Abstract
We demonstrate the utilization of iron oxide (Fe2O3) as light-absorbing material in an erbium-doped fiber laser (EDFL) for the generation of Q-switched pulses. A sandwich-type saturable absorber (SA) with Fe2O3 nanoparticles between fiber ferrules is proposed. A fiber ferrule tip is tapped onto a cap of index-matching gel, which is then dipped into Fe2O3 nanoparticle powder to allow its deposition through the adhesion effect. By incorporating Fe2O3–SA in an EDFL, self-started and stable Q-switched pulses are attained at a threshold power of 50.1 mW. The pulse repetition rate is tunable from 9.92 kHz to 22.47 kHz, whereas the pulse duration reduces from 38.4 µs to 13.8 µs with the pump power increment. The maximum pulse energy achieved is 36.9 nJ. This work offers a simple integration method of Fe2O3 nanoparticles as potential SAs for the generation of Q-switched pulses.
1. Introduction
Q-switched pulses with high energy have gained great interest as a versatile technique for many applications such as laser machining [1], remote sensing [2], range finding [3], and medical treatment [4]. Q-switched fiber lasers can be developed either by passive techniques based on saturable absorbers (SAs) [5] or active techniques, which are enabled by external optical modulators [6]. Compared to the active technique, the passive scheme is preferable due to its low complexity, easy operation, and cost-effectiveness. Early studies have marked semiconductor saturable absorber mirrors (SESAMs) as one of the pioneering SAs with a rigid structure to realize passive Q-switching. However, under a relatively high pulse-repetition rate regime, SESAMs are prone to optical damage due to their low-thermal damage threshold. This reduces their functional lifetime [7], not to mention their complex fabrication process and limited wavelength operation. Then, carbon nanotubes (CNTs) have gained interest as an alternative to SESAMs thanks to their ease of fabrication and wider operating wavelength range. However, the regulation of the optical bandgap in CNTs is rather tough since it strongly depends on the nanotube’s chirality [8].
Following the discovery of graphene as an ultrafast material, numerous two-dimensional (2D) materials have been studied as potential SAs due to their ultrafast carrier responses, broadband absorption, and high susceptibility to nonlinear optical effects [9]. Besides graphene, transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs) are also categorized as one of the 2D materials. TMD is a combination of Group 4–7 transition metals (M) and chalcogen (X) in the form of MX2 [10], such as zirconium diselenide (ZrSe2) [11], titanium diselenide (TiSe2) [12], molybdenum telluride (MoTe2) [13], nickel telluride (NiTe2) [14], platinum diselenide (PtSe2) [15], and zirconium disulfide (ZrS2) [16]. Since the thickness of TMD affects its optoelectronics properties [13], meticulous fabrication procedures are required, which become the limiting factor for tailoring their properties.
Topological insulators (TIs), another class of 2D materials, have also emerged as a remarkable SA, including bismuth selenide (Bi2Se3) [17], antimony telluride (Sb2Te3) [18], and bismuth telluride (Bi2Te3) [19]. However, the topological structure of Tis, which consists of a metallic edge with an insulating interior from two different elements, involves a complex preparation process [20]. Yet black phosphorus, which is also a 2D material, tends to oxidize easily, thus leading to an unstable operation [21]. Undeniably, the performance of the pulse laser is directly influenced by the properties of the SA. Thus, the superiority of other saturable absorption materials, apart from the aforementioned 2D materials, is still worthy of investigation and remains interesting.
Lately, transition metal oxide (TMO) nanoparticles are found to attract wide attention as light-absorbing materials. A tremendous surge in research of the TMOs is driven by their properties of smaller sizes and more regular shapes compared to the 2D materials [21]. These properties are expected to improve pulse stability generated in laser cavities. The reported TMO nanoparticles, which possess a circle-like shape with a homogeneous nanometer particle size, have been proven as high-performance SA; for instances: manganese dioxide (MnO2) [22], titanium dioxide (TiO2) [23], indium tin oxide (InSnO2) [24], aluminum oxide (Al2O3) [25], and iron (III) oxide (Fe3O4) [26]. While most researchers appraise the TMO as SAs, works conducted using iron (II) oxide (Fe2O3) for Q-switched fiber laser generation are relatively few. With particular characteristics of Fe2O3 nanoparticles, such as a high optical nonlinearity susceptibility of 4.0 × 10−10 esu [27], a wide bandgap of 1.9–2.2 eV [28], and an ultrafast response time of 18~30 ps [29], the application of Fe2O3 for pulse-laser generation could be very promising.
It is necessary to point out that the fabrication method of the SA determines its complexity and challenges. Amongst the methods reported to form SAs are by depositing a Fe3O4–polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) thin film on tapered fiber [30] and sandwiching a thin film of Fe3O4–PVA between fiber ferrules [31], whereby the Fe3O4 was previously synthesized by a chemical co-precipitation method. In another work by N. Li et al., the Fe3O4 was synthesized by a thermal decomposition technique, which was then mixed with sodium carboxymethylcellulose (NaCMC) to produce a Fe3O4–NaCMC thin film as the SA [32]. Those reported Fe3O4 thin films have been demonstrated to function well in Q-switched laser generation. However, preparing iron–oxide materials embedded in thin films requires additional steps that are laborious. First, the insertion loss introduced by the host polymer of the thin film needs to be reduced, in which a careful control of the thickness, formulation, and SA–polymer ratio of the thin film is necessary. Moreover, the thickness of the SA thin film also has a large influence on its nonlinear optical properties. For example, thicker SA thin film will result in lower saturation intensity, while thinner SA thin film will result in lower modulation depth [33], whereby both cases can degrade the overall performance of the SA. Second, the SA materials should be uniformly dispersed within the host polymer to minimize the scattering loss. This involves extra steps such as ultrasonication and a spin-coating process. Third, since SA’s non-saturable loss increases with the presence of impurities, more precautions should be taken during the thin film fabrication process. Upon encountering these problems, an alternative fabrication scheme with a potential solution is needed.
