Secure Communication of Electric Drive System Using Chaotic Systems Base on Disturbance Observer and Fuzzy Brain Emotional Learning Neural Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Development of a novel FBELC structure that uniquely combines fuzzy logic and emotional intelligence within a single control architecture;
- (2)
- Integration of a DO to enhance robustness against external perturbations and uncertainties;
- (3)
2. Mathematical Concept
2.1. Mathematical Modeling of Chaotic System
2.2. Problem Formulation
2.3. Fuzzy Brain Emotional Learning Controller
2.4. Robust Controller
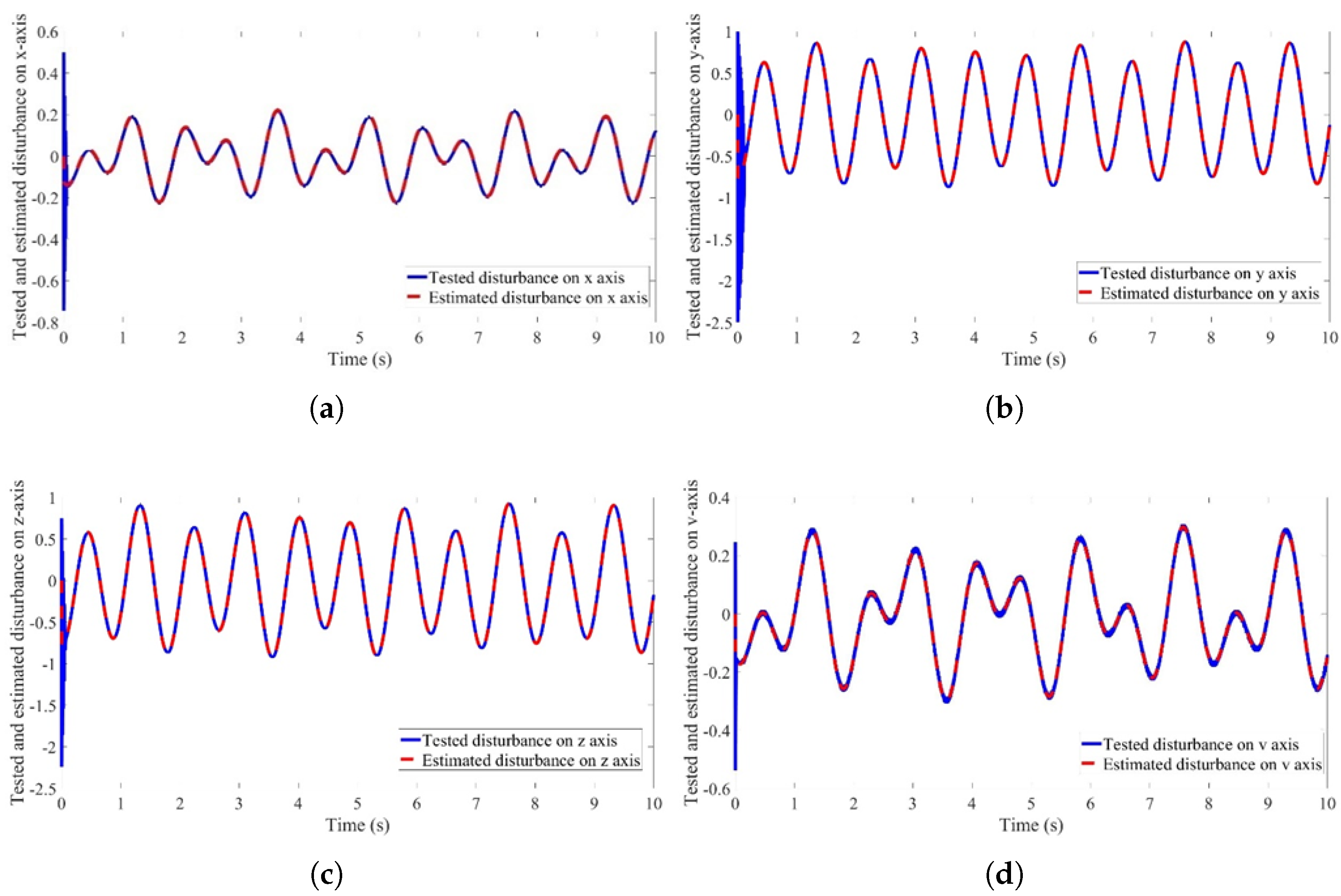
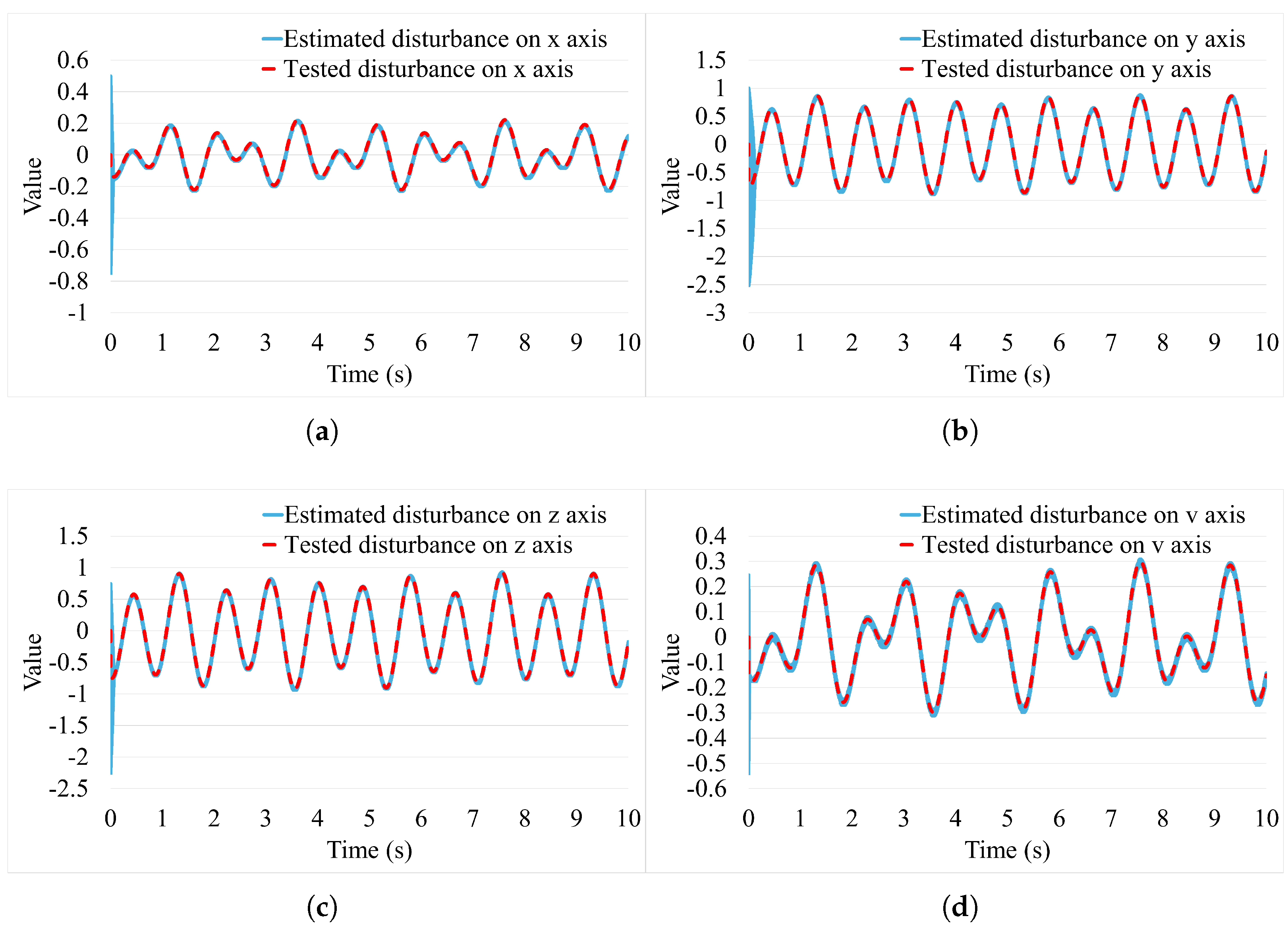
2.5. Disturbance Observer
2.6. Stability Analysis
