High-Resolution Interferometric Temperature Sensor Based on Two DFB Fiber Lasers with High-Temperature Monitoring Potential
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiments and Results
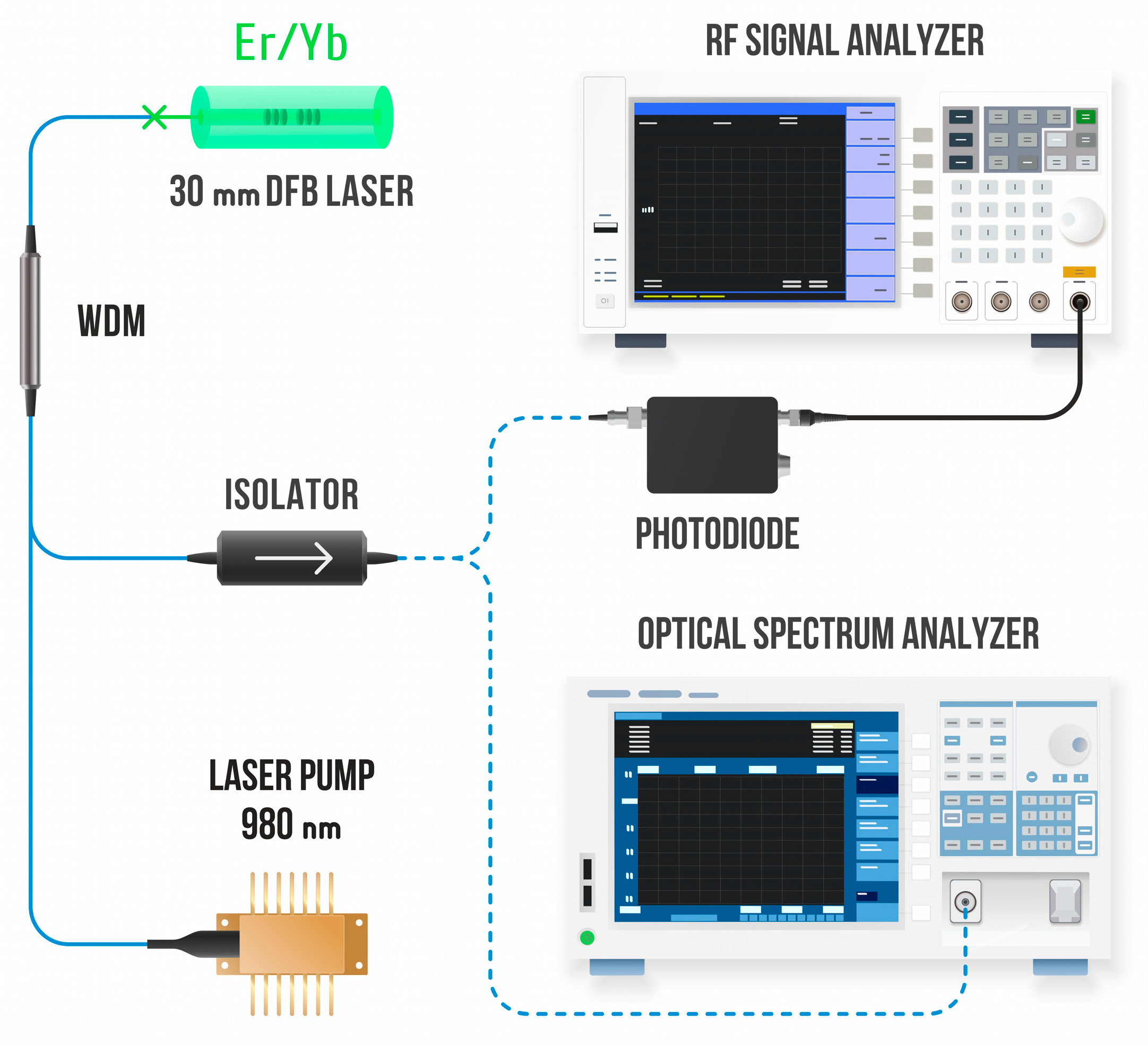
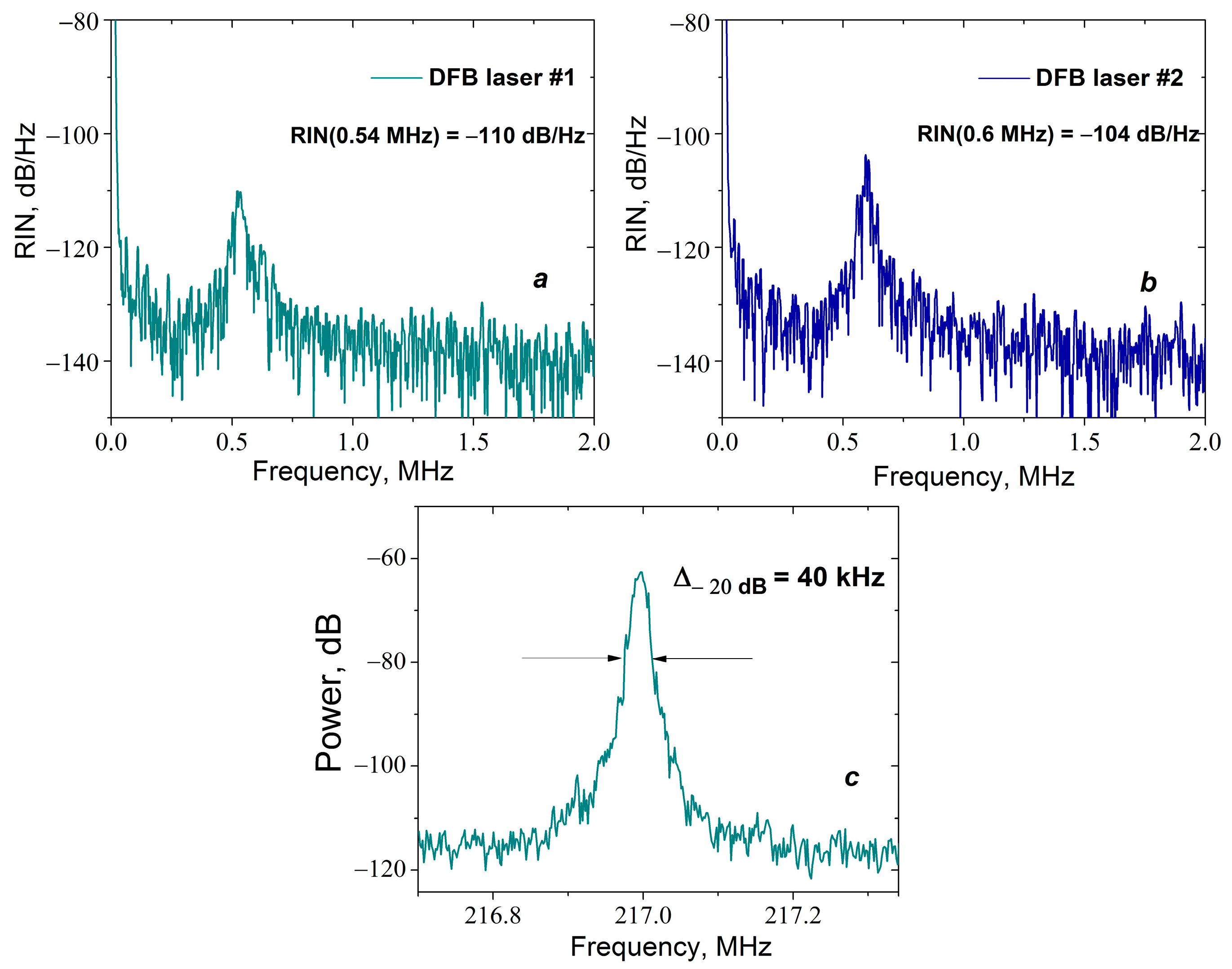
2.1. DFB Laser
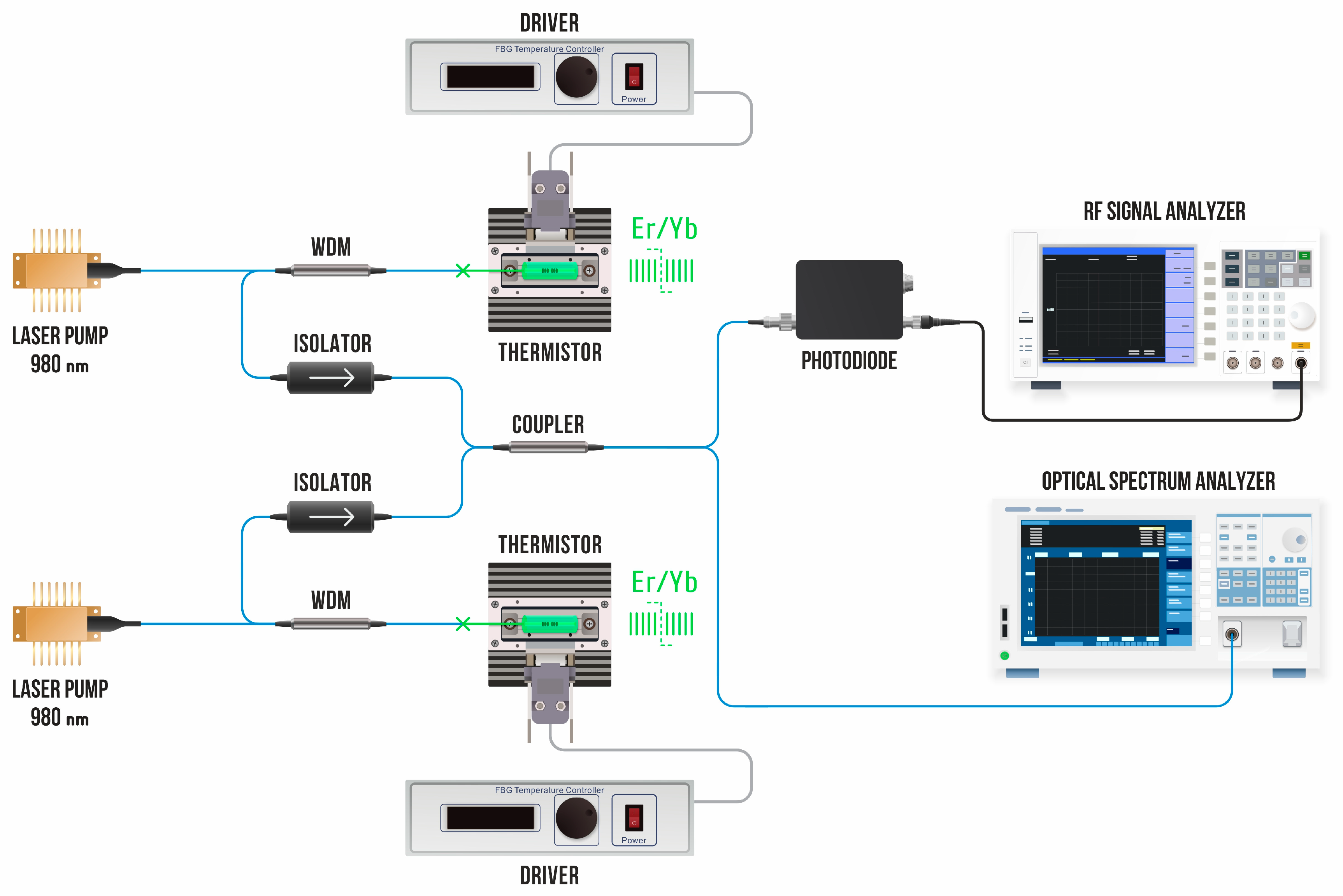
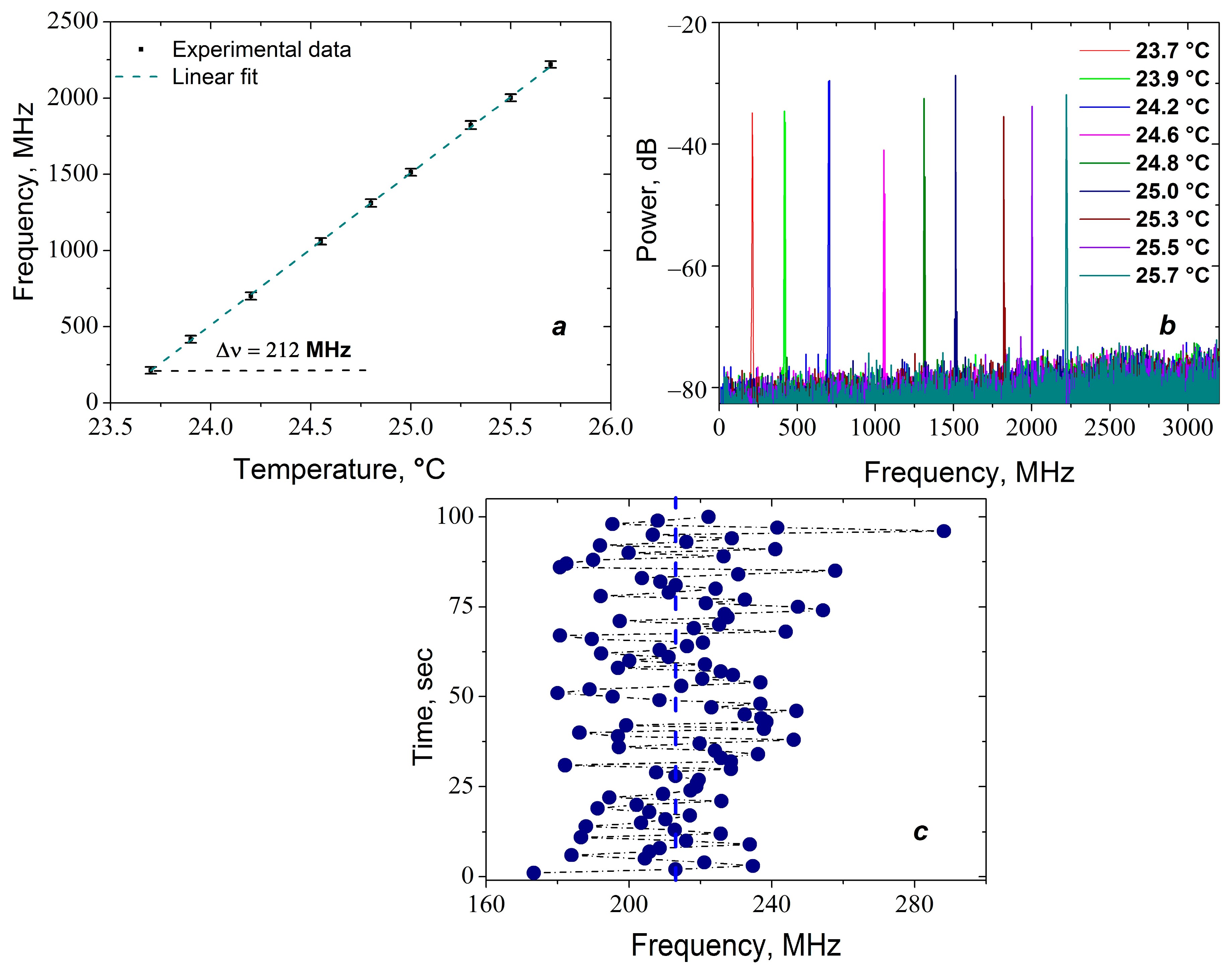
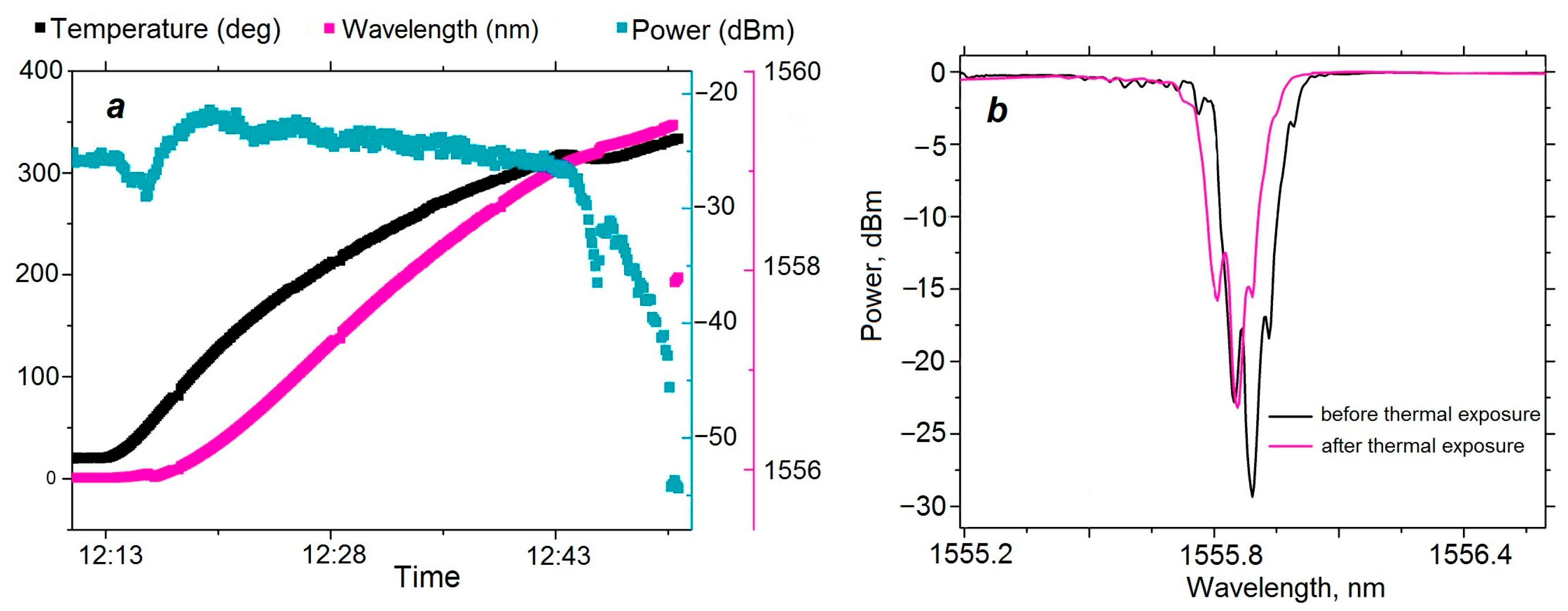
2.2. Temperature Measurements
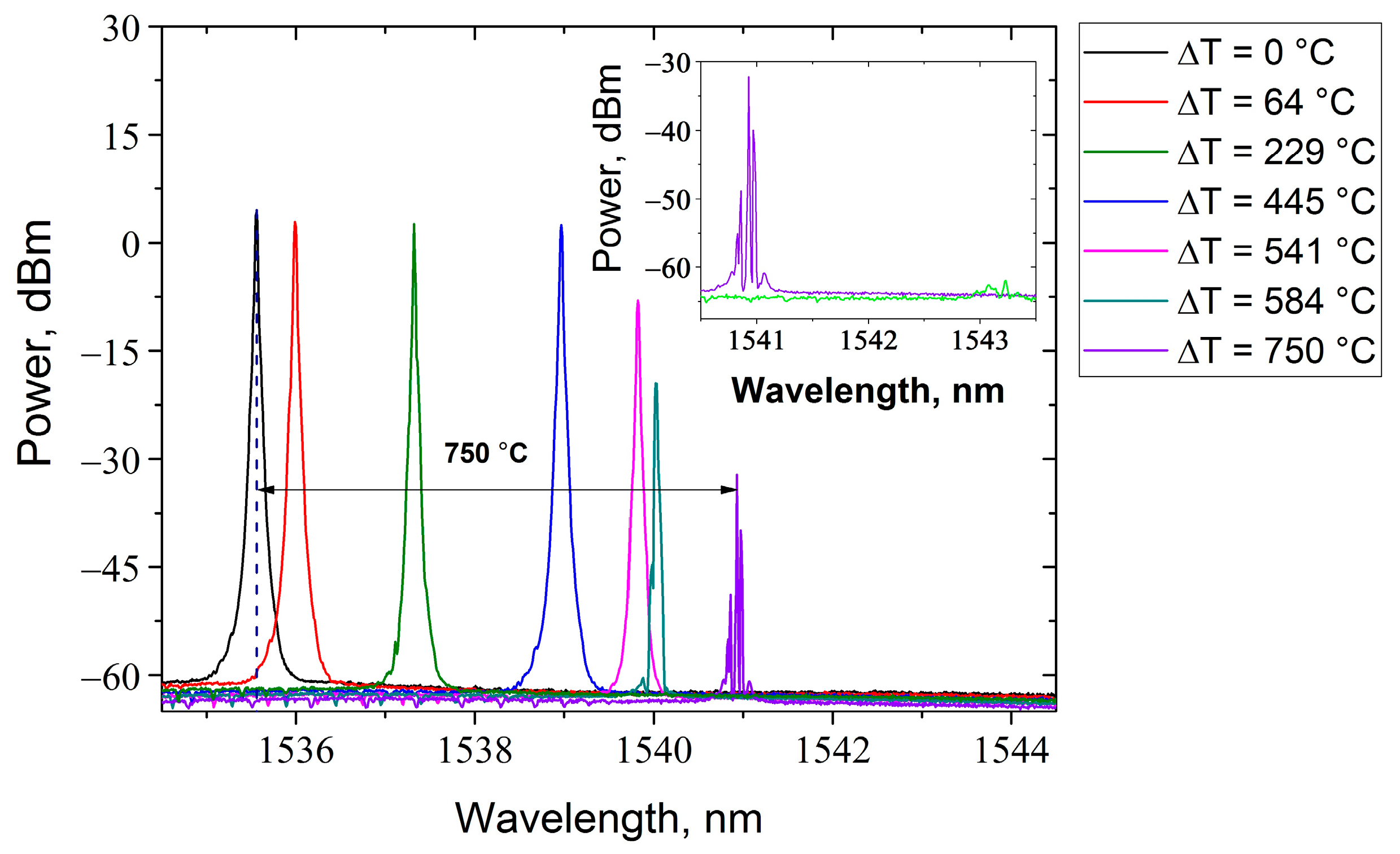
2.3. Temperature Test of DFB-Lasers Based on Phase-Shifted FBGs Inscribed by Different Techniques
3. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sahota, J.K.; Gupta, N.; Dhawan, D. Fiber Bragg grating sensors for monitoring of physical parameters: A comprehensive review. Opt. Eng. 2020, 59, 060901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Feng, S.; Zhang, W.; Li, F. DFB fiber laser static strain sensor based on beat frequency interrogation with a reference fiber laser locked to a FBG resonator. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 12321–12329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Han, M.; Hou, W. High-resolution and fast-response fiber-optic temperature sensor using silicon Fabry-Pérot cavity. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 7237–7247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinet, D.; Mégret, P.; Goossen, K.W.; Qiu, L.; Heider, D.; Caucheteur, C. Fiber Bragg grating sensors toward structural health monitoring in composite