Abstract
According to the theory of atmospheric transmission, the atmospheric optical characteristics of a 700 mm laser ranging telescope system are obtained by the inversion of the experimental data through the telescopic multi-elevation method, and a modified model of the ranging equation of laser diffuse radar is proposed. The variation in the Aerosol Optical Depth and atmospheric transmittance under the multi-elevation method, visibility and the oblique transmission atmospheric stratification model are analyzed and discussed. The model is numerically simulated and compared with the measured data of some space debris. The results show that the relative errors of the average echo photon number obtained by the multi-elevation method are less than 15%, and the average relative errors are 4.643% and 7.934%, respectively. The model improves the calculation accuracy of the laser ranging radar equation to a certain extent.
1. Introduction
Space Debris Laser Ranging (DLR) is a high-precision technology for the real-time detection and orbit determination of space debris using lasers [1], and the DLR accuracy can even reach the centimeter level [2,3]. According to the principles of Rayleigh scattering [4] and Mie scattering [5], when the laser is transmitted in the atmospheric channel, it will interact with gas molecules and aerosol particles in the atmosphere, and the beam will be affected by atmospheric absorption and scattering, resulting in laser energy attenuation, which will affect the transmission efficiency of the laser and seriously affect the ranging effect of the DLR system. In view of this, the aim of this study is to build an atmospheric optical model by introducing the telescope multi-elevation method to avoid the direct calculation of the atmosphere, so as to simplify the calculation process and analyze the echo characteristics.
The essence of atmospheric optics is the change in laser field distribution caused by the effect of external atmospheric environment during laser transmission in free space, in which atmospheric transmittance [6], Aerosol Optical Depth (AOD) and extinction coefficient [7,8] are all important parameters of atmospheric optical characteristics. It is also a key factor that determines the intensity of the laser echo signal and the measurement accuracy of the space target.
At present, researchers at home and abroad have conducted a series of studies on the influence of atmospheric optical properties on debris laser ranging. Jin Yan modified the LiDAR equation by introducing atmospheric visibility and studied the ultimate ranging capability of the laser ranging system under different meteorological conditions [9]. According to the relationship between atmospheric scattering coefficient and horizontal visibility, John J. Degnan analyzed the changes in satellite laser ranging under different visibilities and calculated the corresponding average photon number of echo [10]. According to the Lidar equation, Steinvall proposed to apply the design of space targets and system parameters in different atmospheric environments to the distance calculation of the LiDAR ranging system [11]. V. P. Busygin built a cloud stratification optical model based on the atmospheric stratification theory and analyzed the influence of different types of cloud on laser ranging accuracy [12]. Li Ming et al. assumed the average transmittance of 532 nm laser through the atmosphere of the test site, and applied the sparsity degradation model of the measured data to the limit detection capability of DLR system [13].
Based on the statistics and analysis of the measured data from the 700 mm DLR system, this paper proposes employing the telescopic multi-elevation method [14] to deduce the atmospheric optical characteristics of laser transmission through the atmospheric channel. Subsequently, a correction model for laser diffuse radar ranging is established based on theoretical deductions from the LiDAR ranging equation. The average echo photon number under different atmospheric optical models is calculated and verified with the measured data. The results show that the relative error of the model based on the telescope multi-elevation method is reduced by one order of magnitude compared with the existing model. This study not only provides a theoretical basis for the DLR detection experiment but also provides an important data reference for the subsequent test design and DLR system location.
2. Basic Principle
2.1. Standard Atmospheric Model
The standard atmospheric extinction model reflects the vertical distribution characteristics of annual mean temperature, pressure, and atmospheric density in middle and low latitudes. It is commonly employed for calculating the extinction properties of atmospheric molecules and aerosol particles. In this model, the extinction coefficients and backscattering coefficients of aerosols and atmospheric molecules are expressed as follows:
In Equations (1)–(3), and are extinction coefficients of aerosols and atmospheric molecules, respectively. and are the backscatter coefficients of aerosols and atmospheric molecules, respectively. is the altitude in the vertical direction; is the laser wavelength, which is 1064 nm; and is the aerosol radar ratio related to the laser wavelength, which is 40. The change curve of the extinction coefficients of the aerosol and atmospheric molecules of the 1064 nm laser in the standard atmospheric model is shown in Figure 1.
