An Off-Axis Catadioptric Division of Aperture Optical System for Multi-Channel Infrared Imaging
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Basis
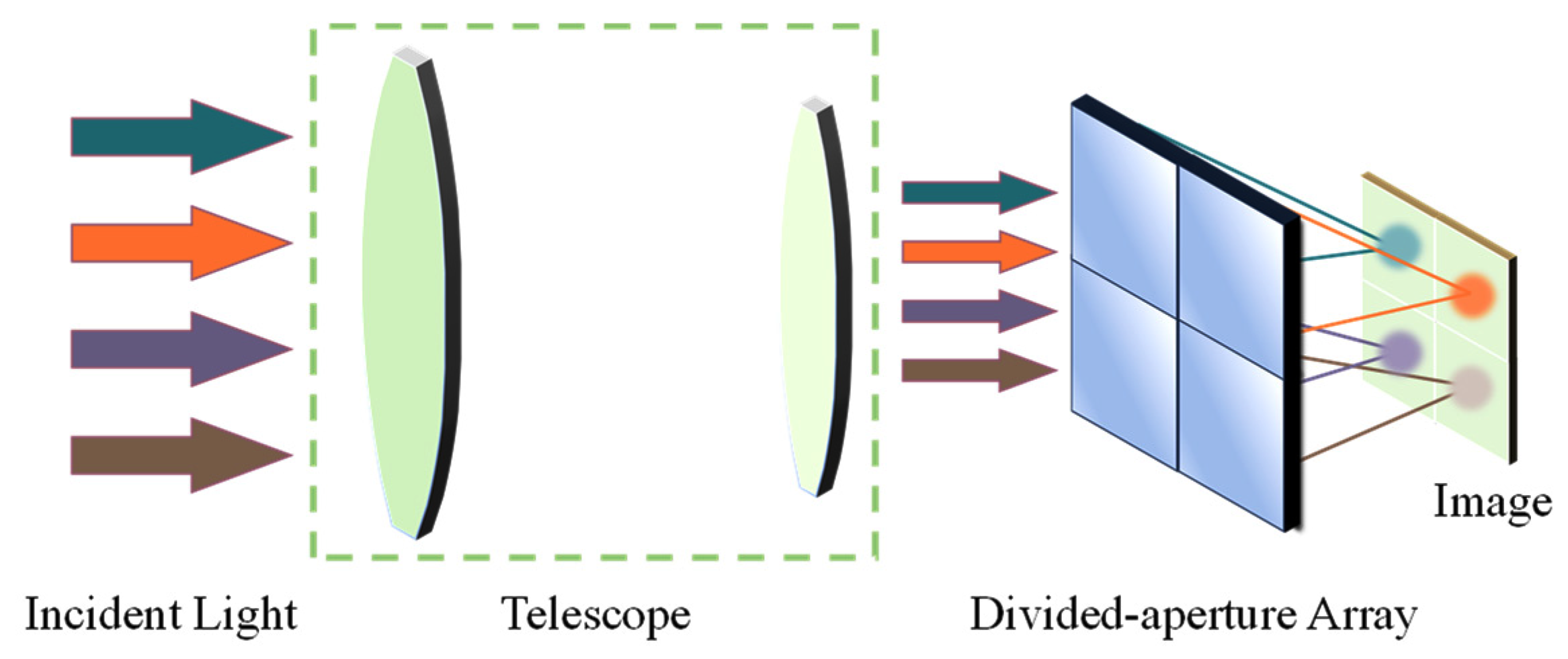
2.1. The Overall Framework of the Aperture-Divided Optical System
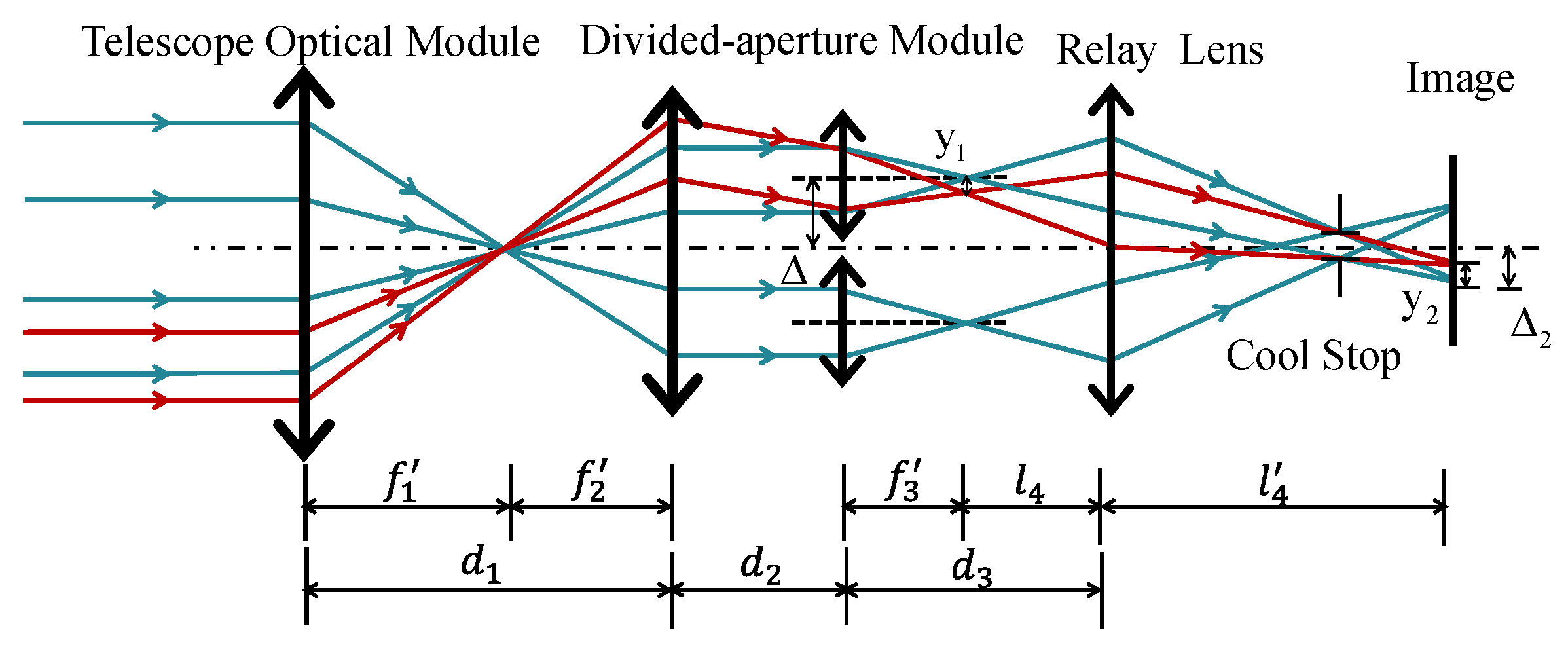
2.2. Design Method of the Off-Axis Two-Mirror Afocal Optical Structure
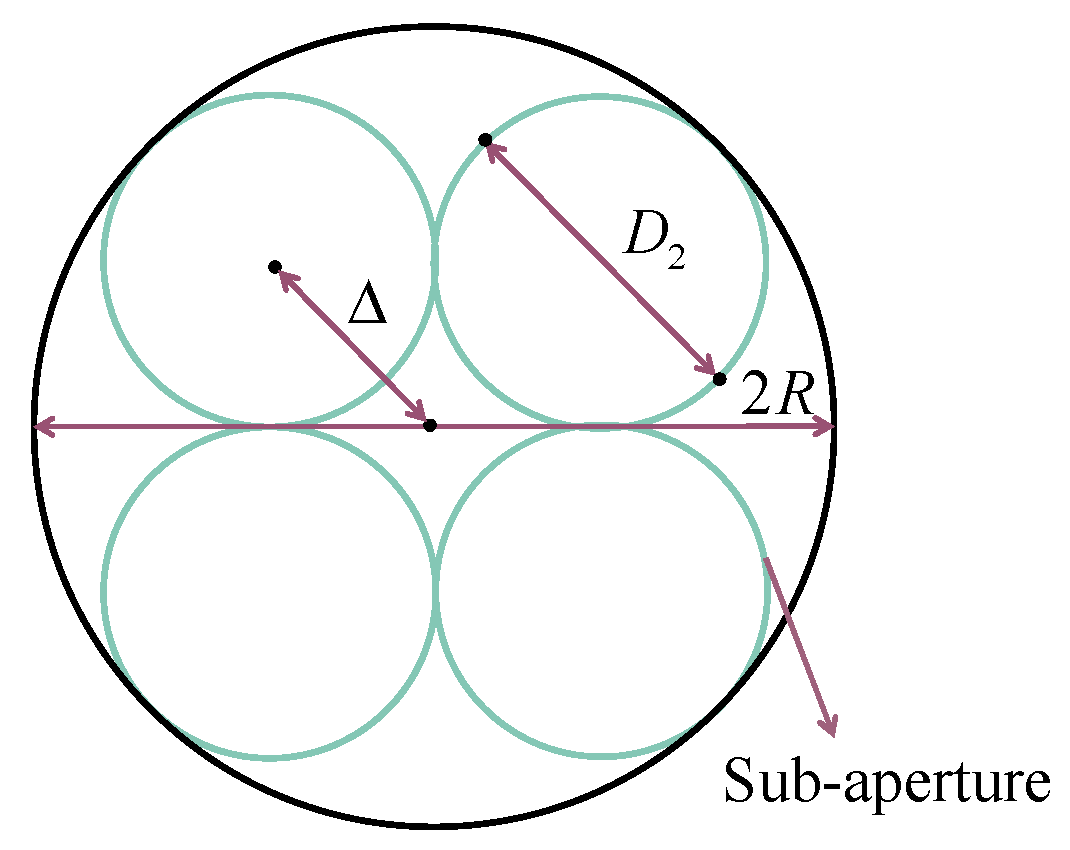
2.3. Calculation of the Aperture Offset for Off-Axis Afocal Systems
2.4. Aperture-Divided Ideal Optical System Model
3. System Design
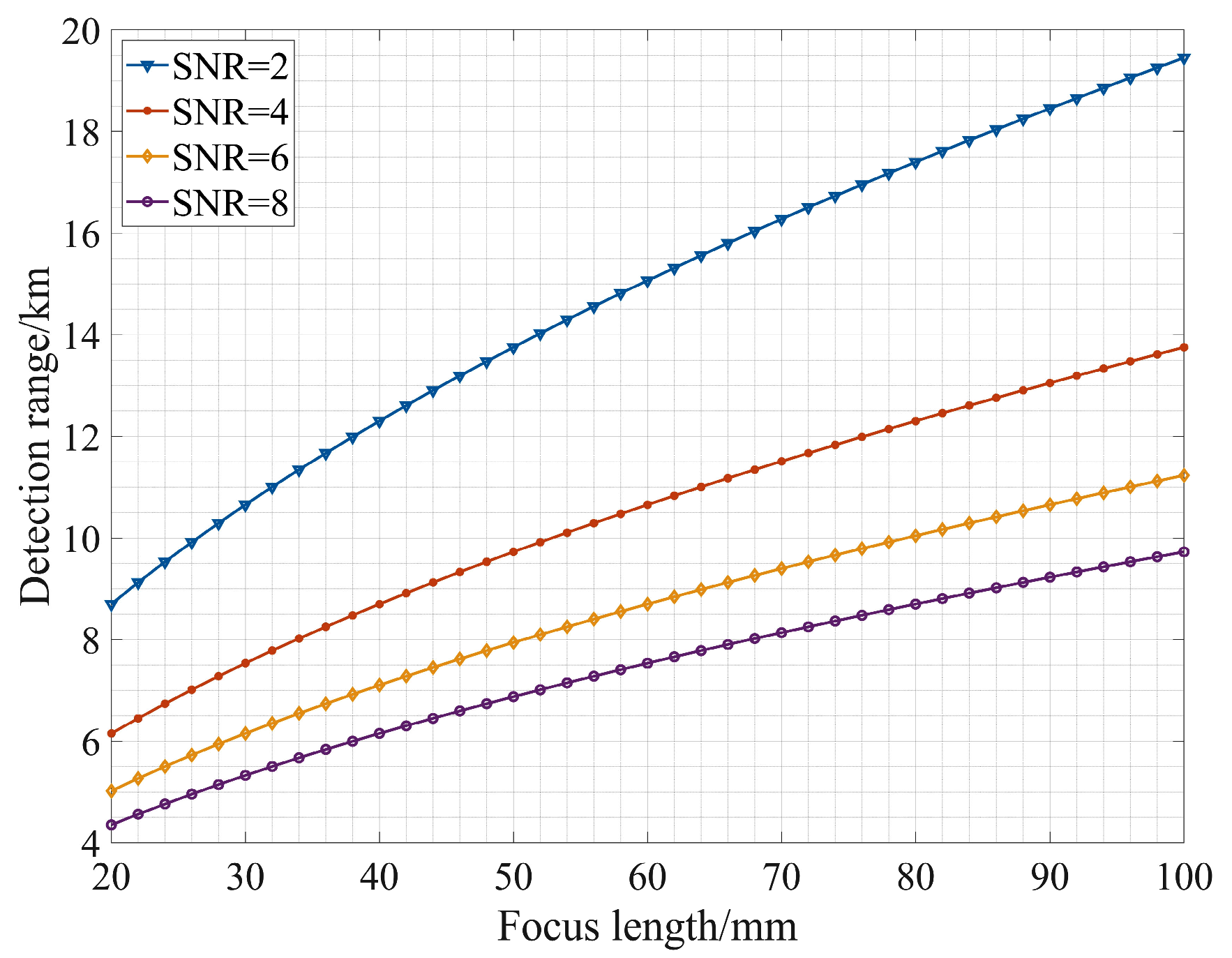
3.1. Detection Performance Analysis
3.2. Design Parameter
4. Design Case and Simulation Results
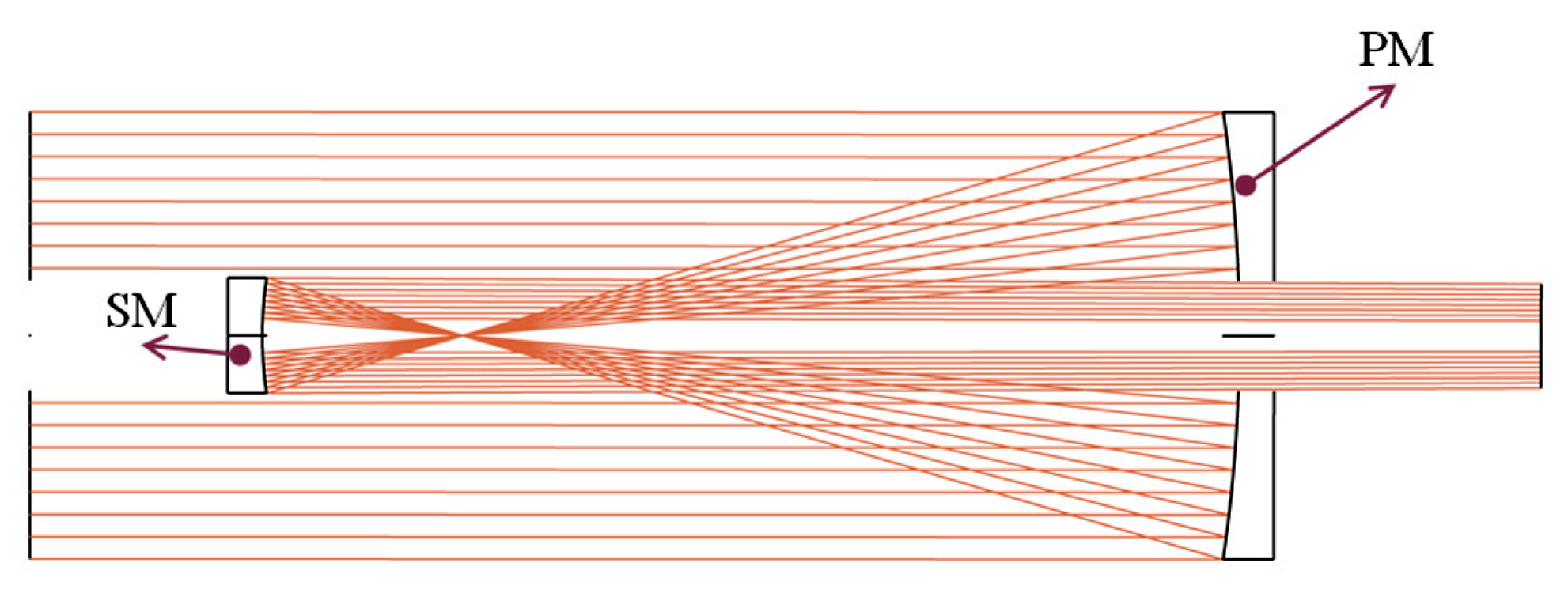
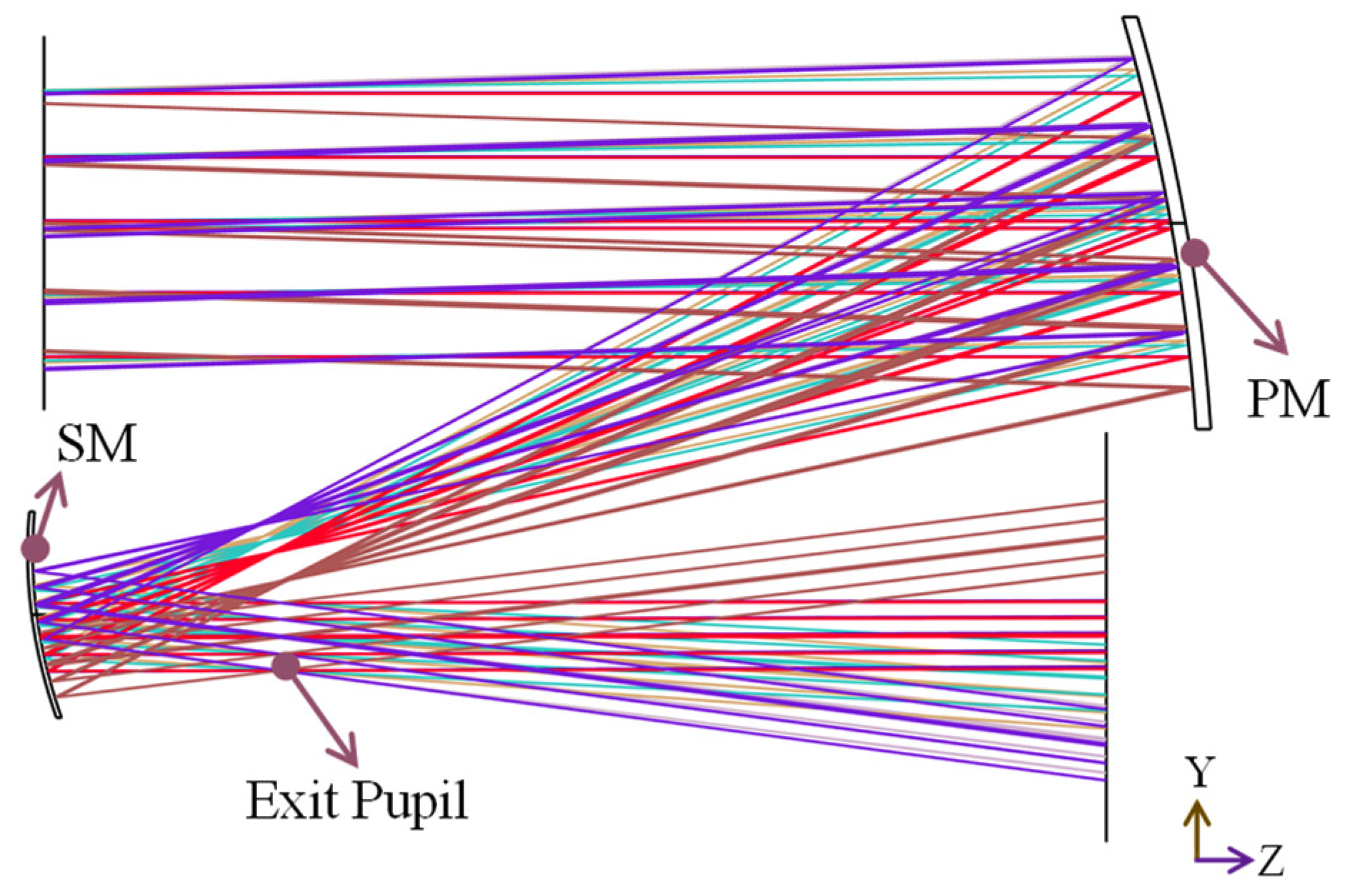
4.1. Structure of the Afocal Optical Telescopic System
4.2. Division of the Aperture System and Relay System
- (1)
- Aperture-divided optical module
- (2)
- Relay lens
4.3. Design Results
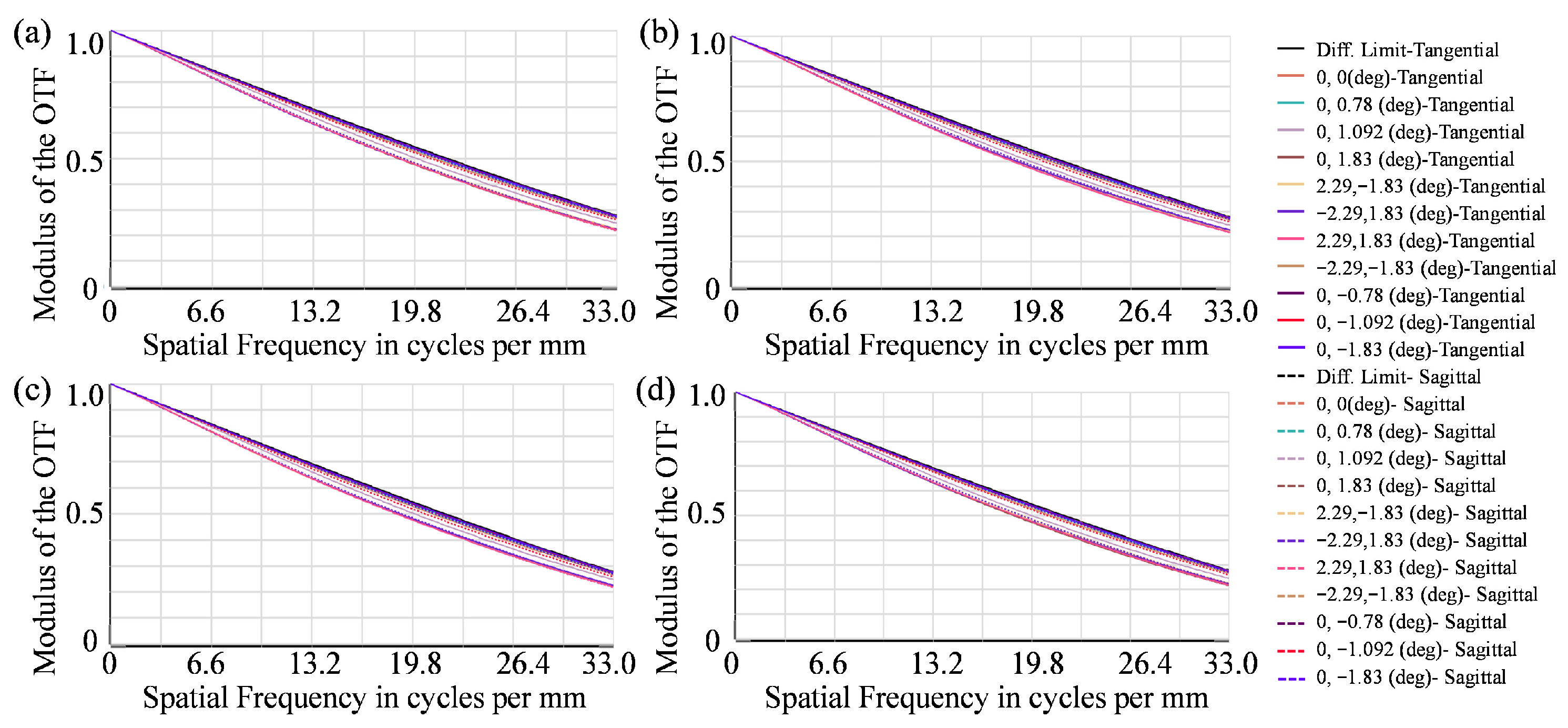
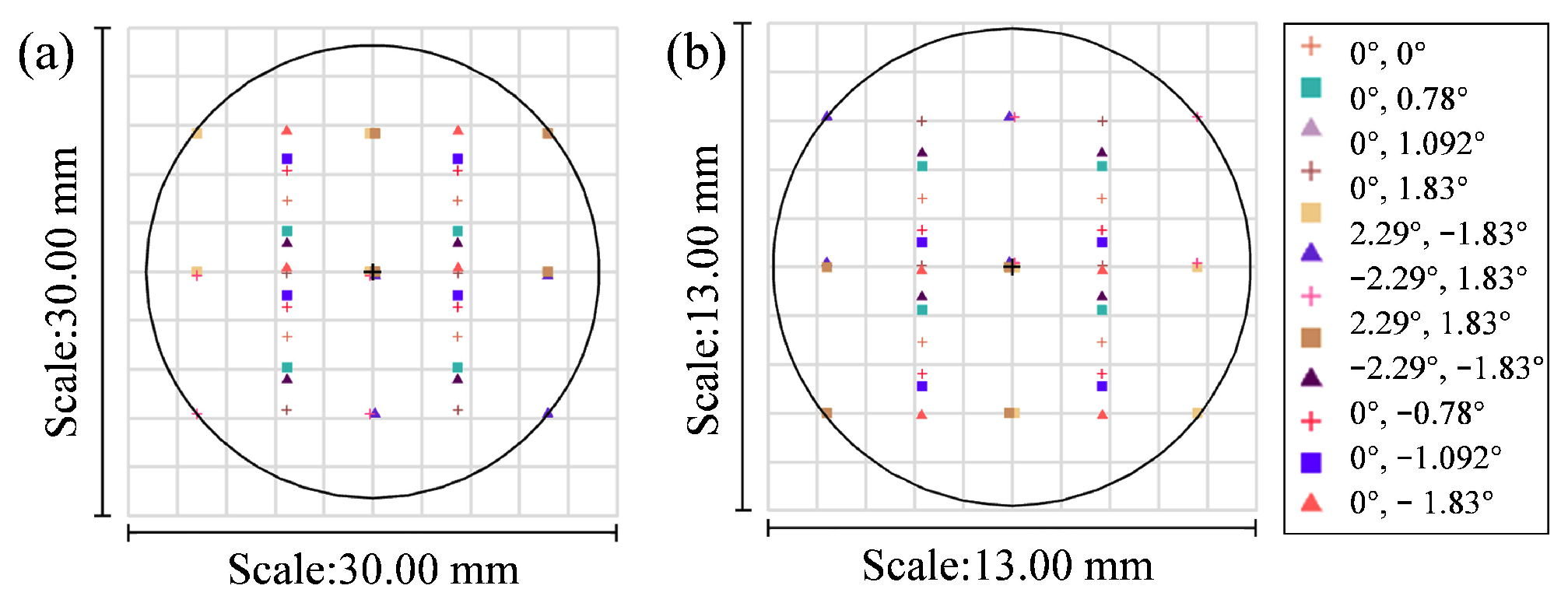
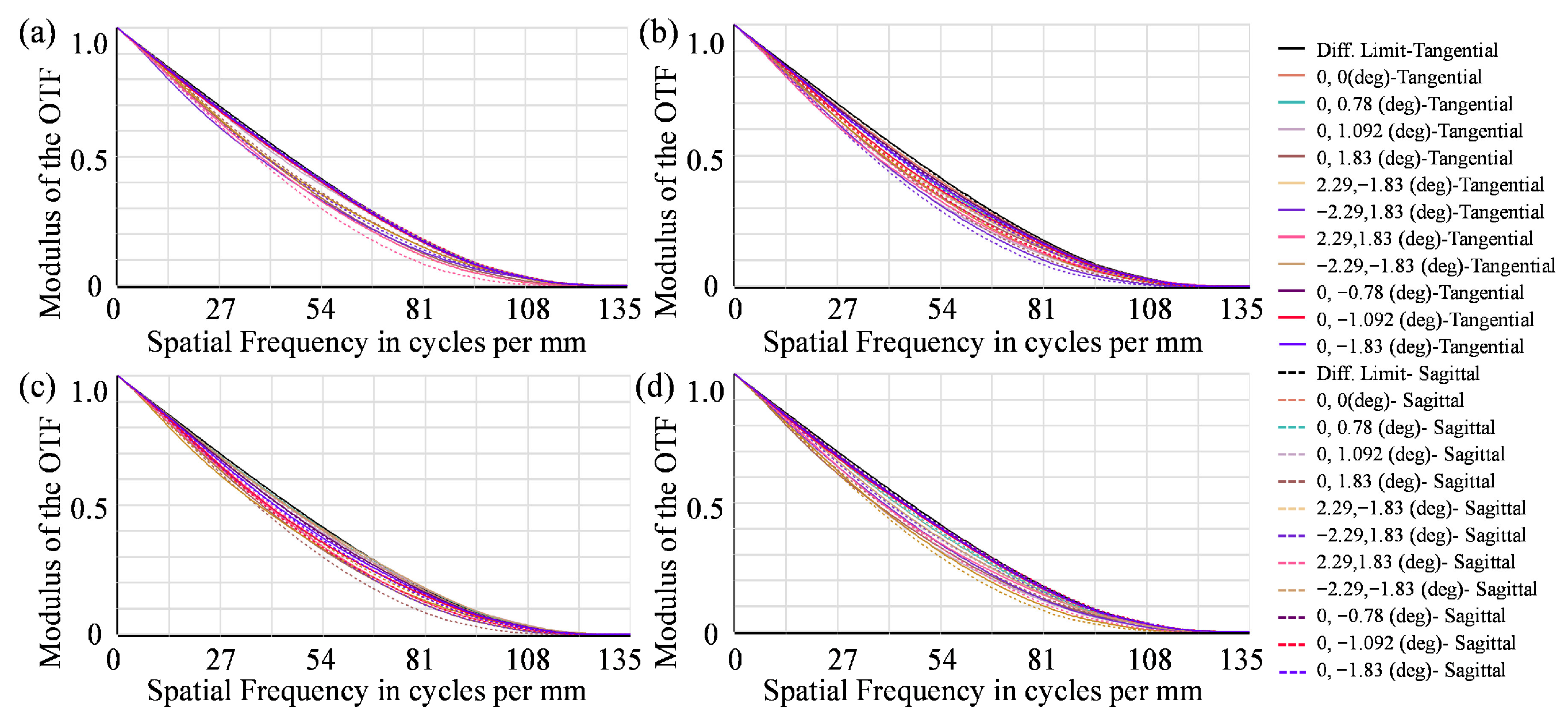
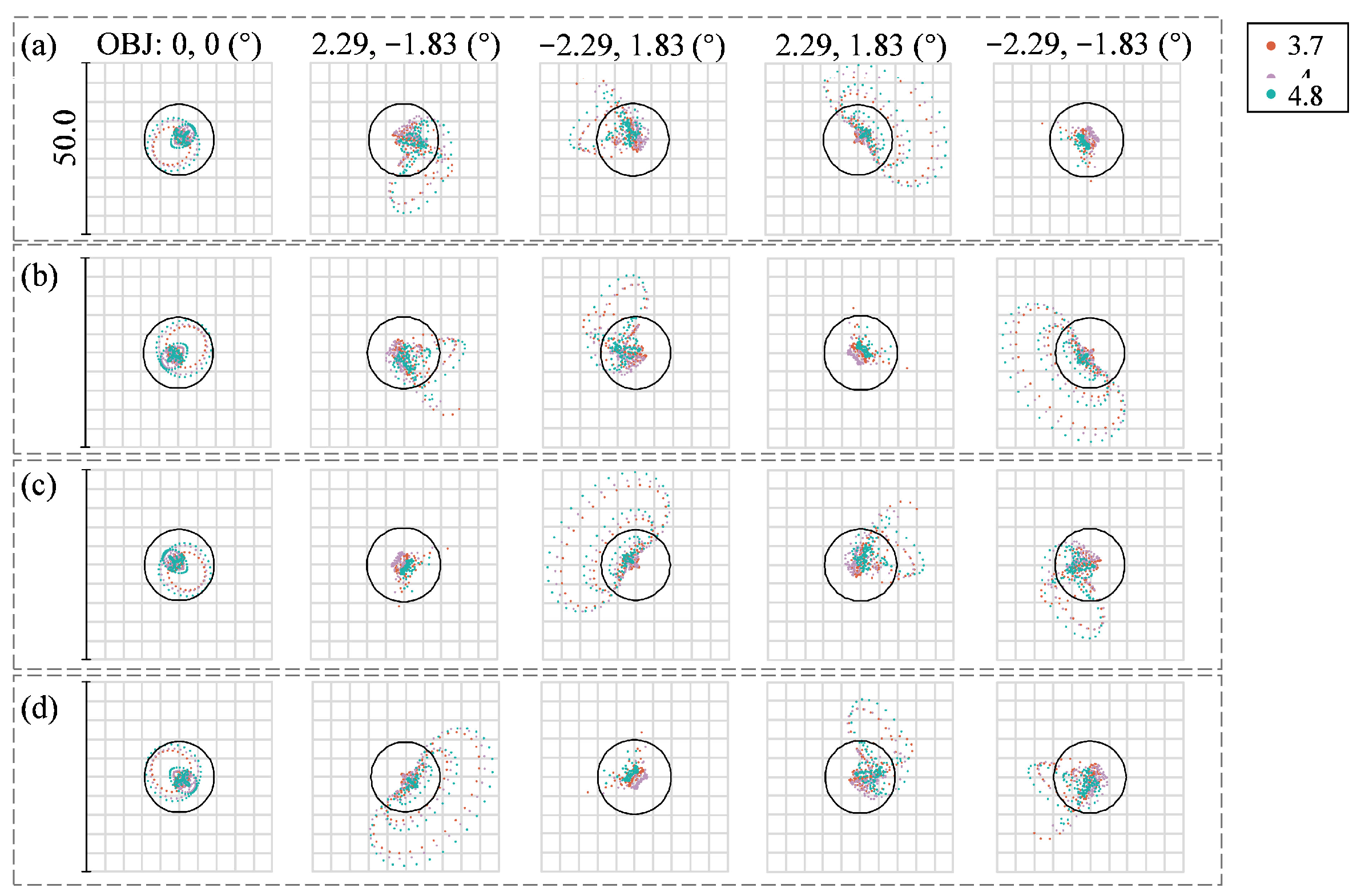
4.4. Manufacturability Analysis
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cao, J.; Huang, Y.; Wang, J.; Chang, J.; Li, D. Design of dual-channel off-axis reflective foveated imaging optical system with high speed. Opt. Laser Technol. 2025, 182, 112110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubold, M.; Montag, E.; Berlich, R.; Brunner, R.; Brüning, R. Multi-aperture system approach for snapshot multispectral imaging applications. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 7361–7378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Fang, F. Optical design and simulation of a compact multi-aperture camera based on a freeform microlens array. Opt. Commun. 2015, 338, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, V.; Rachlin, Y.; Shepard, R.H.; Shih, T. Shift-encoded optically multiplexed imaging. Opt. Eng. 2017, 56, 041314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, C.; Mu, T.; Wang, Y.; He, Y.; Yan, T.; Chen, Z. Coded aperture full-stokes imaging spectropolarimeter. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 150, 107946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, N.A.; D’Aversa, G.; Chevalier, P.; Shi, Z.J.; Chen, W.T.; Capasso, F. Matrix Fourier optics enables a compact full-Stokes polarization camera. Science 2019, 365, eaax1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubin, N.A.; Chevalier, P.; Juhl, M.; Tamagnone, M.; Chipman, R.; Capasso, F. Imaging polarimetry through metasurface polarization gratings. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 9389–9412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Yang, X.; Deng, W.; Shen, H.; Shen, R.; Kuang, C. Smart-phone phase contrast microscope with a singlet lens and deep learning. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 139, 106900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Zhong, X.; Zhang, K.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, J.; Zeng, C. Automatic compact-volume design strategy for unobscured reflective optical systems based on conicoid surfaces. Opt. Commun. 2023, 533, 129304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hugot, E.; Muslimov, E.; Lombardo, S. Compact off-axis reflective optical system design combining freeform mirror and freeform detector. Opt. Commun. 