WDM Optical Access Network for Full-Duplex and Reconfigurable Capacity Assignment Based on PolMUX Technique
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Network Architecture
2.1. Description
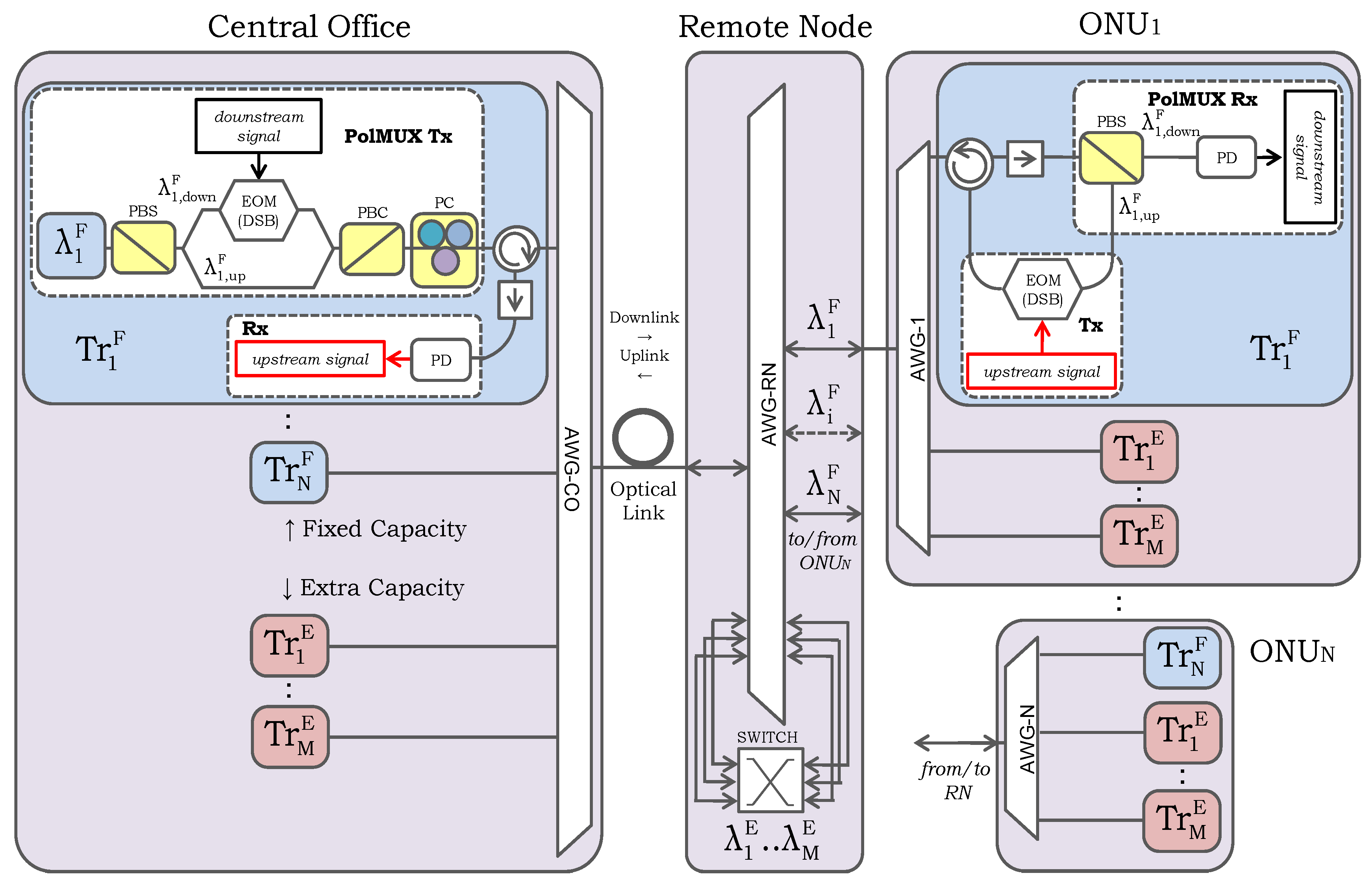
2.2. Wavelengths Plan and Characteristics of the Routing Components
