Sub-Nanosecond Passively Q-Switched Yellow and Orange Raman Lasers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Model and Experimental Setup
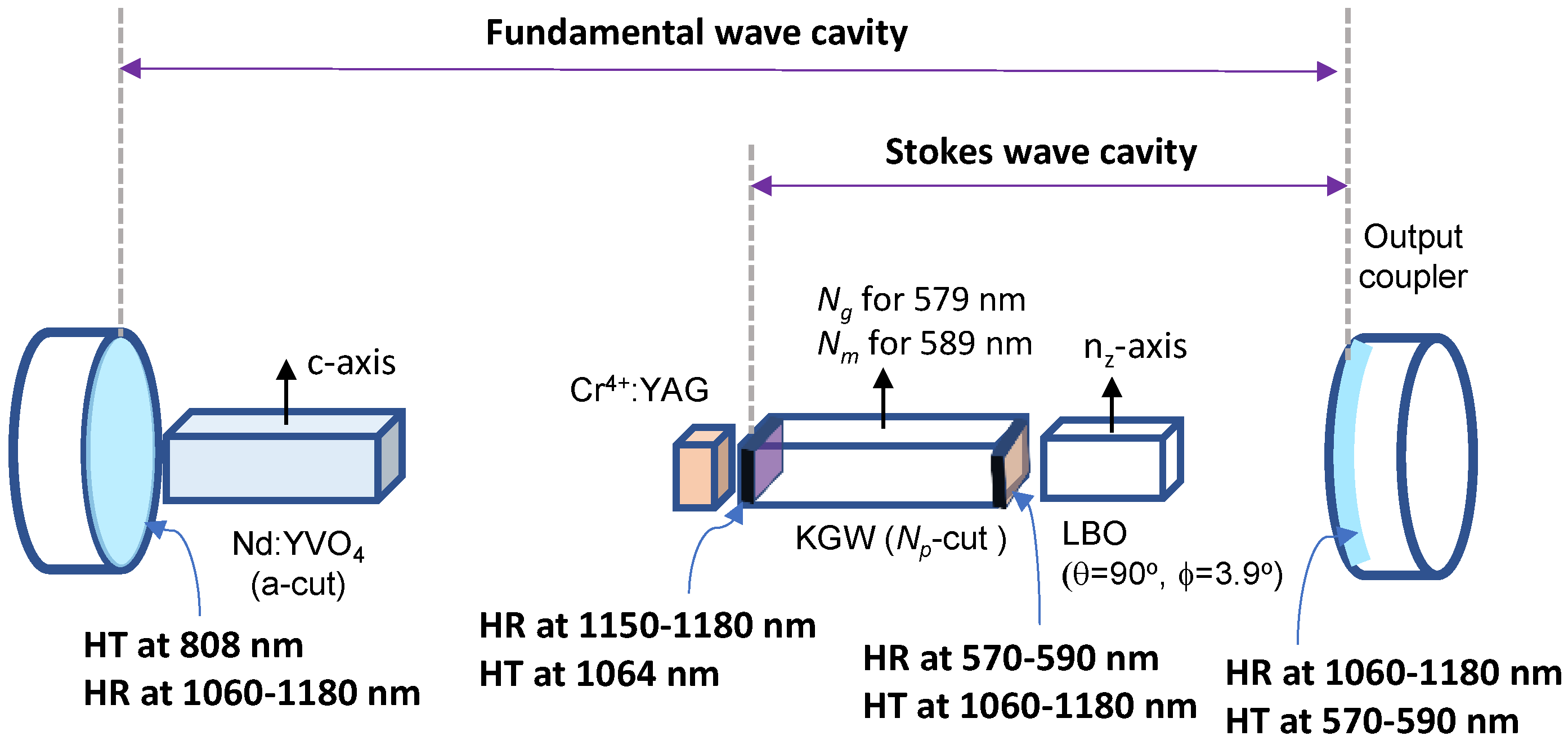
3. Cavity Design
4. Analysis of Second Harmonic Generation
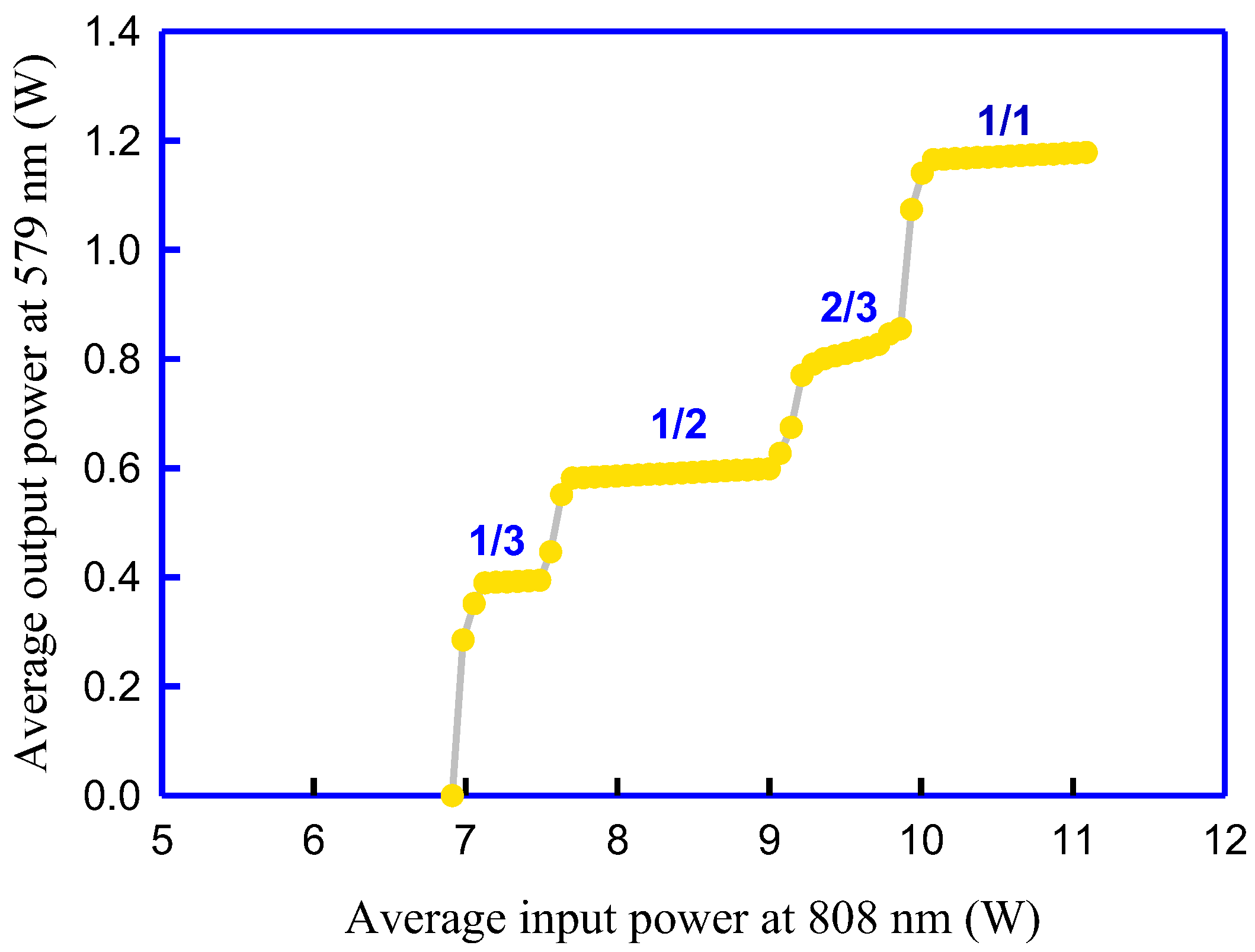
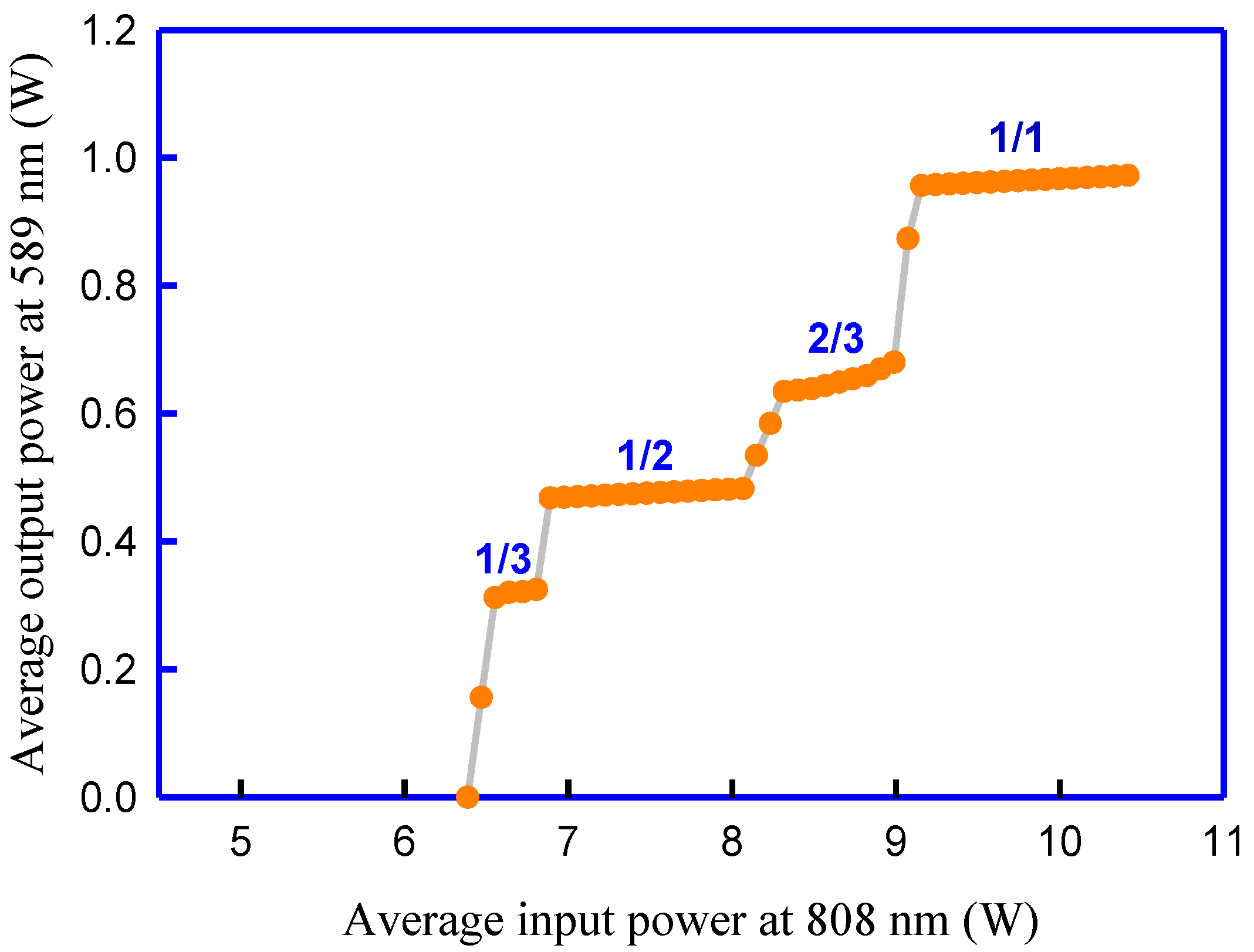
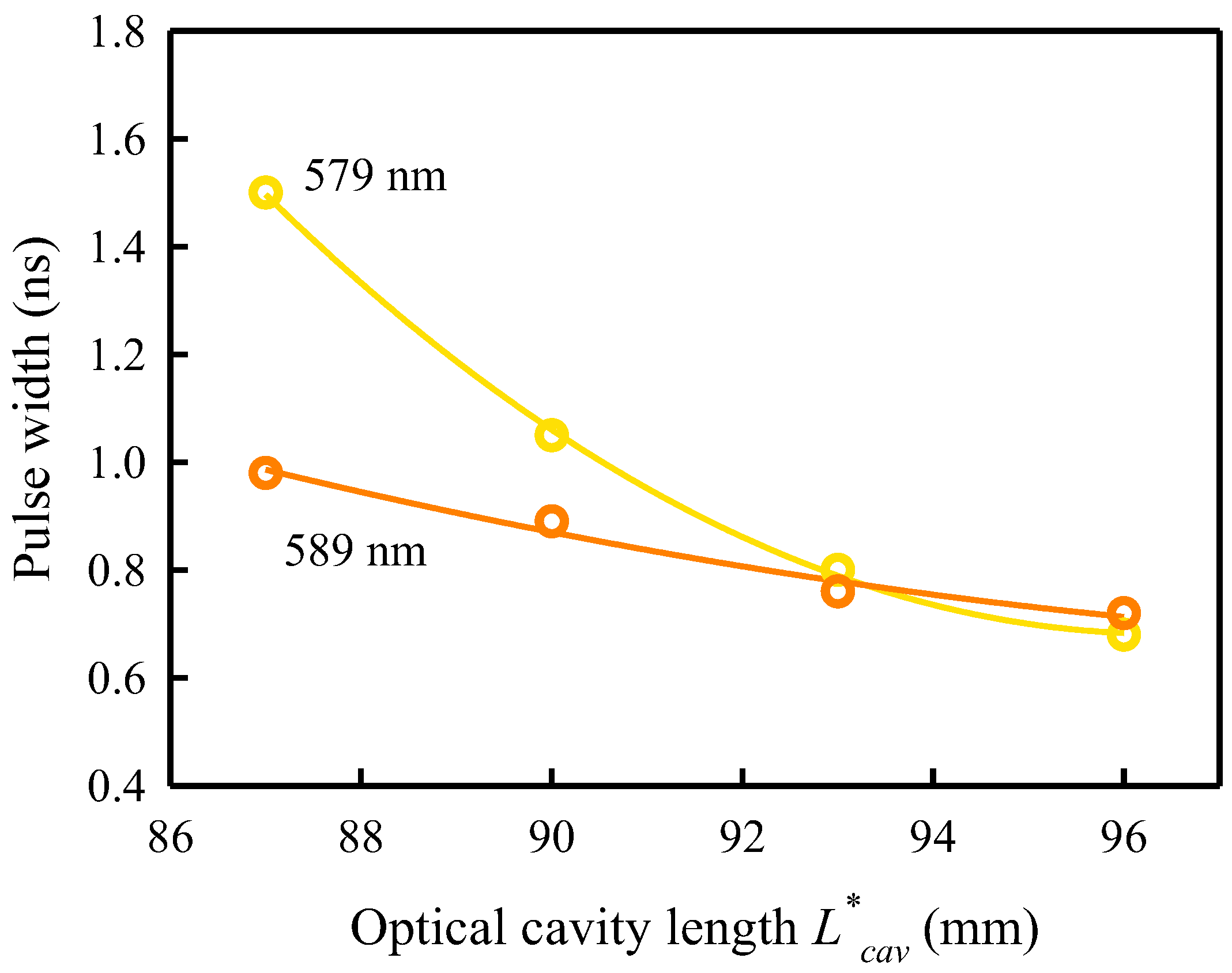
5. Results and Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zayhowski, J.J. Passively Q-switched Nd:YAG microchip lasers and applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2000, 303–304, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swatantran, A.; Tang, H.; Barrett, T.; Decola, P.; Dubayah, R. Rapid, high-resolution forest structure and terrain mapping over large areas using single photon lidar. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisaman, M.D.; Fan, J.; Migdall, A.; Polyakov, S.V. Invited Review Article: Single-photon sources and detectors. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2011, 82, 071101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsunekane, M.; Inohara, T.; Ando, A.; Kido, N.; Kanehara, K.; Taira, T. High Peak Power, Passively Q-switched Microlaser for Ignition of Engines. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 2010, 46, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanner, M.; Sakamoto, F.H.; Avram, M.M.; Chan, H.H.; Alam, M.; Tannous, Z.; Anderson, R.R. Immediate skin responses to laser and light treatments: Therapeutic endpoints: How to obtain efficacy. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2016, 74, 821–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maia, A.M.; Penha, F.M.; Regatieri, C.V.S.; Cardillo, J.A.; Farah, M.E. Micropulse 577nm-yellow laser photocoagulation for central serous chorio-retinopathy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 4273. [Google Scholar]
