Effects of Detector Configuration on X-Ray Luminescence Computed Tomography Imaging
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
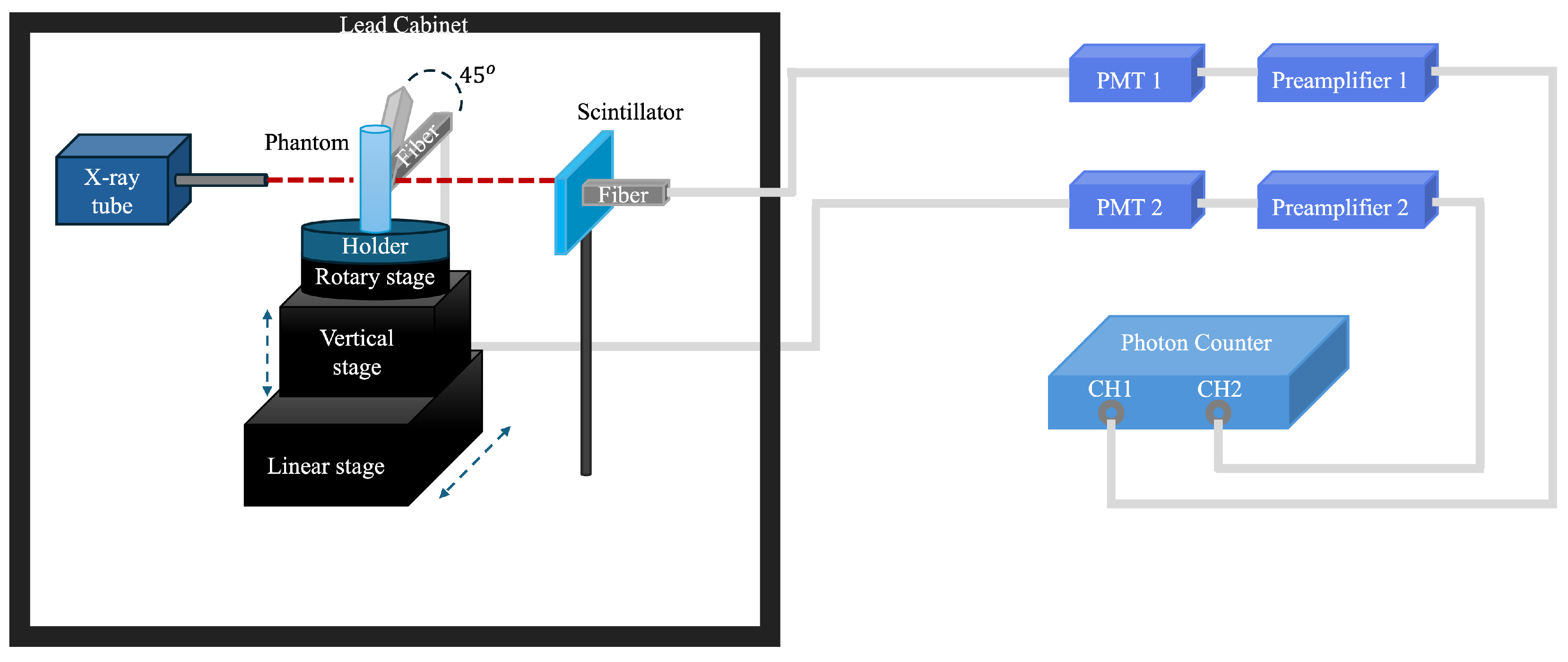
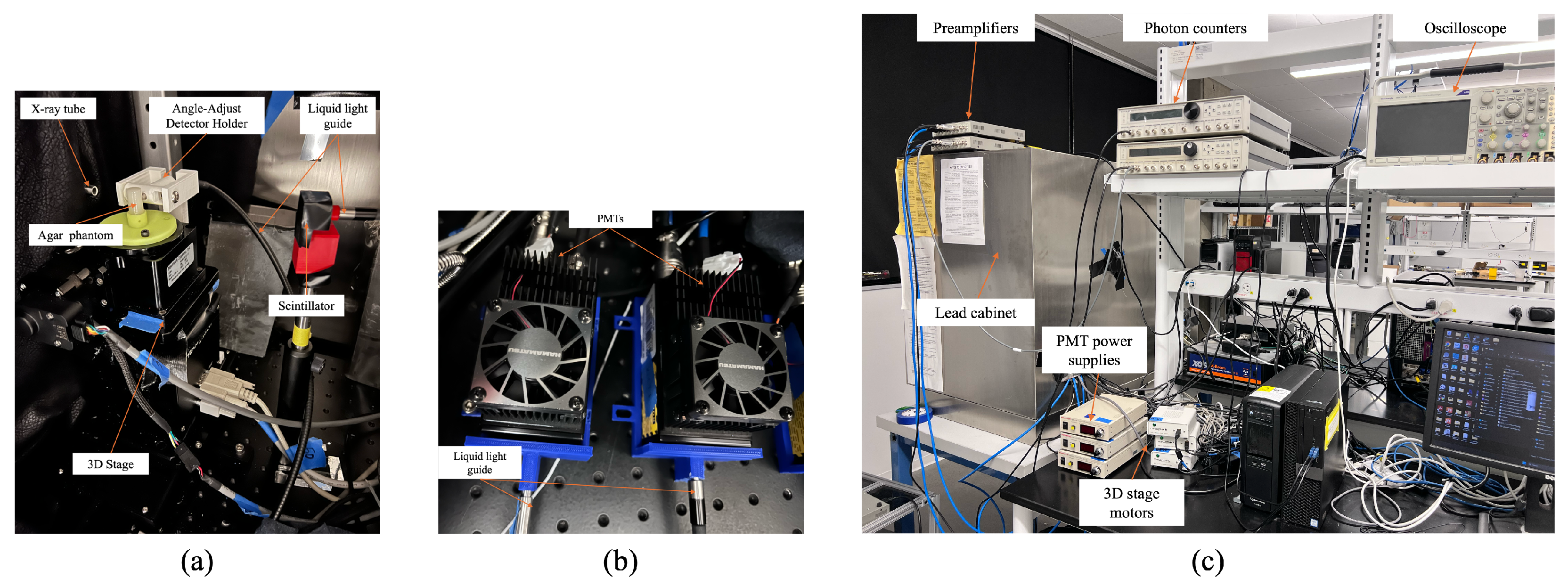
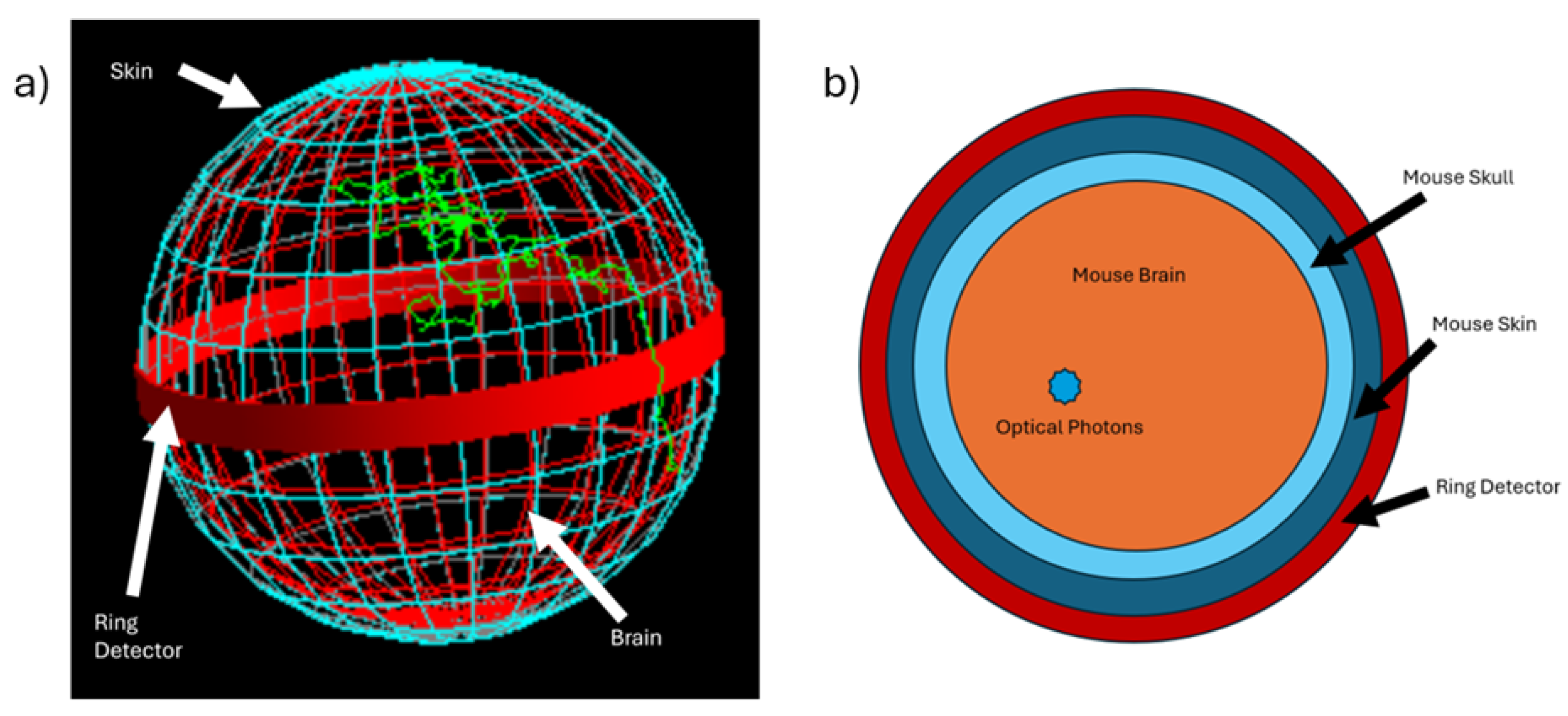
2.1. XLCT Imaging System
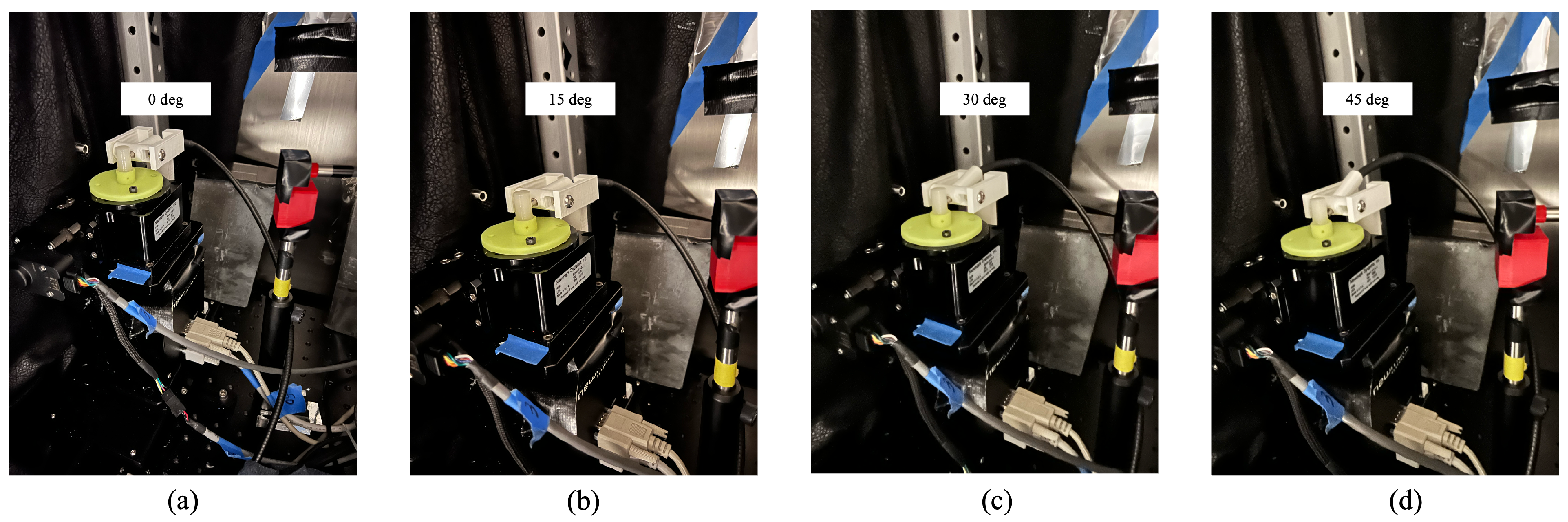
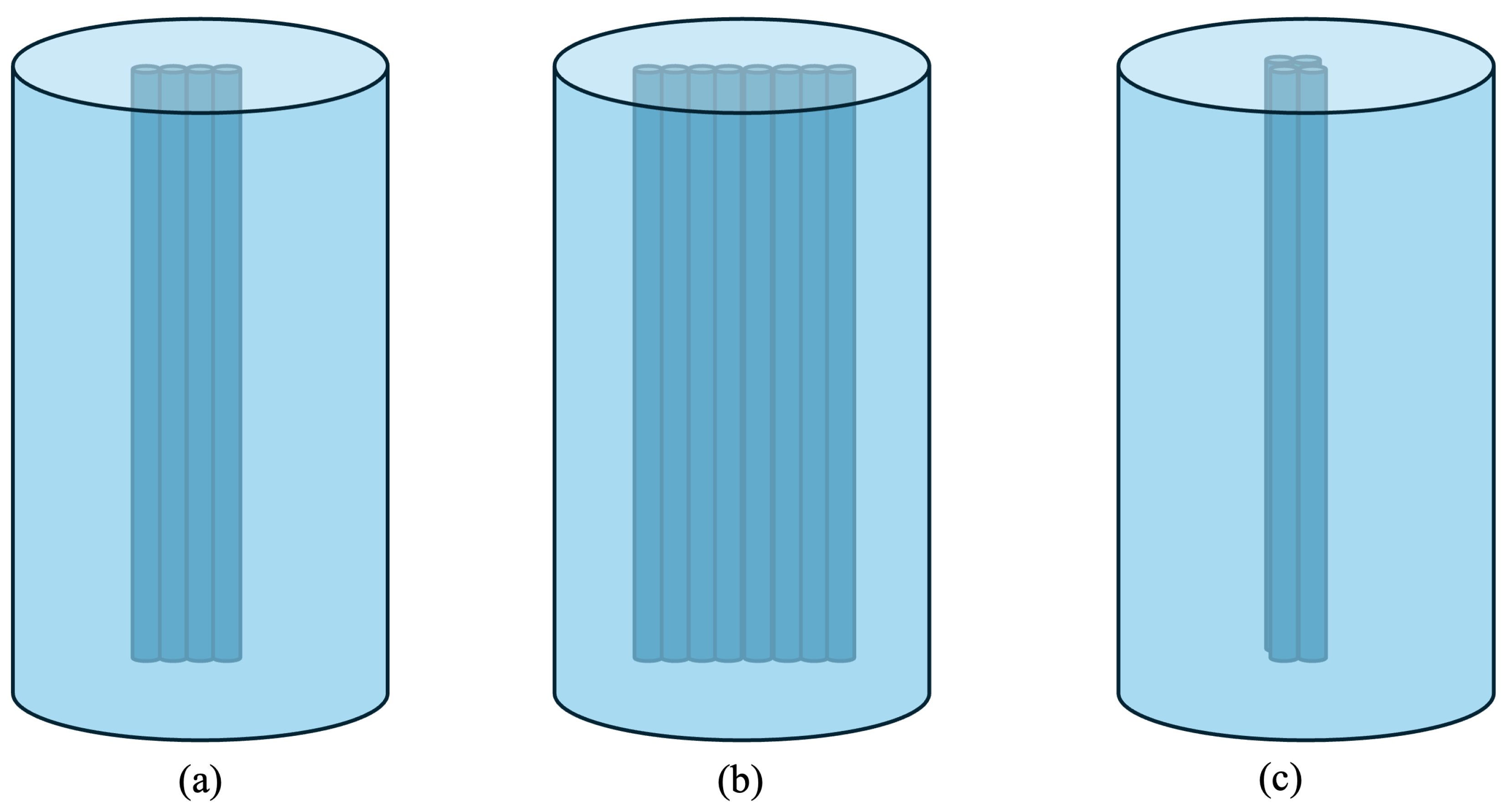
2.1.1. Detector Orientation Adjustment
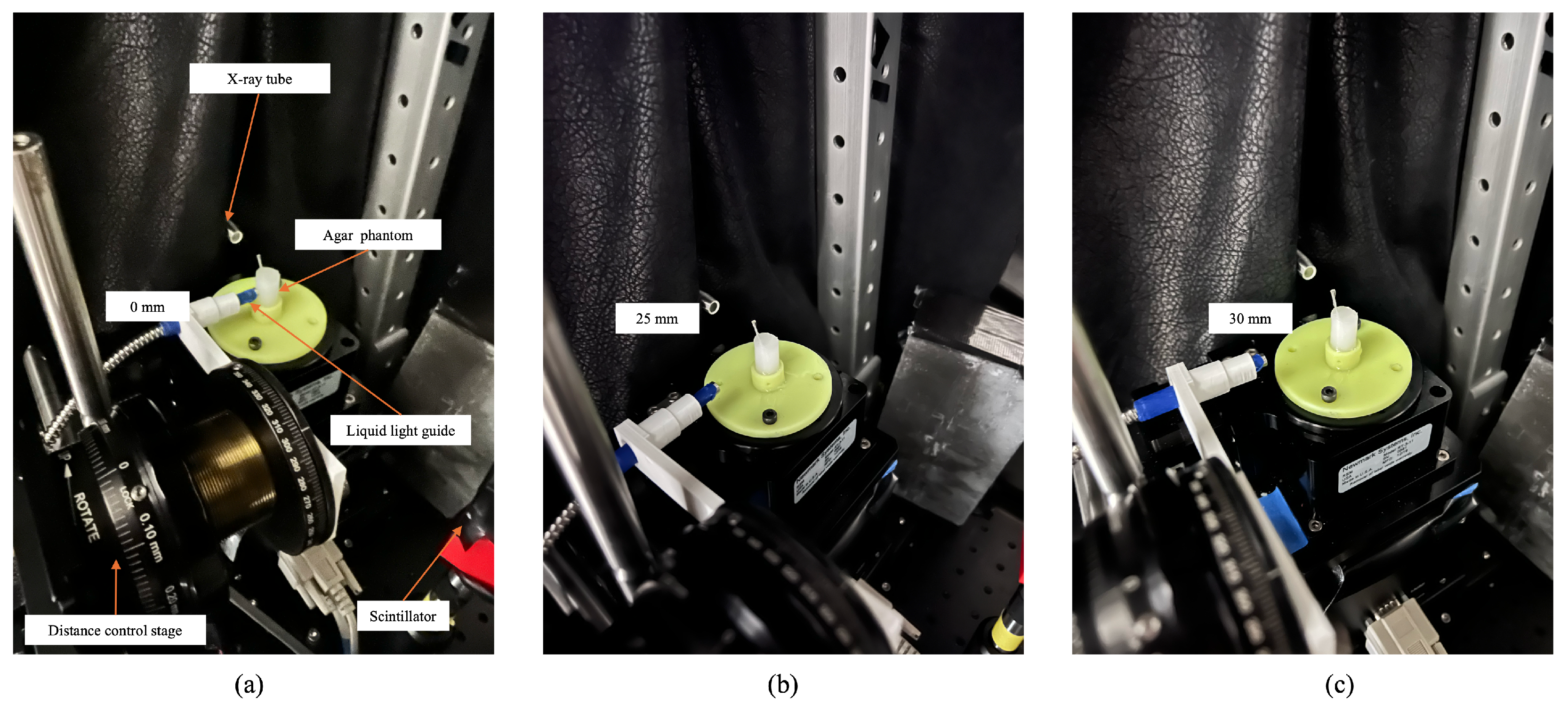
2.1.2. Detector Position Adjustment
2.2. Phantom Design and Fabrication
2.3. XLCT Reconstruction Algorithms
2.4. Criteria of Image Quality
2.5. XLCT Measurement Analysis
2.6. Monte Carlo Simulation Setup
3. Results
3.1. XLCT Imaging with Different Orientations of the Optical Fiber Bundle
3.2. XLCT Measurements at Different Detector Distances
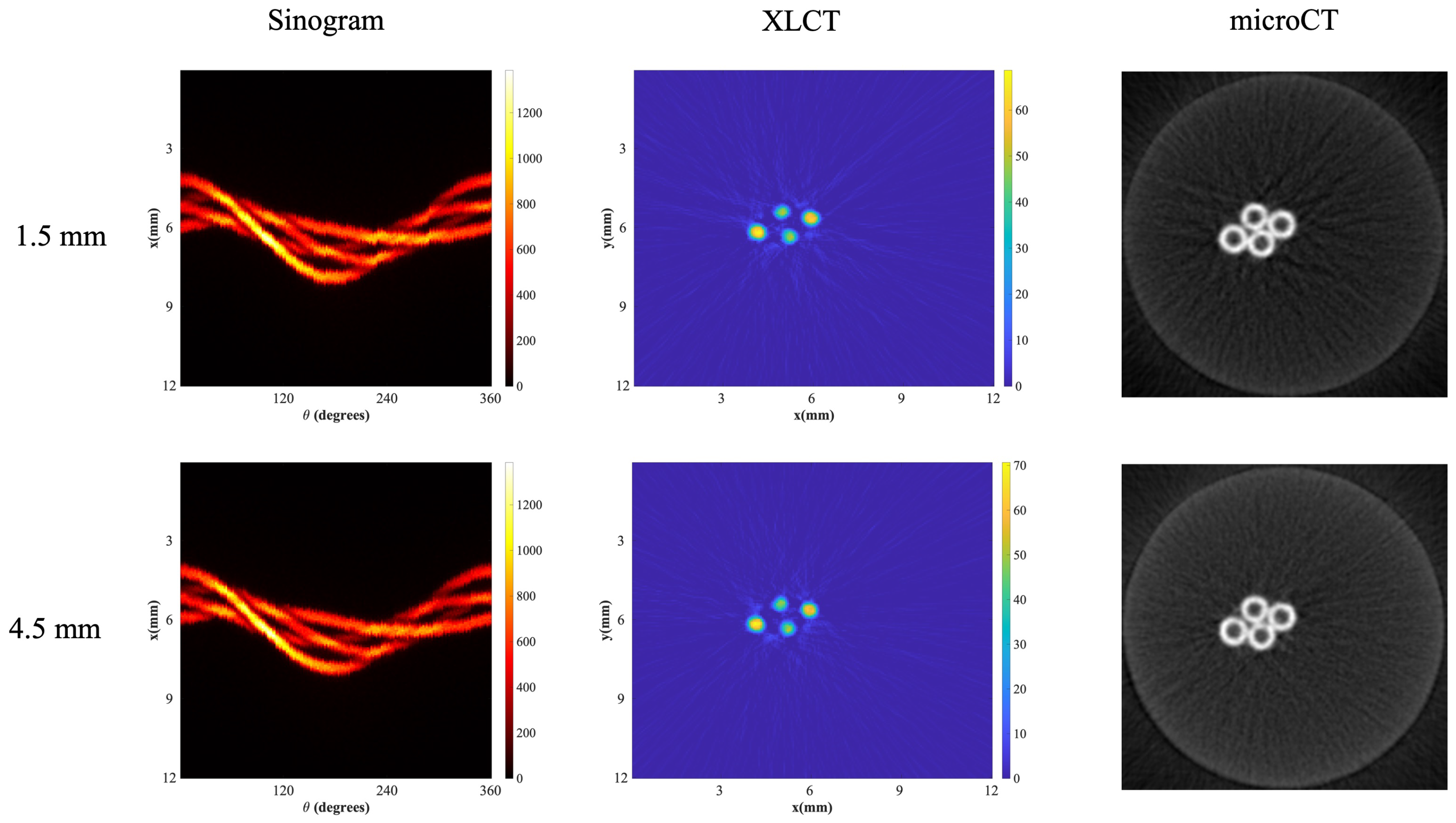
3.3. XLCT Imaging at Different Detector Distances