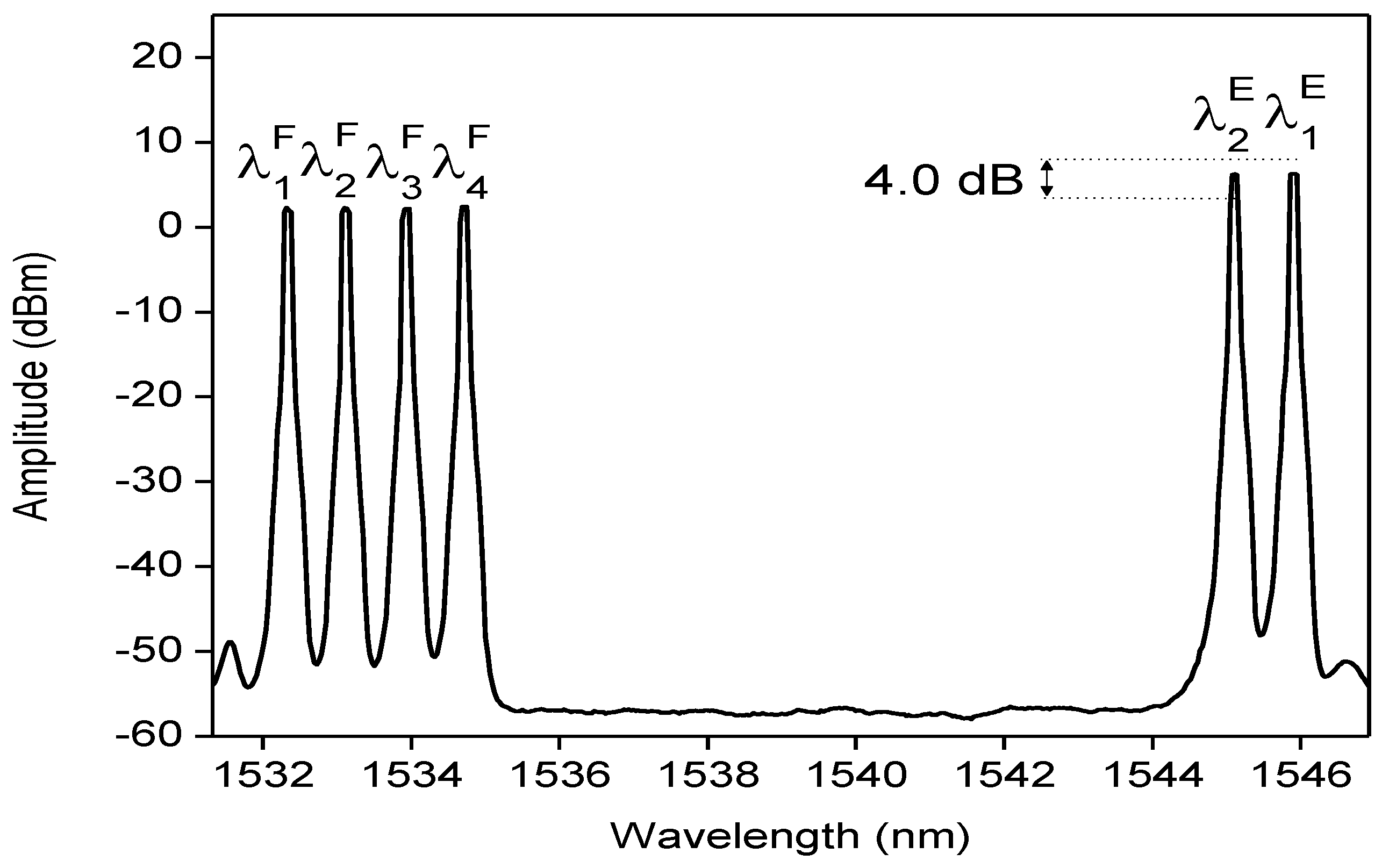
2.3. Definition of the Routing Scenarios
| Scenario 1 | Scenario 2 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed λs | Extra λs | Fixed λs | Extra λs | |||||||||
| ONU1 | ||||||||||||
| ONU2 | ||||||||||||
| ONU3 | ||||||||||||
| ONU4 | ||||||||||||
