Abstract
The propagating evolution of shock waves induced by a nanosecond pulse laser (ns laser) irradiating silicon assisted by a millisecond pulse laser (ms laser) is investigated experimentally. A numerical model of 2D axisymmetric two-phase flow is established to obtain the spatial distribution of shock wave velocity. Two types of shock wave acceleration phenomenon are found. The mechanism of the shock wave acceleration phenomenon is discussed. The experimental and numerical results show that the initial stage of ms laser-induced plasma can provide the initial ions to increase probability of collision ionization between free electrons and vapor atoms. The velocity of the ns laser-induced shock wave is accelerated. Furthermore, the ms laser-induced plasma as the propagation medium can also accelerate the ns laser-induced shock wave. The shock wave acceleration methods obtained in this paper can promote the development of laser propulsion technology.
1. Introduction
Shock waves have an extremely wide range of practical effects on a variety of fields; for instance, laser propulsion, laser cleaning, laser shock peening, and so on [1,2,3,4,5]. For example, Shukla P. reported the laser shock peening of Al2O3 advanced ceramics by an Nd: YAG laser with a pulse duration of 10 ns. It was found that with the increase of shock wave pressure, the surface roughness will also increase [6]. Yu H. utilized an ns laser to remove particles. It revealed that the particle removal mechanism is dominated by the shock wave ejection mechanism, which is due to its strong pressure [7]. Zhaia Z. studied the microhole processing effects of nickel-based alloy by an ns laser in the air and water environment. It was found that the quality of laser drilling was improved in water [8]. Ünaldi S. investigated a mechanical stripping process in water. The results showed that selective laser stripping can remove the aircraft layer without causing damage to the substrate material [9]. Lu J.Z. studied the influences of laser-shock wave on the microstructure of Ni25 coating on H13 steel. They found that the shock wave reduces the coefficient of friction and wear rate of Ni25 coating significantly [10]. Krasyuk I.K. presented the generation of shock waves and spallation on different materials irradiated by a short pulse laser [11]. Abrosimov S.A. investigated the effect of shock wave pressure on specific features of monocrystalline silicon irradiated by a picosecond pulse laser. The results showed that the spallation strength of the target depends on the duration and amplitude of the shock wave [12]. Generally, the velocity of the shock wave is an important factor affecting its pressure; therefore, it will affect the efficiency of laser cleaning, laser propulsion, and laser strengthening [13,14,15].
The velocity of short-pulse laser-induced shock waves has been extensively researched by scholars. Yoh J.J. studied a ns laser-induced shock wave with a wavelength of 1.06 µm, a pulse width of 5 ns, and a laser energy of 200 mJ on a metal target. It was found that the shock wave velocity could reach 4.5 km/s at 950 ns [16]. Gregorčič P. studied ns laser-induced plasma and a shock wave with a wavelength of 1.06 µm, a pulse duration of 4 ns, and a laser energy of 12 mJ in the air. The results revealed that the shock wave morphology changed into a sphere at 55 ns, and its velocity could reach 1.8 km/s [17]. Cao S. researched a ns laser-induced shock wave with a wavelength of 1.06 µm, a pulse duration of 7 ns, and a laser energy of 35 mJ on aluminum alloy. It was found that the shock wave velocity could reach 1.2 km/s at 200 ns and approach the velocity of sound at 6.9 µs [18]. Kraft S. researched the femtosecond laser-produced plasma and a shock wave with a wavelength of 1030 nm, a pulse duration of 600 fs, and a laser energy of 45 μJ on metal. The results showed that the shock wave velocity decreased exponentially from 1 km/s to less than 250 m/s with time [19]. Although the velocity of short-pulse laser-induced shock waves could reach several kilometers per second, due to the limitation of the damage threshold of laser crystal material, it is impossible to obtain sufficient velocity by infinitely increasing laser energy. Therefore, it is very significant to investigate an acceleration method for the combined pulse laser (CPL)-induced shock wave.
