Natural and Anthropogenic Influence on the Physicochemical Characteristics of Spring Water: The Case Study of Medvednica Mountain (Central Croatia)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area

2.2. Data Collection and Analysis
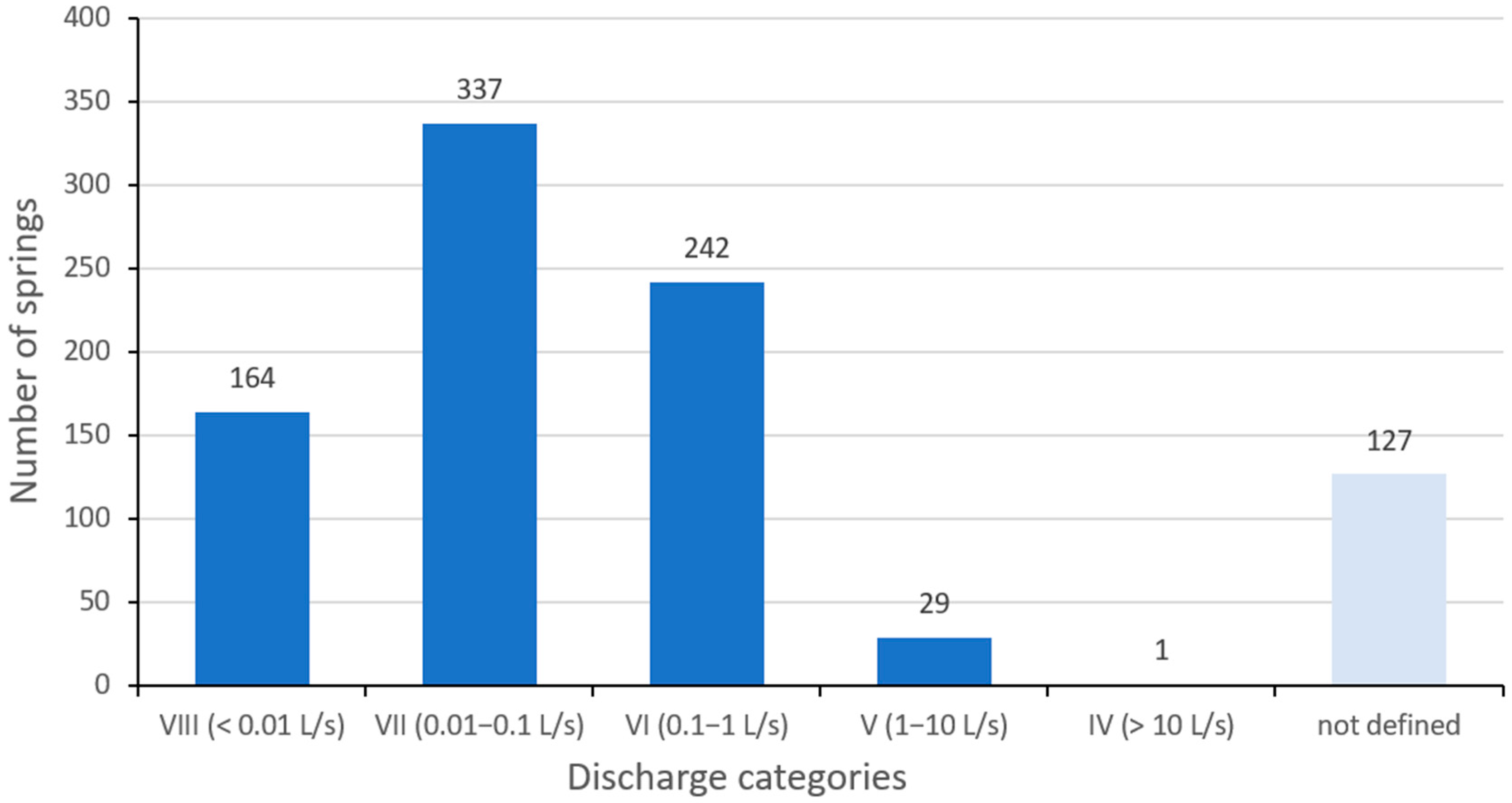
3. Results
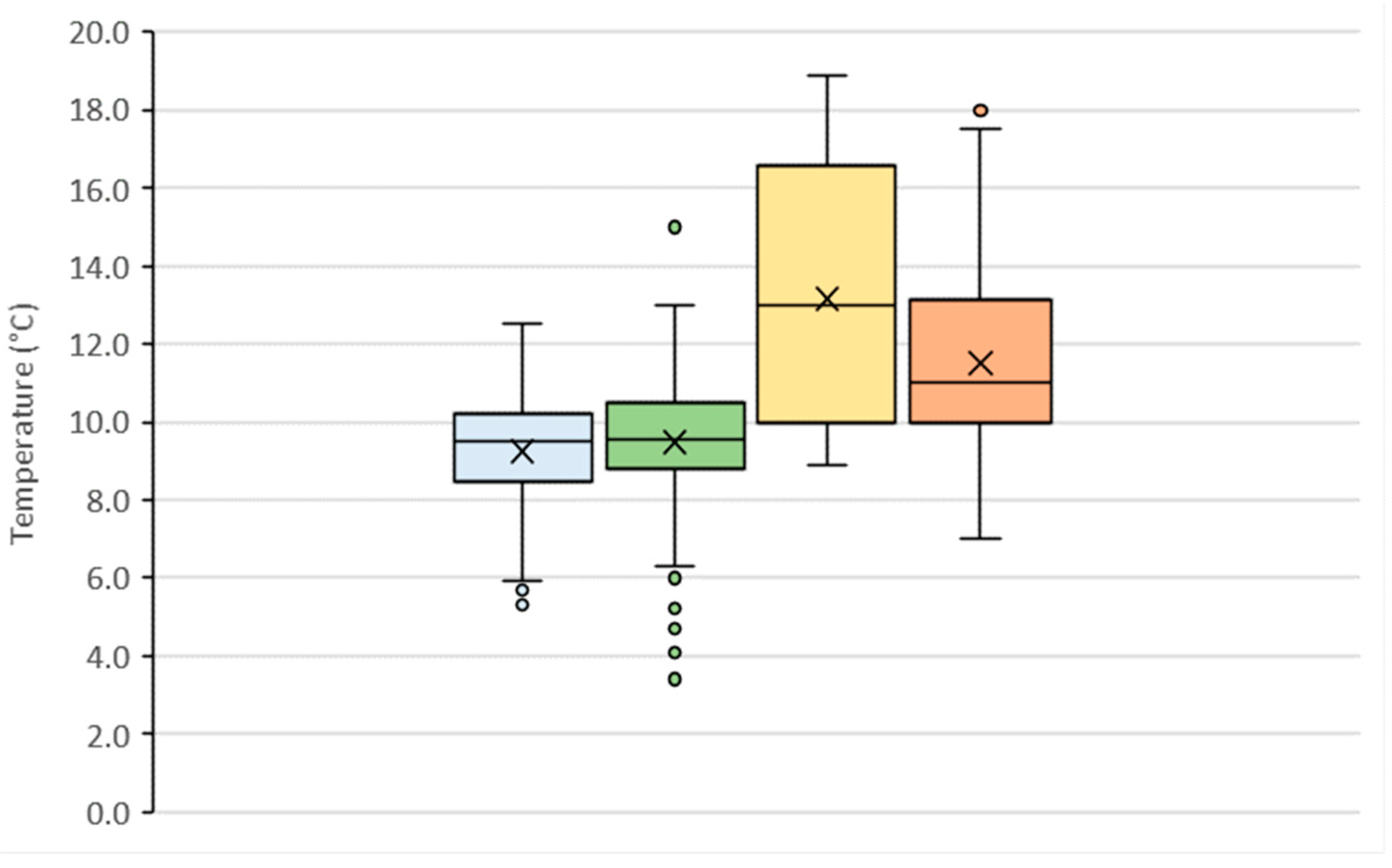
3.1. Temperature of Spring Water
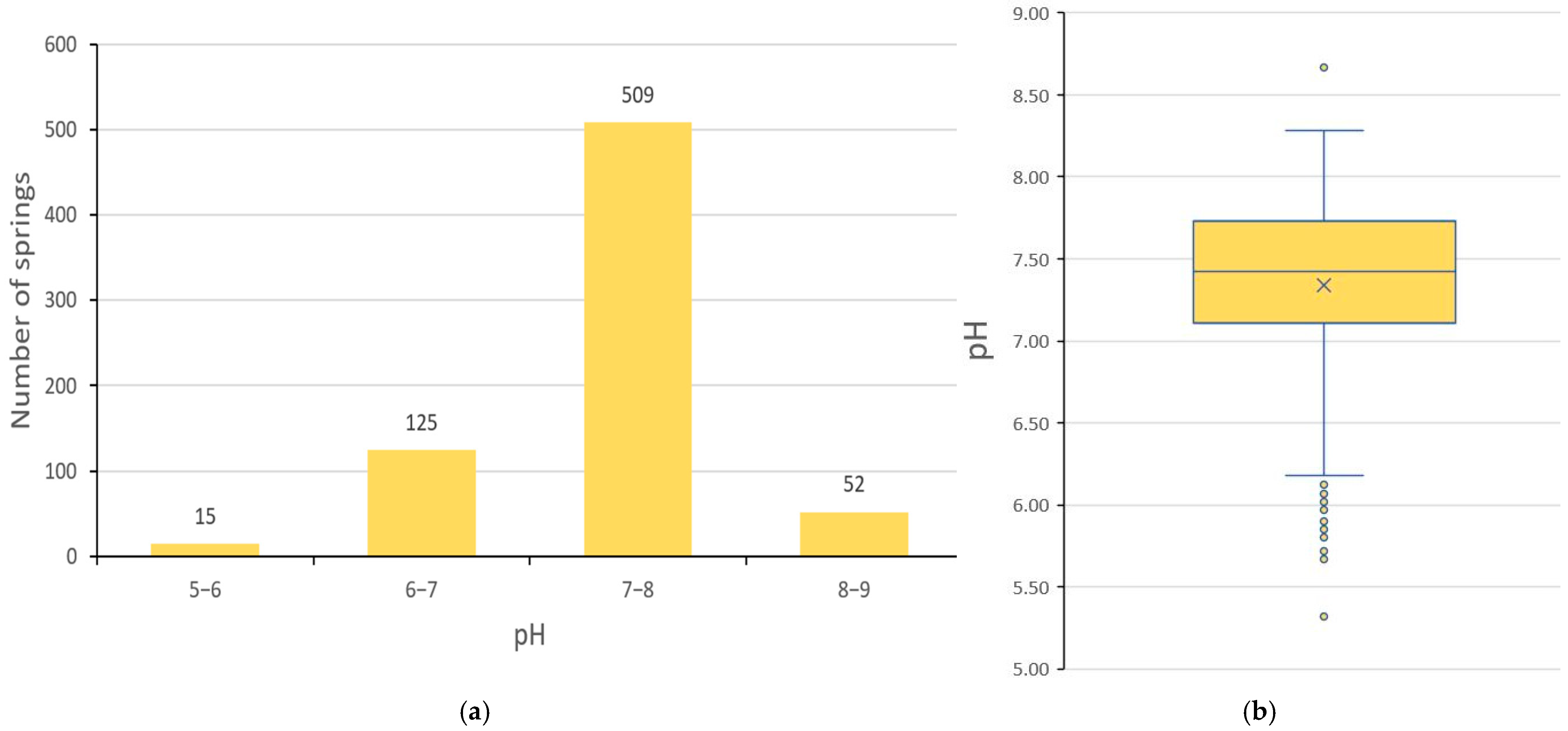
3.2. pH of Spring Water
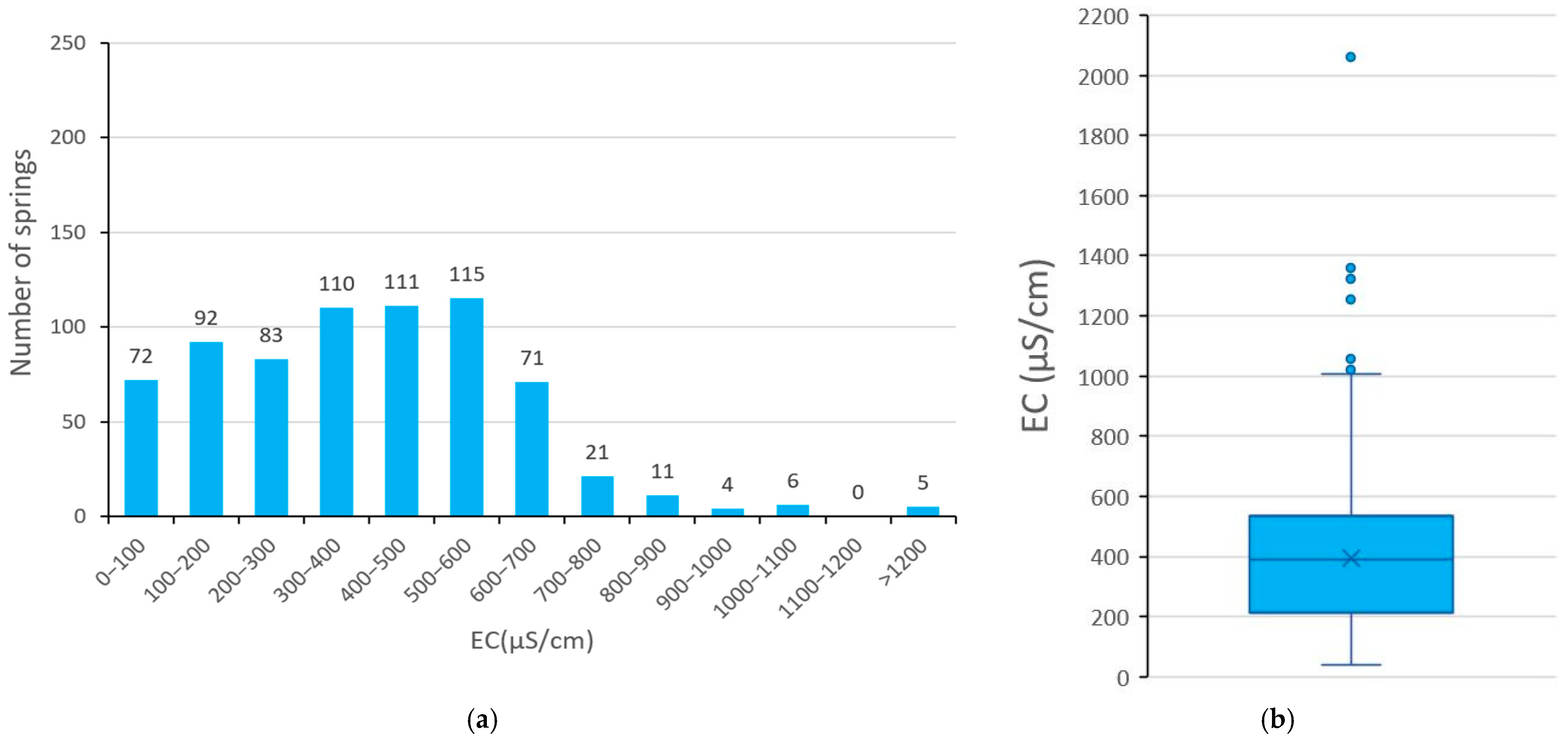
3.3. EC of Spring Water
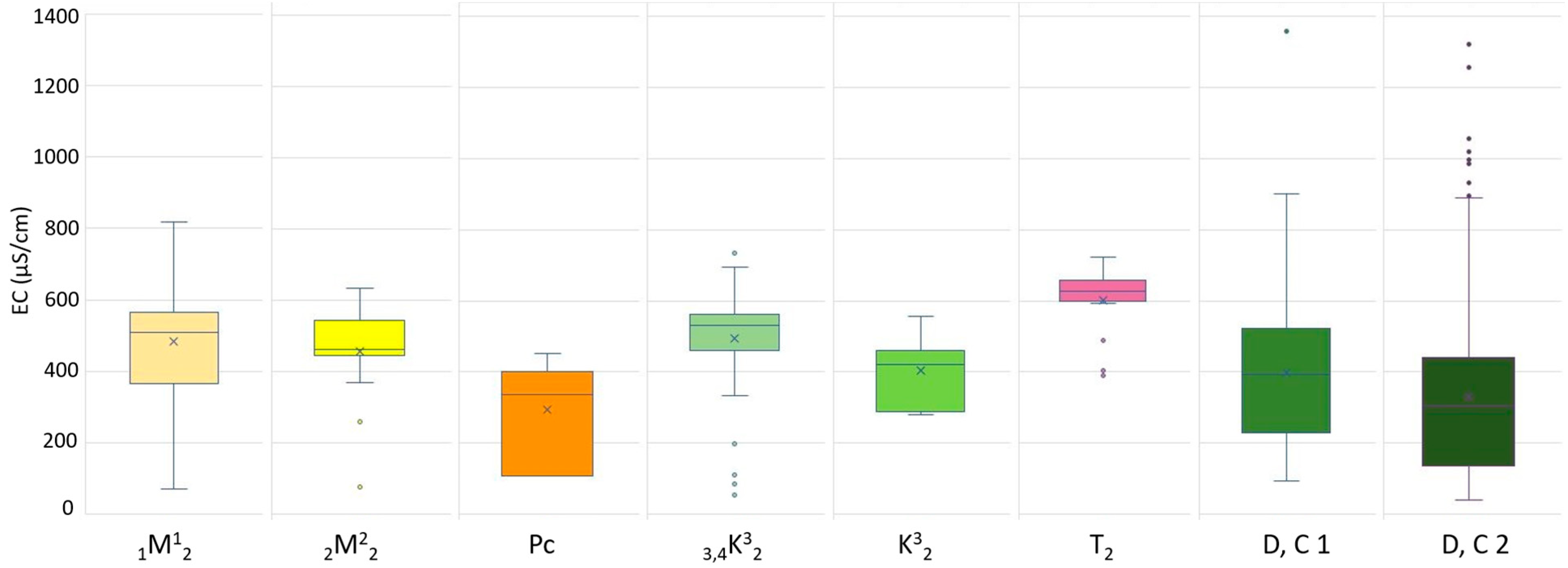
3.4. Physicochemical Parameters and Lithology
4. Discussion
4.1. Factors Influencing Spring Water Temperature
4.2. Factors Influencing EC and pH of Spring Water
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stevens, L.E. Chapter 1: Springs of the World. In Springs of the World: Distribution, Ecology, and Conservation Status; Monograph 1; Stevens, L.E., Ed.; Spring Stewardship Institute: Flagstaff, AZ, USA, 2023; 198p. [Google Scholar]
- Martinić, I. An overview of classifications and modern research of springs in the world and in Croatia. Croat. Geogr. Bull. 2022, 84, 31–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantonati, M.; Fensham, R.J.; Stevens, L.E.; Gerecke, R.; Glazier, D.S.; Goldscheider, N.; Knight, R.L.; Richardson, J.S.; Springer, A.E.; Töckner, K. An urgent plea for global spring protection. Conserv. Biol. 2020, 35, 378–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springer, A.E.; Stevens, L.E.; Ledbetter, J.D.; Schaller, E.M.; Gill, K.; Rood, S.B. Ecohydrology and stewardship of Alberta springs ecosystems. Ecohydrology 2015, 8, 896–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantonati, M.; Stevens, L.E.; Sagadelli, S.; Springer, A.E.; Goldscheider, N.; Celico, F.; Filippini, M.; Ogata, K.; Gargini, A. Ecohydrogeology: The inderdisciplinary convergence needed to improve the study and stewardship of springs and other groundwater-dependent habitats, biota and ecosystems. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 110, 105803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culver, D.C.; Pipan, T.; Gottstein, S. Hypotelminorheic—A Unique Freshwater Habitat. Subterr. Biol. 2006, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Pozojević, I.; Brigić, A.; Gottstein, S. Water mite (Acari: Hydrachnidia) diversity and distribution in undisturbed Dinaric karst springs. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2018, 76, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozojević, I.; Pešić, V.; Gottstein, S. Two water mite species (Acari: Hydrachnidia) from karst springs new for the fauna of Croatia with notes on distribution and environmental preferences. Nat. Croat. 2019, 28, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozojević, I.; Pešić, V.; Goldschmidt, T.; Gottstein, S. Crenal Habitats: Sources of Water Mite (Acari: Hydrachnidia) Diversity. Diversity 2020, 12, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinić, I. Hydrological and Geomorphological Characteristics of Springs on the South Side of the Medvednica Nature Park. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Zagreb, Zagreb, Croatia, 15 October 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Mostowik, K.; Górnik, M.; Jaśkowiec, B.; Maciejczyk, K.; Murawska, M.; Płaczkowska, E.; Rzonca, B.; Siwek, J. High discharge springs in the Outer Flysch Carpathians on the example of the High Bieszczady Mountains (Poland). Carpathian J. Earth Environ. Sci. 2016, 11, 395–404. [Google Scholar]
- Mostowik, K.; Krzyczman, D.; Płaczkowska, E.; Rzonca, B.; Siwek, J.; Wacławczyk, P. Spring Recharge and Groundwater Flow Patterns in a Flysch Aquifer in the Połonina Wetlińska Massif, Carpathian Mountains. J. Mt. Sci. 2021, 18, 819–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervi, F.; Marcaccio, M.; Petronici, F.; Borgatti, L. Hydrogeological Characterization of Peculiar Apenninic Springs. Proc. Int. Assoc. Hydrol. Sci. 