Abstract
Optical imaging systems using varifocal lenses have been widely used in many applications over the past several decades, such as machine vision devices, consumer electronic products, and medical instruments. Traditional varifocal lenses often consist of multiple solid focal length refractive optical elements. The varifocal ability is obtained by dislocating these optical elements along the optical axis over specific distances using mechanical driving mechanisms. It makes the traditional optical varifocal imaging systems suffer from bulky dimensions, slow response speed, complicated configuration, and discrete magnifications. Adaptive varifocal lenses have been a better choice to address the aforementioned limitations of traditional varifocal lenses. Dielectric elastomer actuators (DEA), which can effectively respond to an electric field and result in shape deformation, have been used to develop various adaptive lenses. This paper aims to give a brief review of adaptive varifocal lenses based on DEA. First, this paper describes the basic physical mechanism of DEA. Second, this paper reviews adaptive varifocal liquid lenses based on DEA and introduces their material, structure, and fabrication process, focusing on their unique advantages, such as fast response speed and compactness. However, despite these merits, the adaptive varifocal liquid lens still has challenges in environment stability and liquid leakage. To address these challenges, adaptive varifocal soft solid lenses based on DEA have been proposed, which are also reviewed. In addition, other adaptive varifocal lenses, including metalens, Fresnel lens, microlens array, and Alvarez lens, are also presented. Finally, the prospects and challenges for the development of adaptive varifocal lenses based on DEA are discussed.
1. Introduction
Optical zoom imaging systems using varifocal lenses have attracted great attention in the past couple of decades and have been investigated extensively for wide potential applications. Such optical zoom imaging systems have attractive applications in daily electronic products [1,2,3], medical instruments [4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12], dynamic imaging systems [13,14], interferometers [15,16], and military equipment [17,18]. A conventional optical zoom system consists of several solid lenses with fixed focal lengths. The varifocal ability is often achieved by adjusting the distance between one or more constant-focus lenses along the optical axis via motorized cams. Owing to the need for moving parts, the axial shifting of the lenses inevitably increases the weight and dimensions of the whole optical system, which also leads to slow response time and high consumer power [19]. Therefore, the traditional mechanical varifocal lenses may be inappropriate for many miniaturized devices or dynamic optical zoom imaging applications.
The adaptive varifocal lens, which can change focal length without mechanical movement, has been a better choice to solve the problems of traditional optical zoom imaging systems [19]. Unlike a fixed-focus solid lens, an adaptive lens changes the focus length by varying the curvatures of the surface shape or the refractive indices of the optical medium. Because adaptive varifocal lenses are free from mechanical motion, they can be used in optical zoom imaging applications with space constraints and dynamic range. The working principles of adaptive varifocal lenses include but are not limited to, liquid crystal [20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30], dielectrophoresis effect [31,32], electrowetting [33,34], and elastomer–liquid [35,36,37]. Because the optical anisotropy of liquid crystals is varied by electric fields, the liquid crystal varifocal lenses can tune the focal length by changing the refractive index of the liquid crystal lens by applying different electric fields. However, the fabrication process is complicated, and liquid crystal lenses are often polarization-dependent [38]. Compared with liquid crystal varifocal lenses, adaptive lenses that change the focal length by varying the curvatures of the surface shape have the advantages of a large varifocal range and a large aperture. These adaptive lenses can be based on dielectrophoresis, effect electrowetting, and elastomer–liquid [38]. The electrowetting lenses change the focal length by changing the contact angle of two liquids by applying a voltage. Dielectrophoresis effect-based lenses change the focal length based on the dielectrophoresis effect, which can be defined as the movement of neutral particles in a non-uniform electric field. Adaptive lenses based on electrowetting and dielectrophoresis effect often include two immiscible liquids. They have problems such as the bulky dimension and the degraded optical performance caused by multiple reflections and scattering because of substrate–liquid and liquid–liquid surfaces [38]. The elastomer–liquid lens based on fluidic pressure often exhibits a larger optical aperture and wider tunable optical power range among adaptive varifocal lenses mentioned above. Pumping optical fluid in or out of the cavity via the pump actuator can change the shape of the elastic membrane, and then the focal length of the elastomer–liquid lens is changed [39,40,41,42]. The operation mechanism is simple, but an extra pump is necessary. However, the additional volume requirement for an external pump is also disadvantageous for adaptive varifocal liquid lenses.
Adaptive varifocal lenses using soft electroactive actuators have drawn significant interest over the past decades. Various electroactive actuators such as hydrogel gel [43,44], polyelectrolyte gel [45,46,47], negative Poisson ratio elastomer [48], plasticized polyvinyl chloride (PVC) gel [49,50], and dielectric elastomer (DE) [51,52] have been developed. The hydrogel actuators respond to pH or temperature, which have been employed to chemically varifocal lenses [43]. Polyelectrolyte gel actuators that respond to electric fields have been applied to varifocal liquid lenses. However, the electrical actuation of polyelectrolyte gels will cause electrolysis of the aqueous solution. So, liquid lenses based on polyelectrolyte gel actuators suffer from the leakage of the solvent and current [53]. The PVC gel (a non-ionic gel) actuator is a good choice to change the focal length by electrotactic deformation, as PVC gel has outstanding durability in an electric field. However, the dynamic range of the PVC gel lenses is rather limited [38]. Among them, the DE actuator (DEA), which can generate uniform and large radial strains and have high transmittance, has been a better choice to actuate adaptive varifocal liquid lenses for the advantages of fast response speed, large aperture, small thickness, and low weight. In addition, DE also has attractive applications in the actuation of solid adaptive varifocal lenses.
The structure of this review paper is described as follows. We first briefly describe the working principle of DEA, and then we review adaptive varifocal liquid lenses using DEA classified by material, structure, and fabrication process. Then, we present the adaptive varifocal soft lens based on DEA, as well as present adaptive varifocal metalens, Fresnel lens, microlens array, and Alvarez lenses based on DEA. Finally, challenges and future perspectives of adaptive varifocal lenses based on DEA are analyzed.
2. Adaptive Varifocal Lenses Based on DEA
2.1. Principle of DEA
DE is one kind of artificial rubbery muscle [54], and it is an electrically active polymer whose structure can be changed under an applied electric field excitation [55]. The working principle of DEA is shown in Figure 1. DEA is a rubbery capacitor formed by a polymer elastomer membrane sandwiched between two compliant electrodes [38].
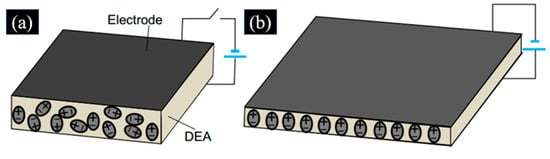
Figure 1.
Working principle of the DEA: (a) voltage-off state and (b) voltage-on state. (Reproduced with permission from [38]. CC BY 4.0).
As shown in Figure 1a, the molecules in the DEA are in a random orientation when there is no voltage applied to the electrode. When a sufficiently high voltage is applied to the electrode, the molecules become reoriented by the longitudinal electric field. Then, compressive stress (Maxwell pressure) will be generated by the attraction of positive and negative electrodes to the DEA, which compresses the structure and expands in the film plane directions, decreasing the thickness of the dielectric elastomer actuator, as shown in Figure 1b. The relationship of actuation pressure P and the applied voltage V can be expressed by [38]
where ε0 and ε are the permittivity of free space and the dielectric constant of the DEA, respectively, and t is the thickness of the DEA.
Due to the advantages of the simple working principle, fine elastic recovery, good flexibility, high efficiency, high response speed, large tension, and low power consumption, DEA has been widely used in developing adaptive varifocal lenses. The common materials used for DEA are as follows: polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), polyacrylate (VHB 4910, VHB 4905), Silicone rubber, and so on.
2.2. Adaptive Varifocal Liquid Lens Based on DEA
Compared with traditional varifocal lenses, the adaptive varifocal liquid lens driven by DEA is superior in terms of compactness, speed, efficiency, and flexibility. The typical structure of the adaptive varifocal liquid lens driven by DEA has a liquid medium fully encapsulated by deformable film or enclosed by a chamber and an elastic membrane, as shown in Figure 2a.DEA is presented wrapped around the lens surface or integrated into the membrane. The fluid is pressurized so that the initial curvature of the lens membrane bulges out when it is not activated [56]. Inspired by the adaptive lens structure of the human eye, Carpi et al. proposed an adaptive varifocal liquid lens driven by DEA [51,57]. As shown in Figure 2a, the proposed lens consisted of a liquid medium enclosed by the annular optically transparent DE, and the remaining part of the membranes is coated with a compliant-electrode material that can apply voltage to the DE. The DEA of the adaptive liquid lens was arranged along the optical path. When a voltage was applied to the electrodes, the surface area of the DE increased because of the decrease in radial tension. It resulted in a decrease in the diameter of the adaptive varifocal liquid lens, which led to an increase in the thickness of the liquid lens. It caused a decrease in the radius of curvature and focal length of the adaptive varifocal liquid lens. The proposed adaptive liquid lens had a focus length range from 16.72 mm to 22.73 mm when the applied voltage increased from 0 to 3.5 kV. The adaptive varifocal liquid lens used an acrylic-polymer-based film as DE material, whose dielectric strength and optical properties of polyacrylate surpass those of PDMS [58]. However, using acrylic elastomer membranes as DE material and carbon grease electrodes applied by hand makes the DEA slow, exhibits large viscoelastic drift, and has short lifetimes [59]. Using silicones or polyurethanes as DE material, which is less viscous, can achieve faster focal length tuning [60,61,62]. By using silicones as DE material, Shea et al. proposed an adaptive liquid lens driven by DEA, as shown in Figure 2b [59]. This adaptive liquid lens had the fastest response time so far, whose response time was less than 175 μs. The proposed liquid lens consisted of two pre-stretched films with a liquid (2–8 μL in volume) sealed between them, ring-shaped flexible electrodes coated on the upper and lower surfaces of the DE, which were fixed by two rigid PCB boards. When the driving voltage was applied to the compliant electrodes, the DE squeezed the fluid causing its radius of curvature to decrease. Thus, the focal length of the liquid lens decreased. The initial focal length of the adaptive varifocal liquid lens depended on the volume of the liquid encapsulated between the two membranes. The settling time of the lens was shorter than 175 µs, and a 20% change in focal length was obtained. This proposed liquid lens driven by DEA had extreme strain, fast response speed, and good stability, which means that it can be used for high-frequency varifocal applications and fields where compliance and speed are needed.
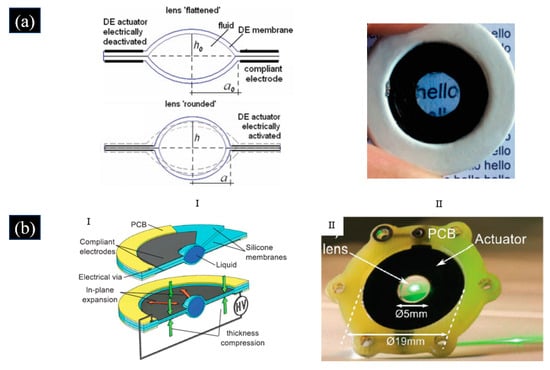
Figure 2.
(a) I. The principle of the adaptive varifocal liquid lens is based on the DEA proposed in [57]. II. Photograph of the adaptive liquid lens proposed in [57]. (Reproduced with permission from [57]). (b) I. Schematic of the adaptive liquid lens proposed in [59]. II. Photograph of fabricated adaptive liquid lens proposed in [59]. (Reproduced with permission from [59]).
