Investigating the Role of Temperature in Laser Assisted Chemical Bath Deposition for ZnO Growth for Photodetector Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Substrates
2.2. Deposition of Nickel (Ni) Pads
2.3. Preparation of Precursor Solution
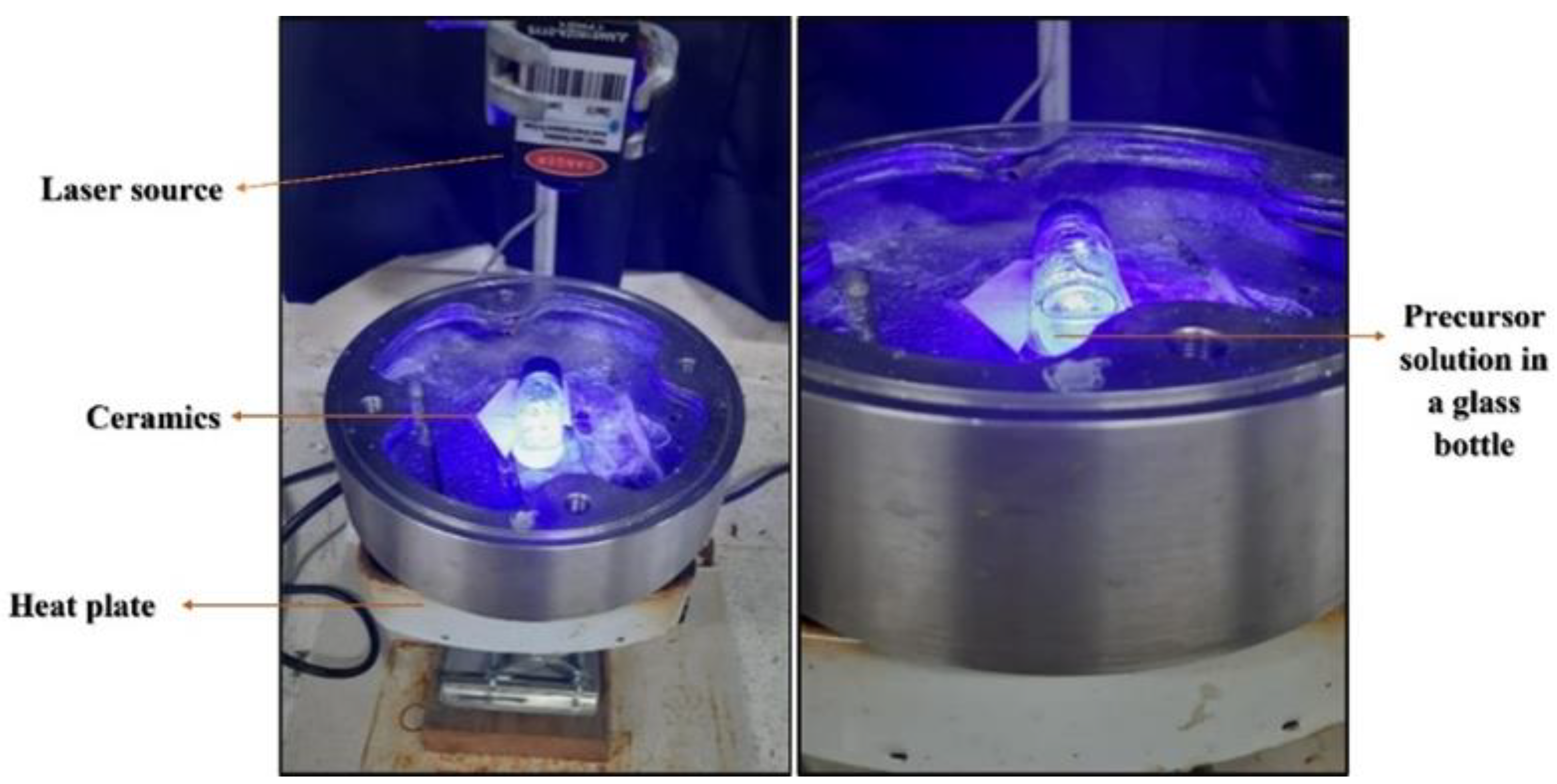
2.4. Growth of ZnO by Continuous Wave Laser-Assisted Chemical Bath Deposition
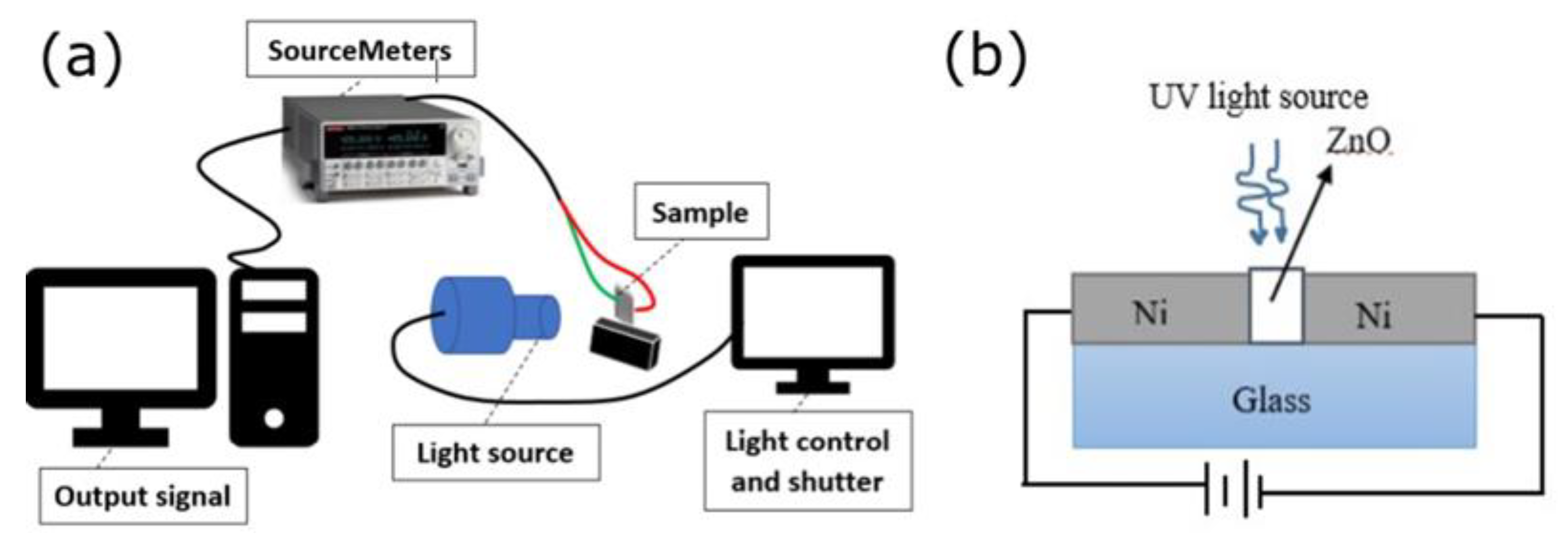
2.5. Characterization and Photodetection Analysis of the Produced Samples
3. Results and Discussion
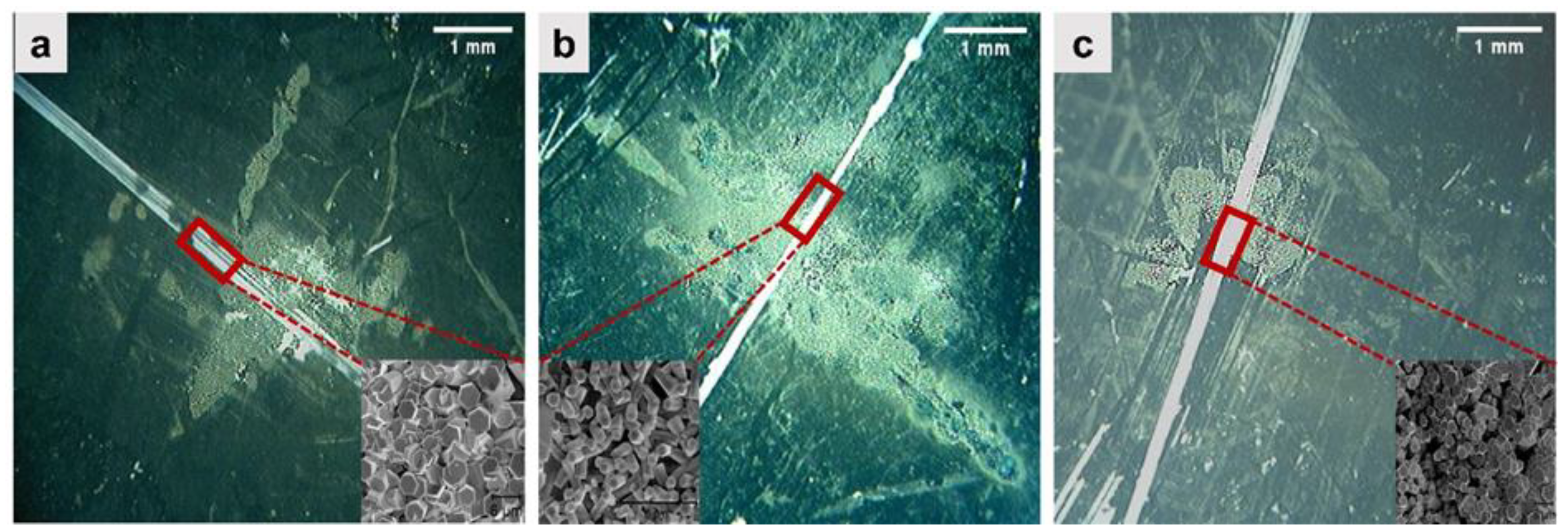
3.1. Zinc Oxide Spot: Stereo Microscopy
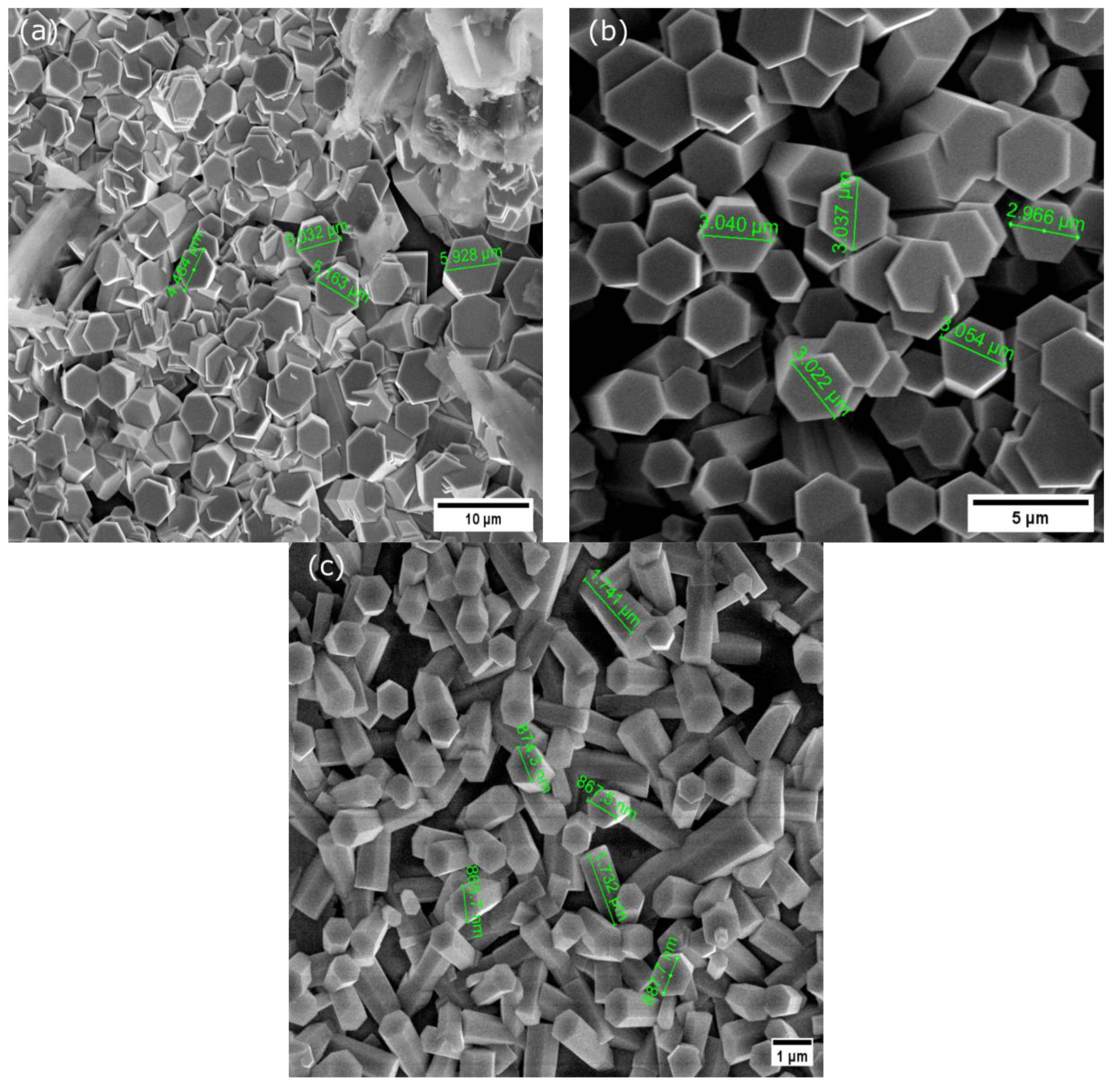
3.2. Characterization of ZnO Microrods: Electron Microscopy
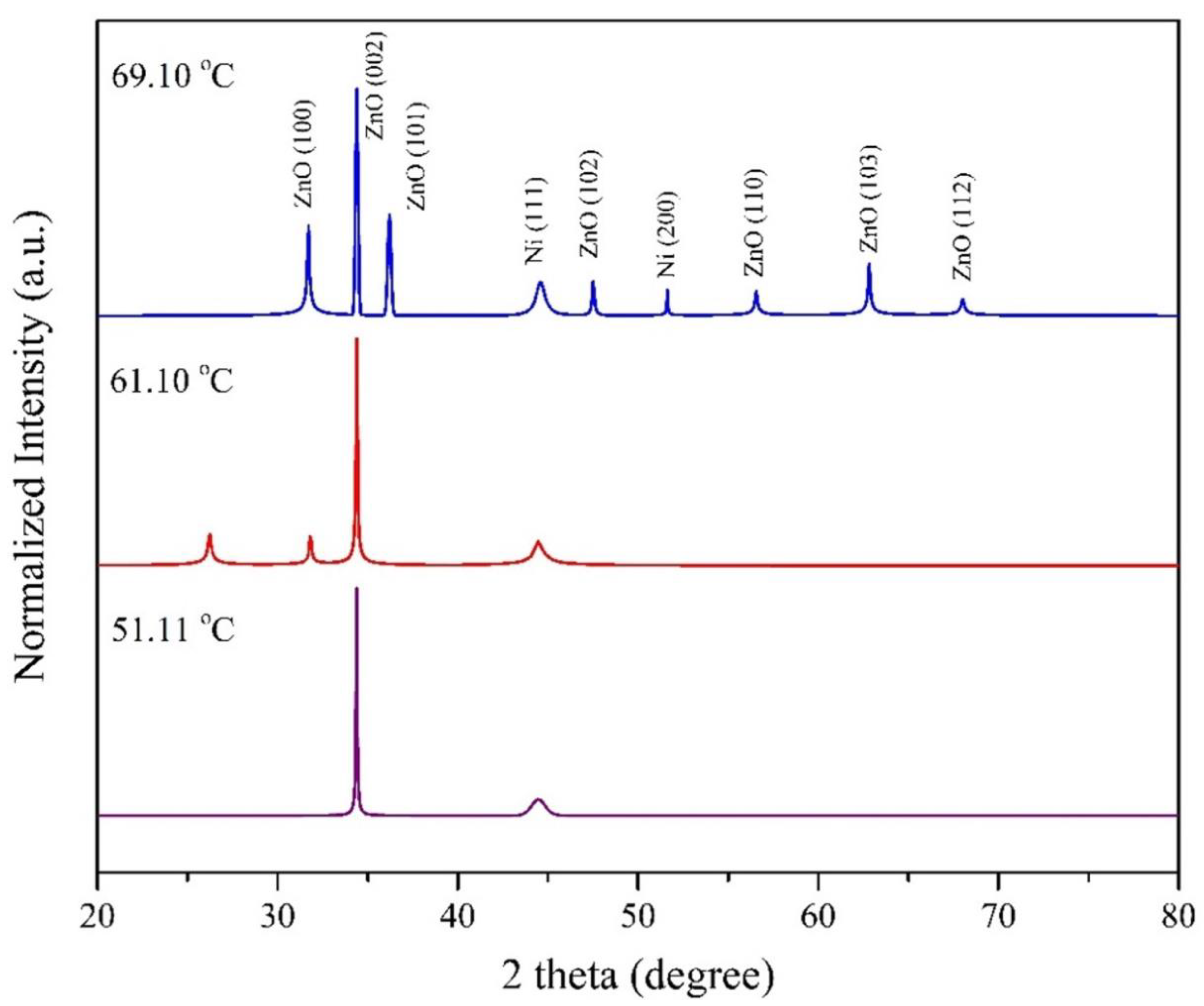
3.3. Characterization of ZnO Microrods: Chemical Composition
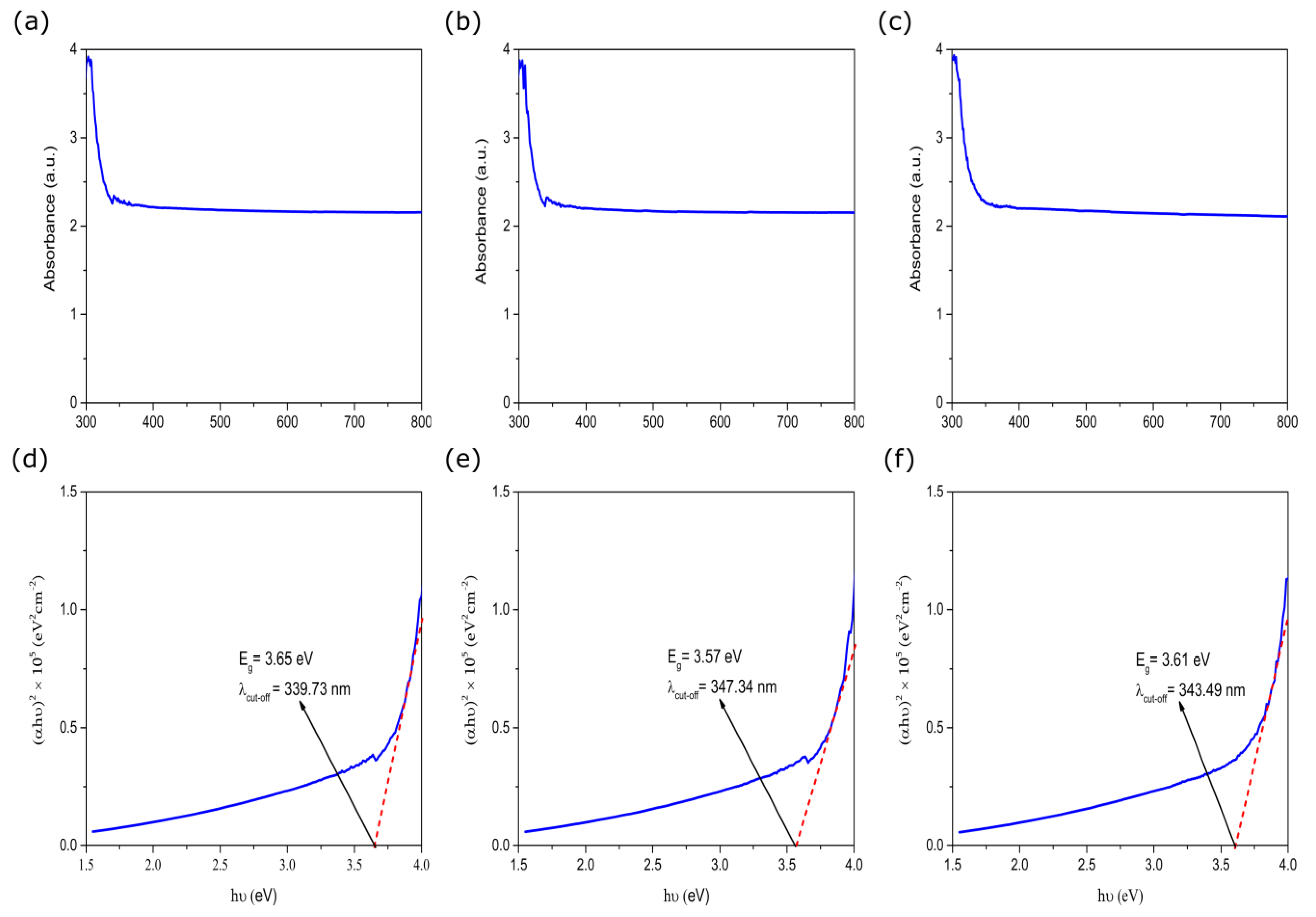
3.4. Characterization of ZnO-Microrods: Optical Profile
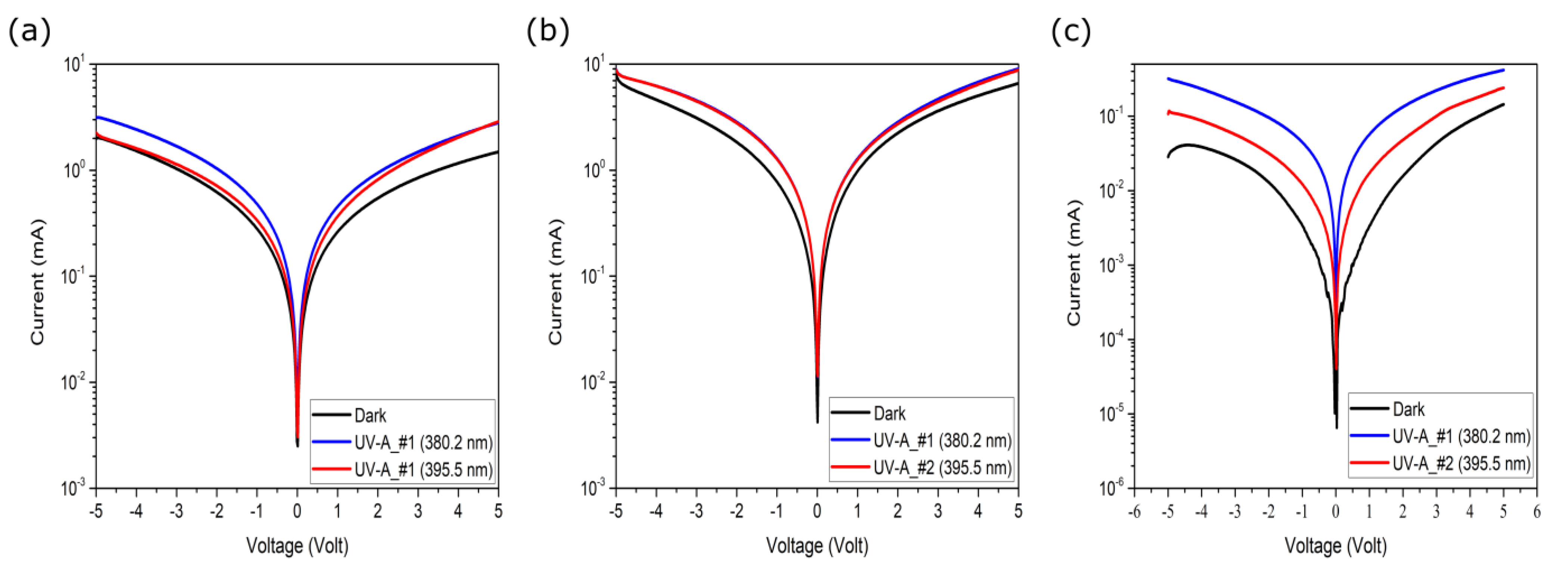
3.5. UV Photoconductive Characterization
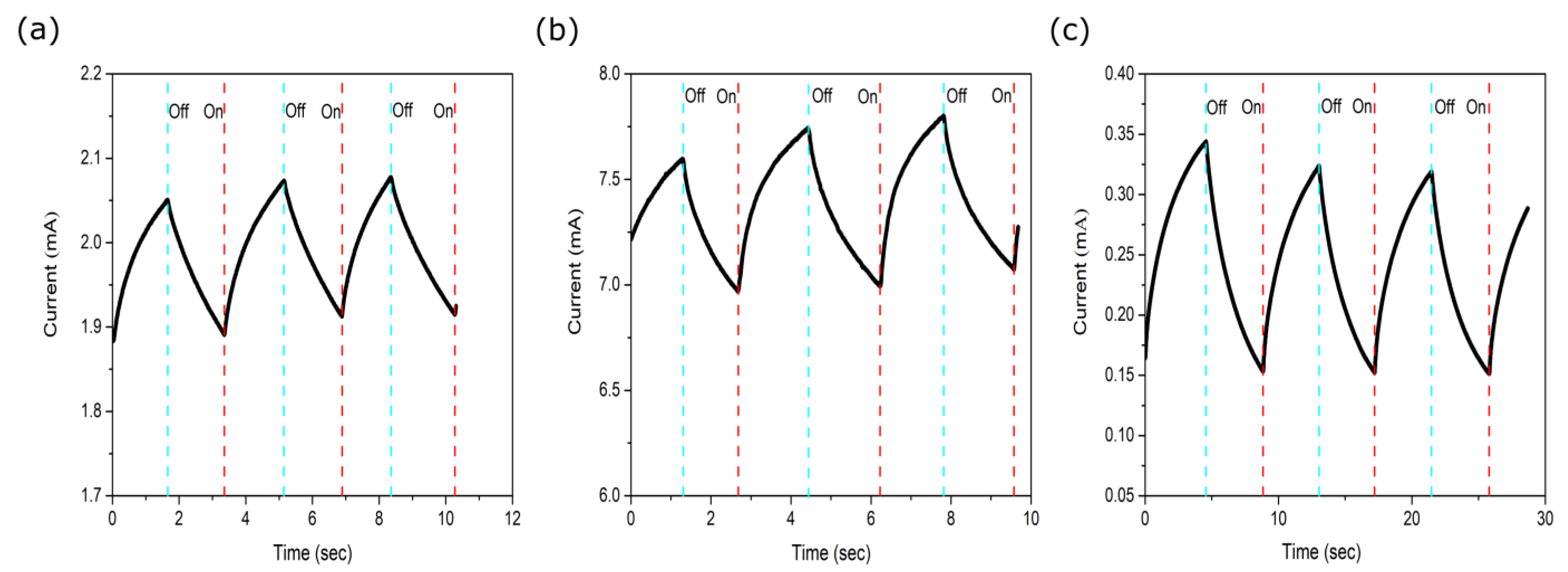
3.6. Photocurrent-Time Characteristics
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, A.; Vishwakarma, H. An existential study on structural, optical and electronic properties of ZnO nanoparticles and microroda. Appl. Phys. 2014, 6, 28–32. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.C.; Liu, C.P.; Huang, J.L.; Chen, S.-J.; Tseng, Y.-K.; Kung, S.-C. ZnO nanopencils: Efficient field emitters. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 87, 013110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, M.; Timbrell, P.; Lamb, R. The influence of film crystallinity on the coupling efficiency of ZnO optical modulator waveguides. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 1995, 10, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, M.A.; Ibupoto, Z.H.; Hussain, M.; Nur, O.; Willander, M. The fabrication of white light-emitting diodes using the n-ZnO/NiO/p-GaN heterojunction with enhanced luminescence. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, S.S.; Lin, L. Fabrication and characterization of ZnO nanowires based UV photodiodes. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2006, 127, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Dandeneau, C.S.; Zhou, X.; Cao, G. ZnO nanostructures for dye-sensitized solar cells. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 4087–4108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-K.; Hong, F.C.-N. The fabrication of ZnO nanowire field-effect transistors combining dielectrophoresis and hot-pressing. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 235202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Li, R.; Lv, C.; Xu, W.; Gou, X. Facile synthesis of ZnO nanorod arrays and hierarchical nanostructures for photocatalysis and gas sensor applications. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 730–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockett, A.M.; Thomas, P.J.; O’Brien, P. Influence of seeding layers on the morphology, density, and critical dimensions of ZnO nanostructures grown by chemical bath deposition. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 8089–8094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabakar, K.; Kim, H. Growth control of ZnO nanorod density by sol–gel method. Thin Solid Film. 2010, 518, e136–e138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, C.-T.; Yang, S.-Y.; Lin, J.-Y. Electrochemical deposition and superhydrophobic behavior of ZnO nanorod arrays. Thin Solid Films 2010, 518, 4884–4889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polsongkram, D.; Chamninok, P.; Pukird, S.; Chow, L.; Lupan, O.; Chai, G.; Khallaf, H.; Park, S.; Schulte, A. Effect of synthesis conditions on the growth of ZnO nanorods via hydrothermal method. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2008, 403, 3713–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zyoud, S.H.; Ahmed, N.M.; Lahewil, A.S.Z.; Bin Omar, A.F. Micro spot ZnO nanotubes using laser assisted chemical bath deposition: A low-cost approach to UV photodetector fabrication. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2022, 338, 113485. [Google Scholar]
- Shaji, S.; Garcia, L.; Loredo, S.; Krishnan, B.; Martinez, J.A.; Das Roy, T.; Avellaneda, D. Antimony sulfide thin films prepared by laser assisted chemical bath deposition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 393, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, L.; Mendivil, M.; Guillen, G.G.; Martinez, J.A.; Krishnan, B.; Avellaneda, D.; Castillo, G.; Das Roy, T.; Shaji, S. CdS thin films prepared by laser assisted chemical bath deposition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 336, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.-T.; Uang, R.-H.; Wang, Y.-M.; Chiou, K.-C.; Lee, T.-M. Laser annealing of gold nanoparticles thin film using photothermal effect. Microelectron. Eng. 2009, 86, 865–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Bian, J.; Sun, J.; Wang, J.; Luo, Y.; Sun, K.; Yu, D. Controllable growth of well-aligned ZnO nanorod arrays by low-temperature wet chemical bath deposition method. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 1698–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, V.R.; Gujar, T.P.; Noda, T.; Fujita, D.; Vinu, A.; Grandcolas, M.; Ye, J. Growth of shape-and size-selective zinc oxide nanorods by a microwave-assisted chemical bath deposition Method: Effect on photocatalysis properties. Chem.