Two New Strains of Microcystis Cyanobacteria from Lake Baikal, Russia: Ecology and Toxigenic Potential
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
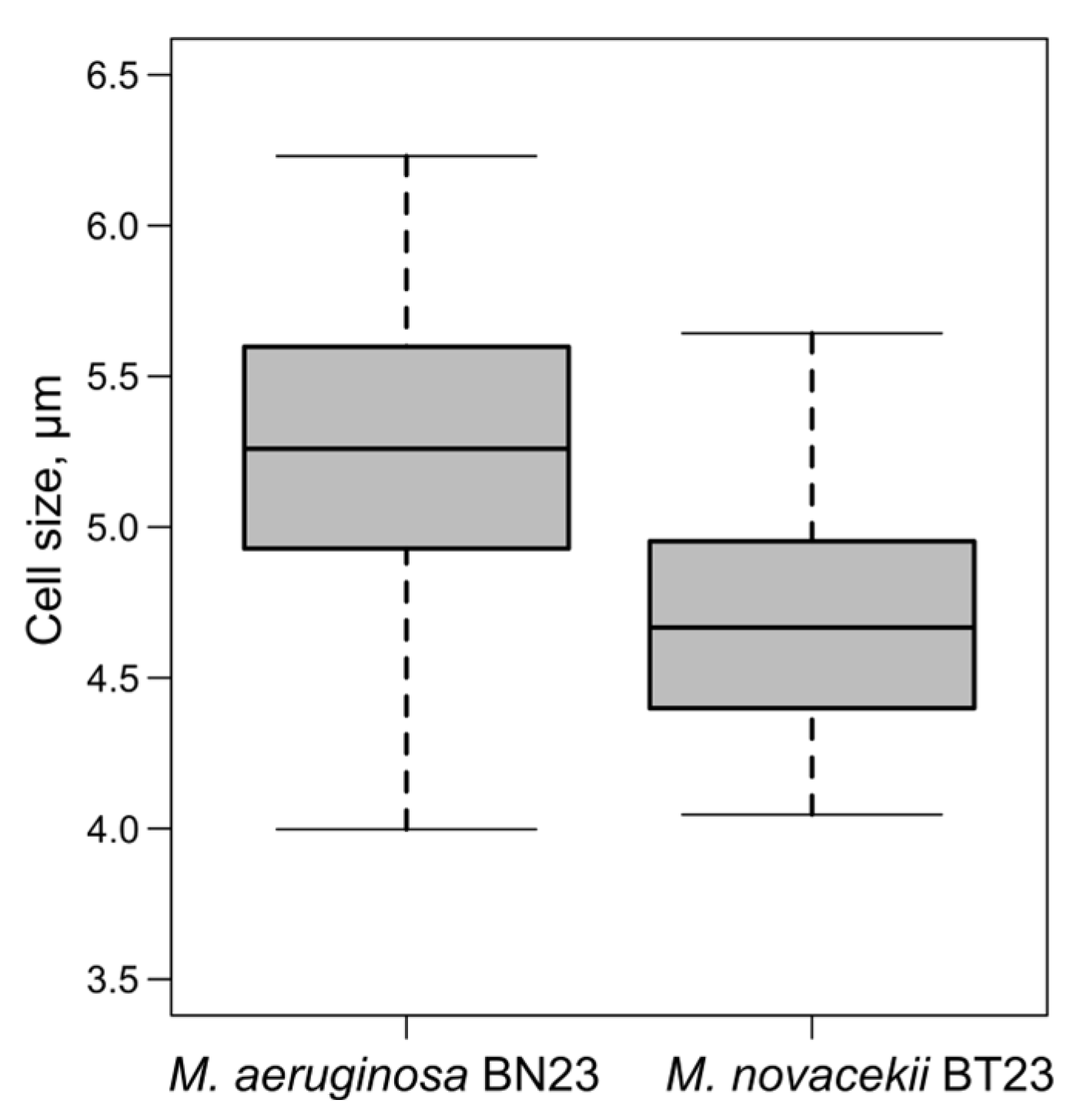
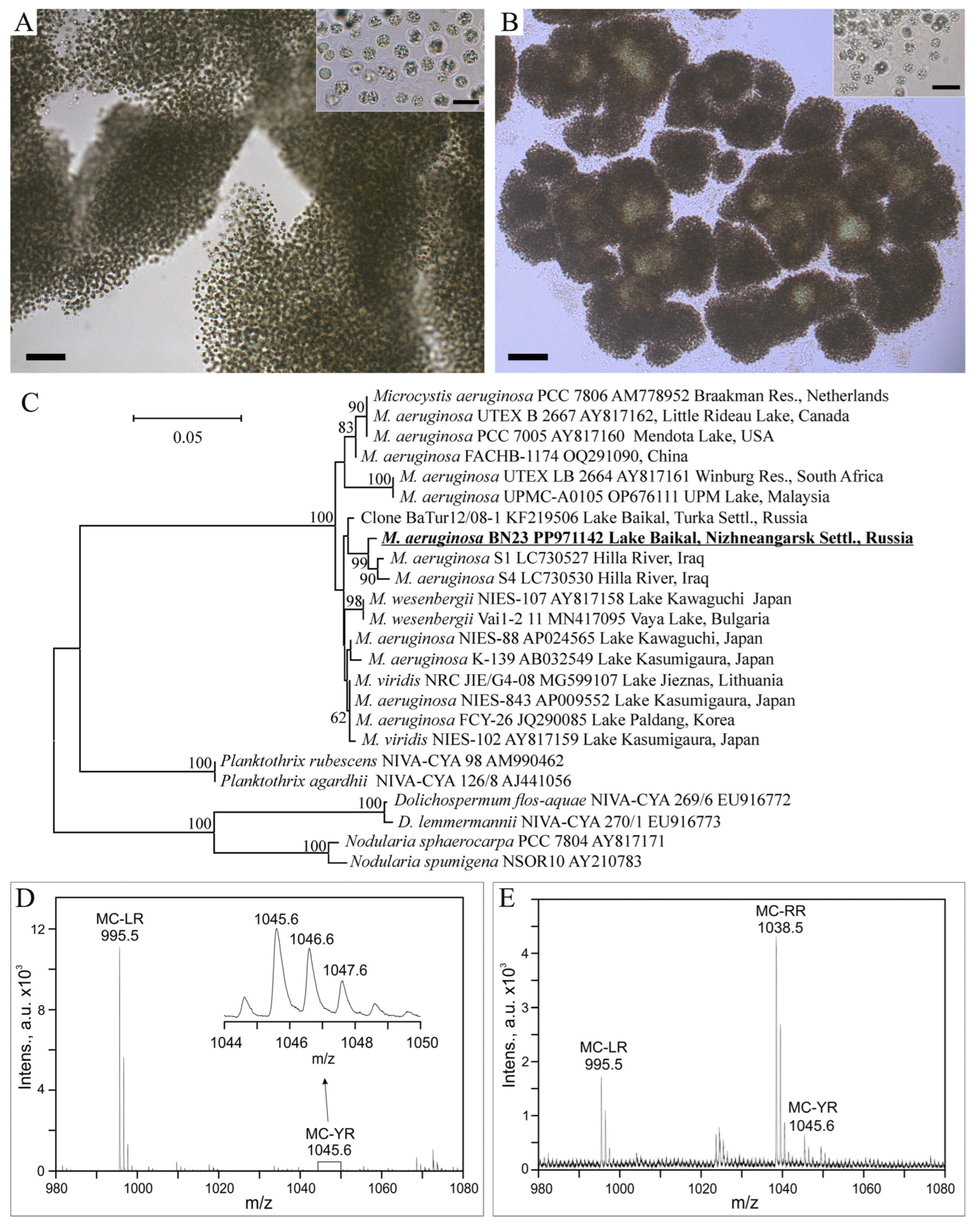
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EC | Electrical conductivity |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| HPLC-UV | High-performance liquid chromatography-ultraviolet |
| MALDI-TOF/TOF MS | Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry |
| MC | Microcystin |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
Appendix A

References
- Preece, E.P.; Hardy, F.J.; Moore, B.C.; Bryan, M. A review of microcystin detections in Estuarine and Marine waters: Environmental implications and human health risk. Harmful Algae 2017, 61, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svirčev, Z.; Drobac, D.; Tokodi, N.; Mijović, B.; Codd, G.A.; Meriluoto, J. Toxicology of microcystins with reference to cases of human intoxications and epidemiological investigations of exposures to cyanobacteria and cyanotoxins. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 621–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belykh, O.I.; Sorokovikova, E.G.; Fedorova, G.A.; Kaluzhnaya, O.V.; Korneva, E.S.; Sakirko, M.V.; Sherbakova, T.A. Presence and genetic diversity of microcystin-producing cyanobacteria (Anabaena and Microcystis) in Lake Kotokel (Russia, Lake Baikal Region). Hydrobiologia 2011, 671, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozhova, O.M.; Izmest’eva, L.R. (Eds.) Lake Baikal. Evolution and Biodiversity; Backhuys Publishers: Leiden, The Netherlands, 1998; p. 447. [Google Scholar]
- Fedotov, A.P.; Khanaev, I.V. Annual temperature regime of the shallow zone of Lake Baikal inferred from high-resolution data from temperature loggers. Limnol. Freshw. Biol. 2023, 4, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timoshkin, O.A. (Ed.) Guide and Key to Pelagic Animals of Baikal; Nauka: Novosibirsk, Russia, 1995; p. 694. [Google Scholar]
- Bondarenko, N.A. List of Planktonic Algae of Lake Baikal. In Guide and Key to Pelagic Animals of Baikal; Timoshkin, O.A., Ed.; Nauka: Novosibirsk, Russia, 1995; pp. 621–630. [Google Scholar]
