Wavelength Effects on the Reflectivity of Niobium by Solid-State Laser Pulses
Abstract
1. Introduction
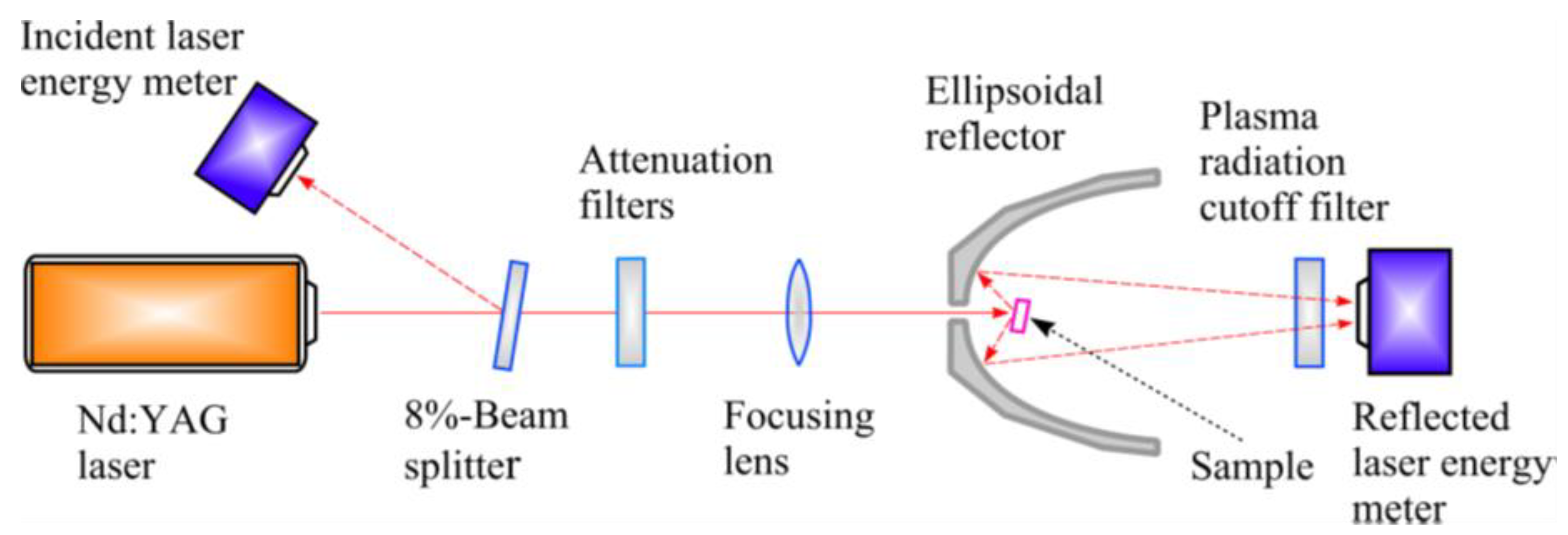
2. Materials and Methods
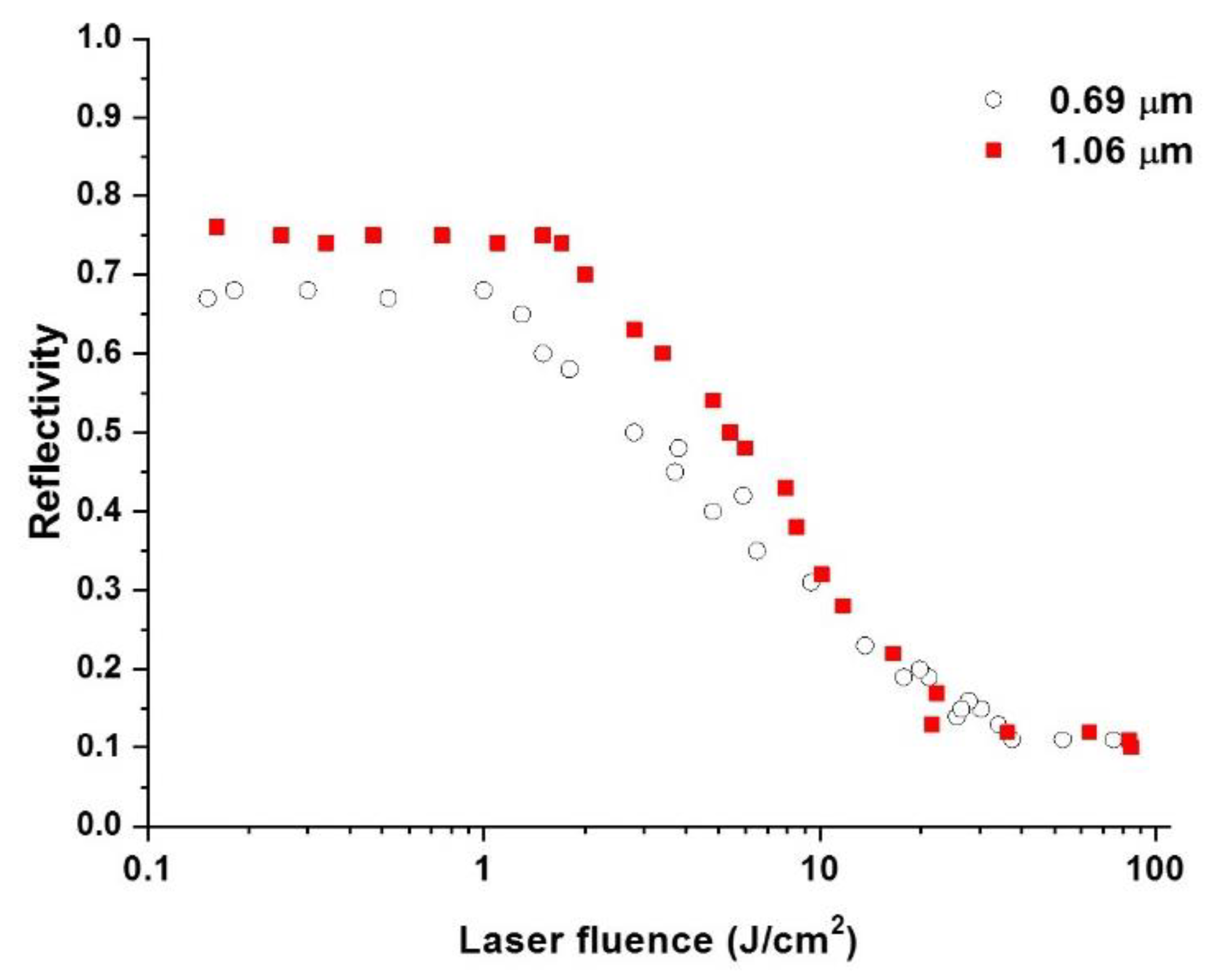
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lazarus, N.; Smith, G.L.; Dickey, M.D. Self-Folding Metal Origami. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2019, 1, 1900059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashfold, M.; Claeyssens, F.; Fuge, G.; Henley, S. Pulser Laser Ablation and Deposition of Thin Films. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2004, 33, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irimiciuc, S.A.; Chertopalov, S.; Lancok, J.; Craciun, V. Langmuir Probe Technique for Plasma Characterization during Pulsed Laser Deposition Process. Coatings 2021, 11, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- György, E.; Pérez, A.; Pérez Del Pino, A.; Serra, P.; Morenza, J. Influence of the ambient gas in laser structuring of the titanium surface. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2004, 187, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgakova, N.M.; Panchenko, A.N.; Tel’minov, A.E.; Shulepov, M.A. Formation of microtower structures on nanosecond laser ablation of liquid metals. Appl. Phys. A 2009, 98, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedraza, A.J.; Fowlkes, J.D.; Guan, Y.F. Surface nanostructuring of silicon. Appl. Phys. A 2003, 77, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.B.; Hong, M.H.; Luk‘yanchuk, B.S.; Huang, S.M.; Wang, Q.F.; Shi, L.P.; Chong, T.C. Parallel nanostructuring of GeSbTe film with particle mask. Appl. Phys. A 2004, 79, 1603–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendow, S.T.; Shakir, S.A. Structuring materials with nanosecond laser pulses. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 10188–10199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visser, C.W.; Pohl, R.; Sun, C.; Römer, G.W.; Huisin‘t Veld, B.; Lohse, D. Toward 3D Printing of Pure Metals by Laser-Induced Forward Transfer. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 4087–4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zorba, V.; Boukos, N.; Zergioti, I.; Fotakis, C. Ultraviolet femtosecond, picosecond and nanosecond laser microstructuring of silicon: Structural and optical properties. Appl. Opt. 2008, 47, 1846–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Hourd, A.C.; Abdolvand, A. Nanosecond pulsed laser blackening of copper. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 101, 231902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, R.E.; Mao, X.L.; Borisov, O.V.; Liu, H. Influence of wavelength on fractionation in laser ablation ICP-MS. J. Anal. Atomic Spectrom. 