—Eur. J. 2010, 16, 10569–10575. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ramadhan, A.; Septiani, N.L.W.; Prabowo, W.A.E.; Melati, A. Temperature Effect of Chemical Bath Deposition (CBD) to Fabrication and Characterization of Zinc Oxide Nanorods Thin Films Based Gas Sensing: Ethanol. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1445, 012017. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulrahman, A.F.; Ahmed, S.M.; Barzinjy, A.A.; Hamad, S.M.; Ahmed, N.M.; Almessiere, M.A. Fabrication and characterization of high-quality UV photodetectors based ZnO nanorods using traditional and modified chemical bath deposition methods. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, H.N.; Bajt, S. A ray-trace analysis of x-ray multilayer Laue lenses for nanometer focusing. J. Opt. 2020, 22, 115610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahewil, A.S.; Al-Douri, Y.; Hashim, U.; Ahmed, N. Structural and optical investigations of cadmium sulfide nanostructures for optoelectronic applications. Sol. Energy 2012, 86, 3234–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carotenuto, G. Sensing Device for Breath Rate Monitoring Fabricated by using Geomorphic Natural Clinoptilolite. J. Adv. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2020, 8, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Nikhil, S.; Nair, R.G. Influence of surface morphology on photocatalytic performance of zinc oxide: A review. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2019, 19, 100353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basinova, N.; Cernohorsky, O.; Grym, J.; Kucerova, S.; Faitova, H.; Yatskiv, R.; Vanis, J.; Vesely, J.; Maixner, J. Highly textured seed layers for the growth of vertically oriented ZnO nanorods. Crystals 2019, 9, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulrahman, A.F.; Ahmed, S.M.; Ahmed, N.M.; Almessiere, M.A. Novel process using oxygen and air bubbling in chemical bath deposition method for vertically well aligned arrays of ZnO nanorods. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. (DJNB) 2016, 11, 1073–1082. [Google Scholar]
- Hur, T.-B.; Hwang, Y.-H.; Kim, H.-K. Quantum confinement in Volmer–Weber-type self-assembled ZnO nanocrystals. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 193113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guruprasad, K.; Marappan, G.; Elangovan, S.; Jayaraman, S.V.; Bharathi, K.K.; Venugopal, G.; Di Natale, C.; Sivalingam, Y. Electrical transport properties and impedance analysis of Au/ZnO nanorods/ITO heterojunction device. Nano Express 2020, 1, 030020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, K.T.; Yam, F.K.; Manaf, A.A.; Beh, K.K. Characteristics and sensing of Sol-gel derived titanium dioxide-based ultraviolet photodetector on flame retardant-4 board. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2021, 323, 112654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moazzami, K.; E Murphy, T.; Phillips, J.D.; Cheung, M.C.-K.; Cartwright, A.N. Sub-bandgap photoconductivity in ZnO epilayers and extraction of trap density spectra. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2006, 21, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, K.; Tudu, B.; Tiwari, A. Growth and characterization of zinc oxide thin films on flexible substrates at low temperature using pulsed laser deposition. Vacuum 2017, 146, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Som, T. Direct evidence of band-bending at grain boundaries of ZnO: SnO2 films: Local probe microscopic studies. Sol. Energy 2020, 208, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krbal, M.; Kucharik, J.; Sopha, H.; Nemec, H.; Macak, J.M. Charge transport in anodic TiO2 nanotubes studied by terahertz spectroscopy. Phys. Status Solidi (RRL)—Rapid Res. Lett. 2016, 10, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.H.; Yu, J.S. Metal-semiconductor-metal near-ultraviolet (~380 nm) photodetectors by selective area growth of ZnO nanorods and SiO2 passivation. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodwihok, C.; Choopun, S.; Ruankham, P.; Gardchareon, A.; Phadungdhitidhada, S.; Wongratanaphisan, D. UV sensing properties of ZnO nanowires/nanorods. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 477, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.-P.; Chen, K.-J. Zinc oxide nanoparticle photodetector. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 602398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemban, T.H.; Haque, M.A.; Ajia, I.; Alwadai, N.; Mitra, S.; Wu, T.; Roqan, I.S. A photodetector based on p-Si/n-ZnO nanotube heterojunctions with high ultraviolet responsivity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 37120–37127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.; Yang, L.; Zhao, J.; Li, J.; He, G.; Yang, D.; Wang, L.; Vadim, A.; Ma, D. Visible-blind ultraviolet narrowband photomultiplication-type organic photodetector with an ultrahigh external quantum efficiency of over 1000000%. Mater. Horiz. 2021, 8, 2293–2302. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulgafour, H.I.; Hassan, Z.; Yam, F.K.; AL-Heuseen, K.; Yusof, Y. Enhancing photoresponse time of low cost Pd/ZnO nanorods prepared by thermal evaporation techniques for UV detection. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 258, 461–465. [Google Scholar]


