Diffractive Deep-Neural-Network-Based Classifier for Holographic Memory
Abstract
1. Introduction
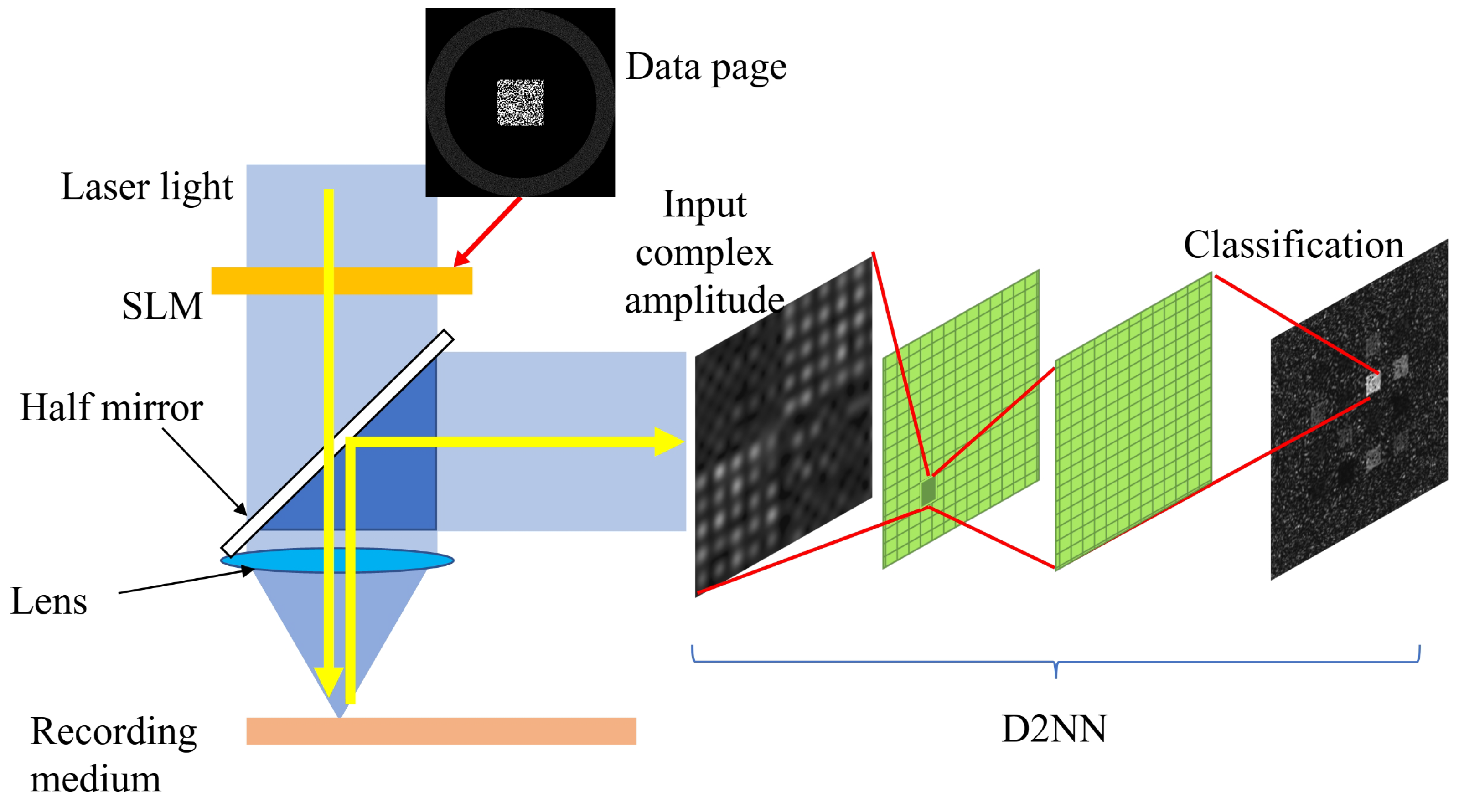
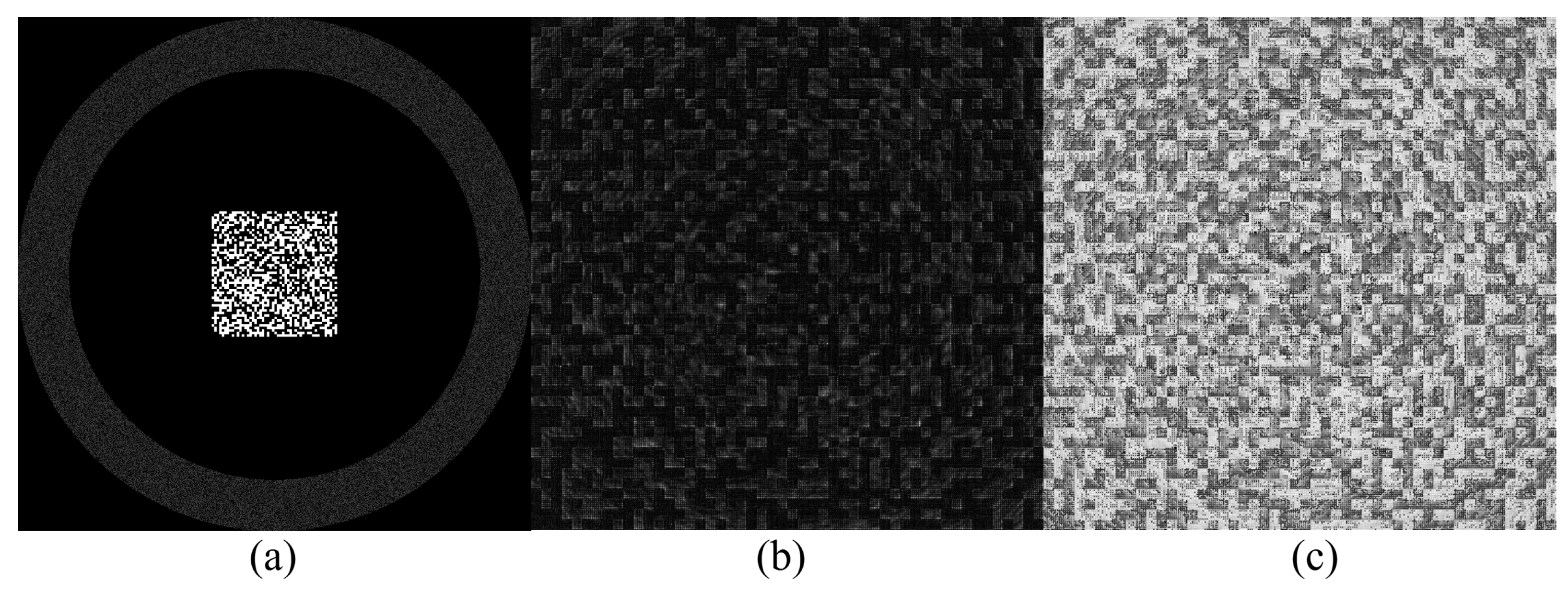
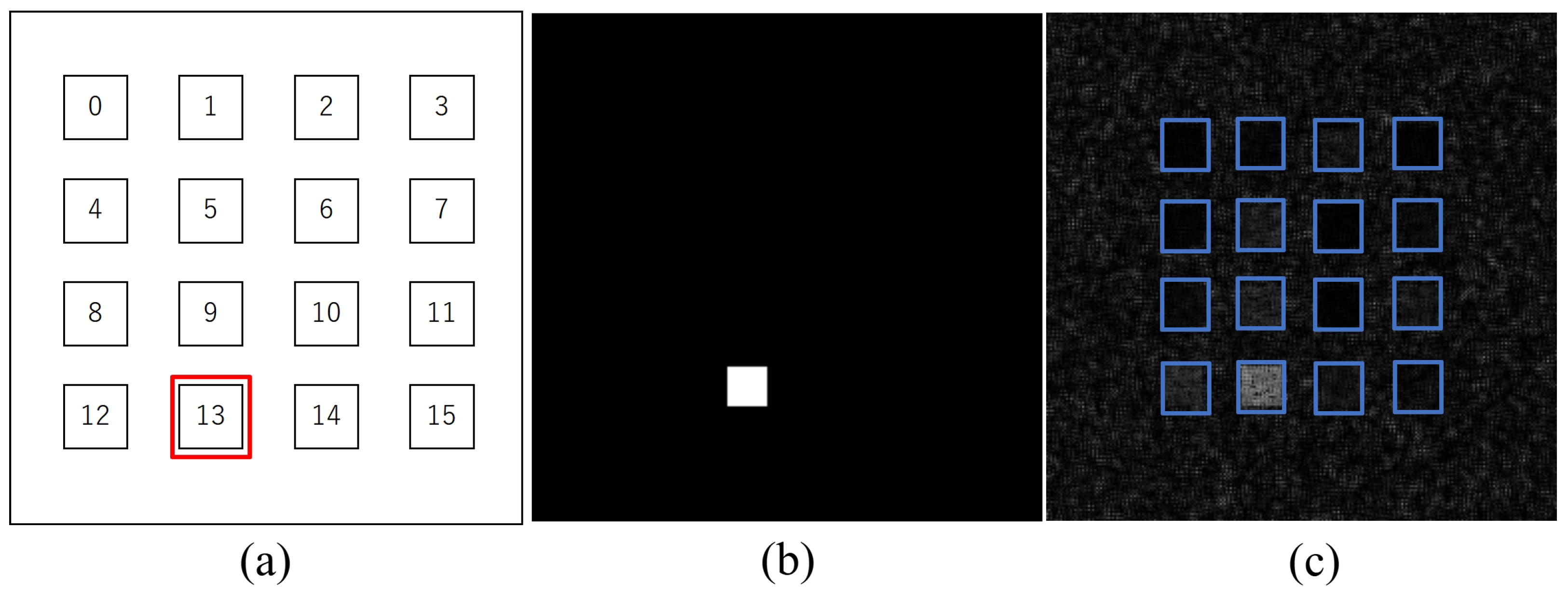
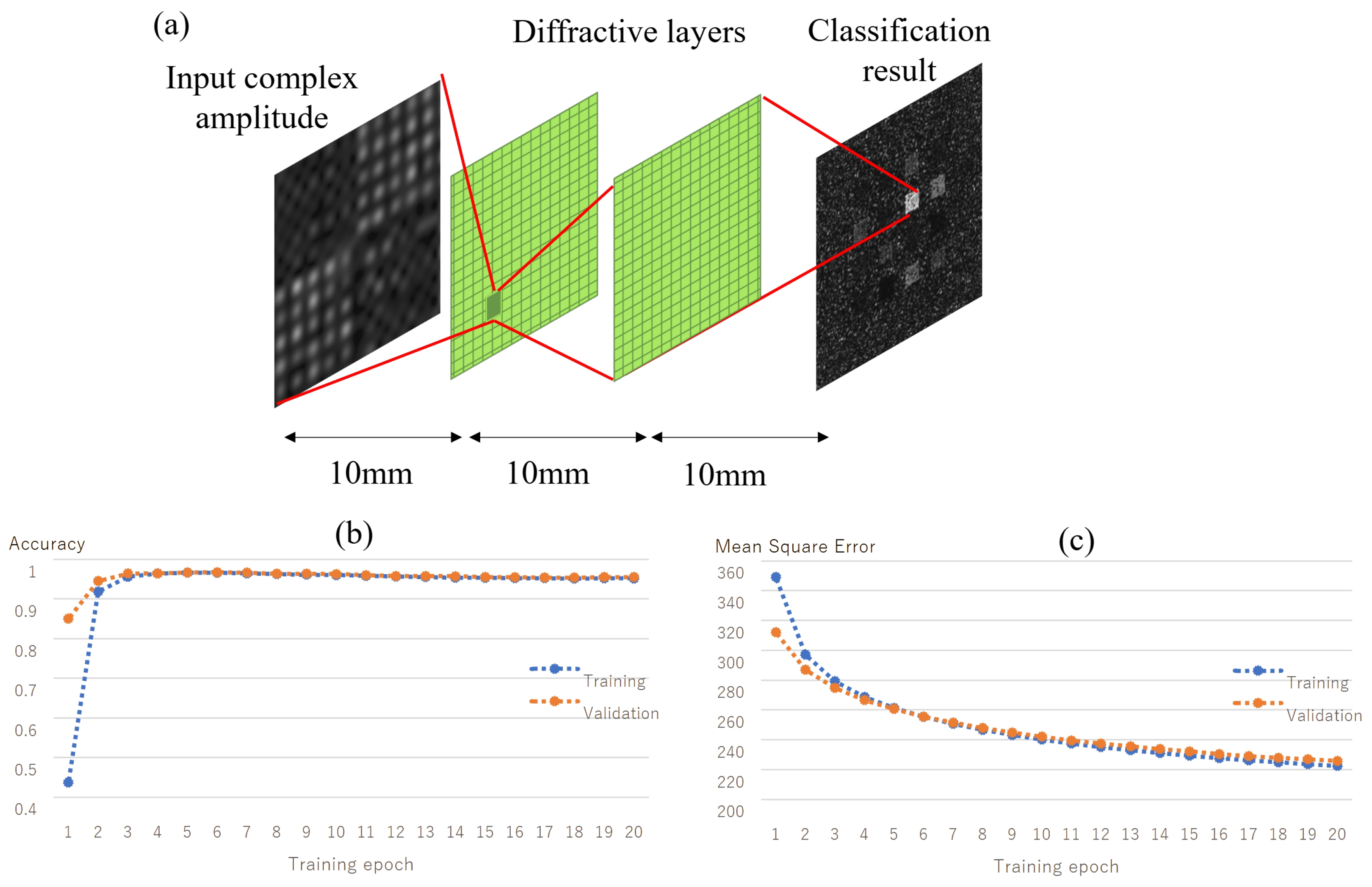
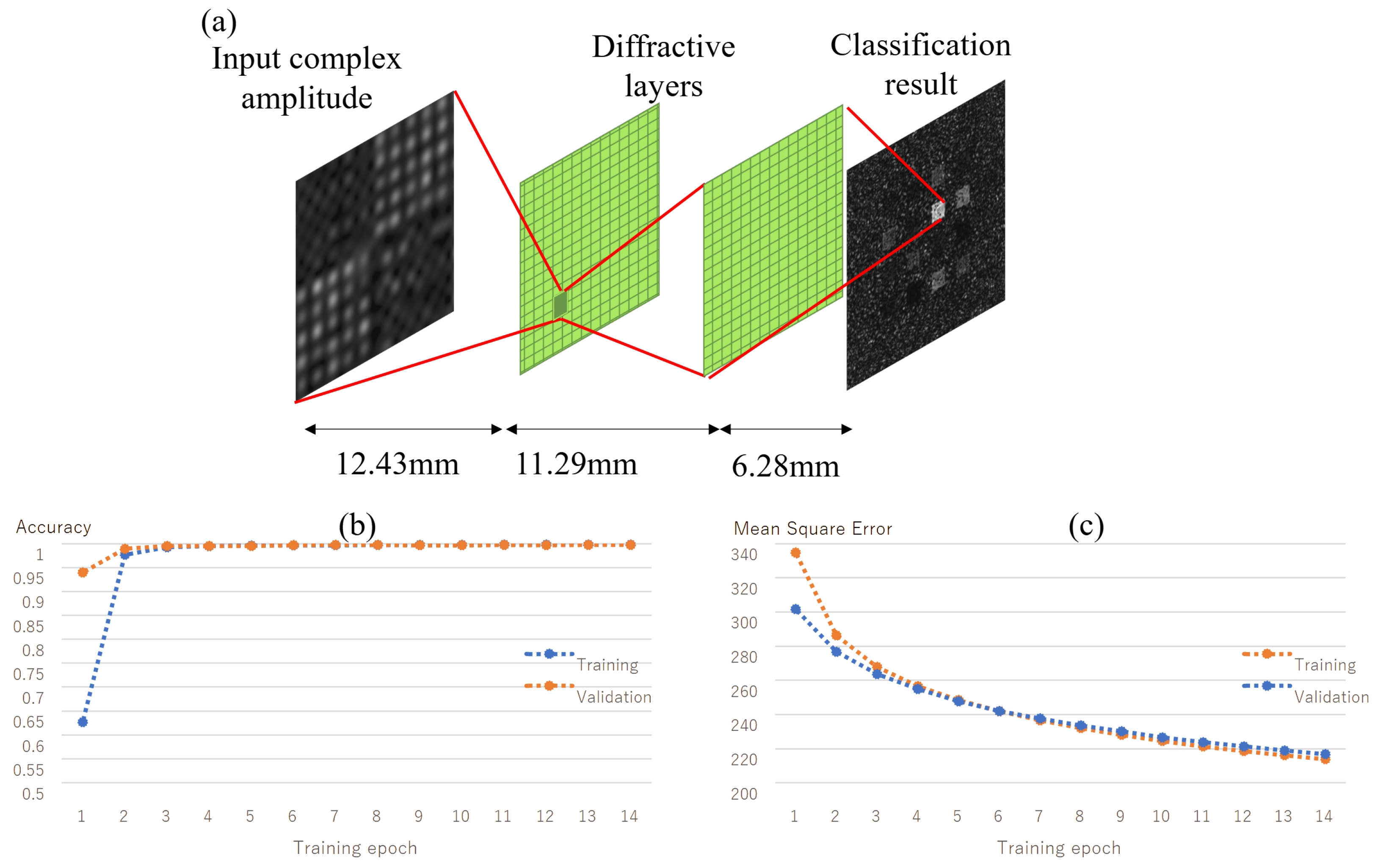
2. Method
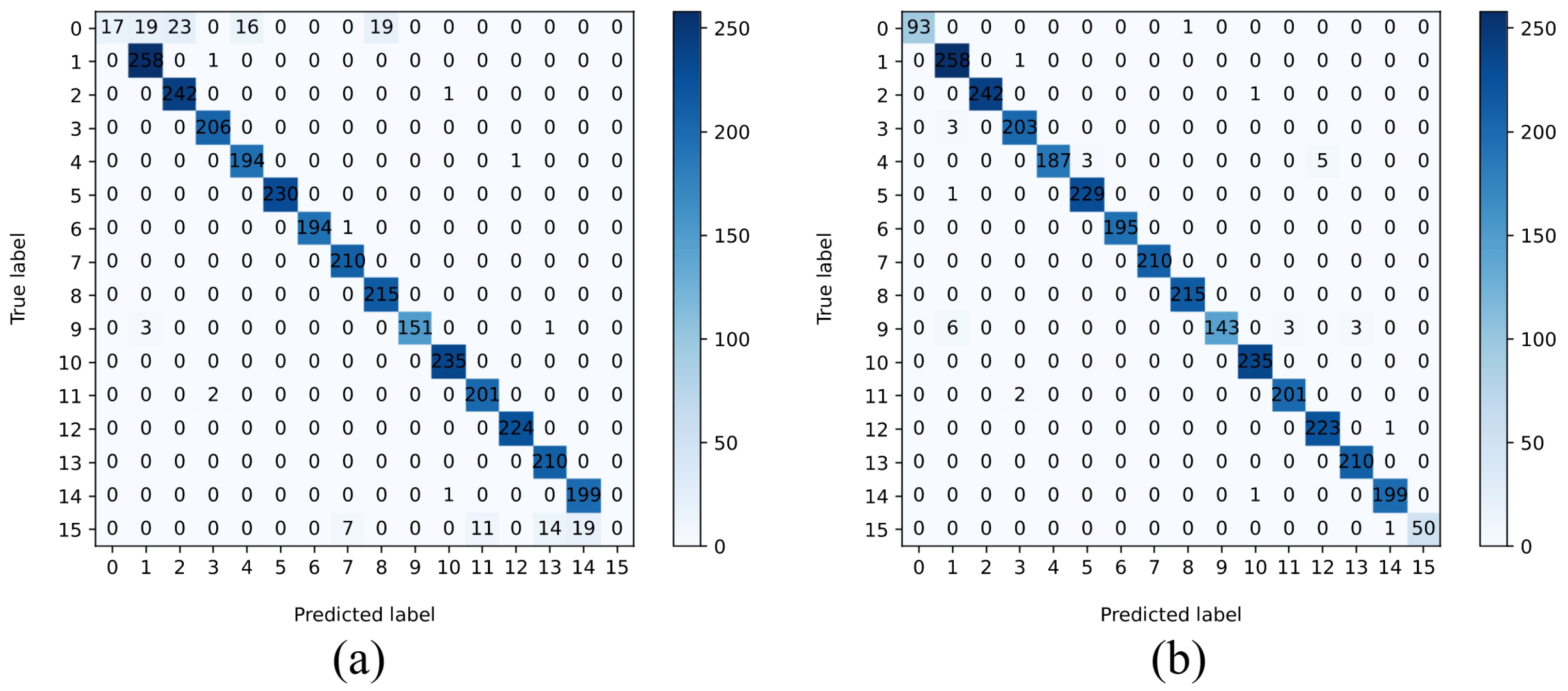
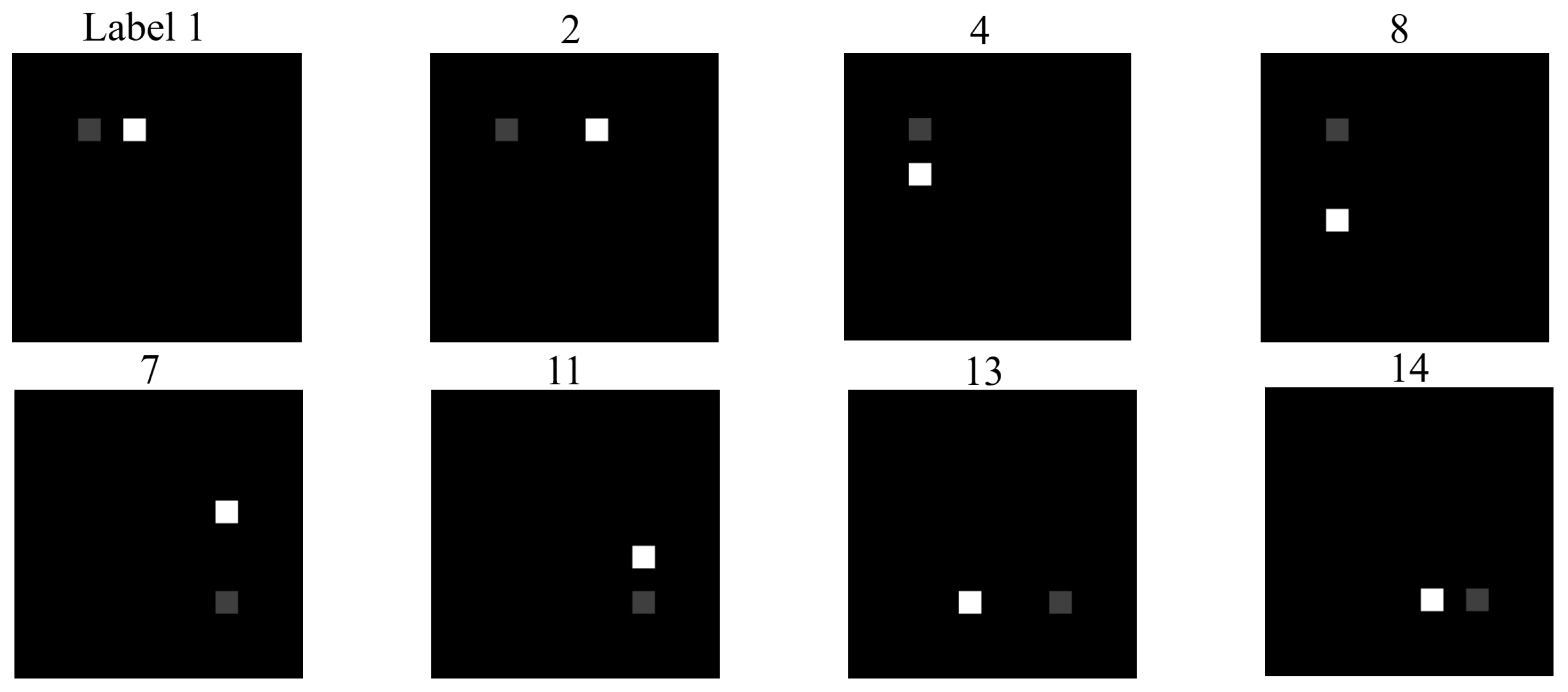
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coufal, H.J.; Psaltis, D.; Sincerbox, G.T. Holographic Data Storage; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; Volume 8. [Google Scholar]
- Katano, Y.; Muroi, T.; Kinoshita, N.; Ishii, N. Prototype holographic data storage drive with wavefront compensation for playback of 8K video data. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2017, 63, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbastathis, G.; Levene, M.; Psaltis, D. Shift multiplexing with spherical reference waves. Appl. Opt. 1996, 35, 2403–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, S.; Kurata, H.; Ozawa, S.; Okubo, K.; Horiuchi, S.; Ushiyama, Z.; Yamamoto, M.; Koga, S.; Tanaka, A. High-density holographic data storage using three-dimensional shift multiplexing with spherical reference wave. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 52, 09LD07. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunoda, Y.; Takeda, Y. High density image-storage holograms by a random phase sampling method. Appl. Opt. 1974, 13, 2046–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, R.; Joseph, J.; Singh, K. Holographic digital data storage using phase-modulated pixels. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2005, 43, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saita, Y.; Nomura, T. Design method of input phase mask to improve light use efficiency and reconstructed image quality for holographic memory. Appl. Opt. 2014, 53, 4136–4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobukawa, T.; Nomura, T. Linear phase encoding for holographic data storage with a single phase-only spatial light modulator. Appl. Opt. 2016, 55, 2565–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honma, S.; Funakoshi, H. A two-step exposure method with interleaved phase pages for recording of SQAM signal in holographic memory. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 58, SKKD05. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Lin, X.; Lin, Y.; Chen, M.; Chen, R.; Situ, G.; Horimai, H.; Tan, X. Lensless complex amplitude demodulation based on deep learning in holographic data storage. Opto-Electron. Adv. 2023, 6, 220157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunsen, M.; Miwa, T. Accurate decoding of data pages in an amplitude-and phase-modulated signal beam detected by the single-shot transport of intensity equation method with convolutional neural network-based classifiers. Opt. Contin. 2023, 2, 1849–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horimai, H.; Tan, X.; Li, J. Collinear holography. Appl. Opt. 2005, 44, 2575–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibukawa, A.; Okamoto, A.; Tomita, A.; Takabayashi, M.; Sato, K. Multilayer collinear holographic memory with movable random phase mask. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 50, 09ME10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobukawa, T.; Nomura, T. Shift multiplexing with a spherical wave in holographic data storage based on a computer-generated hologram. Appl. Opt. 2017, 56, F31–F36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneda, N.; Nobukawa, T.; Morimoto, T.; Saita, Y.; Nomura, T. Common-path angular-multiplexing holographic data storage based on computer-generated holography. Opt. Lett. 2021, 46, 2920–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, A.; Kunori, K.; Takabayashi, M.; Tomita, A.; Sato, K. Holographic diversity interferometry for optical storage. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 13436–13444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Hao, J.; Yu, C.; Zheng, Q.; Qiu, X.; Wang, S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, K.; Lin, D.; Yang, Y.; et al. Dynamic sampling iterative phase retrieval for holographic data storage. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 6726–6736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Hao, J.; Wang, J.; Lin, Y.; Wang, K.; Lin, D.; Lin, X.; Tan, X. Phase retrieval in holographic data storage by expanded spectrum combined with dynamic sampling method. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 18912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneda, N.; Saita, Y.; Komuro, K.; Nobukawa, T.; Nomura, T. Transport-of-intensity holographic data storage based on a computer-generated hologram. Appl. Opt. 2018, 57, 8836–8840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunsen, M.; Tateyama, S. Detection method for the complex amplitude of a signal beam with intensity and phase modulation using the transport of intensity equation for holographic data storage. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 24029–24042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneda, N.; Saita, Y.; Nomura, T. Holographic data storage based on compressive sensing. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Holograhy and Related Technologies 2019 (IWH2019), Toyama, Japan, 5–7 November 2019; pp. 6–a–8. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, L.; Wu, A.; Tanaka, Y.; Shigaki, M.; Shimura, T.; Lin, X.; Tan, X. High noise margin decoding of holographic data page based on compressed sensing. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 7139–7151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimobaba, T.; Kuwata, N.; Homma, M.; Takahashi, T.; Nagahama, Y.; Sano, M.; Hasegawa, S.; Hirayama, R.; Kakue, T.; Shiraki, A.; et al. Convolutional neural network-based data page classification for holographic memory. Appl. Opt. 2017, 56, 7327–7330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimobaba, T.; Endo, Y.; Hirayama, R.; Nagahama, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Nishitsuji, T.; Kakue, T.; Shiraki, A.; Takada, N.; Masuda, N.; et al. Autoencoder-based holographic image restoration. Appl. Opt. 2017, 56, F27–F30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katano, Y.; Muroi, T.; Kinoshita, N.; Ishii, N.; Hayashi, N. Data demodulation using convolutional neural networks for holographic data storage. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2018, 57, 09SC01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katano, Y.; Nobukawa, T.; Muroi, T.; Kinoshita, N.; Ishii, N. CNN-based demodulation for a complex amplitude modulation code in holographic data storage. Opt. Rev. 2021, 28, 662–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Lin, X.; Lin, Y.; Song, H.; Chen, R.; Chen, M.; Wang, K.; Tan, X. Lensless phase retrieval based on deep learning used in holographic data storage. Opt. Lett. 2021, 46, 4168–4171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katano, Y.; Nobukawa, T.; Muroi, T.; Kinoshita, N.; Ishii, N. Efficient decoding method for holographic data storage combining convolutional neural network and spatially coupled low-density parity-check code. ITE Trans. Media Technol. Appl. 2021, 9, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurokawa, S.; Yoshida, S. Demodulation scheme for constant-weight codes using convolutional neural network in holographic data storage. Opt. Rev. 2022, 29, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Lin, X.; Fujimura, R.; Hirayama, S.; Tanaka, Y.; Tan, X.; Shimura, T. Deep learning-based super-resolution holographic data storage. In Proceedings of the Optical Manipulation and Structured Materials Conference, Online, 18 October 2023; Volume 12606, pp. 118–121. [Google Scholar]
- Chijiwa, K.; Takabayashi, M. Deep learning-based design of additional patterns in self-referential holographic data storage. Opt. Rev. 2023, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.A.; Lee, J. A Nonlinear Convolutional Neural Network-Based Equalizer for Holographic Data Storage Systems. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 13029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Hao, J.; Ke, S.; Song, H.; Liu, H.; Lin, X.; Tan, X. Objective defocusing correction of collinear amplitude-modulated holographic data storage system based on deep learning. In Proceedings of the Optical Manipulation and Structured Materials Conference, Online, 18 October 2023; Volume 12606, pp. 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.; Rivenson, Y.; Yardimci, N.T.; Veli, M.; Luo, Y.; Jarrahi, M.; Ozcan, A. All-optical machine learning using diffractive deep neural networks. Science 2018, 361, 1004–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, K.; Li, H.; Tan, X.; Lin, X. Non-interferometric phase retrieval for collinear phase-modulated holographic data storage. Opt. Rev. 2020, 27, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, S.; Shimobaba, T.; Kakue, T.; Ito, T. Hyperparameter tuning of optical neural network classifiers for high-order Gaussian beams. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 11079–11089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sakurai, T.; Ito, T.; Shimobaba, T. Diffractive Deep-Neural-Network-Based Classifier for Holographic Memory. Photonics 2024, 11, 145. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11020145
Sakurai T, Ito T, Shimobaba T. Diffractive Deep-Neural-Network-Based Classifier for Holographic Memory. Photonics. 2024; 11(2):145. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11020145
Chicago/Turabian StyleSakurai, Toshihiro, Tomoyoshi Ito, and Tomoyoshi Shimobaba. 2024. "Diffractive Deep-Neural-Network-Based Classifier for Holographic Memory" Photonics 11, no. 2: 145. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11020145
APA StyleSakurai, T., Ito, T., & Shimobaba, T. (2024). Diffractive Deep-Neural-Network-Based Classifier for Holographic Memory. Photonics, 11(2), 145. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11020145




