Compact Quantum Random Number Generator Based on a Laser Diode and a Hybrid Chip with Integrated Silicon Photonics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. QRNG Structure
3. QRNG Noise
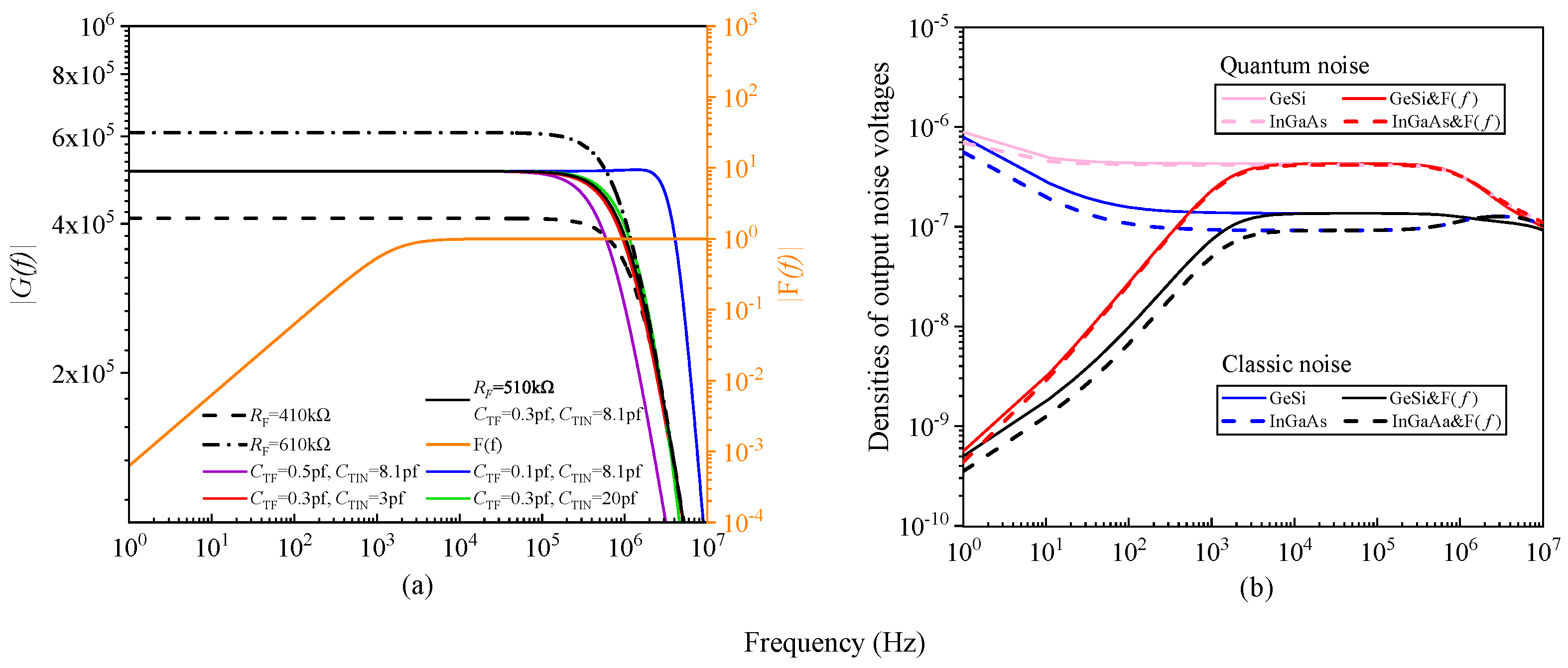
3.1. BHD Noise Analysis
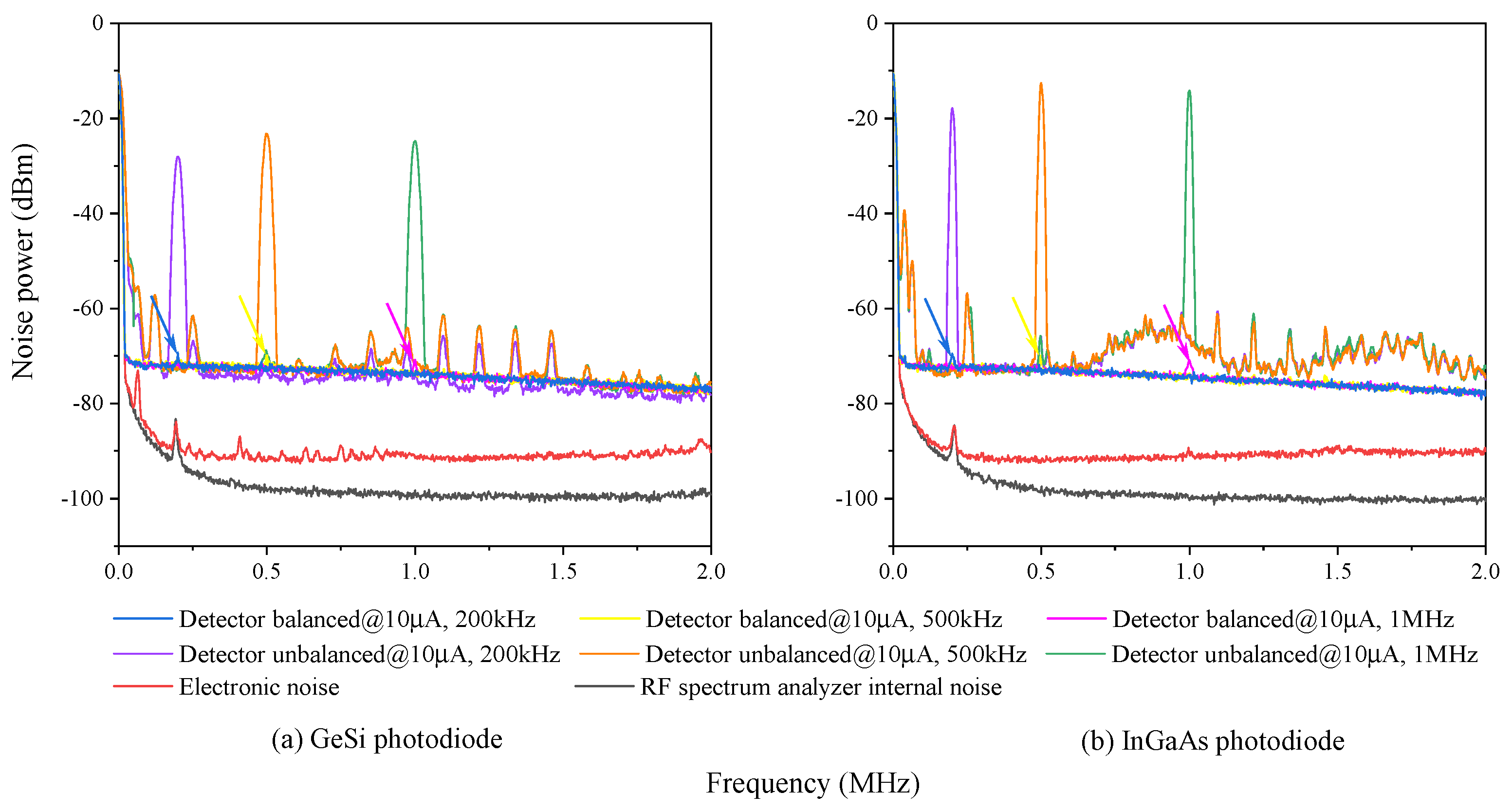
3.2. BHD Noise Power Measurement
3.3. CMRR
4. Generation of Quantum Random Number
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Herrero-Collantes, M.; Garcia-Escartin, J.C. Quantum random number generators. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2017, 89, 015004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Yuan, X.; Cao, Z.; Qi, B.; Zhang, Z. Quantum random number generation. Npj Quantum Inf. 2016, 2, 16021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauke, H.; Mertens, S. Random numbers for large-scale distributed Monte Carlo simulations. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2006, 75, 066701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.; Sanguinetti, B.; Lim, C.C.W.; Houlmann, R.; Zbinden, H. Quantum Random Number Generation for 1.25-GHz Quantum Key Distribution Systems. J. Light. Technol. 2015, 33, 2855–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Lu, Z.; Wang, P.; Tian, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, Y. Experimental demonstration of multiparty quantum secret sharing and conference key agreement. Npj Quantum Inf. 2023, 9, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, P.; Lu, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, Y. High-performance long-distance discrete-modulation continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Opt. Lett. 2023, 48, 2953–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, K.; Li, W.; Tan, H.; Li, Y.; Min, H.; Zhang, W.J.; Li, H.; You, L.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, X.; et al. High-speed measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution with integrated silicon photonics. Phys. Rev. X 2020, 10, 031030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, K.; Hu, X.; Du, Y.; Hua, X.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, Y.; Huang, C.; Xiao, X. Resource-efficient quantum key distribution with integrated silicon photonics. Photonics Res. 2023, 11, 1364–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Zhu, X.; Hua, X.; Zhao, Z.; Hu, X.; Qian, Y.; Xiao, X.; Wei, K. Silicon-based decoder for polarization-encoding quantum key distribution. Chip 2023, 2, 100039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Chen, Y.; Jin, L.; Geng, M.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, K. Experimental secure quantum key distribution in the presence of polarization-dependent loss. Phys. Rev. A 2022, 105, 012421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennewein, T.; Achleitner, U.; Weihs, G.; Weinfurter, H.; Zeilinger, A. A Fast and Compact Quantum Random Number Generator. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2000, 71, 1675–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stipcevic, M.; Rogina, B.M. Quantum random number generator based on photonic emission in semiconductors. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2007, 78, 045104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wayne, M.A.; Jeffrey, E.R.; Akselrod, G.M.; Kwiat, P.G. Photon arrival time quantum random number generation. J. Mod. Opt. 2009, 56, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahl, M.; Leifgen, M.; Berlin, M.; Röhlicke, T.; Rahn, H.J.; Benson, O. An ultrafast quantum random number generator with provably bounded output bias based on photon arrival time measurements. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 171105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fürst, H.; Weier, H.; Nauerth, S.; Marangon, D.G.; Kurtsiefer, C.; Weinfurter, H. High speed optical quantum random number generation. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 13029–13037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, M.; Wu, E.; Liang, Y.; Jian, Y.; Wu, G.; Zeng, H. Quantum random-number generator based on a photon-number-resolving detector. Phys. Rev. A 2011, 83, 023820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Guo, H. Bias-free true random-number generator. Opt. Lett. 2009, 34, 1876–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, C.; Wittmann, C.; Sych, D.; Dong, R.; Mauerer, W.; Andersen, U.L.; Marquardt, C.; Leuchs, G. A generator for unique quantum random numbers based on vacuum states. Nat. Photonics 2010, 4, 711–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Tian, L.; Zou, H. Practical quantum random number generator based on measuring the shot noise of vacuum states. Phys. Rev. A 2010, 81, 063814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Symul, T.; Assad, S.M.; Lam, P.K. Real time demonstration of high bitrate quantum random number generation with coherent laser light. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 231103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Tang, W.; Liu, Y.; Wei, W. Truly random number generation based on measurement of phase noise of a laser. Phys. Rev. E 2010, 81, 051137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, B.; Chi, Y.M.; Lo, H.K.; Qian, L. High-speed quantum random number generation by measuring phase noise of a single-mode laser. Opt. Lett. 2010, 35, 312–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jofre, M.; Curty, M.; Steinlechner, F.; Anzolin, G.; Torres, J.; Mitchell, M.; Pruneri, V. True random numbers from amplified quantum vacuum. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 20665–20672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.R.; Salevan, J.C.; Li, X.; Roy, R.; Murphy, T.E. Fast physical random number generator using amplified spontaneous emission. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 23584–23597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustard, P.J.; Moffatt, D.; Lausten, R.; Wu, G.; Walmsley, I.A.; Sussman, B.J. Quantum random bit generation using stimulated Raman scattering. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 25173–25180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marandi, A.; Leindecker, N.C.; Vodopyanov, K.L.; Byer, R.L. Twin Degenerate OPO for Quantum Random Bit Generation. In Proceedings of the Nonlinear Optics: Materials, Fundamentals and Applications, Kauai, HI, USA, 17–22 July 2011; Optica Publishing Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; p. NME4. [Google Scholar]