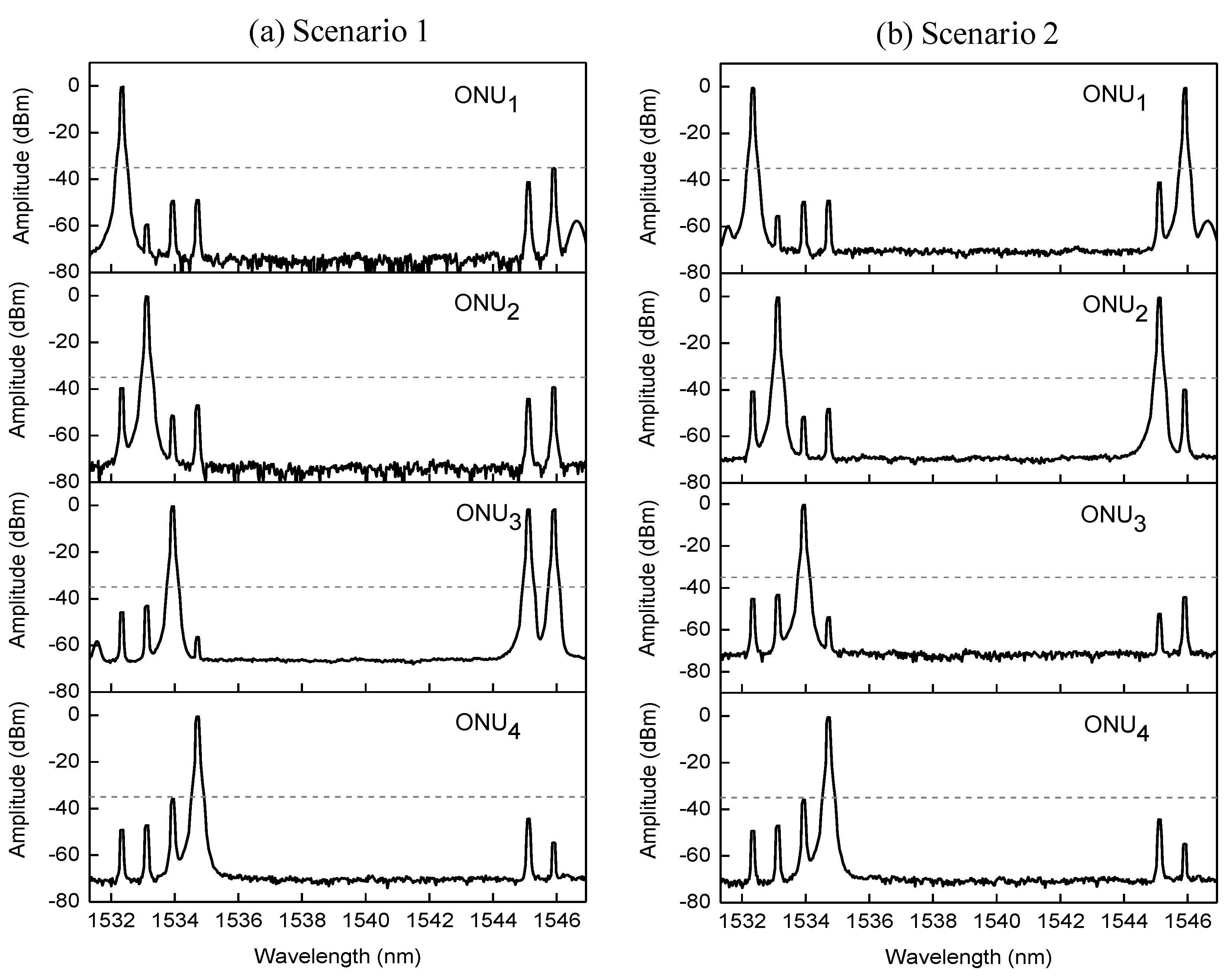
3. Experimental Evaluation of Network Performance
3.1. Degradation of Fixed and Extra Capacity Channels
 ) and 2 (
) and 2 (  )]. [Scenario 1 (
)]. [Scenario 1 (  ) and 2 (
) and 2 (  )].Optical back-to-back (∆). (a) Downlink and (b) uplink propagation.
