Constructing a Micro-Raman Spectrometer with Industrial-Grade CMOS Camera—High Resolution and Sensitivity at Low Cost
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Micro-Raman Spectrometer Construction
2.1. Micro-Raman Probe
2.2. High-Resolution Lens-Based Spectrometer
3. Calibration and Characterization
3.1. Calibration of the Raman Shift Axis
3.2. Spectral Resolution Characterization
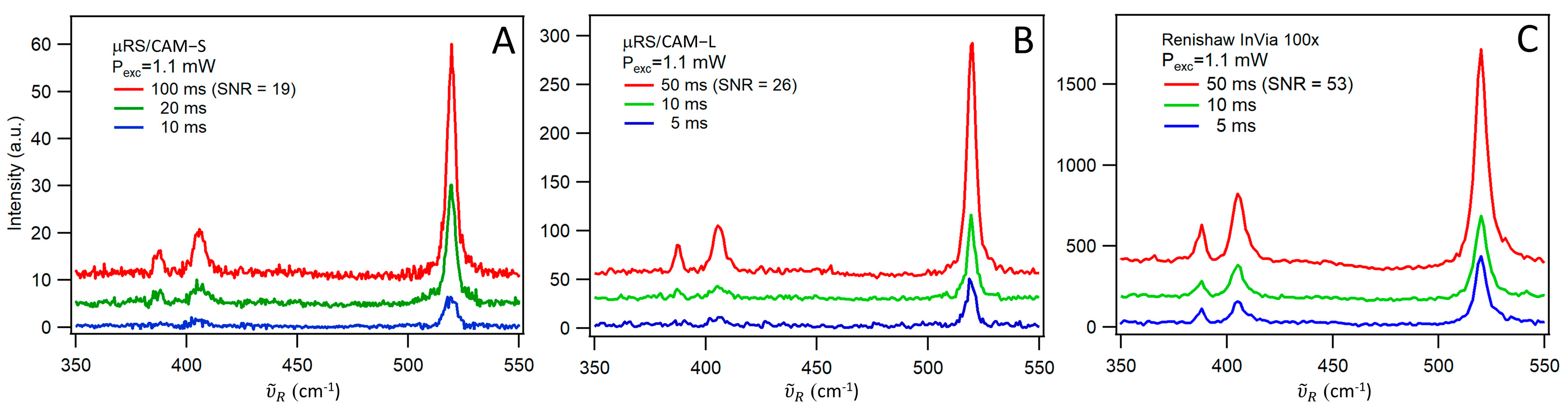
3.3. Signal-to-Noise Comparison with a Commercial High-Resolution Raman Spectrometer
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| µRS | Micro-Raman Spectrometer |
| CMOS | Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor |
| RGRS | Research-Grade Raman Spectrometers |
| FRS | Fiber Raman Spectrometer |
| DN | Dark Noise |
| Qe | Quantum Efficiency |
| OBT | Optical Bench Throughput |
| NIR | Near Infrared |
| VIS | Visible |
| iCMOS | Industrial-Grade CMOS Camera |
| CCD | Charge-Coupled Device |
| sCMOS | Scientific-Grade CMOS |
| EMCCD | Electron-Multiplying CCD |
| sCCD | Scientific-Grade CCD |
| CAM-L | iCMOS with 3.45 µm pixel size |
| CAM-S | iCMOS with 1.85 µm pixel size |
| µRS/CAM−L | Micro-Raman Spectrometer with CAM−L camera |
| µRS/CAM−S | Micro-Raman Spectrometer with CAM−S camera |
| CAM | Industrial-grade CMOS Camera |
| LCAM | Camera Lens |
| LSLT | Slit Lens |
| G | Diffraction Grating with 2400 lines/mm |
| SLT | 5 µm wide slit |
| L | Narrow Linewidth Laser at 532.13 nm |
| BE | Beam Expander |
| M | Folding Mirror |
| FR | Raman Edge Filter at 532 nm |
| LOBJ | Collection Objective |
| LCPL | Coupling Objective |
| SLM | Single Longitudinal Mode |
| DPSS | Diode-Pumped Solid-State |
| RSP | Raman-Scattered Photons |
| ULF | Ultra-Low Frequency |
| FWHM | Full with at half maximum |
| PSF | Point Spread Function |
| NA | Numerical Aperture |
| SNR | Signal-to-noise |
| ASTM | American Society for Testing Materials |
References
- Lee, C.; Yan, H.; Brus, L.E.; Heinz, T.F.; Hone, J.; Ryu, S. Anomalous Lattice Vibrations of Single- and Few-Layer MoS2. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 2695–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Stoneburner, K.; Ladika, M.; Kuo, T.-C.; Kalantar, T.H. High-Throughput Raman Spectroscopy Screening of Excipients for the Stabilization of Amorphous Drugs. Appl. Spectrosc. 2015, 69, 1271–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, A.S.; Batchelder, D.N.; Pyrz, R. Estimation of Crystallinity of Isotactic Polypropylene Using Raman Spectroscopy. Polymer 2002, 43, 2671–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Threlfall, T.L. Analysis of Organic Polymorphs. A Review. Analyst 1995, 120, 2435–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudor, A.M.; Davies, M.C.; Melia, C.D.; Lee, D.C.; Mitchell, R.C.; Hendra, P.J.; Church, S.J. The Applications of Near-Infrared Fourier Transform Raman Spectroscopy to the Analysis of Polymorphic Forms of Cimetidine. Spectrochim. Acta A 1991, 47, 1389–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wermelinger, T.; Spolenak, R. Stress Analysis by Means of Raman Microscopy. In Confocal Raman Microscopy; Toporski, J., Dieing, T., Hollricher, O., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 509–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikushima, Y.; Hatakeda, K.; Saito, N.; Arai, M. An in Situ Raman Spectroscopy Study of Subcritical and Supercritical Water: The Peculiarity of Hydrogen Bonding near the Critical Point. J. Chem. Phys. 1998, 108, 5855–5860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladepo, S.A.; Xiong, K.; Hong, Z.; Asher, S.A. Elucidating Peptide and Protein Structure and Dynamics: UV Resonance Raman Spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2011, 2, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polli, D.; Kumar, V.; Valensise, C.M.; Marangoni, M.; Cerullo, G. Broadband