2014, 364, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Buczyński, S.; Rzonca, B. Influence of geologic structure on the presence, discharge and physical and chemical properties of springs in the Muszynka catchment (Carpathian flysch). Episodes 2018, 48, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siwek, J.; Chełmicki, W. Geology and Land-Use-Related Pattern of Spring Water Quality: Case Study from the Catchments of the Małopolska Upland (S. Poland). Geol. Acta 2004, 2, 167–174. [Google Scholar]
- Andreo, B.; Liñán, C.; Carrasco, F.; Jiménez-de-Cisneros, C.; Caballero, E.; Mudry, J. Groundwater Temperature and Electrical Conductivity as Tools to Characterize Flow Patterns in Carbonate Aquifers: The Sierra de las Nieves Karst Aquifer, Southern Spain. Hydrogeol. J. 2008, 16, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadka, K.; Rijal, M.L.; Gyawali, R. Factors Controlling the Variation in Physicochemical Parameters of Springs in the Melamchi Area, Nepal. J. Nepal Geol. Soc. 2023, 66, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medler, C.J.; Eldridge, W.G. Spring Types and Contributing Aquifers from Water-Chemistry and Multivariate Statistical Analyses for Seeps and Springs in Theodore Roosevelt National Park, North Dakota, 2018; Scientific Investigations Report 2020–5121; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2021; 48p. [CrossRef]
- Brletić, F. Hydrological Objects on Southwestern Hills of the Medvednica Nature Park. Paper for Rector’s reward, University of Zagreb, Zagreb, Croatia, 2017. (In Croatian). [Google Scholar]
- Lovrić, F.; Kapelj, S.; Loborec, J. Assessment of drinking water supplies based on the hydrogeological features in the north-east part of Prigorje. Environ. Eng. 2017, 4, 25–39. (In Croatian) [Google Scholar]
- Šikić, K. Geological Guide to Medvednica; Institut za geološka istraživanja: Zagreb, Croatia, 1995. (In Croatian) [Google Scholar]
