Athermal Design of Star Tracker Optics with Factor Analysis on Lens Power Distribution and Glass Thermal Property
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Merit Function of Thermal Focus Drift for Star Tracker Lens
3. Simulation on Lens Power Distribution and Material Selection for Minimizing Thermal Focus Drift
4. Result Analysis and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LEO | Low Earth Orbit |
| GS | Global Search |
| EFL | Effective Focal Length |
| TTL | Total Track Length |
| DIY | Distortion Index |
| BFL | Back Focal Length |
| MTF | Modulation Transfer Function |
| CRA | Chief Ray Angle |
| Thermo-optic Coefficient | |
| CTE | Coefficient of Thermal Expansion |
| C(H)/C(L) | Crowns with higher/lower thermo-optic coefficient |
| F(H)/F(L) | Flints with higher/lower thermo-optic coefficient |
| OEM | Original Equipment Manufacturer |
| G1 to G7 | Lens elements 1 through 7 |
| G2 to G7 | Lens elements 2 through 7 |
Appendix A
| Symbol | Definition |
|---|---|
| Refractive index of the lens material | |
| Radii of curvature of the incident and exit surfaces of a lens | |
| Curvature difference of a lens, | |
| Optical power (dioptric power) of a lens, | |
| Optical power of the lens element | |
| Total optical power of the multi element lens system | |
| Effective focal length of the multi element lens system, | |
| Normalized ray height at the first surface of lens | |
| Linear coefficient of thermal expansion () of the lens glass material | |