The compliant electrode deposited out of the central region of the DEA above is opaque, which makes the dimensions large and the available optical aperture small [51,57,59]. To address this issue, some DEAs using transparent compliant electrodes were developed to make the structure of adaptive liquid lenses more compact [52,63,64,65]. Liang et al. proposed an adaptive varifocal liquid lens driven by DEA with transparent ionic electrodes, as shown in Figure 3a [63]. The DEA consisted of a curved PDMS thin film sandwiched between a gold electrode and the NaCl solution. Because movable ions in NaCl solution can conduct electricity, it can act as an ion electrode for DEA. The electrostatic force induced radial compression when a bias voltage was applied and caused the lateral deflection of the PDMS. It led to the radius of curvature of the lens being altered and then changing the focal length. The focal length of the adaptive liquid lenses had a focusing range from 16.1 mm to 13.1 mm as the applied voltage increased from 0 to 900 V. Due to the use of NaCl solution, the breakdown voltage of the DEA was only 1400 V. So, the focus length tuning range of this liquid lens was narrow. Moreover, the deposition of the gold layer reduced the transmittance of the adaptive liquid lens. For the wavelength between 390 and 770 nm, the transmittance of the fabricated PDMS plate was higher than 90%, but it decreased to 50–70% after the gold layer was deposited. Shian et al. produced and evaluated highly compliant transparent, compliant electrodes, including single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) and silver nanowires (AgNWs) [66]. The results showed that SWCNT electrodes had better optical transparency and a higher figure of merit for actuation than AgNW electrodes. Shian et al. proposed an adaptive varifocal liquid lens based on DEA using SWCNT electrodes [52,64]. The adaptive varifocal liquid lens required only a minimal number of components, i.e., a frame, a passive membrane, a DEA, and a clear liquid, as shown in Figure 3b [64]. The transparent DE membrane was coated with SWCNT electrodes on both sides, and the passive membrane was arranged along the optical path [66]. When a voltage was applied to the DE, DE deformed then the tension in the membrane decreased, causing a concomitant decrease in liquid pressure resulting in a decrease in fluid pressure. Then, the radius of curvature of DE and the passive film were changed, which changed the focal length. The liquid lens had a focal length change range greater than 100% and a response time of less than 1 s. Building on the foundation above, Shian et al. proposed an adaptive varifocal liquid lens based on DEA coated with SWCNT electrodes, consisting of a stiff frame cavity separated into two same liquid-filled cavities by a transparent DE membrane [52]. The other side of the DE membrane was a passive elastomer membrane in each cavity. As shown in Figure 3c, the liquid pressure in the left cavity (P1) was greater than the environmental pressure (P0), making the adjacent membranes bulge outward, while the liquid pressure in the right cavity (P2) was less than P1. Thus, the curvature of the passive membrane in the first cavity was convex, while the curvature of the passive membrane in the second cavity can be convex (P2 < P0), flat (P2 = P0), or concave (P2 > P0), depending on the amount of fluid in the second cavity. When a voltage was applied to the DE, DE deformed then the tension in the membrane decreased, causing a decrease in P1 and an increase in P2. As the diameters of the passive membrane (D1 and D2) were not equal, the difference in the curvature between the two membranes made the focal length of the adaptive liquid lens change. When the driving voltage varied from 0 to 4500 V, the optical power of the lens changed from 66 m−1 to 17 m−1, the change rate in the focal length was 300%, and the response time was 35 ms.
However, the SWCNT deposition process is complicated, and the strain actuation of the SWCNT is low for a DEA because its high stiffness impedes dielectric deformation [65]. We proposed an adaptive varifocal lens using DE sandwiched by transparent conductive liquid, whose fabrication process is free of the deposition of the opaque compliant electrodes [65]. As shown in Figure 3d, the proposed lens consisted of two PMMA frames, two passive membranes, and a transparent conductive liquid separated by a DE membrane. The volumes of the liquid in the two cavities were constant, and the hydraulic pressures gave the liquid lens an initial focal length. When a driving voltage was applied to the copper foils, the shape of the DE membrane changed, which in turn changed the shapes of the two passive membranes, and then the focal length of the liquid lens was changed [67]. The liquid was made by mixing glycerol and sodium chloride at a 10:0.1 weight ratio, which not only served as the refractive material of the tunable lens but also worked as the compliant electrode of the DE. The lens proposed has a compact structure and high transmittance, and the fabrication process was simpler and free of the deposition of opaque compliant electrodes. The transparent gels generally have a low Young’s modulus and high stretchability, which can response fast and strain largely [68,69]. It is also desirable to replace traditional electrodes with transparent conductive gels for the adaptive liquid lens based on DEA. Zhang et al. proposed an adaptive varifocal lens using EGC (electrocardiogram) conductive gel as the electrode of the DEA, as shown in Figure 3e [70]. Compared with traditional carbon grease electrodes, EGC gels have a greater electrostriction rate and a lower driving voltage. In addition, the ionic gels also possess high transparency and stability. The lens is fabricated by using the negative pressure method which makes the lens structure stable during operation [71]. The proposed lens has potential applications in the biomedical imaging field.
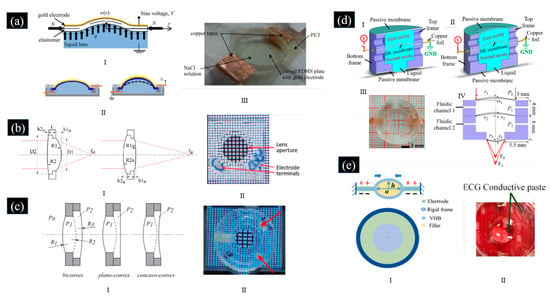
Figure 3.
(a) I. Side view of adaptive liquid lens based on DEA in [63]. II. Side view of the adaptive liquid lens proposed in [63] without applying voltage (left) and lens when a bias voltage was applied (right). III. Photograph of fabricated adaptive liquid lens proposed in [63]. (Reproduced with permission from [63]). (b) I. Schematic of the adaptive liquid lens proposed in [64] at the rest state (left) and during actuation (right). II. Photograph of the adaptive liquid lens proposed in [64]. (Reproduced with permission from [64]). (c) I. Three possible geometrical configurations of the adaptive liquid lens are proposed in [52] at rest. The ambient pressure and pressure in cavities 1 and 2 were indicated by P0, P1, and P2, respectively. II. Photograph of the adaptive liquid lens proposed in [52]. (Reproduced [52] with permission from SPIE Publishing). (d) Architecture of the adaptive liquid lens proposed in [65] at the rest state (I) and the activation state (II). III. Photograph of the fabricated adaptive liquid lens proposed in [65]. IV. Schematic of the adaptive liquid lens proposed in [65]. (Reproduced with permission from [65] © Optical Society of America). (e) I. Schematic of the adaptive liquid lens proposed in [70]. II. Photograph of the adaptive liquid lens proposed in [70]. (Copyright (2023), Reprinted from [70] with permission from Elsevier).
The DEA used in the lenses mentioned above works as an in-plane actuator. Here, several adaptive varifocal liquid lenses using conical DEA were proposed, whose DEA worked as an out-plane actuator [72,73]. Our group proposed an adaptive varifocal liquid lens driven by a conical DE, as shown in Figure 4a, which consisted of two conical DE, compliant electrodes, a liquid droplet, three annular PMMA frames, several screws, screw nuts, as shown in Figure 4a [72]. When a voltage was applied to the electrode, the DEA made the middle PMMA frame move upwards, increasing the surface curvature of the droplet which caused the focal length to decrease. The proposed adaptive liquid lens is 9.4 mm in diameter and 12.5 mm in height. Cai et al. proposed a DEA tunable lens controlled by an electrooculographic (EOG) signal, whose two pre-stretched DE films and lenses form a biconical structure, as shown in Figure 4b [73]. Two DE films and encapsulated salty water form the lens at the central part of the structure. The salty water and the annular carbon grease worked as the electrodes for the DEA. When a voltage was applied to the electrode, the annular electrode area expanded so that the radius of curvature of both sides of the lens decreased and the focal length increased. Each of the two DE films had four separate active areas. The movement of the lens can be controlled by comparing the EOG signals from the left–right channel and the up–down channel. The proposed lens has potential applications in visual prostheses and the medical field.
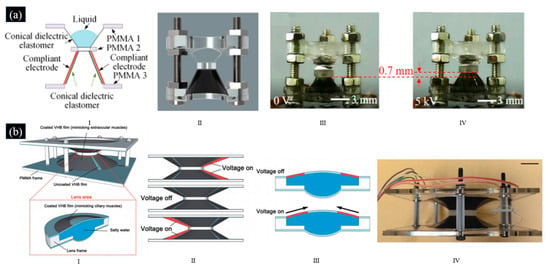
Figure 4.
(a) I. Schematics of the adaptive varifocal liquid lens based on conical DEA proposed in [72]. II. The architecture of the adaptive varifocal liquid lens proposed in [72]. Photograph of the fabricated adaptive varifocal liquid lens proposed in [72] in the initial state (III) and under an actuation voltage of 5.0 kV(IV). (Reproduced with permission from [72] © Optical Society of America). (b) I. The design of the adaptive varifocal liquid lens proposed in [73]. II. When an electrical potential was applied to a pair of DE films on one side (as marked by red), a planar movement of the lens could be induced by the expansion of the DE film. III. The expansion of the annular DE film in the lens could reduce the curvature of the film on both sides and thus increase the focal length of the lens proposed in [73]. IV. Photograph of the adaptive varifocal liquid lens proposed in [73]. (Reproduced with permission from [73]).
As a liquid droplet can present a lens character because of its biconvex shape and its smooth surface, liquid droplet lenses based on DEA, which can be fabricated with a more compact structure, have been proposed [74,75,76,77]. Ren et al. proposed an adaptive varifocal liquid lens for millimeter and micron diameter apertures by filling a droplet into the hole of the DE film, as shown in Figure 5a [74]. Initially, the focal length of the liquid lens was the longest when no voltage was applied. When a drive voltage was applied to the DE, the aperture of each hole shrunk, causing the diameter of the droplet to decrease. It led to an increase in the curvature of the liquid, so the focal length of the liquid lens became shorter. The liquid lens can be easily prepared, and the proposed liquid lens has a fast response. Zhao et al. proposed an adaptive varifocal liquid droplet lens, as shown in Figure 5b [75]. When a voltage was applied to the DE, the DE exhibited an in-plane expansion, which compressed the center areas that were not covered by the carbon black coating. That changes the contact of the droplet and changes the focal length. Our group proposed an adaptive varifocal liquid lens driven by DEA with a transparent conductive droplet, which acted as the material of the lens and the compliant electrode of the lens, as shown in Figure 5c [76]. When a voltage was applied to the droplet, the area of the DE expanded, which decreased the diameter of the droplet and increased the focal length of the lens. The droplet lenses proposed above have a compact structure and a simple fabrication process. To reduce the gravitation effect, the droplet lens should be controlled in micro size and placed in the horizontal position. Due to the small dimension, the droplet lens has potential applications in various compact imaging systems.
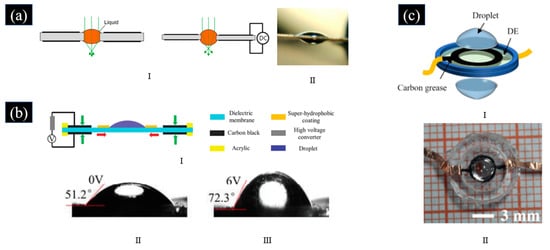
Figure 5.
