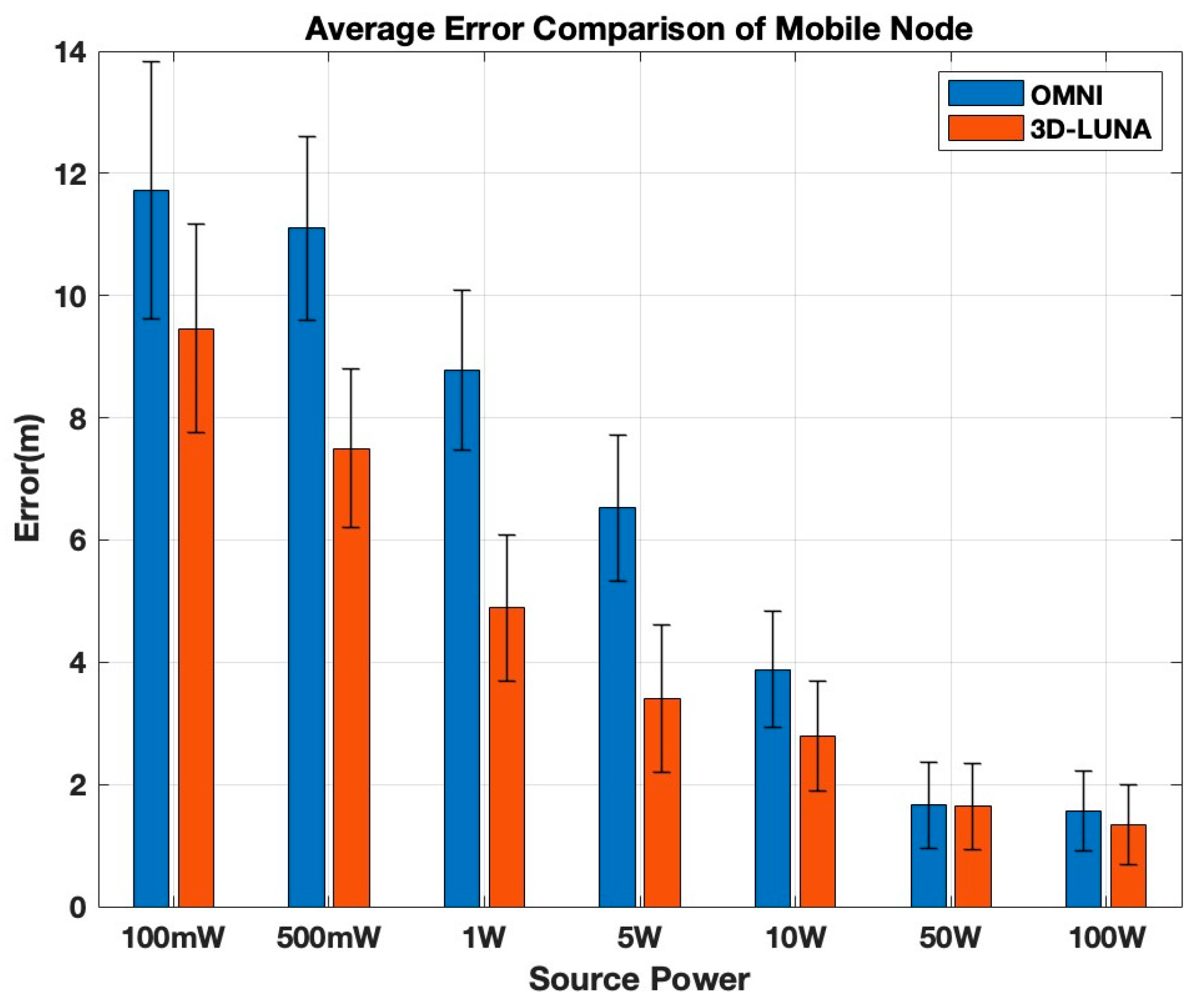
Figure 9 shows the average localization performance for varying transmission power for 100 iterations where a node receives the required number of transmissions to localize itself.