| Athermalization Factor, | |
| Athermalization Factor for the lens element | |
| Temperature variation under consideration | |
| Drift in focal length due to optical effects from temperature change | |
| Total focal plane drift resulting from temperature change | |
| Thermo-optic coefficient (rate of change of refractive index with respect to temperature), provided by glass maker. |
References
- Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Shen, Y.; Ma, Z.; Yan, H. Athermalization of star sensor optical system with large field of view and low distortion. Proc. SPIE 2023, 12557, 125571N. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, J.R. An optically athermalized lens covering a 200-degree temperature range. Proc. SPIE 2018, 11180, 111808E. [Google Scholar]
- Kryszczyński, T.; Leśniewski, M. Material problem in athermalization of optical systems. Opt. Eng. 1997, 36, 1596–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivieri, M.; Pieri, S.; Romoli, A. Analysis of defocusing thermal effects in optical systems. Proc. SPIE 1996, 2774, 283–292. [Google Scholar]
- Benham, P.; Kidger, M. Developments in MTF and Athermal Optimization. In Proceedings of the 1990 International Lens Design Conference, Monterey, CA, USA, 11–14 June 1990; Volume 1354, pp. 68–79. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, N.; Cui, Q.; Sun, L.; Wang, J. Optical athermalization in the visible waveband using the 1+ method. Appl. Opt. 2019, 58, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Cheng, J.; Liu, Y. Multiple lenses athermalization and achromatization by the quantitative replacement method of combined glasses on athermal visible glass map. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 34707–34722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Park, S.C. Simple Graphical Selection of Optical Materials for an Athermal and Achromatic Design Using Equivalent Abbe Number and Thermal Glass Constant. J. Opt. Soc. Korea 2015, 19, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lim, T.-Y.; Kim, Y.-S.; Park, S.-C. Graphical Selection of Optical Materials Using an Expanded Athermal Glass Map and Considering the Housing Material for an Athermal and Achromatic Design. J. Opt. Soc. Korea 2015, 19, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, T.Y.; Park, S.C. Achromatic and athermal lens design by redistributing the element powers on an athermal glass map. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 18049–18057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogers, J.R. Passive athermalization: Required accuracy of the thermo-optical coefficients. Proc. SPIE 2014, 9293, 92931A. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.; Liu, J.; Chen, T.; Wang, J.; Yu, F. Calculation Method for Athermalized Optical Systems and Athermal Design Based on ZEMAX. In Proceedings of the 2020 12th International Conference on Intelligent Human-Machine Systems and Cybernetics (IHMSC), Hangzhou, China, 22–23 August 2020; pp. 1010–1014. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, L.A. Fused silica as an optical material [Invited]. Opt. Mater. Express 2022, 12, 3043–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoletta, C.A.; Eubanks, A.G. Effect of Simulated Space Radiation on Selected Optical Materials. Appl. Opt. 1972, 11, 1365–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kul, M.; Akgül, B.; Karabay, Y.Z.; Hitzler, L.; Sert, E.; Merkel, M. Minimum and Stable Coefficient of Thermal Expansion by Three-Step Heat Treatment of Invar 36. Crystals 2024, 14, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Liu, C.; Liu, S.; Fan, X. Optical Design of Imaging Spectrometer Based on Linear Variable Filter for Nighttime Light Remote Sensing. Sensors 2021, 21, 4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Ishikawa, M. Dynamic Response of Elastomer-Based Liquid-Filled Variable Focus Lens. Sensors 2019, 19, 4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, C.-Y.; Su, G.-D.J. Time-Effective Simulation Methodology for Broadband Achromatic Metalens Using Deep Neural Networks. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
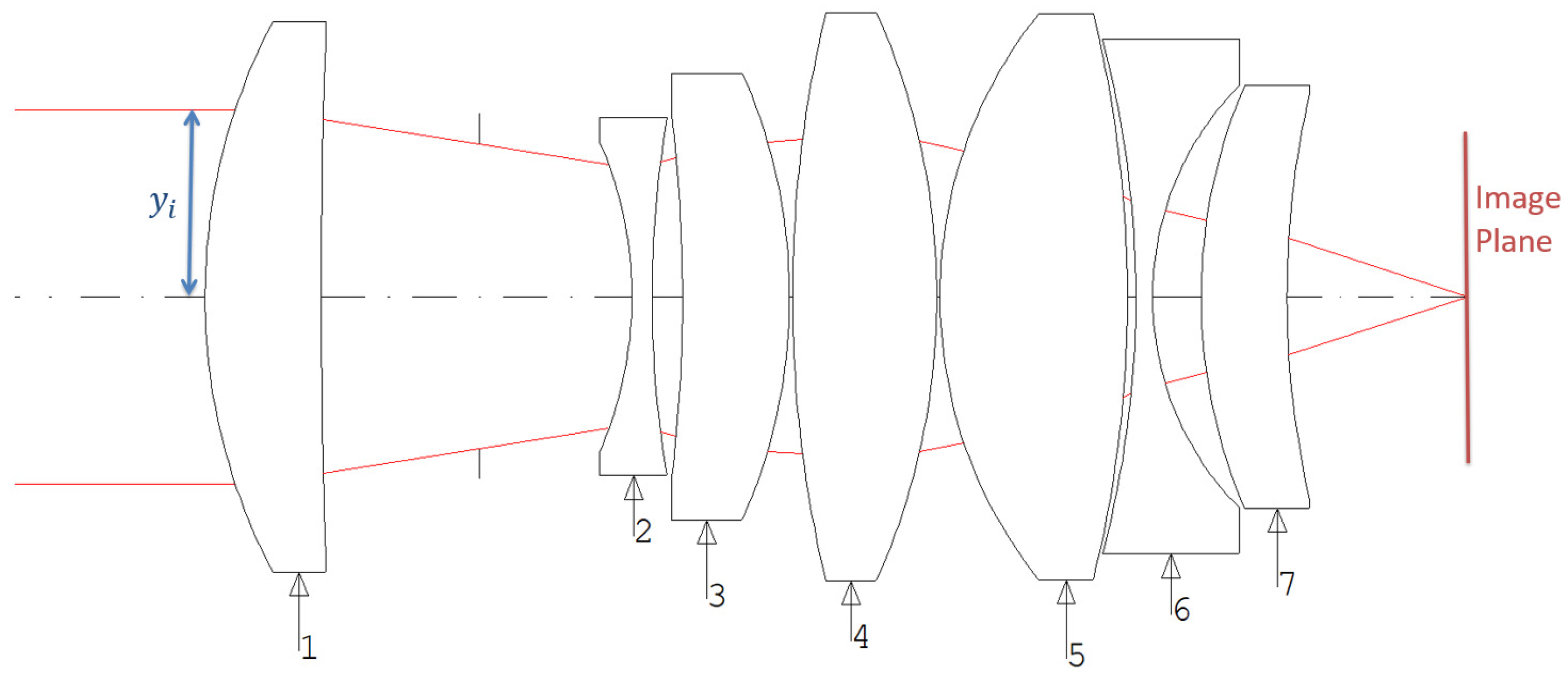
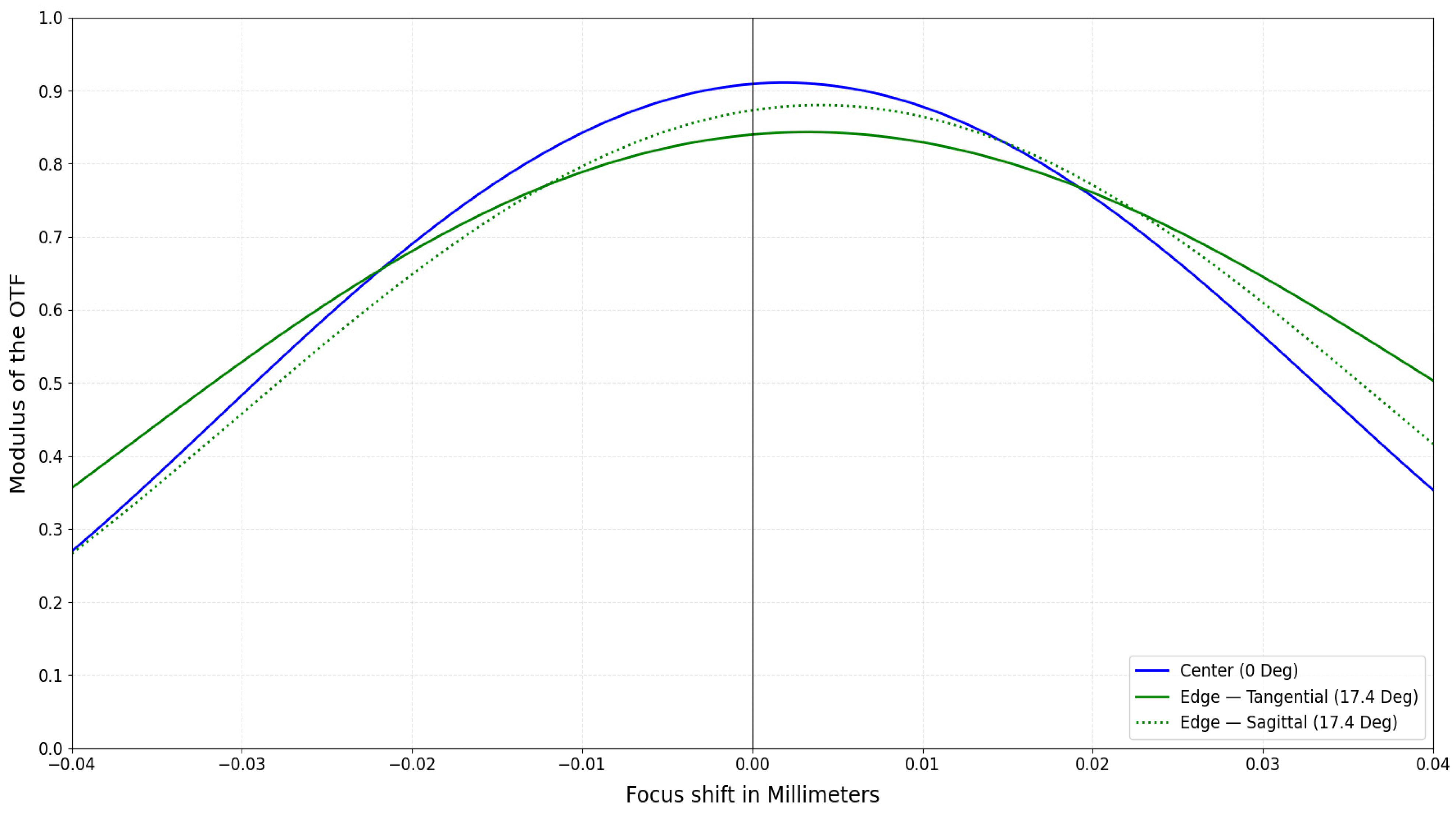
| Items | Symbol | Value | Unit | Description/Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Working wavelength | 470–650 | nm | ||
| Effective Focal Length | 28.3 | mm | System EFL | |