With the continuous development of the study on shock waves, many research works have gradually begun to shift to the research direction of the characteristics of the CPL-induced shock wave [20,21,22,23,24,25]. Such as in the work of Wang Q., the time-resolve spectroscopy of cooper plasmas induced by the femtosecond-nanosecond CPL was investigated and the plasma temperature was calculated. They found that the temperature of plasma and electron density induced by the femtosecond-nanosecond CPL are both higher [26]. Jia X. utilized a continuous wave laser and ns laser as a CPL for drilling Q235B steel. The results showed that the shock wave pressure could improve the drilling efficiency [27]. Pan Y. investigated the processing efficiency and modified sizes of BK7 glass irradiated by ms-ns CPL. They found that laser-supported combustion waves have a contribution to the energy deposition into the sample [28]. Generally, the research direction of CPL-induced shock waves is to mainly concentrate on the spectral characteristics and the influence on the damage depth and morphology of the target [29,30,31].
In this study, the dynamics of the shock waves induced by an ns laser irradiating silicon assisted by an ms laser for different pulse delays and the energy ratio of CPL are investigated. The morphology evolution, velocity of shock waves, and physical process involved in the two types of acceleration phenomenon of shock waves are investigated and analyzed. The results of this paper not only present the acceleration methods of shock waves, but also provide clues for interpreting the behavior of ms-ns CPL-induced shock waves.
2. Experiment
Figure 1 shows the experiment setup of ms-ns CPL irradiating silicon. The laser emission system is composed of a millisecond pulse laser (Melar-100, Beijing Guoke Century Laser Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China) and a nanosecond pulse laser (Vlite-380, Beamtech Optronics Co., Ltd., Beijing, China) with pulse durations of 1 ms and 12 ns and wavelengths of 1064 nm. In order to make the millisecond pulse laser and nanosecond pulse laser irradiate at the same point of silicon, the spatial angle of the two lasers was set to 5°. The function of the two lenses placed on the two-laser optical path is to adjust the spot radius of the laser on the surface of silicon. The ms laser radius was 0.65 mm, and the ns laser radius was 0.5 mm. The morphology radius of laser irradiation on silicon is used to represent the laser radius. The 532 nm CW laser is irradiated to the high-speed camera lens after passing through the beam expander, the focusing lens, and the filter. Its function is to provide the background light for the high-speed camera to take the shock wave evolution image. The high-speed camera exposure time is 1/6,300,000 s. The shock wave propagation distance is measured by the picture, which is taken by the high-speed camera at different times, and the shock wave velocity can be calculated by:
where and represent the shock wave propagation distance at different times, is the time difference between and .
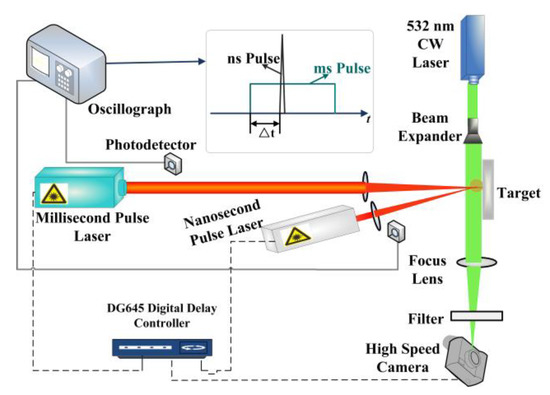
Figure 1.
The experiment setup of ms-ns CPL irradiating silicon.
A digital delay generator DG645 can not only control the ms laser and high-speed camera to be triggered at the same time, but also set the pulse delay of the ms-ns CPL. The oscillograph and photodetector are used to monitor the pulse delay. The ns laser energy density () is fixed at 12 . The energy densities of the ms laser () are 226.13 , 301, 376.88, and 414.58. The pulse delay () is defined as the time that the ns laser lags behind the ms laser. The starting time of ms laser irradiation is defined as 0 s. The range of pulse delay is 0 to 3 ms, and the interval is 0.2 ms. The silicon, with radius of 12.7 mm and thickness of 4 mm, is used as the target. The experiment is carried out at 20 °C in air.