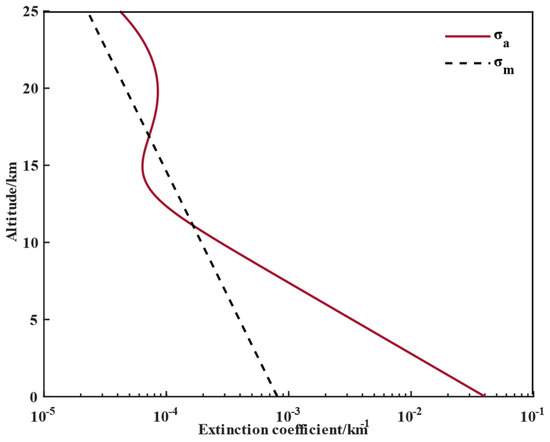
Figure 1.
Extinction coefficients of aerosols and atmospheric molecules of the 1064 nm laser in the atmosphere.
In this paper, the DLR system uses a 1064 nm wavelength laser, and the gas molecules in the atmosphere have little influence on the transmission of 1064 nm laser, where the scattering is an independent event, and when the visibility is greater than 5 km, the multiple scattering of atmospheric molecules to the laser can be ignored. Therefore, in the process of long-distance laser transmission, the main reason for its energy attenuation is the scattering and absorption of aerosol particles, and the influence of the aerosol on the laser is 1 to 2 orders of magnitude higher than that of the atmospheric molecules [15]. Therefore, only the effect of the atmospheric optical properties of aerosols on the echo signal strength is considered in the following section.
2.2. Calculation of Atmospheric Optical Properties Based on Horizontal Visibility
The relationship between the aerosol extinction coefficient and horizontal visibility near the ground was derived by measuring horizontal visibility. According to Angstrom’s revised theory [16], in order to make the extinction coefficient and horizontal visibility near the ground more accurate, the relationship between them and the laser wavelength should be fully considered as follows:
where is the horizontal visibility, is the percentage that the radiation intensity decays to the initial light intensity, and is the empirical coefficient.
Although it is difficult to determine the variation law of the aerosol extinction coefficient in the oblique direction, it can be concluded from the analysis based on the principle of aerosol concentration attenuation with height [17] that the aerosol extinction coefficient profile also decreases in a power exponential manner with the increase in height in the vertical direction, as shown below:
where is the extinction constant of the aerosol near the ground related to the horizontal visibility of the 1064 nm laser, and is the aerosol elevation, which is related to the weather visibility, aerosol density and distribution at that time. The relationship between visibility and aerosol elevation is shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Relationship between visibility and aerosol elevation [18].
AOD and atmospheric transmittance are important parameters reflecting the atmospheric optical properties of aerosols. Among them, when the laser is transmitted obliquely, the calculation equation of the atmospheric optical characteristics after the atmospheric channel is shown as follows:
where and are the AOD and aerosol transmittance of the laser in the inclined direction, and is the angle between the laser transmission direction and the horizontal plane, which is called the pitch angle.
2.3. Atmospheric Optical Properties Are Calculated Based on the Oblique Transmission Atmospheric Stratification Model
Based on Mie scattering, for the distribution of aerosol particles in free space and vertical stratification of the atmosphere [19], the atmosphere is divided into a thickness layer in the vertical direction, within which each layer has thickness. It is assumed that the aerosol particles in each layer are evenly distributed in the horizontal direction, and then the atmospheric optical characteristics of each layer are calculated separately. Oblique AOD is shown below:
where is the optical thickness in the oblique direction corresponding to the layer − 1 of the aerosol, is the total scattering cross-section of a single spherical aerosol particle, is the ratio of aerosol wet particle radius to dry particle radius , and and are scattering coefficients, which are related to the aerosol particle radius, laser wavelength and relative complex refractive index of aerosol particles. The Bessel function recursion and the Hankel function can be used to represent them [20]. The complex refractive index of aerosol particles under the 1064 nm laser is set as . is the aerosol particle concentration near the ground [21]. After the simultaneous simplification of Equations (9)–(11), the whole layer AOD in the oblique direction can be obtained as follows:
Similarly, the oblique atmospheric transmittance can be derived as follows:
where is the atmospheric transmittance of the whole layer in the atmospheric aerosol in the upper laser oblique direction.