)].Optical back-to-back (∆). (a) Downlink and (b) uplink propagation.
 ) and 2 (
) and 2 (  )]. [Scenario 1 (
)]. [Scenario 1 (  ) and 2 (
) and 2 (  )].Optical back-to-back (∆). (a) Downlink and (b) uplink propagation.
)].Optical back-to-back (∆). (a) Downlink and (b) uplink propagation.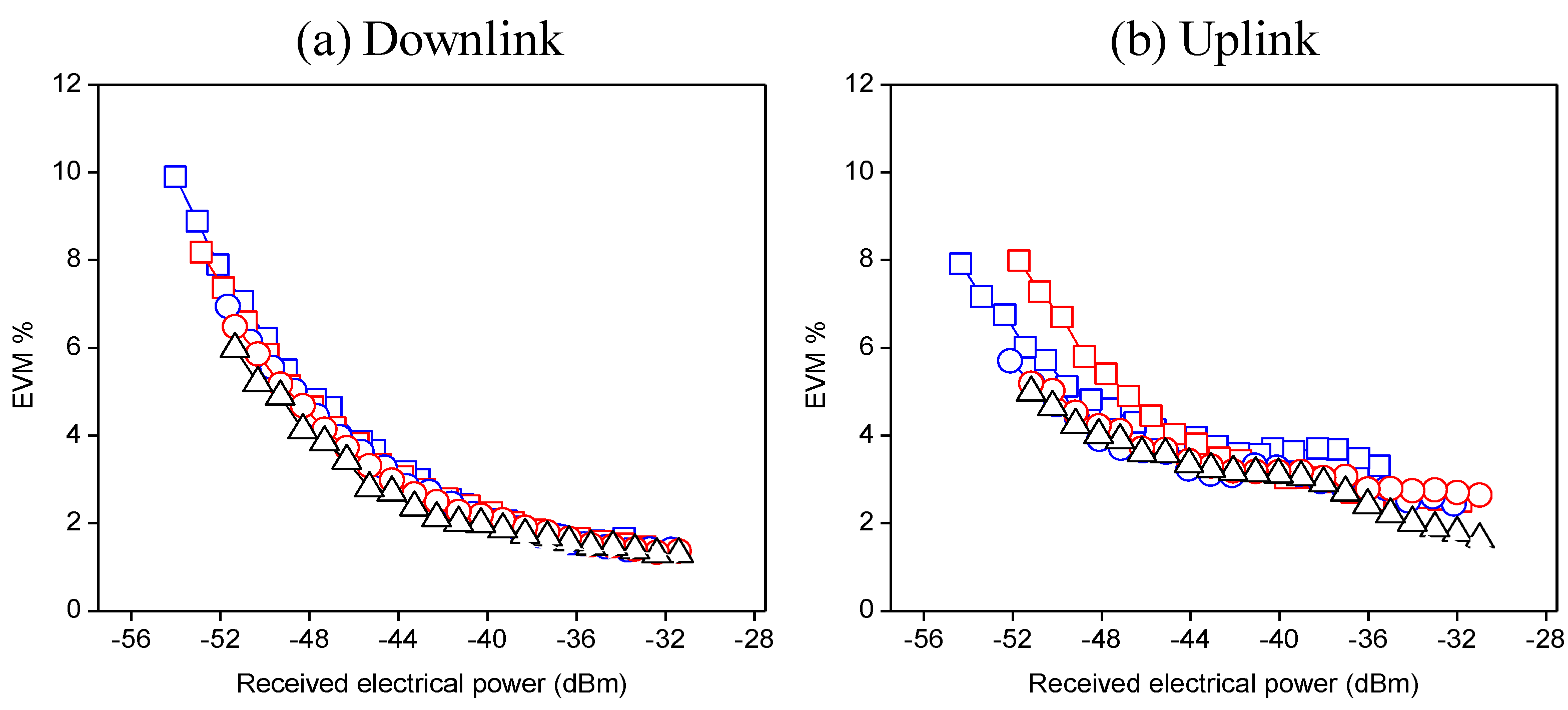
 ) and 2(
) and 2(  )]. λE [Scenario 1(
)]. λE [Scenario 1(  ) and 2(
) and 2(  )].Optical back-to-back (∆). (a) Downlink and (b) uplink propagation.