3. Results
3.1. The Morphology Evolution of the ms-ns CPL-Induced Shock Wave
The propagating morphology evolution of plasma and shock waves is shown in Figure 2. During the experiment, the laser-induced plasma and shock waves can be observed at the surface of silicon. Figure 2a is the result of a single ns laser irradiating silicon with 12. When the ns laser irradiates the target, a large amount of plasma is induced. After the plasma stops expanding, the shock wave is induced and propagates in a contrary direction of the laser irradiation. Figure 2b,e are the results of the single ms laser irradiating silicon with and . The ms laser-induced plasma is thin and moves slowly because of the low peak power density with . The ms laser-induced plasma is formed and slowly expands towards the laser direction with . Figure 2c,d,f,g are the results of ms-ns CPL irradiating silicon with different energy ratios and pulse delays. The plasma expands rapidly when the ns laser irradiates, and a shock wave is ignited. It can be indicated that there is no obvious difference among the evolution morphology shown in Figure 2a,c,d with . However, when the ms laser energy density is 301, the morphology evolution of plasma changes, especially in Figure 2g with and . It is thus clear that the expansion distance of ms laser-induced plasma at 2397 μs is greater than that of ns laser-induced plasma at 2402 μs. This is because the ms laser-induced plasma can no longer absorb the ns laser energy and cannot continue to expand when the ns laser irradiates.
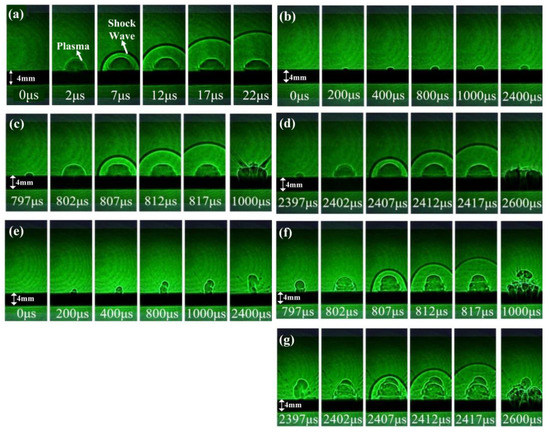
Figure 2.
The propagating morphology of plasma and shock wave induced by an ns laser, ms laser, and ms-ns CPL, respectively. (a) Result of the single ns laser, . (b) Result of the single ms laser, . (c) Result of ms-ns CPL, = 226.13, Δt = 0.8 ms. (d) Result of ms-ns CPL, = 226.13, Δt = 2.4 ms. (e) Result of a single ms laser, 301. (f) Result of ms-ns CPL, = 301, Δt = 0.8 ms. (g) Result of ms-ns CPL, = 301, Δt = 2.4 ms.
3.2. The Velocity of the ms-ns CPL-Induced Shock Wave
In this study, the maximum shock wave velocity during propagation is used to analyze the velocity variation of ms-ns CPL-induced shock waves with different parameters. The relationship among shock wave velocity, energy ratio, and pulse delay is shown in Figure 3. There is a dotted line with a scale of , which represents the velocity of ns laser-induced shock waves. The part over 429.6 m/s belongs to the shock wave acceleration phenomenon. When and , the shock wave velocity increases with , and declines with . It is found that the ms-ns CPL-induced shock wave velocity () is more than the ns laser-induced shock wave velocity () with . When , the increases within a little scale with , then decreases with . Finally, the increases obviously with . It is found that the is obviously more than with . When the ms laser energy densities are 376.88 and 414.58, the changing trend of shock wave velocity is approximately the same. The shock wave velocity decreases with 1.4 ms > Δt > 0.4 ms and increases within a little scale with . Furthermore, the is lower than under different pulse delay conditions.
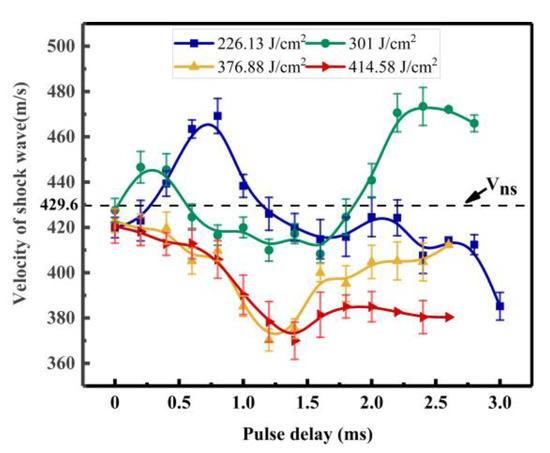
Figure 3.