- Brkić, Ž.; Čakarun, I. Basic Hydrogeological Map of Croatia 1:100,000, Sheet Zagreb; Institut za geološka istraživanja, Zavod za hidrogeologiju i inženjersku geologiju: Zagreb, Croatia, 1998. (In Croatian) [Google Scholar]
- Brkić, Ž.; Čakarun, I. Basic Hydrogeological Map of Croatia 1:100,000, Sheet Zagreb—Interpreter; Institut za geološka istraživanja, Zavod za hidrogeologiju i inženjersku geologiju: Zagreb, Croatia, 1998. (In Croatian) [Google Scholar]
- Slišković, I.; Šarin, A. Basic Hydrogeological Map of Croatia 1:100,000, Sheet Ivanić Grad; Institut za geološka istraživanja, Zavod za hidrogeologiju i inženjersku geologiju: Zagreb, Croatia, 1999. (In Croatian) [Google Scholar]
- Slišković, I.; Šarin, A. Basic Hydrogeological Map of Croatia 1:100,000, Sheet Ivanić Grad—Interpreter; Institut za geološka istraživanja, Zavod za hidrogeologiju i inženjersku geologiju: Zagreb, Croatia, 1999. (In Croatian) [Google Scholar]
- Martinić, I.; Vinković, K.; Płaczkowska, E. Geomorphological and Hydrogeographical Research of Mali and Veliki Potok on Medvednica Mountain. In Book of Abstracts: Proceedings of the 7th Croatian Geographical Congress, Čakovec, Croatia, 9–10 October 2019; Croatian Geographical Society: Zagreb, Croatia, 2019; pp. 57–60. [Google Scholar]
- Dekić, S.; Hrenović, J. Bacteriological Analysis of Spring Water in the Vicinity of Popular Visitor Spots in the Nature Park Medvednica. Hrvatske Vode 2017, 25, 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Erdelez, A. Environmental Protection Report for the Assessment of the Need for Environmental Impact Evaluation: Construction of the Krumpirište Reservoir for Snowmaking on the Sljeme Ski Slopes; Fidon d.o.o.: Zagreb, Croatia, 2019; 171p. (In Croatian) [Google Scholar]
- Vujnović, T. Springs of the Žumberak–Samoborsko Gorje Nature Park. Nat. Croat. 2011, 20, 19–34. [Google Scholar]