- Bondarenko, N.A.; Tomberg, I.V.; Shirokaya, A.A.; Belykh, O.I.; Tikhonova, I.V.; Fedorova, G.A.; Netsvetaeva, O.G.; Eletskaya, E.V.; Timoshkin, O.A. Dolichospermum lemmermannii (Nostocales) bloom in world’s deepest Lake Baikal (East Siberia): Abundance, toxicity and factors influencing growth. Limnol. Freshw. Biol. 2021, 1, 1101–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhonova, I.; Kuzmin, A.; Fedorova, G.; Sorokovikova, E.; Krasnopeev, A.; Tsvetkova, A.; Shtykova, Y.; Potapov, S.; Ivacheva, M.; Zabortzeva, T.; et al. Toxic cyanobacteria blooms of Mukhor Bay (Lake Baikal, Russia) during a period of intensive anthropogenic pressure. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2023, 25, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapomělová, E.; Řeháková, K.; Jezberová, J.; Komárková, J. Polyphasic characterization of eight planktonic Anabaena strains (Cyanobacteria) with reference to the variability of 61 Anabaena populations observed in the field. Hydrobiologia 2010, 639, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagi, O.; Ohkubo, N.; Tomioka, N.; Okada, M. Effect of irradiance and temperature on photosynthetic activity of the cyanobacterium Microcystis spp. Environ. Technol. 1994, 15, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.F.; Oishi, S. Effects of environmental factors on toxicity of a cyanobacterium (Microcystis aeruginosa) under culture conditions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1985, 49, 1342–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Yu, Y.; Shi, X. Temperature triggers the annual cycle of Microcystis, comparable results from the laboratory and a large shallow lake. Chemosphere 2020, 260, 127543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, G.F.; Martin, R.M.; Smith, L.E.; Wei, B.; Hellweger, F.L.; Bullerjahn, G.S.; McKay, R.M.L.; Boyer, G.L.; Wilhelm, S.W. Microcystin aids in cold temperature acclimation: Differences between a toxic Microcystis wildtype and non-toxic mutant. Harmful Algae 2023, 129, 102531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belykh, O.I.; Gladkikh, A.S.; Sorokovikova, E.G.; Tikhonova, I.V.; Butina, T.V. Identification of toxic Cyanobacteria in Lake Baikal. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2015, 463, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 4th ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; p. 631. [Google Scholar]