The relation between shock wave velocity and pulse delays.
Table 1 presents the laser parameters of the maximum ms-ns CPL-induced shock wave acceleration phenomenon. Case 1 is the condition with , , and . Case 2 is the condition with , , and . The acceleration multiple of relative to is approximate with two cases.

Table 1.
The laser parameters of the maximum shock wave acceleration phenomenon.
As shown in Figure 4, the shock wave velocity is inversely proportional to the ms laser energy density with . Otherwise, the shock wave velocity decreases nonmonotonically with . The shock wave velocity reaches the peak value with , and then it is inversely proportional to the energy density of the ms laser. The trend is similar to that with the pulse delay of 0.2 ms. However, the acceleration multiple of relative to with the pulse delay of 0.2 ms is relatively low. The results show that the shock wave acceleration phenomenon occurs when the ms laser energy is relatively low (226.13, 301).
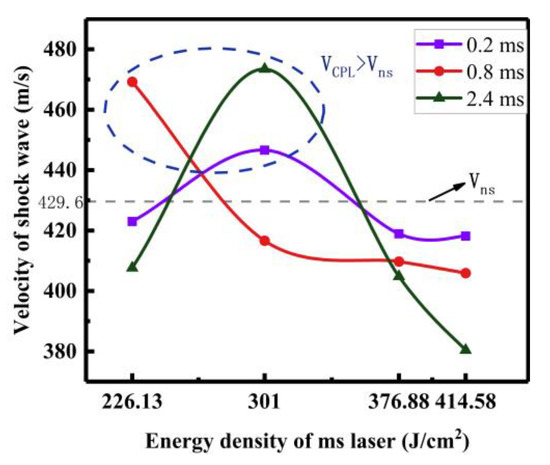
Figure 4.
The relation between shock wave velocity and ms laser energy densities.
3.3. The Simulation Analysis of the ms-ns CPL-Induced Shock Wave
3.3.1. Calculation Model and Theory
To model the flow field of the shock wave, a numerical model of 2D axisymmetric two-phase flow is established as shown in Figure 5. This model is based on the condition that the silicon has been gasified. The temperature of silicon vapor increases and begins to expand when the ms-ns CPL irradiates silicon vapor through the air. When the irradiation of the laser stops, the silicon vapor (plasma) stops expanding and the shock wave continues to propagate in the air. This model analyzes the velocity field of ms-ns CPL-induced shock waves with different parameters in the air. In the model, it assumes that the plasma is mainly composed of opaque silicon vapor. The propagation of ms-ns CPL-induced plasma and shock waves is described by the mass, momentum, and energy conservation equations.
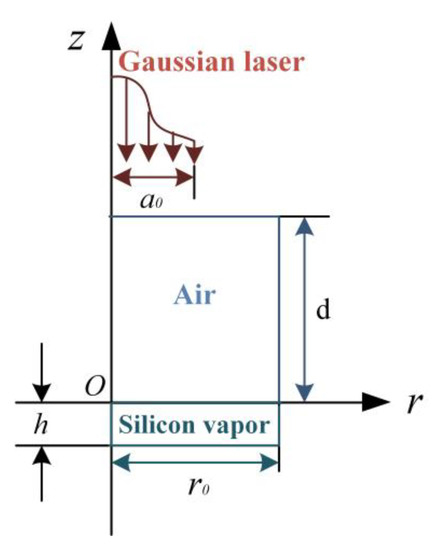
Figure 5.
2D calculation model.