(a) I. Shape change of a droplet liquid lens proposed in [74] in the hole of the DE at a relaxing state (left) and at an actuation stat (right) II. Side view of the adaptive varifocal liquid droplet lens held in the DE hole proposed in [74]. (Reproduced [74] with permission from SPIE Publishing). (b) I. Schematics of the adaptive varifocal liquid droplet lens proposed in [75]. Photograph of the droplet lens proposed at [75] at the rest state (II) and the activation state (III) (Reproduced with permission from [75]). (c) I. Schematics of the adaptive varifocal liquid droplet lens proposed in [76]. II. Photograph of the droplet liquid lens proposed in [76]. (Reproduced [76] with permission from SPIE Publishing).
Most adaptive varifocal liquid lenses based on DEA mentioned above have DE films used as both the lens membrane and the actuator [52,57,59,64]. The main advantages of this architecture are the compact size and the simple fabrication process [78]. Nevertheless, it challenges membrane puncture, the stability of the lens, and the optical property of DEA caused by sharing of the same elastomeric membrane [56]. As the lens with DEA arranged along the optical path suffers from the challenges of membrane puncture and the stability of the lens and the optical property of DEA caused by sharing of the same elastomeric film, Lau et al. proposed an adaptive varifocal liquid lens with a DEA diaphragm pump, as shown in Figure 6b. The DEA diaphragm separated two hydraulic chambers, which were filled with oil [56]. Oil impregnation improved the high dielectric strength and life of DEs. When there was a voltage applied to DE, the DE membrane expanded outward and the fluid pressure of the lens changed, altering the curvature, which led to a change in focal length. The volume of the hydraulic chamber was larger than the volume of the lens chamber. So small deformations in the electroactive film can cause larger deformations in the lens film, resulting in a larger change of the focal length range. The liquid lens had a diameter of 8 mm and could focus on 15 cm and 50 cm targets at a drive voltage of 1.8 kV. Zhao et al. proposed an adaptive varifocal liquid lens driven by a concentric ring DE encapsulated in a self-adapting film, as shown in Figure 6b [79,80]. Since no stretching of the DE membrane was needed, the mechanical instability of the lens was greatly reduced. When a voltage was applied to the ring DE, it led to the transmission of liquid in the lens portion and the driving portion. The focal length variation at 1 kV driving voltage ranged from 25.4 mm to 105.2 mm (when the initial bow height was 273 μm), and the maximum focal length variation exceeded 300%. By separating the lens and actuator, the reliability and performance of the lenses were enhanced. Separating the lens and actuator allows unrestricted choice of lens film materials with better optical properties or stretchability. This also allowed the DE to reduce the thickness independently from the lens film to reduce the driving voltage [56]. However, this architecture occupies a larger volume.
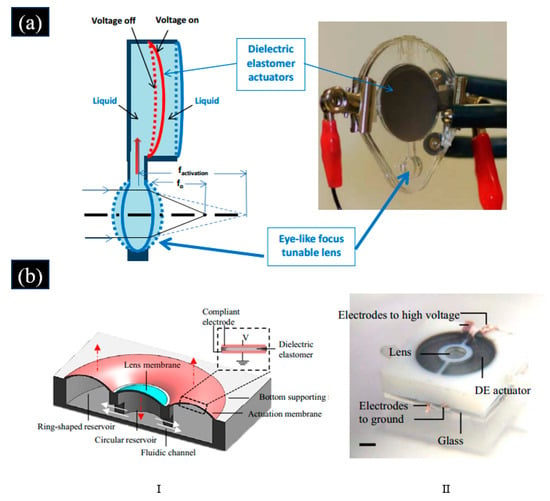
Figure 6.
(a) The adaptive varifocal liquid lens based on the DEA pump proposed in [56]. (Reproduced [56] with permission from SPIE Publishing). (b) I. Perspective view of the adaptive varifocal liquid lens proposed in [79]. II. Photograph of fabricated adaptive liquid lens proposed in [79]. (© (2014) IEEE. Reprinted with permission from [79]).
Using more than one kind of fluid can also develop adaptive varifocal liquid lenses, which change the focal length by controlling the meniscus shape between the fluids. The adaptive liquid lenses using two immiscible liquids driven by DE were proposed [81,82]. Rasti et al. proposed a DE stack actuator-based adaptive varifocal liquid lens, which can reduce the driving voltage [81,83,84]. This liquid lens consisted of two insoluble liquids and a membrane actuator, as shown in Figure 7a. In this case, distilled water and silicon oil were employed, which were separated with a membrane actuator. The center of the membrane had a hole with a diameter of 4 mm. The meniscus acted as a lens whose focal length can be changed by changing the rectangular shape. When a voltage was applied to the DE, DE deformed and resulted in a change in meniscus shape and a change in focal length. The focal length of each lens had a focusing range from 6 to 35 mm as the applied voltage increased from 50 V to 750 V. Ren et al. proposed an adaptive varifocal liquid lens using two immiscible liquids, as shown in Figure 7b [82]. The meniscus acted as a lens and formed in the opening area due to the interfacial tension, and the aperture of the lens was confined using an iris diaphragm (ID). The two liquids had a spherical interface, and their boundary was defined by a variable aperture. By applying a voltage to the bubble driver, the aperture of the aperture can be changed, and the surface profile of the two liquids is altered; thus, the focal length is changed. The two liquids were separated by the blades of the variable aperture, except where they met at the center opening. Due to the interfacial tension of the liquids, a curved surface is formed at the opening area. When a voltage was applied to the electrodes, the DE film expanded and pushed the connector to move upwards. Then, the lever rotated and changed the aperture. When the dimension of the opening area was changed, the contact angle and the focal length were changed because of the balance of the interfacial tension. At an applied voltage of 8 kV, the height of the DE film rose by 6.9 mm, approximately 25% of the initial height, the control rod rotated by 11°, and the aperture increased or decreased by approximately 2 mm. The lens using two immiscible liquids driven by DE has the advantages of large aperture change and good mechanical stability.
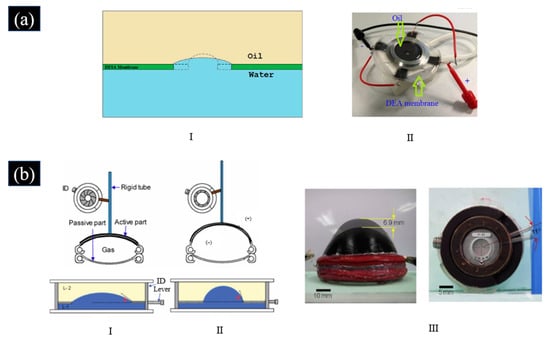
Figure 7.
(a) I. Principle of the adaptive varifocal liquid lens proposed in [81]. II. Photograph of prototype device proposed in [81]. (Reprinted with permission from [81] © Optical Society of America). (b) Principle of the adaptive varifocal liquid lens proposed in [82] in (I) voltage-off and (II) voltage-on states. III. Change in the height of the bubble actuator (the left) and the corresponding change in the angle of the ID lever (the right) produced in [82]. (© (2013) IEEE. Reprinted with permission from [82]).
It is difficult to bind two components together without affecting structural homogeneity and avoiding the formation of defects, so it remains a challenge to create DEA-based lenses with a high dielectric constant together with both mechanical and optical properties. Using electrohydrodynamic (EHD) 3D printing technology, Zhou et al. proposed a polymer-based adaptive varifocal liquid lens driven by DEA, as shown in Figure 8 [85]. EHD printing is an efficient, simple, and low-cost fabrication technique using an electric field to create the fluid flows necessary for delivering inks containing high-content fillers to a substrate [86,87]. The printed lens exhibited a 29% change in focal length from 33.6 mm to 26.1 mm under a dynamic driving voltage signal control. Furthermore, it displayed excellent stability when the focal length was tuned from far to near (30.1 mm to 25.3 mm) for 200 cycles.
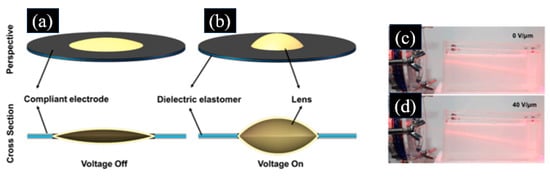
Figure 8.
(a) Diagrammatic views of the adaptive varifocal liquid lens proposed in [85] where the voltage of the focal length is distanced. (b) Diagrammatic views the adaptive varifocal liquid lens proposed in [85] where the voltage on the focal length becomes shorter. The photographs show the focus change of the lens produced in [85] when the laser beam passed through soya milk-based colloid (c) at 0 V/μm and (d) at 40 V/μm. (Reproduced with permission from [85]).
2.3. Adaptive Varifocal Soft Solid Lens Based on DEA
Due to the liquid-based adaptive varifocal lens still having challenges in environment stability and preventing liquid leakage, an all-soft solid adaptive varifocal lens driven by DEA has become a good choice [56,88,89]. The DEA-based soft solid adaptive varifocal lens has the advantages of fast response, large aperture, and small thickness, making it more suitable than a liquid lens for applications that are particularly sensitive to mechanical vibrations, temperature changes, and distortions introduced by gravity [90].
When the DEA of the soft solid lens is involved in optical path refraction, the structure of adaptive varifocal lenses can be more compact. A soft varifocal solid lens driven by DEA was proposed by Kim et al. and it was obtained by bonding a silicon lens and DEA tightly, as shown in Figure 9a [91,92]. The DEA was made of stacked nitrile butadiene rubber film, and liquid carbon was dispensed for creating electrodes. By the application of voltage to the actuator that extends its area, the silicon lens became thicker and had a smaller curvature, and then the focal length was changed. The lens can be zoomed 1.04 times with a high driving voltage. Son et al. proposed a DEA-based varifocal solid lens, as shown in Figure 9b [78,93]. Different from the lens above, the DE film, which acts as a lens, was made of silicone rubber with high transmittance. The thin DE membrane coated with transparent, compliant electrodes was confined by rigid boundaries; the compressive force caused the material to expand when a large enough voltage was applied. Then, the membrane became either convex or concave whose curvature can be changed by applying the voltage, so a variable focal length was achieved. Though this lens did not have a high varifocal ratio, the lens’s structure is simple and compact since the lens itself functions as the actuator.
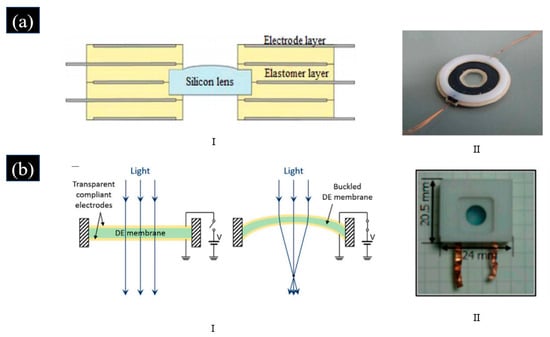
Figure 9.
(a) I. Schematic of the adaptive varifocal solid lens based on DEA proposed in [91]. II. Photograph of the adaptive varifocal solid lens proposed in [91]. (Reproduced [91] with permission from SPIE Publishing). (b) I. Schematic of the adaptive varifocal solid lens based on DEA proposed in [78,93]. II. Photograph of varifocal solid lens based on DEA proposed in [78,93]. (Reproduced with permission from [78,93] © Optical Society of America).