In this research work, we demonstrate a less sophisticated approach for Fe2O3 deposition on fiber ferrule via a simple adhesion process by using index-matching gel. In previous works, thin films were mainly formed using a polymer material, but this process does not require the use of such materials. Without having to confront the difficulties and skillful techniques for thin film preparation as aforementioned, this process is also inexpensive, less time-consuming, easy to implement, and it doesn’t need highly precise instruments. Besides that, the product can be used after the deposition process. Once the prepared Fe2O3–SA device is placed in an erbium-doped fiber laser (EDFL), a stable Q-switched pulse operation is obtained at a 50.1-mW threshold power. This proposed laser system produces 36.9 nJ of pulse energy at the maximum pump power of 174.3 mW. It is noteworthy that the Q-switched operation is reversible, such that the pulse properties are conserved when the experiment is repeated either by increasing or decreasing the pump power.
2. Fabrication of Fe2O3-Based SA
The Fe2O3 material employed in this study is in a nanopowder form with a particle size of 20–40 nm and a purity of 99%, which is purchased from US Research Nanomaterials, Inc. The Fe2O3 nanopowder is first drawn out onto a piece of filter paper, as shown in Figure 1a. Then, a clean single-mode fiber ferrule is slightly dipped into an index matching gel, as illustrated in Figure 1b. The refractive index of the index-matching gel is 1.463, which is very close to that of the single-mode fiber core. As such, light can propagate from one to another with neither reflection nor refraction. The index-matching gel provides a quick and reliable way to reduce Fresnel reflection and insertion loss between two fiber ferrules by minimizing the air gap in their consecutive cores. It offers crystal clarity, mechanical stability, and wide-temperature functionality. They are ready to use, have no intrinsic limit to shelf life, and do not cure or harden due to chemical reactions. For the deposition process, a cotton bud is used to tap out the Fe2O3 nanopowder on the filter paper to be transferred to the fiber ferrule, as illustrated in Figure 1c. The Fe2O3 nanopowder will attach to the facet of the fiber ferrule through the adhesion effect. To ensure the Fe2O3 nanopowder is smoothly dispersed on the fiber ferrule, it is carefully rubbed against a scotch tape, as shown in Figure 1d. In addition, with quasi-solid properties of the index-matching gel, sedimentation of the Fe2O3 could be avoided. Through a fiber adaptor, this Fe2O3-deposited fiber ferrule is attached with another clean fiber ferrule to construct the SA device, as shown in Figure 1e. This Fe2O3–SA device is instantly ready to be used once it is integrated into the EDFL cavity. To verify the attachment of Fe2O3 deposition on the fiber ferrule, the cross-sectional image of the Fe2O3-coated fiber facet is observed from a Pro’s Kit Fiberscope. Figure 2a shows the captured image of the fiber ferule facet under magnification of 200, whereas Figure 2b shows the zoom-in view of its core image. The Fe2O3 layer is visible as the brown spot on the fiber ferrule facet. As can be seen from Figure 2b, the brown spot representing the Fe2O3 layer covers the core center precisely. Oily residue at the edges of the brown spot is the trace of the index-matching gel.
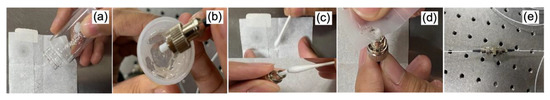
Figure 1.
(a–e) Procedural steps of forming Fe2O3–SA device.
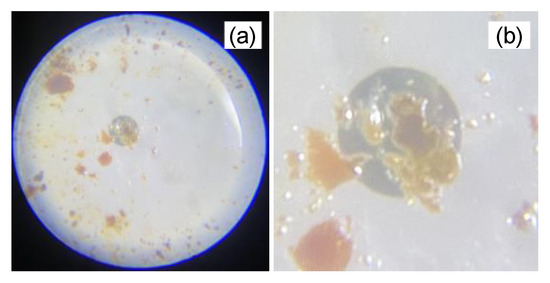
Figure 2.
(a) Optical fiberscope inspection of Fe2O3 layer (brown spot) on fiber ferrule end. (b) Zoom-in view of the core image of fiber ferrule.
3. Fe2O3 Nonlinear Optical Properties
By using a dual-detector power-dependent transmission measurement, we characterize the nonlinear optical properties of the Fe2O3–SA device. The system comprises an ultra-fast laser source with a central wavelength of 1550 nm, a pulse duration of 117 fs, a pulse repetition rate of 250 MHz, and a maximum output power of 250 mW. The result of the recorded transmitted power against varying input power to the Fe2O3–SA is plotted in Figure 3. The nonlinear saturable absorption properties are acquired from the curve fitting of the data using the following instantaneous two-level SA model [34]:
where T(I) is the intensity-dependent transmission coefficient, Tns is the non-saturable transmission loss, is the modulation depth, I is the input intensity, and Isat is the saturation intensity. The estimated , Isat, and Tns of the Fe2O3–SA from the curve fitting are 3.63%, 88.36 MW/cm2, and 75.51%, respectively.