2.4. Determination of Atmospheric Optical Characteristics Using the Telescopic Multi-Elevation Approach
The telescope multi-elevation method is used to analyze the number of echo photons received by the photodetector in different elevation directions and then bring the measured data into the laser diffuse reflection radar ranging equation for deformation simplification, so as to achieve the accurate inversion calculation of atmospheric optical characteristics after laser transmission through the atmospheric channel. This method avoids the trouble of detecting and solving the atmospheric extinction coefficient distribution caused by the atmospheric multiple scattering of laser light. The atmospheric optical thickness and transmittance on the path can be solved by considering the echo signal on the path with different pitch angles, so as to calculate the change in the echo signal in the whole process. The echo signal becomes weak due to the invisibility of the follow-up observation target and the large deviation in the tracking direction of the telescope, and the accuracy is difficult to guarantee at this time, so the intensity of the follow-up echo signal of the target can be estimated according to the results of the multi-elevation method of the telescope.
Figure 2 is the principle diagram of the multi-elevation method of the laser ranging telescope. In this paper, we measure DLR data under the pitch angles and , which are selected for calculation, where the oblique transmission distance in the direction of pitch angle is and the oblique transmission distance in the direction of pitch Angle is . In addition, in order to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the calculation results, the atmospheric regions passed by the laser under different pitch angles are basically the same. Therefore, the difference between the selected pitch angle values should not be too large.
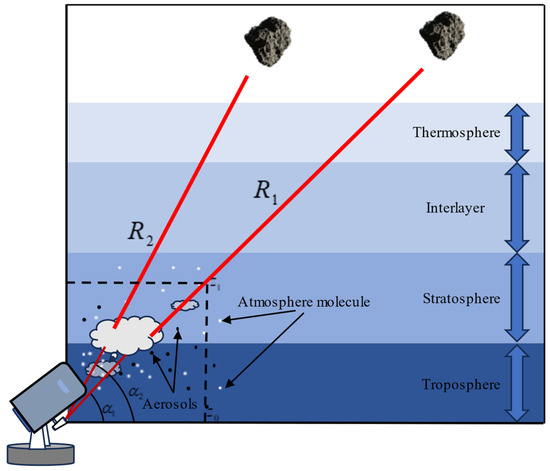
Figure 2.
The principle of the multiple elevation method.
The number of monopulse echo photons diffused back by debris after laser transmission through the atmosphere is shown as follows [22]:
where is the number of echo photons of a single pulse; is the laser pulse energy; is Planck’s constant; is the speed of light in a vacuum; is the effective receiving area of the telescope; is the scattering cross-sectional area of space debris; is the reflectance of space debris; is the initial divergence angle of the laser; is the distance from the laser to the space debris through the oblique path; is the single-photon detector efficiency of DLR system; is DLR system emission efficiency; is the receiving efficiency of DLR system; is the two-way atmospheric transmittance, where is the vertical transmission distance of the laser in the atmospheric channel, that is, the thickness of the whole atmosphere; and is the attenuation factor (that is, the empirical value related to atmospheric turbulence, atmospheric jitter and other factors).
The related parameters of the pitch angles and are, respectively, brought into Equation (14) as follows:
where and are the number of monopulse echo photons returned to the telescope receiver by space debris at the pitch angles and , respectively. The logarithm of the two equations in Equation (16) is taken and then subtracted, and the following equations are identically deformed. After simplification, the optical thickness of the whole layer of the atmosphere in the vertical direction can be obtained:
where is the variable related to , , , and .
Atmospheric molecules and aerosols are the main particles that make up the atmosphere, and the relationship between the atmospheric extinction coefficient and them is as follows:
By substituting Equation (18) into Equation (17), the identity deformation simplification can be obtained as follows:
where and represent the optical thicknesses of aerosol and atmospheric molecules in the vertical direction, respectively. According to the above, the influence of the optical thicknesses of atmospheric molecules can be ignored. Assuming that the aerosol particles are evenly distributed in the horizontal direction, the entire layer AOD of the laser can be obtained after the laser is transmitted under the pitch angle and passes through the atmospheric channel. The oblique path AOD is represented by as follows:
Similarly, the corresponding atmospheric transmittance during oblique transmission is as follows:
At this point, Equations (20) and (21) are brought together into Equation (14). After simplification, the modified laser diffuse radar ranging equation can be obtained, as shown below:
3. Numerical Analysis and Experimental Results Are Discussed
In this paper, the 700 mm DLR system of the Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, the Chinese Academy of Sciences, was used as the measuring experiment equipment, as shown in Figure 3.
