Alignment of Fabry–Pérot Cavities for Optomechanical Acceleration Measurements
Abstract
1. Introduction
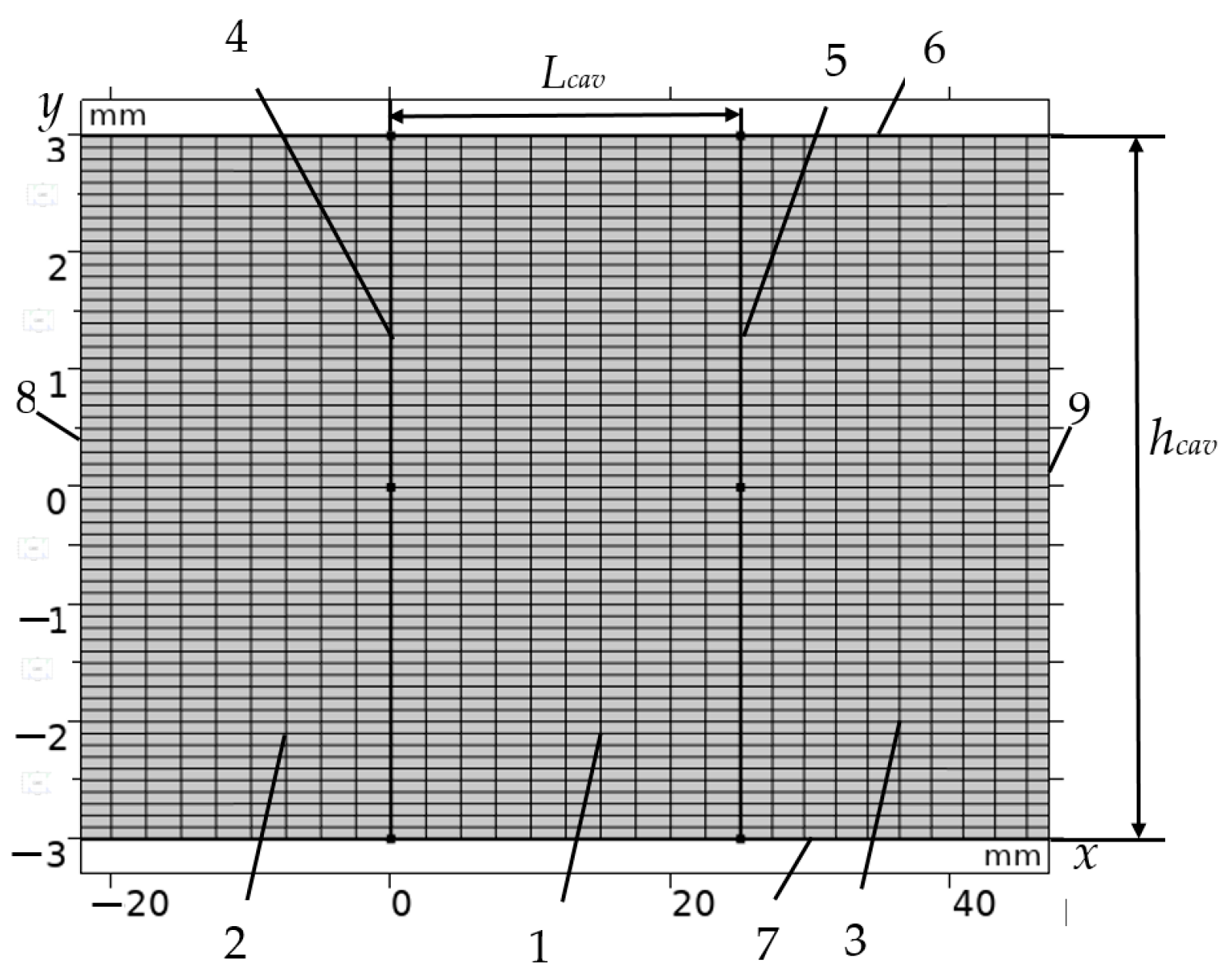
2. The Problem of Calculating Electromagnetic Processes During Wave Propagation in a Fabry–Pérot Cavity
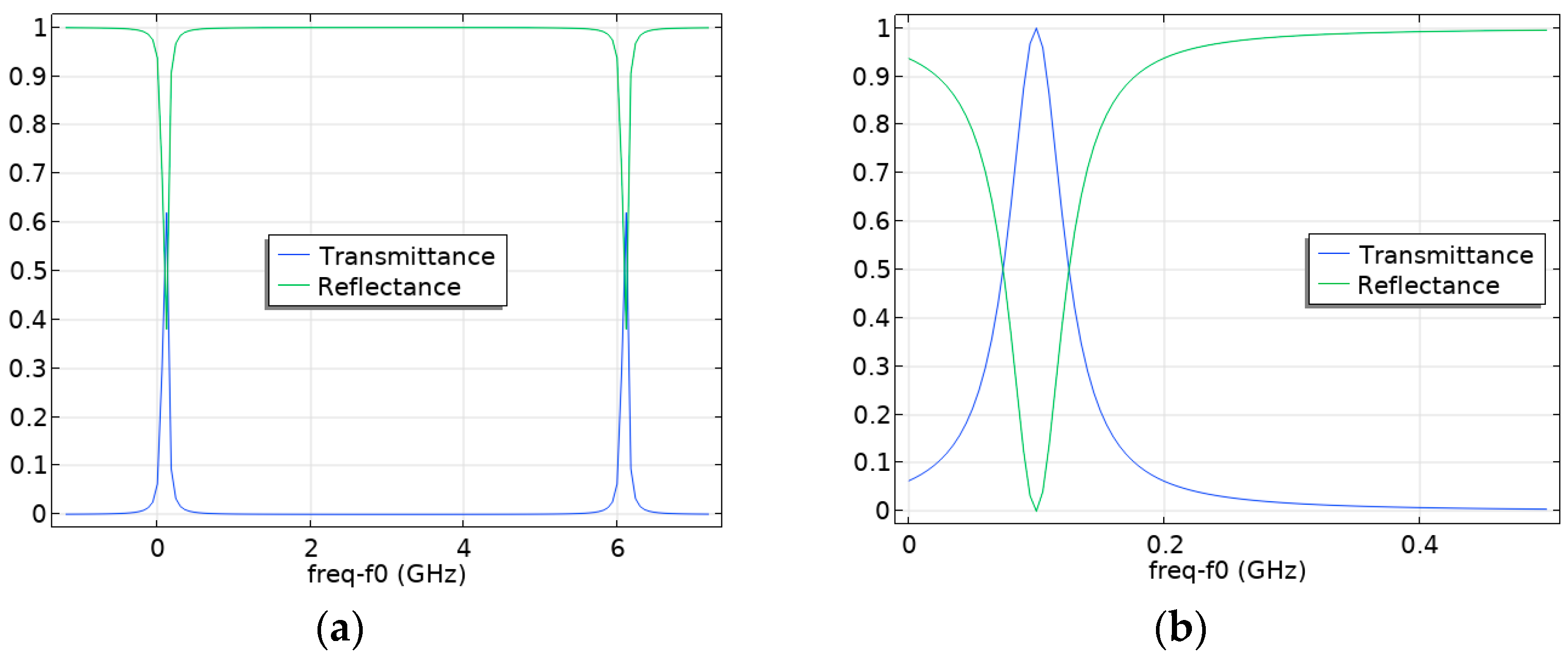
3. Comparison of the Results of the Numerical Calculation of Wave Processes in the Fabry–Pérot Cavity with the Analytical Solution
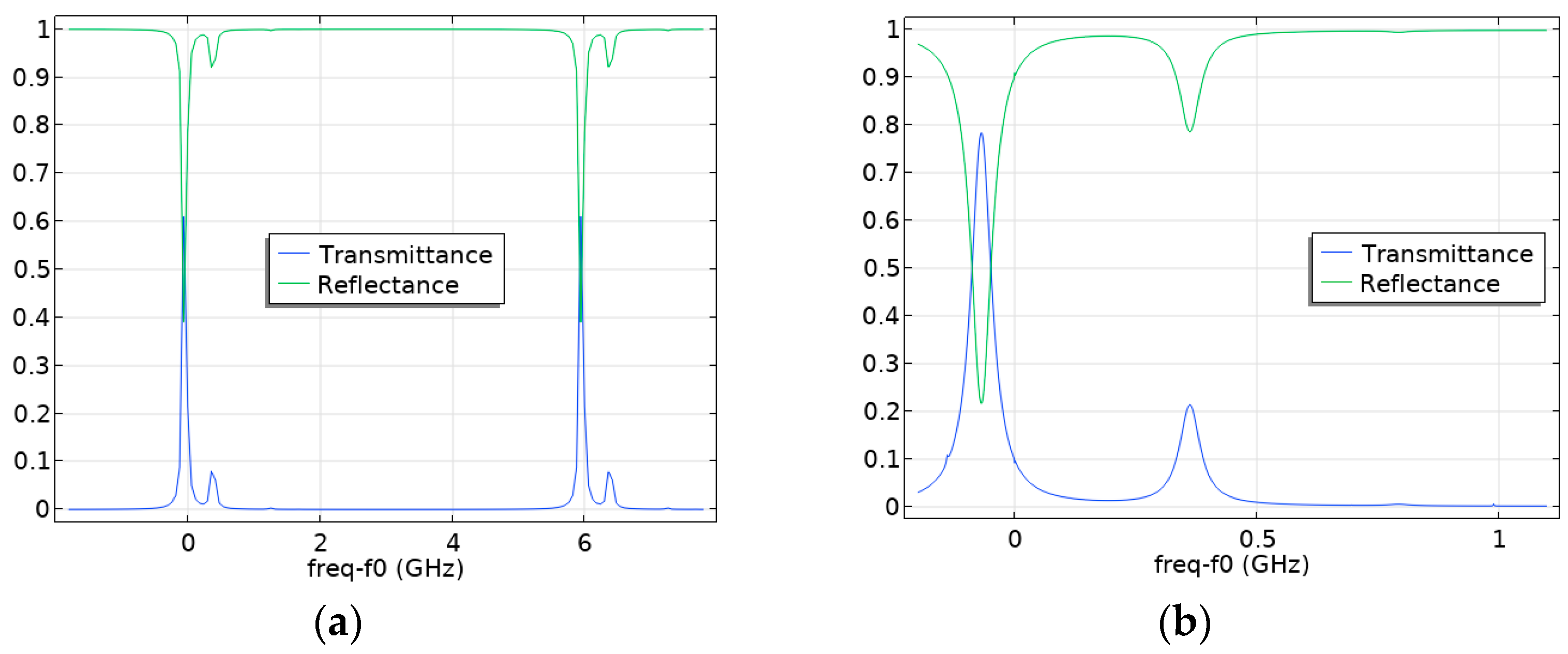
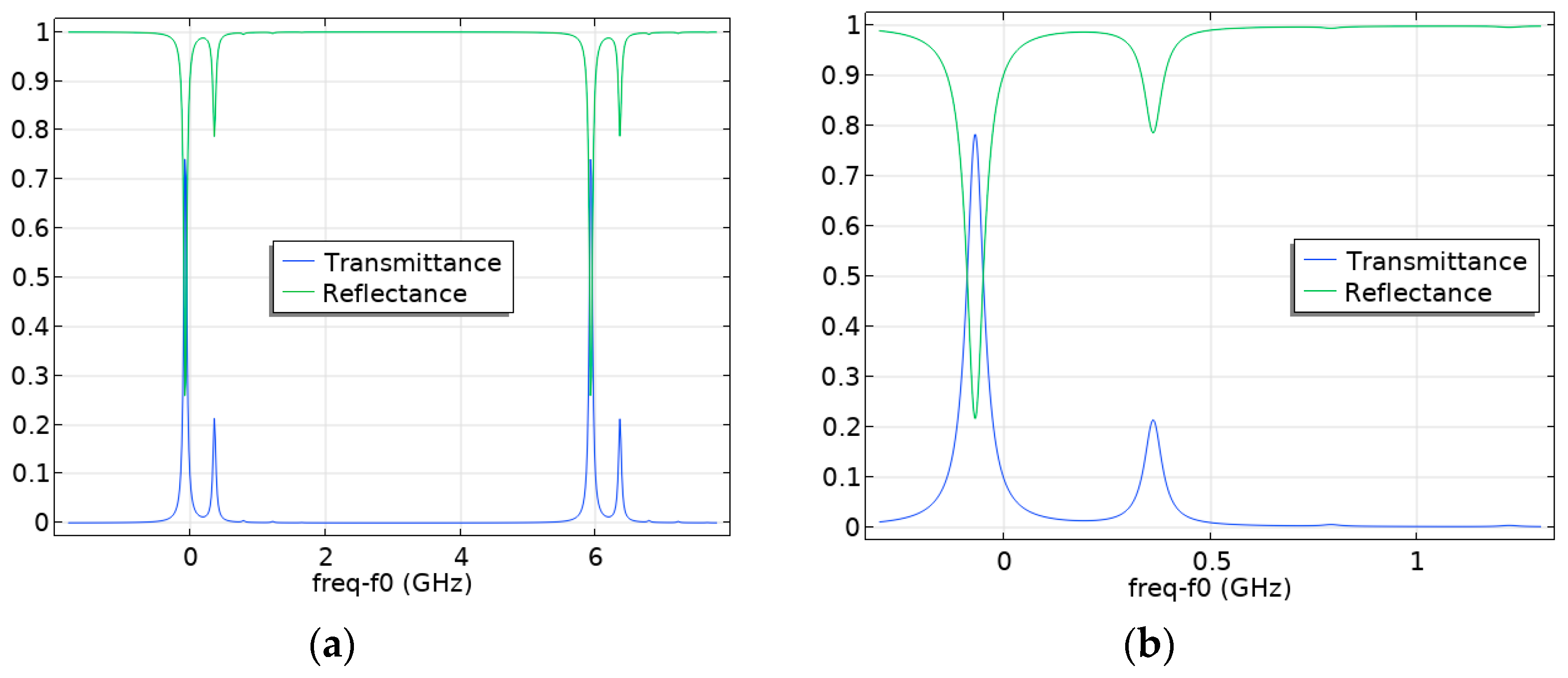
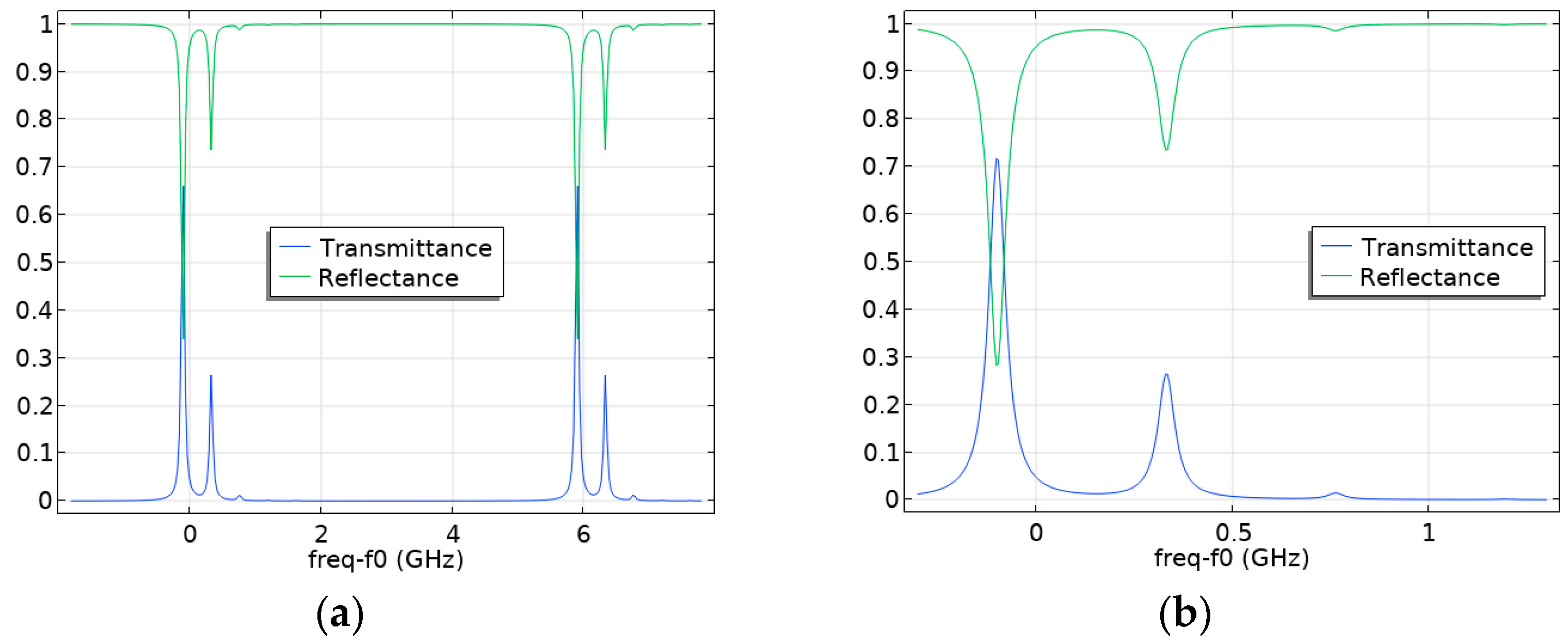
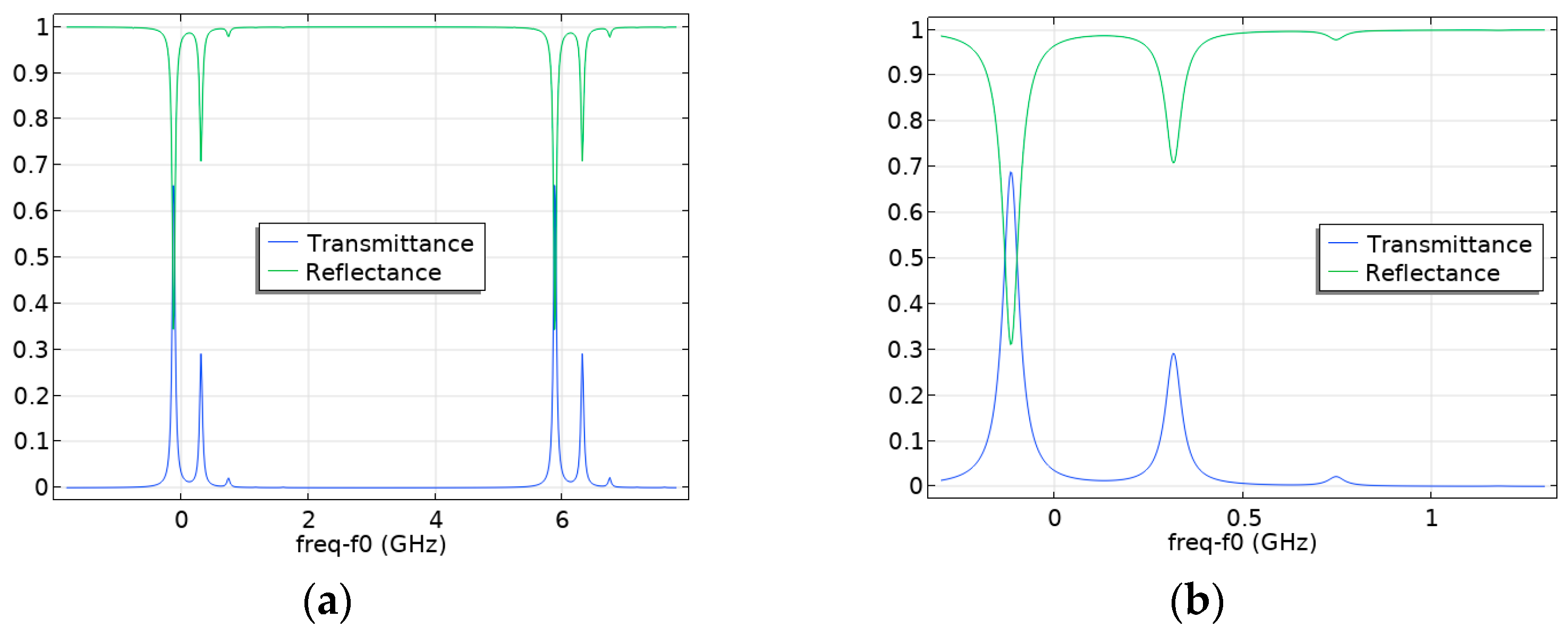
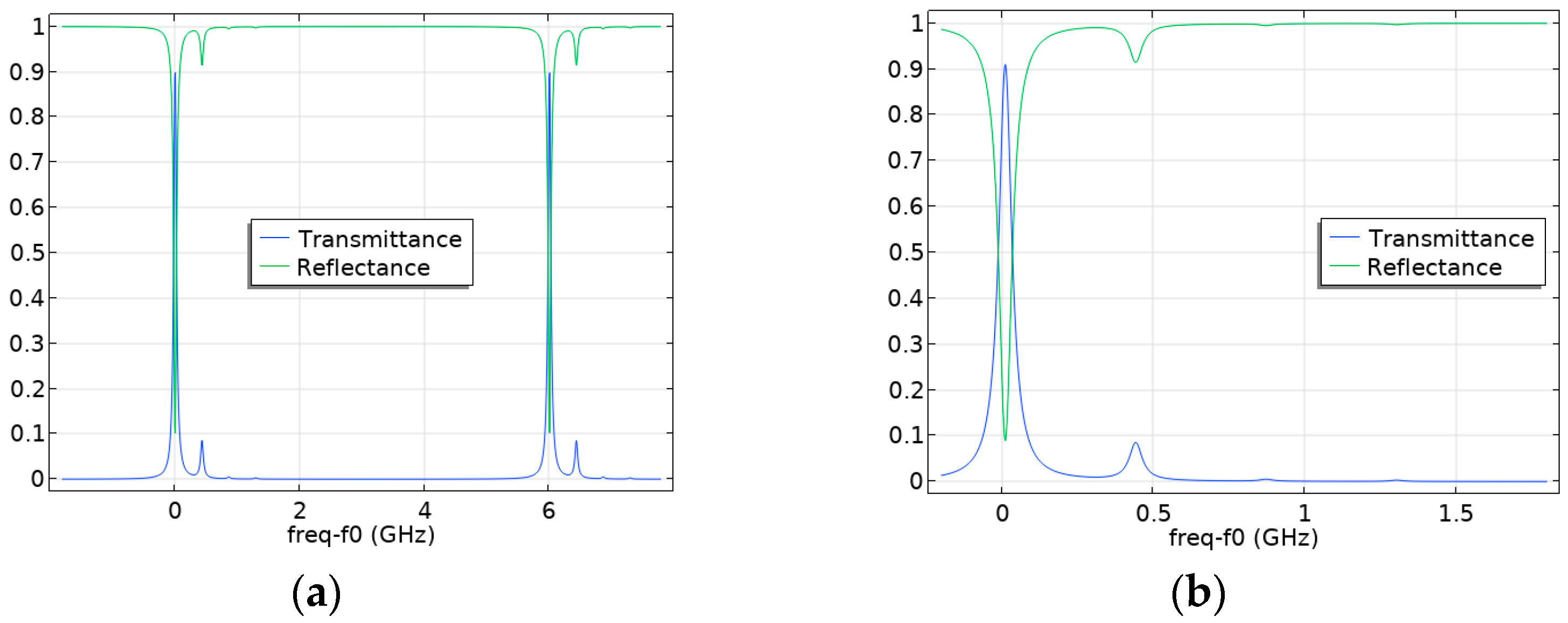
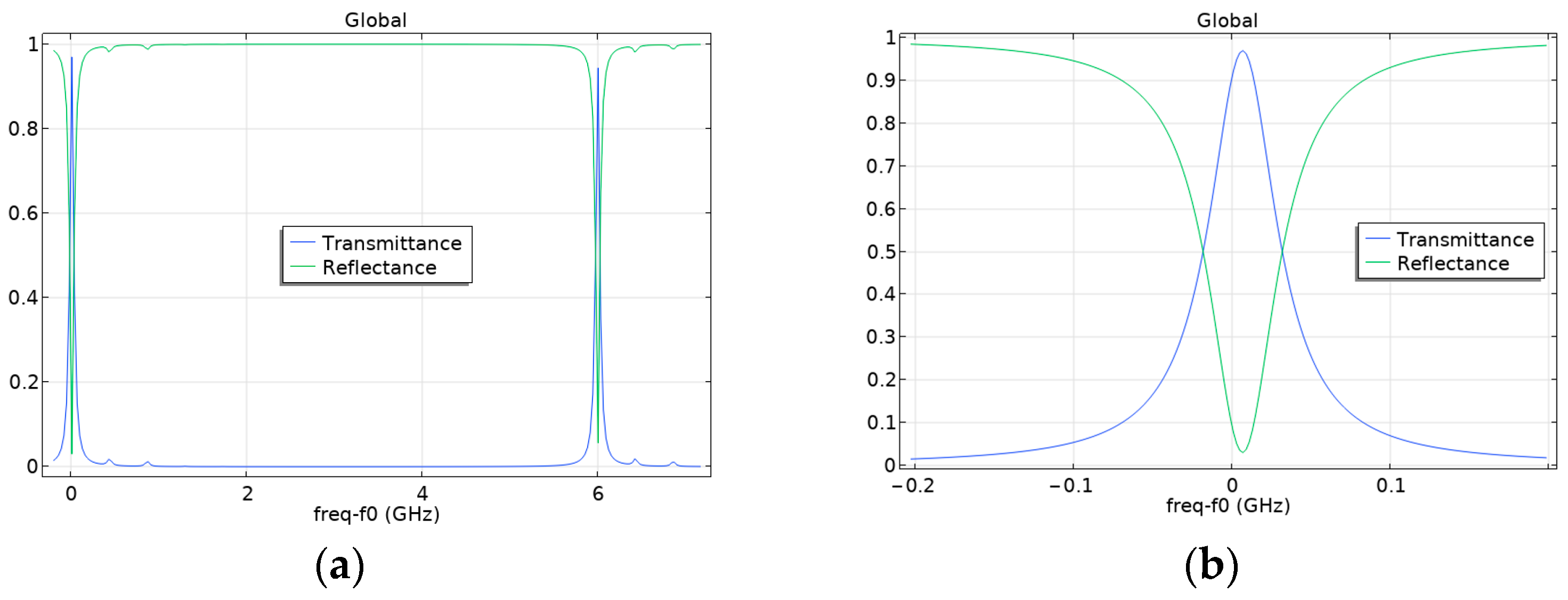
4. Investigation of the Influence of Fabry–Pérot Cavity “Flat Mirror—Spherical Mirror” Displacements on the Appearance of Higher Modes
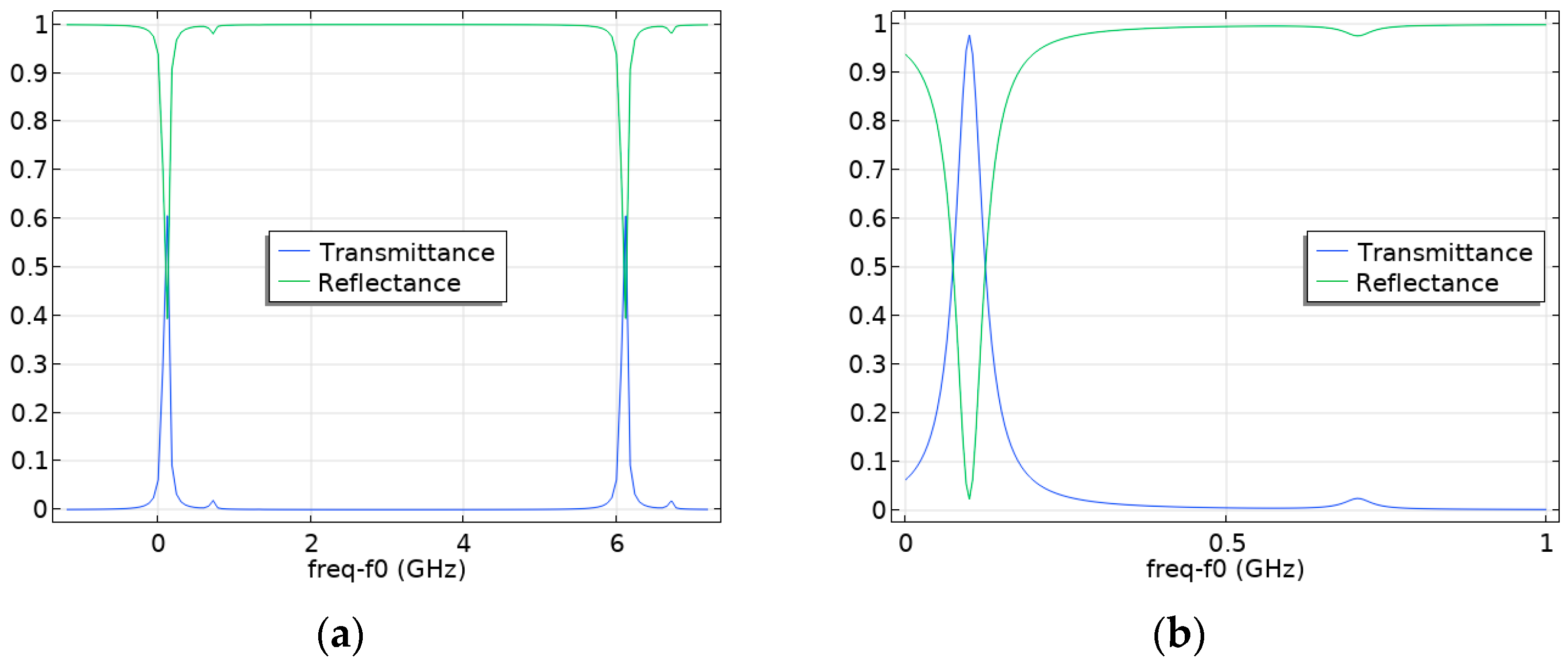
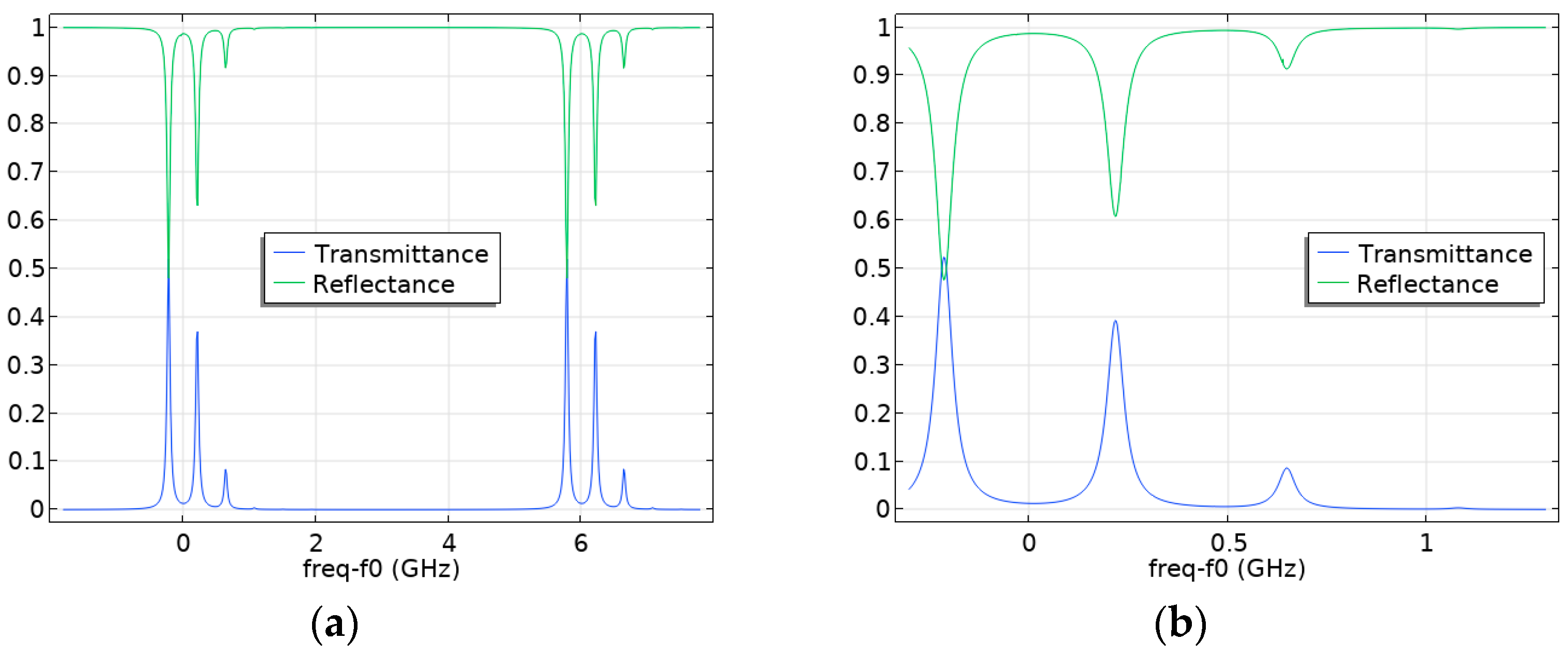
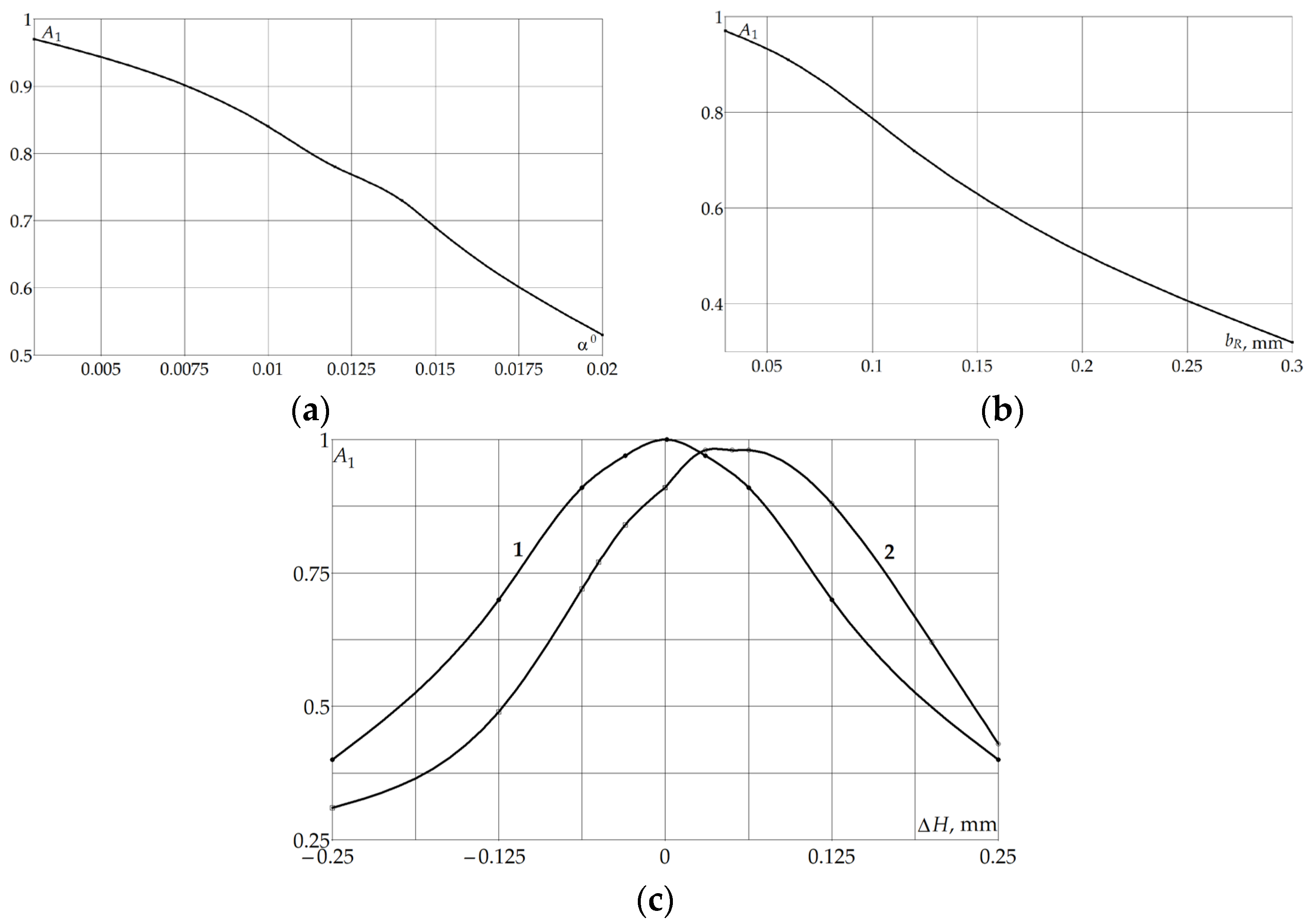