- Roglić, J. Geomorphological Topics: Collected Works of Josip Roglić, Book II; Maras, M., Ed.; Geographic Society: Split, Croatia; Croatian Geographical Society: Zadar, Croatia; Faculty of Science, University of Zagreb: Zagreb, Croatia; University of Zadar: Zadar, Croatia; Meridijani: Samobor, Croatia, 2005; p. 558. (In Croatian) [Google Scholar]
- Farkaš-Topolnik, N. (Ed.) Management Plan of the Medvednica Nature Park; JU Park prirode Medvednica: Zagreb, Croatia, 2009; p. 78. (In Croatian) [Google Scholar]
- Žugaj, R. Big Waters of Small Catchments; Zorić, I., Ed.; Rudarsko-geološko-naftni fakultet, Sveučilište u Zagrebu: Zagreb, Croatia; Hrvatska komora arhitekata i inženjera u graditeljstvu: Zagreb, Croatia, 2010; p. 77. (In Croatian) [Google Scholar]
- Belak, M.; Slovenec, D.; Kolar Jurkovšek, T.; Garašić, V.; Pécskay, Z.; Tibljaš, D.; Mišur, I. Low-Grade Metamorphic Rocks of the Tethys Subduction–Collision Zone in the Medvednica Mt. (NW Croatia). Geol. Carpath. 2022, 73, 207–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šikić, K.; Basch, O.; Šimunić, A. Basic Geological Map of the SFRY 1:100,000, Sheet Zagreb L33–80; Institut za geološka istraživanja: Zagreb, Croatia; Savezni geološki zavod: Belgrade, Serbia, 1977. (In Croatian) [Google Scholar]
- Šikić, K.; Basch, O.; Šimunić, A. Basic Geological Map of the SFRY 1:100,000, Interpreter for Sheet Zagreb L33–80; Institut za geološka istraživanja: Zagreb, Croatia; Savezni geološki zavod: Belgrade, Serbia, 1979. (In Croatian) [Google Scholar]
- National Geographic World Map. National Geographic, Esri, Garmin, HERE, UNEP-WCMC, USGS, NASA, ESA, METI, NRCAN, GEBCO, NOAA, Increment P Corp. Available online: https://www.arcgis.com/home/item.html?id=b9b1b422198944fbbd5250b3241691b6 (accessed on 4 July 2025).
- Kottek, K.; Grieser, J.; Beck, C.; Rudolf, B.; Rubel, F. World Map of the Köppen–Geiger Climate Classification Updated. Meteorol. Z. 2006, 15, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinzer, O.E. Outline of Ground-Water Hydrology; US Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1923; 71p.