- Bruynsteen, C.; Gehring, T.; Lupo, C.; Bauwelinck, J.; Yin, X. 100-Gbit/s integrated quantum random number generator based on vacuum fluctuations. PRX Quantum 2023, 4, 010330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffaelli, F.; Ferranti, G.; Mahler, D.H.; Sibson, P.; Kennard, J.E.; Santamato, A.; Sinclair, G.; Bonneau, D.; Thompson, M.G.; Matthews, J.C. A homodyne detector integrated onto a photonic chip for measuring quantum states and generating random numbers. Quantum Sci. Technol. 2018, 3, 025003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasker, J.F.; Frazer, J.; Ferranti, G.; Allen, E.J.; Brunel, L.F.; Tanzilli, S.; D’Auria, V.; Matthews, J.C. Silicon photonics interfaced with integrated electronics for 9 GHz measurement of squeezed light. Nat. Photonics 2021, 15, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruynsteen, C.; Vanhoecke, M.; Bauwelinck, J.; Yin, X. Integrated balanced homodyne photonic–electronic detector for beyond 20 GHz shot-noise-limited measurements. Optica 2021, 8, 1146–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.; Huang, J.; Qiao, G.R.; Nie, Y.Q.; Tang, W.; Chu, T.; Zhang, J.; Pan, J.W. 18.8 Gbps real-time quantum random number generator with a photonic integrated chip. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2021, 118, 264001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abellan, C.; Amaya, W.; Domenech, D.; Muñoz, P.; Capmany, J.; Longhi, S.; Mitchell, M.W.; Pruneri, V. Quantum entropy source on an InP photonic integrated circuit for random number generation. Optica 2016, 3, 989–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siew, S.Y.; Li, B.; Gao, F.; Zheng, H.Y.; Zhang, W.; Guo, P.; Xie, S.W.; Song, A.; Dong, B.; Luo, L.W.; et al. Review of silicon photonics technology and platform development. J. Light. Technol. 2021, 39, 4374–4389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, P.; Boes, A.; Ren, G.; Nguyen, T.G.; Roelkens, G.; Mitchell, A. Hybrid and heterogeneous photonic integration. APL Photonics 2021, 6, 061102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.Y.; Ding, Y.Y.; Wang, S.; Yin, Z.Q.; Chen, W.; He, D.Y.; Huang, W.; Xu, B.J.; Guo, G.C.; Han, Z.F. Compact quantum random number generation using a linear optocoupler. Opt. Lett. 2021, 46, 3175–3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Wang, X.; Hu, X.; Hua, X.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhang, S.; Xiao, X.; Yu, S.; Zou, J.; et al. Silicon photonics-integrated time-domain balanced homodyne detector in continuous-variable quantum key distribution. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.03419. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Xiang, X.; Zhou, C.; Zhai, Y.; Quan, R.; Wang, M.; Hou, F.; Zhang, S.; Dong, R.; Liu, T. Simulation of high SNR photodetector with LC coupling and transimpedance amplifier circuit and its verification. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2017, 88, 013107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masalov, A.; Kuzhamuratov, A.; Lvovsky, A. Noise spectra in balanced optical detectors based on transimpedance amplifiers. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2017, 88, 113109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Su, J.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, C.; Wang, W.; Peng, K. Balanced homodyne detection with high common mode rejection ratio based on parameter compensation of two arbitrary photodiodes. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 23859–23866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Guo, X.B.; Jia, Y.X.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Z.G.; Liu, J.Q.; Li, Y.M. Accurate shot-noise-limited calibration of a time-domain balanced homodyne detector for continuous-variable quantum key distribution. J. Light. Technol. 2023, 41, 5518–5528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haw, J.Y.; Assad, S.; Lance, A.; Ng, N.; Sharma, V.; Lam, P.K.; Symul, T. Maximization of extractable randomness in a quantum random-number generator. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2015, 3, 054004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, P.; Li, Y.; Peng, K. Quantum random number generator with discarding-boundary-bin measurement and multi-interval sampling. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 12440–12453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Gain | (V) | μA (V) | μA (V) | μA (V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 0.0058 | 0.0153 | 0.0474 | 0.1537 |
| 20 | 0.0112 | 0.0267 | 0.0933 | 0.2923 |
| 50 | 0.0282 | 0.0746 | 0.2068 | 0.6607 |
| 100 | 0.0566 | 0.1386 | 0.4402 | 1.3764 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Zheng, T.; Jia, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhu, X.; Shi, Y.; Wang, N.; Lu, Z.; Zou, J.; Li, Y. Compact Quantum Random Number Generator Based on a Laser Diode and a Hybrid Chip with Integrated Silicon Photonics. Photonics 2024, 11, 468. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11050468
Wang X, Zheng T, Jia Y, Huang J, Zhu X, Shi Y, Wang N, Lu Z, Zou J, Li Y. Compact Quantum Random Number Generator Based on a Laser Diode and a Hybrid Chip with Integrated Silicon Photonics. Photonics. 2024; 11(5):468. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11050468
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xuyang, Tao Zheng, Yanxiang Jia, Jin Huang, Xinyi Zhu, Yuqi Shi, Ning Wang, Zhenguo Lu, Jun Zou, and Yongmin Li. 2024. "Compact Quantum Random Number Generator Based on a Laser Diode and a Hybrid Chip with Integrated Silicon Photonics" Photonics 11, no. 5: 468. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11050468
APA StyleWang, X., Zheng, T., Jia, Y., Huang, J., Zhu, X., Shi, Y., Wang, N., Lu, Z., Zou, J., & Li, Y. (2024). Compact Quantum Random Number Generator Based on a Laser Diode and a Hybrid Chip with Integrated Silicon Photonics. Photonics, 11(5), 468. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11050468