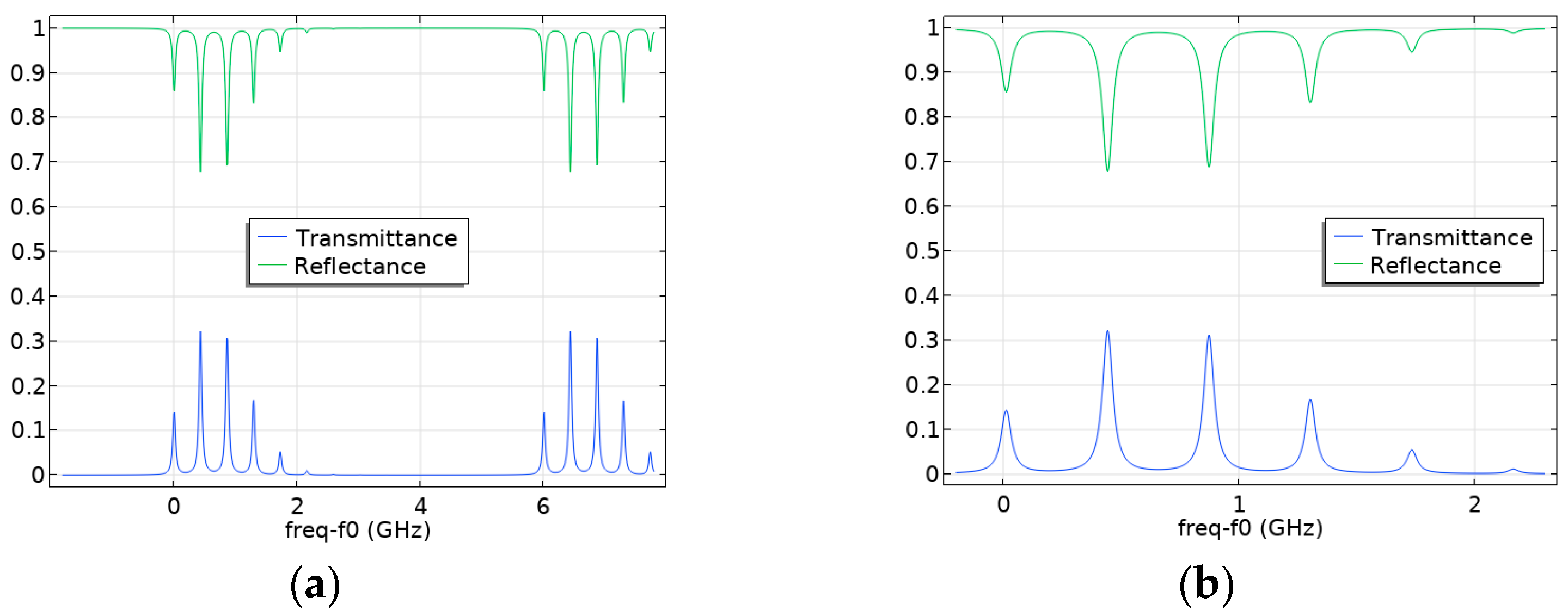
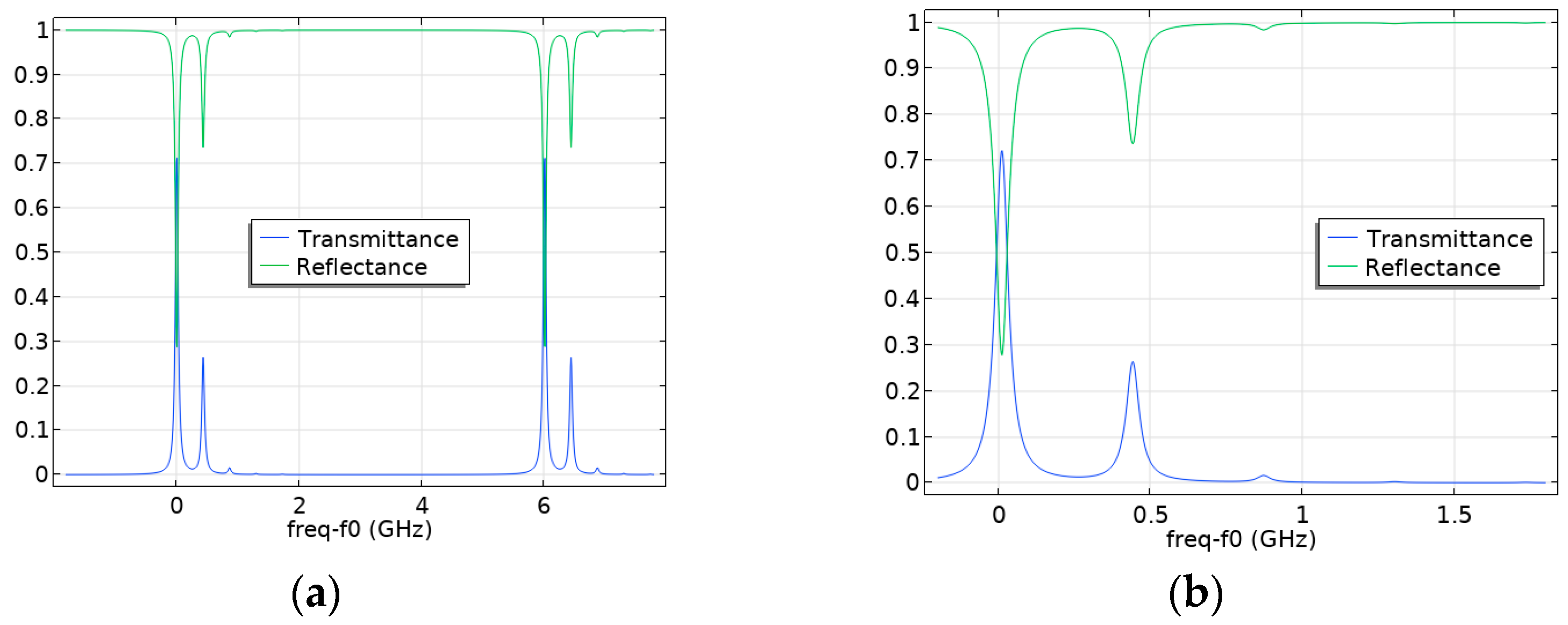
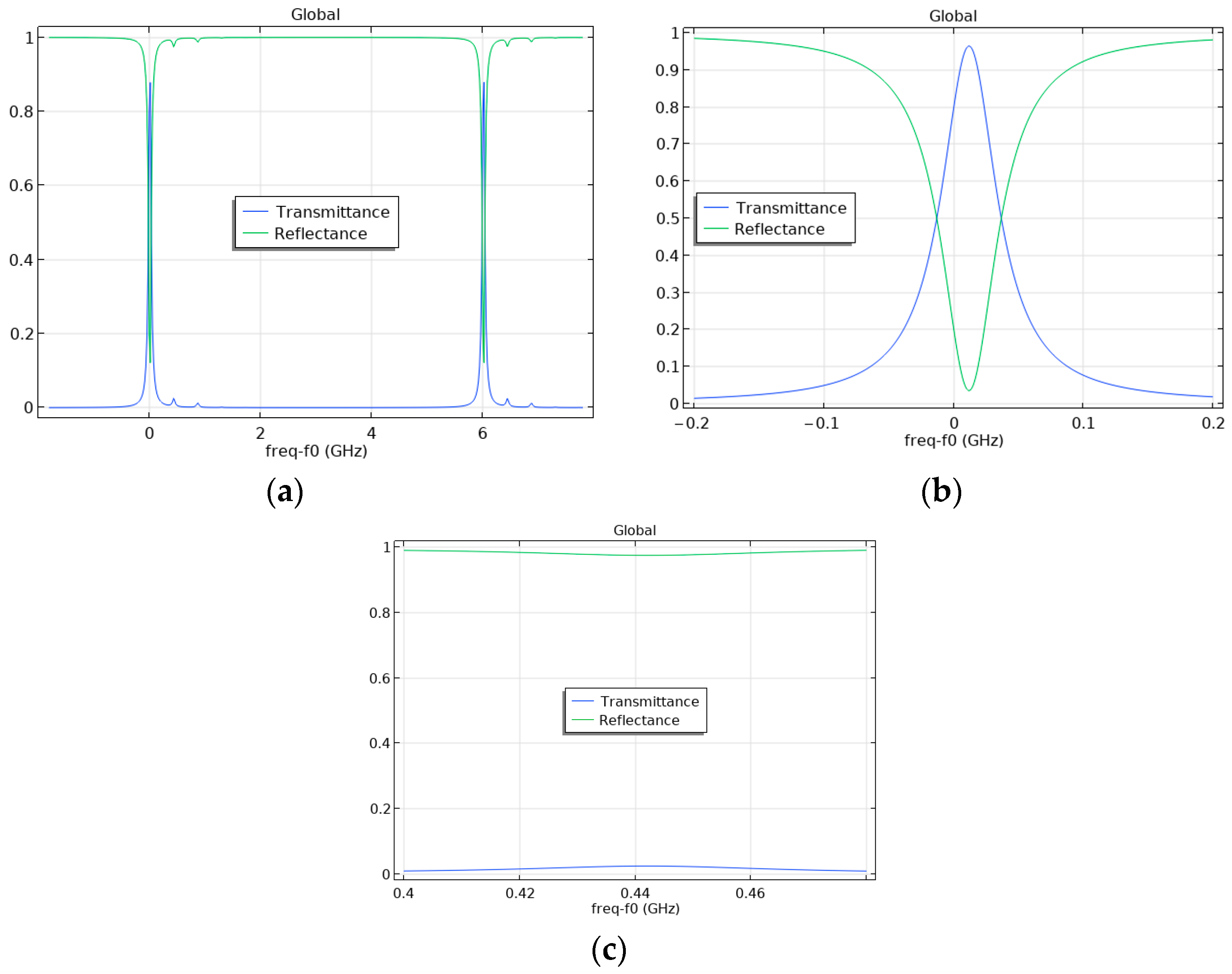
4.1. Investigation of the Influence of the Tilt Angle of a Flat Fabry–Pérot Cavity Mirror on the Appearance of Higher Modes
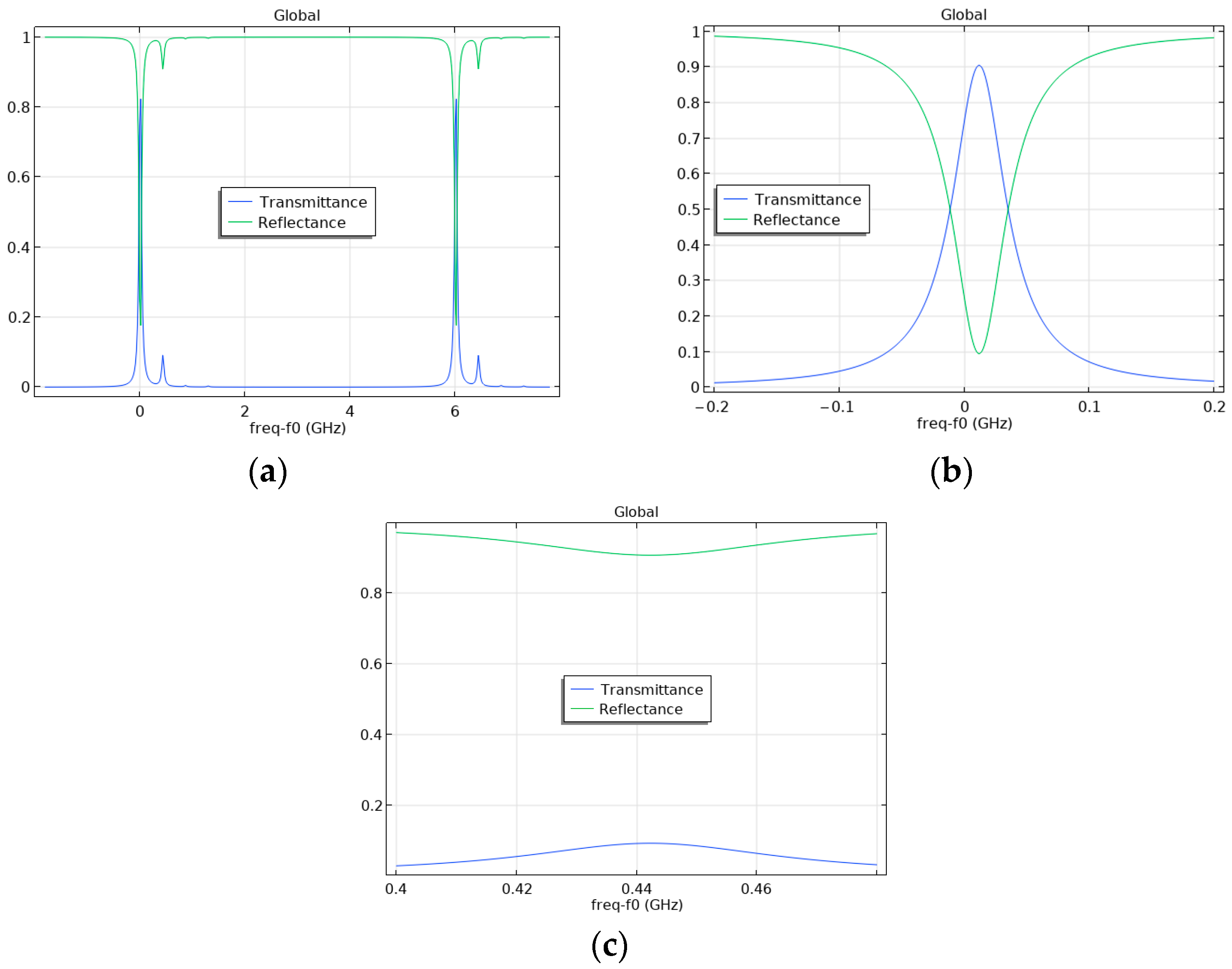
4.2. Investigation of the Influence of the Displacement of the Axis of the Fabry–Pérot Cavity Spherical Mirror on the Occurrence of Higher Modes
4.3. Investigation of the Influence of the Degree of Laser Beam Axis Displacement on the Occurrence of Higher Modes in the Fabry–Pérot Cavity
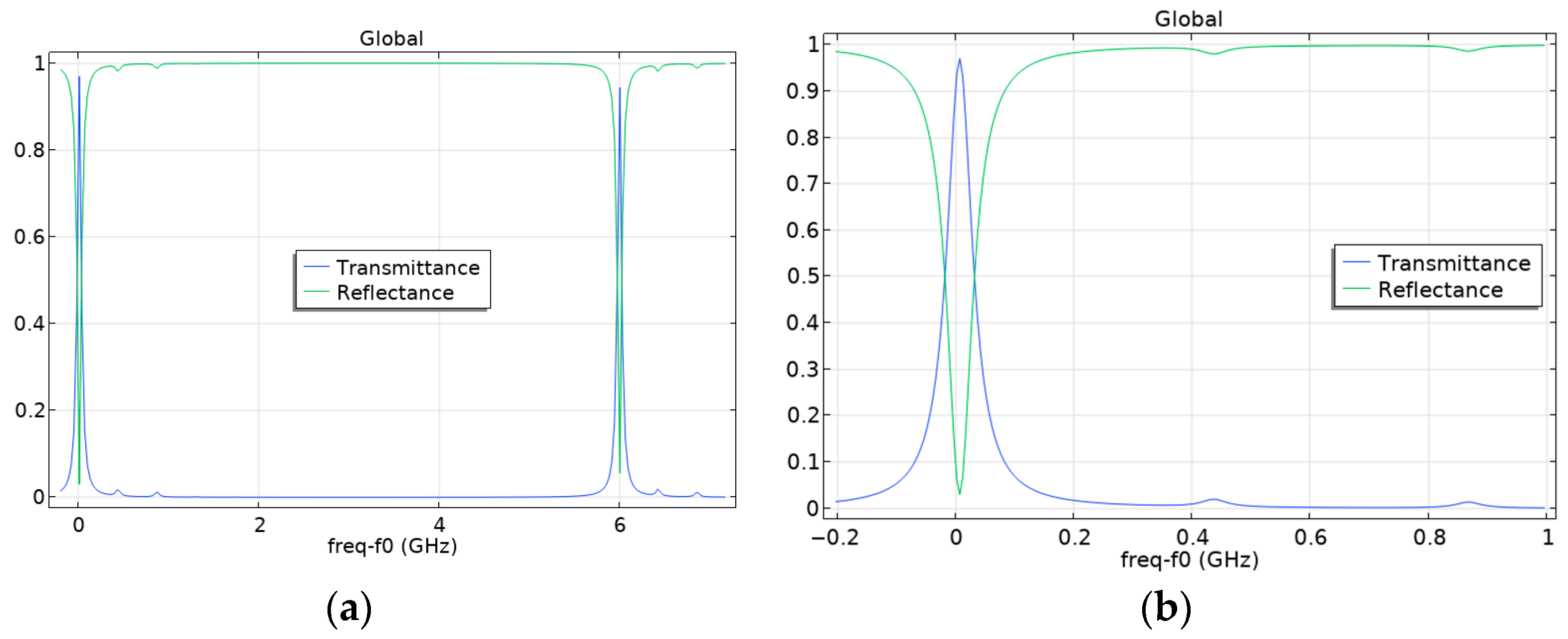
4.4. Investigation of the Influence of the Combinations of Displacements of Various Parameters of the Fabry–Pérot Cavity on the Appearance of Higher Modes
