Short-Term Axial Length Changes in Myopic Eyes Induced by Defocus Spectacles for Myopia Control
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
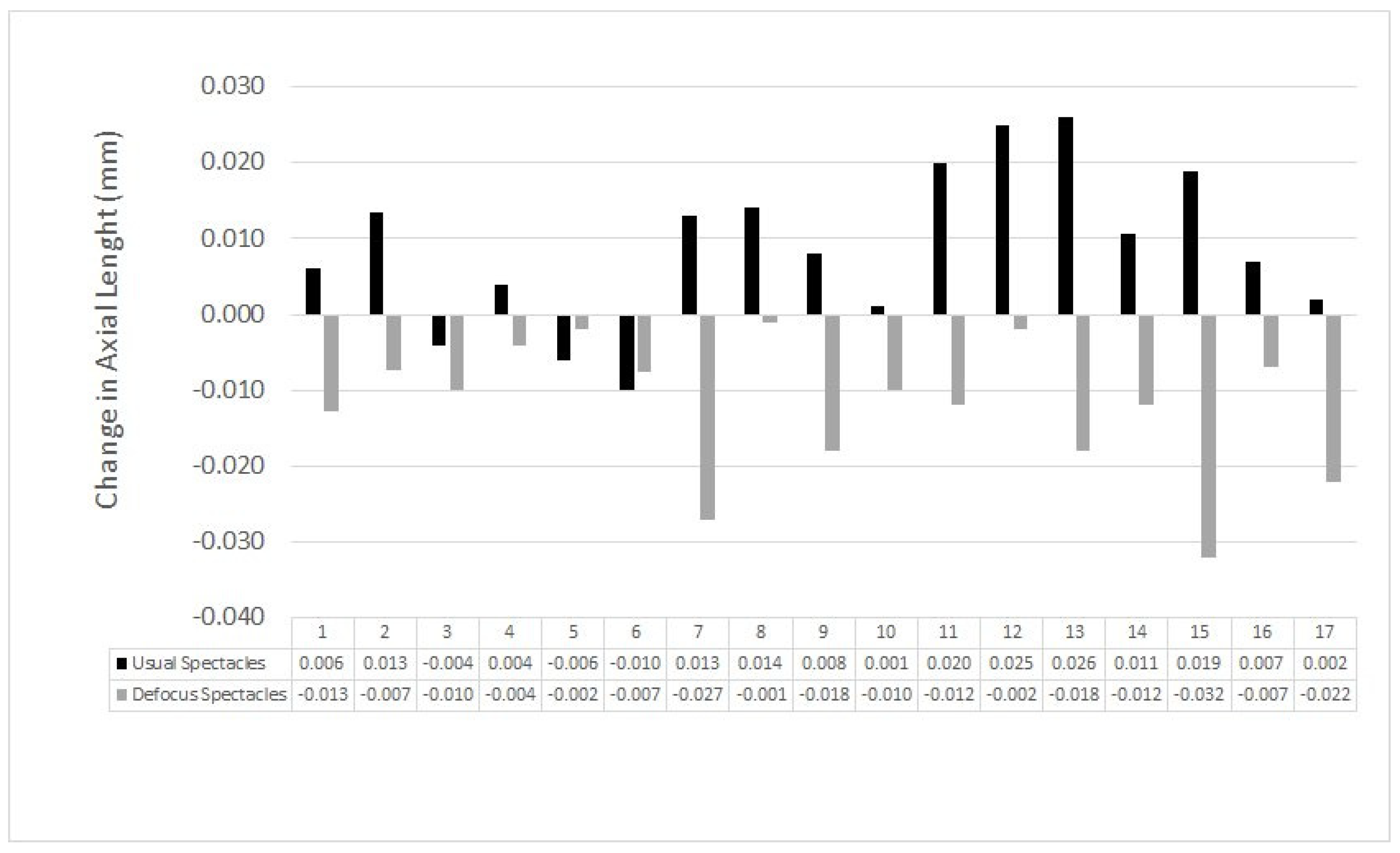
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jonas, J.B.; Ang, M.; Cho, P.; Guggenheim, J.A.; He, M.G.; Jong, M.; Logan, N.S.; Liu, M.; Morgan, I.; Ohno-Matsui, K.; et al. IMI Prevention of Myopia and Its Progression. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2021, 62, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wildsoet, C.F.; Chia, A.; Cho, P.; Guggenheim, J.A.; Polling, J.R.; Read, S.; Sankaridurg, P.; Saw, S.M.; Trier, K.; Walline, J.J.; et al. IMI-Interventions Myopia Institute: Interventions for Controlling Myopia Onset and Progression Report. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2019, 60, M106–M131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charman, W.N.; Radhakrishnan, H. Peripheral refraction and the development of refractive error: A review. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2010, 30, 321–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, C.S.Y.; Tang, W.C.; Tse, D.Y.; Lee, R.P.K.; Chun, R.K.M.; Hasegawa, K.; Qi, H.; Hatanaka, T.; To, C.H. Defocus Incorporated Multiple Segments (DIMS) spectacle lenses slow myopia progression: A 2-year randomised clinical trial. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 104, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, J.; Yang, A.; Huang, Y.; Li, X.; Pan, Y.; Ding, C.; Lim, E.W.; Zheng, J.; Spiegel, D.P.; Drobe, B.; et al. One-year myopia control efficacy of spectacle lenses with aspherical lenslets. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 106, 1171–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberlain, P.; Peixoto-de-Matos, S.C.; Logan, N.S.; Ngo, C.; Jones, D.; Young, G. A 3-year Randomized Clinical Trial of MiSight Lenses for Myopia Control. Optom. Vis. Sci. Off. Publ. Am. Acad. Optom. 2019, 96, 556–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, C.S.; Tang, W.C.; Lee, P.H.; Zhang, H.Y.; Qi, H.; Hasegawa, K.; To, C.H. Myopia control effect of defocus incorporated multiple segments (DIMS) spectacle lens in Chinese children: Results of a 3-year follow-up study. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 106, 1110–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Lam, C.S.Y.; Tang, W.C.; Leung, M.; Qi, H.; Lee, P.H.; To, C.H. Myopia Control Effect Is Influenced by Baseline Relative Peripheral Refraction in Children Wearing Defocus Incorporated Multiple Segments (DIMS) Spectacle Lenses. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galán, M.M.; Tideman, J.W.L.; Iribarren, R. El rol de la longitud axial y la queratometría en el seguimiento de niños miopes. Oftalmol. Clin. Exp. 2021, 14, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, I.G.; Wu, P.C.; Ostrin, L.A.; Tideman, J.W.L.; Yam, J.C.; Lan, W.; Baraas, R.C.; He, X.; Sankaridurg, P.; Saw, S.M.; et al. IMI Risk Factors for Myopia. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2021, 62, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolffsohn, J.S.; Flitcroft, D.I.; Gifford, K.L.; Jong, M.; Jones, L.; Klaver, C.C.W.; Logan, N.S.; Naidoo, K.; Resnikoff, S.; Sankaridurg, P.; et al. IMI – Myopia Control Reports Overview and Introduction. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2019, 60, M1–M19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaridurg, P.; Tahhan, N.; Kandel, H.; Naduvilath, T.; Zou, H.; Frick, K.D.; Marmamula, S.; Friedman, D.S.; Lamoureux, E.; Keeffe, J.; et al. IMI Impact of Myopia. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2021, 62, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorsby, A.; Sheridan, M.; Leary, G.A.; Benjamin, B. Vision, visual acuity, and ocular refraction of young men: Findings in a sample of 1033 subjects. Br. Med. J. 1960, 1, 1394–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortinez, M.F.; Chiappe, J.P.; Iribarren, R. Prevalence of refractive errors in a population of office-workers in Buenos Aires, Argentina. Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 2008, 15, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, P.J.; Suwezda, A.; Schlottmann, P.; Destefanis, M.P.; Rosenstein, R.E.; Iribarren, R.; Grzybowski, A. Analysis of visual disability in Buenos Aires, Argentina. Pathologic myopia is the leading cause in working age. Medicina 2021, 81, 735–741. [Google Scholar]
- Zadnik, K.; Mutti, D.O.; Mitchell, G.L.; Jones, L.A.; Burr, D.; Moeschberger, M.L. Normal eye growth in emmetropic schoolchildren. Optom. Vis. Sci. Off. Publ. Am. Acad. Optom. 2004, 81, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozema, J.; Dankert, S.; Iribarren, R. Emmetropization and non-myopic eye growth. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2023, in press. [CrossRef]
- Iribarren, R.; Morgan, I.G.; Chan, Y.H.; Lin, X.; Saw, S.M. Changes in lens power in Singapore Chinese children during refractive development. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 5124–5130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozema, J.J.; Ni Dhubhghaill, S. Age-related axial length changes in adults: A review. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2020, 40, 710–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; Butterworth, J.; Malecaze, F.; Calvas, P. Axial length of myopia: A review of current research. Ophthalmologica. J. Int. D’ophtalmologie. Int. J. Ophthalmology. Z. Augenheilkd. 2011, 225, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Ding, X.; Guo, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; He, M. Association of Age at Myopia Onset With Risk of High Myopia in Adulthood in a 12-Year Follow-up of a Chinese Cohort. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2020, 138, 1129–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modjtahedi, B.; Abbott, R.L.; Fong, D.S.; Lum, F.; Tan, D. Reducing the Global Burden of Myopia by Delaying the Onset of Myopia and Reducing Myopic Progression in Children The Academy’s Task Force on Myopia. Ophthalmology, 2021, in press. [CrossRef]
- Galan, M.M.; Szeps, A.; Fernandez Irigaray, L.; Rodriguez, G.; Aguirre, R.; Kotlik, C.; Iribarren, R. Myopia Consensus. Oftalmol. Clin. Exp. 2022, 15, e137–e156. [Google Scholar]
- Read, S.A.; Alonso-Caneiro, D.; Vincent, S.J.; Collins, M.J. Longitudinal changes in choroidal thickness and eye growth in childhood. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2015, 56, 3103–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleman, A.C.; Wang, M.; Schaeffel, F. Reading and Myopia: Contrast Polarity Matters. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Aleman, A.C.; Schaeffel, F. Probing the Potency of Artificial Dynamic ON or OFF Stimuli to Inhibit Myopia Development. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2019, 60, 2599–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Tomás, M.; Kotlik, C.; Szeps, A.; Impagliazzo, R.; Iribarren, R. New spectacles for myopia control. Oftalmol. Clin. Exp. 2022, 15, e244–e247. Available online: https://revistaoce.com/index.php/revista/article/view/156 (accessed on 15 June 2022). [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, X.; Wu, J.; Huo, J.