Speckle Reduction in Digital Holography by Fast Logistic Adaptive Non-Local Means Filtering
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Principle
2.1. Non-Local Means Algorithm
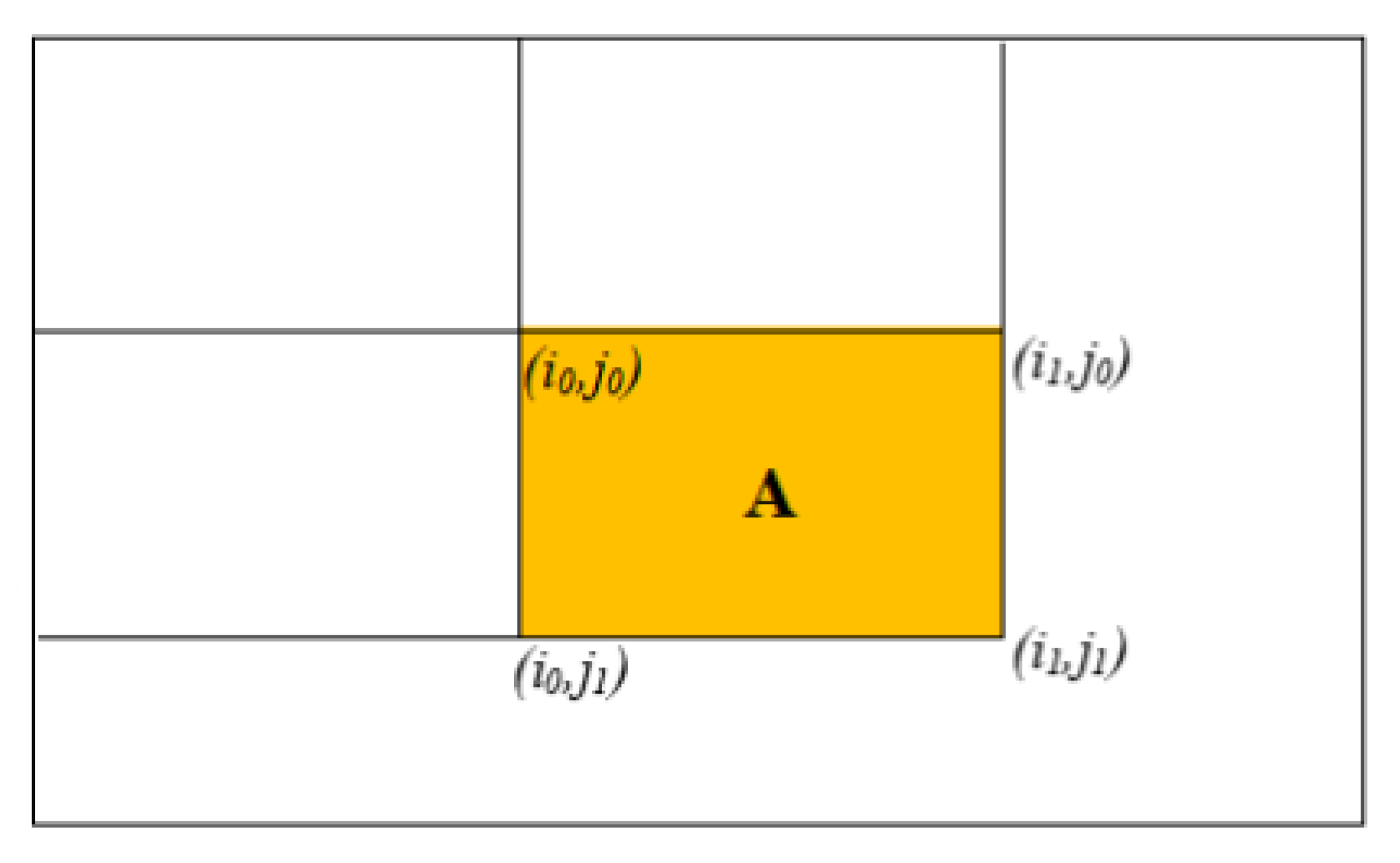
2.2. Integral Image
2.3. Adaptive Filtering
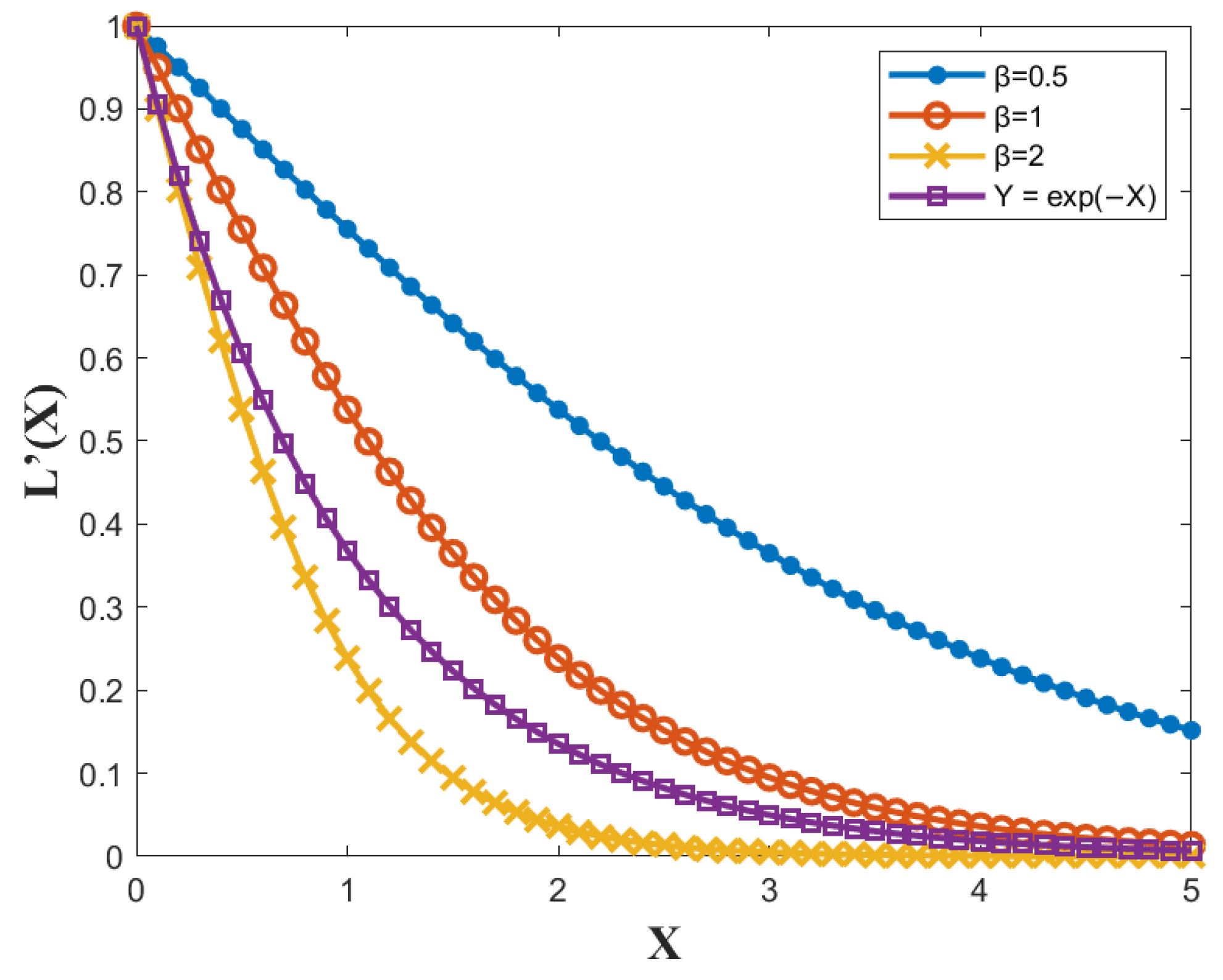
2.4. Logistic Adaptive Non-Local Means (LA-NLM) Algorithm
- Smooth and continuous: the logistic function is a smooth S-shaped curve, ensuring continuity, which enables it to be effectively handled.
- Nonlinear output: the output of the logistic function is nonlinear, allowing it to capture the nonlinear relationships within the input data.