2000, 15, 1115–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottfried, J.L.; De Lucia, F.C., Jr.; Munson, C.A.; Miziolek, A.W. Laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy for detection of explosives residues: A review of recent advances, challenges, and future prospects. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 395, 283–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ta, D.V.; Dunn, A.; Wasley, T.J.; Kay, R.W.; Stringer, J.; Smith, P.J.; Connaughton, C.; Shephard, J.D. Nanosecond laser textured superhydrophobic metallic surfaces and their chemical sensing applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 357, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocaña, J.L.; Jagdheesh, R.; García-Ballesteros, J.J. Direct generation of superhydrophobic microstructures in metals by UV laser sources in the nanosecond regime. Adv. Opt. Technol. 2016, 5, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.-Y.; Yen, M.-H.; Wei, C.-W.; Chuang, Y.-C.; Young, T.-H. Crack-free direct-writing on glass using a low-power UV laser in the manufacture of a microfluidic chip. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2005, 15, 1147–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonch-Bruevich, A.M.; Imas, Y.A.; Romanov, G.S.; Libenson, M.N.; Mal’tsev, L.N. Effect of a laser pulse on the reflecting power of a metal. Sov. Phys. Technol. Phys. 1968, 13, 640–643. [Google Scholar]
- Basov, N.G.; Boiko, V.A.; Krokhin, O.N.; Semenov, O.G.; Sklizkov, G.V. Reduction of reflection coefficient for intense laser radiation of solid surfaces. Sov. Phys. -Technol. Phys. 1969, 13, 1581–1582. [Google Scholar]
- Benavides, O.; de la Cruz May, L.; Flores Gil, A. A comparative study on reflection of nanosecond Nd-YAG laser pulses in ablation of metals in air and in vacuum. Opt. Express 2013, 21, 13068–13073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavides, O.; de la Cruz May, L.; Flores Gil, A.; Jimenez, L.J.A. Experimental study on reflection of high-intensity nanosecond Nd: YAG laser pulses in ablation of metals. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2015, 68, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavides, O.; de la Cruz May, L.; Mejia, E.B.; Hernandez, J.A.R.; Gil, A.F. Laser wavelength effect on nanosecond laser light reflection in ablation of metals. Laser Phys. 2016, 26, 126101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikishina, E.E.; Drobot, D.V.; Lebedeva, E.N. Niobium and tantalum: State of the world market, fields of application, and raw sources. Part I. Rus. J. Non-Ferrous Metals 2013, 54, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grill, R.; Gnadenberger, A. Niobium as mint metal: Production properties processing. Int. J. Refract. Metals Hard Mater. 2006, 24, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laverick, C. Niobium demand and superconductor applications: An overview. J. Less Common Metals 1988, 139, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eason, R. Pulsed Laser Deposition of Thin Films: Applications-Led Growth of Functional Materials; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Li, Y.; Zou, G.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z. Effect of laser wavelength on ablation characteristics of copper. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 239–245. [Google Scholar]