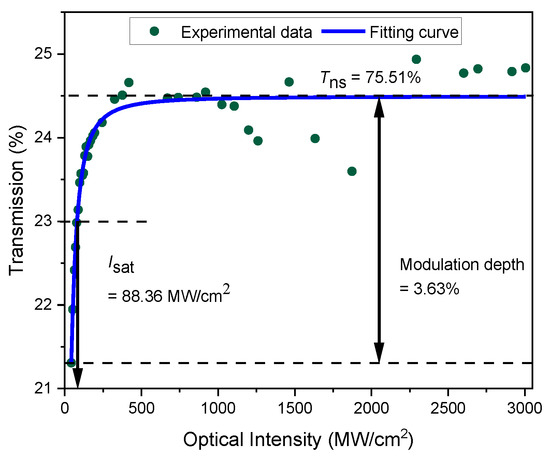
Figure 3.
Nonlinear optical properties of Fe2O3–SA device.
The Fe2O3–SA is then further characterized in terms of its linear transmission by employing a C+L-band amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) source (model BO–ASE–CL–50) and a Yokogawa AQ6370B Optical Spectrum Analyzer (OSA) with a wavelength span of 1530 to 1605 nm. The result is shown in Figure 4, which denotes that transmission at 1560 nm is about 34.26%.
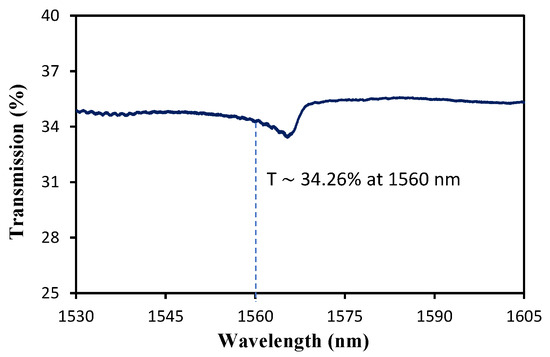
Figure 4.
Linear transmission of Fe2O3–SA device.
4. Fe2O3 Structural Properties
The crystal structure of the Fe2O3 nanoparticles is identified using an X-ray diffraction (PANalytical X’pert PRO PW3040) (Shimadzu Corporation, Kyoto, Japan) with a nickel-filtered CuKα (λ = 1.5418 Å) radiation at an operating voltage of 40 kV and a current supply of 40 mA. To study the diffraction patterns, the Fe2O3 nanoparticles are scanned from a 20°-to-80° angle (2θ) with a scanning speed of 0.005°/s. The experimental finding is depicted in Figure 5. All of the detected peaks match the JCPDS data (File No. 25-1402) as Maghemite–Q (iron oxide), which fits into a hexagonal system. The average crystallite size calculated using Sherrer’s formula based on a (hkl) plane of (131) is 15.9 nm.
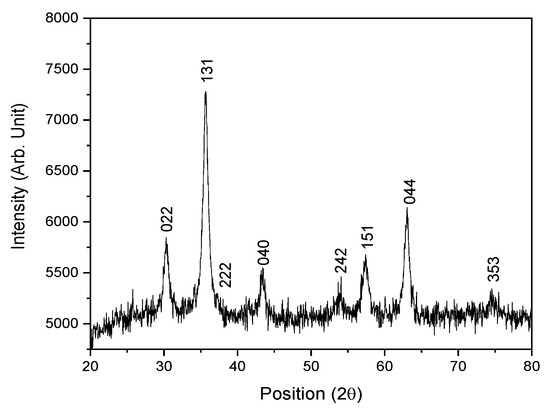
Figure 5.
XRD pattern of Fe2O3 nanoparticles.
To study the Fe2O3 nanoparticle surface morphology, a field emission-scanning electron microscopy (FESEM, GeminiSEM 500) (Carl Zeiss, Cambridge, UK) is employed to examine the sample. Figure 6 shows the micrograph of the Fe2O3 nanoparticles with homogenous and uniform spherical shapes ranging from 20 to 40 nm. From the XRD result, the estimated crystallite size of the Fe2O3 particle is roughly 15.9 nm. Based on these findings, the Fe2O3 particle size attained in FESEM is larger than the calculated ones. The discrepancy of the particle size is influenced by a high surface energy of smaller particles that attract each other as a result of agglomeration.
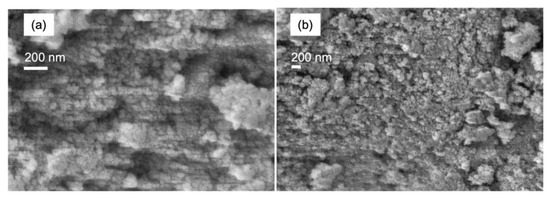
Figure 6.
FESEM image of Fe2O3 nanoparticles at (a) 50,000; and (b) 20,000 magnification.
The compositional analysis of the Fe2O3 nanoparticles is conducted using the energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) analysis technique. Figure 7 displays the EDX spectrum of the Fe2O3 nanoparticles spot with their elemental mapping analysis, as shown in Figure 8. The EDX spectrum and elemental mapping show four prominent peaks that refer to Fe, Se, C, and Pt elements. The detected Pt signal is the result of the sample coating to prevent charging during the measurement. However, the presence of the C peak is due to the background environment. Moreover, it could be due to the carbon tape used in gripping the Fe2O3 sample. Other impurities elements are not found in this analysis. The average atomic percentage of Fe:O is 43.86:55.44 in the ratio range of 2.0:2.6, which matches the stoichiometric ratio of 2:3.