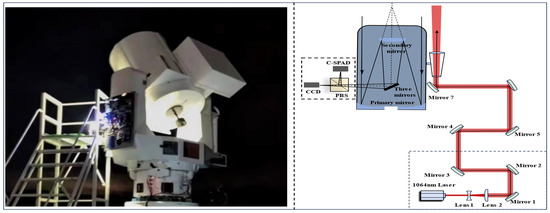
Figure 3.
The 700 mm DLR system experimental device and schematic diagram.
The schematic diagram of the DLR system can be seen in Figure 3. In the process of laser ranging, the beam is emitted from the laser, and after first-stage beam expansion through the Lens 1 and Lens 2 beam expansion system, it is reflected by the reflector in turn, and it reaches the laser emitter through the optical path of the telescope and shoots at the space debris. The echo signal reflected from the space debris is reflected to the photoelectronic detector of the DLR system through the primary mirror, secondary mirror and third mirror for analysis and processing. In addition, some parameters of the 700 mm DLR system are shown in Table 2 below.

Table 2.
The 700 mm DLR system parameter.
The following is based on the space debris measured by the DLR system during the three days of 14 April, 15 April and 18 April 2024, as shown in Figure 4. The measured data of some space debris are selected for calculation and analysis, as shown in Table 3.
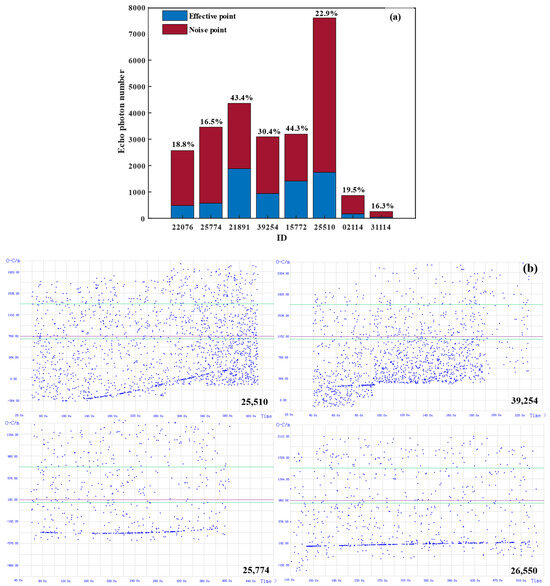
Figure 4.
(a) Statistical diagram of space debris echo signal data; (b) Space debris echo signal data processing range residual map.

Table 3.
The ranging results of the 700 mm DLR system.
Figure 4 shows the statistics of space debris echo signal data and the residual of the processing distance of part of the echo signal data. It can be seen from Figure 4 and Table 3 that the space debris ranging accuracy (RMS) measured in the experiment is within the range of 50~150 cm, which meets the requirements of DLR system design accuracy. Combined with part of the experimental data in Table 4 and Table 5, it can be seen that in terms of unit time, the average photon number of echoes is greater than the threshold value 2, which can be regarded as the DLR system successfully detecting the effective echo signal reflected back from the space debris, that is, the experiment successfully detects the space debris target. At this time, DLR system can successfully analyze the orbit information of space debris and its own characteristics [23].

Table 4.
Space debris error analysis (ID:26550).

Table 5.
Space debris error analysis (ID: 39254).
In order to ensure the accuracy of the atmospheric optical characteristics calculated based on the visibility and oblique transmission atmospheric stratification model, this paper selects the same meteorological environment as the above DLR experiment environment for simulation calculation. After measurement, the atmospheric horizontal visibility of the experimental site is 13 km, the atmospheric temperature is 13.7 °C, the atmospheric humidity is 52.2%, and the atmospheric pressure is 795.0 hpa.