materials: Challenges and solutions. Sensors 2014, 14, 7394–7419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, L.; Müller, M.S.; Krämer, S.; Giebel, M.; Schwotzer, G.; Wieduwilt, T. Applications of fibre optic temperature measurement. Proc. Est. Acad. Sci. Eng. 2007, 13, 363–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Liu, G.; Han, M. A novel, high-resolution, high-speed fiber-optic temperature sensor for oceanographic applications. In Proceedings of the IEEE/OES Eleveth Current, Waves and Turbulence Measurement (CWTM), St. Petersburg, FL, USA, 2–6 March 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Collin, E.; Moutonet, T.; Heron, J.S.; Bourgeois, O.; Bunkov, Y.N.; Godfrin, H. Nonlinear parametric amplification in a triport nanoelectromechanical device. Phys. Rev. B. 2011, 84, 059909E. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.M.; Tai, Y.C. Micro-electro-mechanical-systems (MEMS) and fluid flows. Annu. Rev. Fluid. Mech. 1998, 30, 579–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, R.; Khomenko, A.V.; Starodumov, A.N.; Arzate, N.; Zenteno, L.A. Interferometric fiber-optic temperature sensor with spiral polarization couplers. Opt. Commun. 1998, 154, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, G.; Meltz, G.; Morey, W. Polarimetric heterodyning Bragg-grating fiber-laser sensor. Opt. Lett. 1993, 18, 1976–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Kim, S.; Park, H.; Kim, B. Polarimetric fiber laser sensors. Opt. Lett. 1993, 18, 317–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Chen, L.; Huang, L.; Chen, X. Multimode fiber laser for simultaneous measurement of strain and temperature based on beat frequency demodulation. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 22517–22522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, H.; Latif, A.A.; Zulkifli, M.Z.; Awang, N.A.; Harun, S.W. Temperature Sensing Using Frequency Beating Technique from Single-Longitudinal Mode Fiber Laser. IEEE Sens. J. 2012, 12, 2496–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Zhang, H.; Shi, W.; Yang, X.; Lu, Y.; Yao, J. High-Resolution Temperature Sensor Based on Single-Frequency Ring Fiber Laser via Optical Heterodyne Spectroscopy Technology. Sensors 2018, 18, 3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dusablon, L.; Fortin, V.; Boilard, T.; Bernier, M.; Galarneau, P.; Babin, F.; Vallée, R. High resolution temperature sensor based on frequency beating between twin DFB fiber lasers. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 26067–26075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, H.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, X.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, G.; Wang, X. Performance of high-temperature thermosetting polyimide composites modified with thermoplastic polyimide. Polym. Test. 2020, 90, 106746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.-Y.; Ji, M. Polyimide matrices for carbon fiber composites. In Advanced Polyimide Materials; Yang, S.-Y., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 93–136. [Google Scholar]
- Belwal, S.; Revanth, V.; Dinesh, K.S.V.V.; Reddy, B.V.; Bhagvanth Rao, M. Development and Scale up of a Chemical Process in Pharmaceutical Industry: A Case Study. Int. J. Eng. Res. Appl. 2016, 6, 81–88. [Google Scholar]
- Paulsson, A.; Xing, K.; Fosshaug, H.; Lundvall, A.; Bjoernberg, C.; Karlsson, J. Managing effects in CD control from PED and PEB in advanced DUV photomask manufacturing using FEP-171 resist. In Proc. SPIE 5753, Advances in Resist Technology and Processing XXII; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2005; Volume 5753, pp. 1119–1128. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Tang, C.; Cain, J.; Hui, A.; Hsieh, T.; Maccrae, N.; Singh, B.; Poolla, K.; Spanos, C.J. Across-wafer CD uniformity control through lithography and etch process: Experimental verification. In Proc. SPIE 6518, Metrology, Inspection, and Process Control for Microlithography XXI; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2007; Volume 65182C, pp. 810–819. [Google Scholar]
- Ulanovskiy, A.; Edler, F.; Fischer, J.; Oleynikov, P.; Zaytsev, P.; Pokhodun, A. Features of high-temperature calibration of W/Re thermocouples. Int. J. Thermophys. 2015, 36, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, W.C.; Gakhar, R.; Horne, G.P.; Layne, B.; Iwamatsu, K.; Ramos-Ballesteros, A.; Shaltry, M.R.; LaVerne, J.A.; Pimblott, S.M.; Wishart, J.F. Design and performance of high-temperature furnace and cell holder for in situ spectroscopic, electrochemical, and radiolytic investigations of molten salts. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2020, 91, 083105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atabay, S.E.; Sanchez-Mata, O.; Muñiz-Lerma, J.A.; Brochu, M. Effect of heat treatment on the microstructure and elevated temperature tensile properties of Rene 41 alloy produced by laser powder bed fusion. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 858, 157645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Xu, Y.; Pang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Qin, Z.; Liu, Z.; Lu, P.; Bao, X. Optical Fiber Sensors for High-Temperature Monitoring: A Review. Sensors 2022, 22, 5722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Chen, T.; Si, J.; Pham, X.; Hou, X. Fiber laser based on a fiber Bragg grating and its application in high temperature sensing. Opt. Commun. 2019, 452, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybaltovsky, A.A.; Lipatov, D.S.; Lobanov, A.S.; Abramov, A.N.; Umnikov, A.A.; Bazakutsa, A.P.; Bobkov, K.K.; Butov, O.V.; Gur’yanov, A.N. Photosensitive highly Er/Yb co-doped phosphosilicate optical fibers for continuous-wave single-frequency fiber laser applications. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2020, 37, 3077–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skvortsov, M.I.; Wolf, A.A.; Dostovalov, A.V.; Vlasov, A.A.; Akulov, V.A.; Babin, S.A. Distributed feedback fiber laser based on a fiber Bragg grating inscribed using the femtosecond point-by-point technique. Laser Phys. Lett. 2018, 15, 035103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauridsen, V.C.; Povlsen, J.H.; Varming, P. Optimising erbium-doped DFB fibre laser length with respect to maximum output power. Electron. Lett. 1999, 35, 300–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoshi, T.; Kikuchi, K.; Nakayama, A. Novel method for high resolution measurement of laser output spectrum. Electron. Lett. 1980, 16, 630–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Grattan, K.T.V.; Palmer, A.W.; Meggitt, B.T.; Sun, T. Fluorescence decay-time characteristics of erbium-doped optical fiber at elevated temperatures. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1997, 68, 2764–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, J.; Feng, J.; Ye, L.; Xu, F.; Lu, Y. Miniaturized fiber taper reflective interferometer for high temperature measurement. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 14245–14250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, A.; Esmaeelpour, M.; Bernier, M.; Digonnet, M.J.F. High-resolution slow-light fiber Bragg grating temperature sensor with phase-sensitive detection. Opt. Lett. 2018, 43, 3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skvortsov, M.I.; Abdullina, S.R.; Podivilov, E.V.; Vlasov, A.A.; Kharasov, D.R.; Fomiryakov, E.A.; Nikitin, S.P.; Treshchikov, V.N.; Babin, S.A. Extreme narrowing of