Passively Mode-Locked Erbium-Doped Fiber Laser and Application in Laser Thrombolysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
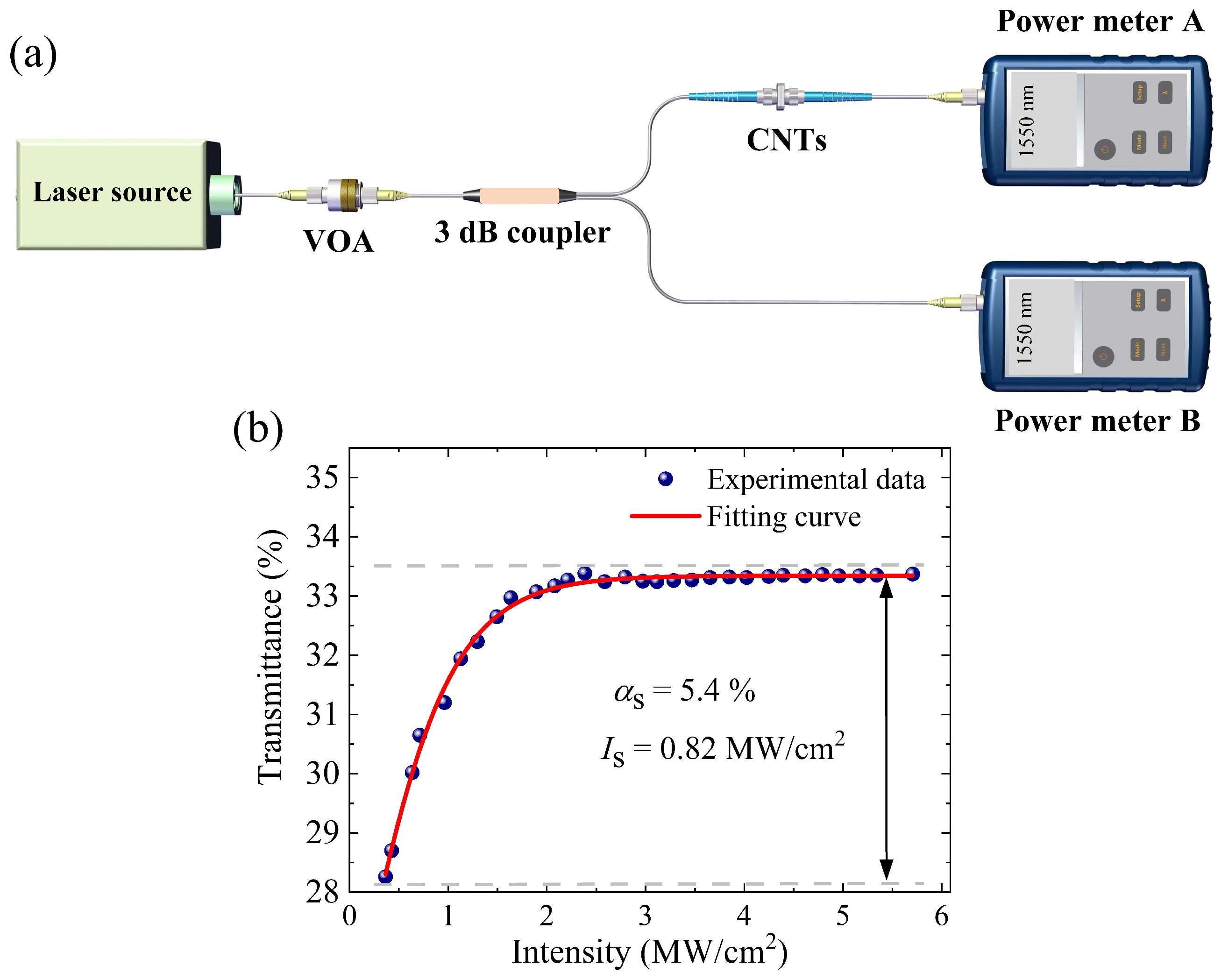
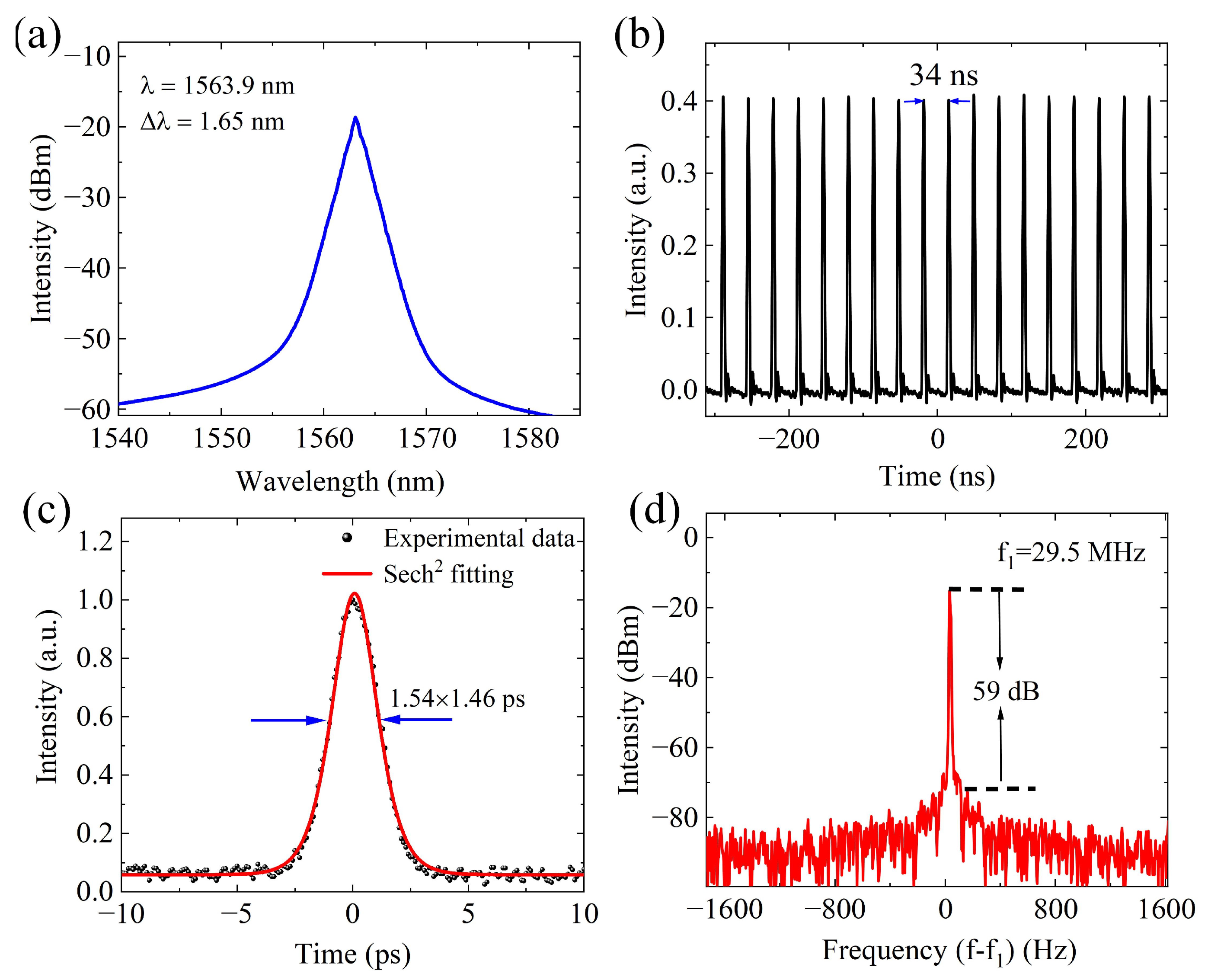
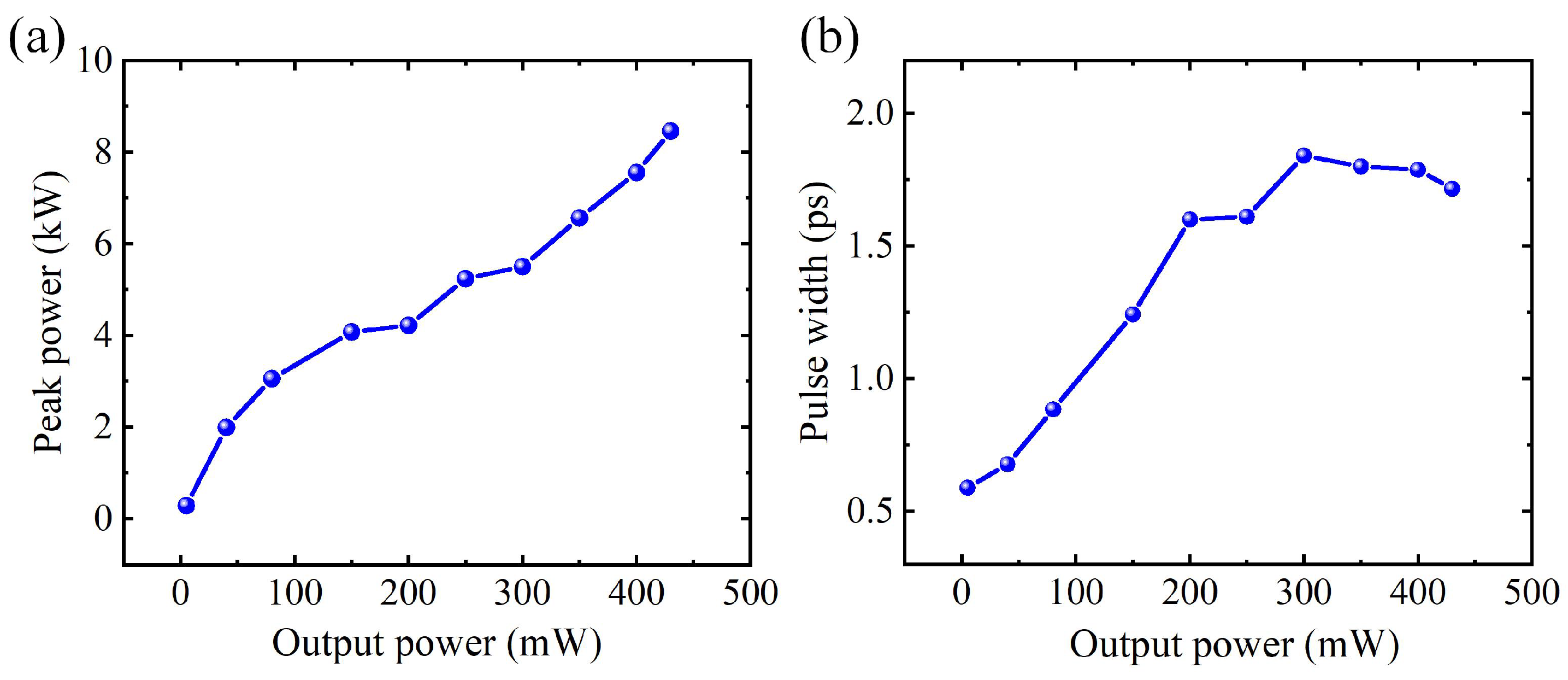
2.1. Mode-Locked Fiber Laser Based on CNTs
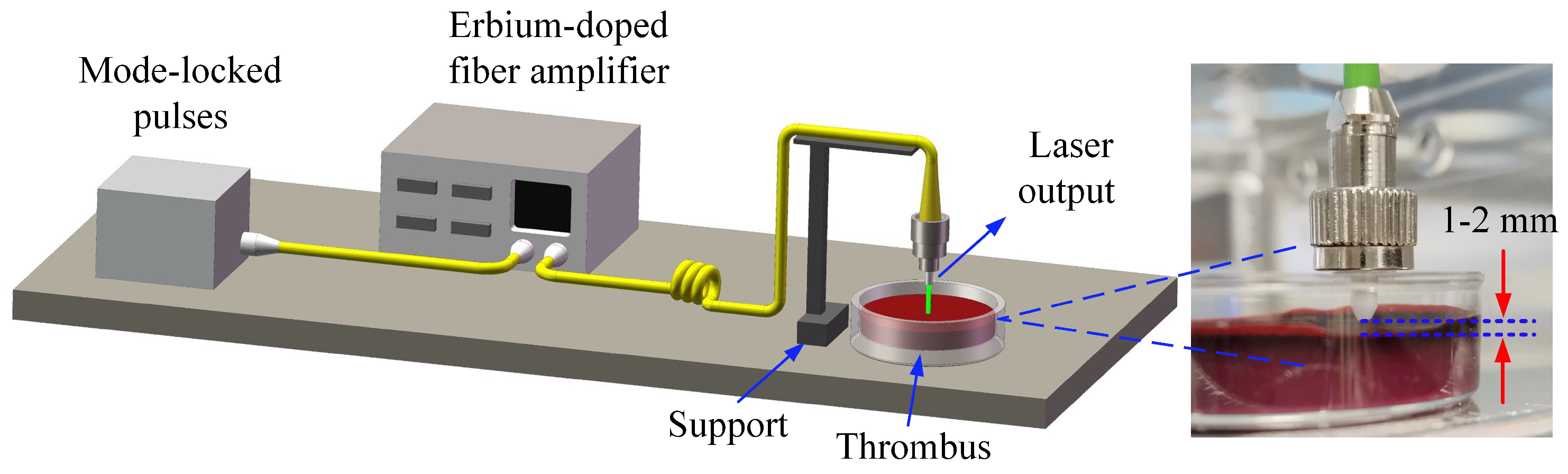
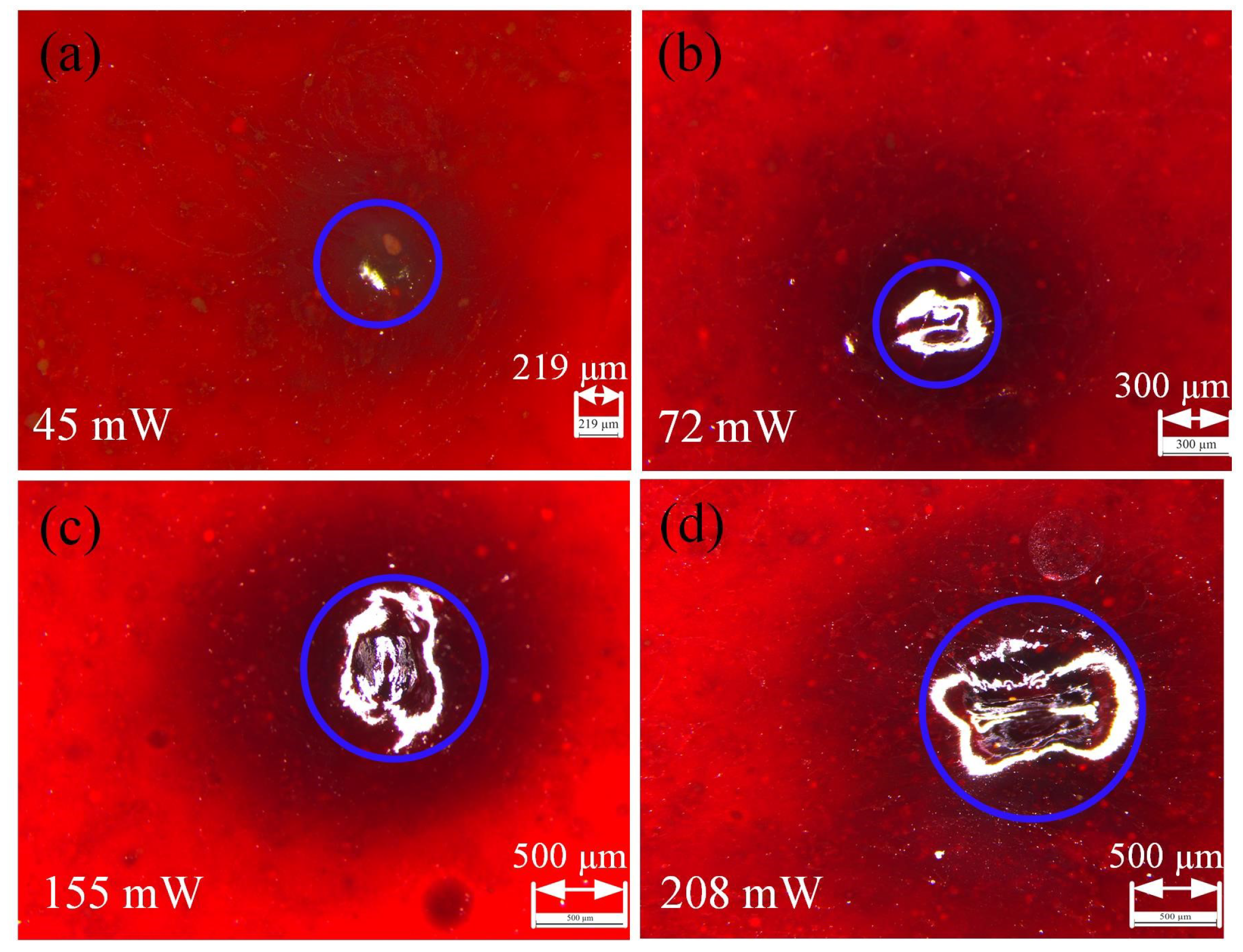
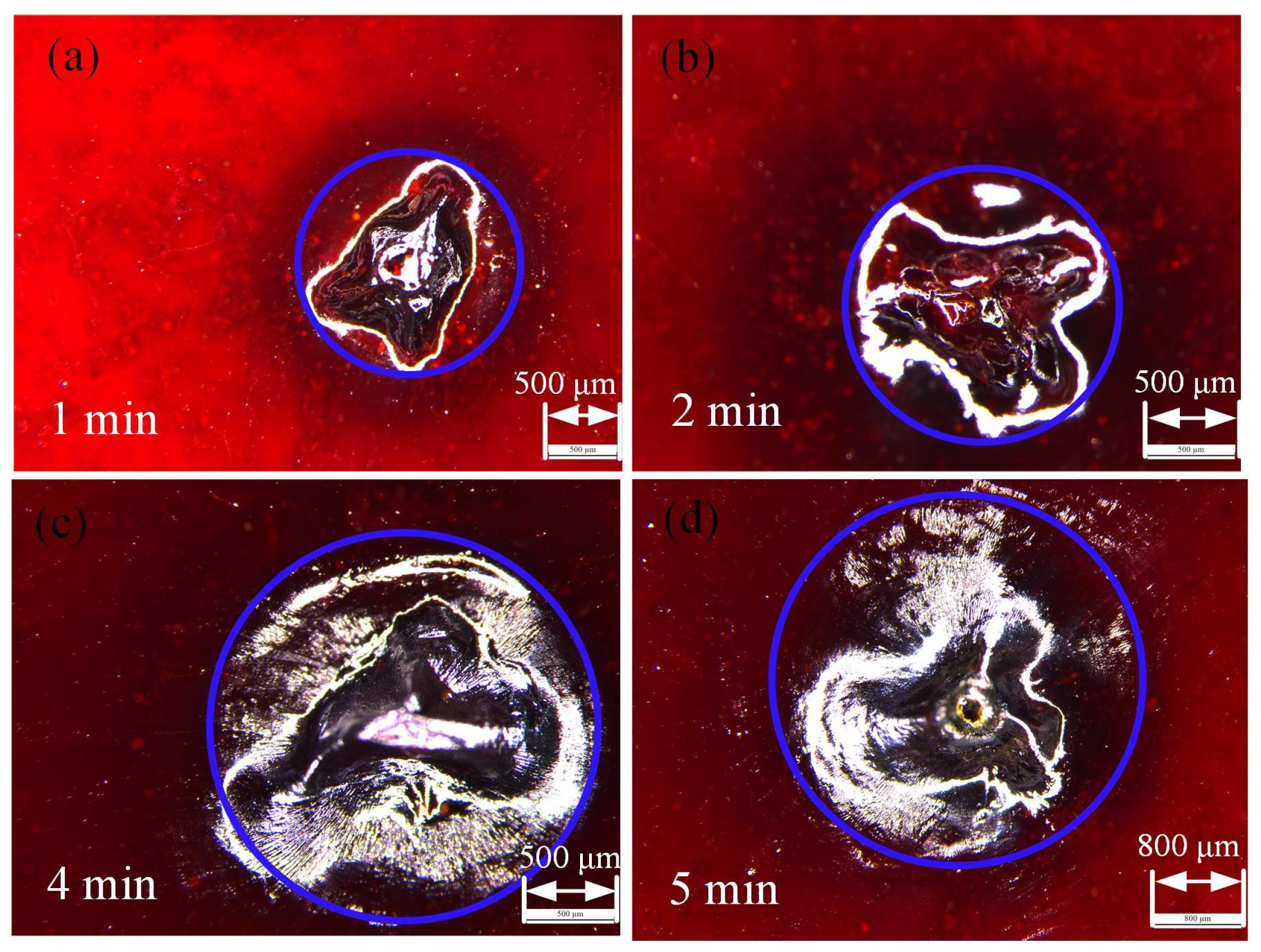
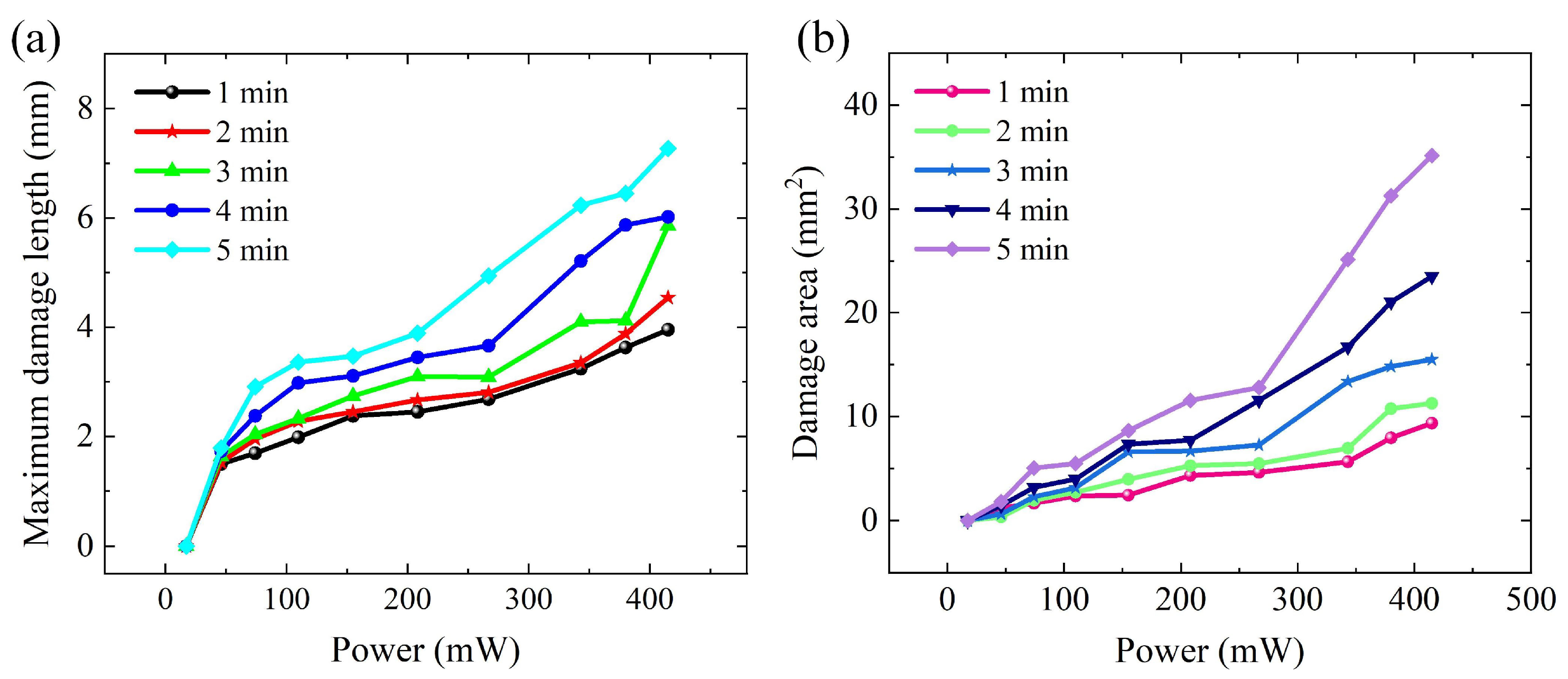
2.2. Laser Thrombolysis Application
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sroka, R.; Stepp, H.; Hennig, G.; Brittenham, G.M.; Rühm, A.; Lilge, L. Medical laser application: Translation into the clinics. J. Biomed. Opt. 2015, 20, 061110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamkouri, H.; Si, J.; Chen, P.; Niu, C.; Chen, L. Biomedical optics and photonics for advanced clinical technologies. Opt. Laser Technol. 2024, 179, 111265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierce, M.C.; Jackson, S.D.; Golding, P.S.; Dickinson, B.; Dickinson, M.R.; King, T.A.; Sloan, P. Development and application of fiber lasers for medical applications. In Proceedings of the Optical Fibers and Sensors for Medical Applications, San Jose, CA, USA, 20–21 January 2001; Volume 4253, pp. 144–154. [Google Scholar]