| F-number | 1.8 | — | ||
| Field of View | FOV | 34.8 | degree | Full field of view |
| Total Track Length | TTL | 60 | mm | First lens R1 to image plane |
| Back Focal Length | BFL | 8 | mm | Last lens R2 to image plane |
| Chief Ray Angle | CRA | <10 | degree | Incident angle to image plane |
| Optical Distortion | DIY | <1.1 | % | |
| Modulation Transfer Function | MTF | Center > 0.8 Edge > 0.7 | — | At spatial frequency 40 lp/mm |
| Role of Power | H/L | Glass | (×10−7/°C) | (×10−7/°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (+) | High | S-LAL21 | 77 | 50 |
| (+) | Low | S-LAL12 | 10 | 72 |
| (−) | High | S-TIH10 | 27 | 80 |
| (−) | Low | S-TIH11 | 13 | 89 |
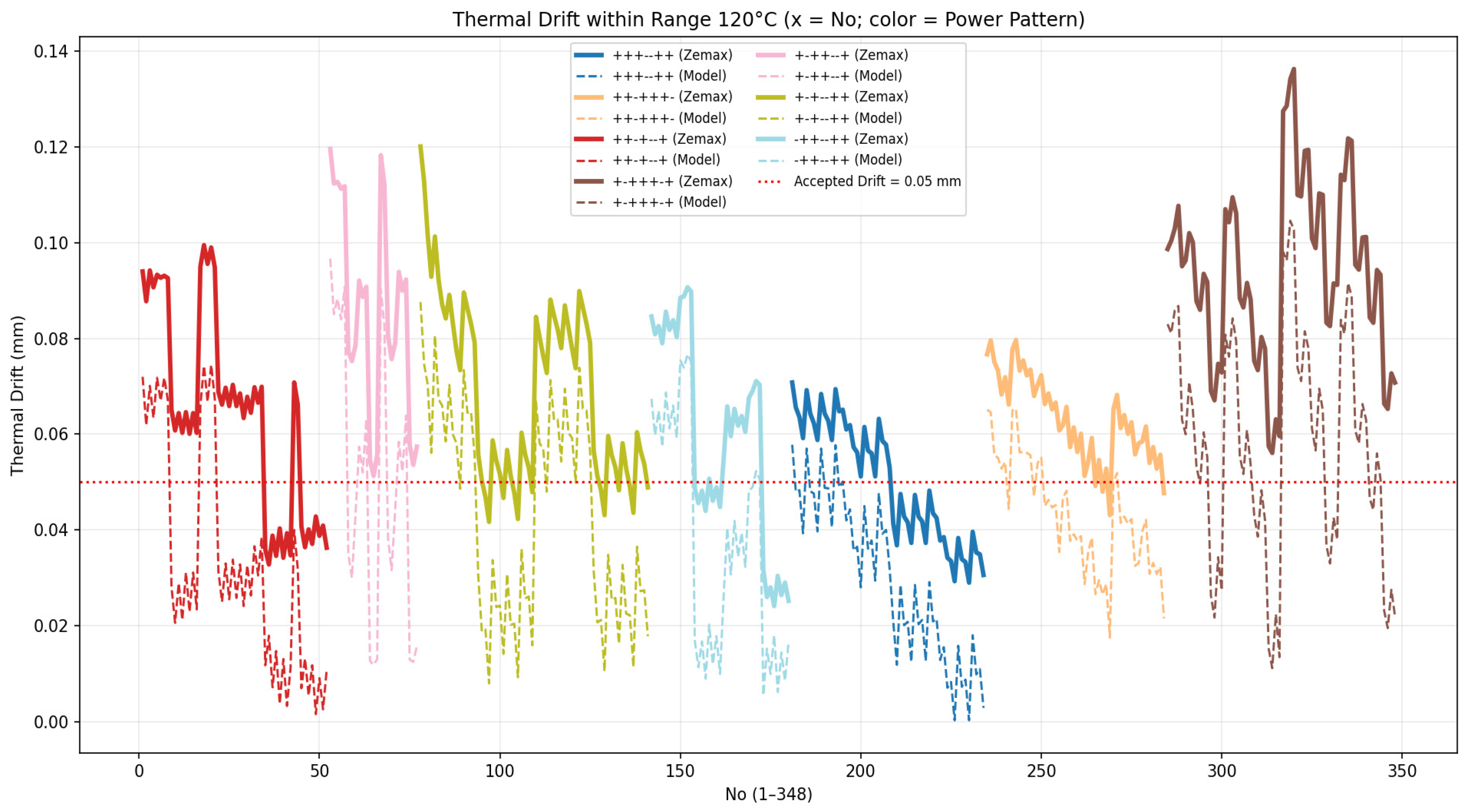
| Power Sign G1 to G7 | Focus Drift 120 °C Equation (9) (mm) | G2 to G7 Materials | G2 to G7_Crown/Flint (H/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| +++--++ | 0.0003 | SLAL12, SLAL12, STIH10, STIH11, SLAL12, SLAL12 | C(L), C(L), F(H), F(L), C(L), C(L) |
| +++--++ | 0.0029 | SLAL12, SLAL12, STIH11, STIH11, SLAL12, SLAL12 | C(L), C(L), F(L), F(L), C(L), C(L) |
| -++--++ | 0.0055 | SLAL12, SLAL12, STIH10, STIH10, SLAL21, SLAL21 | C(L), C(L), F(H), F(H), C(H), C(H) |
| -++--++ | 0.0062 | SLAL12, SLAL12, STIH10, STIH11, SLAL21, SLAL21 | C(L), C(L), F(H), F(L), C(H), C(H) |
| +++--++ | 0.0071 | SLAL12, SLAL12, STIH10, STIH11, SLAL21, SLAL12 | C(L), C(L), F(H), F(L), C(H), C(L) |