the distributed feedback fiber laser linewidth due to the Rayleigh backscattering in a single-mode fiber: Model and experimental test. Photonics 2022, 9, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal-Junior, A.; Silva, J.; Macedo, L.; Marchesi, A.; Morau, S.; Valentino, J.; Valentim, F.; Costa, M. The role of optical fiber sensors in the new generation of healthcare devices: A review. Sens. Diagn. 2024, 3, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Vera, E.; Valencia-Arias, A.; García-Pineda, V.; Aurora-Vigo, E.F.; Alvarez Vásquez, H.; Sánchez, G. Machine learning applications in optical fiber sensing: A research agenda. Sensors 2024, 24, 2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Reference | Sensitivity | Resolution | Operating Temperature | Sensing Scheme 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| This paper | 7.85 pm/°C | 2 × 10−6 °C * | 20−750 °C | Beating between twin single longitudinal mode DFB lasers |
| [3] | 84.6 pm/°C | 6 × 10−4 °C | 20−100 °C | Fabry–Pérot silicon pillar tip |
| [14] | 14.74 pm/°C | 0.005 °C | 3−85 °C | Beating between SFFL and reference laser |
| [15] | 23.4 pm/°C | 7 × 10−4 °C | 15−35 °C | Beating between twin single longitudinal mode DFB lasers |
| [31] | 20 pm/°C | 0.58 °C | 19−520 °C | Miniaturized fiber taper reflective interferometer |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Skvortsov, M.I.; Kolosova, K.V.; Dostovalov, A.V.; Golikov, E.V.; Vlasov, A.A.; Abdullina, S.R.; Rybaltovsky, A.A.; Lipatov, D.S.; Lobanov, A.S.; Likhachev, M.E.; et