- Runcorn, T.H.; Görlitz, F.G.; Murray, R.T.; Kelleher, E.J.R. Visible Raman-shifted Fiber Lasers for Biophotonic Applications. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quant. Electron. 2018, 24, 1400208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, V.; Karpov, V.; Linton, C.F.; Subach, V.; Verkhusha, V.V.; Telford, W.G. Solid state yellow and orange lasers for flow cytometry. Cytom. Part A 2008, 73, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maslov, K.; Zhang, H.F.; Hu, S.; Wang, L.V. Optical-resolution photoacoustic microscopy for in vivo imaging of single capillaries. Opt. Lett. 2008, 33, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadick, N.S.; Weiss, R. The utilization of a new yellow light laser (578 nm) for the treatment of class I red telangiectasia of the lower extremities. Dermatol. Surg. 2002, 28, 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.I. Clinicopathologic efficacy of copper bromide plus/yellow laser (578 nm with 511 nm) for treatment of melasma in Asian patients. Dermatol. Surg. 2010, 36, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ernstberger, B.; Enderlein, M.; Friedenauer, A.; Schwerdt, R.; Wei, D.; Karpov, V.; Leisching, P.; Clements, W.R.L.; Kaenders, W.G. Robust remote-pumping sodium laser for advanced LIDAR and guide star applications. In Optics in Atmospheric Propagation and Adaptive Systems XVIII; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2015; Volume 9641. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, X.