Here, represents the velocity of fluid, p stands for the pressure, signifies the gradient operator, is the density of the silicon vapor, is the density of the air, represents gravity acceleration, η is the viscosity coefficient of silicon vapor, signifies the heat capacity of silicon vapor, T is the temperature, is the thermal conductivity of silicon vapor, and S is the deformation rate tensor. The power density of the heat source in plasma is described as [32]:
The represents the laser power density, stands for the inverse bremsstrahlung absorption factor of plasma, RL signifies the radius of the laser, stands for the equilibrium electron density, and represents the electron pressure. The values of and can be calculated by thermal ionization in Equation (7). I is the ionization potential of the silicon atom, k is Boltzmann constant, signifies the ms-ns CPL power density, signifies the ms laser power density, signifies the ns laser power density, represents the ms laser radius, represents the ns laser radius, and and represent the temporal distribution of two lasers:
Here, and signify the pulse width of two lasers, signifies the time interval of two lasers. The power density with thermal radiation transmission of heat source is [33]:
Here, , , and stand for the group values of Planck opacity, the plasma radiant density, and the ideal blackbody radiant density. The expressions of the main physical parameters with temperature involved in the calculation are enumerated in Table 2 [34].

Table 2.
The main physical parameters.
3.3.2. Calculation Results and Analysis
The laser parameters of ms-ns CPL-induced acceleration phenomena are shown in Table 1. The velocity field under the condition of the maximum shock wave acceleration is analyzed. The velocity distribution in different spatial positions is shown in Figure 6, and here we refer to the velocity distribution in different positions of the axial z at r = 0. The distribution of the velocity field is different. Figure 6a,b shows the distributions of shock wave velocity with , at 807 and , at 2407, respectively. As shown in Figure 6a, the maximum velocity region is mainly concentrated on the silicon surface in case 1. The recoil pressure of the ms-ns CPL-induced shock wave propagates to the silicon surface. The convection between the recoil pressure and silicon vapor overflowing from the silicon increase the velocity of the plasma near the silicon surface. Hence, the maximum velocity region is mainly concentrated on the silicon surface. However, two relatively large velocities distribute on the target surface and the shock wave front in case 2, which is shown in Figure 6b. This is because the ms laser-induced plasma as a propagation medium can accelerate the shock wave velocity. To more clearly compare the changes of velocity values in different axial (z) positions of r = 0, we add a probe in the process of solving the model by Comsol to accurately obtain the velocity values at different axial (z) positions of r = 0, and the curves drawn by these velocity values are shown in Figure 7. It shows that the shock wave velocity in case 1 and case 2 are approximately equal. But the difference of plasma velocity between case 1 and case 2 near the target surface is 200 m/s. This is caused by the state of ms laser-induced plasma before the ns laser irradiation.
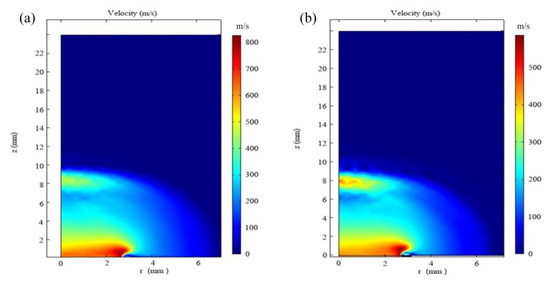
Figure 6.
The spatial distribution of shock wave velocity (a) in case 1 at 807 and (b) in case 2 at 2407.
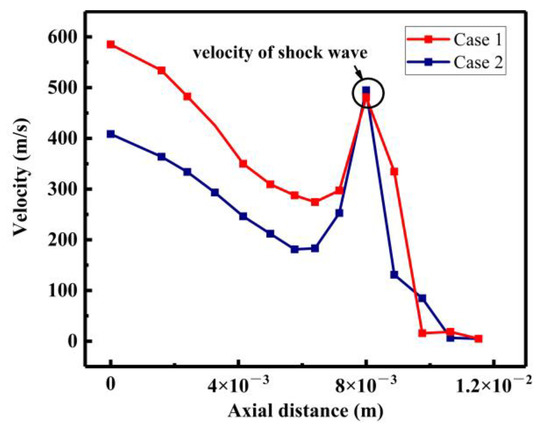
Figure 7.
The axial distribution of velocity in case 1 at 807 and case 2 at 2407.