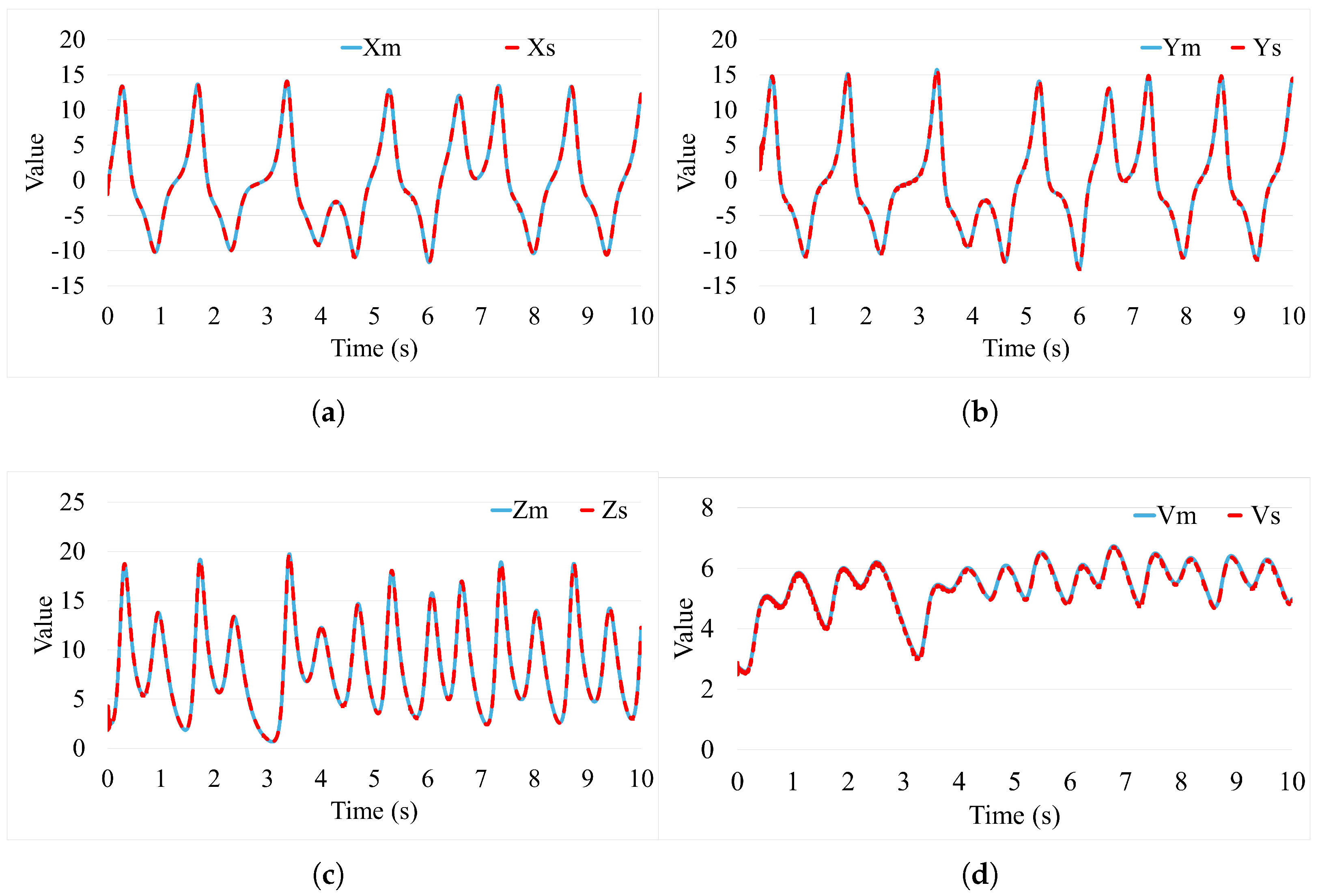
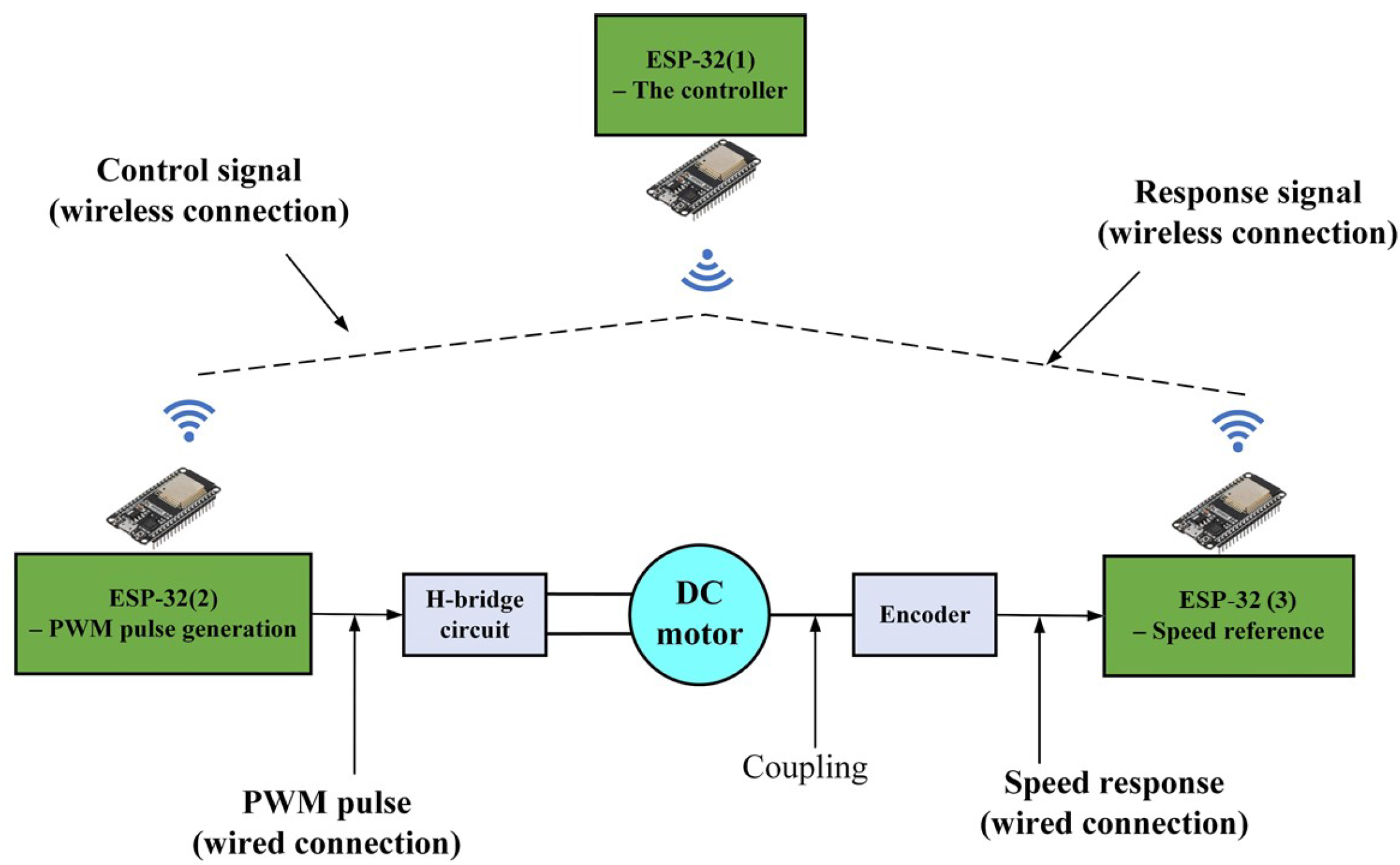
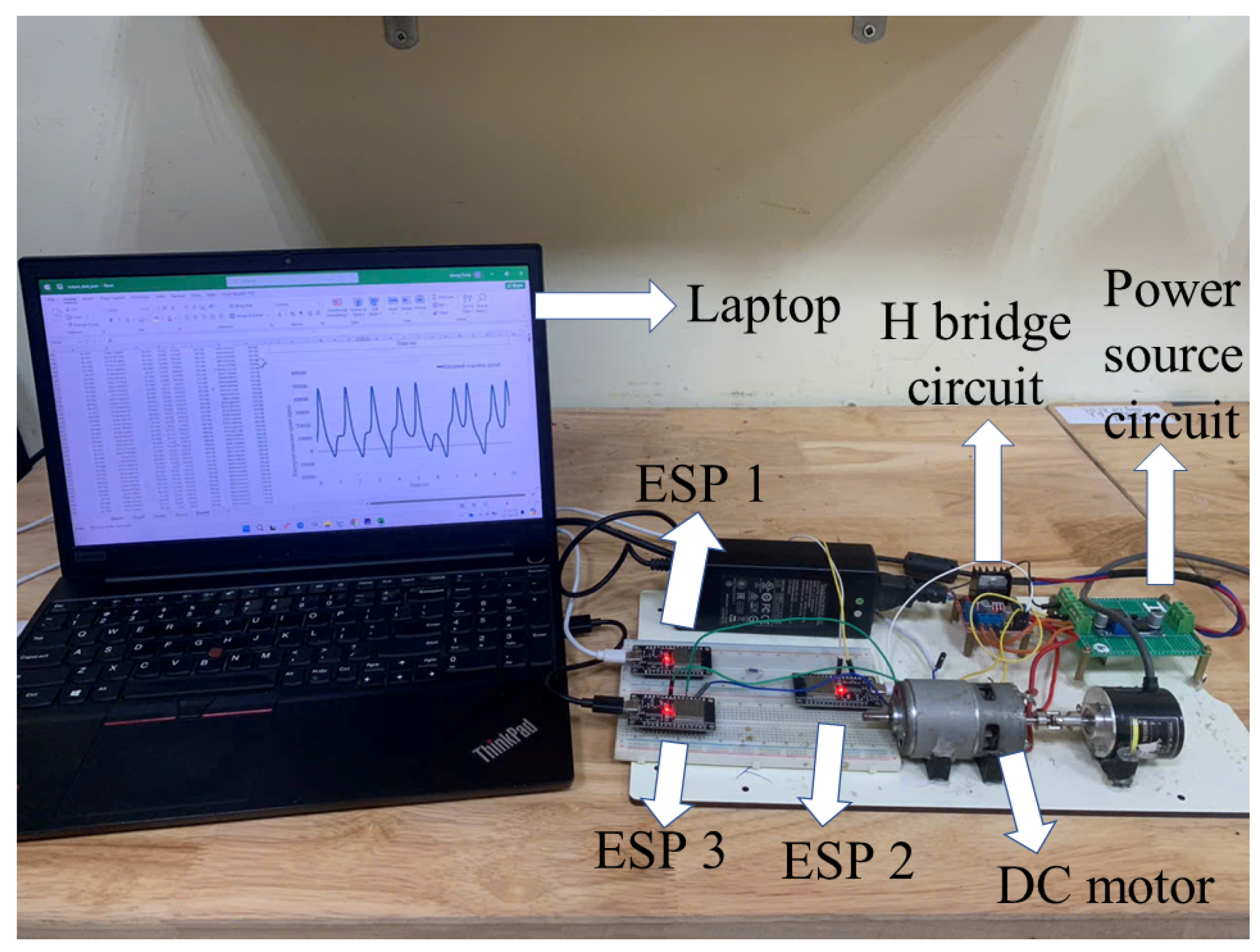
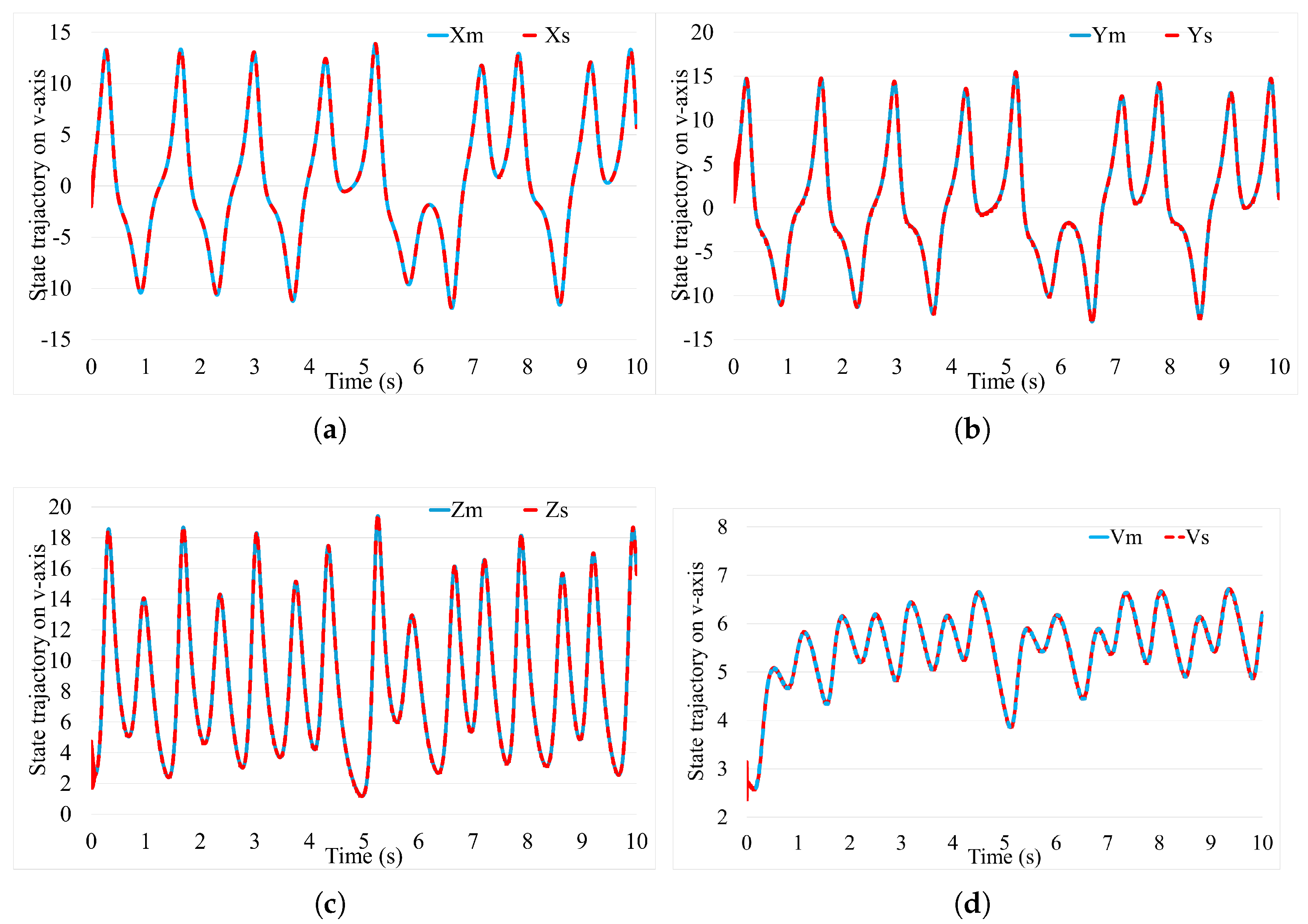
