Rotational Doppler Effect of Vector Beams
Abstract
1. Introduction
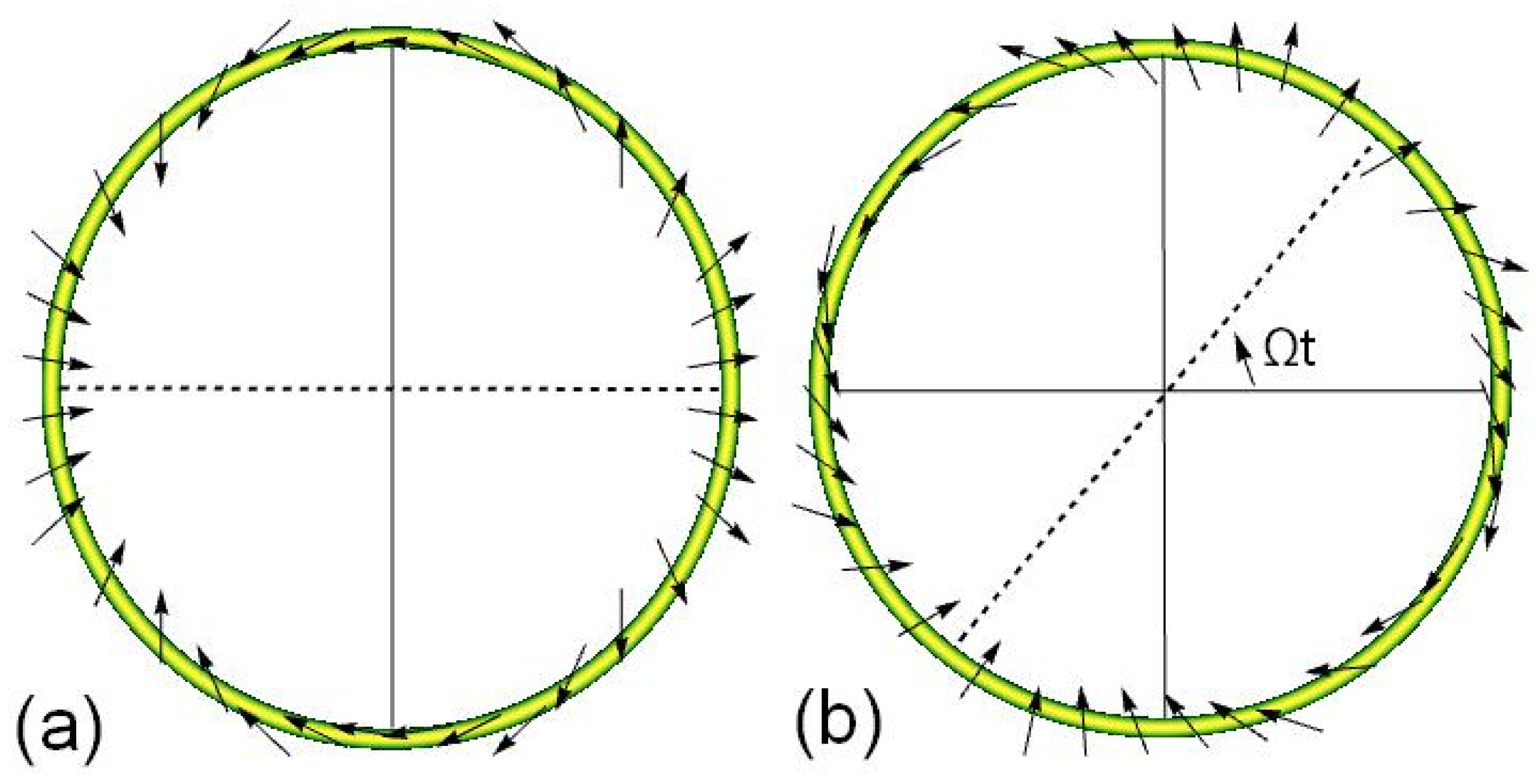
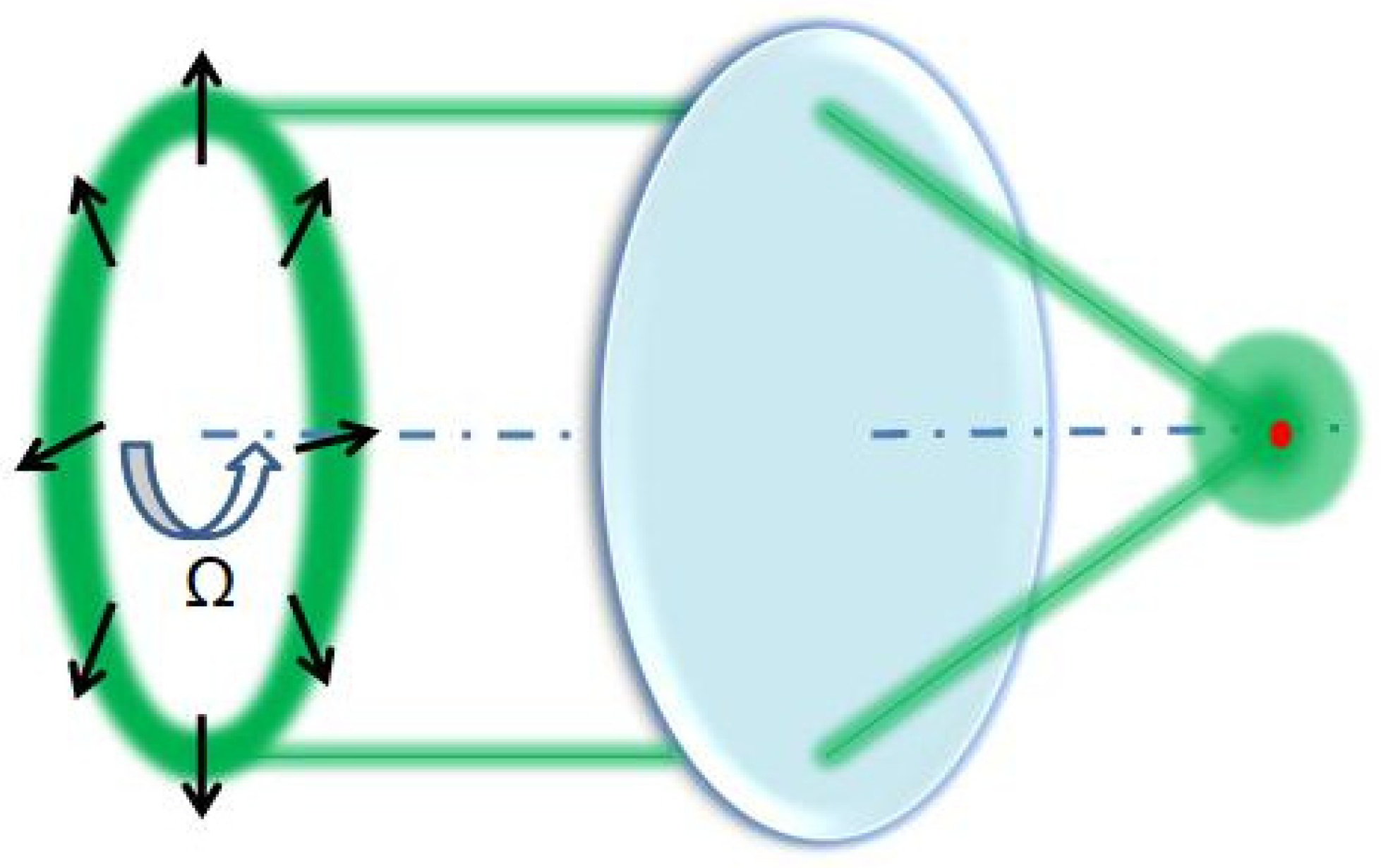
2. Basic Theory
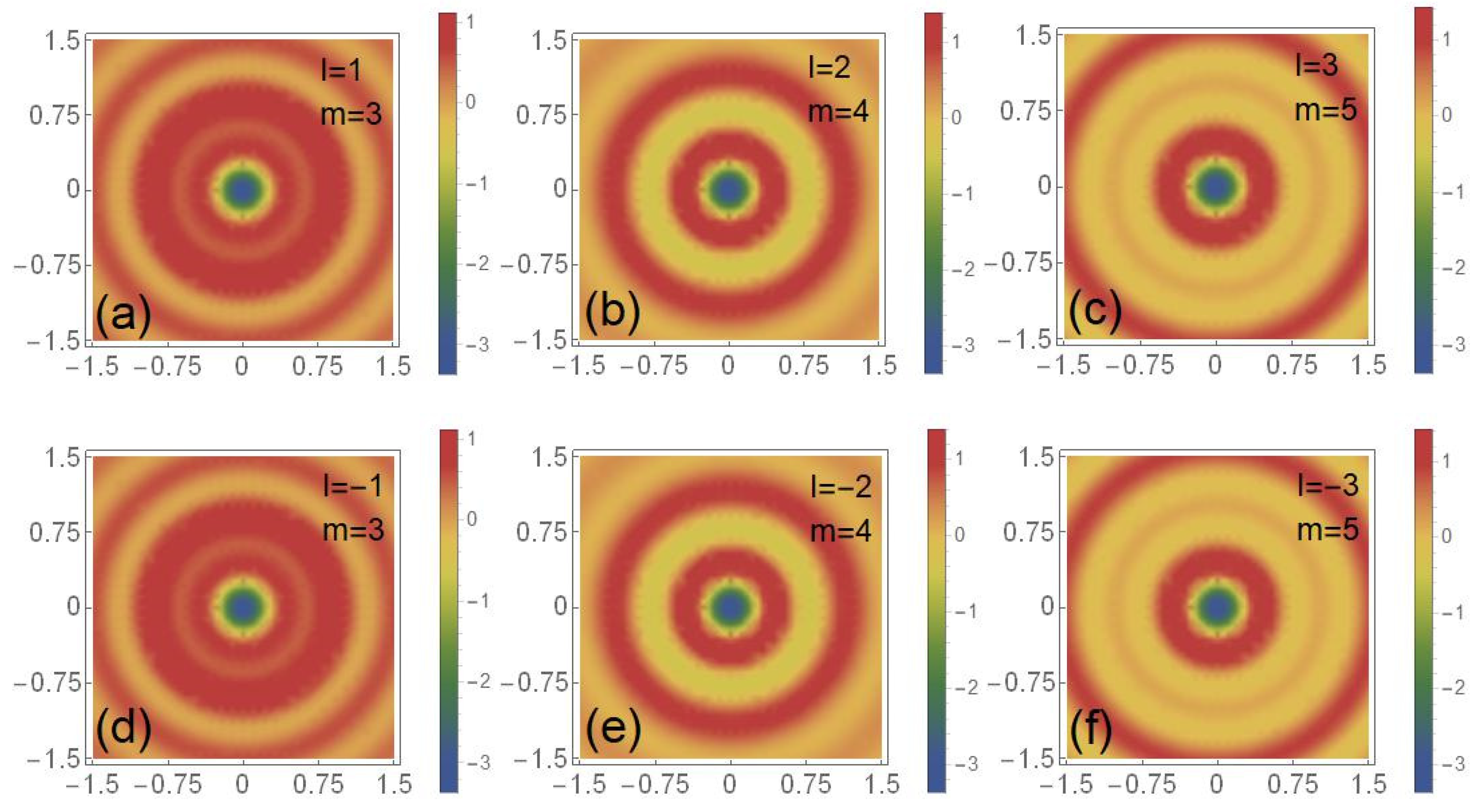
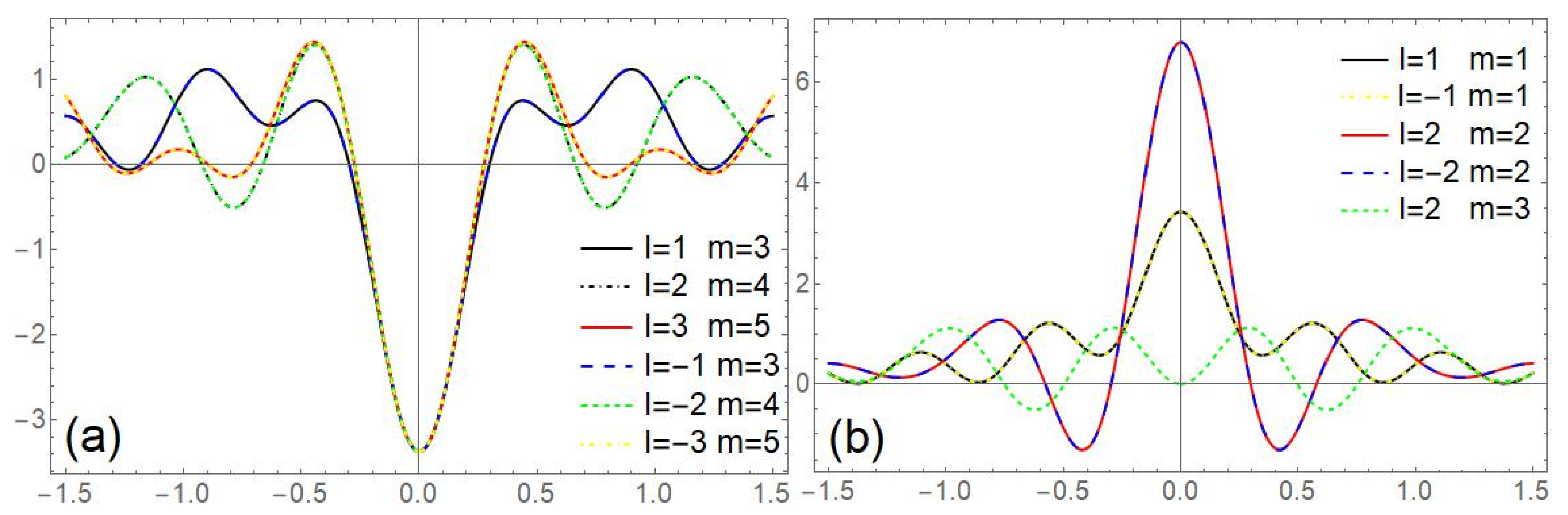
3. Analyses and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seddon, N.; Bearpark, T. Observation of the inverse Doppler effect. Science 2003, 302, 1537–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truax, B.E.; Demarest, F.C.; Sommargren, G.E. Laser Doppler velocimeter for velocity and length measurements of moving surfaces. Appl. Opt. 1984, 23, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courtial, J.; Dholakia, K.; Robertson, D.A.; Allen, L.; Padgett, M.J. Measurement of the rotational frequency shift imparted to a Rotating light beam possessing orbital angular momentum. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 80, 3217–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtial, J.; Robertson, D.A.; Dholakia, K.; Allen, L.; Padgett, M.J. Rotational frequency shift of a light beam. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 81, 4828–4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Wen, S.; Shu, W.; Tang, Z.; Zou, Y.; Fan, D. Rotational Doppler effect in left-handed materials. Phys. Rev. A 2008, 78, 033805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavery, M.P.J.; Speirits, F.C.; Barnett, S.M.; Padgett, M.J. Detection of a spinning object using light’s orbital angular momentum. Science 2013, 341, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, D.B.; Lee, M.P.; Speirits, F.C.; Simpson, S.M.; Lavery, M.P.J.; Padgett, M.J.; Gibsion, G.M. Rotational Doppler velocity to probe the angular velocity of spinning microparticles. Phys. Rev. A 2014, 90, 011801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavery, M.P.J.; Barnett, S.M.; Speirits, F.C.; Padgett, M.J. Observation of the rotational Doppler shift of a white-light, orbital-angular-momentum carrying beam backscattered from a rotating body. Optica 2014, 1, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Gao, X.; Xie, M.; Zhai, W.; Xu, W.; Huang, S.; Gu, W. Measurement of the rotational Doppler frequency shift of a spinning object using a radio frequency orbital angular momentum beam. Opt. Lett. 2016, 41, 2549–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Fu, D.; Dong, J.