| Average Temperature | 51.11 | 61.10 | 69.10 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area of ZnO spot | 3.072 | 1.175 | 6.657 | |
| Mean length of slit | 0.269 | 0.265 | 0.131 |
| Temperature (°C) | Number of Measurements | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|
| 51.11 | 51 | 0.8793 |
| 61.10 | 191 | 0.8564 |
| 69.10 | 238 | 0.2926 |
| Solution Temperature | Atomic % of Element | Zn/O Ratio | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zn | O | ||
| 51.11 | 51.42 | 48.58 | 1.0585 |
| 61.10 | 52.74 | 47.26 | 1.1160 |
| 69.10 | 51.81 | 48.19 | 1.0751 |
| Average Temperature | 51.11 | 61.10 | 69.10 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diffraction angle | 2 () | 34.385 | 34.395 | 34.399 |
| FWHM | 1.2381 | 1.0554 | 2.6747 | |
| Interplanar spacing | 2.6084 | 2.6076 | 2.6074 | |
| Mean crystalline size | 1173.3043 | 1376.4933 | 543.1481 | |
| Lattice constant | 3.0119 | 3.0109 | 3.0107 | |
| 5.2168 | 5.2153 | 5.2147 | ||
| Strain value | −7.4361 | −7.4633 | −7.4738 | |
| 0.1349 | 0.1054 | 0.0941 | ||
| Dislocation density | 0.7264 | 0.5278 | 3.3897 |
| ZnO | Method | Solution Temperature | Irradiation | Bias | Source | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NR | LACBD | 51.11 | 380.2 | 5 | 1.379 | 1.388 | 70.377 | 8.556 | This work |
| Mircorod | LACBD | 61.10 | 380.2 | 5 | 1.260 | 1.398 | 131.443 | 9.575 | This work |
| Microrod | LACBD | 69.10 | 380.2 | 5 | 3.143 | 3.062 | 4.608 | 111.797 | This work |
| NR | Hydrothermal | 90 | 380 | 5 | 55.50 | 33.10 | 102 | - | [34] |