- Vasser, S.P.; Kondrat’eva, N.V.; Masyuk, N.P. (Eds.) Algae: A Handbook; Naukova Dumka: Kiev, USSR, 1989; p. 608. [Google Scholar]
- Komárek, J.; Anagnostidis, K. Süβwasserflora von Mitteleuropa, Band 19/1. Cyanoprokaryota. 1. Teil/Part 1: Chroococcales; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 1999; p. 554. [Google Scholar]
- Jungblut, A.D.; Neilan, B.A. Molecular identification and evolution of the cyclic peptide hepatotoxins, microcystin and nodularin, synthetase genes in three orders of cyanobacteria. Arch. Microbiol. 2006, 185, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyatt, D.; Chen, G.-L.; LoCascio, P.F.; Land, M.L.; Larimer, F.W.; Hauser, L.J. Prodigal: Prokaryotic gene recognition and translation initiation site identification. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchfink, B.; Xie, C.; Huson, D.H. Fast and sensitive protein alignment using DIAMOND. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorokovikova, E.G.; Tikhonova, I.V.; Naidanova, Y.A.; Belykh, O.I. Identification of microcystin producing cyanobacteria in the plankton of Lake Baikal and Irkutsk Reservoir. Limnol. Freshw. Biol. 2024, 4, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozovik, P.A.; Efremenko, N.A. (Eds.) Analytical, Kinetic and Calculation Methods in Hydrochemical Practice; Nestor-Istoriya Publ.: St. Petersburg, Russia, 2017; p. 272. [Google Scholar]
- Boeva, L.V. (Ed.) Guide to Chemical Analysis of Land Surface Waters; NOK Publ.: Rostov-on-Don, Russia, 2009; p. 1150. [Google Scholar]
- Likens, G.E. Primary Production of Inland Aquatic Ecosystems. In Primary Production of the Biosphere; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1975; pp. 185–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabyshev, V.A.; Sidelev, S.I.; Chernova, E.N.; Vilnet, A.A.; Davydov, D.A.; Barinova, S.; Gabysheva, O.I.; Zhakovskaya, Z.A.; Voronov, I.V. Year-Round Presence of Microcystins and Toxin-Producing Microcystis in the Water Column and Ice Cover of a Eutrophic Lake Located in the Continuous Permafrost Zone (Yakutia, Russia). Toxins 2023, 15, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, B.M.; Jones, G.J.; Orr, P.T. Cellular microcystin content in N-limited Microcystis aeruginosa can be predicted from growth rate. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.M.; Lee, S.J.; Jang, M.H.; Yoon, B.D. Microcystin production by Microcystis aeruginosa in a phosphorus-limited chemostat. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouaïcha, N.; Miles, C.O.; Beach, D.G.; Labidi, Z.; Djabri, A.; Benayache, N.Y.; Nguyen-Quang, T. Structural diversity, characterization and toxicology of microcystins. Toxins 2019, 11, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibelings, B.W.; Kurmayer, R.; Azevedo, S.M.F.O.; Wood, S.A.; Chorus, I.; Welker, M. Understanding the occurrence of cyanobacteria and cyanotoxins. In Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water: A guide to Their Public Health Consequences, Monitoring and Management; Chorus, I., Welker, M., Eds.; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2021; pp. 261–262. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Tikhonova, I.V.; Potapov, S.A.; Krasnopeev, A.Y.; Zhuchenko, N.A.; Niao, X.; Wang, L.; Sorokovikova, E.G.; Wang, W.; Belykh, O.I. World’s largest oligotrophic Lake Baikal: Concerns about cyanobacterial blooms and potential microcystin producers along the littoral zone. Harmful Algae 2025, 144, 102841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barinova, S.; Gabyshev, V.A.; Gabysheva, O.I.; Naidanova, Y.A.; Sorokovikova, E.G. Phytoplankton Diversity, Abundance and Toxin Synthesis Potential in the Lakes of Natural and Urban Landscapes in Permafrost Conditions. Land 2025, 14, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaitomaa, J.; Rantala, A.; Halinen, K.; Rouhiainen, L.; Tallberg, P.; Mokelke, L.; Sivonen, K. Quantitative real-time PCR for determination of microcystin synthetase E copy numbers for Microcystis and Anabaena in lakes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 7289–7297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popovskaya, G.I. Phytoplankton. In Problems of Baikal. Proceedings of the Limnological Institute; Galaziy, G.I., Votintsev, G.Y., Eds.; Nauka: Novosibirsk, USSR, 1978; Volume 16, pp. 158–168. [Google Scholar]
