Coalitional Game Theory-Based Resource Allocation Strategy for Robust IRS-VLC System
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose a novel resource allocation strategy using coalitional game theory to optimize the LED power distribution and IRS energy consumption in multi-AP IRS-VLC systems with multiple obstacles. The EE is enhanced significantly under practical energy constraints.
- We apply coalitional game theory to facilitate the formation of coalitions among IRS elements, centered around a pivotal reference unit. This coordinates the IRS elements to improve the system performance.
- We address the challenge of non-convex optimization in robust IRS-VLC systems by breaking down the problem into manageable phases. This ensures that the effective deployment of IRS arrays maintains the achievable data rate and minimizes the mean square error of the received power.
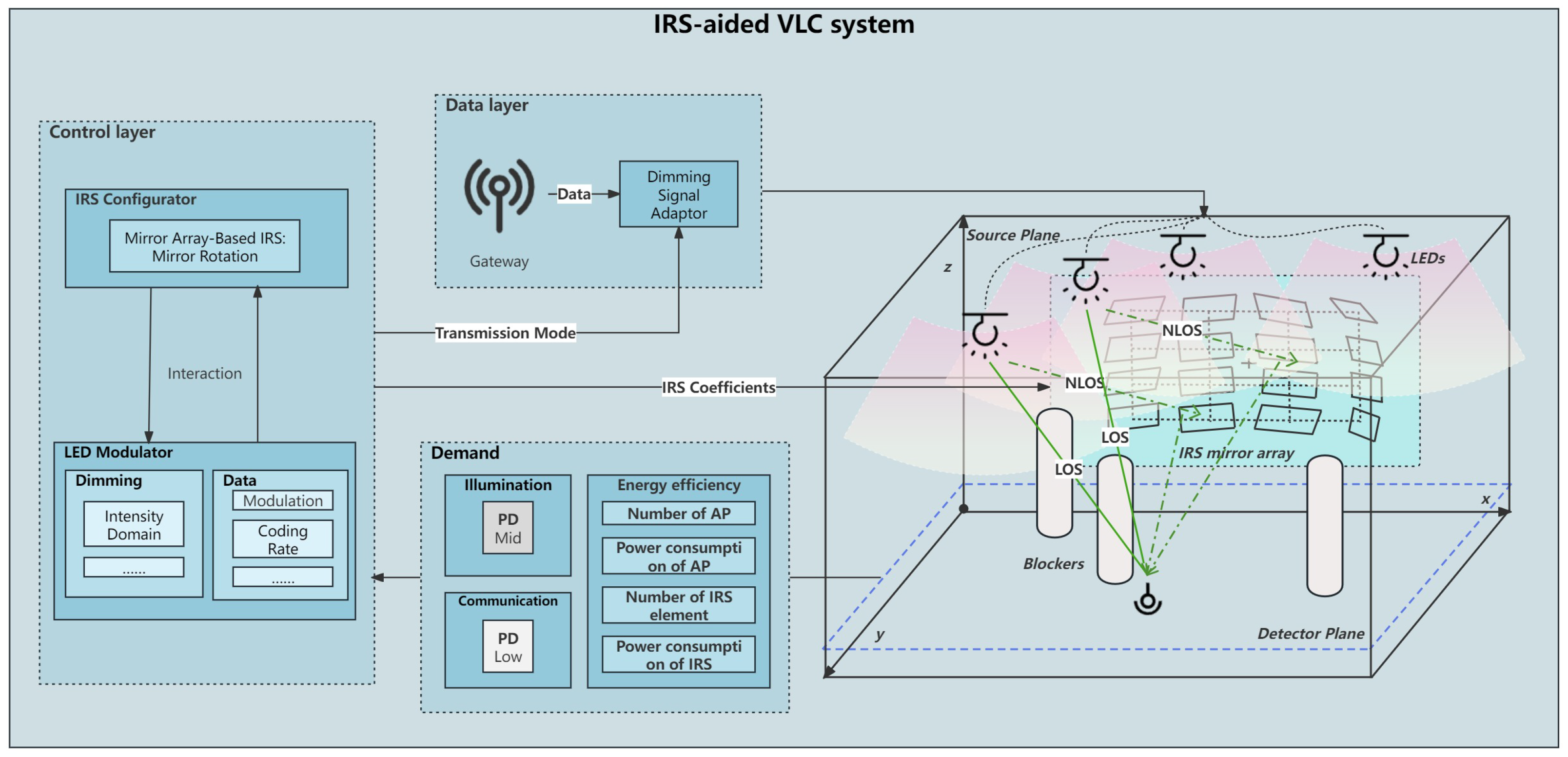
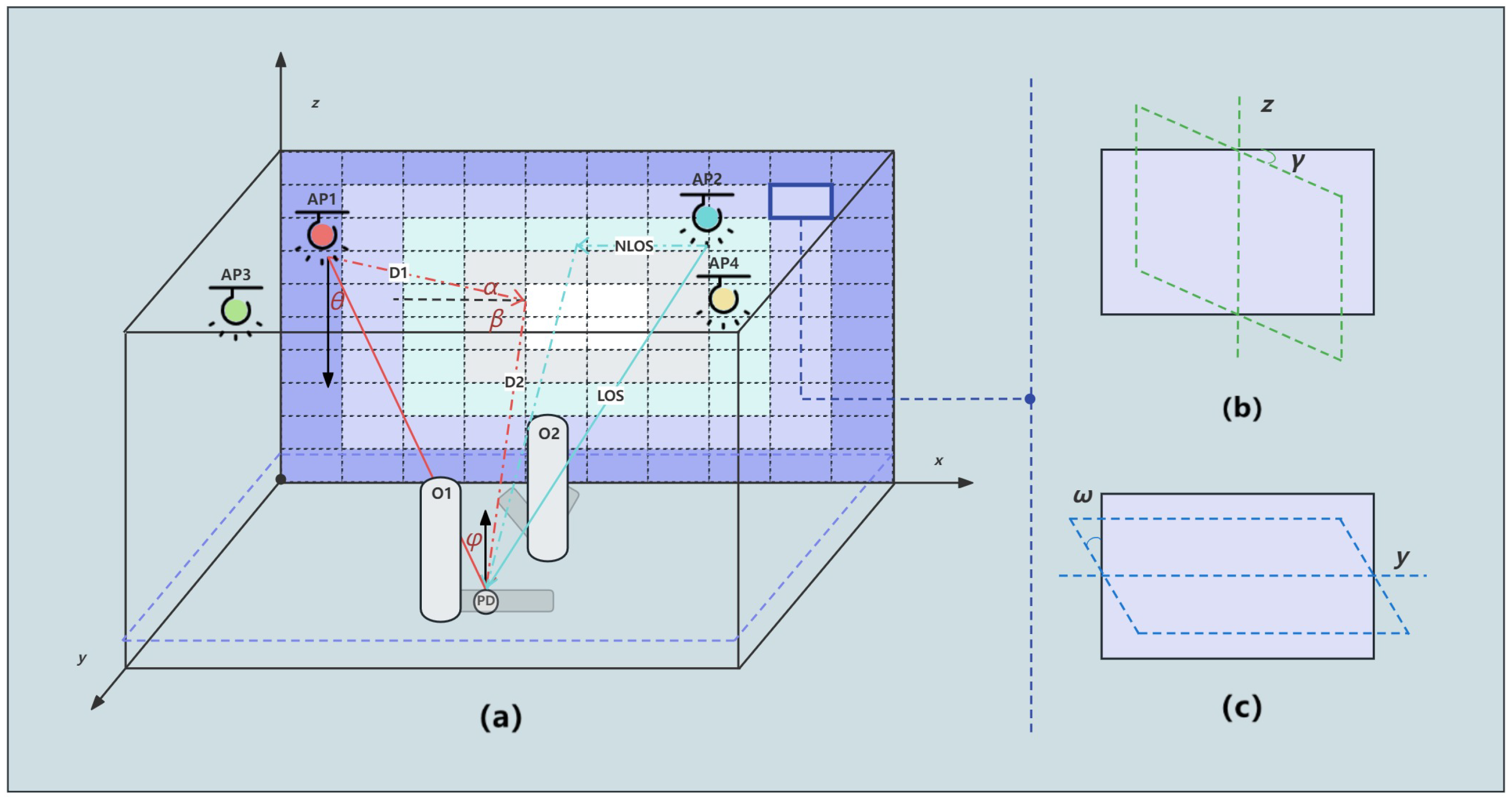
2. System Model
3. Problem Formulation and Coalitional Game Theory-Based Resource Allocation
3.1. Problem Formulation
3.2. Coalitional Game Strategy
3.3. Coalition Formation Algorithm
| Algorithm 1 Integrated Game-Theoretical Approach for IRS-Assisted VLC Optimization |
|