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, J.; Yang, A.; Spiegel, D.P.; Chen, H.; Bao, J. Effect of spectacle lenses with aspherical lenslets on choroidal thickness in myopic children: A 2-year randomised clinical trial. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2022; Online First. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swiatczak, B.; Schaeffel, F. Transient Eye Shortening During Reading Text With Inverted Contrast: Effects of Refractive Error and Letter Size. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2022, 11, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swiatczak, B.; Schaeffel, F. Emmetropic, But Not Myopic Human Eyes Distinguish Positive Defocus From Calculated Blur. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2021, 62, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, C.S.Y.; Tang, W.C.; Qi, H.; Radhakrishnan, H.; Hasegawa, K.; To, C.H.; Charman, W.N. Effect of Defocus Incorporated Multiple Segments Spectacle Lens Wear on Visual Function in Myopic Chinese Children. Transl. Vis. Sci. Technol. 2020, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallman, J.; Winawer, J. Homeostasis of eye growth and the question of myopia. Neuron 2004, 43, 447–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winawer, J.; Wallman, J. Temporal constraints on lens compensation in chicks. Vision Res. 2002, 42, 2651–2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickla, D.L.; Thai, P.; Zanzerkia Trahan, R.; Totonelly, K. Myopic defocus in the evening is more effective at inhibiting eye growth than defocus in the morning: Effects on rhythms in axial length and choroid thickness in chicks. Exp. Eye Res. 2017, 154, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| 20 min. | 60 min. | 100 min. | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean axial length (mm) | 24.317 | 24.325 | 24.314 |
| Standard deviation (SD) (mm) | 0.637 | 0.641 | 0.641 |
| Monofocal | Defocus | |
|---|---|---|
| Mean change in axial length (microns) (±SD) | +8.1 ± 10.4 | −10.6 ± 8.9 |
| Paired Student’s t-test | p = 0.0108 | p = 0.0028 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iribarren, R.; Szeps, A.; Kotlik, C.; Laurencio, L.; De Tomas, M.; Impagliazzo, R.; Martin, G. Short-Term Axial Length Changes in Myopic Eyes Induced by Defocus Spectacles for Myopia Control. Photonics 2023, 10, 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10060668
Iribarren R, Szeps A, Kotlik C, Laurencio L, De Tomas M, Impagliazzo R, Martin G. Short-Term Axial Length Changes in Myopic Eyes Induced by Defocus Spectacles for Myopia Control. Photonics. 2023; 10(6):668. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10060668
Chicago/Turabian StyleIribarren, Rafael, Abel Szeps, Carlos Kotlik, Liliana Laurencio, MartÍn De Tomas, Ricardo Impagliazzo, and Gabriel Martin. 2023. "Short-Term Axial Length Changes in Myopic Eyes Induced by Defocus Spectacles for Myopia Control" Photonics 10, no. 6: 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10060668
APA StyleIribarren, R., Szeps, A., Kotlik, C., Laurencio, L., De Tomas, M., Impagliazzo, R., & Martin, G. (2023). Short-Term Axial Length Changes in Myopic Eyes Induced by Defocus Spectacles for Myopia Control. Photonics, 10(6), 668. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10060668