- Bhu-Shan, B. Springer Handbook of Nanotechnology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- L’Huillier, J.A.; Allen, C.B. Wavelength dependence of the reflectivity of aluminum and copper at normal incidence in the EUV and soft x-ray ranges. J. Appl. Phys. 2015, 118, 205301. [Google Scholar]
- Shafeev, G.A.; Nishimura, T.; Baba, M. Effect of laser wavelength on the efficiency of copper ablation by femtosecond laser pulses. Appl. Phys. A 2003, 77, 489–492. [Google Scholar]
- Tayyab, M.; Bhardwaj, R. Resonance-enhanced ablation of metals: Influence of laser polarization and wavelength. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 22747–22756. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Chen, J.; Li, W.; Li, G. Effect of laser wavelength on ablation threshold and processing characteristics of nickel thin film. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 419, 293–298. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Li, G.; Hu, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, J. Effect of laser wavelength on laser-induced periodic surface structures formation on titanium thin film. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 478, 119–127. [Google Scholar]
- Zuber, M.; Baumeier, B.; Böhme, R. Influence of laser wavelength on material removal rate, roughness and recast layer thickness in micro laser engraving of tool steel. J. Manuf. Proc. 2020, 59, 14–25. [Google Scholar]
- Benavides, O.; De La Cruz May, L.; Flores Gil, A. Handbooks Aplicaciones Laser en la Ingeniería. Ecorfan Editorial, December 2021, Mexico. Available online: https://www.ecorfan.org/handbooks/Handbooks_Aplicaciones_Laser_en_la_Ingenieria_TI/Handbooks_Aplicaciones_Laser_en_la_Ingenieria_TI.pdf (accessed on 26 March 2023).
- Benavides, O.; Golikov, V.; Lebedeva, O. Reflection of high-intensity nanosecond Nd:YAG laser pulses by metals. Appl. Phys. A 2013, 112, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobyev, A.Y.; Guo, C. Reflection of femtosecond laser light in multipulse ablation of metals. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 110, 043102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobyev, A.Y.; Kuzmichev, V.M.; Kokody, N.G.; Kohns, P.; Dai, J.; Guo, C. Residual thermal effects in Al following single ns- and fs-laser pulse ablation. Appl. Phys. A 2006, 82, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, K.M.; Kalucki, J.; Koshel, D. 3-Process technologies for thermochemical surface engineering. In Thermochemical Surface Engineering of Steels; Mittemeijer, E.J., Somers, M.A.J., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 141–206. [Google Scholar]