- Martinić, I.; Čanjevac, I. Distribution and Characteristics of Springs in Two Neighboring Areas of Different Morphogenic Relief Type—Example of SW Medvednica Mountain (Central Croatia). Water 2024, 16, 994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croatian Meteorological and Hydrological Service. Temperature and Precipitation Data; Data set sent to the authors for the research purposes; Croatian Meteorological and Hydrological Service: Zagreb, Croatia, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO). pH in Drinking-Water: Revised Background Document for Development of WHO Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007; Available online: https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/wash-documents/wash-chemicals/ph.pdf (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- Croatian Ministry of Health and Social Welfare. Regulation on the Health Safety of Drinking Water; NN 47/2008; Narodne novine: Zagreb, Croatia, 17 April 2008; Available online: https://narodne-novine.nn.hr/clanci/sluzbeni/2008_04_47_1593.html (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- Clark, I. Groundwater Geochemistry and Isotopes; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, A.M. A Graphic Procedure in the Geochemical Interpretation of Water-Analyses. Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1944, 25, 914–928. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, G.W.; Krygier, J.T. Effects of Clear-Cutting on Stream Temperature. Water Resour. Res. 1970, 6, 1133–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S.L.; Jones, J.A. Stream Temperature Responses to Forest Harvest and Debris Flows in Western Cascades, Oregon. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2000, 57, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzjak, N. Geotouristic potential of caves–example of Veternica Cave (Medvednica Nature Park, Croatia). In Proceedings of the 12th EuroSpeleo Forum, Ebensee, Austria, 23–26 August 2018; Mattes, J., Christian, E., Plan, L., Eds.; Verein für Höhlenkunde Ebensee: Neukirchen, Austria, 2018; pp. 38–41. [Google Scholar]
- Ford, D.C.; Williams, P. Karst Hydrogeology and Geomorphology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann, A.; Goldscheider, N.; Wagener, T.; Lange, J.; Weiler, M. Karst Water Resources in a Changing World: Review of Hydrological Modeling Approaches. Rev. Geophys. 2014, 52, 218–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hem, J.D. Study and Interpretation of the Chemical Characteristics of Natural Water; U.S. Geological Survey Water-Supply Paper 2254; U.S. Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1985.
- Kresic, N. Hydrogeology and Groundwater Modeling; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimunjak, Z.Z. Effects of Winter Road Maintenance on Bridges and Road Structures; Croatian Road Worker, Croatian Economic Interest Group of Road Maintenance Companies: Zagreb, Croatia, 2006; pp. 93–98. (In Croatian) [Google Scholar]
- Bulić, M. Chemical Characteristics of Soil in Medvednica Nature Park Regarding the Application of Road Salt in Winter Maintenance. Bachelor’s Thesis, Faculty of Agriculture, University of Zagreb, Zagreb, Croatia, 2016. (In Croatian). [Google Scholar]
- Jurišić, A.; Bogunović, I.; Vugrek Petljak, K.; Bulić, M.; Kisić, I. Influence of Salt Application in Winter Road Maintenance on Chemical Soil Properties in Medvednica Nature Park. In Vision and Challenges of Protected Area Management in the Republic of Croatia: Active Protection and Sustainable Management in Krka National Park; Marguš, D., Ed.; Public Institution “Krka” National Park: Šibenik, Croatia, 2015; p. 110. [Google Scholar]