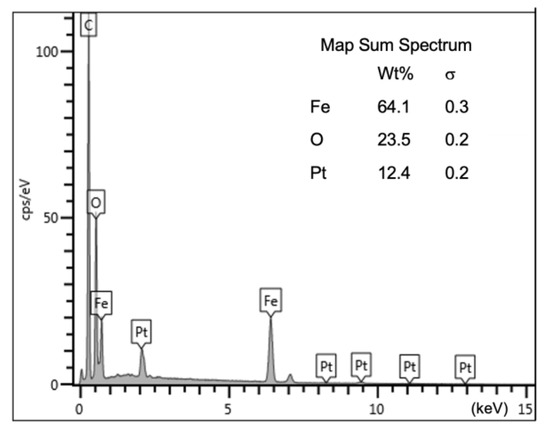
Figure 7.
EDX spectrum of Fe2O3 nanoparticles.
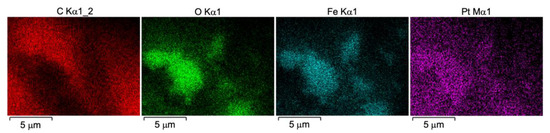
Figure 8.
Elemental mapping of Fe2O3 nanoparticles.
5. Q-Switched EDFL Configuration
Figure 9 depicts the EDFL configuration integrated with the fabricated Fe2O3–SA. A 980-nm laser diode (LD) is employed to excite a 6-m long erbium-doped fiber (EDF, Lucent Technologies HP980) (OFS, Norcross, GA, USA) with an absorption coefficient of 3.5 dB/m at 1530 nm. The 980-nm pump light is coupled to the EDF through a fused 980/1550-nm wavelength selective coupler (WSC). Another end of the EDF is spliced into an optical isolator to form an unidirectional signal oscillation. A three-paddle polarization controller (PC) is utilized to change the birefringence effect of the circulating light. The fabricated Fe2O3–SA device is placed in between the PC and a 70:30 output coupler (OC). Seventy percent of circulating light power is channeled back to the laser cavity, while the remaining 30% is designed as the output. The output spectrum is recorded by an OSA (AQ6370B) (Yokogawa, Tokyo, Japan) with a 0.02-nm resolution bandwidth. A 100 MHz bandwidth digital phosphor oscilloscope (TDS 3012C) (Tektronix, Beaverton, OR, USA) with a 1.25 GS/s sample rate is used to analyze the output pulse train through a 5 GHz bandwidth InGaAs-biased photodetector (DET08CFC) (Thorlabs, Newton, NJ, USA) with a 70-ps rise time.
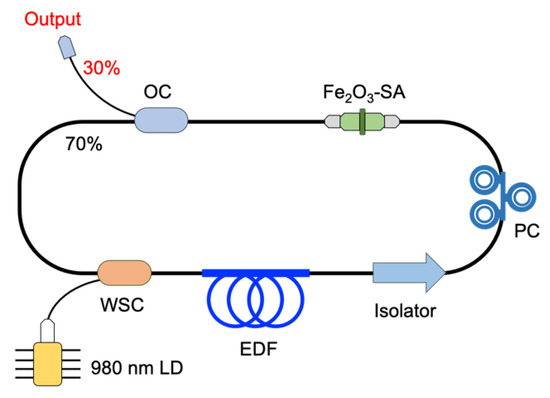
Figure 9.
Configuration of the proposed Q-switched EDFL utilizing Fe2O3–SA device.
6. Results and Discussion
Initially, the proposed EDFL operates in a continuous wave (CW) region after reaching the lasing threshold of ~26 mW. Starting from the 50.1-mW pump power, a stable Q-switching operation is attained until a 174.3-mW maximum pump power. The output spectrum of the Q-switched EDFL obtained from the OSA is shown in Figure 10, which is represented by the red line. This measurement is taken at the pump power of ~98.9 mW. The peak wavelength of the laser output is approximately 1560 nm. For comparison, the output spectrum of the Q-switched EDFL is superimposed on that of the basic EDFL without Fe2O3, as represented by the green line in the figure, which is taken at the same pump power level of ~98.9 mW. From the findings, the laser is blue-shifted with the incorporation of Fe2O3, whereby the peak wavelength is originally at 1564 nm without the Fe2O3 in the cavity. In addition, the bandwidth of the output spectrum of the latter increases from ~1 to ~2.4 nm at a −30-dBm level. This indicates the modulation structure arises when the laser transitions from CW to Q-switching mode owing to perturbations in the cavity and oscillations in multiple modes [35].
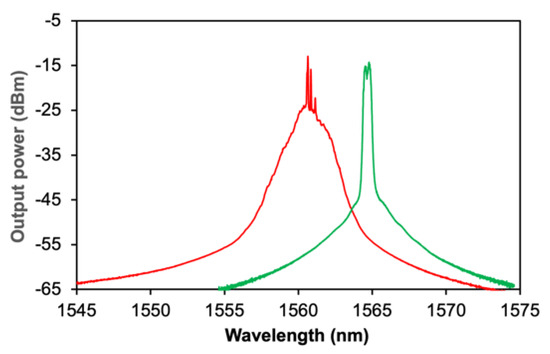
Figure 10.
Output spectra of Q-switched EDFL (red) and CW EDFL (green) at 98.9 mW.