- Belykh, O.I.; Sorokovikova, E.G. Autotrophic picoplankton in Lake Baikal: Abundance, dynamics, and distribution. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2003, 6, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodzher, T.V.; Domysheva, V.M.; Sorokovikova, L.M.; Sakirko, M.V.; Tomberg, I.V. Current chemical composition of Lake Baikal water. Inland. Waters 2017, 7, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domysheva, V.; Vorobyeva, S.; Golobokova, L.; Netsvetaeva, O.; Onischuk, N.; Sakirko, M.; Khuriganova, O.; Fedotov, A. Assessment of the Current Trophic Status of the Southern Baikal Littoral Zone. Water 2023, 15, 1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, K.I. An introduction to flora of algae of Lake Baikal. Byul. MOIP, Otd. Biol., Nov. Ser. 1930, 39, 179–396. [Google Scholar]
- Shimaraev, M.N.; Domysheva, V.M. Trends in Hydrological and Hydrochemical Processes in Lake Baikal under Conditions of Modern Climate Change. In Climatic Change and Global Warming of Inland Waters; Goldman, C., Kumagai, M., Robarts, R.D., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 43–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinl, K.L.; Brookes, J.D.; Carey, C.C.; Harris, T.D.; Ibelings, B.W.; Morales-Williams, A.M.; De Senerpont Domis, L.N.; Atkins, K.S.; Isles, P.D.F.; Mesman, J.P.; et al. Cyanobacterial blooms in oligotrophic lakes: Shifting the high-nutrient paradigm. Freshw. Biol. 2021, 66, 1846–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaffin, J.D.; Mishra, S.; Kane, D.D.; Bade, D.L.; Stanislawczyk, K.; Slodysko, K.N.; Jones, K.W.; Parker, E.M.; Fox, E.L. Cyanobacterial blooms in the central basin of Lake Erie: Potentials for cyanotoxins and environmental drivers. J. Great Lakes Res. 2019, 45, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
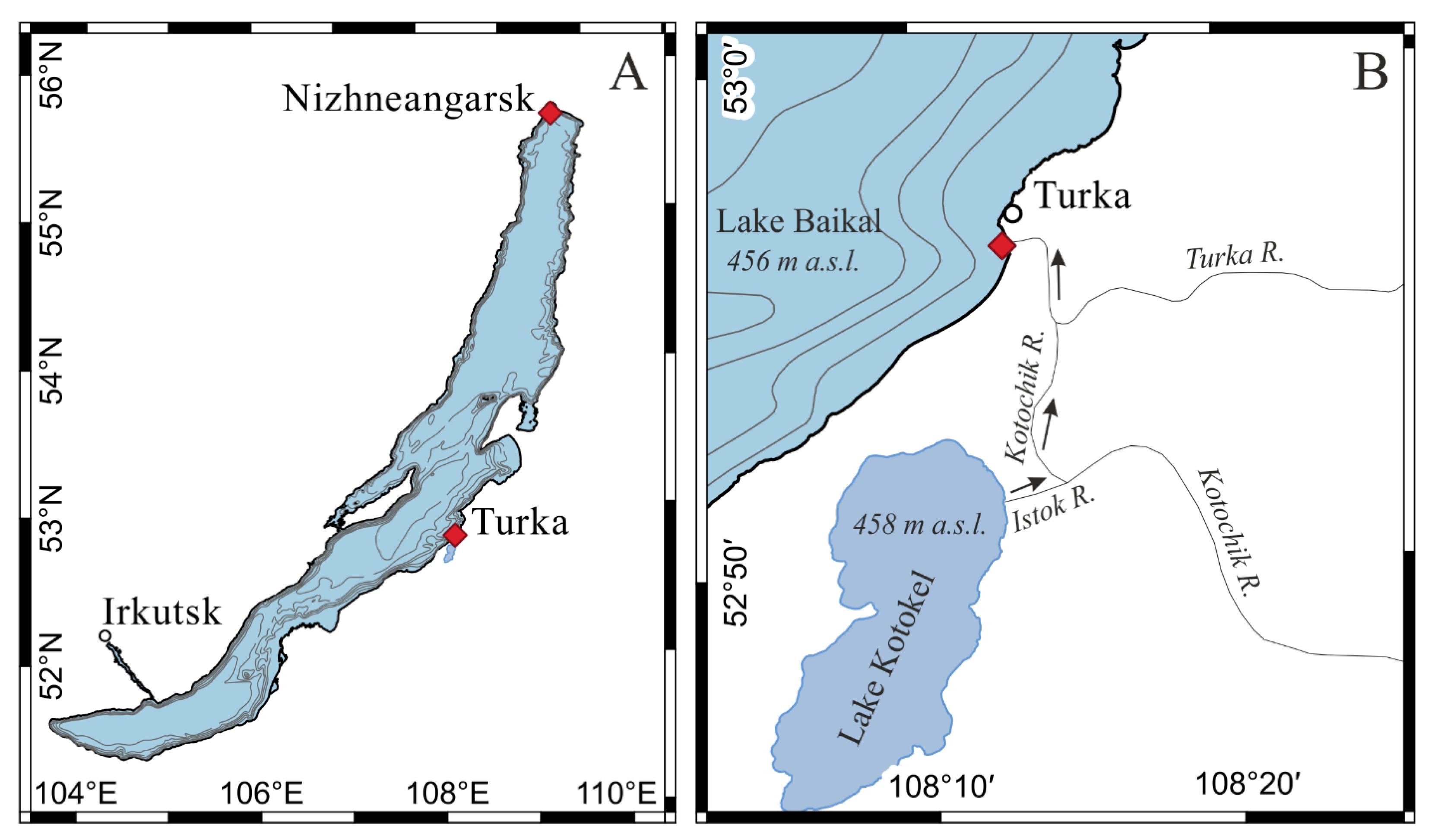
| Sampling Stations | Nizhneangarsk Settlement (55°45.23′ N, 109°34.87′ E) | Turka Settlement (52°56.3′ N, 108°12.7′ E) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | 0 m | 5 m | 0 m | 5 m | 10 m | 17 m | |
| Water temperature, °C | 19.0 | 17.8 | 18.7 | 14.9 | 10.3 | 9.0 | |
| Secchi depth, m | 4.0 | - | 4.7 | - | - | - | |
| Dissolved oxygen, mg/L | 9.4 | 9.7 | 9.9 | 10.9 | 11.2 | 11.2 | |
| EC (25 °C), µS/cm | 91.7 | 96.9 | 130.6 | 128.6 | 129.7 | 127.4 | |
| pH | 8.01 | 8.01 | 8.02 | 7.94 | 7.87 | 7.67 | |
| Total phosphorus, mg/L | 0.012 | 0.009 | 0.008 | 0.010 | 0.011 | 0.012 | |
| Total nitrogen, mg/L | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.15 | 0.16 | 0.12 | 0.17 | |
| Dissolved inorganic nitrogen, mg/L | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.11 | |