- Foos, A. Spatial Distribution of Road Salt Contamination of Natural Springs and Seeps, Cuyahoga Falls, Ohio, USA. Environ. Geol. 2003, 44, 920–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.D.; Williams, N.E.; Cao, Y. Road Salt Contamination of Groundwater in a Major Metropolitan Area and Development of a Biological Index to Monitor Its Impact. Water Res. 1999, 33, 2569–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, A.; Rachlin, J.W. A Review of Road Salt Ecological Impacts. Northeast. Nat. 2018, 25, 123–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandová, V.; Bucková, M.; Hegrová, J.; Dostál, I.; Huzlík, J.; Effenberger, K.; Ličbinský, R. The Relationship among Precipitation, Application of Salt in Winter Road Maintenance and the Quality of Waterways and Soil around Motorway. Water 2020, 12, 2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugan, H.A.; Arnott, S.E. The Ecosystem Implications of Road Salt as a Pollutant of Freshwaters. WIREs Water 2023, 10, e1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagorščak, D. Gypsum from Two Localities in Medvednica (Croatia). Geol. Vjesn. 1988, 41, 75–80. (In Croatian) [Google Scholar]
- Jamičić, D.; Slovenec, D. Tectonic Setting of Recently Found Gypsum Deposits of Mt. Medvednica (Northwestern Croatia). Nat. Croat. 2002, 11, 27–51. [Google Scholar]
- Cantonati, M.; Gerecke, R.; Bertuzzi, E. Springs of the Alps—Sensitive Ecosystems to Environmental Change: From Biodiversity Assessments to Long-Term Studies. Hydrobiologia 2006, 562, 59–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rufino, F.; Busico, G.; Cuoco, E.; De Santis, M.; Tedesco, D. Hydrogeochemical Investigation of the Apennine Carbonate Springs by Factor Analysis. In Recent Advances in Environmental Science from the Euro-Mediterranean and Surrounding Regions, 2nd ed.; Ksibi, M., Ghorbal, A., Chakraborty, S., Chaminé, H.I., Barbieri, M., Guerriero, G., Hentati, O., Negm, A., Lehmann, A., Römbke, J., et al., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siepak, M.; Lewandowska, A.; Sojka, M. Variability in the Chemical Composition of Spring Waters in the Postomia River Catchment (Northwest Poland). Water 2023, 15, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczucińska, A. Spring water chemistry in a formerly glaciated area of western Poland the contribution of natural and anthropogenic factors. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Min | Max | Average | Median | Standard Deviation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature (°C) | 3.4 | 18.9 | 10.23 | 10 | 2.36 |
| EC (μS/cm) | 41 | 2062 | 394 | 390 | 230.19 |
| pH | 5.32 | 8.67 | 7.34 | 7.42 | 0.52 |
| Age (Map Code) | Rock Type | N ** | EC Min (μS/cm) | EC Max (μS/cm) | EC Avg ** (μS/cm) | EC Range (μS/cm) | EC σ *** (μS/cm) | pH Min | pH Max | pH Avg * | pH Range | pH σ *** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Miocene (1M12) | Conglomerates, gravels, sands | 39 | 71 | 817 | 485 | 746 | 175.9 | 6.01 | 8.07 | 7.23 | 2.06 | 0.49 |
| Miocene (2M22) | Limestones, marls, sandstones | 31 | 78 | 635 | 458 | 557 | 132.2 | 6.11 | 8.07 | 7.45 | 1.96 | 0.44 |
| Paleogene (Pc) | Conglomerates, sandstones, marls, and limestones | 7 | 107 | 452 | 294 | 345 | 127.9 | 6.65 | 7.22 | 6.96 | 0-57 | 0.24 |
| Cretaceous (3,4K32) | Breccias, conglomerates, limestones | 95 | 53 | 744 | 493 | 691 | 150 | 5.98 | 8.26 | 7.52 | 2.28 | 0.46 |
| Cretaceous (K32) | Conglomerates, limestones, marls | 11 | 281 | 557 | 405 | 276 | 83.3 | 6.58 | 7.99 | 7.3 | 1.41 | 0.44 |
| Triassic (T2) | Dolomites, subordinately limestones | 22 | 390 | 723 | 602 | 333 | 94.7 | 7.16 | 8.1 | 7.48 | 0.94 | 0.26 |
| Devonian, Carboniferous (D, C 2) | Orthometamorphic rocks–schists, gabbros, diabases | 120 | 93 | 1358 | 397 | 1265 | 210.4 | 6.27 | 8.67 | 7.49 | 2.4 | 0.4 |
| Devonian, Carboniferous (D, C 1) | Parametamorphic rocks–conglomerates, greywackes, siltstones, limestones, dolomites | 350 | 41 | 1322 | 331 | 1281 | 239.5 | 5.32 | 8.28 | 7.23 | 2.96 | 0.58 |
| Spring Name (Lithostratigraphic Unit) | F− (mg/L) | Cl− (mg/L) | NO3− (mg/L) | SO42− (mg/L) | HCO3− (mg/L) | Li+ (mg/L) | Na+ (mg/L) | K+ (mg/L) | Mg2+ (mg/L) | Ca2+ (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mali (D, C 2) | 0.072 | 48.917 | 5.579 | 19.994 | 117.91 | 0.007 | 9.857 | 0.734 | 5.225 | 42.495 |