For the mobile node, the comparison between OMNI and 3D-LUNA follows a similar trend to the static node, with 3D-LUNA consistently outperforming OMNI by producing lower localization errors across all power levels. At low power levels (100 mW–1 W), OMNI shows significantly higher errors, reaching approximately 12 m at 100 mW, while 3D-LUNA reduces it to around 10 m. The error remains noticeably higher for OMNI at 500 mW and 1 W, but both methods show a clear improvement as power increases. In the mid-power range (5 W–10 W), OMNI’s error remains significantly higher than 3D-LUNA, though the gap starts to shrink. At higher power levels (50 W–100 W), both methods converge to a similar accuracy level with minimal error, demonstrating that at very high power, the method selection becomes less critical. Overall, 3D-LUNA is a better choice, particularly at lower and mid-power levels, as it ensures greater accuracy without requiring excessive power.
The error rate between consecutive power levels varies for OMNI and 3D-LUNA, but it displays a similar trend to static nodes, with 3D-LUNA consistently outperforming OMNI at lower power levels (100 mW–10 W) due to its more efficient signal distribution. The most significant reduction occurs between 1 W and 5 W, where 3D-LUNA achieves nearly 50% error reduction compared to OMNI’s 30–40%, highlighting its superior power utilization. As power increases to 10 W, the gap narrows, with OMNI beginning to catch up, though 3D-LUNA still maintains a slight advantage (~5–10% more error reduction). Beyond 10 W, and especially from 50 W to 100 W, both methods experience a similar trend, with error reduction rates converging as the power of transmission becomes the dominant factor. This trend suggests that while power distribution optimization is critical at lower power levels, at higher power, the influence of transmission power makes OMNI and 3D-LUNA nearly equivalent in performance.
When comparing static and mobile nodes, the mobile node generally exhibits higher errors across all power levels, indicating that mobility introduces additional localization challenges. At low power levels, the error for mobile nodes is higher than that of static nodes, suggesting that movement increases uncertainty in localization. However, the error reduction pattern remains similar, where higher power levels improve accuracy for both cases, and 3D-LUNA consistently outperforms OMNI. Notably, at high power (50 W and 100 W), the errors in both static and mobile cases converge, showing minimal difference between OMNI and 3D-LUNA, reinforcing the conclusion that transmission power dominates over method selection at these levels. In summary, while both cases benefit from higher power, 3D-LUNA is the superior choice, especially in mobile scenarios where errors tend to be more pronounced.
