Direct Numerical Modeling as a Tool for Optical Coherence Tomography Development: SNR (Sensitivity) and Lateral Resolution Test Target Interpretation
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. SNR and Sensitivity
1.2. USAF 1951 Target
2. Materials and Methods
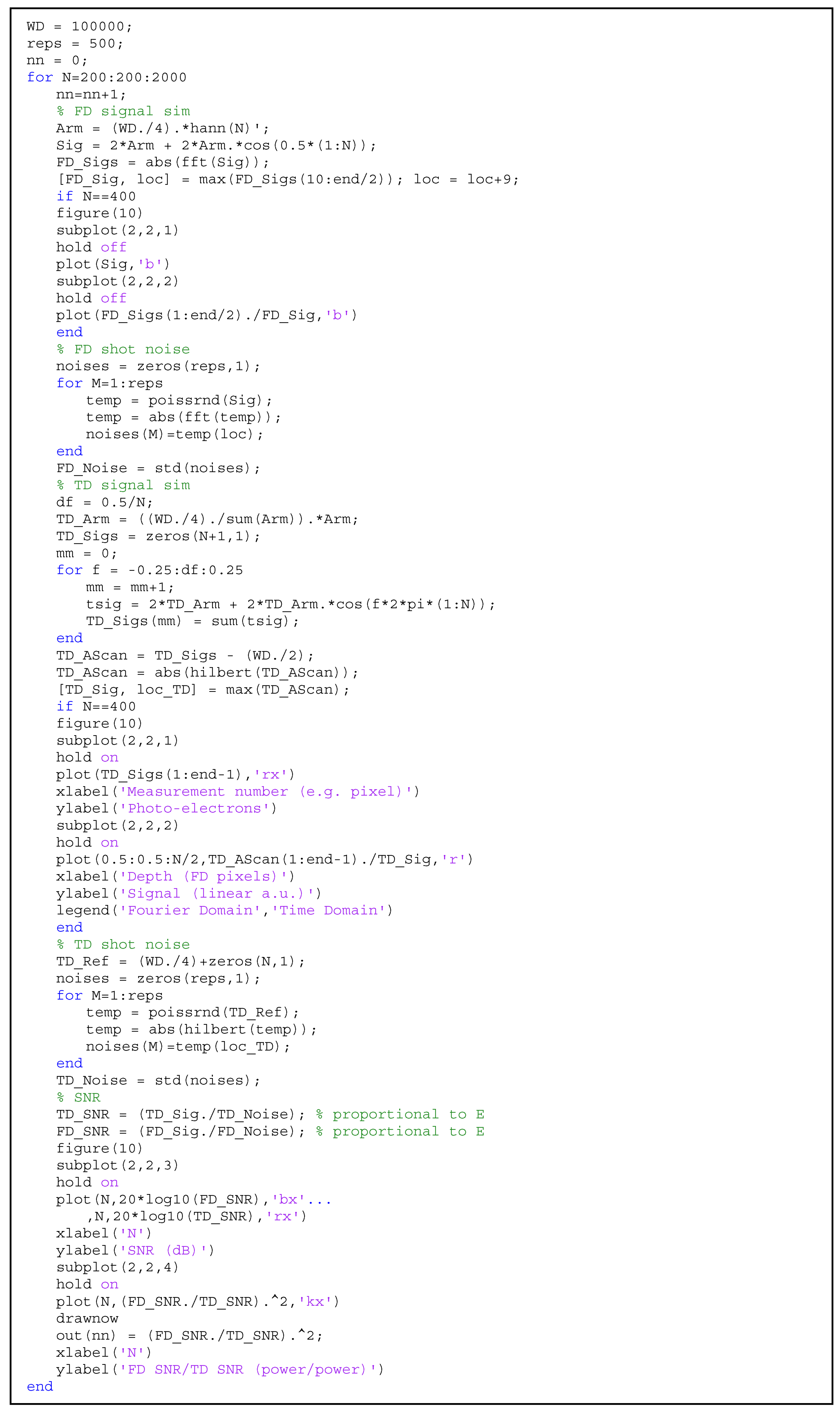
2.1. SNR Model
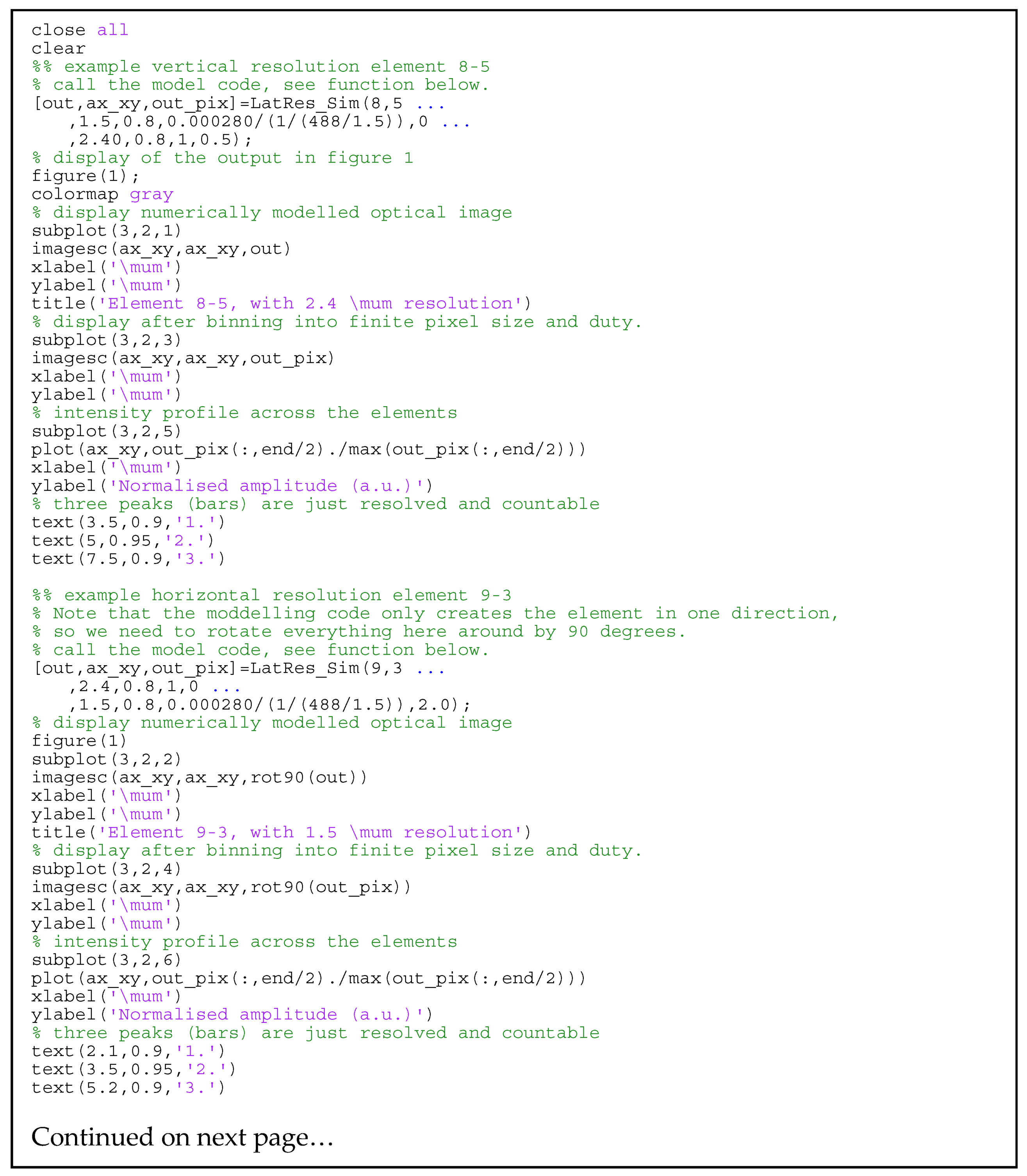
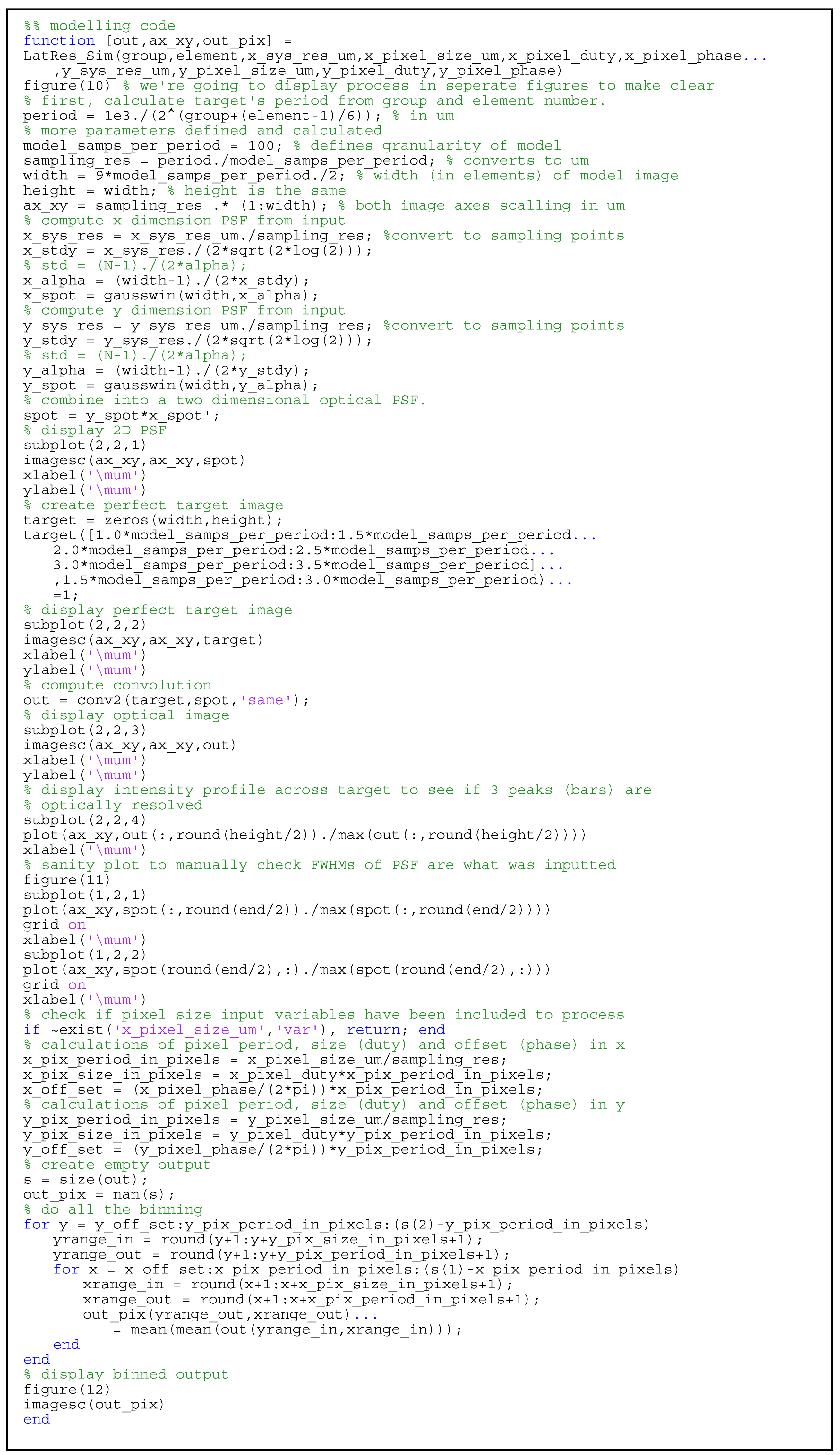
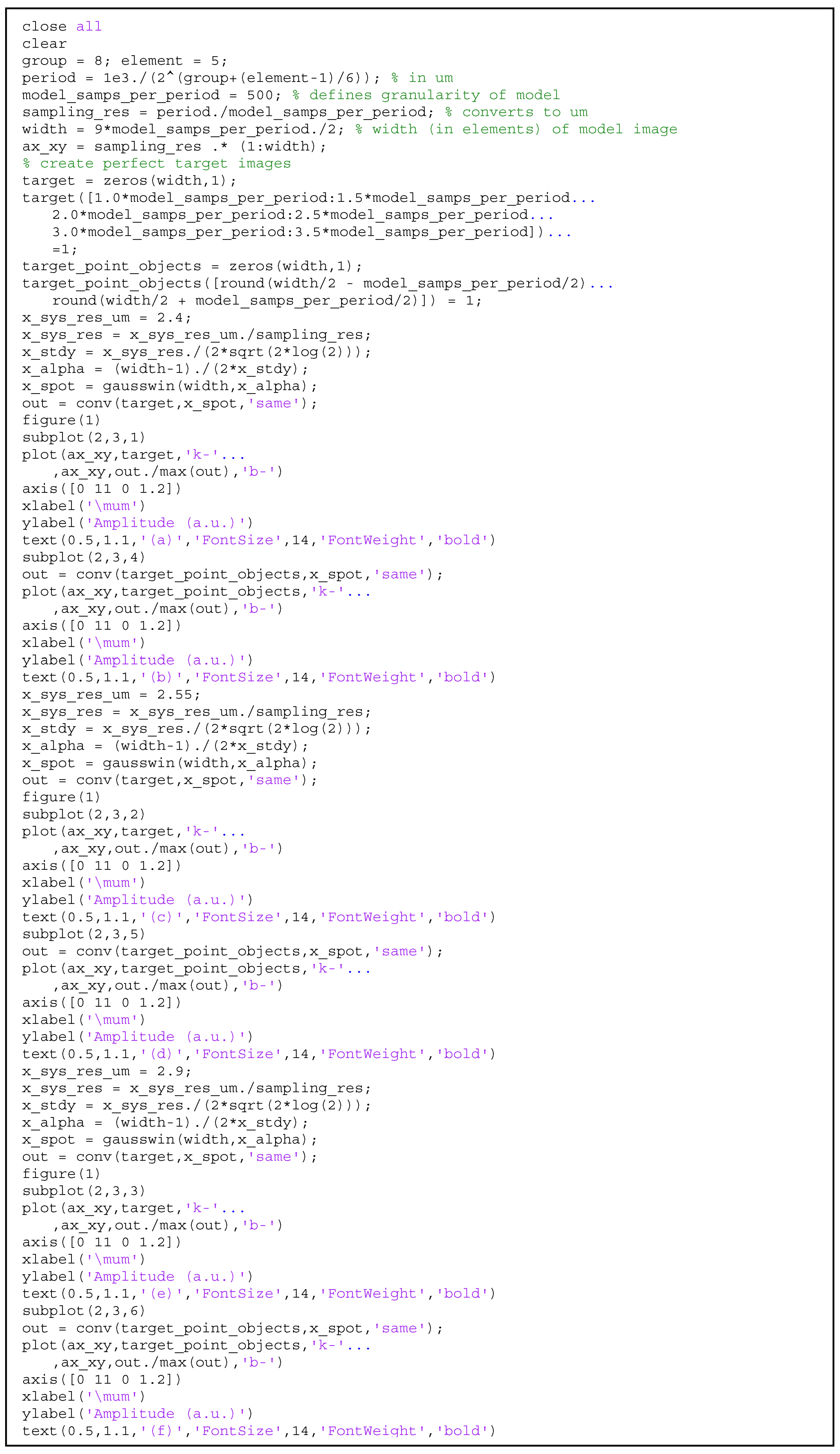
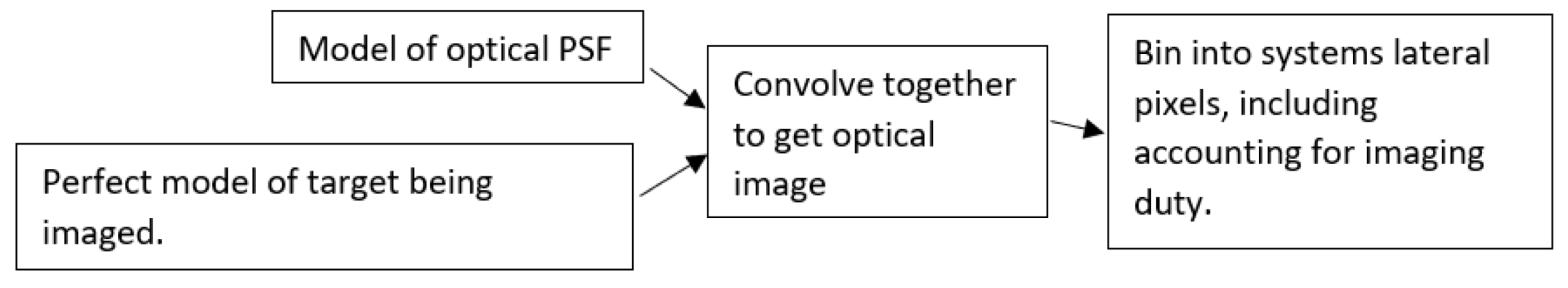
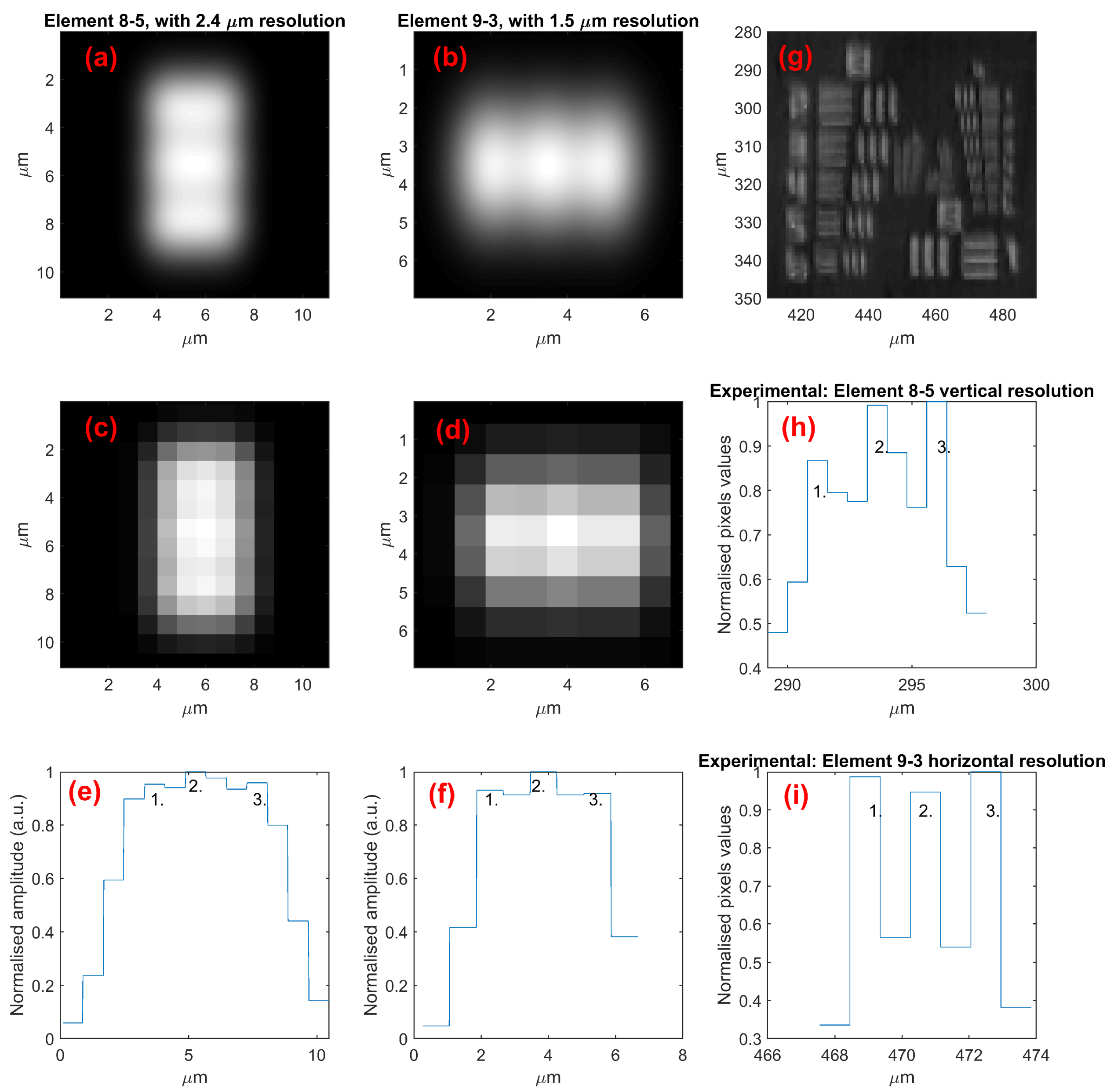
2.2. Lateral Resolution Modeling
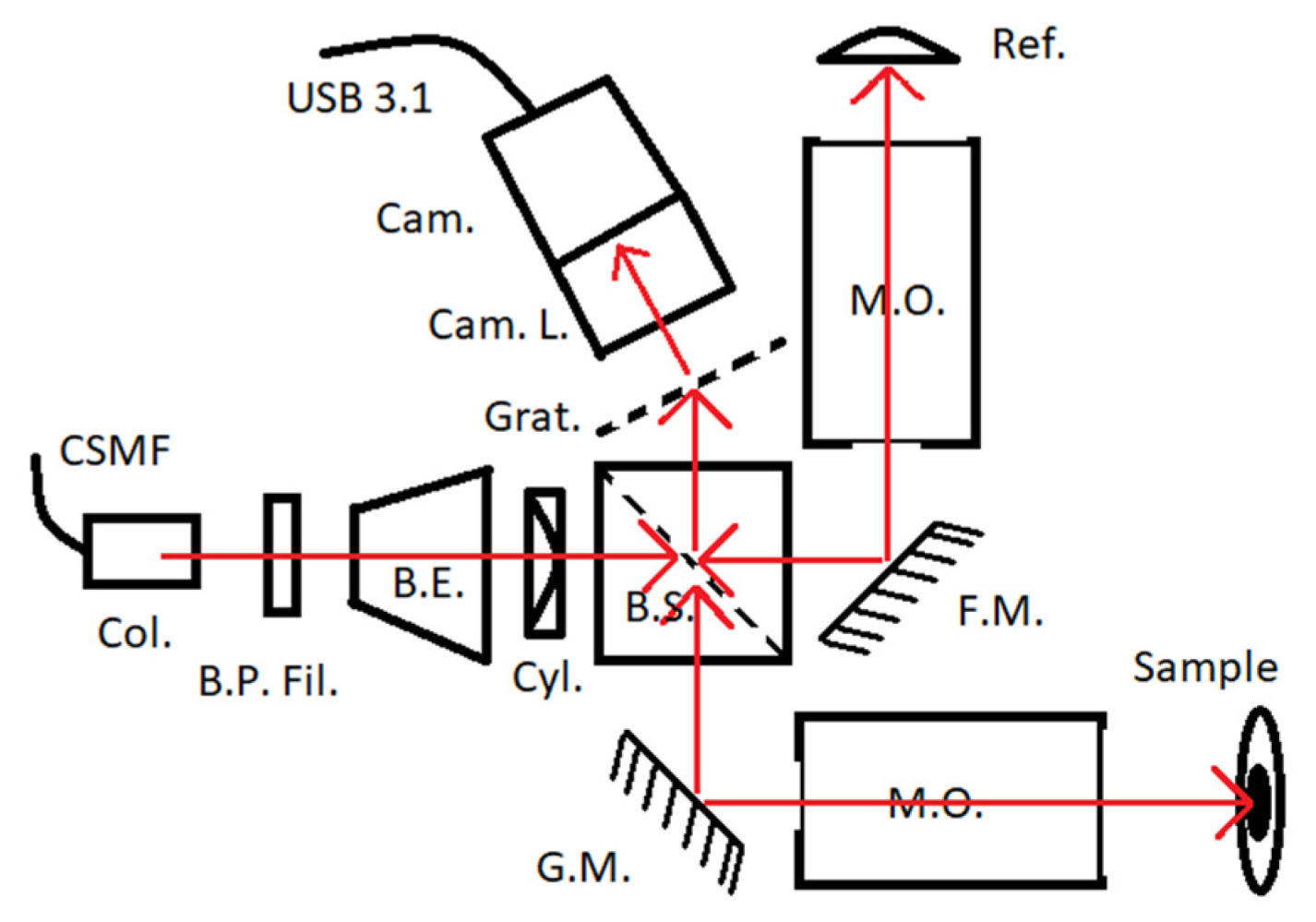
2.3. Hardware Used for Validation
3. Results
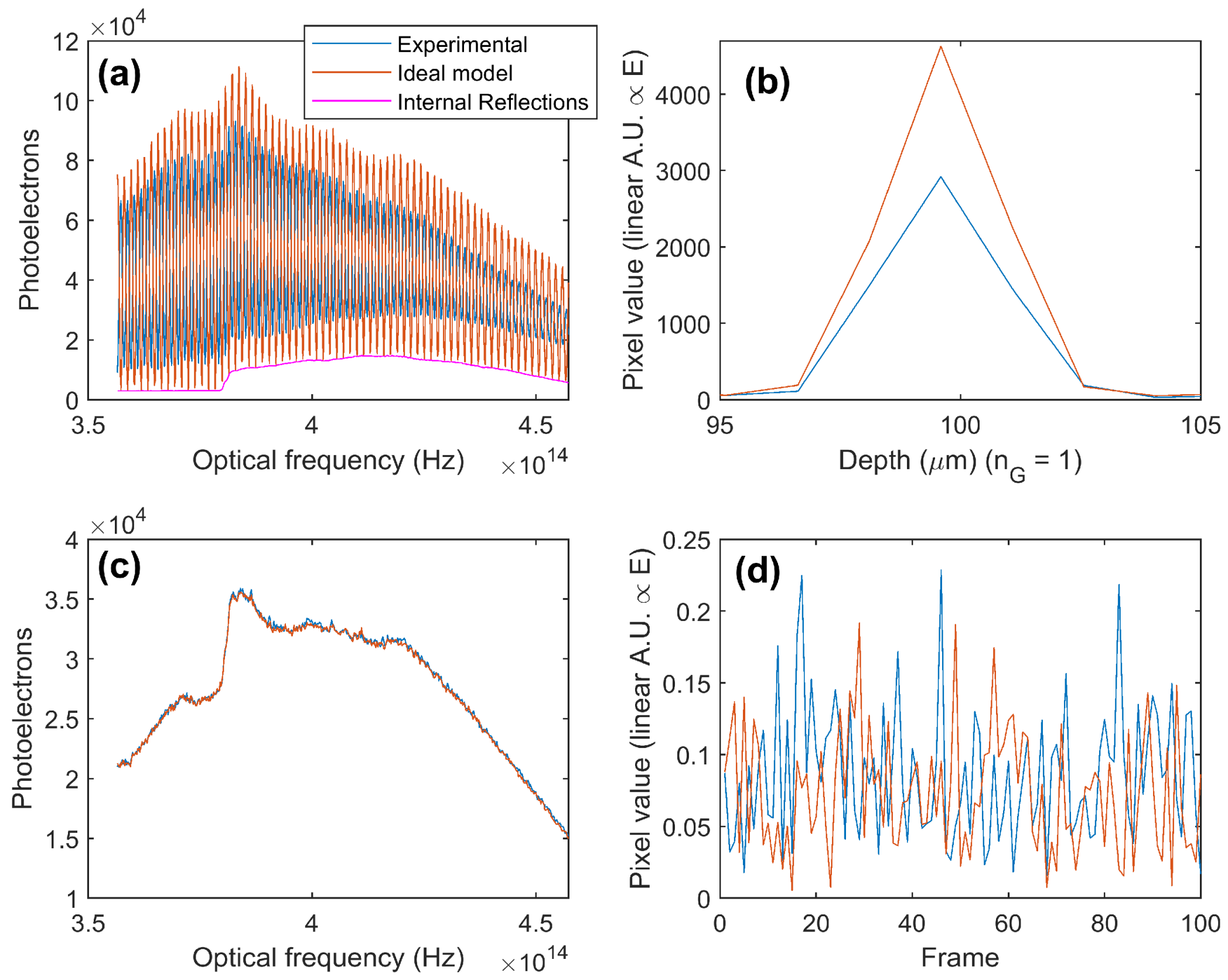
3.1. OCT SNR: Practical Evaluation
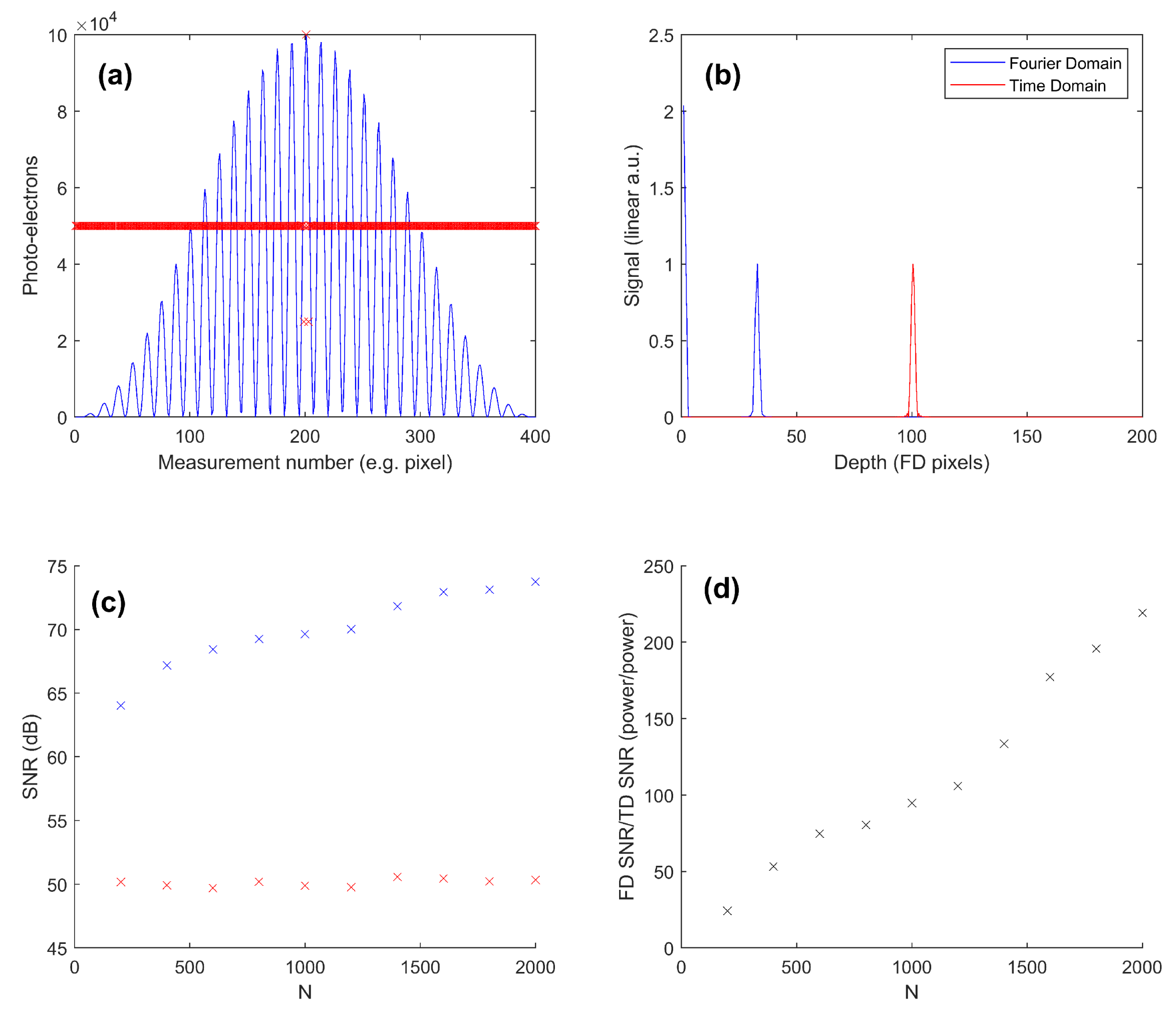
3.2. OCT SNR: Theoretical Comparison of Time-Domain and Fourier-Domain Shot Noise Limits
3.3. Lateral Resolution
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Bouma, B.E.; de Boer, J.F.; Huang, D.; Jang, I.-K.; Yonetsu, T.; Leggett, C.L.; Leitgeb, R.; Sampson, D.D.; Suter, M.; Vakoc, B.J. Optical coherence tomography. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 2022, 2, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fercher, A.F.; Drexler, W.; Hitzenberger, C.K.; Lasser, T. Optical coherence tomography—Principles and applications. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2003, 66, 239–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brezinski, M.E. Optical Coherence Tomography: Principles and Applications; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Duker, J.S.; Waheed, N.K.; Goldman, D. Handbook of Retinal OCT: Optical Coherence Tomography E-Book; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ang, M.; Baskaran, M.; Werkmeister, R.M.; Chua, J.; Schmidl, D.; Aranha Dos Santos, V.; Garhöfer, G.; Mehta, J.S.; Schmetterer, L. Anterior segment optical coherence tomography. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2018, 66, 132–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, B.; Ganier, C.; Du-Harpur, X.; Harun, N.; Watt, F.; Patalay, R.; Lynch, M. Applications and future directions for optical coherence tomography in dermatology. Br. J. Dermatol. 2021, 184, 1014–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araki, M.; Park, S.-J.; Dauerman, H.L.; Uemura, S.; Kim, J.-S.; Di Mario, C.; Johnson, T.W.; Guagliumi, G.; Kastrati, A.; Joner, M. Optical coherence tomography in coronary atherosclerosis assessment and intervention. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2022, 19, 684–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, J.A.; Bouma, B.E.; Bressner, J.; Shishkov, M.; Lauwers, G.Y.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Nishioka, N.S.; Tearney, G.J. Identifying intestinal metaplasia at the squamocolumnar junction by using optical coherence tomography. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2007, 65, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machoy, M.; Seeliger, J.; Szyszka-Sommerfeld, L.; Koprowski, R.; Gedrange, T.; Woźniak, K. The use of optical coherence tomography in dental diagnostics: A state-of-the-art review. J. Healthc. Eng. 2017, 2017, 7560645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spaide, R.F.; Fujimoto, J.G.; Waheed, N.K.; Sadda, S.R.; Staurenghi, G. Optical coherence tomography angiography. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2018, 64, 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larin, K.V.; Sampson, D.D. Optical coherence elastography–OCT at work in tissue biomechanics [Invited]. Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 1172–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, E.S.; Strimbu, C.E. Cochlear mechanics: New insights from vibrometry and optical coherence tomography. Curr. Opin. Physiol. 2020, 18, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawman, S.; Madden, P.W.; Romano, V.; Dong, Y.; Mason, S.; Williams, B.M.; Kaye, S.B.; Willoughby, C.E.; Harding, S.P.; Shen, Y.-C.; et al. Deformation velocity imaging using optical coherence tomography and its applications to the cornea. Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 5579–5593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.R. Optical Coherence Tomography and Its Non-Medical Applications; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Stifter, D. Beyond biomedicine: A review of alternative applications and developments for optical coherence tomography. Appl. Phys. B Lasers Opt. 2007, 88, 337–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawman, S.; Zhang, J.; Williams, B.M.; Zheng, Y.; Shen, Y. Applications of optical coherence tomography in the non-contact assessment of automotive paints. In Proceedings of the SPIE Optical Metrology, Munich, Germany, 25–29 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Markl, D.; Hannesschlager, G.; Sacher, S.; Leitner, M.; Khinast, J.G.; Buchsbaum, A. Automated pharmaceutical tablet coating layer evaluation of optical coherence tomography images. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2015, 26, 035701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Swanson, E.A.; Lin, C.P.; Schuman, J.S.; Stinson, W.G.; Chang, W.; Hee, M.R.; Flotte, T.; Gregory, K.; Puliafito, C.A.; et al. Optical Coherence Tomography. Science 1991, 254, 1178–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuhaus, K.; Khan, S.; Thaware, O.; Ni, S.; Aga, M.; Jia, Y.; Redd, T.; Chen, S.; Huang, D.; Jian, Y. Real-time line-field optical coherence tomography for cellular