In this study, we integrate the atmospheric environment parameters during the experiment into the above model and comprehensively analyze the atmospheric optical characteristics after laser transmission through the atmospheric channel. The variation in oblique AOD and atmospheric transmittance with pitch angle is numerically simulated, as shown in Figure 5. Under different models, the oblique AOD decreases with the increase in the pitch angle, while the atmospheric transmittance increases with the increase in the pitch angle. The above changes are due to the fact that with the increase in the pitch angle, the actual distance of laser transmission in the atmospheric channel is shortened, resulting in the weakening of the scattering and absorption of the aerosol particles on the laser, so that the oblique AOD decreases and the atmospheric transmittance increases.
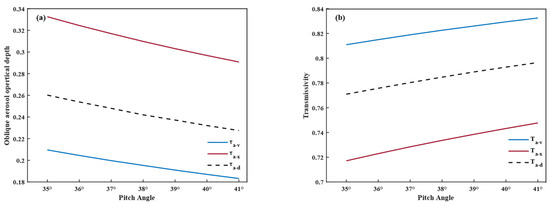
Figure 5.
Variation in the atmospheric optical properties with pitch angle: (a) Aerosol Optical Depth; (b) atmospheric transmittance.
By combining the above data with Equation (22), the number of echo photons under different models can be calculated. In order to verify the reliability of the model, the error between the average echo photon number and the experimental data under different models can be calculated, as shown below:
where is the laser pulse emission frequency.
According to Equations (14) and (23), the numerical simulation is performed to obtain the average photon number per second of echoes based on visibility and the oblique transmission atmospheric stratification and telescope multi-elevation models, and a comparison is made with the measured data of some space debris. The analysis results are shown in Table 4 and Table 5 below.
As can be seen from Table 4 and Table 5, the average relative errors between the average number of photons per second of the monopulse laser echo calculated by the visibility model and the experimental data within a certain pitch angle are 12.850% and 16.4921%, respectively. The average relative errors calculated based on the oblique transmission atmospheric stratification model are about 10.316% and 15.879%. Compared with the above model, the average photon number calculated based on the telescope multi-elevation method is closer to the measured value, in which the relative error is greatly reduced and the error is less than 15%. The average relative errors decreased by more than 50%, 4.643% and 7.934%, respectively. The relative error affecting the mean photon number of echoes is primarily caused by the pointing error of the DLR system. In the process of DLR measurement, the predicted orbit of space debris is generated based on two-line elements (TLEs). Consequently, there is a certain deviation between the telescope’s pointing position and the actual position of the space debris, making it challenging for the DLR system to accurately detect the space debris. According to error calculation and analysis, the pointing error at this time exhibits a deviation of approximately 1” [24]. This error results in a relative error of approximately 2% in the echo photon number. It can be concluded that the modified model meets the basic requirements of DLR system, and the relative error is small and the precision is higher, which is of great significance for improving the accuracy and reliability of the calculation of echo signal characteristics.
4. Conclusions
In this paper, a new method combining the measured data of the DLR echo photon signal is proposed. The optical characteristics of the whole layer atmosphere in the oblique direction of the experiment are obtained by the telescopic multi-elevation method, and the ranging equation of laser diffuse radar is modified accordingly. In this paper, the variation in the atmospheric optical characteristics under different atmospheric optical models is also discussed. Combined with the lidar equation, the average number of photons per second received by 700 mm DLR system is numerically calculated, and the measured data of space debris 26550 and 39254 obtained by the DLR system are compared and analyzed. The results show that the relative error between the average echo photon number calculated by the multi-elevation method and the measured value is less than 15%, and the average relative errors are 4.643% and 7.934%, respectively. Compared with the existing atmospheric optical model, this model effectively improves the calculation accuracy of the echo photon characteristics. This paper not only provides important reference data for the subsequent experimental design and data analysis but also can accurately predict and evaluate the performance of the DLR system, so as to provide support for more reliable and accurate space debris monitoring and ranging.