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Costa, G.K.B.; Gouvêa, P.M.P.; Soares, L.M.B.; Pereira, J.M.B.; Favero, F.; Braga, A.M.; Palffy-Muhoray, P.; Bruno, A.C.; Carvalho, I.C. In–fiber Fabry–Perot interferometer for strain and magnetic field sensing. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 14690–14696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazão, O.; Aref, S.H.; Baptista, J.M.; Santos, J.L.; Latifi, H.; Farahi, F.; Kobelke, J.; Schuster, K. Fabry–Pérot Cavity Based on a Suspended–Core Fiber for Strain and Temperature Measurement. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 2019, 21, 1229–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.S.; Coelho, L.; Schuster, K.; Kobelke, J.; Santos, J.L.; Frazão, O. Fabry–Perot cavity based on a diaphragm–free hollow–core silica tube. Opt. Lett. 2011, 36, 4029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, M.S.; Bierlich, J.; Kobelke, J.; Schuster, K.; Santos, J.L.; Frazao, O. Towards the control of highly sensitive Fabry–Perot strain sensor based on hollow–core ring photonic crystal fiber. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 21946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yang, K.; Wang, Y.; Qu, J.; Liao, C.; He, J.; Li, Z.; Yin, G.; Sun, B.; Zhou, J.; et al. High–sensitivity strain sensor based on in–fiber rectangular air bubble. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 7624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.R.; Ali, M.M.; Lai, M.-H.; Lim, K.-S.; Ahmad, H. Chronology of Fabry–Perot Interferometer Fiber–Optic Sensors and Their Applications: A Review. Sensors 2014, 14, 7451–7488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzmán, C.F.; Kumanchik, L.; Pratt, J.; Taylor, J.M. High sensitivity optomechanical reference accelerometer over 10 kHz. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 221111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Ou, L.; Lei, Y.; Liu, Y. Cavity optomechanical sensing. Nanophotonics 2021, 10, 2799–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reschovsky, B.J.; Long, D.A.; Zhou, F.; Bao, Y.; Allen, R.A.; LeBrun, T.W.; Gorman, J.J. Intrinsically accurate sensing with an optomechanical accelerometer. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 19510–19523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines, A.; Nelson, A.; Zhang, Y.; Valdes, G.; Sanjuan, J.; Stoddart, J.; Guzmán, F. Optomechanical Accelerometers for Geodesy. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, N.; Kores, C.C.; Geskus, D.; Pollnau, M. Fabry–Pérot resonator: Spectral line shapes, generic and related Airy distributions, linewidths, finesses, and performance at low or frequency–dependent reflectivity. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 16366–16389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, D.Z. Alignment of resonant optical cavities. Appl. Opt. 1984, 23, 2944–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takamori, A.; Araya, A.; Morii, W.; Telada, S.; Uchiyama, T.; Ohashi, M. A 100-m Fabry–Pérot Cavity with Automatic Alignment Controls for Long-Term Observations of Earth’s Strain. Technologies 2014, 2, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, T.; Chen, J.; Liu, S.; Fan, X. Optofluidic laser array based on stable high-Q Fabry–Pérot microcavities. Lab A Chip 2015, 15, 3862–3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerberding, O.; Guzmán, C.F.; Melcher, J.; Pratt, J.R.; Taylor, J.M. Optomechanical reference accelerometer. Metrologia 2015, 52, 654–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, M.; Wang, Y.; Lawall, J. Accurate Gouy phase measurement in an astigmatic optical cavity. Appl. Phys. B 2012, 108, 749–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Feynman Lectures on Physics. Available online: https://mathphyche.wordpress.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/the-feynman-lectures-on-physics-vol.-ii_-the-new-millennium-edition_-mainly-electromagnetism-and-matter.pdf (accessed on 10 October 2024).
- Kogelnik, H.; Li, T. Laser Beams and Resonators. Appl. Opt. 1966, 5, 1550–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezinkina, M.; Braxmaier, C. Designs of Miniature Optomechanical Sensors for Measurements of Acceleration with Frequencies of Hundreds of Hertz. Designs 2024, 8, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://doc.comsol.com/5.6/doc/com.comsol.help.models.woptics.fabry_perot_resonator/fabry_perot_resonator.html (accessed on 10 October 2024).
- Available online: https://doc.comsol.com/5.4/doc/com.comsol.help.woptics/WaveOpticsModuleUsersGuide.pdf (accessed on 10 October 2024).