| +++--++ | 0.0083 | SLAL12, SLAL12, STIH10, STIH11, SLAL12, SLAL21 | C(L), C(L), F(H), F(L), C(L), C(H) |
| +++--++ | 0.0088 | SLAL12, SLAL12, STIH11, STIH10, SLAL12, SLAL21 | C(L), C(L), F(L), F(H), C(L), C(H) |
| ++-+--+ | 0.0091 | SLAL12, STIH11, SLAL12, STIH11, STIH10, SLAL12 | C(L), F(L), C(L), F(L), F(H), C(L) |
| +++--++ | 0.0099 | SLAL12, SLAL12, STIH11, STIH11, SLAL21, SLAL12 | C(L), C(L), F(L), F(L), C(H), C(L) |
| ++-+--+ | 0.0108 | SLAL12, STIH11, SLAL12, STIH11, STIH11, SLAL12 | C(L), F(L), C(L), F(L), F(L), C(L) |
| No. | Power Sign G1 to G7 | Drift 120 °C Equation (9) (mm) | Drift 120 °C ZEMAX (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | +++--++ | 0.0003 | 0.0293 |
| 2 | +++--++ | 0.0029 | 0.0306 |
| 3 | -++--++ | 0.0055 | 0.0317 |
| 4 | -++--++ | 0.0062 | 0.0304 |
| 5 | +++--++ | 0.0071 | 0.0342 |
| 6 | +++--++ | 0.0083 | 0.0335 |
| 7 | +++--++ | 0.0088 | 0.0333 |
| 8 | ++-+--+ | 0.0091 | 0.0388 |
| 9 | +++--++ | 0.0099 | 0.0353 |
| 10 | ++-+--+ | 0.0108 | 0.0363 |
| No | Layout | MTF at 20 °C | MTF at −40 °C and +80 °C |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |  | 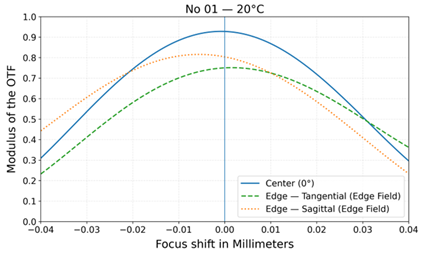 | 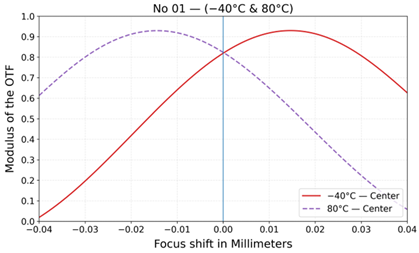 |
| 2 | 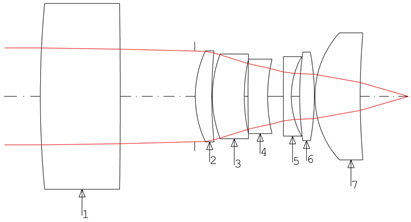 | 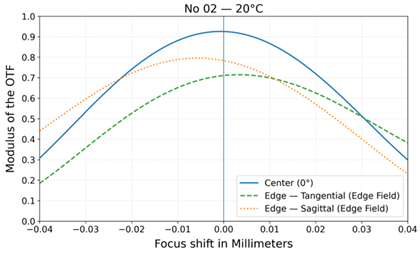 | 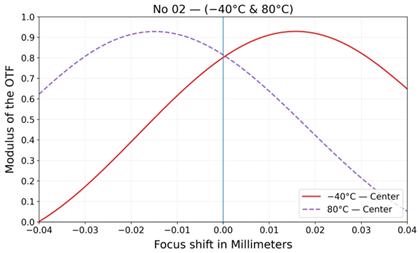 |
| 3 | 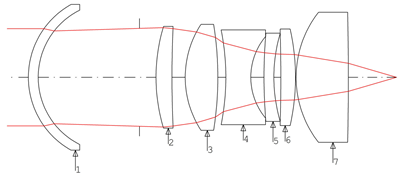 |  |  |
| 4 | 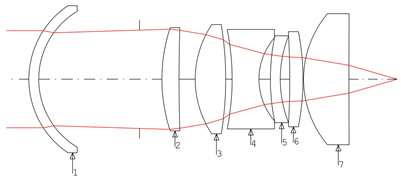 |  | 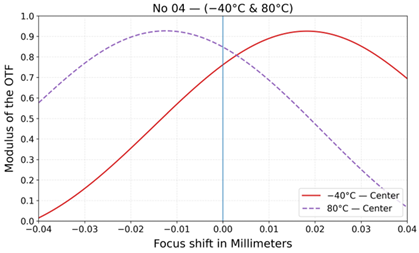 |