4. Discussion
To reveal the mechanism of the shock wave acceleration phenomenon mentioned above, it can be obtained from experimental and simulation results. In case 1, as illustrated in Figure 8a, a thin layer of ms laser-induced plasma forms in front of the target before the ns laser irradiating with and . The morphology evolution is presented in Figure 2c. Microscopically, the electrons in ms laser-induced plasma increase electron density in ns laser-induced plasma. Thus, the collision ionization probability between free electrons and silicon vapor atoms increases. Macroscopically, the expansion velocity of ns laser-induced plasma increases during laser irradiation. That is to say, the laser-supported absorption wave velocity increases. Finally, the shock wave acceleration phenomenon occurs after the laser stops irradiation. The distribution of shock wave velocity is illustrated in Figure 6a. The maximum velocity region is mainly concentrated on the target surface. This is caused by the convective acceleration effect between the shock wave recoil pressure and the silicon vapor overflowing from the target surface [35,36].
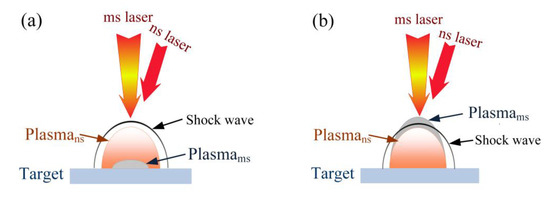
Figure 8.
The schematic diagram of shock wave acceleration mechanism (a) in case 1 and (b) in case 2.
In case 2, the density of plasma decreases after the ms laser stops irradiating with , and the ms laser-induced plasma can no longer absorb the ns laser energy and cannot continue to expand during the irradiation of the ns laser, as shown in Figure 8b. This leads to the ms laser-induced plasma expansion distance at 2397 μs being larger than the ns laser-induced plasma expansion distance at 2402 μs. It is shown in Figure 2g. Therefore, the propagation medium of ns laser-induced shock waves changes from air to the ms laser-induced plasma. The propagation essence of shock waves is continuous ionization of the propagation medium [37]. The ms laser-induced plasma is more easily ionized than air. Therefore, the shock wave velocity propagated in ms laser-induced plasma is higher than in air. The shock wave acceleration phenomenon occurs. The distribution of shock wave velocity is shown in Figure 6b. The maximum velocity region is not only concentrated on the target surface, but also nearby the front of the shock wave. It is illustrated that the ms laser-induced plasma as the propagation medium can accelerate shock waves.
The existing research on shock waves is to increase their velocity by adding single short laser energy [16,17,18,19]. However, due to the limitation of laser crystals, it is impossible to increase the shock wave velocity by infinitely increasing laser energy. This limits the application of shock waves in industrial processing, aviation, and other fields. In this paper, the acceleration methods of ms-ns CPL-induced shock waves are proposed, which breaks the technical barrier of traditional shock wave acceleration methods. The shock wave velocity is improved by adjusting the energy ratio and pulse delay of ms-ns CPL. The ms-ns CPL-induced shock wave velocity can be increased by 10% compared with the single ns laser-induced shock wave velocity by using two acceleration methods of ms-ns CPL-induced shock waves mentioned above.
5. Conclusions
The shock waves induced by the ns laser irradiating silicon assisted by the ms laser with different pulse delays and ms laser energies are investigated. Two types of shock wave acceleration phenomenon are found. The ns laser energy density of 12, ms laser energy density of 226.13, and pulse delay of 0.8 ms are used for the first acceleration phenomenon. The ns laser energy density of 12, ms laser energy density of 301, and pulse delay of 2.4 ms are used for the second acceleration phenomenon. It is revealed that the initial stage of ms laser-induced plasma will provide the initial ions to increase the probability of collision ionization between free electrons and vapor atoms in the course of ns laser irradiation. Then, the ns laser-induced plasma expansion velocity increases. The shock wave acceleration phenomena appear. Moreover, when the ms laser-induced plasma becomes the propagation medium of the shock wave, the ns laser-induced shock wave can also be accelerated. The numerical results can verify the analysis of the acceleration mechanism. The shock wave acceleration methods obtained in this research promote development in the application of laser propulsion.