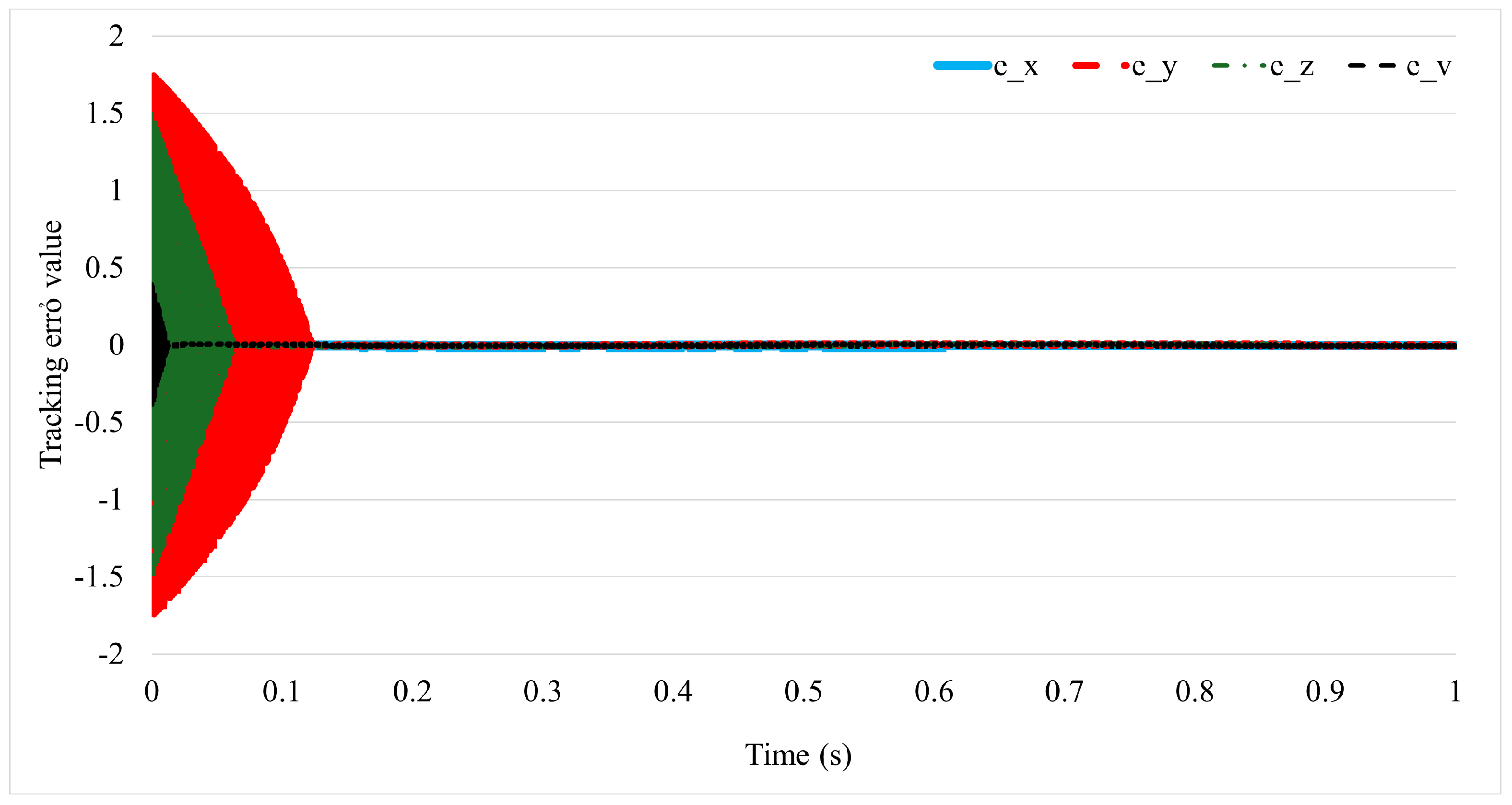
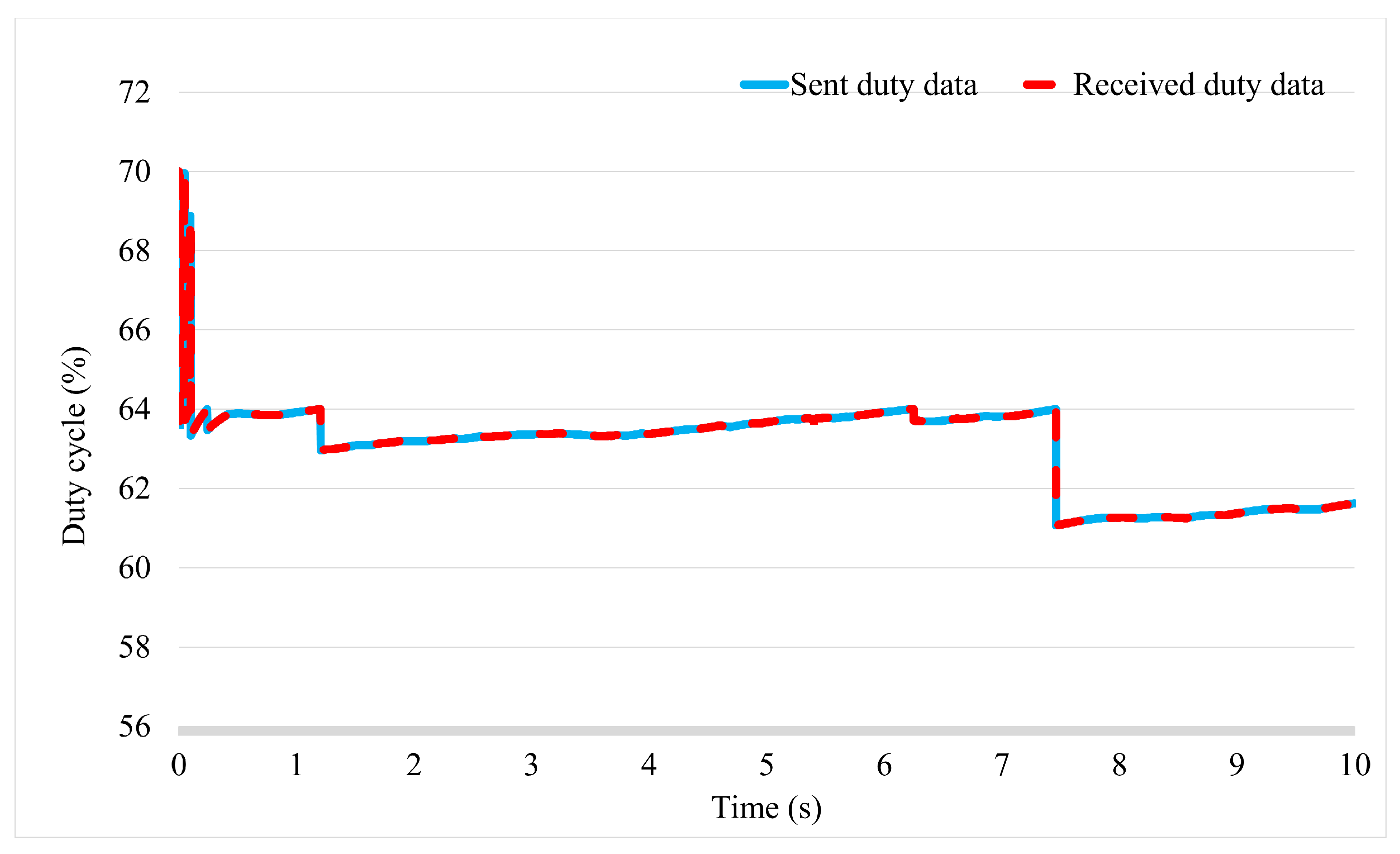
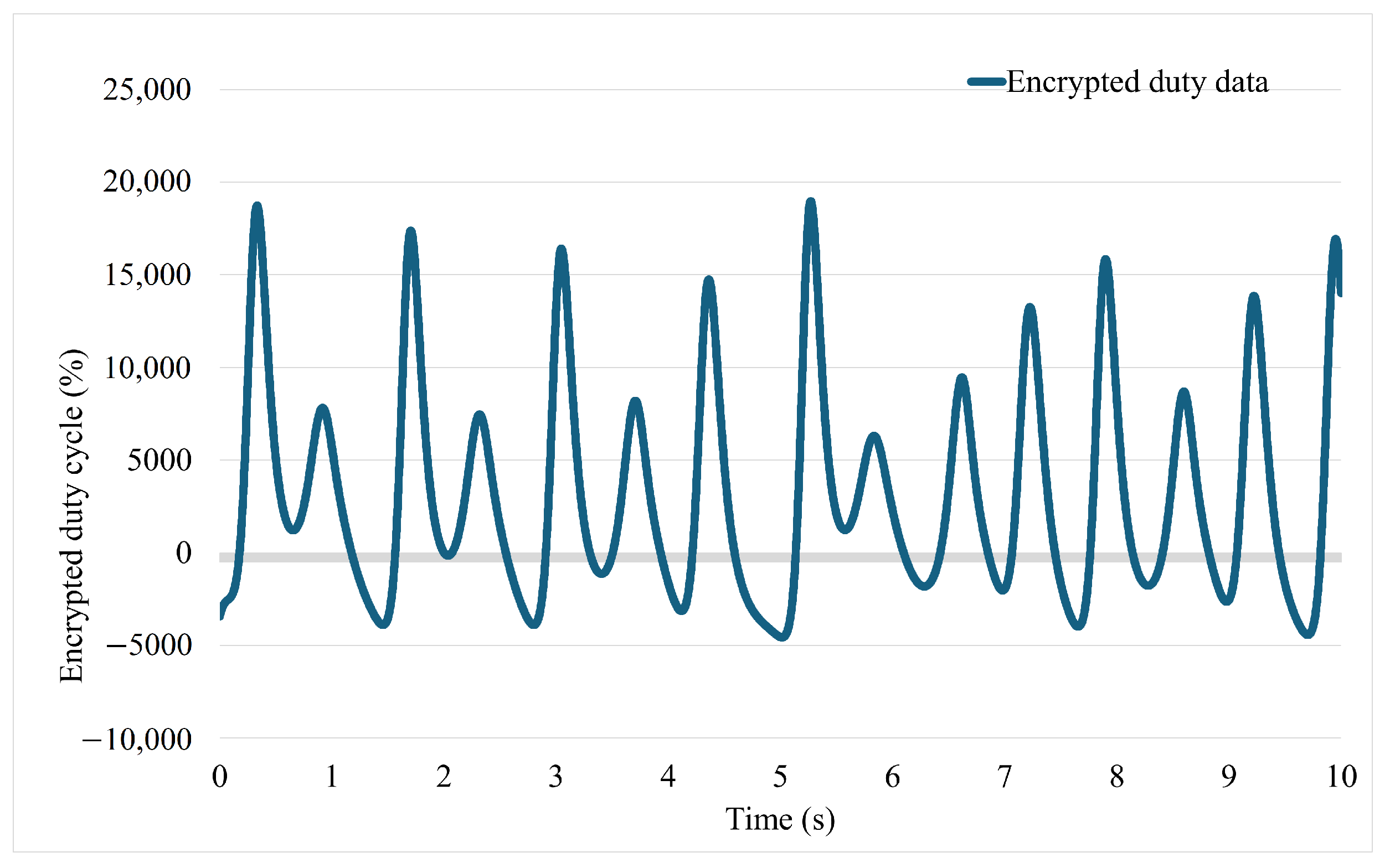