3.4. Monte Carlo Simulation Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ou, X.; Chen, X.; Xu, X.; Xie, L.; Chen, X.; Hong, Z.; Bai, H.; Liu, X.; Chen, Q.; Li, L.; et al. Recent development in x-ray imaging technology: Future and challenges. Research 2021, 2021, 9892152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Ling, R.; Huang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, Z.; Huang, M.; Stankovic, V.; Zhang, J.; Hu, Z. Feasibility exploration of myocardial blood flow synthesis from a simulated static myocardial computed tomography perfusion via a deep neural network. J. X-Ray Sci. Technol. 2025, 33, 578–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Ding, Y.; Wang, L.; Hu, S.; Dong, N.; Sheng, J.; Ren, Y.; Wang, Z. Radiomics and deep learning features of pericoronary adipose tissue on non-contrast computerized tomography for predicting non-calcified plaques. J. X-Ray Sci. Technol. 2025, 33, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Yu, H.; De Man, B. An outlook on x-ray CT research and development. Med. Phys. 2008, 35, 1051–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Liang, N.; Zhong, X.; Ren, J.; Zheng, Z.; Li, L.; Yan, B. CT image super-resolution under the guidance of deep gradient information. J. X-Ray Sci. Technol. 2025, 33, 58–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maire, E.; Withers, P.J. Quantitative X-ray tomography. Int. Mater. Rev. 2014, 59, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusic, H.; Grinstaff, M.W. X-ray-computed tomography contrast agents. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 1641–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thilagavathi, P.; Geetha, R.; Jothi Shri, S.; Somasundaram, K. An effective COVID-19 classification in X-ray images using a new deep learning framework. J. X-Ray Sci. Technol. 2025, 33, 297–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Zhong, Q.; Lu, J.; Xiong, C. A novel detail-enhanced wavelet domain feature compensation network for sparse-view X-ray computed laminography. J. X-Ray Sci. Technol. 