Figure 11 illustrates the output pulse train at a maximum pump power of 174.3 mW. The time interval between adjacent pulses is 44.5 µs, which yields a repetition rate value of 22.47 kHz. It is worth to note that the existence of the CW component in the Q-switched output spectrum as observed in Figure 10 does not impair its pulse operation. This is validated by a stable and uniform pulse train obtained throughout this work. Thus, it can be implied that the Q-switched operation is dominant over the CW operation, such that the uneven and unstable temporal pulse due to the CW component is not significant over the pulse train. Since the pulse formation originates from the saturable absorption effect of Fe2O3 and maintains throughout the pump power increment after the transient, it is possible that the pulsed laser experiences multistability, which holds multiple long-term behaviors of both CW and Q-switching. The multistability state has been numerically analyzed using a basic model of two coupled lasers with saturable absorption as reported in Ref. [36]. Apparently, it is almost improbable to observe the coexistence of both CW and Q-switching at the same pump power [37], where these two operation regimes could not arise synchronously. For different cases, the multistability region is slightly applicable to self-pulsation phenomena. The self-pulsation typically occurs at the beginning of laser action, immediately after the transient phase. As the stable CW state appears, the pulsation gradually decays. However, in this work, the long-term operation of both CW and Q-switching beyond the CW threshold indicates that the system is not undergoing self-pulsation. The output pulse train at different pump powers, and their corresponding output spectrums, is shown in Figure 12. To clarify that the Q-switched pulse is solely induced by the nonlinear effect of Fe2O3, the SA device is replaced with a fiber ferrule that is only applied with index-matching gel. Results show that there is no pulse generated, indicating that the saturable absorption effect purely originates from the deposited Fe2O3. This also verifies that the Q-switching behavior is not attributed to the nonlinear response of the EDFL towards harmonic modulation of the pump laser diode as reported in Ref. [38], in which the Q-switching is realized without the incorporation of a saturable absorber. In a different laser system reported by Otupiri et al., whereby the Q-switched pulse was realized in an all-fiber laser with a saturable absorber section, the excitable regime of the laser operation was clearly demonstrated [39]. More interestingly, they developed an enhanced theoretical laser model for EDFL that addressed the experimental results perfectly.
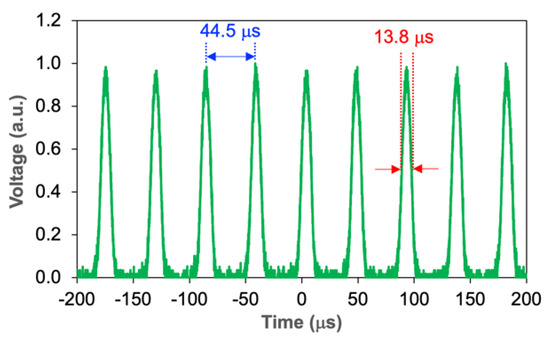
Figure 11.
Q-switched output pulse train of 22.47 kHz at 174.3 mW pump power.
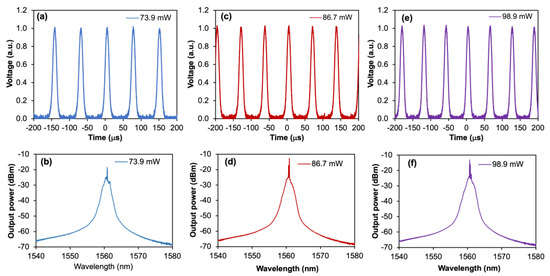
Figure 12.
Pulse train and output spectrum property in variation with pump powers at (a,b) 73.9 mW; (c,d) 86.7 mW; and (e,f) 98.9 mW.
Figure 13 illustrates the changes in pulse repetition rate and pulse width with a variation in pump power. For the pulse repetition rate, it increases almost linearly from 9.92 to 22.47 kHz with the increment of pump power from 50.1 to 174.3 mW. The Q-switching threshold obtained in this work is relatively lower than the one achieved in Ref. [31], which uses a similar type of SA. Conversely, the recorded pulse width reduces from 38.4 to 13.8 µs within the same pump power range. Since laser cavity design is one of the factors that influences the pulse width of a Q-switched laser, it can be possibly further optimized by minimizing the total cavity length.
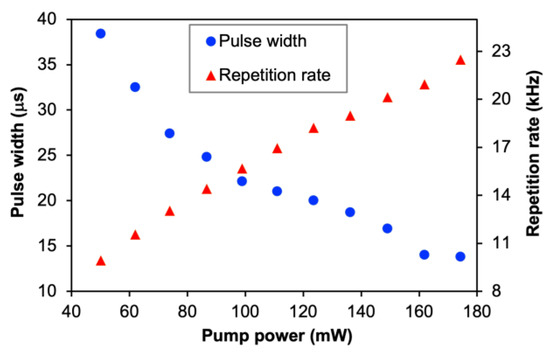
Figure 13.
Characteristic of pulse repetition rate and pulse width of Q-switched pulses with variation of pump powers.
The average output power of this Fe2O3-based Q-switched EDFL has a linear increment against the pump power after surpassing the lasing threshold of ~26 mW as plotted in Figure 14. Based on the recorded data, the slope efficiency is approximately around 0.6%. The maximum operating point of this system is limited to 174.3-mW pumping power. Beyond this point, the pulse output performance starts to degrade slowly, whereby the pulse train becomes unstable. This is due to the over-saturation effect of the gain medium, which means the energy stored is no longer efficiently extracted for the Q-switching phenomenon [40]. Moreover, the performance degradation might be caused by a high average loss experienced by the system due to other nonlinear effects that occur beyond 174.3 mW [41]. However, the Q-switched operation is reversible, whereby upon decreasing the pump power, the resulting Q-switched pulse properties are similar. It is also observed that the findings are consistent after long sessions of experimentation, thus verifying the reliability of our proposed Fe2O3–SA device.