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, B.; Bai, Z.; Ding, J.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Z. Research development of 589 nm laser for sodium laser guide stars. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2020, 134, 106207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, L.; Cui, S.; Fan, T.; Dong, J.; Feng, Y. Sodium guide star laser pulsed at Larmor frequency. Opt. Lett. 2017, 42, 4351–4354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Duan, Y.; Sun, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, G.; Tang, D. Passively Q-switched multiple visible wavelengths switchable YVO4 Raman laser. J. Lumin. 2020, 228, 117650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.M.; Zhu, H.Y.; Huang, C.H.; Zhang, G.; Wei, Y. Potential sodium D2 resonance radiation generated by intra-cavity SHG of a c-cut Nd:YVO4 self-Raman laser. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 6333–6338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, L.; Feng, Y.; Calia, D.B. High power narrowband 589 nm frequency doubled fibre laser source. Opt. Express 2009, 17, 14687–14693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledentsov, N.N.; Shchukin, V.A.; Shernyakov, Y.M.; Kulagina, M.M.; Payusov, A.S.; Gordeev, N.Y.; Maximov, M.V.; Zhukov, A.E.; Denneulin, T.; Cherkashin, N. Room-temperature yellow-orange (In,Ga,Al)P-GaP laser diodes grown on (n11) GaAs substrates. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 13985–13994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leinonen, T.; Korpijärvi, V.