Coherent Raman Scattering Microscopy. Laser Photonics Rev. 2018, 12, 1800020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Machine Vision Association. EMVA Standard 1288—Standard for Characterization of Image Sensors and Cameras. Available online: https://www.emva.org/standards-technology/emva-1288/emva-standard-1288-downloads-2/ (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- Dieing, T.; Hollricher, O.; Toporski, J. Confocal Raman Microscopy, 2nd ed; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieing, T.; Hollricher, O. High-Resolution, High-Speed Confocal Raman Imaging. Vib. Spectrosc. 2008, 48, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossum, E.R. The Invention of CMOS Image Sensors: A Camera in Every Pocket. In Proceedings of the 2020 Pan Pacific Microelectronics Symposium (Pan Pacific), Big Island, HI, USA, 10–13 February 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FLIR. Camera Sensor Review. 2023. Available online: https://www.flir.com/landing/iis/machine-vision-camera-sensor-review/ (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- Ma, H.; Fu, R.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y. A Simple and Cost-Effective Setup for Super-Resolution Localization Microscopy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diekmann, R.; Till, K.; Müller, M.; Simonis, M.; Schüttpelz, M.; Huser, T. Characterization of an Industry-Grade CMOS Camera Well Suited for Single Molecule Localization Microscopy—High Performance Super-Resolution at Low Cost. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasinoff, S.W.; Durand, F.; Freeman, W.T. Noise-Optimal Capture for High Dynamic Range Photography. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010; pp. 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.L.; Ran, F.R.; Qiao, X.F.; Wu, J.B.; Shi, W.; Zhang, Z.H.; Xu, X.Z.; Liu, K.H.; Li, H.; Tan, P.H. Ultralow-Frequency Raman System down to 10 cm−1 with Longpass Edge Filters and Its Application to the Interface Coupling in t(2+2)LGs. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2016, 87, 053122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawley, J.B. Handbook of Biological Confocal Microscopy, 3rd ed; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M. Advanced Optical Imaging Theory; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zerubia, J.; Olivo-Marin, J.-C. Gaussian Approximations of Fluorescence Microscope Point-spread Function Models. Appl. Opt. 2007, 46, 1819–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freebody, N.A.; Vaughan, A.S.; MacDonald, A.M. On Optical Depth Profiling Using Confocal Raman Spectroscopy. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 396, 2813–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, A.M.; Vaughan, A.S. Numerical Simulations of Confocal Raman Spectroscopic Depth Profiles of Materials: A Photon Scattering Approach. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2007, 38, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zgrablić, G.; Senkić, A.; Vidović, N.; Užarević, K.; Čapeta, D.; Brekalo, I.; Rakić, M. Building a Cost-Effective Mechanochemical Raman System: Improved Spectral and Time Resolution for in Situ Reaction and Rheology Monitoring. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2025, 27, 5909–5920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntziouni, A.; Thomson, J.; Xiarchos, I.; Li, X.; Bañares, M.A.; Charitidis, C.; Portela, R.; Lozano Diz, E. Review of Existing Standards, Guides, and Practices for Raman Spectroscopy. Appl. Spectrosc. 2022, 76, 747–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E2529-06; Standard Guide for Testing the Resolution of a Raman Spectrometer. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2014. [CrossRef]