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, X. Theoretical analysis and experimental verification on optical rotational Doppler effect. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 10050–10056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Zheng, S.; Shao, Z.; Zhang, X. Analysis of rotational Doppler effect based on radio waves carrying orbital angular momentum. J. Appl. Phys. 2018, 124, 164907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Liu, T.; Ren, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, C.; Shao, Q. Detection of spinning objects at oblique light incidence using the optical rotational Doppler effect. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 24781–24792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, Y.; Fu, S.; Yin, C.; Zhou, H.; Gao, C. Detection of angular acceleration based on optical rotational Doppler effect. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 15518–15526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A.Q.; Strong, E.F.; Heffernan, B.M.; Siemens, M.E.; Rieker, G.B.; Gopinath, J.T. Detection technique effect on rotational Doppler measurements. Opt. Lett. 2020, 45, 2636–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belmonte, A.; Rosalesguzmán, C.; Torres, J.P. Measurement of flow vorticity with helical beams of light. Optica 2015, 2, 1002–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryabtsev, A.; Pouya, S.; Safaripour, A.; Koochesfahani, M.; Dantus, M. Fluid flow vorticity measurement using laser beams with orbital angular momentum. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 11762–11767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, F.; Zhao, Y.; Hu, H.; Zhang, Y. Optical fiber sensing technology based on Mach-Zehnder interferometer and orbital angular momentum beam. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018, 112, 221105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Qiu, X.; Qiu, S.; Hong, L.; Lin, F.; Ren, Y.; Chen, L. Frequency upconversion detection of rotational Doppler effect. Photonics Res. 2022, 10, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, D.; Qiu, X.; Chen, L. Quantum remote sensing of angular rotation of structured objects. Phys. Rev. A 2019, 100, 043832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hautakorpi, M.; Lindberg, J.; Setälä, T.; Kaivola, M. Rotational frequency shifts in partially coherent optical fields. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2006, 23, 1159–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skeldon, K.D.; Wilson, C.; Edgar, M.; Padgett, M.J. An acoustic spanner and its associated rotational Doppler shift. New J. Phys. 2008, 10, 013018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekshaev, A.Y.; Soskin, M.S.; Vasnetsov, M.V. Angular momentum of a rotating light beam. Opt. Commun. 2005, 249, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speirits, F.C.; Lavery, M.P.J.; Padgett, M.J.; Barnett, S.M. Optical angular momentum in a rotating frame. Opt. Lett. 2014, 39, 2944–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mashhoona, B.; Neutzeb, R.; Hannamc, M.; Stedman, G.E. Observable frequency shifts via spin-rotation coupling. Phys. Lett. A 1998, 294, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakobyan, D.; Brasselet, E. Optical torque reversal and spin-orbit rotational Doppler shift experiments. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 031230–031239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Q. Cylindrical vector beams: From mathematical concepts to applications. Adv. Opt. Photon. 2009, 1, 1–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Guo, C.; Ding, J.; Wang, H. A new type of vector fields with hybrid states of polarization. Opt. Express 2010, 28, 10786–10795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Ding, J.; Guo, C.; Wang, H. Optical orbital angular momentum from the curl of polarization. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 105, 253602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckley, A.M.; Brown, T.G.; Alonso, M.A. Full Poincare beams. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 10777–10785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckley, A.M.; Brown, T.G.; Alonso, M.A. Full Poincare beams II: Partial polarization. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 9357–9362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Kong, L.; Li, S.; Qian, S.; Tu, Y.L.C.; Wang, H. Generalized Poincare sphere. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 26586–26595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, P.; Du, L.P.; Yuan, X.C. Structured spin angular momentum in highly focused cylindrical vector vortex beams for optical manipulation. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 23449–23459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, P.; Man, Z.; Konijnenberg, A.P.; Urbach, H.P. Angular momentum properties of hybrid cylindrical vector vortex beams in tightly focused optical systems. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 35336–35348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, B.; Wolf, E. Electromagnetic diffraction in optical systems. II. Structure of the aplanatic system. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1959, 253, 358. [Google Scholar]
- Khonina, S.N.; Ustinov, A.V.; Degtyarev, S.A. Inverse energy flux of focused radially polarized optical beams. Phys. Rev. A 2018, 98, 043823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotlyar, V.V.; Kovalev, A.A.; Nalimov, A.G. Energy density and energy flux in the focus of an optical vortex: Reverse flux of light energy. Opt. Lett. 2018, 43, 2921–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotlyar, V.V.; Stafeev, S.S.; Nalimov, A.G. Energy backflow in the focus of a light beam with phase or polarization singularity. Phys. Rev. A 2019, 99, 033840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, C.; Tang, M.; Li, X. Controlled negative energy flow in the focus of a radial polarized optical beam. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 18607–18615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Edgar, J.S.; Jeffries, G.D.M.; McGloin, D.; Chiu, D.T. Spin-to-orbital angular momentum conversion in a strongly focused optical beam. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 073901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bliokh, K.Y.; Ostrovskaya, E.A.; Alonso, M.A.; Rodríguez-Herrera, O.G.; Lara, D.; Dainty, C. Spin-to-orbital angular momentum conversion in focusing, scattering, and imaging systems. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 26132–26149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Friese, M.E.J.; Heckenberg, N.R.; Rubinsztein-Dunlop, H. Direct Observation of Transfer of Angular Momentum to Absorptive Particles from a Laser Beam with a Phase Singularity. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1995, 75, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friese, M.E.J.; Nieminen, T.A.; Heckenberg, N.R.; Rubinsztein-Dunlop, H. Optical alignment and spinning of laser-trapped microscopic particles. Nature 1998, 394, 348–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Transverse components | ||||||
| Longitudinal components |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Xu, D.; Li, X. Rotational Doppler Effect of Vector Beams. Photonics 2025, 12, 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12030240
Li H, Xu D, Li X. Rotational Doppler Effect of Vector Beams. Photonics. 2025; 12(3):240. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12030240
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Hehe, Dong Xu, and Xinzhong Li. 2025. "Rotational Doppler Effect of Vector Beams" Photonics 12, no. 3: 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12030240
APA StyleLi, H., Xu, D., & Li, X. (2025). Rotational Doppler Effect of Vector Beams. Photonics, 12(3), 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12030240