al. High-Resolution Interferometric Temperature Sensor Based on Two DFB Fiber Lasers with High-Temperature Monitoring Potential. Photonics 2025, 12, 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12101019
Skvortsov MI, Kolosova KV, Dostovalov AV, Golikov EV, Vlasov AA, Abdullina SR, Rybaltovsky AA, Lipatov DS, Lobanov AS, Likhachev ME, et al. High-Resolution Interferometric Temperature Sensor Based on Two DFB Fiber Lasers with High-Temperature Monitoring Potential. Photonics. 2025; 12(10):1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12101019
Chicago/Turabian StyleSkvortsov, Mikhail I., Kseniya V. Kolosova, Alexander V. Dostovalov, Evgeniy V. Golikov, Alexander A. Vlasov, Sofia R. Abdullina, Andrey A. Rybaltovsky, Denis S. Lipatov, Aleksey S. Lobanov, Mikhail E. Likhachev, and et al. 2025. "High-Resolution Interferometric Temperature Sensor Based on Two DFB Fiber Lasers with High-Temperature Monitoring Potential" Photonics 12, no. 10: 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12101019
APA StyleSkvortsov, M. I., Kolosova, K. V., Dostovalov, A. V., Golikov, E. V., Vlasov, A. A., Abdullina, S. R., Rybaltovsky, A. A., Lipatov, D. S., Lobanov, A. S., Likhachev, M. E., Egorova, O. N., & Babin, S. A. (2025). High-Resolution Interferometric Temperature Sensor Based on Two DFB Fiber Lasers with High-Temperature Monitoring Potential. Photonics, 12(10), 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12101019