Inspired by reptile and bird accommodation, Carpi et al. proposed a soft varifocal solid lens driven by a peripheral annular DE, which can achieve large tuning ranges, as shown in Figure 10a [90]. The thin DE coated with transparent, compliant electrodes on both sides was radially pre-stretched on a circular rigid frame. When a voltage was applied, the DE squeezed towards the center part while the outward expansion was blocked by the rigid frame, causing a decrease in the diameter of the electrodeless part that hosts the lens. Thus, the focal length of the lens can be changed, and the tunable lens was capable of focal length variations up to 55%. Using an acrylic-based DE with high optical transparency simplified the fabrication process and reduced drive voltage but also made the lens have a low response speed and hysteretic behavior.
Compared with acrylic and polyurethane elastomers used as the material of the DEA field, silicone has lower viscoelastic losses, higher response speed, and higher stability in general [55,59,94]. By using silicone as the material of both a solid lens and DE, Carpi et al. proposed a varifocal solid lens driven by DEA [55]. The proposed lens was an electrically reconfigurable, fully elastomeric, tunable lens with motor-less electrical controllability of astigmatism in the visible range [55]. As shown in Figure 10b, four independently controlled electrodes (S1-S4) are printed on one side of the actuator, and zoom and dispersion can be achieved by applying voltages to each of the four electrodes, depending on the situation. Using silicone materials with high dielectric coefficient and low Young’s modulus, Yoon et al. proposed a varifocal solid lens driven by disk type DEA, which has the features of simple structure, compactness, and good performance, as shown in Figure 10c [95]. The lens consisted of a soft lens and a DEA which can enable purely in-plane radial actuation of lens diameter and consequent curvature change. Performance test results showed the lens had 93% focus length change capability and a response time of 7 ms, which was 1.4 times the focusing capability (65%) and 9.4 times the response time (67 ms) of previous lenses [96]. The results indicated that the material of the DEA has a strong influence on the performance of the lens. Using silicones can have a lower viscoelastic loss, more stable performance, and higher response speeds [90].
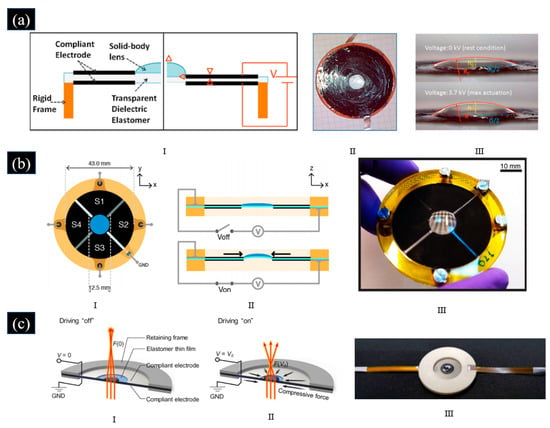
Figure 10.
(a) I. Schematic of the adaptive varifocal solid lens proposed in [90] at relaxed state (the left) and accommodated state (the right) II. Top view of the adaptive varifocal solid lens proposed in [90]. III. Lateral view of a prototype adaptive varifocal solid lens proposed in [90] at electrical rest(top) and under maximum actuation (bottom). (© IOP Publishing. Reproduced with permission from [90]. All rights reserved). (b) I. Schematic of the varifocal solid lens proposed in [55]. II. Schematic lateral sectional view of the lens proposed in [55] at electrical rest (top) and under actuation (bottom). III. Photograph of the varifocal solid lens proposed in [55]. (Reproduced with permission from [55]). (c) Structure and operation principle of the adaptive varifocal solid lens proposed in [95] with no voltage (I) and with a voltage value of Vd (II). III. Photograph of the adaptive varifocal solid lens proposed in [95]. (Reproduced with permission from [95]).
The DEA-based soft varifocal solid lens needs stretchable, robust, and highly conductive electrodes [97]. Grease or particulate electrodes for DEAs are not stable and difficult to pattern for a miniaturized varifocal lens. Therefore, Lau et al. proposed a DEA-based varifocal solid lens with inkjet-printed and patterned silver nanoparticles as electrodes, which had better stretchability and conductivity than metal electrodes [97]. Some conductive gel can act both as a lens and electrodes of DEA, so it has been a better choice to use the conductive gel as the electrodes of the DEA-based varifocal solid lens [88,98]. Liu et al. proposed a new self-contained varifocal lens based on transparent and conductive gels, as shown in Figure 11a [98]. The convex gels can be used as both lenses and actuator electrodes, whose desirable curvature was precisely patterned by inkjet 3D printing, making the lens system an unprecedented compact structure. The lens had a large focal length variation of 32–81% and a fast response speed of 80–153 ms. Zhong et al. proposed a solid tunable lens driven by a DEA based on a polyelectrolyte elastomer, as shown in Figure 11b [88]. The polyelectrolyte elastomer was directly synthesized by a mold-free technique on a DE membrane, which was used as both a lens and actuator electrode. It compacted the structure and simplified the fabrication procedure of the adaptive varifocal lens.
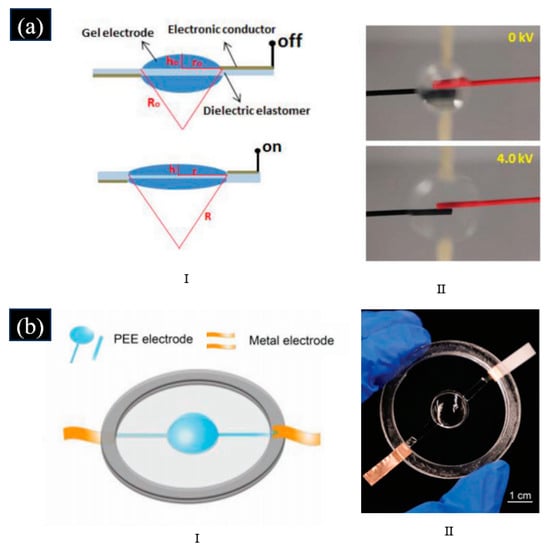
Figure 11.
(a) I. Schematic of the adaptive varifocal solid lens proposed in [98] in the relaxed state (the top) and accommodated state (the bottom). II. Photograph of the adaptive varifocal solid lens proposed in [98] at electrical rest (the top) and under an electrical activation of 4 kV(the bottom). (Reproduced with permission from [98]). (b) I. Schematic of the varifocal solid lens proposed in [88]. II. Photograph of the adaptive varifocal solid lens proposed in [88]. (Reproduced with permission from [88]).
Ren et al. proposed a DEA-driven solid lens module that tunes the focal length by changing the position of the lens, as shown in Figure 12 [99]. A solid lens was tightly attached within a through-hole of a DE film with electrodes on the left side of the DE and no electrodes on the right side. When a voltage was applied to the electrodes of the DE, the expansion and contraction of the DE caused the solid lens to move to the right along a direction perpendicular to the optical axis. Since the shape of the lens did not change, the optical properties did not deteriorate. When combined with a solid lens, it becomes a lens group that can change the focal length by changing the position of the lens. When the driving voltage was 5.5 kV, the lens shift displacement was about 1.7 mm, and it took about 3.5 s to reach displacement stability.
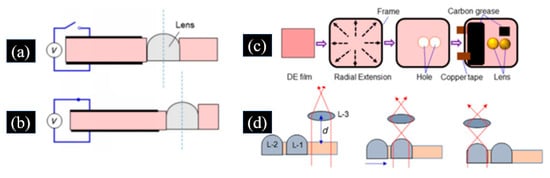
Figure 12.
Mechanism of shifting a lens in the hole of a DE film proposed in [99] at contracting state (a) and stressing state (b). (c) Fabrication of a DEA integrating with lenses produced in [99]. (d) Schematic of a variable focal length in a lens system produced in [99]. (Reproduced [99] with permission from SPIE Publishing).
The variable focal length range is an important indicator for an adaptive varifocal lens. For the varifocal solid lens in static conditions, the achievable range of focal length changing is mainly determined by three factors: the compliance of the lens, the area of the compliant electrodes, and the driving electric field [90]. While dynamically tunable optical systems can achieve a wider range of focal length [89,100]. Kyung et al. proposed a dynamic varifocal solid lens driven by DEA [100]. The lens consisted of a plano-convex PDMS lens as an aperture and a DEA. The DE bent upward when a voltage was applied to the electrodes, causing dynamic translational movement of the aperture in the vertical direction. It means the focal point of this lens can be dynamically adjusted by parallel movement in the vertical direction when the applied voltage changes, as shown in Figure 13a. The focal length of the lens can be varied by 18.4%. The response time was less than 1 ms, and it was highly repeatable. Building on the foundation above, Kyung et al. proposed a DEA-based varifocal solid lens module for a dynamically varying focal system, which consisted of two parallel plano-convex and plano-concave lenses, as shown in Figure 13b [89]. Each active lens in the lens module consisted of a thin DE membrane with annular silver nanowires (AgNWs) electrodes, a hemispherical DE lens structure, and ground layers with a thin annular gold electrode. When a voltage was applied to the electrodes, the active lenses can produce electrically bi-directionally controllable and large translational movement ranging from −3.0 mm to 3.0 mm. A hybrid driving force was produced by silver nanowires and gold layers as well as the electromechanical pressure was produced from DE. The movement produced by the hybrid drive of the DE drive and electrostatic drive was as high as 230% of the movement produced by the DE drive alone. Based on the inverse mechanism of the expansion-tunable lens, Kyung et al. proposed a varifocal solid lens module consisting of a soft lens coupled with a radially expanding DEA pair, which can achieve a wider range focal length, as shown in Figure 13c [96]. The lens had a large focal length range since an expansion-based approach took advantage of larger focal length tunability over the contraction-based counterpart. The plano-convex soft lens in the middle of the ring was effectively stretched when the disk-type DE was driven by voltage, thus changing its focal length. Under the 5 kV driving voltage, the module operated with a focal length range of 65.7%. The soft lens had a diameter of 3 mm, and the focal length of the lens had a focusing range from 14.3 mm to 23.7 mm as the applied voltage increased from 0 to 4.6 kV.
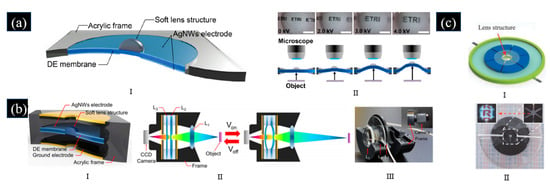
Figure 13.
(a) I. An illustrated configuration of the adaptive varifocal soft solid lens proposed in [100]. II. Images obtained from the varifocal solid lens proposed in [100] (diameter: 1 mm) by applying different electric voltages. (Reproduced from [100], with the permission of AIP Publishing). (b) I. Structural configurations of the varifocal solid lens proposed in [89]. II. Schematic diagram of focal length changing process of the lens proposed in [89]. III. Photograph of the optical system using the varifocal solid lens proposed in [89]. (Reproduced from [89], with the permission of AIP Publishing). (c) I. Schematic of the adaptive varifocal solid lens module proposed in [96]. II. Photograph of the fabricated varifocal solid lens module proposed in [96]. (Reproduced with permission from [96]).
2.4. Adaptive Varifocal Metalens Based on DEA
Metalenses is a planar lens that uses subwavelength-spaced nanostructures to focus light rays based on generalized Snell’s law [101]. It can replace traditional curved lenses with thin sheets a fraction of the thickness of a micrometer level, and it shows considerable potential to replace traditional bulk optical devices [102,103].