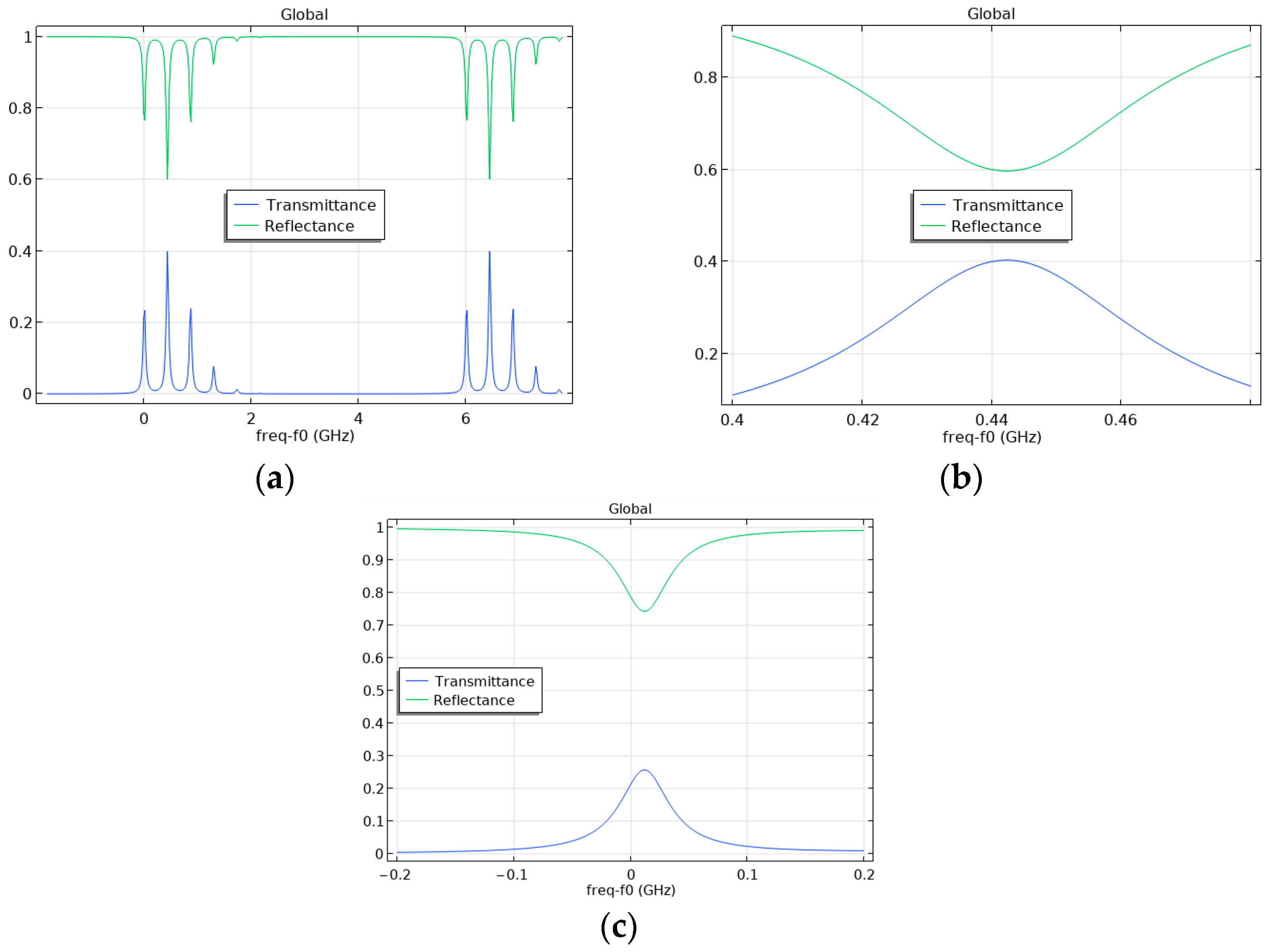
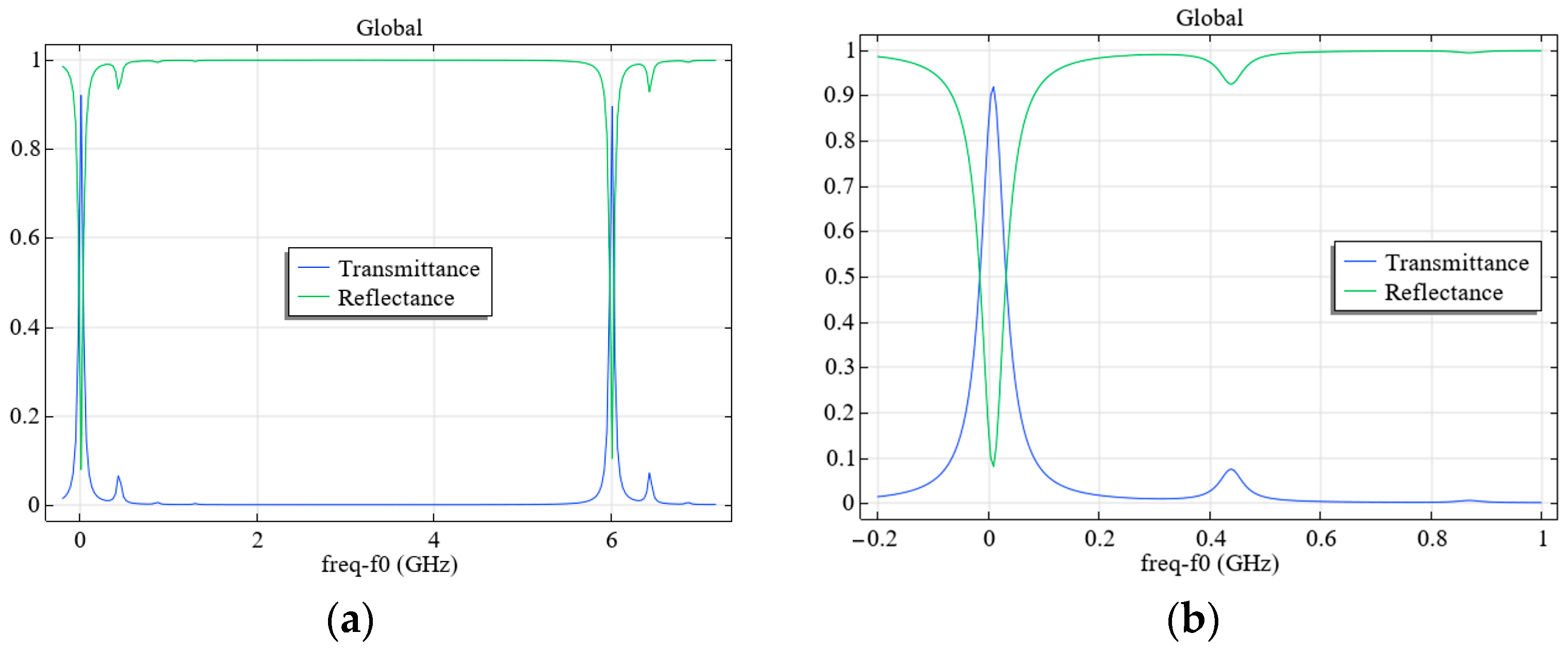
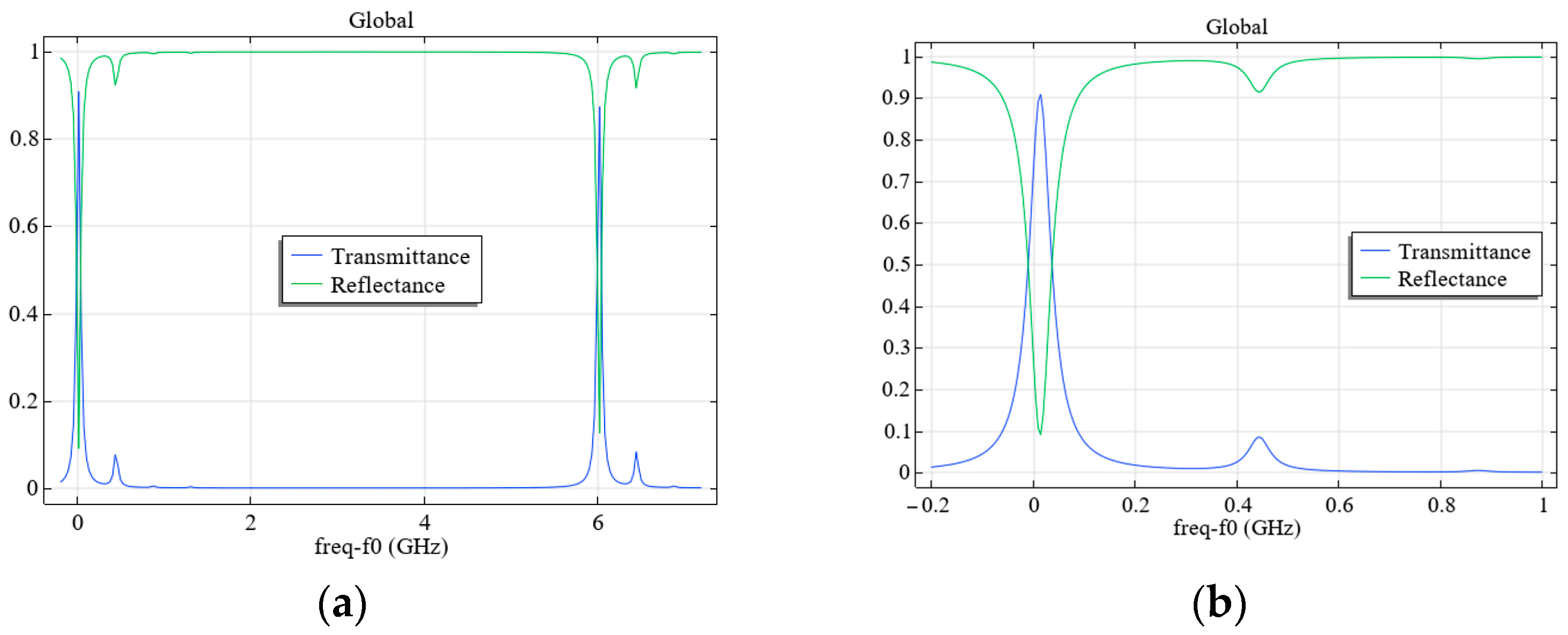
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rezinkina, M.; Braxmaier, C. Alignment of Fabry–Pérot Cavities for Optomechanical Acceleration Measurements. Photonics 2025, 12, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12010015
Rezinkina M, Braxmaier C. Alignment of Fabry–Pérot Cavities for Optomechanical Acceleration Measurements. Photonics. 2025; 12(1):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12010015
Chicago/Turabian StyleRezinkina, Marina, and Claus Braxmaier. 2025. "Alignment of Fabry–Pérot Cavities for Optomechanical Acceleration Measurements" Photonics 12, no. 1: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12010015
APA StyleRezinkina, M., & Braxmaier, C. (2025). Alignment of Fabry–Pérot Cavities for Optomechanical Acceleration Measurements. Photonics, 12(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics12010015