-M.; Härkönen, A.; Guina, M. 7.4W yellow GaInNAs-based semiconductor disk laser. Electron. Lett. 2011, 47, 1139–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.J.; Spence, D.J.; Piper, J.A.; Pask, H.M. A wavelength-versatile, continuous-wave, self-Raman solid-state laser operating in the visible. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 20013–20018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.F.; Pan, Y.Y.; Liu, Y.C.; Cheng, H.P.; Tsou, C.H.; Liang, H.C. Efficient high-power continuous-wave lasers at green-lime-yellow wavelengths by using a Nd:YVO4 self-Raman crystal. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 2029–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.F.; Li, D.; Lee, Y.M.; Lee, C.C.; Huang, H.Y.; Tsou, C.H.; Liang, H.C. Highly efficient solid-state Raman yellow-orange lasers created by enhancing the cavity reflectivity. Opt. Lett. 2021, 46, 797–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.C.; Ho, Y.W.; Tu, Y.C.; Liang, H.C.; Chen, Y.F. High-Peak-Power Passively Q-Switched Laser at 589 nm with Intracavity Stimulated Raman Scattering. Crystals 2023, 13, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.F.; Chen, K.Y.; Liu, Y.C.; Chen, C.M.; Tsou, C.H.; Liang, H.C. Criterion for optimizing high-power acousto-optically Q-switched self-Raman yellow lasers with repetition rates up to 500 kHz. Opt. Lett. 2020, 45, 1922–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zayhowski, J. Q-switched operation of microchip lasers. Opt. Lett. 1991, 16, 575–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayhowski, J.; Dill, C. Diode-pumped passively Q-switched picosecond microchip lasers. Opt. Lett. 1994, 19, 1427–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negri, J.R.; Pirzio, F.; Agnesi, A. Jitter investigation of