5.3. Two- vs. Three-Dimensional Localization Comparison
We have also compared 3D-LUNA performance with our previous work, which utilizes a depth sensor to convert the localization scheme into a 2D problem for both static [
4] and mobile [
5] nodes. In both 3D and 2D modality, the transmission scheme is exactly the same, but 3D-LUNA does not require the depth information acquired from the depth sensor.
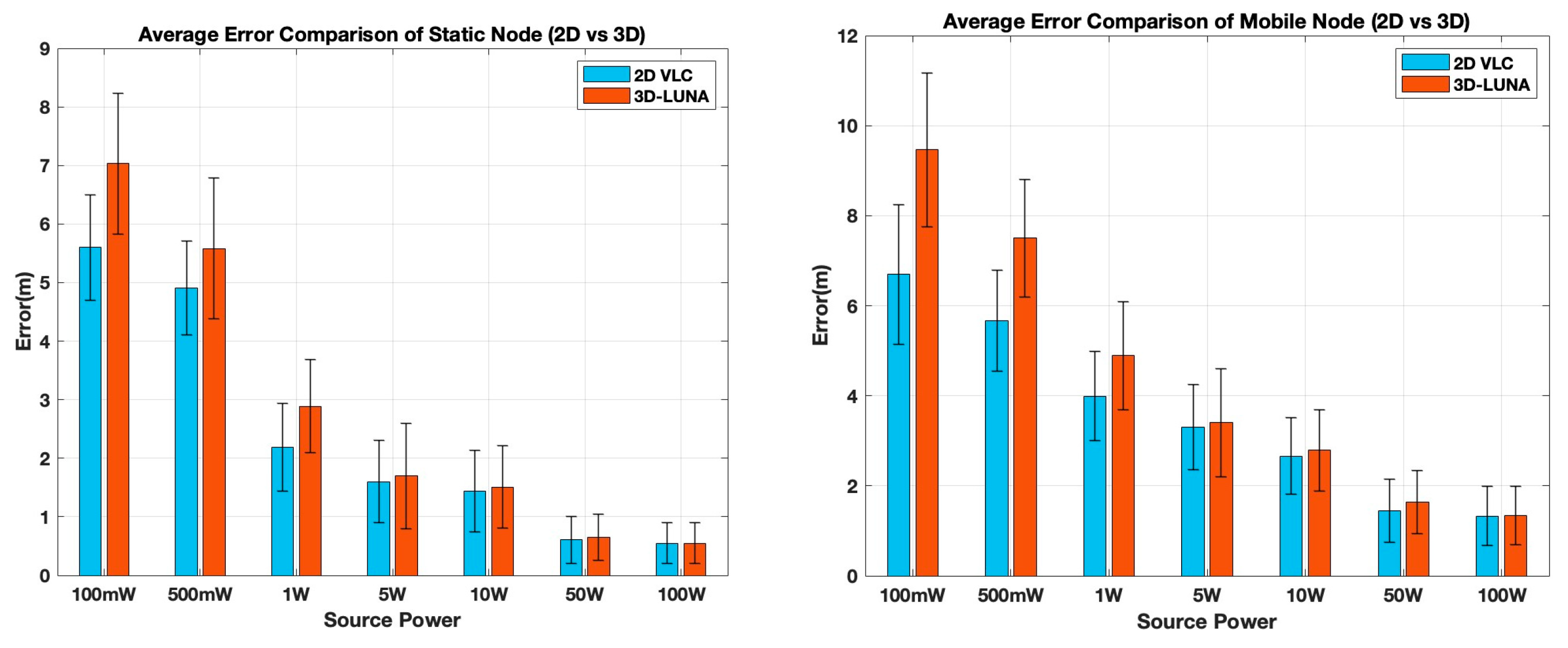
Figure 10 shows a comparison of performance for both static and mobile modality.
For static nodes, the results show that both methods experience higher localization errors at lower power levels (100 mW and 500 mW), with 3D-LUNA exhibiting higher errors than 2D VLC. This is expected, as 2D VLC benefits from an external depth measurement, improving its localization accuracy in weaker signal conditions. However, as the source power increases, the errors for both methods progressively and significantly decrease, and beyond 10 W, the difference between 2D VLC and 3D-LUNA becomes negligible. At 50 W and 100 W, both approaches yield nearly identical performance, demonstrating that 3D-LUNA can achieve similar accuracy without relying on a pressure sensor when sufficient power is available. This is a significant advantage, as it eliminates the dependency on external sensors, making 3D-LUNA a more autonomous and hardware-efficient solution.
For mobile nodes, a similar trend is observed, but with generally higher errors compared to static nodes, emphasizing the challenges introduced by movement. At lower power levels, 2D VLC again has an advantage, as the depth information from the pressure sensor provides a more stable reference. However, as power levels increase, the error difference between 2D VLC and 3D-LUNA shrinks, and by 50 W and 100 W, their performances are nearly indistinguishable. The error bars also indicate that the variability in localization accuracy decreases with increasing power, making high-power scenarios more reliable for both methods.
The most critical takeaway from this analysis is that while 2D VLC gains an initial advantage by incorporating a pressure sensor, 3D-LUNA ultimately achieves comparable localization accuracy without requiring any additional hardware. This makes 3D-LUNA a more flexible and practical solution, particularly in environments where sensor failures, calibration issues, or additional hardware costs are of concern. By eliminating the need for pressure sensors while maintaining accuracy at moderate-to-high power levels, 3D-LUNA offers a scalable and efficient approach to localization, making it a strong candidate for real-world deployment in both static and mobile scenarios.