| NR | CBD with air bubbles | 95 | 380 | 5 | 0.968 | 0.504 | 2285.1 | 3172.811 | [20] |
| NW/NR | CVD | 450 | 365 | 3 | 41.30 | 30.70 | - | 465.2 | [35] |
| NP | Spin coating | - | 375 | 5 | 204 | 486 | 3750 | - | [36] |
| NT | PLD | 650 | 365 | −2 | 0.440 | 0.599 | 21500 | - | [37] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmed, N.M.; Qi, L.X.; Alshammari, A.S.; Muhson Naji, A.; Cabrera, H.; M. Binzowaimil, A.; Aldaghri, O.A.; Ibnaouf, K.H. Investigating the Role of Temperature in Laser Assisted Chemical Bath Deposition for ZnO Growth for Photodetector Application. Photonics 2023, 10, 910. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10080910
Ahmed NM, Qi LX, Alshammari AS, Muhson Naji A, Cabrera H, M. Binzowaimil A, Aldaghri OA, Ibnaouf KH. Investigating the Role of Temperature in Laser Assisted Chemical Bath Deposition for ZnO Growth for Photodetector Application. Photonics. 2023; 10(8):910. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10080910
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmed, Naser M., Loh Xue Qi, Anoud Saud Alshammari, Amel Muhson Naji, Humberto Cabrera, Ayed M. Binzowaimil, Osamah A. Aldaghri, and Khalid H. Ibnaouf. 2023. "Investigating the Role of Temperature in Laser Assisted Chemical Bath Deposition for ZnO Growth for Photodetector Application" Photonics 10, no. 8: 910. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10080910
APA StyleAhmed, N. M., Qi, L. X., Alshammari, A. S., Muhson Naji, A., Cabrera, H., M. Binzowaimil, A., Aldaghri, O. A., & Ibnaouf, K. H. (2023). Investigating the Role of Temperature in Laser Assisted Chemical Bath Deposition for ZnO Growth for Photodetector Application. Photonics, 10(8), 910. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10080910