narrow-bandwidth passively Q-switched Nd:YAG unidirectional ring laser. Opt. Lett. 2019, 44, 3094–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavel, N.; Tsunekane, M.; Taira, T. Composite, all-ceramics, high-peak power Nd:YAG/Cr4+:YAG monolithic micro-laser with multiple-beam output for engine ignition. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 9378–9384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.F.; Chien, P.Y.; Lee, C.C.; Huang, K.F.; Liang, H.C. Timing jitter reduction of passively Q-switched solid-state lasers by coupling resonance between pumping and firing rates. Opt. Lett. 2020, 45, 2902–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.F.; Hsieh, M.X.; Tu, Y.C.; Lee, C.C.; Yu, Y.T.; Tsou, C.H.; Liang, H.C. Pedagogically fast model to evaluate and optimize passively Q-switched Nd-doped solid-state lasers. Opt. Lett. 2021, 46, 1588–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, A.; Wu, B.; You, G.; Li, R.; Lin, S. New nonlinear-optical crystal: LiB3O5. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 1989, 6, 616–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Y.; Sua, Y.M.; Fan, H.; Huang, Y.P. Modal phase matched lithium niobate nanocircuits for integrated nonlinear photonics. OSA Continuum 2018, 1, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, F. Ion-cut lithium niobate on insulator technology: Recent advances and perspectives. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2021, 8, 011307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Huang, C.; Zhang, H. Crystal growth and properties of lithium triborate. J. Cryst. Growth 1990, 99, 805–810. [Google Scholar]