| 5 |  |  | 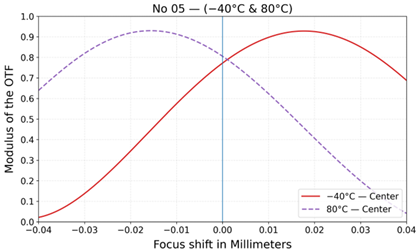 |
| 6 | 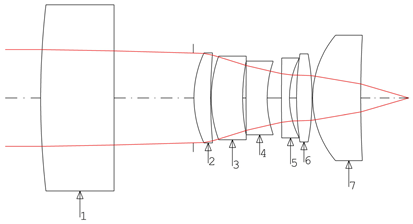 |  |  |
| 7 |  | 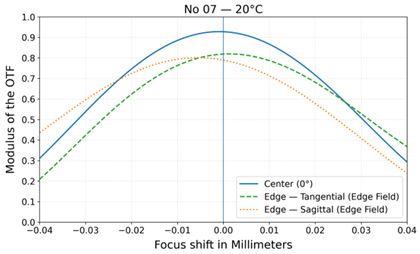 | 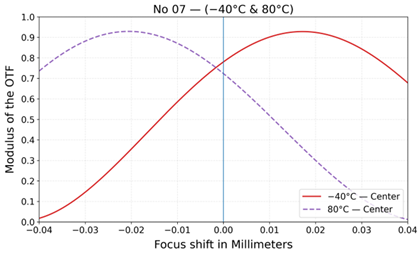 |
| 8 |  |  | 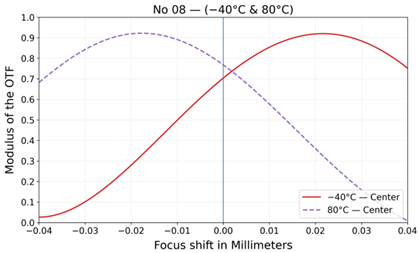 |
| 9 |  | 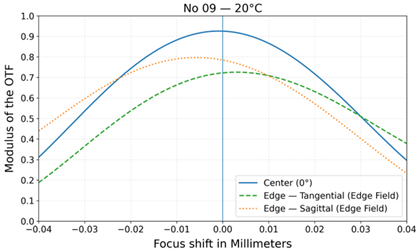 | 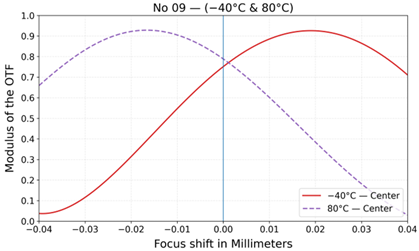 |
| 10 |  | 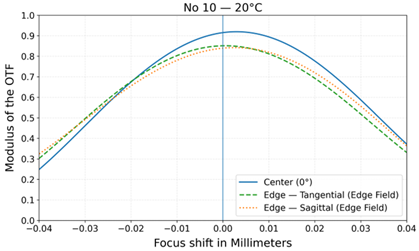 | 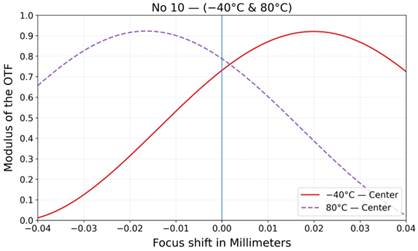 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, K.-C.; Chen, C.-H. Athermal Design of Star Tracker Optics with Factor Analysis on Lens Power Distribution and Glass Thermal Property. Photonics 2025, 12, 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12111057
Wang K-C, Chen C-H. Athermal Design of Star Tracker Optics with Factor Analysis on Lens Power Distribution and Glass Thermal Property. Photonics. 2025; 12(11):1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12111057
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Kuo-Chuan, and Cheng-Huan Chen. 2025. "Athermal Design of Star Tracker Optics with Factor Analysis on Lens Power Distribution and Glass Thermal Property" Photonics 12, no. 11: 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12111057
APA StyleWang, K.-C., & Chen, C.-H. (2025). Athermal Design of Star Tracker Optics with Factor Analysis on Lens Power Distribution and Glass Thermal Property. Photonics, 12(11), 1057. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12111057