- Saturation: the saturation of the logistic function means that, as the input becomes significantly large or small, the output tends to a finite value. This characteristic makes it insensitive to extreme noise values (excessive or insufficient interference); as in the saturation region, excessive disturbances do not lead to substantial changes in the output.
- Input the speckle noise image;
- Determine the value of each parameter: ds, Ds, and β;
- Calculate the integral image about the pixel difference St according to Equation (7);
- Calculate the distance d(p, qn) between patches N(p) and N(qn) according to Equation (8);
- Estimate the standard deviation σnp of the local speckle noise according to Equation (9), and determine the parameter h according to Equation (10);
- Obtain the value of w(p,qn) according to Equation (14);
- Obtain the denoised image according to Equation (1).
3. Results and Discussion
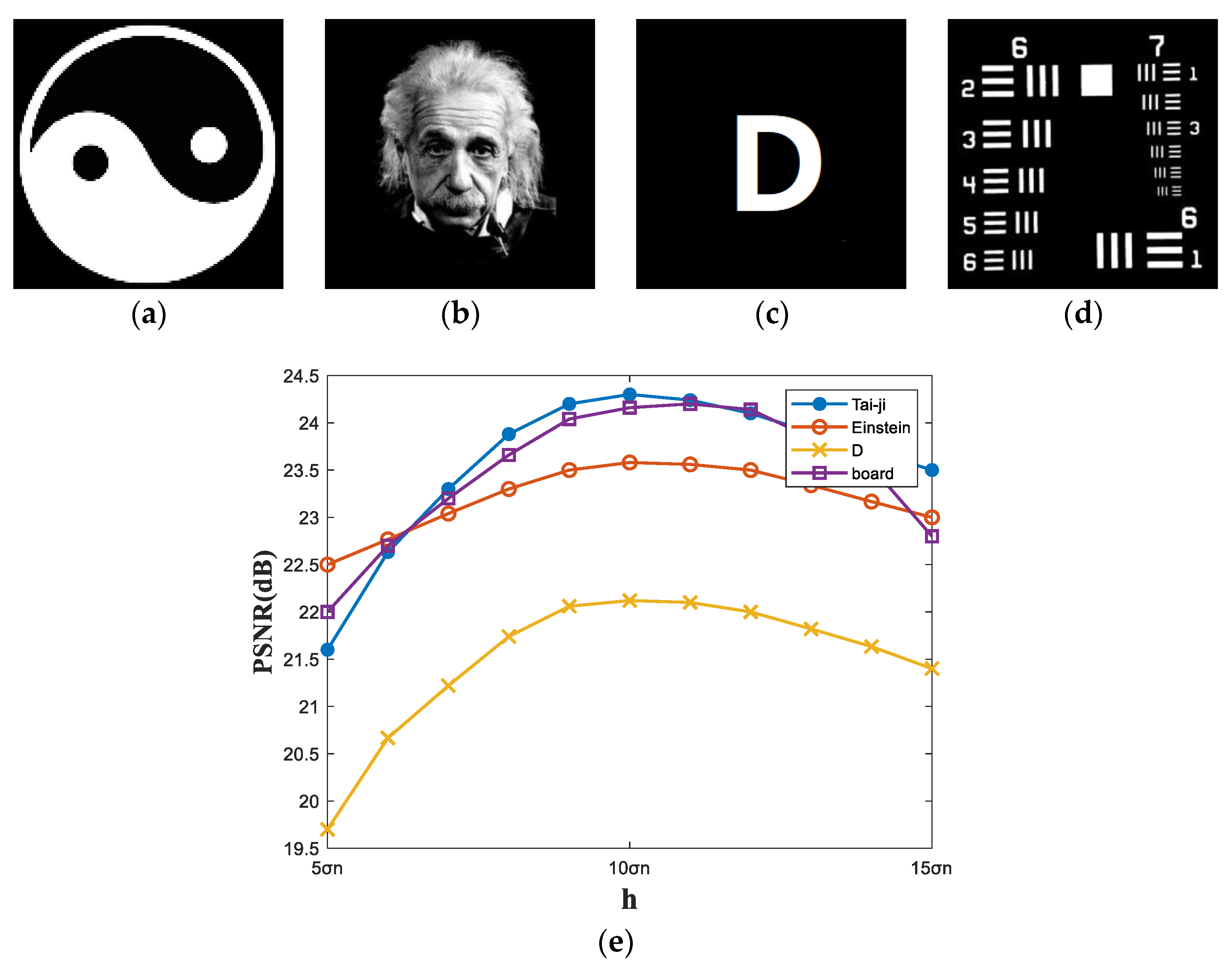
3.1. Simulation Results
3.2. Choice of h
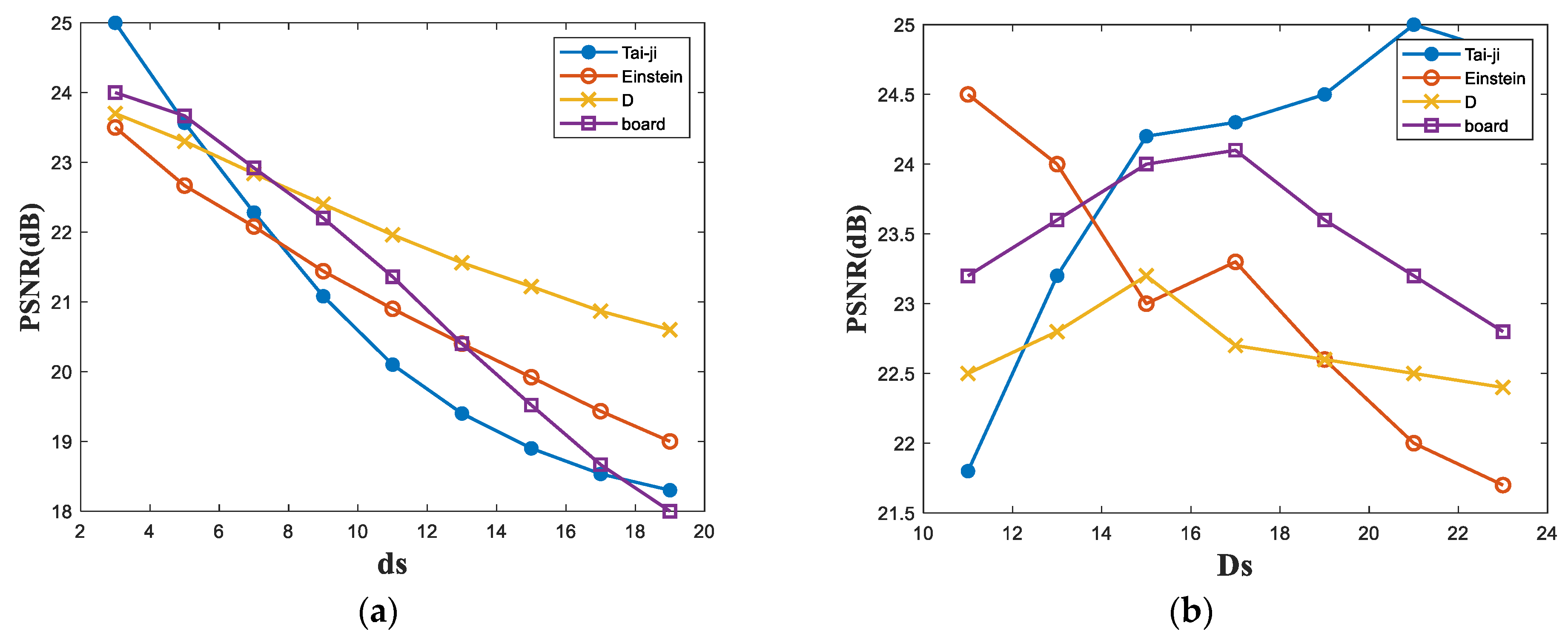
3.3. Choice of Windows
3.4. Choice of β
3.5. Comparison of Methods
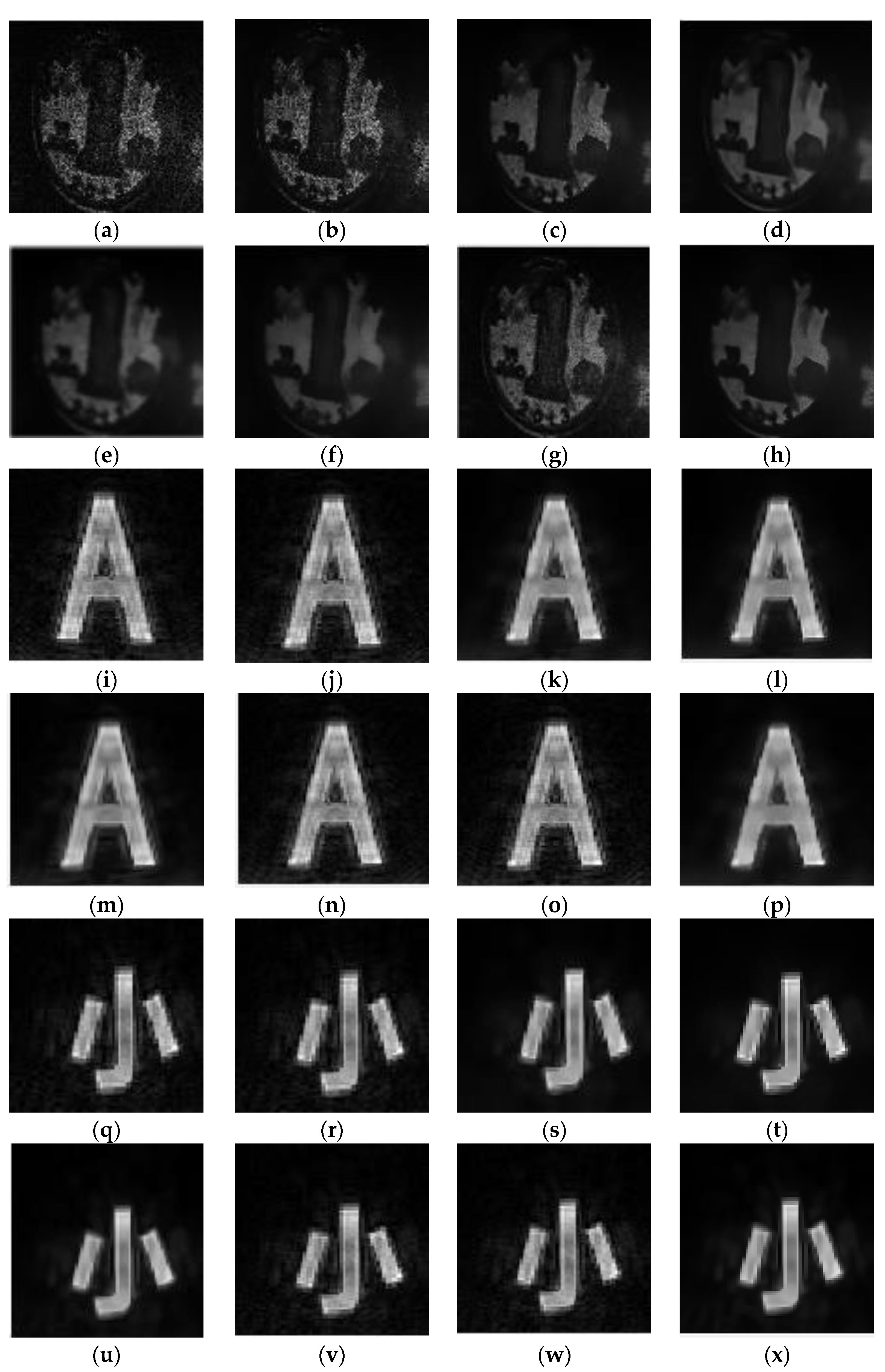
4. Experiment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, H.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.; Jeon, P.; Lee, S.A.; Kim, D. Noniterative sub-pixel shifting super-resolution lensless digital holography. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 29996–30006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tian, A.; Wang, H.; Zhu, X.; Wang, C.; Liu, B.; Asundi, A. Microstructure measurement of digital holography. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Photonics and Optical Engineering (icPOE 2014), Xi’an, China, 13–15 October 2014; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, DC, USA, 2014; Volume 9449, p. 94493O. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.; Han, Y.; Lou, S.; Li, Z. High spectral and spatial resolved encryption and decryption of 3D color object based on holographic imaging spectroscopy. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2021, 145, 106669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Matoba, O.; Quan, X.; Rajput, S.K.; Awatsuji, Y.; Tamada, Y. Single-shot common-path off-axis digital holography: Applications in bioimaging and optical metrology [Invited]. Appl. Opt. 2021, 60, A195–A204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Jia, S.; Yu, H. Hybrid method for speckle noise reduction in digital holography. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2019, 36, D14–D22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monroy, F.; Rincon, O.; Torres, Y.M.; Garcia-Sucerquia, J. Quantitative assessment of lateral resolution improvement in digital holography. Opt. Commun. 2008, 281, 3454–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, T.; Okamura, M.; Nitanai, E.; Numata, T. Image quality improvement of digital holography by superposition of reconstructed images obtained by multiple wavelengths. Appl. Opt. 2008, 47, D38–D43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.-W.; Isikman, S.O.; Bishara, W.; Tseng, D.; Erlinger, A.; Ozcan, A. Multi-angle lensless digital holography for depth resolved imaging on a chip. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 9690–9711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, C.-K.; Pan, J.-W. Speckle reduction with fast electrically tunable lens and holographic diffusers in a laser projector. Opt. Commun. 2019, 454, 124301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Meng, P.; Wang, D.; Rong, L.; Panezai, S. Speckle noise suppression in digital holography by angular diversity with phase-only spatial light modulator. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 19568–19578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hincapie, D.; Herrera-Ramírez, J.; Garcia-Sucerquia, J. Single-shot speckle reduction in numerical reconstruction of digitally recorded holograms. Opt. Lett. 2015, 40, 1623–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuoka, T.; Mori, Y.; Nomura, T. Speckle reduction by spatial-domain mask in digital holography. J. Disp. Technol. 2015, 12, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassine, T.; Ahmed, S.; Abdelkrim, N. Speckle noise reduction in digital speckle pattern interferometry using riesz wavelets transform. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Advanced Technologies for Signal and Image Processing (ATSIP), Fez, Morocco, 22–24 May 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, D.G.A. Improving the intensity-contrast image of a noisy digital hologram by convolution of Chebyshev type 2 and elliptic filters. Appl. Opt. 2021, 60, 3823–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leng, J.M.; Li, F.B.; Li, H.L. Speckle reduction by optical pre-processing and digital filtering in digital holography. Lasers Eng. (Old City Publ.) 2019, 44, 227–238. [Google Scholar]
- Buades, A.; Coll, B.; Morel, J.M. Non-local means denoising. Image Process. Line 1 2011, 1, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buades, A.; Coll, B.; Morel, J.M. A Review of Image Denoising Algorithms, with a New One. Multiscale Model. Simul. 2005, 4, 490–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tounsi, Y.; Kumar, M.; Nassim, A.; Mendoza-Santoyo, F. Speckle noise reduction in digital speckle pattern interferometric fringes by nonlocal means and its related adaptive kernel-based methods. Appl. Opt. 2018, 57, 7681–7690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, J.L.J.; Sang, X.S.X.; Yan, B.Y.B. Speckle noise reduction in digital holography with spatial light modulator and nonlocal means algorithm. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2014, 12, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Coupe, P.; Hellier, P.; Kervrann, C.; Barillot, C. Nonlocal Means-Based Speckle Filtering for Ultrasound Images. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2009, 18, 2221–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabov, K.; Foi, A.; Katkovnik, V.; Egiazarian, K. Image denoising by sparse 3-D transform-domain collaborative filtering. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2007, 16, 2080–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manjon, J.V.; Carbonellcaballero, J.; Lull, J.J.; Garciamarti, G.; Martibonmati, L.; Robles, M. MRI denoising using non-local means. Med. Image Anal. 2013, 17, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabov, K.; Foi, A.; Katkovnik, V.; Egiazarian, K. Image denoising with block-matching and 3d filtering. In Proceedings of the Image Processing: Algorithms and Systems, Neural Networks, and Machine Learning, San Jose, CA, USA, 16–18 January 2006; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, DC, USA, 2006; Volume 6064, pp. 354–365. [Google Scholar]
- Goodman, J.W. Some fundamental properties of speckle. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1976, 66, 1145–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, J.S. The Origins of Logistic Regression. Econom. Ejournal 2002, 2002-119/4(2-119/4). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viola, P.; Jones, M. Rapid object detection using a boosted cascade of simple features. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Kauai, HI, USA, 8–14 December 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Froment, J. Parameter-Free Fast Pixel wise Non-Local Means Denoising. Image Process. Line 2014, 4, 300–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseeuw, P.J.; Croux, C. Alternatives to the Median Absolute Deviation. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1993, 88, 1273–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, J.W. Introduction to Fourier Optics; Roberts & Company Publishers: Greenwood Village, CO, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Tay, P.C.; Garson, C.D.; Acton, S.T.; Hossack, J.A. Ultrasound Despeckling for Contrast Enhancement. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2010, 19, 1847–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Acton, S.T. Speckle reducing anisotropic diffusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2002, 11, 1260–1270. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Pu, Y.-F.; Liu, P.; Hao, Y. Multiscale hybrid method for speckle reduction of medical ultrasound images. Multimedia Tools Appl. 2023, 66, 102396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




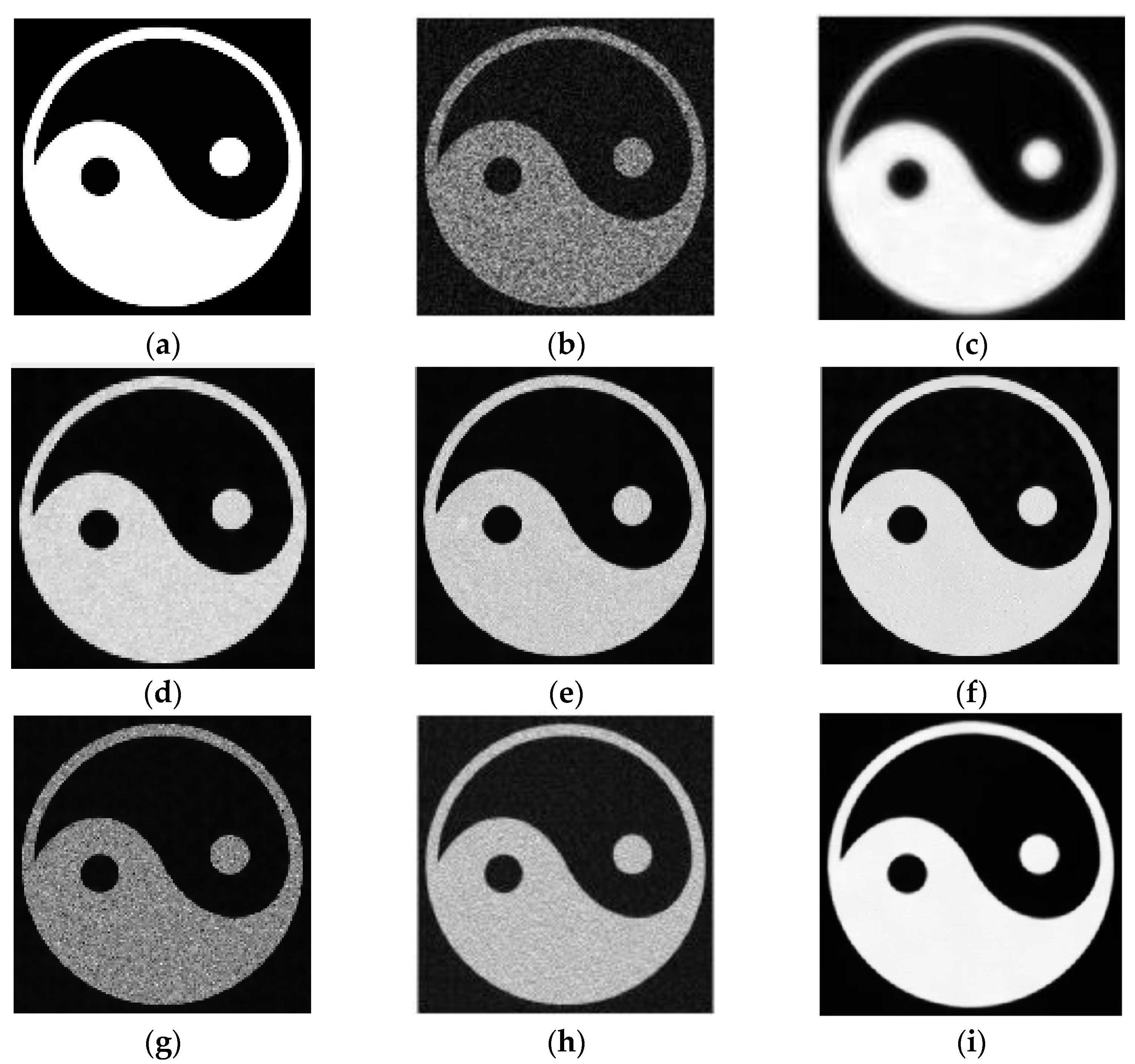


| Tai-ji | D | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSNR (dB) | SI | SSIM | Time (s) | PSNR (dB) | SI | SSIM | Time (s) | |
| Direct Reconstruction | 9.016 | 0.677 | 0.105 | / | 15.018 | 0.696 | 0.108 | / |
| NLM | 10.235 | 0.523 | 0.334 | 136.68 | 15.258 | 0.573 | 0.375 | 125.33 |
| Improved NLM | 18.011 | 0.173 | 0.519 | 136.69 | 19.955 | 0.299 | 0.602 | 125.32 |
| LA-NLM | 24.359 | 0.171 | 0.703 | 2.56 | 22.733 | 0.275 | 0.714 | 2.12 |
| Methods | PSNR (dB) | SI | SSIM | Time (s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Reconstruction | 9.016 | 0.677 | 0.105 | / |
| SBF | 18.323 | 0.175 | 0.201 | 155.33 |
| OBNLM | 20.479 | 0.210 | 0.598 | 139.64 |