| PO43−, mg/L | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.003 | 0.002 | 0.005 | 0.028 | |
| NH4+, mg/L | 0.002 | 0.001 | <lod * | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.038 | |
| NO2−, mg/L | 0.001 | 0.001 | <lod | <lod | 0.002 | 0.003 | |
| NO3−, mg/L | 0.12 | 0.09 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.17 | 0.35 | |
| Chlorophyll a, µg/L | 3.1 | 2.9 | 1.5 | 2.1 | 2.8 | 4.5 | |
| Phytoplankton abundance, cells/L | 171,000 | - | 321,000 | - | - | - | |
| Cyanobacteria abundance, cells/L | 71,000 | - | 211,000 | - | - | - | |
| Phytoplankton biomass, mg/m3 | 90 | - | 74 | - | - | - | |
| Cyanobacteria biomass, mg/m3 | 9 | - | 5.6 | - | - | - | |
| Microcystin variants | <lod | - | MC-LR, -YR, -RR | - | - | - | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sorokovikova, E.; Tikhonova, I.; Fedorova, G.; Chebunina, N.; Kuzmin, A.; Suslova, M.; Naidanova, Y.; Potapov, S.; Krasnopeev, A.; Gladkikh, A.; et al. Two New Strains of Microcystis Cyanobacteria from Lake Baikal, Russia: Ecology and Toxigenic Potential. Limnol. Rev. 2025, 25, 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/limnolrev25030031
Sorokovikova E, Tikhonova I, Fedorova G, Chebunina N, Kuzmin A, Suslova M, Naidanova Y, Potapov S, Krasnopeev A, Gladkikh A, et al. Two New Strains of Microcystis Cyanobacteria from Lake Baikal, Russia: Ecology and Toxigenic Potential. Limnological Review. 2025; 25(3):31. https://doi.org/10.3390/limnolrev25030031
Chicago/Turabian StyleSorokovikova, Ekaterina, Irina Tikhonova, Galina Fedorova, Nadezhda Chebunina, Anton Kuzmin, Maria Suslova, Yanzhima Naidanova, Sergey Potapov, Andrey Krasnopeev, Anna Gladkikh, and et al. 2025. "Two New Strains of Microcystis Cyanobacteria from Lake Baikal, Russia: Ecology and Toxigenic Potential" Limnological Review 25, no. 3: 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/limnolrev25030031
APA StyleSorokovikova, E., Tikhonova, I., Fedorova, G., Chebunina, N., Kuzmin, A., Suslova, M., Naidanova, Y., Potapov, S., Krasnopeev, A., Gladkikh, A., & Belykh, O. (2025). Two New Strains of Microcystis Cyanobacteria from Lake Baikal, Russia: Ecology and Toxigenic Potential. Limnological Review, 25(3), 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/limnolrev25030031