)].Optical back-to-back (∆). (a) Downlink and (b) uplink propagation.
 ) and 2(
) and 2(  )]. λE [Scenario 1(
)]. λE [Scenario 1(  ) and 2(
) and 2(  )].Optical back-to-back (∆). (a) Downlink and (b) uplink propagation.
)].Optical back-to-back (∆). (a) Downlink and (b) uplink propagation.
3.2. Impact of the Electrical Subcarrier Frequency
 ) and 2 (
) and 2 (  )] and λ3F [scenario 1 (
)] and λ3F [scenario 1 (  ) and 2 (
) and 2 (  )]. Optical back-to-back (∆). Note: both extra capacity wavelengths λ1E and λ2E carry 10 Mb/s 64-QAM data over 5 GHz SCM tones.
)]. Optical back-to-back (∆). Note: both extra capacity wavelengths λ1E and λ2E carry 10 Mb/s 64-QAM data over 5 GHz SCM tones.
 ) and 2 (
) and 2 (  )] and λ3F [scenario 1 (
)] and λ3F [scenario 1 (  ) and 2 (
) and 2 (  )]. Optical back-to-back (∆). Note: both extra capacity wavelengths λ1E and λ2E carry 10 Mb/s 64-QAM data over 5 GHz SCM tones.
)]. Optical back-to-back (∆). Note: both extra capacity wavelengths λ1E and λ2E carry 10 Mb/s 64-QAM data over 5 GHz SCM tones.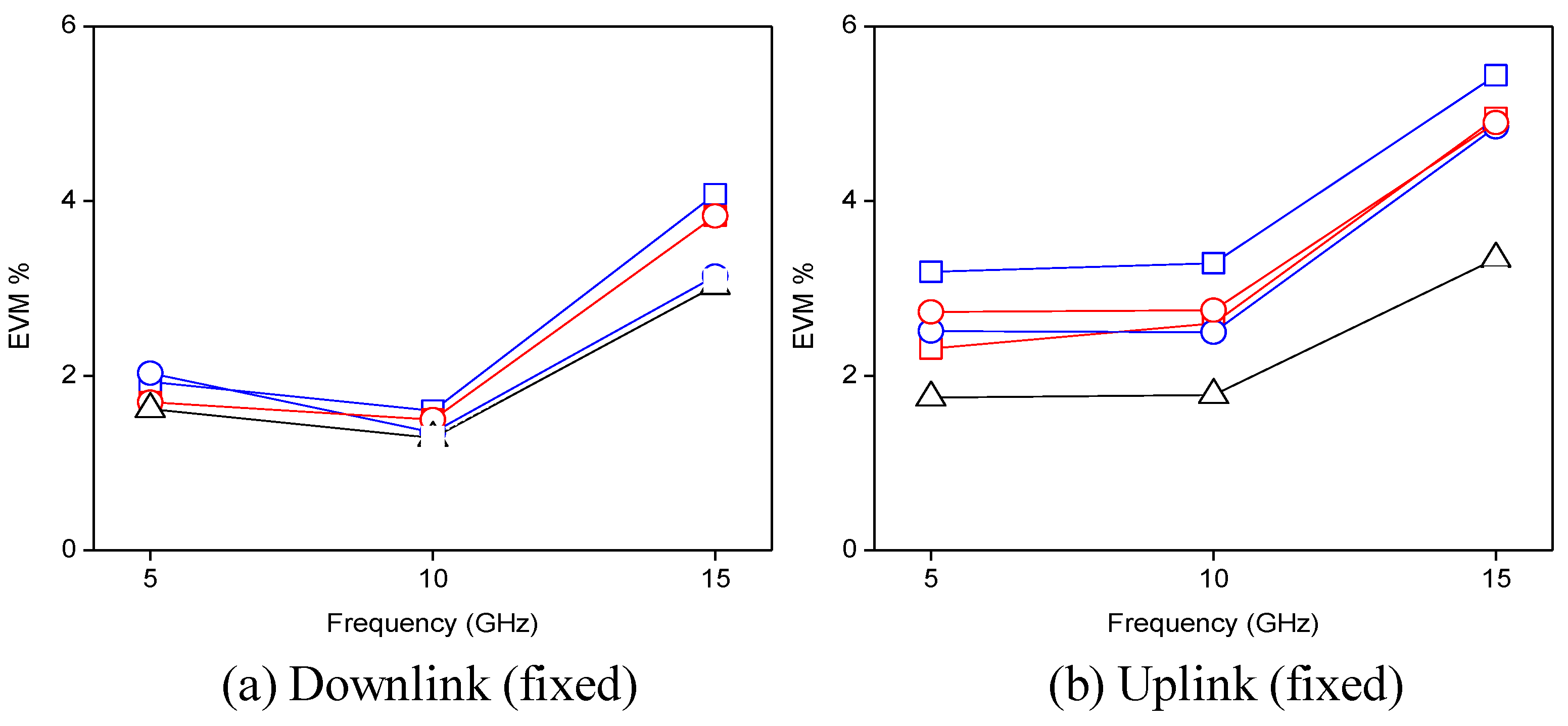
 ) and 2 (
) and 2 (  )] and λ2E [scenario 1 (
)] and λ2E [scenario 1 (  ) and 2 (
) and 2 (  )]. Optical back-to-back (∆). Note: all fixed capacity wavelengths carry 5 Mb/s QPSK data over 10 GHz SCM tones.