2025, 33, 488–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratx, G.; Carpenter, C.M.; Sun, C.; Xing, L. X-ray luminescence computed tomography via selective excitation: A feasibility study. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2010, 29, 1992–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badea, C.; Stanton, I.; Johnston, S.; Johnson, G.; Therien, M. Investigations on X-ray luminescence CT for small animal imaging. In Proceedings of the SPIE, San Diego, CA, USA, 2 March 2012; Volume 8313, p. 83130T. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Lun, M.C.; Nguyen, A.A.T.; Li, C. X-ray luminescence computed tomography using a focused x-ray beam. J. Biomed. Opt. 2017, 22, 116004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lun, M.C.; Li, C.; Zhou, Z. Method for improving the spatial resolution of narrow x-ray beam-based x-ray luminescence computed tomography imaging. J. Biomed. Opt. 2019, 24, 086002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lun, M.C.; Zhang, W.; Li, C. Sensitivity study of x-ray luminescence computed tomography. Appl. Opt. 2017, 56, 3010–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Rong, J.; Gao, P.; Zhang, W.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, H. Cone-beam x-ray luminescence computed tomography based on x-ray absorption dosage. J. Biomed. Opt. 2018, 23, 026006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Liu, F.; Liu, J.; Luo, J.; Xie, Y.; Bai, J.; Xing, L. Cone beam x-ray luminescence computed tomography based on Bayesian method. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2016, 36, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Zhu, S.; Yi, H.; Zhang, X.; Chen, D.; Liang, J.; Tian, J. Cone beam x-ray luminescence computed tomography: A feasibility study. Med. Phys. 2013, 40, 031111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Zhu, D.; Lun, M.; Li, C. Collimated superfine x-ray beam based x-ray luminescence computed tomography. J. X-Ray Sci. Technol. 