Far-Detuning Laser Frequency Disturbance Suppression for Atomic Sensor Based on Intrinsic Fiber Fabry–Pérot Cavity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theory
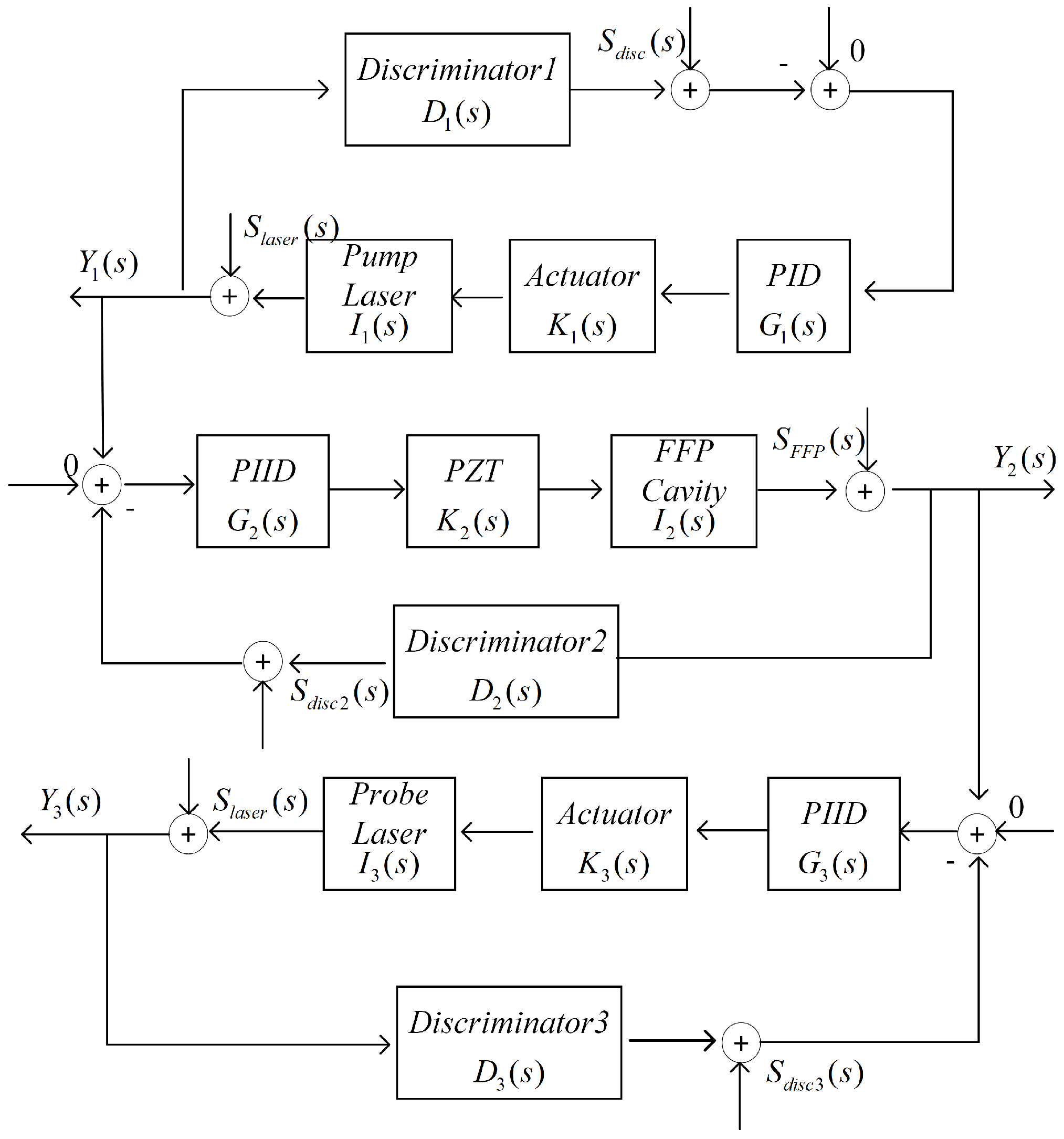
2.1. Principle of Transferred FFP Frequency Locking
2.2. Locked Frequency Stability Analysis
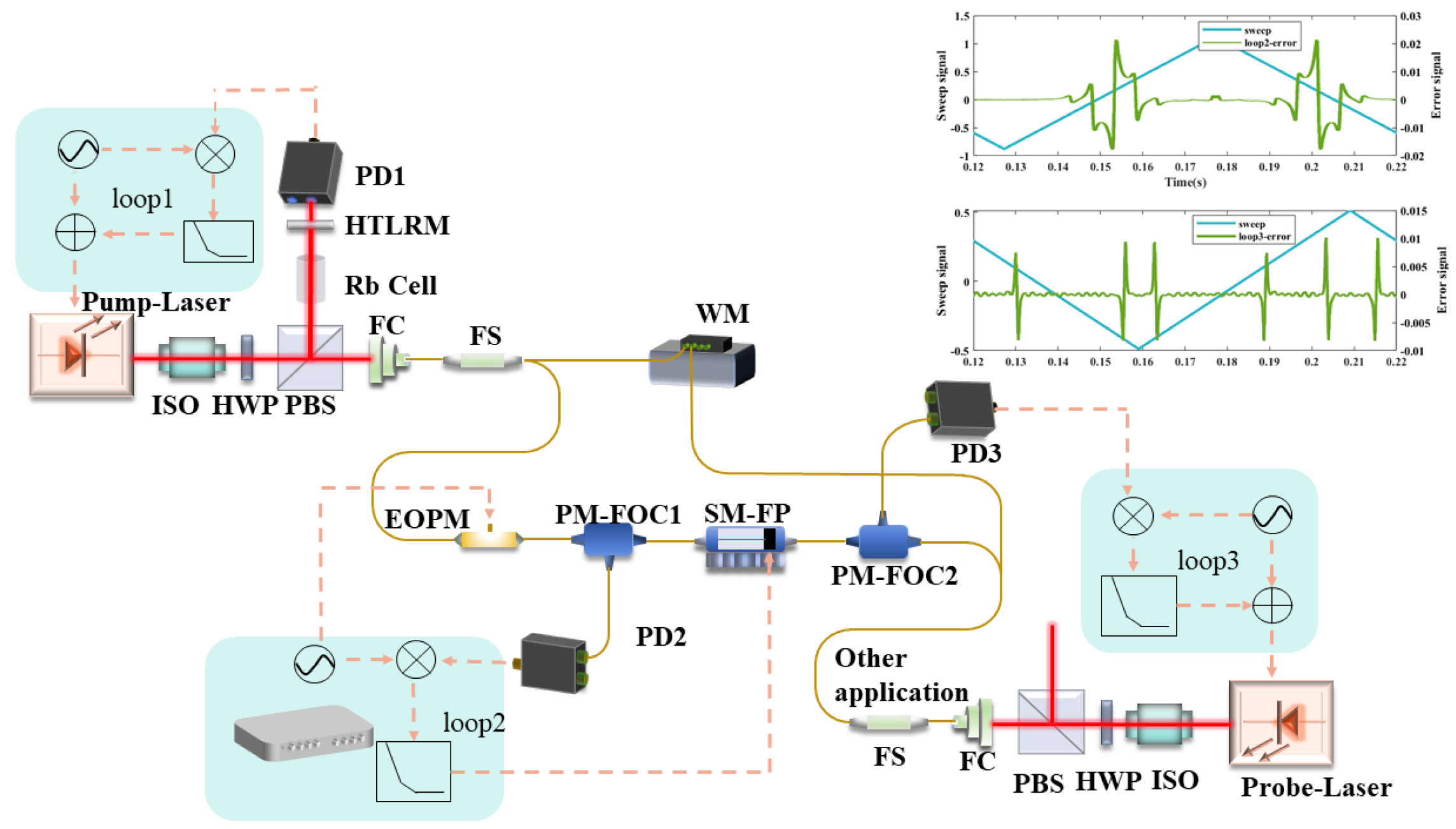
3. Experimental Setup
4. Experimental Results
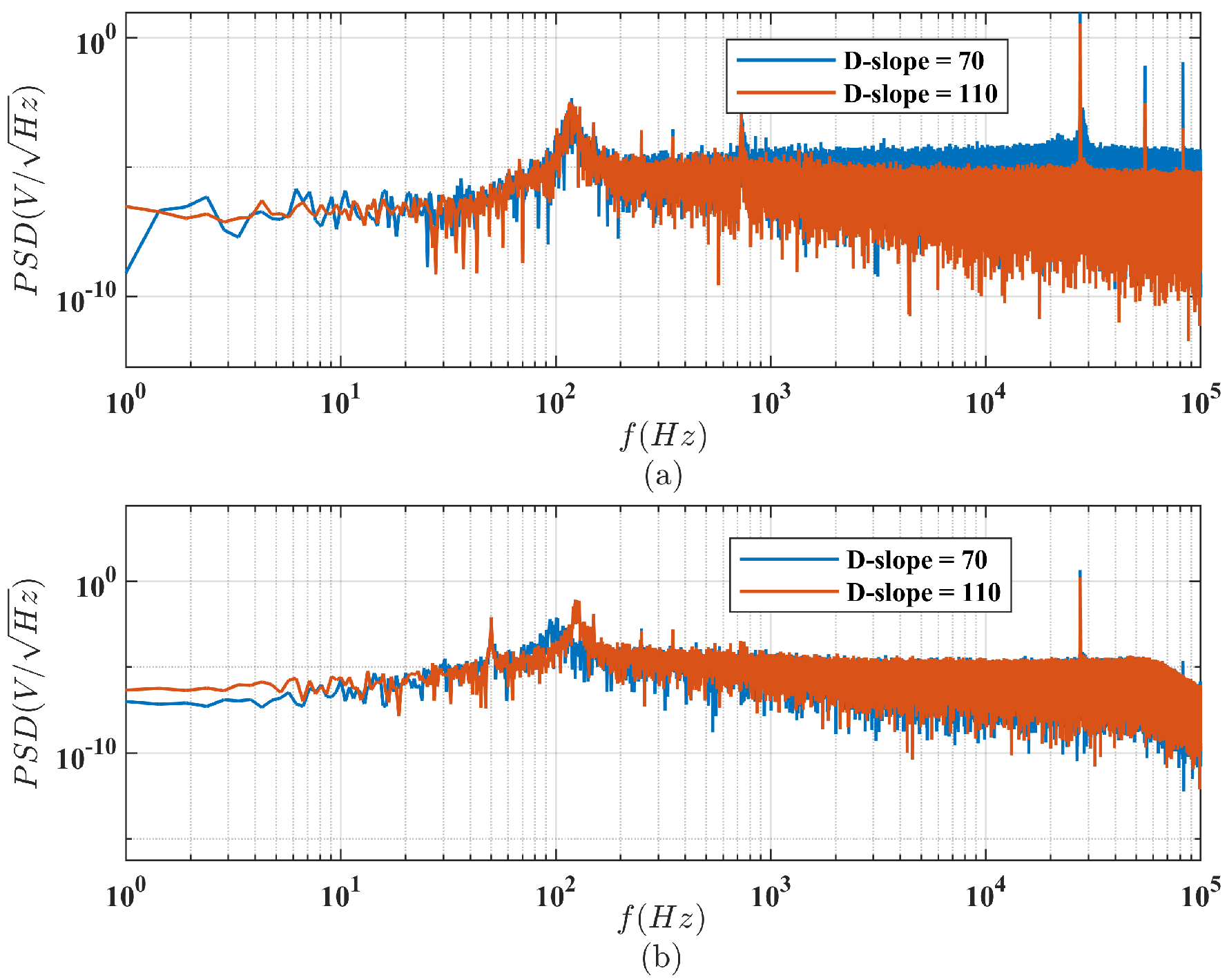
4.1. Parameter Optimization
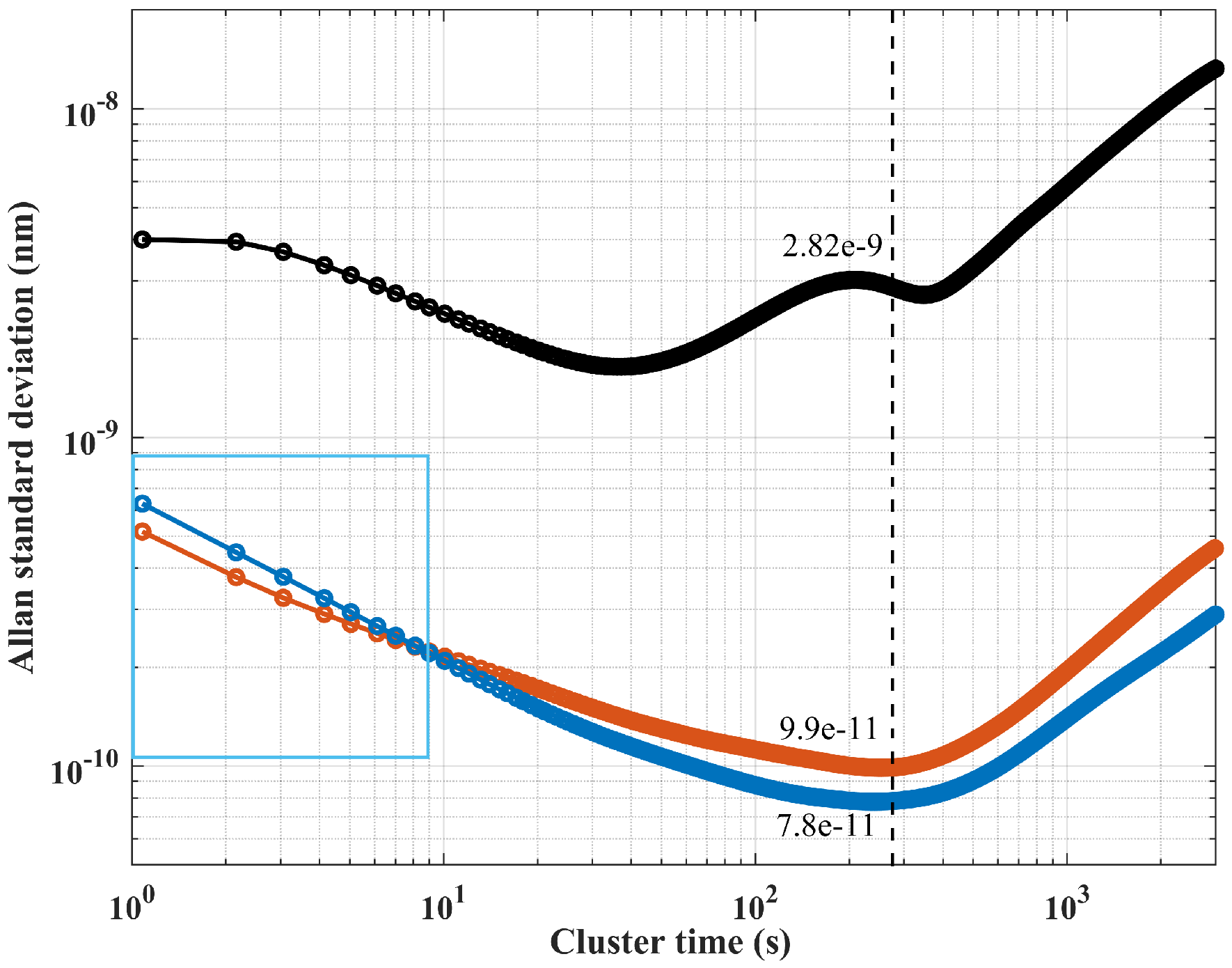
4.2. Pump and Probe Laser Locking Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tian, M.; Quan, W.; Jiang, L.; Liu, J.; Lu, Z. Single-beam NMOR atomic magnetometer based on a fiberized EOM. Opt. Lett. 2023, 48, 3075–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Z.; Lin, S.; Liu, Y.; Tang, J.; Zhai, Y. Gradient phase and amplitude errors in atomic magnetic gradiometers for bio-magnetic imaging systems. iSicence 2024, 27, 109250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Bi, W.; Li, Y.; Hu, Y.; Chang, M.; Zhang, X. A review of fiber-coupled atomic magnetometer. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. Opt. Technol. 2023, 65, 1516–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, R.; Yuan, L.; Wu, J.; Yuan, Q.; Zhu, J.; Fan, W.; Wang, Z.; Du, P. Transverse light-shift in a spin-exchange relaxation-free co-magnetometer: Measurement, decoupling, and suppression. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 15310–15326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Pang, H.; Wang, Z.; Fan, W.; Liu, F.; Liu, Y.; Quan, W. A New Design Method for a Triaxial Magnetic Field Gradient Compensation System Based on Ferromagnetic Boundary. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2024, 71, 13361–13371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Liu, Z.; Ding, M.; Chai, Z.; Liang, X.; Wu, W. The effect of tensor light shift on residual magnetic field compensation in a nuclear spin co-magnetometer. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2020, 116, 142405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Liu, S.; Liu, F.; Fan, W.; Zhai, Y.; Quan, W. The optimization and stabilization of detuned probe light frequency to suppress electron spin polarization error in SERF co-magnetometer. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2023, 359, 114467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seltzer, J.S. Developments in Alkali-Metal Atomic Magnetometry. Ph.D. Thesis, Princeton University, Princeton, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Talker, E.; Arora, P.; Zektzer, R.; Sebbag, Y.; Dikopltsev, M.; Levy, U. Light-Induced Atomic Desorption in Microfabricated Vapor Cells for Demonstrating Quantum Optical Applications. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2021, 15, L051001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Yang, B.; Zhao, H.; Ling, X.; Deng, J.; Cheng, H. Narrow Linewidth Laser Frequency Stabilization System for Integrating Sphere Cold Atom Clock. Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 2023, 60, 1514008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Huang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ye, M.; Li, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, L. All-fiber-based photonic microwave generation with 10−15 frequency instability. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2022, 20, 021406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, P.; Sun, H.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Q. Transfer of laser frequency from 729 nm to 1.5 µm with precision at the level of 10−20. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2022, 20, 081403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, Z.; Zhai, Y.; Yin, Y.; Ning, X.; Quan, W. Impact analysis of cavity length on transfer cavity frequency locking system for atomic inertial measurement device. AIP Adv. 2020, 10, 015340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhadnov, N.O.; Masalov, A.V. Temperature-compensated optical cavities for laser frequency stabilization. Laser Phys. Lett. 2023, 20, 030001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Duan, L.; Zhou, X.; Quan, W. Transfer matrix analysis of the birefringent fiber Fabry–Perot cavity and laser frequency locking. Results Phys. 2024, 57, 107375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Shi, X.H.; Zeng, X.Y.; Lu, X.L.; Deng, K.; Lu, Z.H. Characterization of electrical noise limits in ultra-stable laser systems. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2016, 87, 123105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamoun, J.; Digonnet, M.J. Aircraft-navigation-grade laser-driven FOG with Gaussian-noise phase modulation. Opt. Lett. 2017, 42, 1600–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Komanec, M.; Suslov, D.; Dousek, D.; Zvanovec, S.; Fokoua, E.R.N.; Bradley, T.D.; Poletti, F.; Richardson, D.J.; Slavik, R. Long-Length and Thermally Stable High-Finesse Fabry-Perot Interferometers Made of Hollow Core Optical Fiber. J. Light. Technol. 2020, 38, 2423–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Su, J.; Fan, Z.; Qiu, Q. High Precision Temperature Insensitive Strain Sensor Based on Fiber-Optic Delay. Sensors 2017, 17, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedger, J.P.; Elsmann, T.; Becker, M.; Tiess, T.; Luiten, A.N.; Sparkes, B.M. High performance fiber-Fabry-Perot resonator targeting quantum optics applications. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2020, 32, 879–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.X.; Cui, J.M.; Ai, M.Z.; Qian, Z.H.; Cao, H.; Huang, Y.F.; Jia, X.J.; Li, C.F.; Guo, G.C. Large-tuning-range frequency stabilization of an ultraviolet laser by an open-loop piezoelectric ceramic controlled Fabry–Pérot cavity. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 24674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, M.; Shen, K.; Song, Q.; Dai, Y.; Xiao, X.; Sun, Q.; Yan, Z. Sub-kHz linewidth laser generation by self-injection locked distributed feedback fiber laser. Opt. Laser Technol. 2024, 169, 110022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Locking Method | Locking Duration | Locking Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Presented in this article | 48 h | Drift 6.4 MHz |