)]. Optical back-to-back (∆). Note: all fixed capacity wavelengths carry 5 Mb/s QPSK data over 10 GHz SCM tones.
 ) and 2 (
) and 2 (  )] and λ2E [scenario 1 (
)] and λ2E [scenario 1 (  ) and 2 (
) and 2 (  )]. Optical back-to-back (∆). Note: all fixed capacity wavelengths carry 5 Mb/s QPSK data over 10 GHz SCM tones.
)]. Optical back-to-back (∆). Note: all fixed capacity wavelengths carry 5 Mb/s QPSK data over 10 GHz SCM tones.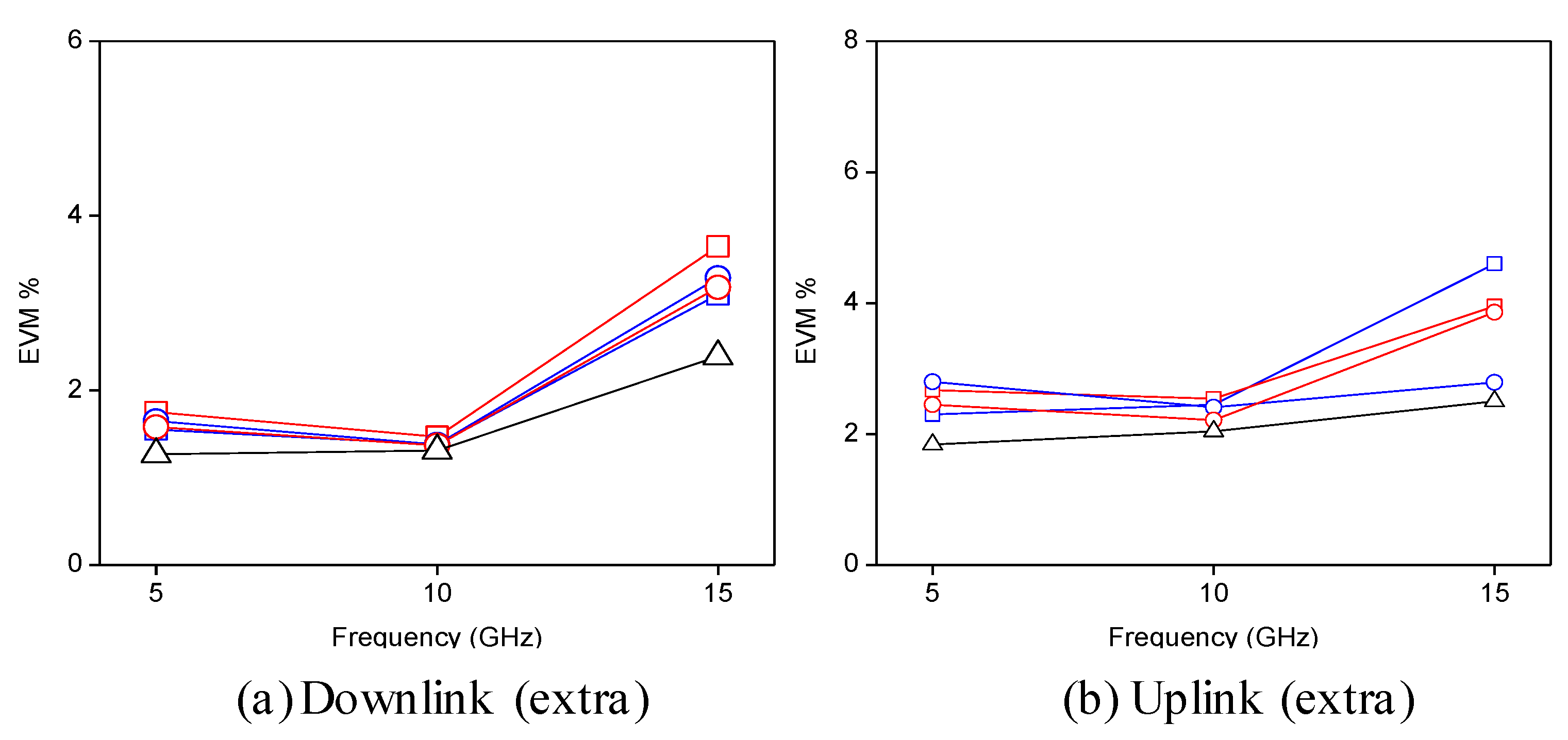
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflict of Interest
References
- Banerjee, A.; Park, Y.; Clarke, F.; Song, H.; Yang, S.; Kramer, G.; Kim, K.; Mukherjee, B. Wavelength-division-multiplexed passive optical network (WDM PON) technologies for broadband access: A review. J. Opt. Netw. 2005, 4, 737–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Sorin, W.V.; Kim, B.Y. Fiber to the Home Using a PON Infrastructure. IEEE J. Lightwave Technol. 2006, 24, 4568–4583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazovsky, L.G.; Shaw, W.-T.; Gutierrez, D.; Cheng, N.; Wong, S.-W. Next-Generation Optical Access Networks. IEEE J. Lightwave Technol. 2007, 25, 3428–3442. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Q.; Tran, A.V. Wavelength-reused WDM access network supporting 40 Gb/s downlink and 10 Gb/s uplink. In Proceedings of the Optical Fiber Communication Conference (OFC) 2013, Anaheim, CA, USA, 17–21 March 2013. paper NTh4F.2.
- Hsueh, Y.; Rogge, M.S.; Yamamoto, S.; Kazovsky, L.G. A Highly Flexible and Efficient Passive Optical Network Employing Dynamic Wavelength Allocation. IEEE J. Lightwave Technol. 2005, 23, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, B.; Mora, J.; Puerto, G.; Capmany, J. Symmetric reconfigurable capacity assignment in a bidirectional DWDM access network. Opt. Express 2007, 15, 16781–16786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, P.J.; Huiszoon, B.; Roy, R.; de Laat, M.M.; Huijskens, F.M.; Klein, E.J.; Khoe, G.D.; Koonen, A.M.J.; de Waardt, H. High-Bit-Rate Dynamically Reconfigurable WDM-TDM access network. J. Opt. Commun. Netw. 2009, 1, A143–A159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrenk, B.; Lazaro, J.A.; Polo, V.; Prat, J. Multi-operability in WDM-PONs with electrically reconfigurable RSOA-Based optical network units. In Proceedings of the Access Networks and In-house Communications (ANIC) 2010, Karlsruhe, Germany, 21–24 June 2010. paper ATuB4.