2024, 565, 130675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, N.A.; Shi, Z.; Capasso, F. Polarization in diffractive optics and metasurfaces. Adv. Opt. Photonics 2021, 13, 836–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Li, P.; Chen, T.; Tian, X.; Gao, S.; Yang, Z.; Li, G.; Li, M. Microspherical Lens Assembly for Super-Wide Field of View of Super-Resolution Optical Imaging. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 20th International Conference on Nanotechnology (IEEE-NANO), Virtual, 29–31 July 2020; pp. 168–171. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, Y.; Hu, Y.; Cheng, X.; Hao, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Li, T.; Tao, X. Freeform Surface Graded Optimization of Deformable Mirrors in Integrated Zoom and Image Stabilization System Through Vectorial Ray Tracing and Image Point Freezing Method. IEEE Photonics J. 2020, 12, 6900316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, M.E.; Chenault, D.B.; Vaden, J.P.; Lompado, A.; Voelz, D.; Schulz, T.J.; Givens, R.N.; Gamiz, V.L. Synthetic Aperture Imaging Polarimeter. In Proceedings of the Polarization: Measurement, Analysis, and Remote Sensing IX, Orlando, FL, USA, 5–9 April 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Jin, W.Q.; Xia, R.Q.; Li, L.; Wang, X. Radiation correction method for infrared polarization imaging system with front-mounted polarizer. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 26414–26430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, H.; Jiang, H. Polarization Aberration of a Non-Rotationally Symmetric Optical System with Freeform Surfaces. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 145538–145553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyo, J.S.; Goldstein, D.L.; Chenault, D.B.; Shaw, J.A. Review of passive imaging polarimetry for remote sensing applications. Appl. Opt. 2006, 45, 5453–5469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meriaudeau, F.; Ferraton, M.; Stolz, C.; Morel, O.; Bigué, L. Polarization Imaging for Industrial Inspection; SPIE: San Jose, CA, USA, 2008; Volume 6813. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wang, H.; Xu, X.; Ju, L.; Fan, Z.; Chen, S. Mid-infrared full-Stokes polarization detection based on dielectric metasurfaces. Opt. Commun. 2021, 484, 126690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, N.; Xiao, Y.; Huang, L.; Rao, C. Polarization imaging based on time-integration by a continuous rotating polarizer. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 3497–3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, M.; Bhandare, R.; Kumar, S.; Verma, Y.; Raja, S. A compact full Stokes polarimeter. Optik 2022, 267, 169645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudge, J.; Virgen, M.; Dean, P. Near-Infrared Simultaneous Stokes Imaging Polarimeter; SPIE: San Jose, CA, USA, 2009; Volume 7461. [Google Scholar]
- Perkins, R.; Gruev, V. Signal-to-noise analysis of Stokes parameters in division of focal plane polarimeters. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 25815–25824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudenov, M.W.; Pezzaniti, J.L.; Gerhart, G.R. Microbolometer-infrared imaging Stokes polarimeter. Opt. Eng. 2009, 48, 063201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, D.; Liang, H.; Campos, J.; Yan, L.; Yan, C.; Jiang, C.; Tan, S.; Liang, C.; Wang, H.; Meng, L.; et al. Calculation and restoration of lost spatial information in division-of-focal-plane polarization remote sensing using polarization super-resolution technology. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 116, 103155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.F.; Liang, J.; Ren, L.Y.; Ju, H.J.; Qu, E.S.; Bai, Z.F.; Tang, Y.; Wu, Z.X. Real-time image haze removal using an aperture-division polarimetric camera. Appl. Opt. 2017, 56, 942–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moultrie, S.; Roche, M.; Lompado, A.; Chenault, D. Design of a dual use imager incorporating polarimetric capabilities—Art. no. 66820B. In Proceedings of the Conference on Polarization Science and Remote Sensing III, San Diego, CA, USA, 29–30 August 2007; p. B6820. [Google Scholar]
- Mu, T.K.; Zhang, C.M.; Liang, R.G. Demonstration of a snapshot full-Stokes division-of-aperture imaging polarimeter using Wollaston prism array. J. Opt. 2015, 17, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, T.K.; Bao, D.H.; Han, F.; Sun, Y.Y.; Chen, Z.Y.; Tang, Q.; Zhang, C.M. Optimized design, calibration, and validation of an achromatic snapshot full-Stokes imaging polarimeter. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 23009–23028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, W.C.; Jia, W.G.; Zhang, Z.J.; Wang, C.S. Optimization of the Infrared Stokes Imaging Polarimeter. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference of the Chinese-Society-for-Optical-Engineering (CSOE) on Applied Optics and Photonics China (AOPC)—Optical Spectroscopy and Imaging, Beijing, China, 4–6 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Pezzaniti, J.L.; Chenault, D.B. A Division of Aperture MWIR Imaging Polarimeter. In Proceedings of the Conference on Polarization Science and Remote Sensing II, 20050802-04. San Diego, CA, USA, 31 July–4 August 2005. [Google Scholar]
- He, H.; Ji, Y.; Shen, W. Polarization aberration of optical systems in imaging polarimetry. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2012, 10, S11102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, T.K.; Zhang, C.M.; Li, Q.W.; Liang, R.G. Error analysis of single-snapshot full-Stokes division-of-aperture imaging polarimeters. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 10822–10835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, F.; Xu, R.; Liu, X.; Yuan, H. Design of Hyperspectral Polarization Imaging System with Multiple Simultaneous Apertures Based on Orthogonal Dual-Polarization. Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 2018, 55, 031104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Xie, H.; Wang, Y.; Yang, L. Design of aperture-divided multispectral imaging system in mid-infrared band. J. Appl. Opt. 2018, 39, 767–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, L.G. Three Mirror Anastigmatic Optical System. U.S. Patent US4265510A, 5 May 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Q.; Wang, D.; Wang, X.; Li, W.; Yang, X.; Yan, D.; Li, Y.; Cao, Z.; Ji, Q.; Sun, T.; et al. High Resolution Imaging Camera (HiRIC) on China’s First Mars Exploration Tianwen-1 Mission. Space Sci. Rev. 2021, 217, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsch, D. Reflective Optics; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1991; pp. 207–213. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Li, Z.; Duan, Y.; Fang, F. A Design for a Manufacturing-Constrained Off-Axis Four-Mirror Reflective System. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geary, J.M. Introduction to Lens Design: With Practical ZEMAX Examples; Willmann-Bell: Richmond, VA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Welford, W.T. Aberrations of Optical Systems, 1st ed.; Routledge: New York, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, L.-p.; Yu, J.; Zhang, X.; Jin, C.-s. Design of off-axis multi-reflective optical system based on particle swarm optimization. Chin. Opt. 2021, 14, 1435–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, R.D. Infrared System Engineering; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]





| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Focal length of the aperture-divided system | 60 mm |
| Entrance pupil diameter | 30 mm |
| Wavelength | 3.7–4.8 μm |
| Pixel number | 640 × 512 |
| Pixel size | 15 μm |
| Material | Radius (mm) | Conic | Decenter X (mm) | Decenter Y (mm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The afocal telescopic system | PM | mirror | −449.59 | −1 | 0 | −80 | |
| SM | mirror | 114.11 | −1 | 0 | −20.34 | ||
| The aperture-divided lens group | Material | Radius (mm) | |||||
| Polarizer | SILICON | Infinity | |||||
| Infinity | |||||||
| Lens1 | SILICON | 1.331 | |||||
| 18.43 | |||||||
| Lens2 | GERMANIUM | 34.67 | |||||
| 10.92 | |||||||
| Lens3 | ZNS | 24.86 | |||||
| −31.24 | |||||||
| Lens4 | GERMANIUM | −406.83 | |||||
| −61.10 | |||||||
| The realy lens | Material | Radius(mm) | Conic | Aspheric Surface High-order Term | |||