By using DEA, Capasso et al. proposed an adaptive varifocal metalens with simultaneous electrical control of focal length, astigmatism, and shift [104]. The polarization-insensitive, converging metalens combined with a transparent DEA is shown in Figure 14. The DEA consisted of transparent polyacrylate elastomers as DE film and single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) as stretchable patterned electrodes. The metalens were located in the center of the pre-stretched DE, which was electrically connected to SWCNTs through silver paste and carbon ribbon. Different functions can be achieved by driving different electrodes, and when a voltage was applied to the electrode, the area of the DE film expanded. Focal length tuning was achieved by applying a voltage through the center electrode V5 to increase focal length or from V1 through V4 to decrease focal length. Controlling of vertical image dispersion in the x,y direction was achieved by activating opposing electrode pairs. Image shifting was achieved by activating a peripheral electrode V1 to V4 so that its expansion causes the entire metasurface to shift in space.
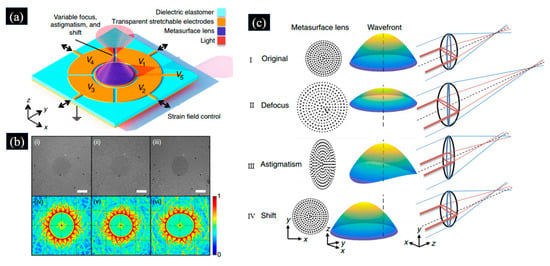
Figure 14.
(a) Schematic of adaptive varifocal metalenses based on DEA proposed in [104]. (b) Optical microscope images in [104]. Optical microscope images at (i) no voltage, (ii) 2.5 kV applied to the center electrode, and (iii) 2.75 kV applied to tune x astigmatism. (c) Principle of strain field-mediated tunable metalens in [104]. (Reproduced with permission from [104]).
2.5. Adaptive Varifocal Fresnel Zone Plate Lens Based on DEA
DEA films can also be used to prepare Fresnel zone plate (FZP) lenses. Park et al. proposed an all-solid-state Fresnel zone plate (FZP) lens with thin and lightweight structures, which was capable of continuously modulating focal length [105]. The prepared FZP consisted of a pre-stretched thin DE film and a ring flexible electrode of AgNWs, which had a prominent two-phase microstructure in the central region. The side-view of the structure is shown in Figure 15. The focal length (F) of the lens was related to the zone number (N), the zone radius (RN), and the wavelength of the incident light (λ),
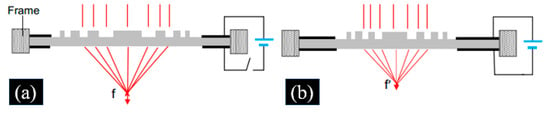
Figure 15.
Side-view of the adaptive varifocal Fresnel zone plate lens based on DEA proposed in [105] structure (a) no voltage and (b) with a voltage. (Reproduced with permission from [38]. CC BY 4.0).
The N-th zone radius (RN) of the FZP lens is given by:
where R1 was the radius of the inner zone, it shows that the focal length of the Fresnel lens can be changed by changing the radius of the zone of the Fresnel lens.
At the voltage-off state, the N-th zone radius (RN) reached its maximum value (Figure 15a). At the voltage-off state, the focal length was the longest. If the voltage applied to the electrode was high enough, it caused the DEA film to shrink laterally, resulting in a decrease in the zone radius of the FZP lens; thus, the focal length (f′) of the FZP lens decreases according to Equation (2) as shown in Figure 15b. The proposed FZP lens has an all-solid-state structure, meaning that it is stable and compact. The device has potential applications in sensor, optical communication, and macro imaging [106]. However, the fabrication of the Fresnel lens is still complicated, and the diffraction efficiency of the FZP lens is low [38].
2.6. Adaptive Varifocal Microlens Array Based on DEA
Microlens array has the advantages of a large field of view angle, low aberration and distortion, and infinite depth of field [107]. Microlens array has potential applications in the fields of 3D imaging, artificial compound eye imaging, multisize imaging, and so on [107,108]. DEA films can be used to prepare an adaptive varifocal microlens array.
Niklaus proposed a 2 × 2 array of liquid mm-scale diameter lenses with individually tunable focal lengths based on DEA, as shown in Figure 16a [109]. Instead of using conventional carbon powder or carbon grease electrodes, which were not transparent as electrodes, the PDMS layer was implanted on both sides with 5 keV gold ions to define the transparent electrodes for actuation. Applying a voltage to one of the lens/actuators led to an area expansion and, hence, to a change in the radius of curvature, then varying the focal length. The completed device is shown in Figure 16a; it has four actuators and can also serve as lenses. The focal length of each lens had a focusing range from 4 mm to 8 mm as the applied voltage increased [109].
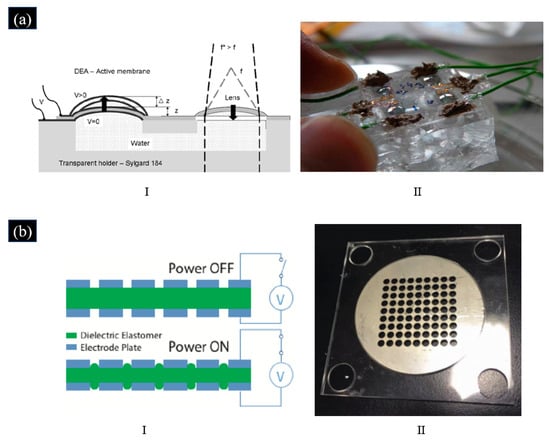
Figure 16.
(a) I. Principle of operation of the lens in [109]: applying a voltage to the left membrane increases its area, leading to a larger radius of curvature, a decreased focal length of the left membrane, and a smaller radius of curvature and an increased focal length of the right membrane. II. A completed device with a set of four membranes proposed in [109]. (Reproduced [109] with permission from SPIE Publishing). (b) I. Schematic of the adaptive varifocal microlens array based on DE proposed in [110]. II. Photograph of the adaptive varifocal microlens array prototype based on DEA proposed in [110]. (Reproduced with permission from [110]).
Compared with adaptive liquid lenses, adaptive solid lenses have better robustness to thermal expansion, gravity, and vibration, making them more suitable for practical applications. Wang et al. proposed a solid-based tunable microlens array using a DE sandwiched between two electrode plates as the lens material, as shown in Figure 16b [110]; the radius of curvature of the DE material can be changed by adjusting the voltage applied to the metal electrode plate. When a voltage was applied to the metal plate, a gradient voltage distribution was formed in the lens aperture zones. The zones on or close to the electrode plates were subject to high voltage, and the zones within the aperture of the lens array were subject to low voltage. The high voltage zones on the electrode plate were subject to higher electromechanical pressure, and the low voltage zones were subject to lower electromechanical pressure. The gradient pressure drop caused the soft DE to be squeezed, resulting in a lens profile of the DE in the aperture profile. The focal length of each lens had a focusing range from 950 mm to ∞, and the imaging resolution is 161.30 lp/mm [110].
2.7. Adaptive Varifocal Alvarez Lenses Base on DEA
Different from the conventional varifocal lens that changes the focal length through the axial movement of the lens group, the Alvarez lens is a novel kind of adaptive varifocal lens rediscovered by Alvarez and Lohmann, which can achieve a large focal length change through a small lateral movement [111,112,113].
The Alvarez lens consists of two-phase plates with non-rotationally symmetric complementary cubic surface profiles, and the focal length is changed by the movement of the plate’s lateral perpendicular to the optical axis. The existing actuator to produce the lateral translation for the Alvarez lens includes MEMS-driven units, motors, and manual movement platforms [114]. Compared with the actuator described above, the DE has many advantages, such as large displacement, quick response speed, low cost, and absence of noise pollution [115,116]. Continuous optical zoom of the Alvarez lens can be achieved by using DE, so DE has been a better choice of soft actuator [114,117,118,119,120].
The principle of the Alvarez lens is not difficult to understand; the profiles of the two-phase plates can be described by the following equations [111,112,113]:
where A, D, and E are constants to be determined as well as x and y is the transverse coordinate normal to the z-direction, and t1 and t2 are the phase profile of the Alvarez lens. A is the vector height modulation coefficient of the free-form surface, which controls the focal power of the Alvarez lens on the surface of a given area by controlling the height difference between the peaks and valleys of the surface; D is the influence factor of wedge quantity; E is the thickness of the center of each lens, ensuring that the thinnest part of the lens has sufficient mechanical strength.
Assuming the lateral displacement is δ, the focal length of the Alvarez lens (f) can be expressed as:
where n is the refractive index of the Alvarez lens material.
According to Equation (6), when δ = 0, the focal power of the Alvarez lens is 0, which is similar to a parallel plate. When δ > 0, the focal power of the Alvarez lens is greater than 0, which is similar to a plano-convex lens with positive focal power; when δ < 0, it resembles a plano-concave lens with negative focal power, as shown in Figure 17 [121].
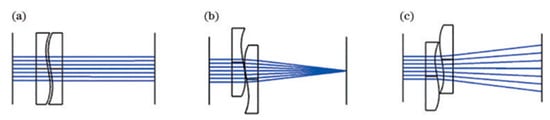
Figure 17.
Varifocal schematic diagrams of the Alvarez lenses. (a) The focal power is 0; (b) the focal power is greater than 0; (c) the focal power is less than 0. (Reproduced with permission from [121]).
The varifocal function can be achieved by applying actuation on the compliant electrodes of the DE adhered to the Alvarez lenses. The varifocal principle of the Alvarez lens actuated by the DEA is shown in Figure 18. Two-phase plates were mounted on two DE film surfaces, respectively, to form the Alvarez lens [114]. When no voltage was applied to the compliant electrode, the Alvarez lens was similar to a parallel plate; as shown in Figure 18a, the focal length of the lens was infinite. When a driving voltage was applied to the compliant electrode, the DE was radially compressed by Maxwell’s stress, then made the phase plate move laterally towards the edge. Applying voltage to different electrodes can change the direction of phase plate movement, as shown in Figure 18b,c [114].
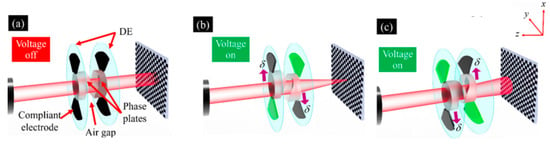
Figure 18.
(a) The architecture of the varifocal Alvarez lenses actuated by DEA. No voltage was applied to the compliant electrodes. (b) Voltages were applied to compliant electrodes. The green compliant electrodes represented that these compliant electrodes were actuated. The gray compliant electrodes represented that no voltage was applied to these compliant electrodes. The first phase plate moved in the x − direction, and the second phase plate moved in the x + direction. Therefore, the Alvarez lens acted as a convex lens. (c) The Alvarez lens acted as a concave lens when the first phase plate moved in the x + direction as well as the second phase plate moved in the x − direction. (Reproduced with permission from [114]).
Alvarez lenses based on DEA can be fabricated to achieve continuous optical zoom compound eye imaging [119], ultra-wide varifocal imaging with a selectable ROI [120], continuous high-magnification zoom imaging [114], two-dimensional varifocal scanning [118,122], and thin wide range varifocal diffraction [117]. The optical systems using the Alvarez lenses have potential applications in large field-of-view imaging, machine vision, consumer electronics, virtual reality, endoscopy, and microscopy in the future.