5.4. Number of Received Transmissions
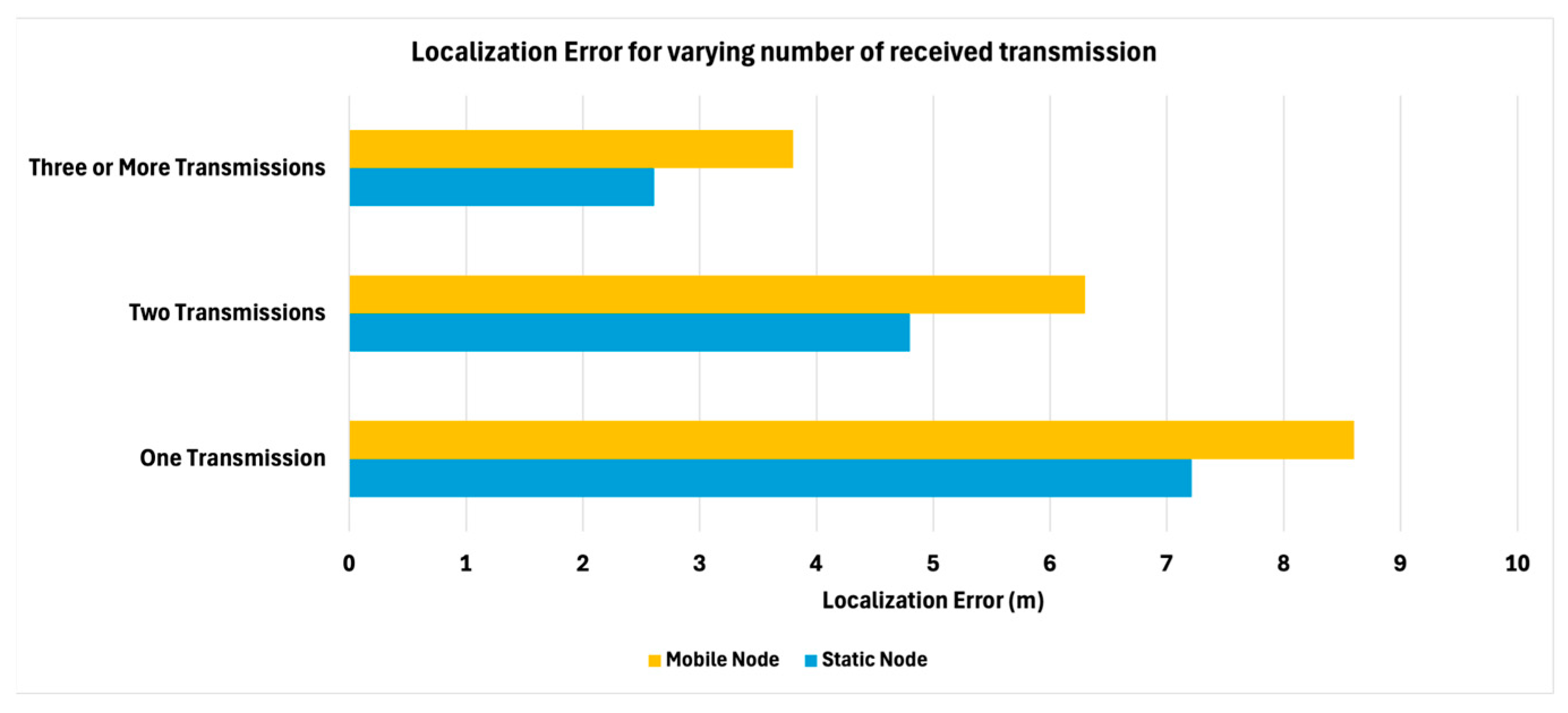
We have also investigated how the number of received transmissions affects the accuracy of 3D-LUNA for both static and mobile nodes using a fixed transmission power (10 W).
In
Figure 11, the results indicate that localization error decreases as the number of received transmissions increases for both node types. When only one transmission is received, the mobile node exhibits the highest error, whereas the static node shows a slightly lower error. With two transmissions, the localization error improves for both cases. The best accuracy is achieved when three or more transmissions are received, where the mobile node’s error is around 4 m, and the static node demonstrates the least error.
6. Conclusions
This paper presents 3D-LUNA, a novel approach for 3D localization of underwater nodes using airborne VLC beams. By leveraging the intensity of light received by submerged nodes, 3D-LUNA eliminates the need for surface-based reference points, making it a viable solution for stealth-sensitive applications such as military operations, environmental monitoring, and underwater exploration. Simulation results confirm that 3D-LUNA achieves superior accuracy compared to omni-directional VLC methods, particularly when depth information is unavailable. The method remains effective across a range of transmission powers and demonstrates adaptability to both stationary and mobile underwater nodes. Additionally, the proposed error mitigation strategies improve localization robustness under uncertain measurement conditions. The results presented in this work demonstrate the potential of 3D-LUNA as a reliable and infrastructure-free localization framework for underwater environments. Compared to traditional acoustic-based localization methods, which often report localization errors ranging from 1.5 to 5 m under similar simulation conditions, 3D-LUNA consistently achieves sub-meter accuracy, often within 0.3 to 0.7 m, depending on beam configuration.
As part of future work, we intend to extend the 3D-LUNA framework in several key directions. First, we plan to incorporate learning-based techniques to enhance localization robustness under highly dynamic and optically heterogeneous underwater conditions. We also aim to refine the physical modeling by accounting for complex aquatic phenomena such as surface-wave-induced refraction, turbidity variations, and thermocline effects. In addition, we seek to validate the proposed approach through experimental testing in real or controlled underwater environments.