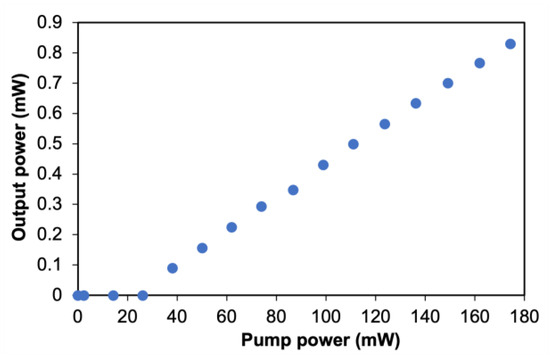
Figure 14.
Power development response of the Q-switched EDFL employing Fe2O3–SA.
Based on the value of the average output power, pulse width, and pulse repetition rate, the pulse energy and peak power can be calculated as shown in Figure 15. Both quantities exhibit an increase with pumping power, which is consistent with the characteristic behavior of a Q-switched laser system. For the case of pulse energy, the value evolves from 15.8 to 36.9 nJ. However, the maximum peak power is measured at 2.67 mW. It is possible to enhance the overall pulse performance by optimizing the laser cavity design by shortening the cavity length. In addition, despite having low maximum achievable pulse energy and peak power in this work, there is still a possibility that, beyond 180-mW pumping power, the Q-switched pulse regenerates with higher values of pulse repetition rate, output power, and pulse energy. However, since this work is limited by a maximum available pumping power of 180 mW, further investigation exceeding this pump power could not be demonstrated. It is also expected that by proper selection of the output coupler ratio, the average output power, as well as the pulse energy, could be further improved.
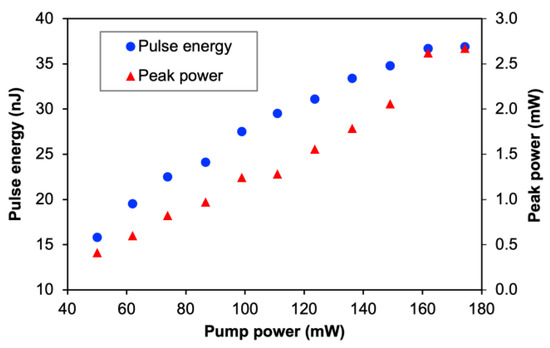
Figure 15.
Pulse energy and peak power evolution against pump power.
Table 1 summarizes the output pulse characteristics of previous works on iron oxide-based Q-switched fiber laser in the C-band region by different integration methods. Previous works used a thin-film technique [32,42,43], a magnetic fluid deposition, drop-casting [44,45,46], and bubble-poking [47] methods. Comparing these two techniques, the use of magnetic fluid seems to have advantages compared to its simpler fabrication steps. The drop-casting and bubble-poking methods are suitable for materials in solutions. However, for powder materials, our proposed method is a straightforward approach to transfer material on a fiber ferrule assisted by index-matching gel. Even though the performance of the output pulse in this work does not outperform other research works overall, the pulse characteristics obtained are notable in certain aspects. For example, this work offers higher maximum pulse energy and pulse repetition rate compared to Ref. [44] and Refs. [32,45], respectively. In addition, the Q-switched threshold and the minimum pulse width achieved in this work are lower than those reported in Refs. [32,45,46] and Ref. [45], respectively. The working range of the Q-switched pulse from this work is 124 mW, which is larger than those attained in Refs. [32,43,44,45]. Overall, the distinguishing factor in this work can be viewed in terms of its simpler technique for SA deposition by tapping the Fe2O3 nanopowder onto a ferrule end that is priorly applied with index-matching gel.

Table 1.
Comparison of pulse characteristics with iron oxide-based SA by different integration methods.
7. Conclusions
We introduce a simple deposition method of Fe2O3 nanoparticles onto the fiber ferrule by using index-matching gel as the adhesive element. A sandwich structure of the SA is formed by connecting the deposited Fe2O3 with another fiber ferrule through a fiber adaptor. The fabricated Fe2O3–SA device is subsequently incorporated into the EDFL cavity to enable the generation of Q-switched pulses. A power level of 50.1 mW is the minimum power required to achieve self-initiated and consistent Q-switching operations. When the pump power is set at 174.3 mW, the proposed Q-switched EDFL yields a 1560-nm central wavelength, 22.47-kHz pulse-repetition rate, 13.8-µs pulse width, 0.83-mW average output power, and 36.9 nJ of pulse energy. This implies the feasibility of the proposed Fe2O3 for pulse laser generation, which can find many applications in the pertinent field.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.D.M. and M.A.M.; methodology, F.D.M., A.N.M.A., E.K.N. and M.A.M.; software, J.L.Y.C. and M.T.A.; validation, F.D.M. and M.A.M.; formal analysis, F.D.M., J.L.Y.C. and M.A.M.; investigation, A.N.M.A. and E.K.N.; resources, A.N.M.A., E.K.N. and M.T.A.; data curation, A.N.M.A.; writing—original draft preparation, F.D.M. and J.L.Y.C.; writing—review and editing, F.D.M. and M.A.M.; visualization, M.T.A., E.K.N. and M.A.M.; supervision, F.D.M. and M.A.M.; project administration, F.D.M. and M.A.M.; funding acquisition, J.L.Y.C. and M.T.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Ministry of Higher Education Malaysia under Fundamental Research Grant Scheme (FRGS/1/2018/STG07/UPM/02/5) and the King Saud University, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia under Researchers Supporting Project (RSP2023R336).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chen, X.; Xu, Y.; Chen, N.K.; Shy, S.; Chui, H.C. In-situ depth measurement of laser micromachining. Photonics 2021, 8, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelatos, C.; Tsaknakis, G.; Bakopoulos, P.; Papadopoulos, D.; Avdikos, G.; Papayannis, A.; Tzeremes, G. Actively Q-switched multisegmented Nd:YAG laser pumped at 885 nm for remote sensing. IEEE Photonics Technol. Lett. 2014, 26, 1890–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adachi, S.; Koyamada, Y. Analysis and design of Q-switched erbium-doped fiber lasers and their application to OTDR. J. Light. Technol. 2002, 20, 1506–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannarozzo, G.; Del Re, C.; Negosanti, F.; Bennardo, S.; Amoruso, G.F.; Nisticò, S.P.; Bennardo, L. Q-switched Nd:YAG laser to manage hyperpigmentation in Asians: A multicenter study. Cosmetics 2023, 10, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hiti, A.S.; Hassan, H.; Yasin, M.; Harun, S.W. Passively Q-switched 2 µm fiber laser with WO3 saturable absorber. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2023, 75, 103193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, N.; He, C.; Lin, X. Development of all-fiber nanosecond oscillator using actively Q-switched technologies and modulators. Opt. Laser Technol. 2023, 157, 108709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, R.M. Laser-Induced Damage of Optical Materials; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zalkepali, N.U.H.H.; Awang, N.A.; Ghosh, B.K.; Mohamad, K.A.; Alias, A.; Mahmud, N.N.H.E.N.; Zamri, A.Z.M.; Muhammad, N.A.M. Tunable performance of indium tin oxide-zinc oxide as Q-switcher. Optik 2023, 281, 170852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; Xu, N.; Zhang, H.; Li, D. Nonlinear photoresponse of high damage threshold titanium disulfide nanocrystals for Q-switched pulse generation. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 151, 107988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhowalla, M.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, H. Two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenide (TMD) nanosheets. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 2584–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.J.; Li, Z.Y.; Tsay, S.Y.; Song, Y.F.; Zhang, H.; Lin, J.H. Wavelength tunable Q-switched Er-doped fiber laser based on ZrSe2. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 147, 107598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; Guo, L.; Zhang, H.; Li, D.; Yue, Q. Passive mode-locked Er-doped fiber laser pulse generation based on titanium disulfide saturable absorber. Front. Inf. Technol. Electron. Eng. 2021, 22, 756–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, H.; Azmy, N.F.; Yusoff, N.; Reduan, S.A.; Aidit, S.N.; Bayang, L.; Samion, M.Z. MoTe2-PVA as saturable absorber for passively Q-switched thulium-doped fluoride and erbium-doped fiber laser. Optik 2021, 243, 167157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Lu, H.; Tao, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Zhou, B. Novel two-dimensional semi-metallic NiTe2 based saturable absorber for ultrafast mode-locked fiber laser. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2022, 123, 104195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhang, F.; Chen, B.; Zhao, Y.; Cui, N.; Sun, D.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H. Nonlinear optical property and mid-infrared Q-switched laser application at 2.8 μm of PtSe2 material. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 139, 106983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, Z.; Yang, F.; Han, Y.; Fan, W.; Li, S.; Bai, C.; Lu, C.; Zhang, W.; Wang, G.; Fu, S.; et al. Large energy mode-locked phenomenon based on ZrS2 in Er-doped fiber laser. Opt. Laser Technol. 2023, 157, 108725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haris, H.; Batumalay, M.; Tan, S.J.; Markom, A.M.; Muhammad, A.R.; Harun, S.W.; Hasnan, M.M.I.M.; Saad, I. Mode-locked YDFL using topological insulator bismuth selenide nanosheets as the saturable absorber. Crystals 2022, 12, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Yu, Q.; Guo, K.; Shi, X.; Kan, X.; Xu, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhang, K.; Zhou, P. Sb2Te3 topological insulator for 52 nm wideband tunable Yb-doped passively Q-switched fiber laser. Front. Inf. Technol. Electron. Eng. 2021, 22, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haris, H.; Muhammad, A.R.; Tan, S.J.; Markom, A.M.; Harun, S.W.; Megat Hasnan, M.M.I.; Saad, I. Generation of Kelly and dip type sidebands soliton employing topological insulator (Bi2Te3) as saturable absorber. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2022, 123, 104154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, L.; Ma, Y.; Sun, Z.; Heine, T.; Chen, C. Two-dimensional topological insulators: Progress and prospects. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2017, 8, 1905–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Hu, J.; Luo, H.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Liu, Y. Fe3O4 nanoparticles as a saturable absorber for a tunable Q-switched dysprosium laser around 3 μm. Photonics Res. 2020, 8, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Huang, X.; Han, Y.; Chen, E.; Guo, P.; Zhang, W.; An, M.; Pan, Z.; Xu, Q.; Guo, X.; et al. High-performance γ-MnO2 dual-core, pair-hole fiber for ultrafast photonics. Ultrafast Sci. 2023, 3, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.H.M.; Yusoff, N.M.; Abdullah, C.A.C.; Alresheedi, M.T.; Rosli, N.S.; Talib, Z.A.; Mahdi, M.A. Nanosized titanium dioxide saturable absorber for soliton mode-locked thulium-doped fiber laser. Results Phys. 2021, 31, 104930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zhang, H.N.; Zhang, C.; Li, Z.; Sheng, Y.Q.; Li, C.H.; Bao, X.H.; Man, B.Y.; Jiao, Y.; Jiang, S.Z. Indium tin oxide nanocrystals as saturable absorbers for passively Q-switched erbium-doped fiber laser. Opt. Mater. Express 2017, 7, 3494–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hayali, S.K.M.; Mohammed, D.Z.; Khaleel, W.A.; Al-Janabi, A.H. Aluminum oxide nanoparticles as saturable absorber for C-band passively Q-switched fiber laser. Appl. Opt. 2017, 56, 4720–4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.Y.; Xu, Y.T.; Jing, Y.Y.; Wu, H.D.; Hu, H.F.; Zhang, H.; Jin, L.; Zou, Y.G.; Ma, X.H. Output characteristics regulation of Q-switched fiber laser by Fe3O4 nanoparticle-polyimide film. Opt. Mater. 