- Tran, N.; Tangdiongga, E.; Okonkwo, C.; Jung, H-D.; Koonen, T. Flexibility Level Adjustment in Reconfigurable WDM-TDM Optical Access Networks. IEEE J. Lightwave Technol. 2012, 30, 2542–2550. [Google Scholar]
- Sleiffer, V.; van den Borne, D.; Veljanovski, V.; Kuschnerov, M.; Hirano, M.; Yamamoto, Y.; Takashi, J.; Sander, L.; de Waardt, H. Transmission of 448-Gb/s dual-carrier POLMUX-16QAM over 1230 km with 5 flexi-grid ROADM passes. In Proceedings of the 2012 and the National Fiber Optic Engineers Conference Optical Fiber Communication Conference (OFC), Los Angeles, CA, USA, 4–8 March 2012. paper OW4C.3.
- Chen, Z.; Yan, L.; Pan, W.; Luo, B.; Guo, Y.; Jiang, H.; Yi, A.; Sun, Y.; Wu, X. Transmission of multi-polarization-multiplexed signals: Another freedom to explore? Opt. Express 2013, 21, 11590–11605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, T.; Yao, J. Millimeter-Wave and UWB over a Colorless WDM-PON Based on Polarization Multiplexing Using a Polarization Modulator. IEEE J. Lightwave Technol. 2013, 31, 2742–2751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, F.; Mora, J.; Ortega, B.; Capmany, J. Centralized light-source optical access network based on polarization multiplexing. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 4250–4245. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Z.; Yu, J.; Ellinas, G.; Chang, G. Key Enabling Technologies for Optical–Wireless Networks: Optical Millimeter-Wave Generation, Wavelength Reuse, and Architecture. IEEE J. Lightwave Technol. 2007, 25, 3542–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Fu, S.; Wu, J.; Xu, K.; Lin, J.; Shum, P. A Wavelength-Division-Multiplexed Passive Optical Network with Simultaneous Centralized Light Source and Broadcast Capability. IEEE Photon. J. 2010, 2, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrenk, B.; Bonada, F.; Lazaro, J.A.; Prat, J. Remotely Pumped Long-Reach Hybrid PON with Wavelength Reuse in RSOA-Based ONUs. IEEE J. Lightwave Technol. 2011, 29, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Cui, W.; Tong, S. Wavelength Reuse in a UWB Over WDM-PON Based on Injection Locking of a Fabry–Pérot Laser Diode and Polarization Multiplexing. IEEE J. Lightwave Technol. 2014, 32, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodward, S.L.; Phillips, M.R. Optimizing Subcarrier-Multiplexed WDM Transmission Links. IEEE J. Lightwave Technol. 2004, 22, 773–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buset, J.M.; El-Sahn, Z.A.; Plant, D.V. Experimental Demonstration of a 10 Gb/s Subcarrier Multiplexed WDM PON. IEEE Photon. Technol. Lett. 2013, 25, 1435–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mora, J.; Ortega, B.; Grassi, F.; Capmany, J. WDM Optical Access Network for Full-Duplex and Reconfigurable Capacity Assignment Based on PolMUX Technique. Photonics 2014, 1, 503-515. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics1040503
Mora J, Ortega B, Grassi F, Capmany J. WDM Optical Access Network for Full-Duplex and Reconfigurable Capacity Assignment Based on PolMUX Technique. Photonics. 2014; 1(4):503-515. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics1040503
Chicago/Turabian StyleMora, Jose, Beatriz Ortega, Fulvio Grassi, and Jose Capmany. 2014. "WDM Optical Access Network for Full-Duplex and Reconfigurable Capacity Assignment Based on PolMUX Technique" Photonics 1, no. 4: 503-515. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics1040503
APA StyleMora, J., Ortega, B., Grassi, F., & Capmany, J. (2014). WDM Optical Access Network for Full-Duplex and Reconfigurable Capacity Assignment Based on PolMUX Technique. Photonics, 1(4), 503-515. https://doi.org/10.3390/photonics1040503