| Mini (D, C 2) | 0.050 | 54.006 | 5.480 | 19.825 | 124.12 | - | 9.122 | 0.649 | 4.985 | 43.628 |
| Kraljičin zdenac (D, C 1) | 0.042 | 74.143 | 3.708 | 18.533 | 167.56 | - | 21.624 | 0.338 | 5.461 | 50.278 |
| Karlov izvor (D, C 2) | 0.048 | 22.904 | 4.548 | 13.601 | 167.56 | - | 5.392 | 0.359 | 3.389 | 43.176 |
| Jambrišakovo vrelo (T2) | 0.069 | 1.536 | 1.806 | 12.025 | 422.01 | - | 1.539 | 0.723 | 31.370 | 69.555 |
| Spring Name (Lithostratigraphic Unit) | F− (mg/L) | Cl− (mg/L) | NO3− (mg/L) | SO42− (mg/L) | HCO3− (mg/L) | Li+ (mg/L) | Na+ (mg/L) | K+ (mg/L) | Mg2+ (mg/L) | Ca2+ (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mali (D, C 2) | 0.035 | 38.270 | 4.762 | 16.122 | 116.362 | - | 7.389 | 0.569 | 4.943 | 32.809 |
| Mini (D, C 2) | 0.095 | 67.849 | 4.213 | 13.671 | 93.089 | - | 31.184 | 0.777 | 6.034 | 37.689 |
| Kraljičin zdenac (D, C 1) | 0.038 | 58.353 | 5.315 | 13.900 | 170.664 | - | 21.672 | 0.497 | 6.628 | 54.512 |
| Karlov izvor (D, C 2) | 0.102 | 13.052 | 4.429 | 12.540 | 147.391 | - | 5.682 | 0.716 | 4.030 | 44.667 |
| Jambrišakovo vrelo (T2) | 0.087 | 1.389 | 3.092 | 6.851 | 310.298 | - | 2.294 | 0.761 | 28.170 | 56.208 |
| Winter | Spring | Summer | Autmn | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average temperature (°C) | 9.25 | 9.49 | 13.16 | 11.50 |
| Min temperature (°C) | 5.30 | 3.40 | 8.90 | 7.00 |
| Q25 (°C) * | 8.48 | 8.80 | 10.00 | 10.00 |
| Q75 (°C) ** | 10.20 | 10.50 | 16.53 | 13.20 |
| Max temperature (°C) | 12.50 | 15.00 | 18.90 | 18.00 |
| Range (°C) | 7.20 | 11.60 | 10.00 | 11.00 |
| Q75–Q25 (°C) | 1.73 | 1.70 | 6.53 | 3.20 |
| Standard deviation (°C) | 1.46 | 1.52 | 3.27 | 2.41 |
| Coefficient of variation | 15.83 | 16.05 | 24.84 | 20.97 |
| Discharge Category | VIII (<0.01 L/s) | VII (0.01–0.1 L/s) | VI (0.1–1 L/s) | V (>1 L/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average temperature (°C) | 10.80 | 10.30 | 9.80 | 10.30 |
| Min temperature (°C) | 3.40 | 3.40 | 5.30 | 6.60 |
| Q25 (°C) * | 8.90 | 8.70 | 9.00 | 9.25 |
| Q75 (°C) ** | 12.80 | 11.10 | 10.50 | 10.65 |
| Max temperature (°C) | 18.90 | 17.50 | 18.30 | 16.80 |
| Range (°C) | 15.50 | 14.10 | 13.00 | 10.20 |
| Q75–Q25 (°C) | 3.90 | 2.40 | 1.50 | 1.40 |
| Standard deviation (°C) | 3.09 | 2.52 | 1.61 | 1.86 |
| Coefficient of variation | 28.57 | 24.51 | 16.44 | 18.09 |
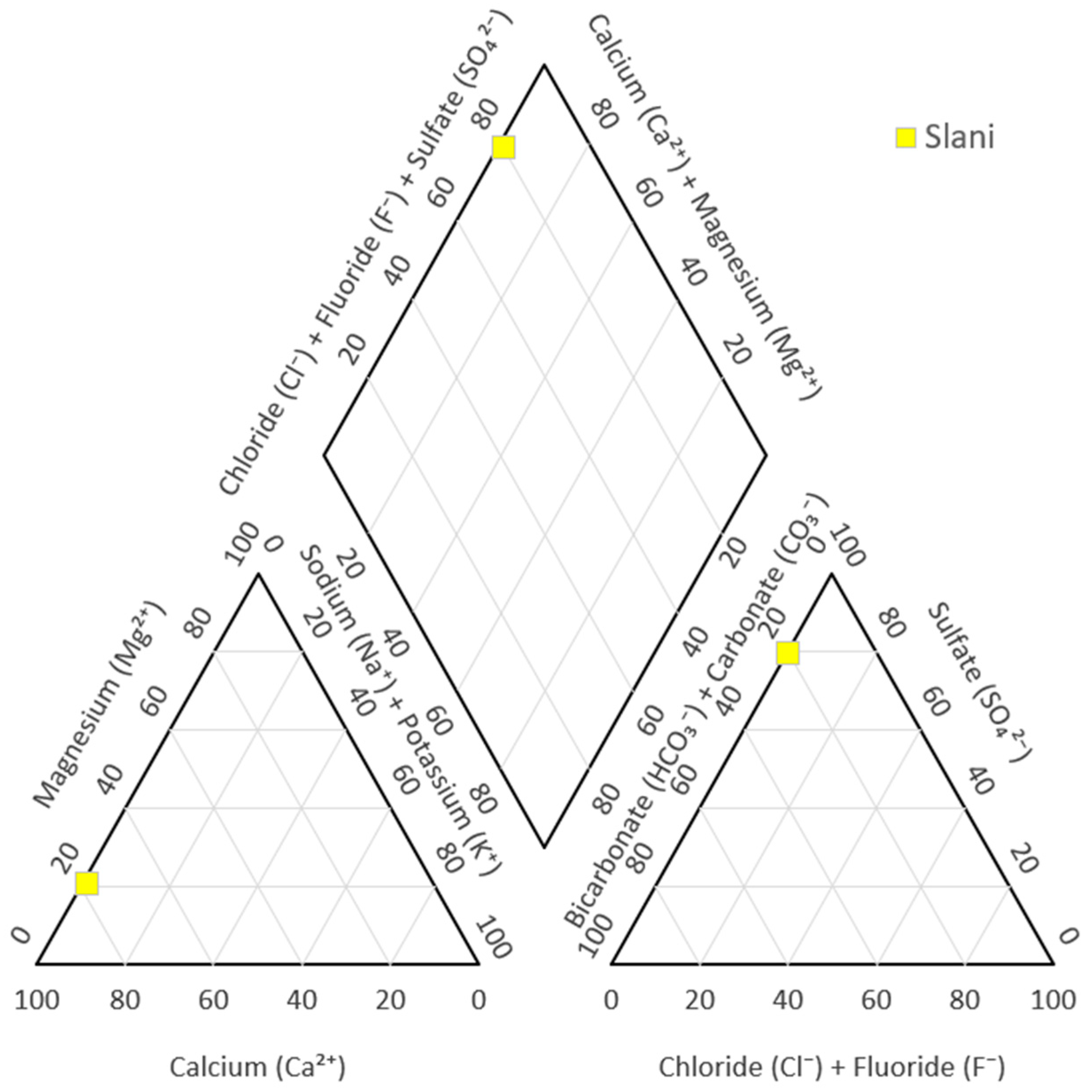
| Spring Name | F− (mg/L) | Cl− (mg/L) | NO3− (mg/L) | SO42− (mg/L) | HCO3− (mg/L) | Li+ (mg/L) | Na+ (mg/L) | K+ (mg/L) | Mg2+ (mg/L) | Ca2+ (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slani | 0.256 | 1.569 | 0.306 | 1197.863 | 382.045 | 0.011 | 4.881 | 2.627 | 76.074 | 467.394 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martinić, I.; Čanjevac, I. Natural and Anthropogenic Influence on the Physicochemical Characteristics of Spring Water: The Case Study of Medvednica Mountain (Central Croatia). Limnol. Rev. 2025, 25, 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/limnolrev25030036
Martinić I, Čanjevac I. Natural and Anthropogenic Influence on the Physicochemical Characteristics of Spring Water: The Case Study of Medvednica Mountain (Central Croatia). Limnological Review. 2025; 25(3):36. https://doi.org/10.3390/limnolrev25030036
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartinić, Ivan, and Ivan Čanjevac. 2025. "Natural and Anthropogenic Influence on the Physicochemical Characteristics of Spring Water: The Case Study of Medvednica Mountain (Central Croatia)" Limnological Review 25, no. 3: 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/limnolrev25030036
APA StyleMartinić, I., & Čanjevac, I. (2025). Natural and Anthropogenic Influence on the Physicochemical Characteristics of Spring Water: The Case Study of Medvednica Mountain (Central Croatia). Limnological Review, 25(3), 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/limnolrev25030036