- Libenson, M.N.; Romanov, G.S.; Imas, Y.A. Temperature dependence of the optical constants of a metal in heating by laser radiation. Sov. Phys. -Technol. Phys. 1969, 13, 925–927. [Google Scholar]
- Ujihara, K. Reflectivity of Metals at High Temperatures. J. Appl. Phys. 1972, 43, 2376–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ready, J.R. Effects of High-Power Laser Radiation; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1971. [Google Scholar]
- Anisimov, S.I.; Khokhlov, V.A. Instabilities in Laser-Matter Interaction. L.D. Landau Institute for Theoretical Physic; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1995; ISBN 0-8493-8660-8. [Google Scholar]
- Prokhorov, A.M.; Konov, V.I.; Ursu, I.; Mihailescu, I.N. Laser Heating of Metals; Adam Hilger: Briston, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Walters, C.T.; Barnes, R.H.; Beverly III, R.E. Initiation of laser-supported-detonation (LSD) waves. J. Appl. Phys. 1978, 49, 2937–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobyev, A.Y.; Kuz’michev, V.M. Absorption of laser radiation in craters on metal targets. Sov. J. Quantum Electr. 1980, 7, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokarev, V.N.; Lunney, J.G.; Marine, W.; Sentis, M. Analytical thermal model of ultraviolet laser ablation with single-photon absorption in the plume. J. Appl. Phys. 1995, 78, 1241–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.-B.; Mao, X.; Greif, R.; Russo, R.E. Laser ablation induced vapor plume expansion into a background gas. II. Experimental analysis. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 101, 023115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radziemski, L.J.; Cremers, D.A. Laser-Induced Plasmas and Applications; Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Born, M.; Wolf, E. Principles of Optics; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Kirkwood, S.E.; Tsui, Y.Y.; Fedosejevs, R.; Brantov, A.V.; Bychenkov, V.Y. Experimental and theoretical study of absorption of femtosecond laser pulses in interaction with solid copper targets. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 79, 144120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golovashkin, A.I.; Leksina, I.E.; Motulevich, G.P.; Shubin, A.A. The Optical Properties of Niobium. Zh. Eksp. Teor. Fiz. 1968, 56, 51–64. [Google Scholar]