3.4. Theoretical Analysis
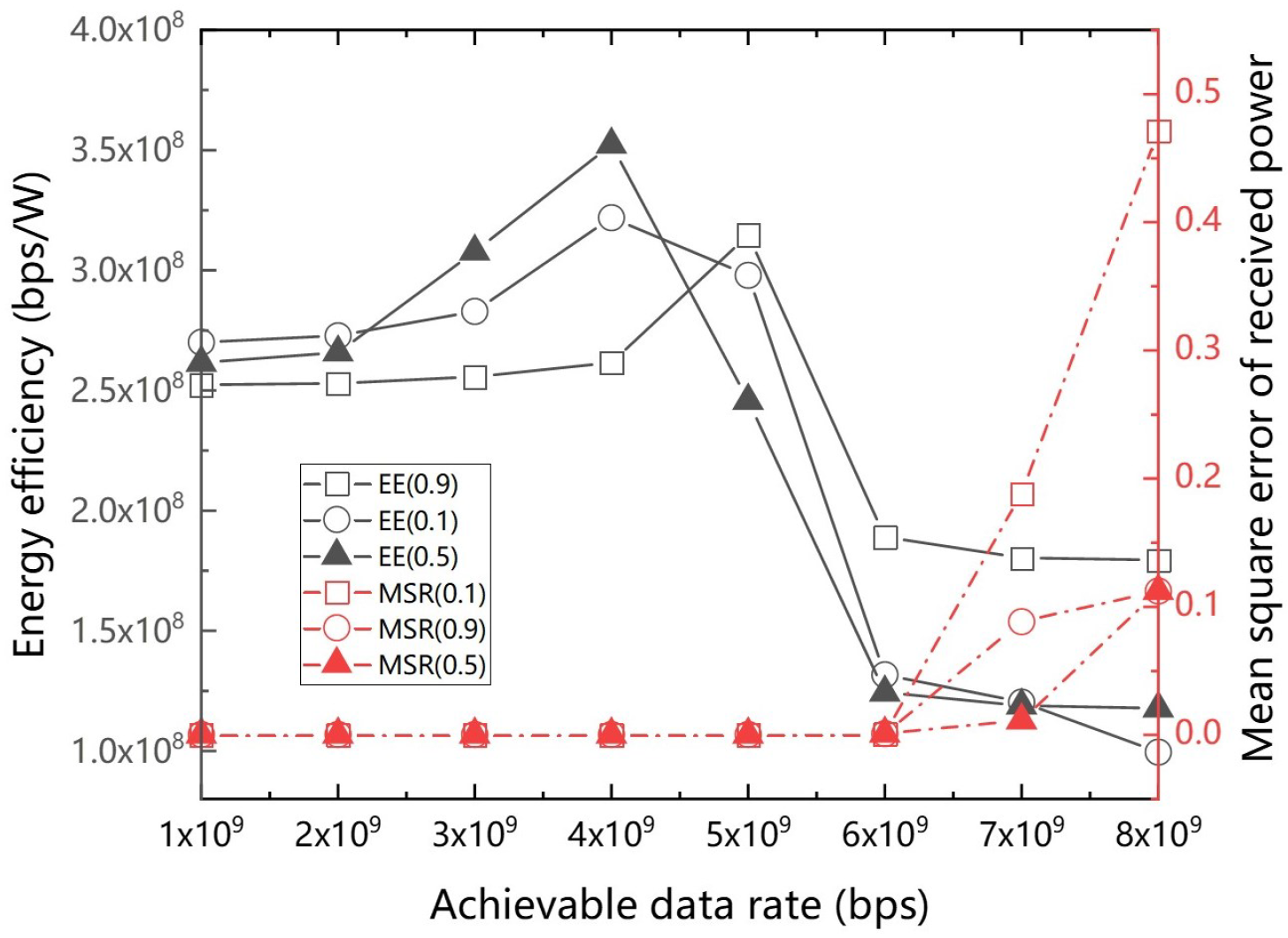
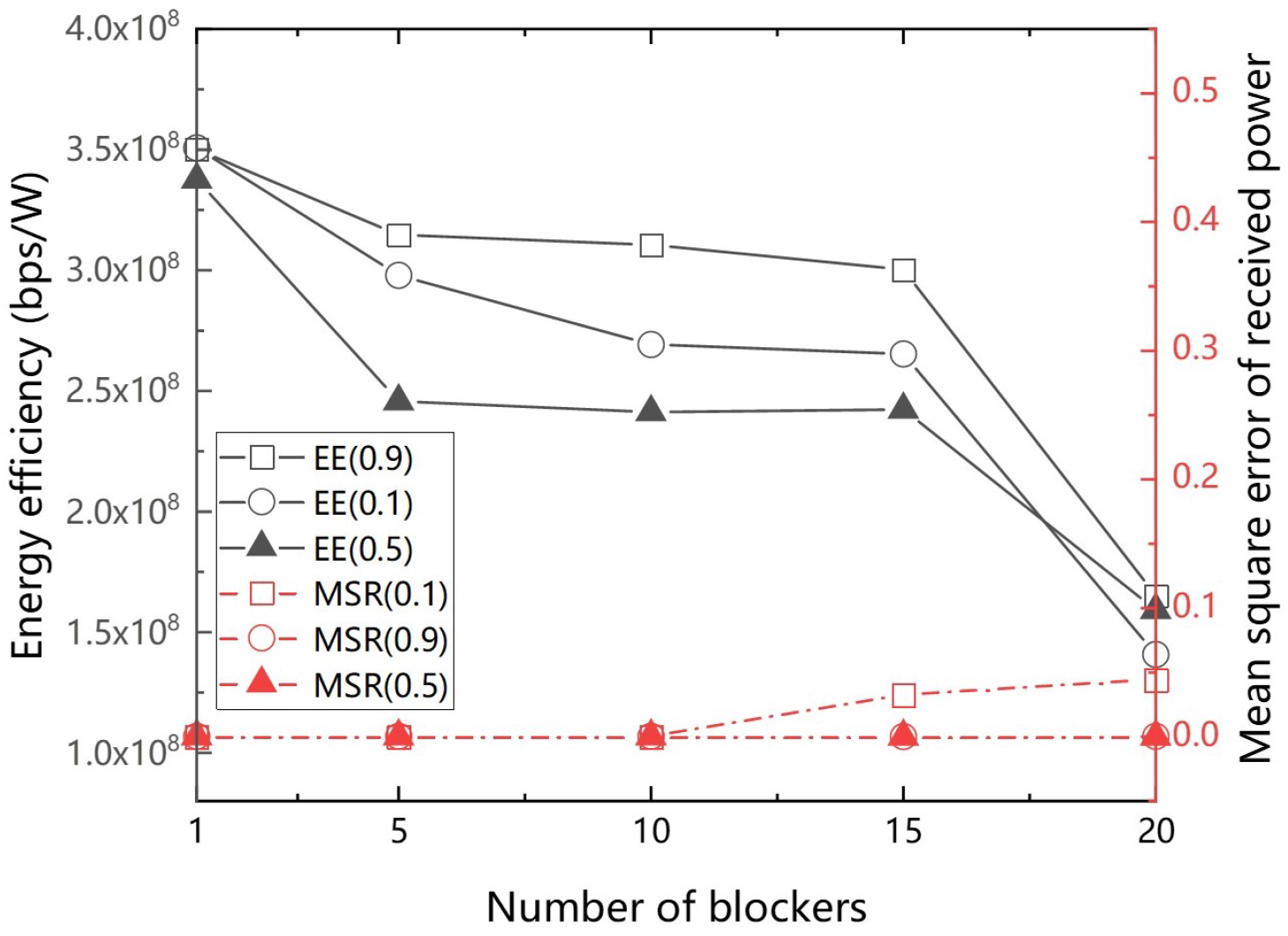
4. Simulation Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saad, W.; Bennis, M.; Chen, M. A vision of 6G wireless systems: Applications, trends, technologies, and open research problems. IEEE Netw. 2019, 34, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Yang, F.; Song, J.; Han, Z. Joint resource management for intelligent reflecting surface–aided visible light communications. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2022, 21, 6508–6522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Chen, M.; Saad, W.; Xu, W.; Shikh-Bahaei, M.; Poor, H.V.; Cui, S. Energy-efficient wireless communications with distributed reconfigurable intelligent surfaces. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2021, 21, 665–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Zhou, G.; Zhi, K.; Hong, S.; Wu, T.; Pan, Y.; Ren, H.; Di Renzo, M.; Swindlehurst, A.L.; Zhang, R.; et al. An overview of signal processing techniques for RIS/IRS-aided wireless systems. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2022, 16, 883–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hail, C.U.; Michel, A.K.U.; Poulikakos, D.; Eghlidi, H. Optical metasurfaces: Evolving from passive to adaptive. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2019, 7, 1801786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.G.; Sun, Y.L.; Zhu, B.; Jiang, W.X.; Yu, Q.; Tian, H.W.; Qiu, C.W.; Zhang, Z.; Cui, T.J. A metasurface-based light-to-microwave transmitter for hybrid wireless communications. Light Sci. Appl. 2022, 11, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X. Wireless power transfer empowered by reconfigurable intelligent surfaces. IEEE Syst. J. 2020, 15, 2121–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Liang, Y.C.; Chen, J.; Larsson, E.G. Weighted sum-rate maximization for reconfigurable intelligent surface aided wireless networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2020, 19, 3064–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zappone, A.; Alexandropoulos, G.C.; Debbah, M.; Yuen, C. Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces for energy efficiency in wireless communication. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2019, 18, 4157–4170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhady, A.M.; Salem, A.K.S.; Amin, O.; Shihada, B.; Alouini, M.S. Visible light communications via intelligent reflecting surfaces: Metasurfaces vs mirror arrays. IEEE Open J. Commun. Soc. 2020, 2, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Sun, Z.; Jornet, J.M.; Pados, D. Increasing indoor spectrum sharing capacity using smart reflect-array. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 22–27 May 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ndjiongue, A.R.; Ngatched, T.M.; Dobre, O.A.; Haas, H. Toward the use of re-configurable intelligent surfaces in VLC systems: Beam steering. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2021, 28, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abumarshoud, H.; Selim, B.; Tatipamula, M.; Haas, H. Intelligent reflecting surfaces for enhanced NOMA-based visible light communications. In Proceedings of the ICC 2022-IEEE International Conference on Communications, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 16–20 May 2022; pp. 571–576. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.; Huang, H.; Wang, J.B.; Qiu, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y. Energy-Efficient Precoding Design for Downlink IRS-Assisted URLLC System. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Information Communication and Software Engineering (ICICSE), Chongqing, China, 18–20 March 2022; pp. 141–145. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Jin, D.; Yuan, J.; Han, Z. Coalitional games for resource allocation in the device-to-device uplink underlaying cellular networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2014, 13, 3965–3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komine, T.; Nakagawa, M. Fundamental analysis for visible-light communication system using LED lights. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2004, 50, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboagye, S.; Ngatched, T.M.; Dobre, O.A.; Ndjiongue, A.R. Intelligent reflecting surface-aided indoor visible light communication systems. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2021, 25, 3913–3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Wang, P.; Li, G.; Wang, H.; Li, S.; Shi, H.; He, H.; Shi, F.; Chi, S. Average signal-to-noise ratio maximization for an intelligent reflecting surface and angle diversity receiver jointly assisted indoor visible light communication system. Appl. Opt. 2022, 61, 10390–10399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basar, E. Reconfigurable intelligent surface-based index modulation: A new beyond MIMO paradigm for 6G. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2020, 68, 3187–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björnson, E.; Özdogan, Ö.; Larsson, E.G. Intelligent reflecting surface versus decode-and-forward: How large surfaces are needed to beat relaying? IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2019, 9, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, J.; Feng, L.; Chen, H.; Xue, Z. Robust layout optimization for intelligent reflecting surfaces-based visible light communication systems. Appl. Opt. 2024, 63, 2020–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.B.; Hu, Q.S.; Wang, J.; Chen, M.; Wang, J.Y. Tight bounds on channel capacity for dimmable visible light communications. J. Light. Technol. 2013, 31, 3771–3779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, Y.; Song, Q. Energy efficiency maximization for IRS-aided WPCNs. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2021, 10, 2304–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
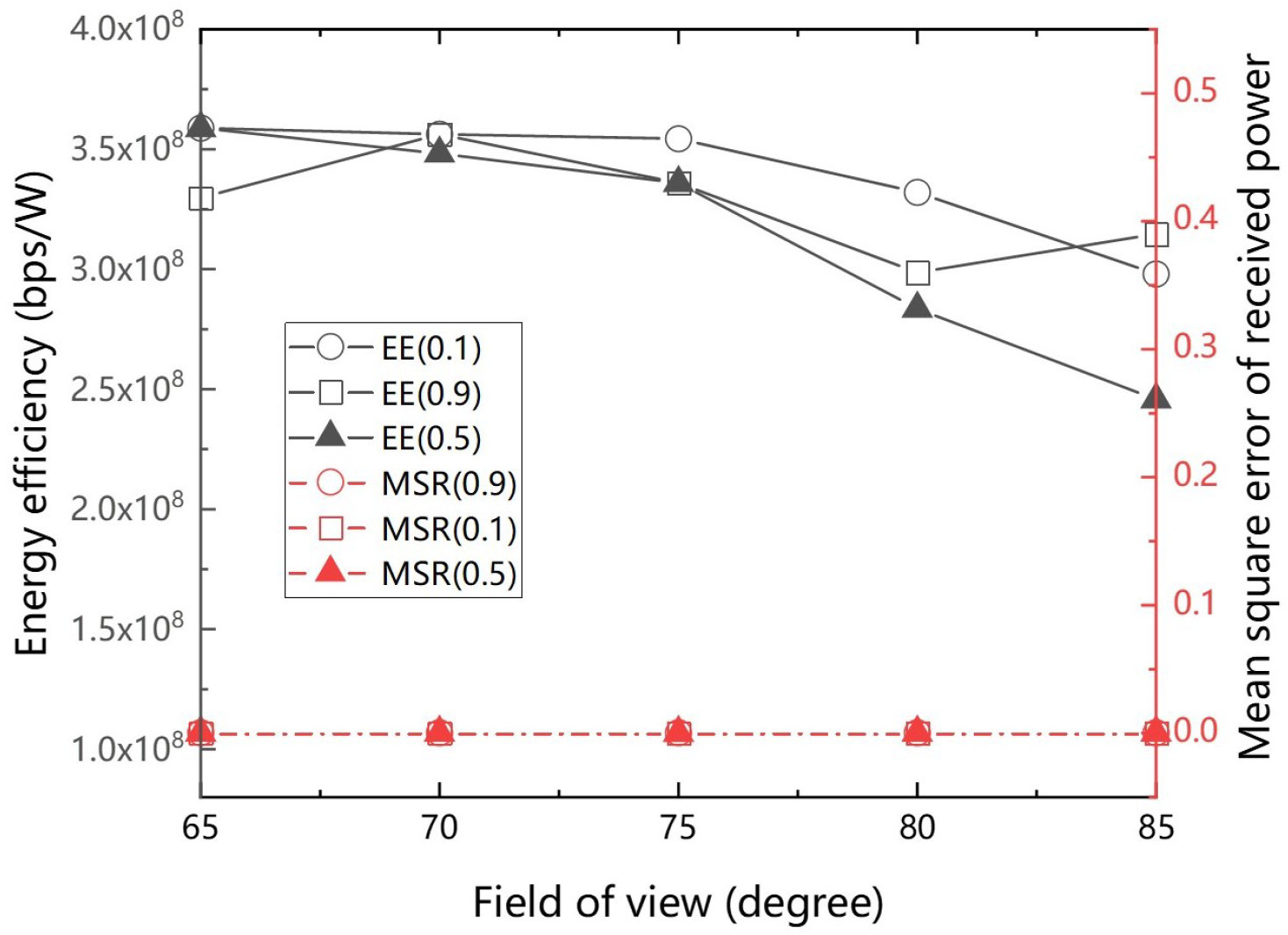
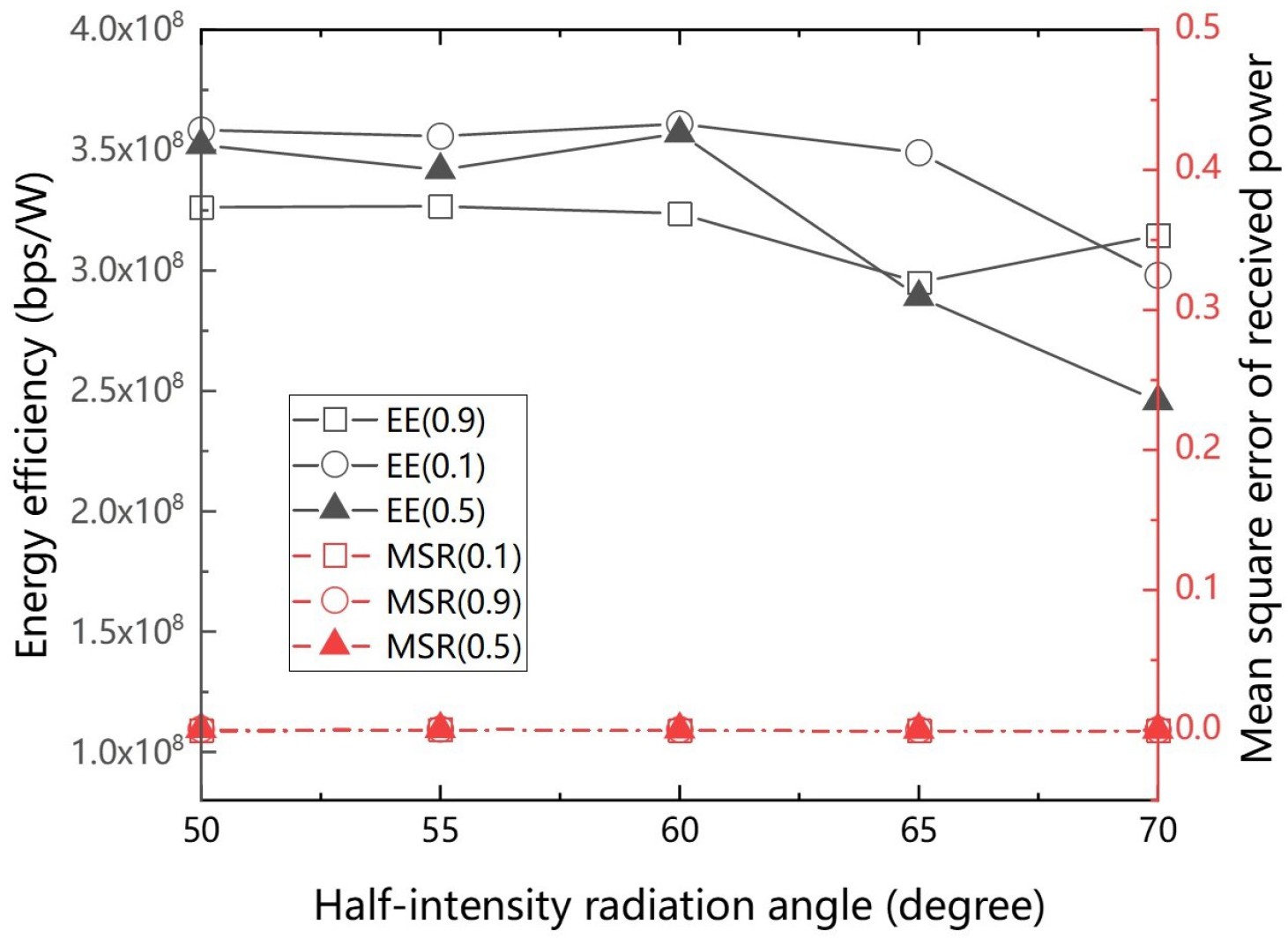

| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Scene size (length × width × height) | 5 × 5 × 3 |
| IRS element size (length × height) | × |
| FOV | |
| PD responsivity | 0.53 A/W |
| Power spectral density of noise | /Hz |
| Optical filter gain | 1 |
| Lens index of refraction | 1.5 |
| 0.8 | |
| 0.95 | |
| System bandwidth | 200 MHz |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.; Wang, J.; Feng, L.; Lu, H.; Sun, H.; Hu, R.Q. Coalitional Game Theory-Based Resource Allocation Strategy for Robust IRS-VLC System. Photonics 2024, 11, 582. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11060582
Liu C, Wang J, Feng L, Lu H, Sun H, Hu RQ. Coalitional Game Theory-Based Resource Allocation Strategy for Robust IRS-VLC System. Photonics. 2024; 11(6):582. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11060582
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Changling, Jianping Wang, Lifang Feng, Huimin Lu, Haijian Sun, and Rose Qingyang Hu. 2024. "Coalitional Game Theory-Based Resource Allocation Strategy for Robust IRS-VLC System" Photonics 11, no. 6: 582. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11060582
APA StyleLiu, C., Wang, J., Feng, L., Lu, H., Sun, H., & Hu, R. Q. (2024). Coalitional Game Theory-Based Resource Allocation Strategy for Robust IRS-VLC System. Photonics, 11(6), 582. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11060582