- Aparajit, C.; Jana, K.; Lad, A.D.; Ved, Y.M.; Couairon, A.; Ravindra Kumar, G. Efficient second-harmonic generation of a high-energy, femtosecond laser pulse in a lithium triborate crystal. Opt. Lett. 2021, 46, 3540–3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikogosyan, D.N. Nonlinear Optical Crystals: A Complete Survey; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Velsko, S.P.; Webb, M.; Davis, L.; Huang, C. Phase matched harmonic generation in lithium triborate (LBO). IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 1991, 27, 2182–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Cui, Y.; Dunn, M.H. Thermal dependence of the principal refractive indices of lithium triborate. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 1995, 12, 638–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ho, Y.-W.; Chen, J.-C.; Tu, Y.-C.; Liang, H.-C.; Chen, Y.-F. Sub-Nanosecond Passively Q-Switched Yellow and Orange Raman Lasers. Photonics 2024, 11, 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11020157
Ho Y-W, Chen J-C, Tu Y-C, Liang H-C, Chen Y-F. Sub-Nanosecond Passively Q-Switched Yellow and Orange Raman Lasers. Photonics. 2024; 11(2):157. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11020157
Chicago/Turabian StyleHo, Yu-Wen, Jian-Cheng Chen, Yueh-Chi Tu, Hsing-Chih Liang, and Yung-Fu Chen. 2024. "Sub-Nanosecond Passively Q-Switched Yellow and Orange Raman Lasers" Photonics 11, no. 2: 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11020157
APA StyleHo, Y.-W., Chen, J.-C., Tu, Y.-C., Liang, H.-C., & Chen, Y.-F. (2024). Sub-Nanosecond Passively Q-Switched Yellow and Orange Raman Lasers. Photonics, 11(2), 157. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11020157