Our group’s work focuses on preparing lenses driven by DEA, including Alvarez lenses. We proposed a continuous optical zoom imaging system based on Alvarez lenses actuated by DEs consisting of two Alvarez lenses and a solid lens, as shown in Figure 19a [114]. The 10× proposed optical zoom imaging system can achieve a large continuous magnification from 1.58× to 15.80× with a response time of 150 ms at 1.0 mm lateral displacement. The presented Alvarez lenses actuated by DEA, which had a variable focus function based on an Alvarez lens structure and DEA, as well as a scanning function based on the DE-based four-quadrant actuators, as shown in Figure 19b [120]. Based on the proposed lens elements, an imaging system was built to achieve ultra-wide varifocal imaging with a selectable region of interest by our group. The focal length variation in the proposed varifocal component was up to 30.5 times, where the maximum focal length was 181 mm, and the minimum focal length was 5.94 mm. We proposed a novel two-dimensional varifocal scanning element actuated by DE, which consisted of two pairs of Alvarez lenses and a pair of decentred lenses, as shown in Figure 19c [118,122]. The focal length variation was up to 3.75 times, where the maximum and minimum focal lengths were 19.5 mm and 5.2 mm, respectively. The maximum scanning angle was 14.18°. The rise and fall response times were 124 ms and 203 ms, respectively. We also proposed a continuous optical zoom compound eye imaging system based on Alvarez lenses consisting of a curved Alvarez lens array (CALA) and two Alvarez lenses, as shown in Figure 19d [119]. By adjusting the focal length of the CALA and the two Alvarez lenses, the proposed system can achieve continuous zoom imaging without any mechanical movement vertically to the optical axis. The experimental results showed that the paraxial magnification of the target can range from ~0.30× to ~0.9×. The overall dimensions of the optical imaging part were 54 mm × 36 mm × 60 mm (L × W × H). The response time was 180 ms. Moreover, the FOV of the proposed lens was 30°. We designed a thin, wide range of varifocal diffractive Alvarez lenses actuated by DEA, as shown in Figure 19e [117]. The focal length ratio was up to 10×, where the maximum the minimum focal lengths were 300 mm and 30 mm, respectively. The rise time and fall time were 134 ms and 206 ms. As it is difficult to process the complex free-form surface of the Alvarez lenses, we proposed a planar liquid crystal varifocal Alvarez lens based on DEA by combining the Alvarez varifocal principle with liquid crystal materials, as shown in Figure 19f [123]. Compared with the varifocal liquid crystal lenses with a similar aperture, the proposed lens can change the focus length by simply actuating the two-phase plates to move laterally without changing the arrangement of the liquid crystal molecules. The proposed liquid crystal Alvarez lens based on DEA can achieve a varifocal range from 1476 mm to 118 mm at a lateral displacement from 0.2 mm to 2.5 mm. The rise time and fall time were 185 ms and 296 ms, respectively.
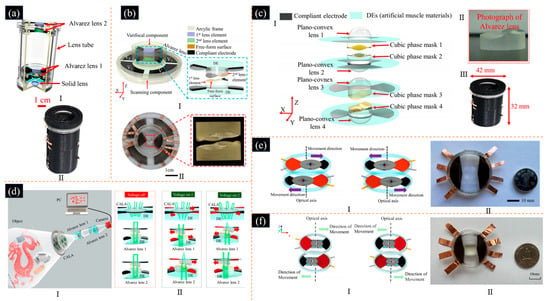
Figure 19.
(a) I. Schematic of the varifocal element using adaptive varifocal Alvarez lens driven by DEA proposed in [114]. II. The photograph of the fabricated varifocal element proposed in [114]. (Reproduced with permission from [114]). (b) I. Architecture of the varifocal scanning element using Alvarez lens driven by DEA proposed in [120]. II. The photograph of the fabricated Alvarez lens proposed in [120]. (Reproduced with permission from [120]). (c) I. Architecture of the varifocal scanning element using Alvarez lens driven by DEA proposed in [122]. II. The photograph of the fabricated Alvarez lenses based on DEA proposed in [118]. III. The photograph of the fabricated varifocal element proposed in [118]. (Reproduced with permission from [118,122]). (d) I. Architecture of the continuous optical zoom compound eye imaging system proposed in [119]. II. Schematic of the compound eye using Alvarez lenses based on DEA proposed in [119]. (Reproduced with permission from [119]). (e) I. Schematic of lateral movement of Alvarez lenses driven by DEA proposed in [117]. II. The photograph of the fabricated Alvarez lens proposed in [117]. (Reproduced with permission from [117]). (f) I. Schematic of lateral movement of Alvarez lenses driven by DE proposed in [123]. II. The photograph of the fabricated Alvarez lenses based on DEA proposed in [123]. (Reproduced with permission from [123]).
Figure 20 shows the relationship between the F-number and lens diameter of some adaptive varifocal lenses. (The F-number is calculated by dividing focal distance by lens diameter). Table 1 lists the parameters of adaptive varifocal lenses based on DEA. The response time of the lenses directly influences the imaging speed. The focal length range is also an important performance parameter in optical varifocal imaging systems. A wide varifocal range and a high varifocal ratio are supposed. The focal length range of some lenses is described by the object distance range for clear imaging. The driving voltage of adaptive lenses is another important performance parameter in optical varifocal imaging systems, which is influenced by the material of DEA and compliant electrodes. A low driving voltage is supposed. The functional principle shows how it changes the focal length.
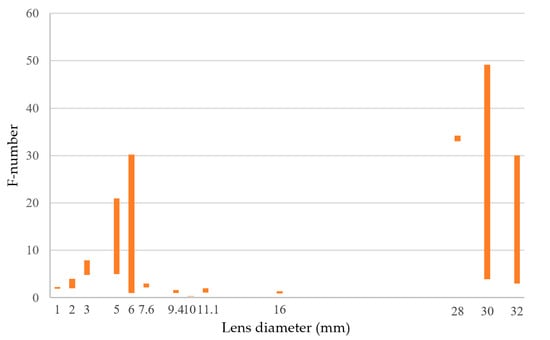
Figure 20.
F-number vs lens diameter.

Table 1.
Comparison of the state-of-the-art adaptive varifocal lenses based on DEA (‘/’ means unknown).
3. Prospects and Challenges
Compared with the traditional varifocal lens, the adaptive varifocal lens shows great strength in terms of compact structure, fast response speed, flexibility, and tunable focal length [19]. Figure 21 shows how adaptive varifocal lenses based on DEA have developed in recent years. The adaptive varifocal liquid lens and the soft solid lens are suitable in constrained spaces for their compact structure, which is seen as a good choice for miniaturized optical lenses in the future. Since adaptive varifocal lenses can change the focal length without changing the placement of the optical elements, they can reduce the complexity of the optical zoom system. Adaptive lenses have potential applications in machine vision, biomedical imaging, consumer electronics, and telescopes [38]. Although adaptive lenses are compact, the size of the actuator is still large. The small actuator of adaptive lenses is desirable for application in optical systems in the future. Compared with a soft solid lens, the adaptive varifocal liquid lens still faces challenges in environmental stability and preventing liquid leakage. In addition, an adaptive liquid lens suffers little adequate imaging quality as it is hard to obtain an optimized aspherical surface. So, solid lenses with an aspherical surface are needed to correct the optical aberration. Adaptive varifocal metalenses, which are a fraction of the thickness of a micrometer, show considerable potential to replace traditional bulk optical devices. Adaptive varifocal Fresnel zone plate lenses have potential applications in sensor, optical communication, and macro imaging. The adaptive varifocal microlens array has potential applications in the fields of 3D imaging, artificial compound eye imaging, and multisize imaging. Adaptive varifocal Alvarez lenses have potential applications in large field-of-view imaging, virtual reality, endoscopy, and microscopy in the future.
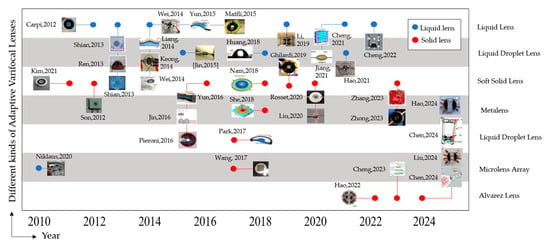
Figure 21.
Notional View of development of Adaptive Varifocal Lenses based on DEA.
4. Conclusions
Adaptive varifocal lenses have been a superordinate substitution compared with traditional varifocal lenses, which change the focal length by displacing the lens bodies in the optical zoom system. The focal length tunability of an adaptive varifocal lens can be achieved by many approaches, such as thermal driving, liquid crystals, electrowetting, dielectrophoresis effect, ferrofluidic piston, and DE. Among the approaches mentioned above, DE attracts great attention because of the advantages of high transmittance, solvent-free condition, compact structure, flexibility, large apertures, and lightweight among the actuators. DE also has a preferable actuator for the adaptive varifocal lenses, such as liquid lenses, soft solid lenses, metalenses, Fresnel lenses, microlens arrays, and Alvarez lenses. The adaptive varifocal lens driven by DEA has potential applications in machine vision, consumer electronics, virtual reality, and medical and industrial imaging.
However, the drawbacks of the adaptive varifocal lenses driven by DEA are also not negligible. As for adaptive liquid lenses, there are still challenges in terms of liquid leakage, gravitational stability, thermal fluctuation, and restriction in the profile of the lens. Furthermore, liquid lenses do not prevail in fabrication compared with solid lenses. Research has been dedicated to improving the performance of the adaptive lens based on DEA to reduce negative impacts. Liquid leakage is usually caused by a breakdown of the DE; to address the issue, DE materials with higher permittivity have been obtained [95]. Some DEA can be separated from the liquid lens, which is fully oil-impregnated, to ensure long life and high dielectric strength [56]. To achieve a compact structure and improve transmittance, DEA lenses using transparent electrodes and conductive gels have been developed [64,65,70]. Using the negative pressure method to fabricate lenses makes the structure stable during operation [71]. For soft solid lenses, it is necessary to improve the optical properties of DE and the lens manufacturing process. It remains a challenge to create DE-actuated tunable lenses with a high dielectric constant together with both transparency and high electromechanical properties [85]. For all the tunable lenses driven by DEA, the high drive voltage is a challenge that cannot be ignored. A lower driving voltage can be achieved by the synthesis of new elastomers with a higher dielectric constant [124,125], or it can be achieved by the usage of thinner actuation membranes whose feasibility has been demonstrated [126]. Stacking DE films into a multilayer structure can reduce the driving voltage [81,127,128]. To overcome this problem, future developments should be aimed at lowering the voltages to 100–200 V, which is the standard for the low-cost and low-size drives of commercial piezoelectric transducers [55].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.L. and Y.C.; methodology, S.L. and Y.C.; investigation, S.L., L.L. and H.X.; writing—original draft preparation, S.L.; writing—review and editing, Y.C.; visualization, S.L. and Z.L.; supervision, Y.C.; project administration, Y.C.; funding acquisition, Y.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 62275017) and Preliminary Study (No. 202303042).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Dataset available on request from the authors.