2021, 119, 111302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, T.; Yamada, T.; Yoko, T. Third-order nonlinear optical properties of sol–gel derived α-Fe2O3, γ-Fe2O3, and Fe3O4 thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 1996, 80, 3184–3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, O.; Tayal, A.; Kim, J.; Song, C.; Chen, Y.; Hiroi, S.; Katsuya, Y.; Ina, T.; Sakata, O.; Ikeya, Y.; et al. Tuning of structural, optical band gap, and electrical properties of room-temperature-grown epitaxial thin films through the Fe2O3:NiO ratio. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, G.; Jiang, J.; Ying, J.Y.; Ji, W. Fe3O4-Ag nanocomposites for optical limiting: Broad temporal response and low threshold. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 6183–6190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ban, X.; Sun, P.; Qyyum, A.; Li, X.; Song, Z.; Zhong, M.; Little, B.E.; Zhao, W. Fe3O4 nanoparticle-enabled Q-switched pulse generation in fiber laser. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2022, 71, 102909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, L.; Song, C.; Lv, R.; Chen, Z.; Liu, S.; Wu, R.; Lv, Y.; Liu, W. High stable polarization-insensitive Er-doped Q-switched fiber laser with iron oxide nanoparticles as saturable absorber. Opt. Laser Technol. 2019, 113, 379–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Jia, H.; Guo, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.Y.; Guo, Z.X.; Li, M.X.; Jia, Z.X.; Qin, G.S. Broadband Fe3O4 nanoparticles saturable absorber for Q-switched fiber lasers. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2021, 61, 102421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, N.A.M.; Awang, N.A.; Basri, H. Recent advancements review in zinc oxide and titanium dioxide saturable absorber for ultrafast pulsed fiber laser. Optik 2023, 283, 170855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Jin, Z.; Shi, L.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Q.; Qin, P.; Jiang, K.; Wang, J.; Tang, W.; Xia, W. Two types of ultrafast mode-locking operations from an Er-doped fiber laser based on germanene nanosheets. Front. Optoelectron. 2023, 16, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husin, S.A.S.; Muhammad, F.D.; Abdullah, C.A.C.; Ribut, S.H.; Zulkifli, M.Z.; Mahdi, M.A. Zinc-oxide nanoparticle-based saturable absorber deposited by simple evaporation technique for Q-switched fiber laser. Chin. Phys. B 2019, 28, 084207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doedel, E.J.; Krauskopf, B.; Pando Lambruschini, C.L. A numerical bifurcation study of a basic model of two coupled lasers with saturable absorption. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2014, 223, 2847–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doedel, E.J.; Pando, L.C.L. Isolas of periodic passive Q-switching self-pulsations in the three-level:two-level model for a laser with a saturable absorber. Phys. Rev. E 2011, 84, 056207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisarchik, A.N.; Kir’yanov, A.V.; Barmenkov, Y.O.; Jaimes-Reátegui, R. Dynamics of an erbium-doped fiber laser with pump modulation: Theory and experiment. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2005, 22, 2107–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otupiri, R.; Garbin, B.; Broderick, N.G.R.; Krauskopf, B. Excitability in an all-fiber laser with a saturable absorber section. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2021, 38, 1695–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degnan, J.J. Optimization of passively Q-switched lasers. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 1995, 31, 1890–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, H.; Muhammad, F.D.; Zulkifli, M.Z.; Harun, S.W. Graphene-oxide-based saturable absorber for all-fiber Q-switching with a simple optical deposition technique. IEEE Photonics J. 2012, 4, 2205–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.; Cui, X.; Zhang, W.; Li, M.; Feng, T.; Du, B.; Lu, H.; Zhao, J. Q-switched fiber laser based on saturable absorption of ferroferric-oxide nanoparticles. Photonics Res. 2017, 5, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.; Cui, X.; He, Z.; Lu, H.; Zhang, W.; Wang, L.; Zhuang, Q.; Hua, S.; Mei, T.; Zhao, J. Broadband polarization-insensitive saturable absorption of Fe2O3 nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 21219–21224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.; Mou, C.; Xu, L.; Wang, S.; Pu, S.; Zeng, X. Passively Q-switched erbium-doped fiber laser using Fe3O4-nanoparticle saturable absorber. Appl. Phys. Express 2016, 9, 042701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, P.; Du, Y.; Han, M.; Shu, X. Mode-locked and Q-switched mode-locked fiber laser based on a ferroferric-oxide nanoparticles saturable absorber. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 13177–13186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, D.Z.; Khaleel, W.A.; Al-Janabi, A.H. Tunable Q-switched erbium doped fiber laser based on metal transition oxide saturable absorber and refractive index characteristic of multimode interference effects. Opt. Laser Technol. 2017, 97, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Jiang, X.; Wang, A.; Wang, J.; Chen, R.; Zhang, J.; Zhan, Q. Wavelength switchable Q-switched fiber laser based on Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Optik 2021, 243, 167279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).