| SRAD | 19.652 | 0.199 | 0.616 | 124.52 |
| BM3D | 22.187 | 0.193 | 0.697 | 64.17 |
| NLM | 10.235 | 0.523 | 0.334 | 136.68 |
| Improved NLM | 18.011 | 0.173 | 0.519 | 136.69 |
| LA-NLM | 24.359 | 0.171 | 0.703 | 2.56 |
| Objects | Coin | A | 小 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indices | SI | Time (s) | SI | Time (s) | SI | Time (s) | |
| Methods | |||||||
| Direct Reconstruction | 0.624 | / | 0.448 | / | 0.512 | / | |
| SBF | 0.147 | 170.32 | 0.149 | 161.54 | 0.166 | 164.88 | |
| OBNLM | 0.189 | 156.36 | 0.201 | 134.75 | 0.199 | 140.74 | |
| SRAD | 0.260 | 134.85 | 0.309 | 129.27 | 0.297 | 128.14 | |
| BM3D | 0.155 | 89.65 | 0.157 | 74.37 | 0.160 | 81.75 | |
| NLM | 0.331 | 147.62 | 0.431 | 139.51 | 0.507 | 142.63 | |
| Improved NLM | 0.195 | 145.96 | 0.185 | 138.74 | 0.193 | 141.55 | |
| LA-NLM | 0.146 | 3.45 | 0.141 | 3.08 | 0.164 | 3.22 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, Y.; Leng, J.; Xu, Z. Speckle Reduction in Digital Holography by Fast Logistic Adaptive Non-Local Means Filtering. Photonics 2024, 11, 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11020147
Fu Y, Leng J, Xu Z. Speckle Reduction in Digital Holography by Fast Logistic Adaptive Non-Local Means Filtering. Photonics. 2024; 11(2):147. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11020147
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Yiping, Junmin Leng, and Zhenqi Xu. 2024. "Speckle Reduction in Digital Holography by Fast Logistic Adaptive Non-Local Means Filtering" Photonics 11, no. 2: 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11020147
APA StyleFu, Y., Leng, J., & Xu, Z. (2024). Speckle Reduction in Digital Holography by Fast Logistic Adaptive Non-Local Means Filtering. Photonics, 11(2), 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11020147