resolution imaging of biological tissue. Biomed. Opt. Express 2024, 15, 1059–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Hosseinaee, Z.; Han, L.; Kralj, O.; Sorbara, L.; Bizheva, K. 250 kHz, 1.5 µm resolution SD-OCT for in-vivo cellular imaging of the human cornea. Biomed. Opt. Express 2018, 9, 6569–6583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labbé, A.; Khammari, C.; Dupas, B.; Gabison, E.; Brasnu, E.; Labetoulle, M.; Baudouin, C. Contribution of in vivo confocal microscopy to the diagnosis and management of infectious keratitis. Ocul. Surf. 2009, 7, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petropoulos, I.N.; Ponirakis, G.; Ferdousi, M.; Azmi, S.; Kalteniece, A.; Khan, A.; Gad, H.; Bashir, B.; Marshall, A.; Boulton, A.J. Corneal confocal microscopy: A biomarker for diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Clin. Ther. 2021, 43, 1457–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veselka, L.; Krainz, L.; Mindrinos, L.; Drexler, W.; Elbau, P. A quantitative model for optical coherence tomography. Sensors 2021, 21, 6864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, P.E.; Thrane, L.; Yura, H.T.; Tycho, A.; Jørgensen, T.M.; Frosz, M.H. Advanced modelling of optical coherence tomography systems. Phys. Med. Biol. 2004, 49, 1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choma, M.A.; Sarunic, M.V.; Yang, C.H.; Izatt, J.A. Sensitivity