Acknowledgments
We thank Yi Zhao at The Ohio State University for his technical support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Kuiper, S.; Hendriks, B.H. Variable-focus liquid lens for miniature cameras. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 85, 1128–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saurei, L.; Mathieu, G.; Berge, B. Design of an autofocus lens for VGA ¼-inch CCD and CMOS sensors. In Optical Design and Engineering; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Hendriks, B.H.W.; Kuiper, S.; van As, M.A.J.; Renders, C.A.; Tukker, T.W. Variable liquid lenses for electronic products. In ICO20: Optical Design and Fabrication; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Akram, M.N.; Asghar, M.H. Step-zoom dual-field-of-view infrared telescope. Appl. Opt. 2003, 42, 2312–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Zheng, D.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, X. Combination of mechanical athermalization with manual in IR zoom telescope. In Infrared Technology XVII; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, R.B.; Hadaway, J.B.; Burleson, T.A.; Watts, B.; Park, E.D. All-reflective four-element zoom telescope: Design and analysis. In International Lens Design Conference; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, F.S.; Johnson, D.; Francis, C.S.; Cho, S.H.; Qiao, W.; Arianpour, A.; Mintz, Y.; Horgan, S.; Talamini, M.; Lo, Y.-H. Fluidic lens laparoscopic zoom camera for minimally invasive surgery. J. Biomed. Opt. 2010, 15, 030504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpi, D.; Tullis, I.D.C.; Barber, P.R.; Augustyniak, E.M.; Smart, S.C.; Vallis, K.A.; Vojnovic, B. Electrically tunable fluidic lens imaging system for laparoscopic fluorescence-guided surgery. Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 3232–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Chau, F.S.; Zhou, G. Ultra-compact optical zoom endoscope using solid tunable lenses. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 20675–20688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouzounov, D.G.; Rivera, D.R.; Webb, W.W.; Bentley, J.; Xu, C. Miniature varifocal objective lens for endomicroscopy. Opt. Lett. 2013, 38, 3103–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Chen, H. Electrically tunable-focusing and polarizer-free liquid crystal lenses for ophthalmic applications. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 9428–9436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chen, M.; Lin, Y. Electrically tunable ophthalmic lenses for myopia and presbyopia using liquid crystals. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2014, 596, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Wang, M.R.; Liu, Z.; Yang, J.J. Dynamic spectral imaging with spectral zooming capability. Opt. Lett. 2007, 32, 1518–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greisukh, G.I.; Ezhov, E.G.; Sidyakina, Z.A.; Stepanov, S.A. Design of plastic diffractive–refractive compact zoom lenses for visible–near-IR spectrum. Appl. Opt. 2013, 52, 5843–5850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajima, M.; Minoshima, K. Optical zooming interferometer for subnanometer positioning using an optical frequency comb. Appl. Opt. 2010, 49, 5844–5850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajima, M.; Matsumoto, H. Picometer positioning system based on a zooming interferometer using a femtosecond optical comb. Opt. Express 2008, 16, 1497–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigwood, C.; Wood, A. Two-element lenses for military applications. Opt. Eng. 2011, 50, 121705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, F.; Bagwell, B.E.; Pinon, V.; Krishna, S. Adaptive polymer lens for rapid zoom shortwave infrared imaging applications. Opt. Eng. 2014, 53, 125101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Cao, J.; Tang, X.; Hao, Q. Optical zoom imaging systems using adaptive liquid lenses. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2021, 16, 041002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, K.; He, Z.; Wu, S.T. Reflective polarization volume lens with small f-number and large diffraction angle. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2020, 8, 2000170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Lin, Y. An electrically tunable-focusing liquid crystal lens with a low voltage and simple electrodes. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 2045–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, F.; Tian, L.-L.; Li, R.; Gu, X.-Q.; Zhou, X.-Y.; Wang, D.; Wang, Q.-H. Adaptive nematic liquid crystal lens array with resistive layer. Liq. Cryst. 2020, 47, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.-L.; Li, C.-Y.; Pan, J.-T.; Ji, Y.-E.; Jiang, C.; Zheng, R.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.-X.; Lu, Y.-Q. Self-assembled liquid crystal architectures for soft matter photonics. Light Sci. Appl. 2022, 11, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, R.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Ma, L.; Wang, Y.; Huang, L.; Lu, Y. Stimuli-responsive active materials for dynamic control of light field. Responsive Mater. 2023, 1, e20230017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wu, S.; Cao, H.; Chen, Q.; Lu, Y.; Hu, W. Electrically Tunable Microlens Array Enabled by Polymer-Stabilized Smectic Hierarchical Architectures. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2022, 10, 2201015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, R.; Ma, L.; Feng, W.; Pan, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Chen, P.; Bisoyi, H.K.; et al. Autonomous Self-Sustained Liquid Crystal Actuators Enabling Active Photonic Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2301142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.-L.; Wu, S.-B.; Hu, W.; Liu, C.; Chen, P.; Qian, H.; Wang, Y.; Chi, L.; Lu, Y.-Q. Self-Assembled Asymmetric Microlenses for Four-Dimensional Visual Imaging. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 13709–13715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, E.J.; Reynolds, M.; Raistrick, T.; Berrow, S.R.; Jull, E.I.L.; Reshetnyak, V.; Mistry, D.; Gleeson, H.F. Controlling the Optical Properties of Transparent Auxetic Liquid Crystal Elastomers. Macromolecules 2024, 57, 2030–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rešetič, A. Shape programming of liquid crystal elastomers. Commun. Chem. 2024, 7, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palto, S.P.; Geivandov, A.R.; Kasyanova, I.V.; Simdyankin, I.V.; Artemov, V.V.; Gorkunov, M.V. Liquid crystal microlenses based on binary surface alignment controlled by focused ion beam treatment. Opt. Lett. 2021, 46, 3376–3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Li, T.; Li, Z.; Lu, C.; Zhang, X. Dielectrophoresis-actuated liquid lenses with dual air/liquid interfaces tuned from biconcave to biconvex. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 3849–3854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Tong, X.; Zhu, Y.; Tsoi, C.C.; Jia, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X. Aberration-free aspherical in-plane tunable liquid lenses by regulating local curvatures. Lab Chip 2020, 20, 995–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendriks, B.H.W.; Kuiper, S.; VAN As, M.A.J.; Renders, C.A.; Tukker, T.W. Electrowetting-based variable-focus lens for miniature systems. Opt. Rev. 2005, 12, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murade, C.U.; Oh, J.M.; Ende, D.v.D.; Mugele, F. Electrowetting driven optical switch and tunable aperture. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 15525–15531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, N.; Banerjee, A.; Kim, H.; Mastrangelo, C.H. Tunable-focus lens for adaptive eyeglasses. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 1221–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, K.; Zeng, H.; Zhao, Y. Insect–Human Hybrid Eye (IHHE): An adaptive optofluidic lens combining the structural characteristics of insect and human eyes. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 3594–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berge, B.; Peseux, J. Variable focal lens controlled by an external voltage: An application of electrowetting. Eur. Phys. J. E 2000, 3, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Wu, S. Adaptive Lenses Based on Soft Electroactive Materials. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, K.; Zhao, Y. A three-dimensional deformable liquid lens array for directional and wide angle laparoscopic imaging. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE 26th International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), Taipei, Taiwan, 20–24 January 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Oku, H.; Ishikawa, M. Variable-focus lens with 30 mm optical aperture based on liquid–membrane–liquid structure. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 131111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Wei, K.; Zhao, Y. Variable focus smartphone based microscope using an elastomer liquid lens. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 29th International conference on micro electro mechanical systems (MEMS), Shanghai, China, 24–28 January 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, H.; Wu, S. Variable-focus liquid lens. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 5931–5936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrick, J.D.; Stokes, S.; Bachas-Daunert, S.; Moschou, E.A.; Deo, S.K.; Bachas, L.G.; Daunert, S. Chemically Tunable Lensing of Stimuli-Responsive Hydrogel Microdomes. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 4024–4027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Agarwal, A.K.; Beebe, D.J.; Jiang, H. Adaptive liquid microlenses activated by stimuli-responsive hydrogels. Nature 2006, 442, 551–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osada, Y.; Okuzaki, H.; Hori, H. A polymer gel with electrically driven motility. Nature 1992, 355, 242–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, K.; Tanaka, N.; Tatsuma, T. A redox actuator based on reversible formation of bond between poly(acrylic acid) gel and Cu2+ ion. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2005, 585, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Nishio, I.; Sun, S.-T.; Ueno-Nishio, S. Collapse of Gels in an Electric Field. Science 1982, 218, 467–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Jang, B.; Song, H.; Kim, S.; Kwon, Y.W.; Kang, H.S.; Kim, M.S.; Park, I.; Kim, T.S.; Jang, J.; et al. A seamless auxetic substrate with a negative Poisson’s ratio of −1. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, H.; Takasaki, M.; Hirai, T. Actuation mechanism of plasticized PVC by electric field. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2010, 157, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Ueki, T.; Tsurumi, D.; Hirai, T. Influence of plasticizer content on the transition of electromechanical behavior of PVC gel actuator. Langmuir 2011, 27, 7902–7908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpi, F.; Frediani, G.; Turco, S.; De Rossi, D. Bioinspired Tunable Lens with Muscle-Like Electroactive Elastomers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 4152–4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shian, S.; Diebold, R.M.; Clarke, D.R. High-Speed, Compact, Adaptive Lenses Using in-Line Transparent Dielectric Elastomer Actuator Membranes; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hirai, T.; Ogiwara, T.; Fujii, K.; Ueki, T.; Kinoshita, K.; Takasaki, M. Electrically Active Artificial Pupil Showing Amoeba-Like Pseudopodial Deformation. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 2886–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajiesmaili, E.; Clarke, D.R. Dielectric elastomer actuators. J. Appl. Phys. 2021, 129, 151102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghilardi, M.; Boys, H.; Török, P.; Busfield, J.J.C.; Carpi, F. Smart Lenses with Electrically Tuneable Astigmatism. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keong, G.-K.; La, T.-G.; Shiau, L.-L.; Tan, A.W.Y. Challenges of Using Dielectric Elastomer Actuators to Tune Liquid Lens; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Carpi, F.; Frediani, G.; De Rossi, D. Bioinspired Tunable Lens Driven by Electroactive Polymer Artificial Muscles; Prescott, T.J., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 74–82. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Zappe, H.; Seifert, A. Polyacrylate membranes for tunable liquid-filled microlenses. Opt. Eng. 2013, 52, 046601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maffli, L.; Rosset, S.; Ghilardi, M.; Carpi, F.; Shea, H. Ultrafast All-Polymer Electrically Tunable Silicone Lenses. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 1656–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brochu, P.; Pei, Q. Advances in dielectric elastomers for actuators and artificial muscles. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2010, 31, 10–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpi, F.; Bauer, S.; De Rossi, D. Stretching dielectric elastomer performance. Science 2010, 330, 1759–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpi, F.; De Rossi, D.; Kornbluh, R.; Pelrine, R.E.; Sommer-Larsen, P. Dielectric Elastomers as Electromechanical Transducers: Fundamentals, Materials, Devices, Models and Applications of an Emerging Electroactive Polymer Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, D.; Lin, Z.; Huang, C.; Shih, W. Tunable lens driven by dielectric elastomer actuator with ionic electrodes. Micro Nano Lett. 2014, 9, 869–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shian, S.; Diebold, R.M.; Clarke, D.R. Tunable lenses using transparent dielectric elastomer actuators. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 8669–8676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Chen, C.; Cao, J.; Bao, C.; Yang, A.; Hao, Q. Tunable lens using dielectric elastomer sandwiched by transparent conductive liquid. Opt. Lett. 2021, 46, 4430–4433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shian, S.; Diebold, R.M.; McNamara, A.; Clarke, D.R. Highly compliant transparent electrodes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 61101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Q.; Chen, C.; Cao, J.; Cheng, Y. Response Time of Liquid Lens Actuated by Dielectric Elastomer Under Different Input Voltage Functions; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Markert, C.D.; Guo, X.; Skardal, A.; Wang, Z.; Bharadwaj, S.; Zhang, Y.; Bonin, K.; Guthold, M. Characterizing the micro-scale elastic modulus of hydrogels for use in regenerative medicine. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2013, 27, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Bai, Y.; Xiang, F.; Sun, J.; Chen, Y.M.; Wang, H.; Zhou, J.; Suo, Z. Stretchable and transparent hydrogels as soft conductors for dielectric elastomer actuators. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2014, 52, 1055–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhu, J.; Wen, H.; Xia, Z.; Zhang, Z. Biomimetic human eyes in adaptive lenses with conductive gels. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2023, 139, 105689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xia, Z.; Zhang, Z. Focus-tunable imaging analyses of the liquid lens based on dielectric elastomer actuator. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2021, 44, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, C.; Cao, J.; Bao, C.; Ning, Y.; Hao, Q. Varifocal liquid lens driven by a conical dielectric elastomer actuator. Appl. Opt. 2022, 61, 4633–4637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Xu, S.; Liu, Y.; Leng, J.; Cai, S. A Biomimetic Soft Lens Controlled by Electrooculographic Signal. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1903762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.; Lee, J.-H.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, G.; Lee, G.-B.; Ren, H.; Nah, C. Liquid lens driven by elastomer actuator. Opt. Eng. 2016, 55, 017107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhao, Y. Smartphone based focus-free macroscopy using an adaptive droplet lens. In Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems Workshop Hilton Head Island; Transducer Research Foundation: San Diego, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, Q.; Li, Z.; Chen, C.; Cao, J.; Cheng, Y. Adaptive Liquid Lens Actuated by Dielectric Elastomer with Transparent Conductive Droplet; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, B.; Lee, J.-H.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, G.; Lee, G.-B.; Ren, H.; Nah, C. Adaptive liquid lens driven by elastomer actuator. Opt. Eng. 2016, 55, 017107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ghilardi, M.; Busfield, J.J.C.; Carpi, F. Electrically Tunable Lenses: A Review. Front. Robot AI 2021, 8, 678046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, K.; Domicone, N.W.; Zhao, Y. A tunable liquid lens driven by a concentric annular electroactive actuator. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 27th International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), San Francisco, CA, USA, 26–30 January 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, K.; Domicone, N.W.; Zhao, Y. Electroactive liquid lens driven by an annular membrane. Opt. Lett. 2014, 39, 1318–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasti, P.; Hous, H.; Schlaak, H.F.; Kiefer, R.; Anbarjafari, G. Dielectric elastomer stack actuator-based autofocus fluid lens. Appl Opt. 2015, 54, 9976–9980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Lee, R.H.; Park, H.R.; Ren, H.; Nah, C.; Yoo, I.S. A Liquid Lens Driven by Bubble Actuator. J. Microelectromechanical Syst. 2013, 22, 1222–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasti, P.; Kesküla, A.; Haus, H.; Schlaak, H.F.; Anbarjafari, G.; Aabloo, A.; Kiefer, R. A Passive Autofocus System by Using Standard Deviation of the Image on a Liquid Lens; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Rasti, P.; Kiefer, R.; Anbarjafari, G. Autofocus Liquid Lens by Using Sharpness Measurement. In Proceedings of the 2015 23nd Signal Processing and Communications Applications Conference (SIU), Malatya, Turkey, 16–19 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Ning, F.; Wen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, S.; Betts, A.; Jerrams, S.; Zhou, F.-L. Electrohydrodynamic printing of a dielectric elastomer actuator and its application in tunable lenses. Composites. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2021, 147, 106461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liashenko, I.; Rosell-Llompart, J.; Cabot, A. Ultrafast 3D printing with submicrometer features using electrostatic jet deflection. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onses, M.S.; Sutanto, E.; Ferreira, P.M.; Alleyne, A.G.; Rogers, J.A. Mechanisms, capabilities, and applications of high-resolution electrohydrodynamic jet printing. Small 2015, 11, 4237–4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Xue, Q.; Li, J.; He, Y.; Xie, Y.; Yang, C. Stretchable Transparent Polyelectrolyte Elastomers for All-Solid Tunable Lenses of Excellent Stability Based on Electro–Mechano–Optical Coupling. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2023, 8, 2200947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.; Park, S.; Nam, S.; Park, B.; Park, S.K.; Mun, S.; Lim, J.M.; Kyung, K.-U. An electro-active polymer based lens module for dynamically varying focal system. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 109, 141908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieroni, M.; Lagomarsini, C.; De Rossi, D.; Carpi, F. Electrically tunable soft solid lens inspired by reptile and bird accommodation. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2016, 11, 065003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.-C.; Chung, J.; Lee, Y.; Nam, J.-D.; Moon, H.; Choi, H.R.; Koo, J.C. Biomimetic Small Scale Variable Focal Length Lens Unit Using Synthetic Elastomer Actuators; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, B.-C.; Lee, Y.; Nam, J.-D.; Moon, H.; Choi, H.R.; Koo, J.C. Smart Material Actuators for Micro Optical Zoom Lens Driving Systems. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2011, 47, 1999–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.-I.; Pugal, D.; Hwang, T.; Choi, H.R.; Koo, J.C.; Lee, Y.; Kim, K.; Nam, J.-D. Electromechanically driven variable-focus lens based on transparent dielectric elastomer. Appl. Opt. 2012, 51, 2987–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosset, S.; Shea, H.R. Small, fast, and tough: Shrinking down integrated elastomer transducers. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2016, 3, 031105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.J.; Park, S.; Choi, M.; Park, S.K.; Yun, S.; Shin, E.; Yoon, J.W. Monolithic focus-tunable lens technology enabled by disk-type dielectric-elastomer actuators. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, S.; Yun, S.; Yoon, J.W.; Park, S.; Park, S.K.; Mun, S.; Park, B.; Kyung, K.-U. A Robust Soft Lens for Tunable Camera Application Using Dielectric Elastomer Actuators. Soft Robot 2018, 5, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, M.; La, T.; Lau, G.K. Inkjet Printed Stretchable Electrodes for Tunable Focus Lens; Nanyang Technological University: Singapore, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Qiu, Y.; Yu, W. Self-Contained Focus-Tunable Lenses Based on Transparent and Conductive Gels. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2020, 305, 2000393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.; Ren, H. Position-movable lens driven by dielectric elastomer actuator. Opt. Eng. 2016, 55, 075101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.; Park, S.; Park, B.; Nam, S.; Park, S.K.; Kyung, K.-U. A thin film active-lens with translational control for dynamically programmable optical zoom. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107, 081907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, N.; Genevet, P.; Kats, M.A.; Aieta, F.; Tetienne, J.-P.; Capasso, F.; Gaburro, Z. Light propagation with phase discontinuities: Generalized laws of reflection and refraction. Science 2011, 334, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, N.; Capasso, F. Flat optics with designer metasurfaces. Nat. Mater. 2014, 13, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genevet, P.; Capasso, F.; Aieta, F.; Khorasaninejad, M.; Devlin, R. Recent advances in planar optics: From plasmonic to dielectric metasurfaces. Optica 2017, 4, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, A.; Zhang, S.; Shian, S.; Clarke, D.R.; Capasso, F. Adaptive metalenses with simultaneous electrical control of focal length, astigmatism, and shift. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaap9957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Park, B.; Nam, S.; Yun, S.; Park, S.K.; Mun, S.; Lim, J.M.; Ryu, Y.; Song, S.H.; Kyung, K.U. Electrically tunable binary phase Fresnel lens based on a dielectric elastomer actuator. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 23801–23808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, N.Y.J.; Zhang, X.; Neo, D.W.K.; Huang, R.; Liu, K.; Kumar, A.S. A review of recent advances in fabrication of optical Fresnel lenses. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 71, 113–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Li, L.-H.; Lee, W.-B.; Chan, C.-Y. Fabrication of Microlens Array and Its Application: A Review. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2018, 31, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zheng, Y.; Yuan, R.; Jiang, Z.; Xu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Xing, Y.; Wang, Q. Tunable Liquid Lenses: Emerging Technologies and Future Perspectives. Laser Photonics Rev. 2023, 17, 2300274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niklaus, M.; Rosset, S.; Shea, H. Array of Lenses with Individually Tunable Focal-Length Based on Transparent Ion-Implanted EAPs; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Hayakawa, T.; Ishikawa, M. Dielectric-elastomer-based fabrication method for varifocal microlens array. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 31708–31717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohmann, A.W. Improvements relating to lenses and to variable optical lens systems formed of such lenses. Br. Pat. 1965, 998, 29. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez, L.W. Two-Element Wariable-Power Spherical Lens. 2017. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/TWO-ELEMENT-WARIABLE-POWER-SPHERICAL-LENS-Alvarez/62365fdd78a5a215f361b2e84d9de707cdf34533 (accessed on 26 February 2025).
- Wang, L.-Y.; Li, B.-C.; Sheng, B.; Xu, B.-L.; Huang, Y.-S.; Ni, Z.-J.; Zhang, D.-W. Optimized multielement accommodative intraocular lens with a four-freeform-surface Alvarez lens and a separate aspheric lens. Appl. Opt. 2019, 58, 7609–7614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Hao, Q.; Liu, L.; Cao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, Y. 10× continuous optical zoom imaging using Alvarez lenses actuated by dielectric elastomers. Opt. Express 2024, 32, 1246–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.-J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, J.; Yang, M.; Zhao, H.; Pei, J.-Y.; Zhong, S.-L.; Dang, Z.-M. Soft, tough, and fast polyacrylate dielectric elastomer for non-magnetic motor. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheima, Y.; von Szczepanski, J.; Danner, P.M.; Künniger, T.; Remhof, A.; Frauenrath, H.; Opris, D.M. Transient elastomers with high dielectric permittivity for actuators, sensors, and beyond. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 40257–40265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Q.; Liu, L.; Cao, J.; Liu, M.; Ou, Y.; Cheng, Y. Thin wide range varifocal diffractive Alvarez lenses actuated by dielectric elastomers. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2024, 182, 108453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Hao, Q.; Cao, J.; Xu, Y.; Cheng, Y. Two-dimensional varifocal scanning imaging based on Alvarez and decentred lenses actuated by dielectric elastomer. Opt. Laser Technol. 2023, 167, 109805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Hao, Q.; Liu, L.; Cao, J.; Qiao, Z.; Cheng, Y. Continuous Optical Zoom Compound Eye Imaging Using Alvarez Lenses Actuated by Dielectric Elastomers. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Q.; Chen, C.; Cao, J.; Li, Z.; Cheng, Y. Ultra-wide varifocal imaging with selectable region of interest capacity using Alvarez lenses actuated by a dielectric elastomer. Photonics Res. 2022, 10, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, O.; Qi, O.; Liu, M.; Ning, Y.; Cao, J.; Qun, H.; Cheng, Y. Design of a Compact Infrared Continuous Optical Zoom System Based on Alvarez Lenses. Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 2024, 61, 1022001. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Chen, C.; Liu, L.; Cao, J.; Xu, Y.; Hao, Q. A Compact Two-Dimensional Varifocal Scanning Imaging Device Actuated by Artificial Muscle Material. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Hao, Q.; Li, Z.; Xiong, J.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, Y. Design and demonstration of DEA-based tunable planar liquid crystal Alvarez lenses. Opt. Laser Technol. 2025, 182, 112068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, F.B.; Daugaard, A.E.; Hvilsted, S.; Skov, A.L. The current state of silicone-based dielectric elastomer transducers. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2016, 37, 378–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dünki, S.J.; Ko, Y.S.; Nüesch, F.A.; Opris, D.M. Self-repairable, high permittivity dielectric elastomers with large actuation strains at low electric fields. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 2467–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulin, A.; Rosset, S.; Shea, H.R. Printing low-voltage dielectric elastomer actuators. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 107, 244104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotz, P.; Matysek, M.; Schlaak, H.F. Fabrication and Application of Miniaturized Dielectric Elastomer Stack Actuators. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2011, 16, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlaak, H.F.; Jungmann, M.; Matysek, M.; Lotz, P. Novel multilayer electrostatic solid state actuators with elastic dielectric. In Smart Structures and Materials 2005: Electroactive Polymer Actuators and Devices (EAPAD); SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).