2017, 25, 945–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhu, D.; Lun, M.; Li, C. Multiple pinhole collimator based x-ray luminescence computed tomography. Biomed. Opt. Express 2016, 7, 2506–2523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lun, M.C.; Li, C. Superfast scan of focused X-ray luminescence computed tomography imaging. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 134183–134190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michail, C.; Valais, I.; Seferis, I.; Kalyvas, N.; David, S.; Fountos, G.; Kandarakis, I. Measurement of the luminescence properties of Gd2O2S: Pr, Ce, F powder scintillators under X-ray radiation. Radiat. Meas. 2014, 70, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez, J.; Romero, I.; Ngo, J.; Azam, M.S.T.; Niu, C.; Almeida-da Silva, C.L.C.; Cabido, L.F.; Ojcius, D.M.; Chin, W.C.; Wang, G.; et al. Multiple energy X-ray imaging of metal oxide particles inside gingival tissues. J. X-Ray Sci. Technol. 2024, 32, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, I.O.; Fang, Y.; Li, C. Correlation between X-ray tube current exposure time and X-ray photon number in GATE. J. X-Ray Sci. Technol. 2022, 30, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soleimanzad, H.; Gurden, H.; Pain, F. Optical properties of mice skull bone in the 455- to 705-nm range. J. Biomed. Opt. 2017, 22, 010503. [Google Scholar]
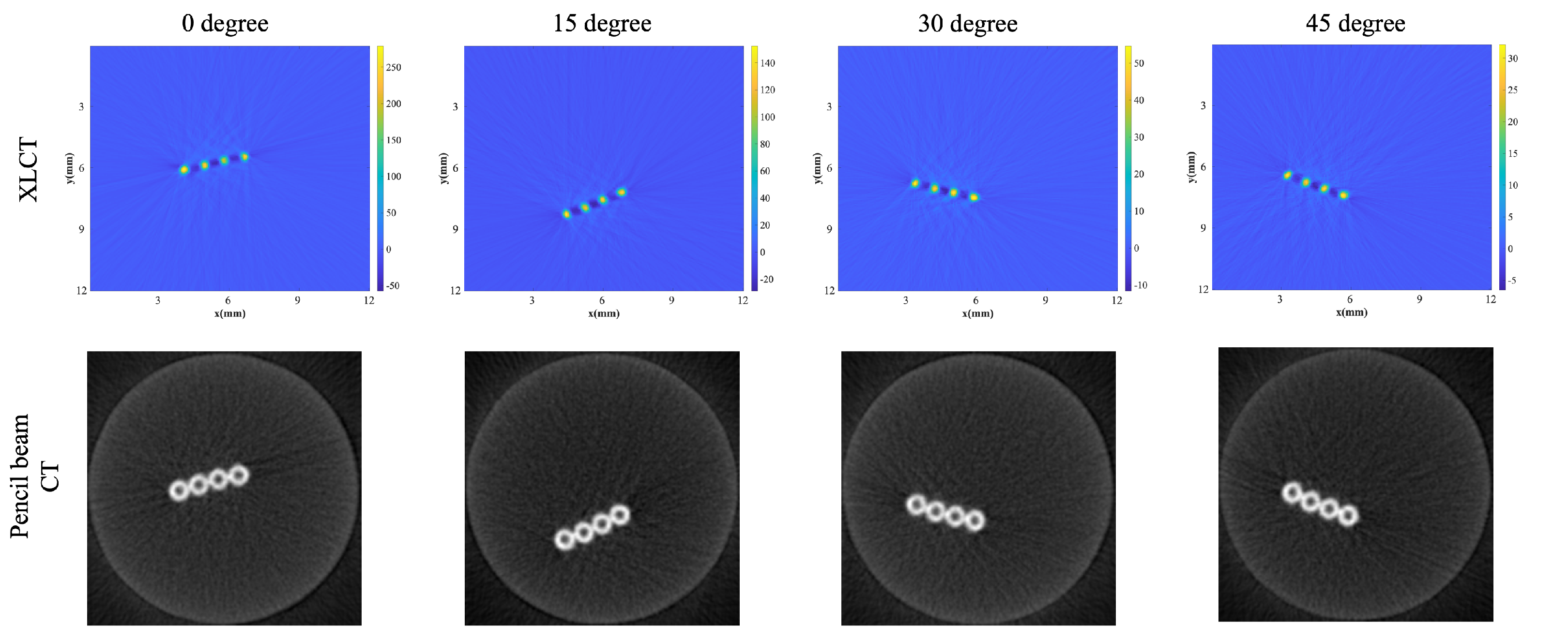
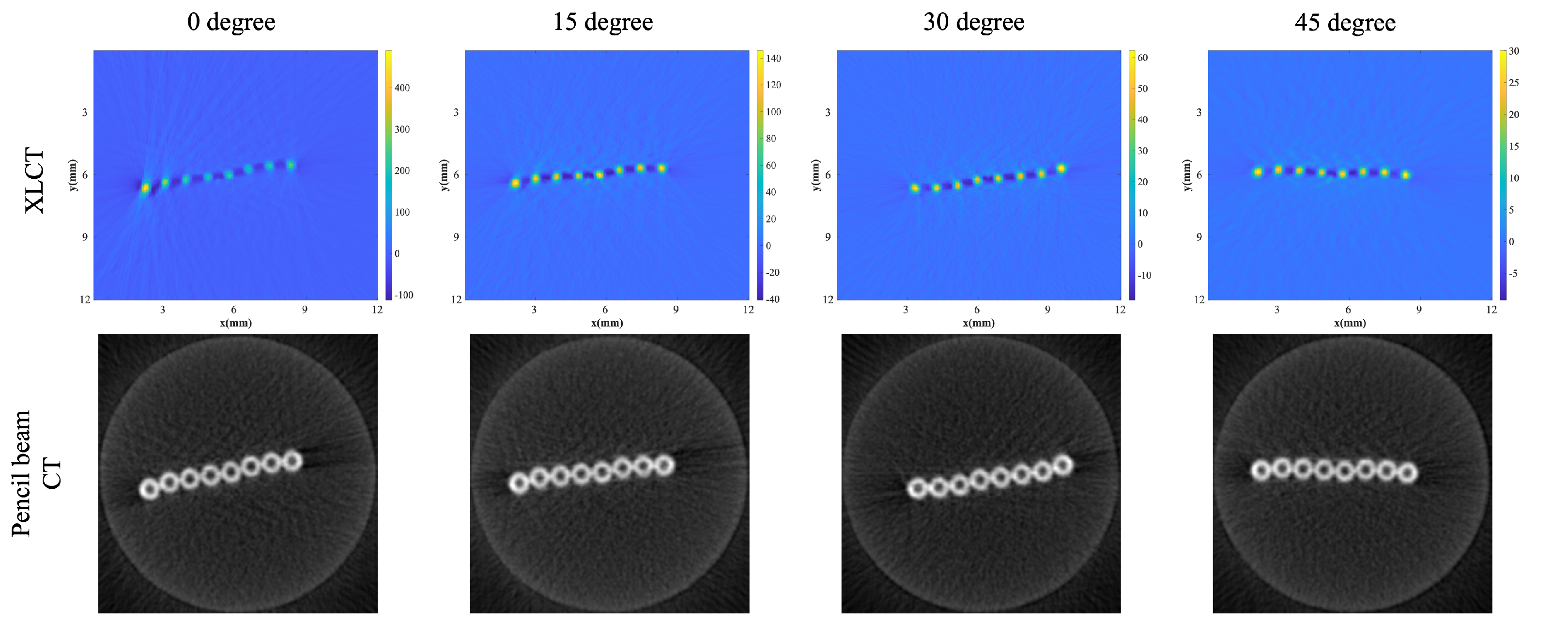
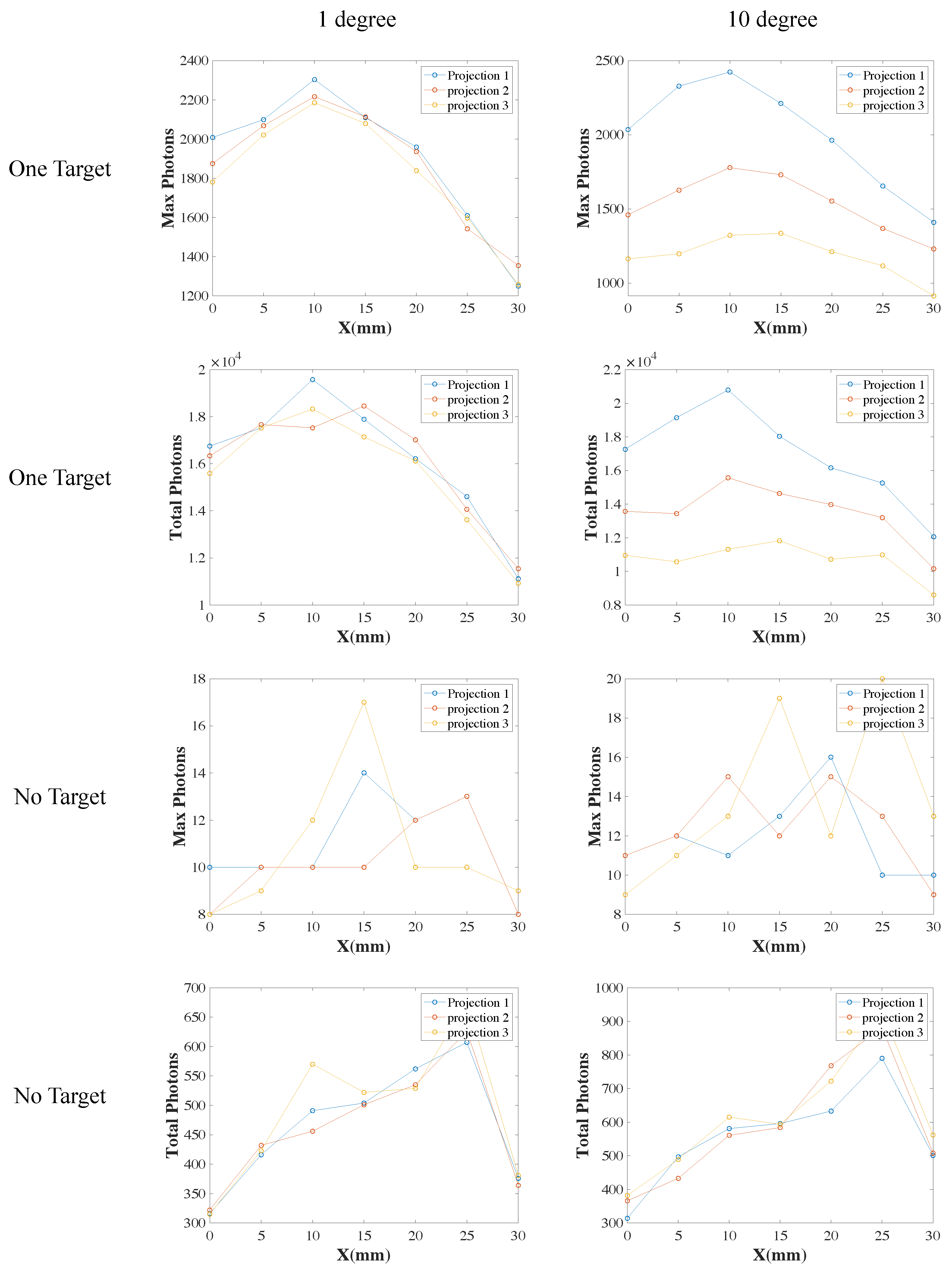
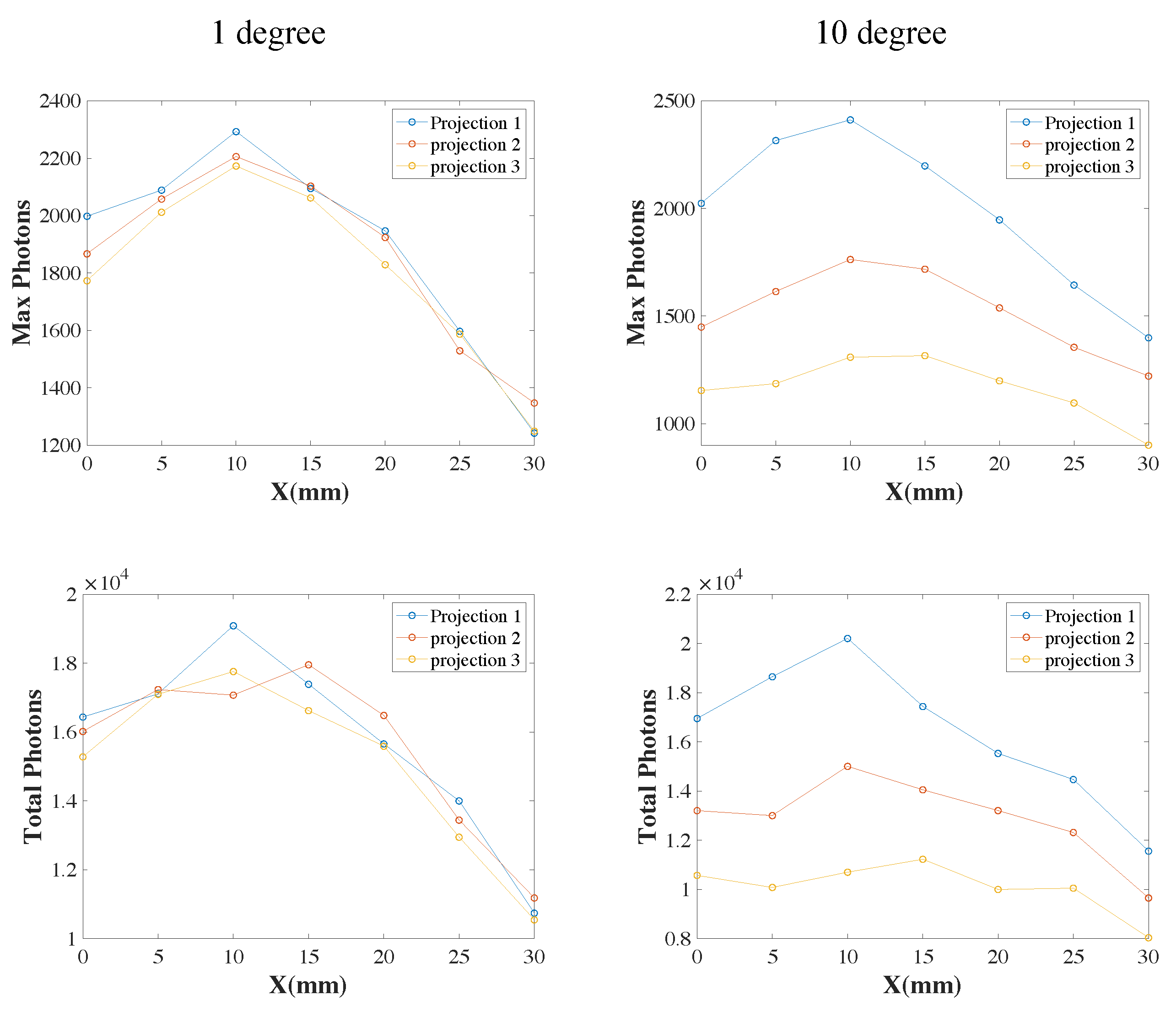
| Phantom | Degree | DICE | CNR |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4 Targets | 0 deg | 86.9% | 14.9 |
| 15 deg | 83.77% | 14.29 | |
| 30 deg | 85.99% | 14.11 | |
| 45 deg | 83.17% | 14.15 | |
| 8 Targets | 0 deg | 76.21% | 8.34 |
| 15 deg | 82.5% | 9.45 | |
| 30 deg | 85.99% | 9.84 | |
| 45 deg | 83.91% | 9.38 |
| Distance | Max (ROI) | Sum (ROI) | DICE | CNR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.5 mm | 66.94 | 10715.82 | 71.92% | 8.73 |
| 4.5 mm | 68.68 | 10451.23 | 79.28% | 8.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Cortez, J.N.; Li, C. Effects of Detector Configuration on X-Ray Luminescence Computed Tomography Imaging. Photonics 2025, 12, 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12050483
Zhang Y, Cortez JN, Li C. Effects of Detector Configuration on X-Ray Luminescence Computed Tomography Imaging. Photonics. 2025; 12(5):483. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12050483
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yibing, Jarrod N. Cortez, and Changqing Li. 2025. "Effects of Detector Configuration on X-Ray Luminescence Computed Tomography Imaging" Photonics 12, no. 5: 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12050483
APA StyleZhang, Y., Cortez, J. N., & Li, C. (2025). Effects of Detector Configuration on X-Ray Luminescence Computed Tomography Imaging. Photonics, 12(5), 483. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12050483