advantage of swept source and Fourier domain optical coherence tomography. Opt. Express 2003, 11, 2183–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leitgeb, R.; Hitzenberger, C.K.; Fercher, A.F. Performance of fourier domain vs. time domain optical coherence tomography. Opt. Express 2003, 11, 889–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boreman, G.D. Modulation Transfer Function in Optical and Electro-Optical Systems; SPIE Press: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2001; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- MIL-STD-150A; Photographic Lenses. Department of Defense: Washington, DC, USA,, 1959.
- Khan, S.; Neuhaus, K.; Thaware, O.; Ni, S.; Ju, M.J.; Redd, T.; Huang, D.; Jian, Y. Corneal imaging with blue-light optical coherence microscopy. Biomed. Opt. Express 2022, 13, 5004–5014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawman, S.; Dong, Y.; Williams, B.M.; Romano, V.; Kaye, S.; Harding, S.P.; Willoughby, C.; Shen, Y.C.; Zheng, Y.L. High resolution corneal and single pulse imaging with line field spectral domain optical coherence tomography. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 2395–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawman, S.; Romano, V.; Madden, P.; Mason, S.; Williams, B.; Zheng, Y.; Shen, Y.-C. Supercontinuum ultra-high resolution line-field OCT; experimental spectrograph comparison and comparison with current clinical OCT systems by the imaging of a human cornea. In Proceedings of the Second Canterbury Conference on Optical Coherence Tomography, Canterbury, UK, 6–8 September 2017; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2018; Volume 10591. [Google Scholar]
- Ossowski, P.; Curatolo, A.; Sampson, D.D.; Munro, P.R. Realistic simulation and experiment reveals the importance of scatterer microstructure in optical coherence tomography image formation. Biomed. Opt. Express 2018, 9, 3122–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawman, S.; Mason, S.; Kaye, S.B.; Shen, Y.-C.; Zheng, Y. Accurate In vivo bowman’s thickness measurement using Mirau ultrahigh axial resolution line field optical coherence tomography. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2022, 11, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao DS, S.; Jensen, M.; Grüner-Nielsen, L.; Olsen, J.T.; Heiduschka, P.; Kemper, B.; Schnekenburger, J.; Glud, M.; Mogensen, M.; Israelsen, N.M. Shot-noise limited, supercontinuum-based optical coherence tomography. Light Sci. Appl. 2021, 10, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.G.; Song, S.H.; Han, Y.B.; Kim, K.M.; Hong, S.J. Lens implementation on the GATE Monte Carlo toolkit for optical imaging simulation. J. Biomed. Opt. 2018, 23, 026003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwiegerling, J. Image simulation using decomposition of the point spread function. In Proceedings of the SPIE Optical Systems Design, Frankfurt, Germany, 14–17 May 2018; p. 1069006. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lawman, S.; Shen, Y.-C. Direct Numerical Modeling as a Tool for Optical Coherence Tomography Development: SNR (Sensitivity) and Lateral Resolution Test Target Interpretation. Photonics 2024, 11, 419. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11050419
Lawman S, Shen Y-C. Direct Numerical Modeling as a Tool for Optical Coherence Tomography Development: SNR (Sensitivity) and Lateral Resolution Test Target Interpretation. Photonics. 2024; 11(5):419. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11050419
Chicago/Turabian StyleLawman, Samuel, and Yao-Chun Shen. 2024. "Direct Numerical Modeling as a Tool for Optical Coherence Tomography Development: SNR (Sensitivity) and Lateral Resolution Test Target Interpretation" Photonics 11, no. 5: 419. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11050419
APA StyleLawman, S., & Shen, Y.-C. (2024). Direct Numerical Modeling as a Tool for Optical Coherence Tomography Development: SNR (Sensitivity) and Lateral Resolution Test Target Interpretation. Photonics, 11(5), 419. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11050419