- Weaver, J.H.; Lynch, D.W.; Olson, C.G. Optical Properties of Niobium from 0.1 to 36.4 eV. Phys. Rev. B 1973, 7, 4311–4318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marla, D.; Bhandarkar, U.V.; Joshi, S.S. A model of laser ablation with temperature-dependent material properties, vaporization, phase explosion and plasma shielding. Appl. Phys. A 2014, 116, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, R.; Miotello, A. Comments on explosive mechanisms of laser sputtering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1996, 96–98, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porneala, C.; Willis, D. Observation of nanosecond laser-induced phase explosion in aluminum. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 211121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillemot, F.; Prima, F.; Tokarev, V.N.; Belin, C.; Porté-Durrieu, M.C.; Gloriant, T.; Lazare, S. Single-pulse KrF laser ablation and nanopatterning in vacuum of β-titanium alloys used in biomedical applications. Appl. Phys. A 2004, 79, 811–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, N.V. The optical properties of liquid metals. Adv. Phys. 1967, 16, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, J.N. The optical properties of liquid indium, cadmium, bismuth and antimony. Philos. Mag J. Theor. Exp. Appl. Phys. 1962, 7, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeles, F. (Ed.) Optical Properties and Electronic Structure of Metals and Alloys; North-Holland: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Kudryashov, S.I.; Tikhov, A.A.; Zvorykin, V.D. Near-critical nanosecond laser-induced phase explosion on graphite surface. Appl. Phys. A 2011, 102, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Shin, Y.C. Absorption coefficient of aluminum near the critical point and the consequences on high-power nanosecond laser ablation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 111902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Shin, Y.C. Analysis of nanosecond laser ablation of aluminum with and without phase explosion in air and water. J. Laser Appl. 2013, 25, 032002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Benavides, O.; de la Cruz May, L.; Flores Gil, A.; Mejia Beltran, E. Wavelength Effects on the Reflectivity of Niobium by Solid-State Laser Pulses. Photonics 2023, 10, 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10040402
Benavides O, de la Cruz May L, Flores Gil A, Mejia Beltran E. Wavelength Effects on the Reflectivity of Niobium by Solid-State Laser Pulses. Photonics. 2023; 10(4):402. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10040402
Chicago/Turabian StyleBenavides, Olena, Lelio de la Cruz May, Aaron Flores Gil, and Efrain Mejia Beltran. 2023. "Wavelength Effects on the Reflectivity of Niobium by Solid-State Laser Pulses" Photonics 10, no. 4: 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10040402
APA StyleBenavides, O., de la Cruz May, L., Flores Gil, A., & Mejia Beltran, E. (2023). Wavelength Effects on the Reflectivity of Niobium by Solid-State Laser Pulses. Photonics, 10(4), 402. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics10040402