Author Contributions
Data curation, J.W.; Formal analysis, J.W.; Funding acquisition, Y.Z.; Methodology, J.W.; Project administration, Y.Z.; Resources, B.G. and Y.Z.; Supervision, Y.Z.; Writing—original draft, J.W.; Writing—review and editing, J.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data supporting this study’s findings are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Fried, D.L. Aperture Averaging of Scintillation. Opt. Soc. Am. 1967, 57, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wriedt, T. Mie Theory: A Review. The Mie Theory: Basics and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 53–71. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Hou, A.; Zhang, X.; Han, F.; Zhao, N.; Xu, S.; Ma, Q.; Gu, Y.; Dong, X.; Chen, Y.; et al. Assessment of Lateral Structural Details of Targets Using Principles of Full Waveform Light Detection and Ranging. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 5704416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hu, Y.; Shen, S.; Fang, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Han, F. Kilometer-level laser reflective tomography experiment and debris barycenter stimation. Acta Phys. Sin. 2022, 71, 114205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohmann, U.; Feichter, J. Global indirect aerosol effects: A review. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 715–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaRocca, A.J. Methods of calculating atmospheric transmittance and radiance in the infrared. Proc. IEEE 1975, 63, 75–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.; Hansen, J.E.; McCormick, M.P.; Pollack, J.B. Stratospheric aerosol optical depths, 1850–1990. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1993, 98, 22987–22994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sserunjogi, M.; Ambrose, K. Light extinction coefficient and particle size correlation for real-time prediction and quantitative measurement of suspended dust concentrations. Adv. Powder Technol. 2024, 35, 104354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinvall, O. Laser system range calculations and the Lambert W function. Appl. Opt. 2009, 48, B1–B7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degnan, J. An upgraded SGSLR link analysis which includes the effects of atmospheric scintillation and target speckle. In Proceedings of the 20th ILRS Workshop, Potsdam, Germany, 9–14 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, D.; Qin, Y.C.; Wang, X.P. Sensitivity Analysis of Atmospheric Delay Correction for Spaceborne Laser Altimeter. Prog. Laser Optoelectron. 2019, 56, 61–68. [Google Scholar]
- Busygin, V.P.; Ginzburg, A.S.; Kuzmina, I.Y. Transfer of Laser Pulses through the Atmosphere into Space in the Presence of Clouds of the Upper and Middle Tiers. Izv. Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 2021, 57, 594–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Xue, L.; Huang, C. Estimation of detection range or space debris laser ranging system based on efficient echo probability. Opt. Precis. Eng. 2016, 24, 260–267. [Google Scholar]
- Du, J.M. Oblique Visibility Estimation Algorithm and Experiment for Double Elevation Optical Thickness of Laser Radar. Master’s Thesis, Xi’an University of Technology, Xi’an, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.; Yin, Z.; Mao, S.; Wang, L.; Yi, Y.; Chen, Q.; Müller, D.; Wang, X. Measurements of particle extinction coefficients at 1064 nm with lidar: Temperature dependence of rotational Raman channels. Opt. Express 2024, 32, 4650–4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angstrom, A. The parameters of atmospheric turbidity. Tellus 1964, 16, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiscombe, W.J. Improved Mie scattering algorithms. Appl. Opt. 1980, 19, 1505–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.F.; Zhang, J.L.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.B.; Chen, Y.Y. Study on the extinction characteristics of aerosols in the vertical direction of space. J. Light Scatt. 2013, 25, 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Bohren, C.F.; Huffman, D.R. Absorption and Scattering of Light by Small Particles; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, H.M.; Zhao, W.; Dai, X.C. Influence of fog and aerosol particles’ forward-scattering on light extinction. Opt. Precis. Eng. 2018, 26, 1354–1361. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, E.; Saxena, P.; Musarra, S.; Hildemann, L.; Koutrakis, P.; McMurry, P.; Olmez, I.; White, W. Concentration and composition of atmospheric aerosols from the 1995 SEAVS experiment and a review of the closure between chemical and gravimetric measurements. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2000, 50, 648–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, W.D.; Zhang, H.F.; Deng, H.R.; Kai, T.; Zhi-Bo, W.; Yu-Rong, W.; Guang, W.; Zhong-Ping, Z.; Xin-Yang, C. 1.06 μm wavelength based high accuracy satellite laser ranging and space debris detection. Acta Phys. Sin. 2020, 69, 019502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhou, M.; Yu, Z.; Jiang, X.; Huo, Y.; Zang, K.; Zhang, J.; Harris, J.S.; Jin, G.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Simulation of a high efficiency and low jitter nanostructured silicon single photon avalanche diode. Optica 2015, 2, 974–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.M. Research and Realization of Key Technology of Space Debris Laser Ranging. Ph.D. Thesis, Liaoning Technical University, Fuxin, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).