| Locked on a fiber Fabry Perot cavity [20] | 35 h | Drift 10 MHz |
| Locked on open-loop PZT—controlled Fabry Perot cavity [21] | 41 h | Drift 11 MHz |
| Injection—locked to a fiber ring resonator [22] | 15 min | Drift less than 15 MHz |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, G.; Duan, L.; Zhou, X.; Quan, W. Far-Detuning Laser Frequency Disturbance Suppression for Atomic Sensor Based on Intrinsic Fiber Fabry–Pérot Cavity. Photonics 2024, 11, 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11111027
Li G, Duan L, Zhou X, Quan W. Far-Detuning Laser Frequency Disturbance Suppression for Atomic Sensor Based on Intrinsic Fiber Fabry–Pérot Cavity. Photonics. 2024; 11(11):1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11111027
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Guanghui, Lihong Duan, Xinxiu Zhou, and Wei Quan. 2024. "Far-Detuning Laser Frequency Disturbance Suppression for Atomic Sensor Based on Intrinsic Fiber Fabry–Pérot Cavity" Photonics 11, no. 11: 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11111027
APA StyleLi, G., Duan, L., Zhou, X., & Quan, W. (2024). Far-Detuning Laser Frequency Disturbance Suppression for Atomic Sensor Based on Intrinsic Fiber Fabry–Pérot Cavity. Photonics, 11(11), 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11111027