- Gursel, A.T. Fiber lasers and their medical applications. Opt.-Amplifiers-Few Differ. Dimens. 2018, 10, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Piao, Z.; Zeng, L.; Chen, Z.; Kim, C.S. Q-switched erbium-doped fiber laser at 1600 nm for photoacoustic imaging application. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 108, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Jin, H.; Liu, J.; Chao, J.; Liu, T.; Zhang, H.; Wang, G.; Lyu, W.; Wageh, S.; Al-Hartomy, O.A.; et al. Integration and applications of nanomaterials for ultrafast photonics. Laser Photonics Rev. 2022, 16, 2200386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogusławski, J.; Sterczewski, Ł.; Stachowiak, D.; Soboń, G. Intracavity filtering in SESAM mode-locked fiber lasers: Soliton effects and noise performance. Opt. Express 2023, 31, 27667–27676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.B.; He, X.; Wang, D. Passively mode-locked fiber laser based on a hollow-core photonic crystal fiber filled with few-layered graphene oxide solution. Opt. Lett. 2011, 36, 3024–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Hua, Y.; Xiao, X.; Zhu, H.; Sun, Z.; Yang, C. Broadband graphene saturable absorber for pulsed fiber lasers at 1, 1.5, and 2 µm. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2014, 20, 411–415. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Lin, J.; Zhang, X.; Xu, L.; Gu, C.; Sun, B.; Wang, A.; Zhan, Q. Self-starting passively mode-locked all fiber laser based on carbon nanotubes with radially polarized emission. Photonics Res. 2016, 4, 327–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Cheng, H.; Xu, L.; Fu, B.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H. Ag/MXene composite as a broadband nonlinear modulator for ultrafast photonics. ACS Photonics 2023, 10, 3133–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Sun, J.; Wang, C.; Shang, C.; Xu, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, H. MXenes: Synthesis, optical properties, and applications in ultrafast photonics. Small 2021, 17, 2006054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Tian, X.; Gao, B.; Wu, G. Dynamic evolution of the dissipative soliton in passively mode-locked fiber laser based on black phosphorus as a new saturable absorber. Opt. Commun. 2018, 406, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, W.; An, J.; Lin, Y.; Qiu, P.; Wang, G.; Chao, J.; Fu, B. Fabrication and applications of heterostructure materials for broadband ultrafast photonics. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2023, 11, 2300124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zheng, X.W.; Liu, M.; Zhao, N.; Luo, A.P.; Luo, Z.C.; Xu, W.C.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, C.J.; Wen, S.C. Femtosecond pulse generation from a topological insulator mode-locked fiber laser. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 6868–6873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Lin, R.; Ruan, S.; Liu, A.; Chen, H.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, S.; Guo, C.; Hu, J. A practical topological insulator saturable absorber for mode-locked fiber laser. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Huang, Z.; Huang, Q.; Zhao, C.; Rozhin, A.; Sergeyev, S.; Al Araimi, M.; Mou, C. Carbon nanotube mode-locked fiber lasers: Recent progress and perspectives. Nanophotonics 2020, 10, 749–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.R.; Parrish, J.A. Selective photothermolysis: Precise microsurgery by selective absorption of pulsed radiation. Science 1983, 220, 524–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.; Guo, Z. Modeling of ultrashort pulsed laser ablation in water and biological tissues in cylindrical coordinates. Appl. Phys. B 2011, 103, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidinger, J.; Ackermann, R.; Cattaneo, G.; Kammel, R.; Nolte, S. A feasibility study on femtosecond laser thrombolysis. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2014, 32, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzog, A.; Oszkinis, G.; Planer, D.; Ziaja, K.; Kruszyna, Ł.; Stanisić, M.G.; Ziaja, D.; Ishaaya, A.A.; Kuczmik, W. Atherectomy using a solid-state laser at 355 nm wavelength. J. Biophotonics 2017, 10, 1271–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, K.; Huang, J. Simulation of the effect of spot size on temperature field and weld forming in laser tissue welding. Optik 2018, 155, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, W.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, T. Study on the mechanism of thrombus ablation in vitro by burst-mode femtosecond laser. J. Biophotonics 2022, 15, e202200197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Zhai, S.; Li, B.; Gao, S. High power and conversion efficiency intracavity ultraviolet laser at 355 nm. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2023, 128, 104485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.M.; Feit, M.D.; Rubenchik, A.M.; Joslin, E.J.; Celliers, P.M.; Eichler, J.r.; Da Silva, L.B. Influence of pulse duration on ultrashort laser pulse ablation of biological tissues. J. Biomed. Opt. 2001, 6, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garmire, E. Resonant optical nonlinearities in semiconductors. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2000, 6, 1094–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, K.; Hou, D. Recent research and advances of material-based saturable absorber in mode-locked fiber laser. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 137, 106826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhu, Z.; Qi, Y.; Jin, L.; Li, L.; Lin, X. Internal motion within pulsating pure-quartic soliton molecules in a fiber laser. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2023, 172, 113544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runge, A.F.; Hudson, D.D.; Tam, K.K.; de Sterke, C.M.; Blanco-Redondo, A. The pure-quartic soliton laser. Nat. Photonics 2020, 14, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janis, A.D.; Buckley, L.A.; Nyara, A.N.; Prahl, S.A.; Gregory, K. A reconstituted in vitro clot model for evaluating laser thrombolysis. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2002, 13, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennes, H.H. Analysis of tissue and arterial blood temperatures in the resting human forearm. J. Appl. Physiol. 1948, 1, 93–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemz, M. Laser-Tissue Interactions; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Ziegler, Z.M.; Wright, L.G.; Wise, F.W. Megawatt peak power from a Mamyshev oscillator. Optica 2017, 4, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsun, T.; Islam, M.; Chu, P. High-energy femtosecond figure-eight fiber laser. Opt. Commun. 1997, 141, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Xie, J.; Liu, Q.; He, C.; Qi, Y.; Li, L.; He, L.; Liu, C.; Lin, X.; Yang, S. Generation of high-energy self-mode-locked pulses in a Tm-doped fiber laser. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2024, 125, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagha, H.Z.; Gülsoy, M. Photothermal ablation of liver tissue with 1940-nm thulium fiber laser: An ex vivo study on lamb liver. J. Biomed. Opt. 2016, 21, 015007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Jivraj, J.; Zhou, J.; Ramjist, J.; Wong, R.; Gu, X.; Yang, V.X. Pulsed and CW adjustable 1942 nm single-mode all-fiber Tm-doped fiber laser system for surgical laser soft tissue ablation applications. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 16674–16686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, X.; Cong, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, C.; Ahmad, I.; Fu, B. Passively Mode-Locked Erbium-Doped Fiber Laser and Application in Laser Thrombolysis. Photonics 2024, 11, 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11111006
Zhao X, Cong L, Zhang C, Zhang C, Ahmad I, Fu B. Passively Mode-Locked Erbium-Doped Fiber Laser and Application in Laser Thrombolysis. Photonics. 2024; 11(11):1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11111006
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Xiaoli, Linyu Cong, Congyu Zhang, Chenxi Zhang, Ijaz Ahmad, and Bo Fu. 2024. "Passively Mode-Locked Erbium-Doped Fiber Laser and Application in Laser Thrombolysis" Photonics 11, no. 11: 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11111006
APA StyleZhao, X., Cong, L., Zhang, C., Zhang, C., Ahmad, I., & Fu, B. (2024). Passively Mode-Locked Erbium-Doped Fiber Laser and Application in Laser Thrombolysis. Photonics, 11(11), 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics11111006