- Bowie, B.T.; Griffiths, P.R. Determination of the Resolution of a Multichannel Raman Spectrometer Using Fourier Transform Raman Spectra. Appl. Spectrosc. 2003, 57, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delač Marion, I.; Čapeta, D.; Pielić, B.; Faraguna, F.; Gallardo, A.; Pou, P.; Biel, B.; Vujičić, N.; Kralj, M. Atomic-Scale Defects and Electronic Properties of a Transferred Synthesized MoS2 Monolayer. Nanotechnology 2018, 29, 305703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-H.; Zhang, X.-Q.; Zhang, W.; Chang, M.-T.; Lin, C.-T.; Chang, K.-D.; Yu, Y.-C.; Wang, J.T.-W.; Chang, C.-S.; Li, L.-J.; et al. Synthesis of Large-Area MoS2 Atomic Layers with Chemical Vapor Deposition. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 2320–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temple, P.A.; Hathaway, C.E. Multiphonon Raman Spectrum of Silicon. Phys. Rev. B 1973, 7, 3685–3697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menendez, J.; Cardona, M. Temperature Dependence of the First-Order Raman Scattering by Phonons in Si, Ge, and a-Sn: Anharmonic Effects. Phys. Rev. B 1984, 29, 2051–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Berg, R.W. Determining the Spectral Resolution of a Charge-Coupled Device (CCD) Raman Instrument. Appl. Spectrosc. 2012, 66, 1034–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, E. Optics; Addison-Wesley: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Gadomski, W.; Ratajska-Gadomska, B.; Polok, K. Fine Structures in Raman Spectra of Tetrahedral Tetrachloride Molecules in Femtosecond Coherent Spectroscopy. J. Chem. Phys. 2019, 150, 244505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teich, M.C.; Saleh, B.E.A. Fundamentals of Photonics; Wiley-Interscience: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hauer, P.; Grand, J.; Djorovic, A.; Willmott, G.R.; Le Ru, E.C. Spot Size Engineering in Microscope-Based Laser Spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 21104–21113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbe, E. On the Estimation of Aperture in the Microscope. J. Royal Microsc. Soc. 1881, 1, 388–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermans, R.I.; Seddon, J.; Shams, H.; Ponnampalam, L.; Seeds, A.J.; Aeppli, G. Ultra-high-resolution software-defined photonic terahertz spectroscopy. Optica 2020, 7, 1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Detector | [cm−1] | [cm−1] | [cm−1] | [cm−1] | [µm] | [µm] | [µm] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAM−L | 280 | 9 | 10.3 | 3.6 | 14.5 | 14.3 | 0.5402 |
| 710 | 2 | 3.9 | 2.7 | 11.6 | 11.4 | 0.5530 | |
| 1085 | 1 | 3.0 | 2.4 | 10.8 | 10.6 | 0.5648 | |
| CAM−S | 280 | 9 | 10.1 | 3.4 | 13.7 | 13.5 | 0.5402 |
| 710 | 2 | 3.8 | 2.6 | 11.2 | 11.0 | 0.5530 | |
| 1085 | 1 | 3.1 | 2.5 | 11.3 | 11.1 | 0.5648 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zgrablić, G.; Čapeta, D.; Senkić, A.; Rakić, M. Constructing a Micro-Raman Spectrometer with Industrial-Grade CMOS Camera—High Resolution and Sensitivity at Low Cost. Photonics 2025, 12, 389. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12040389
Zgrablić G, Čapeta D, Senkić A, Rakić M. Constructing a Micro-Raman Spectrometer with Industrial-Grade CMOS Camera—High Resolution and Sensitivity at Low Cost. Photonics. 2025; 12(4):389. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12040389
Chicago/Turabian StyleZgrablić, Goran, Davor Čapeta, Ana Senkić, and Mario Rakić. 2025. "Constructing a Micro-Raman Spectrometer with Industrial-Grade CMOS Camera—High Resolution and Sensitivity at Low Cost" Photonics 12, no. 4: 389. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12040389
APA StyleZgrablić, G., Čapeta, D., Senkić, A., & Rakić, M. (2025). Constructing a Micro-Raman Spectrometer with Industrial-Grade CMOS Camera—High Resolution and Sensitivity at Low Cost. Photonics, 12(4), 389. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12040389