Author Contributions
J.L. performed the experiment; performed the data analyses and wrote the manuscript; W.Z. contributed significantly to analysis and manuscript preparation; G.J. and Y.L. contributed to the conception of the study. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. U19A2077) and Changchun Science and Technology Development Plan Project No. 21ZY34.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for the research equipment and materials provided by Jilin Key Laboratory of Solid-State Laser Technology and Application.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Esmiller, B.; Jacquelard, C.; Eckel, H.A.; Wdwin, E. Space debris removal by ground-based lasers: Main conclusions of the European project cleanspace. Appl. Opt. 2014, 53, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soulard, R.; Quinn, M.N.; Tajima, T.; Mourou, G. ICAN: A novel laser architecture for space debris removal. Acta Astronaut. 2014, 105, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; Wu, B. Nanosecond laser pulse interactions with breakdown plasma in gas medium confined in a microhole. Appl. Phys. B Lasers Opt. 2013, 113, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wu, X.; Yuan, Y.; Li, H.; Yang, J. Confined geometry and laser energy affect laser plasma propulsion. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 9763–9772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Tan, R.; Wu, J.; Lu, Y.; Zhu, Y. Air-breathing mode laser propulsion with a long-pulse TE CO2 laser. Chin. Opt. Lett. 2010, 8, 771–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, P.; Crookes, R.; Wu, H. Shock-wave induced compressive stress on alumina ceramics by laser peening. Mater. Design 2019, 167, 107626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wu, X.; Li, G.; Yuan, Y.; Yang, J. Particle removal is explored by the motion of individual particles based on laser-induced plasma shock wave. Opt. Commun. 2020, 460, 125205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhaia, Z.; Wang, W.; Meia, X.; Wanga, K.; Yanga, H. Influence of plasma shock wave on the morphology of laser drilling in different environments. Opt. Commun. 2017, 390, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unaldi, S.; Papadopoulos, K.; Rondepierre, A.; Rouchausse, Y.; Karanika, A.; Deliane, F.; Tserpes, K.; Floros, G.; Richaud, E.; Berthe, L. Towards selective laser paint stripping using shock waves produced by laser-plasma interaction for aeronautical applications on AA 2024 based substrates. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 414, 107095. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.Z.; Xue, K.N.; Lu, H.F.; Xing, F.; Luo, K.Y. Laser shock wave-induced wear property improvement and formation mechanism of laser cladding Ni25 coating on H13 tool steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2021, 296, 117207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasyuk, I.K.; Pashinin, P.P.; Semenov, A.Y.; Khishchenko, K.V.; Fortov, V.E. Study of extreme states of matter at high energy densities and high strain rates with powerful lasers. Laser Phys. 2016, 26, 094001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrosimov, S.A.; Bazhulin, A.P.; Voronov, V.V.; Geras’kin, A.A.; Krasyuk, I.K.; Pashinin, P.P.; Semenov, A.Y.; Stuchebryukhov, I.A.; Khishchenko, K.V.; Fortov, V.E. Specific features of the behaviour of targets under negative pressures created by a picosecond laser pulse. Quantum Electron. 2013, 43, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.Q.; Su, M.; Jiao, Z.H.; Qi, M. Dynamics and density distribution of laser-produced plasma using optical interferometry. Phys. Plasmas 2018, 25, 063302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Li, C. Evolution of ns pulsed laser induced shock wave on aluminum surface by numerical simulation. Results Phys. 2021, 22, 103920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nechay, A.N.; Perekalov, A.A.; Chkhalo, N.I.; Salashchenko, N.N.; Korepanov, M.A.; Koroleva, M.R. Emission properties of targets based on shock waves excited by pulsed laser radiation. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 142, 107250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoh, J.J.; Lee, H.; Choi, J.; Lee, K.; Kim, K. Ablation-induced explosion of metal using a high-power Nd:YAG laser. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 103, 043511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorčič, P.; Možina, J. High-speed two-frame shadowgraphy for velocity measurements of laser-induced plasma and shock-wave evolution. Opt. Lett. 2011, 36, 2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Su, M.; Min, Q.; Sun, D.; Ma, P.; Wang, K.; Jiao, Z.; Dong, C. Dynamics and density distribution of laser-produced Al plasmas using optical interferometry and optical emission spectroscopy. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2019, 225, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraft, S.; Schille, J.; Mauersberger, S.; Schneider, L.; Loeschner, U. Pump-probe imaging for process control and optimization in high-speed laser micro machining. In Proceedings of the Laser-based Micro- and Nanoprocessing XIV, San Francisco, CA, USA, 12 March 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, S.; Su, M.; Ma, P.; Wang, K.; Dong, C. Expansion dynamics and emission characteristics of nanosecond–picosecond collinear double pulse laser-induced Al plasma in air. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2019, 242, 106773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Su, M.; Liu, J.; Min, Q.; Dong, C. Expansion dynamics and compression layer in collinear double-pulse laser produced plasmas in a vacuum. Phys. Plasmas 2020, 27, 052101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wei, W.; Han, J.; Jian, W.; Jia, S. Experimental study of the behavior of two laser produced plasmas in air. Phys. Plasmas 2015, 22, 073511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Yuan, B.; Cai, J.; Jin, G. The acceleration mechanism of shock wave induced by millisecond-nanosecond combined-pulse laser on silicon. Plasma Sci. Technol. 2021, 23, 055507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.H.; Smijesh, N.; Chetty, D.; Litvinyuk, I.V.; Sang, R.T. Effect of double pulse laser irradiation on the dynamics of picosecond laser-produced plasma. Phys. Plasmas 2020, 27, 083518. [Google Scholar]
- Smijesh, N.; Rao, K.H.; Chetty, D.; Litvinyuk, I.V.; Sang, R.T. Plasma plumes produced by laser ablation of Al with single and double pulse schemes. Opt. Lett. 2017, 43, 6081–6084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Qi, H.; Zeng, X.; Chen, A.; Gao, X.; Jin, M. Time-resolved spectroscopy of collinear femtosecond and nanosecond dual-pulse laser-induced Cu plasmas. Plasma Sci. Technol. 2021, 23, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, G.; Wang, H.; Zhu, X. Experimental study on the optimum matching of CW-nanosecond combined pulse laser drilling. Appl. Opt. 2019, 58, 9105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Lv, X.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Han, B.; Shen, Z.; Lu, J.; Ni, X. Millisecond laser machining of transparent materials assisted by a nanosecond laser with different delays. Opt. Lett. 2016, 41, 2807–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoya, N.; Katsumata, T.; Kajiwara, I.; Onuma, T.; Kanda, A. Measurements of S0 mode Lamb waves using a high-speed polarization camera to detect damage in transparent materials during non-contact excitation based on a laser-induced plasma shock wave. Opt. Laser Eng. 2022, 148, 106770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Yu, Q.; Bai, X.; Jin, G.; Cai, J.; Yuan, B. Substrate Cleaning Threshold for Various Coated Al Alloys Using a Continuous-Wave Laser. Photonics 2021, 8, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Dong, Y.; Jin, G. The Effect of Spot Size Combination Mode on Ablation Morphology of Aluminum Alloy by Millisecond-Nanosecond Combined-Pulse Laser. Materials 2018, 11, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Cai, J. Study on the effect of focal position change on the expansion velocity and propagation mechanism of plasma generated by millisecond pulsed laser-induced fused silica. Plasma Sci. Technol. 2023, 25, 035507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wei, Z.; Wang, Y.B.; Jin, G.Y. Numerical simulation of laser-supported combustion wave induced by millisecond-pulsed laser on aluminum alloy. Laser Phys. 2016, 26, 015001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcbride, B.J.; Gordon, S.; Reno, M.A. Coefficients for Calculating Thermodynamic and transport Properties of Individual Species, 1st ed.; NASA TM-4513: Washington, DC, USA, 1993; pp. 9–47. [Google Scholar]
- Andreopoulos, J.; Muck, K.C.; Dussauge, J.P.; Smits, A.J. Turbulence structure in a shock wave/turbulent boundary-layer interaction. AIAA J. 2012, 27, 862–869. [Google Scholar]
- Liou, W.W.; Huang, G.; Shih, T.H. Turbulence model assessment for shock wave/turbulent boundary-layer interaction in transonic and supersonic flows. Comput. Fluids 2000, 29, 275–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, W.E.; Hall, R.B.; Johnson, R.R. Experimental study of igition and propagation of laser-supported detonation waves. J. Appl. Phys. 1974, 45, 2138–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).