| 4th | 6th | 8th | |||||
| Lens5 | IRG204 | 46.04 | |||||
| 160.38 | |||||||
| Lens6 | IRG105 | −42.90 | |||||
| −58.50 | |||||||
| Lens7 | GERMANIUM | −19.95 | −1 | −5.22 × 10−5 | −8.17 × 10−8 | −1.23 × 10−10 | |
| −52.96 | |||||||
| Lens8 | SILICON | −163.44 | −1 | −8.24 × 10−6 | 7.68 × 10−9 | −2.97 × 10−12 | |
| −28.99 | |||||||
| Tolerance Types | Value |
|---|---|
| Radius (fringe) | 2 |
| Thickness (mm) | ±0.02 |
| Surface irregularity (fringe) | 0.5 |
| Surface decenter (mm) | ±0.02 |
| Surface tilt (°) | ±0.033 |
| Element decenter (mm) | ±0.02 |
| Element tilt (°) | ±0.033° |
| Refractive index | ±0.001 |
| Abbe number (%) | ±0.8 |
| Surface error of the PM and SM (μm) | PV < 0.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, J.; Yang, T.; Xie, H.; Yang, L. An Off-Axis Catadioptric Division of Aperture Optical System for Multi-Channel Infrared Imaging. Photonics 2025, 12, 1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12101008
Chen J, Yang T, Xie H, Yang L. An Off-Axis Catadioptric Division of Aperture Optical System for Multi-Channel Infrared Imaging. Photonics. 2025; 12(10):1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12101008
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Jie, Tong Yang, Hongbo Xie, and Lei Yang. 2025. "An Off-Axis Catadioptric Division of Aperture Optical System for Multi-Channel Infrared Imaging" Photonics 12, no. 10: 1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12101008
APA StyleChen, J., Yang, T., Xie, H., & Yang, L. (2025). An Off-Axis Catadioptric Division of Aperture Optical System for Multi-Channel Infrared Imaging. Photonics, 12(10), 1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12101008