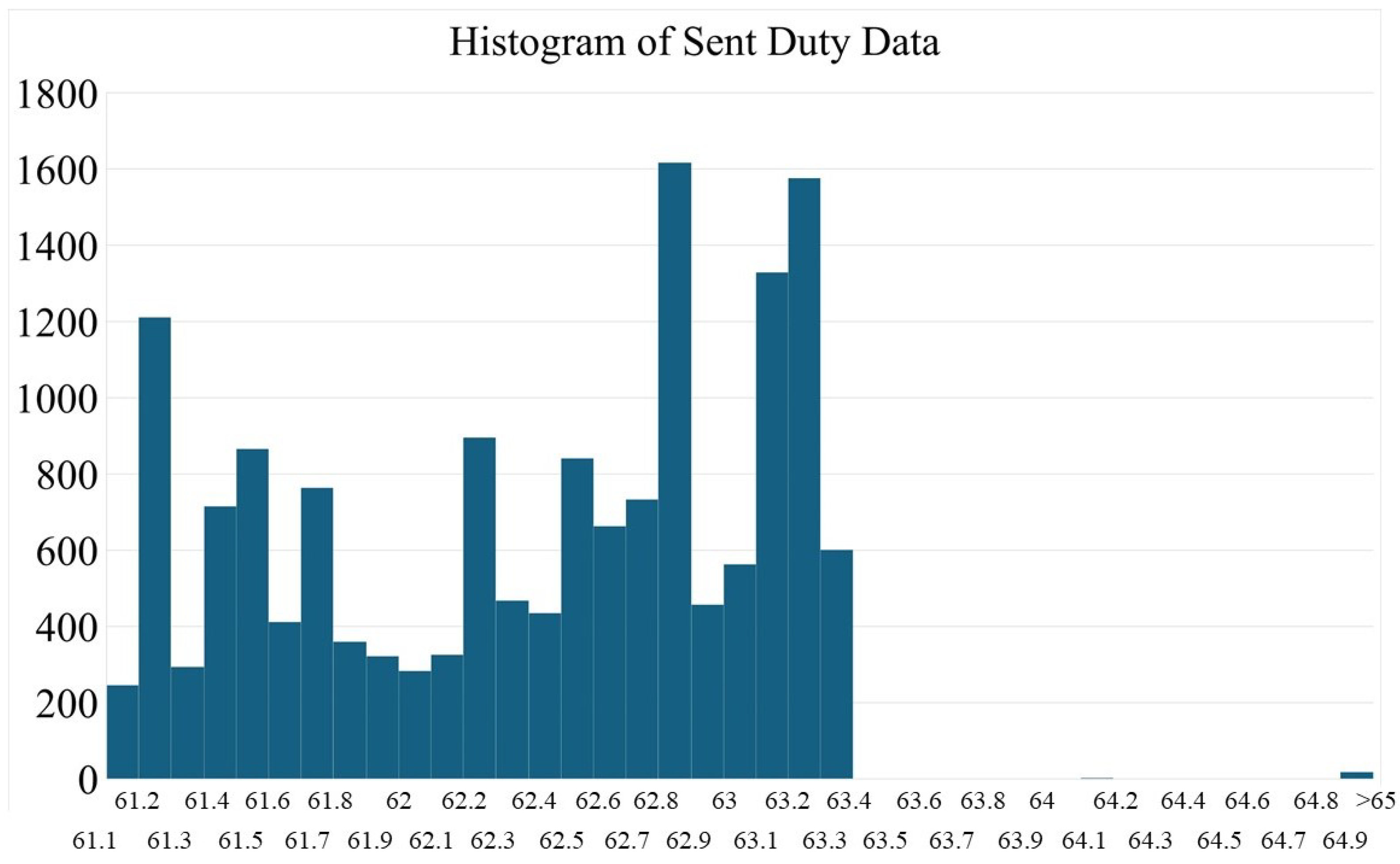
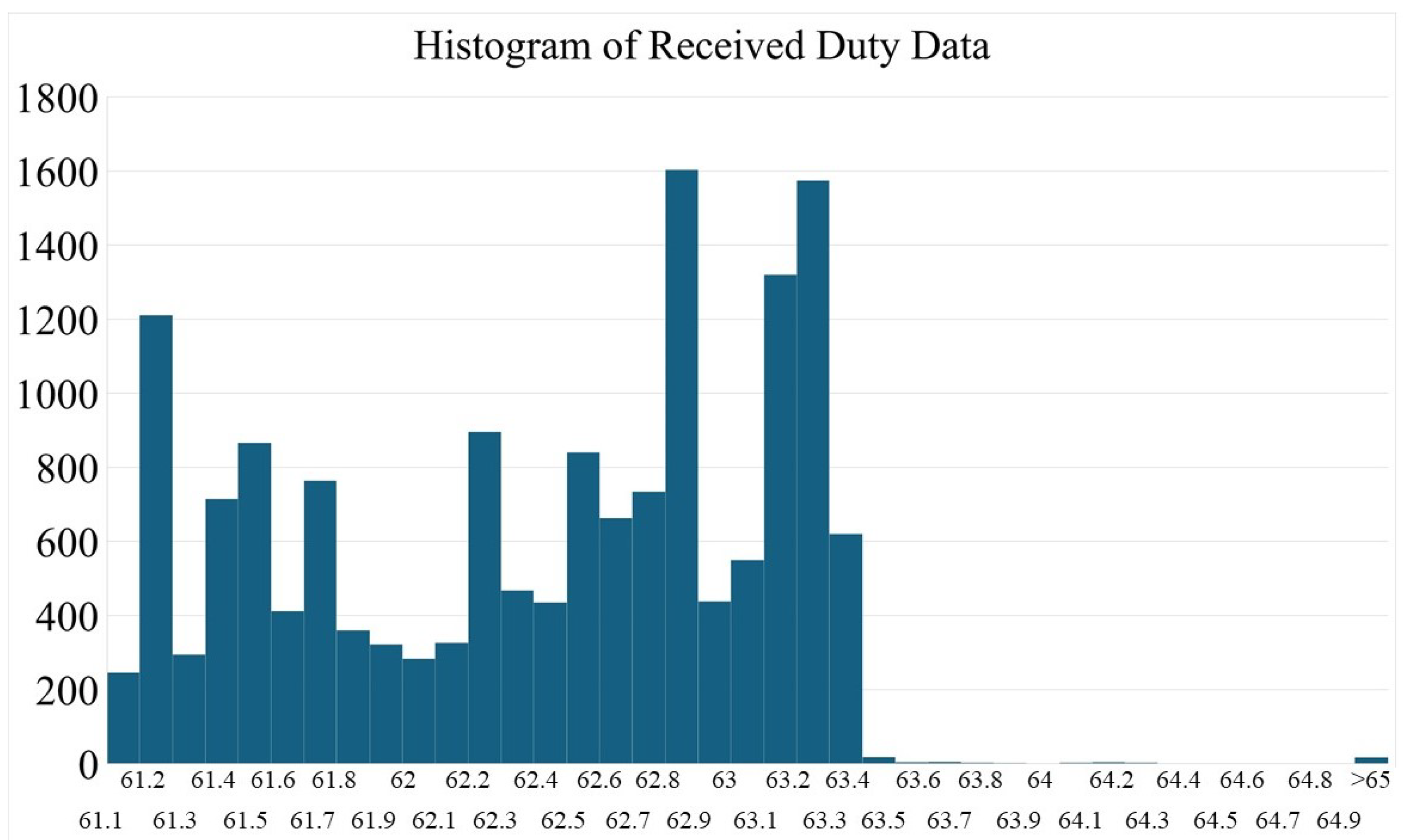
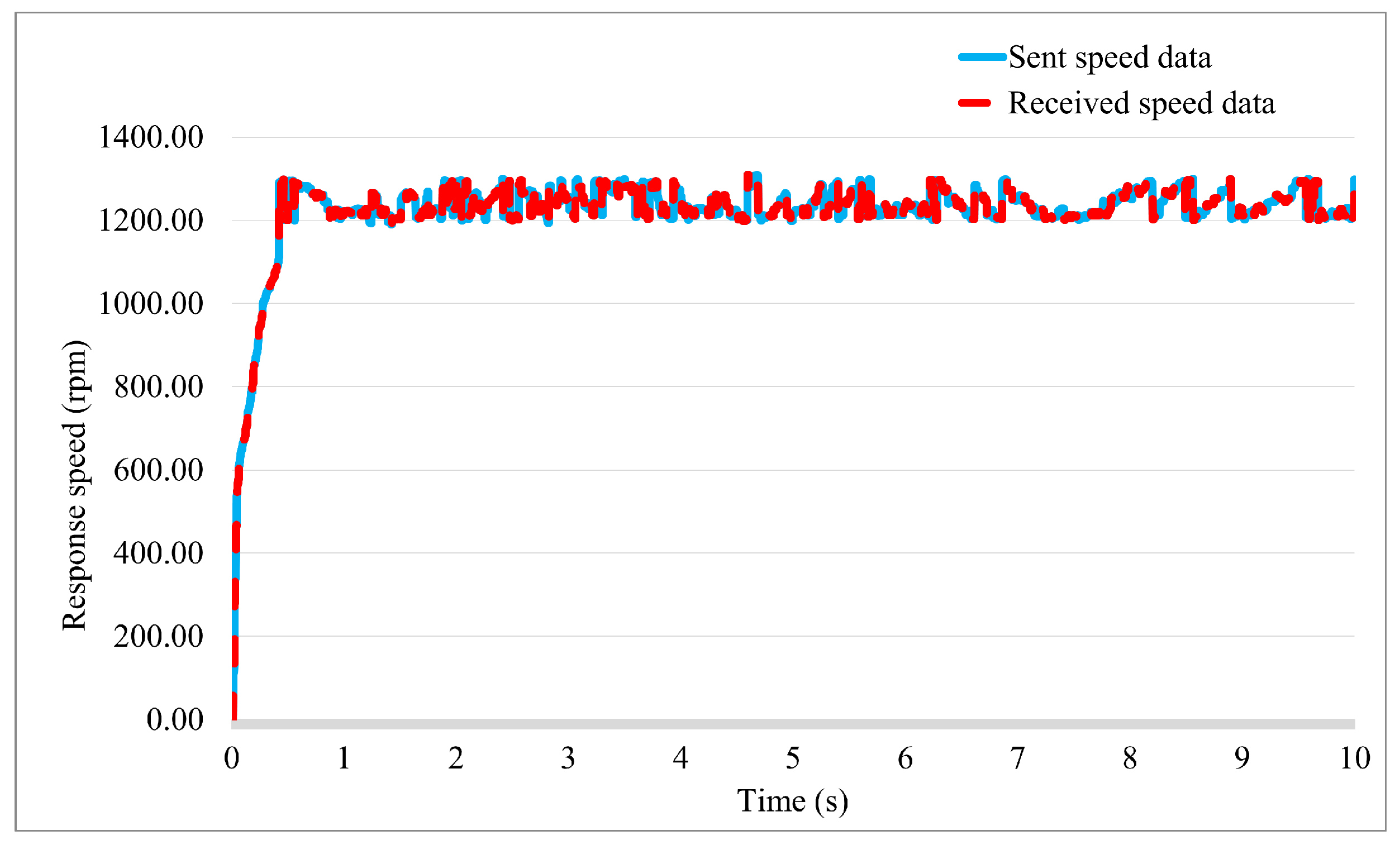
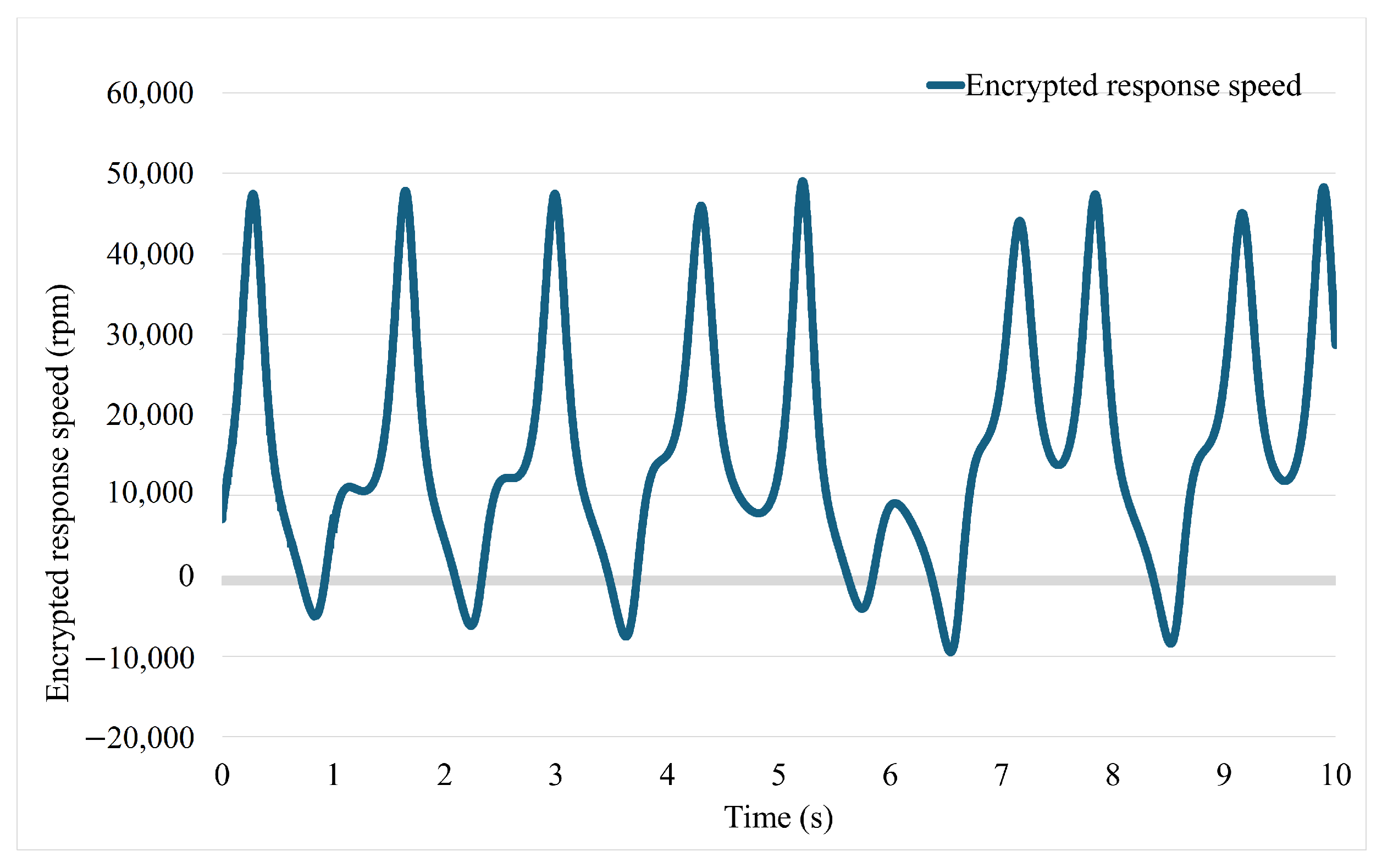
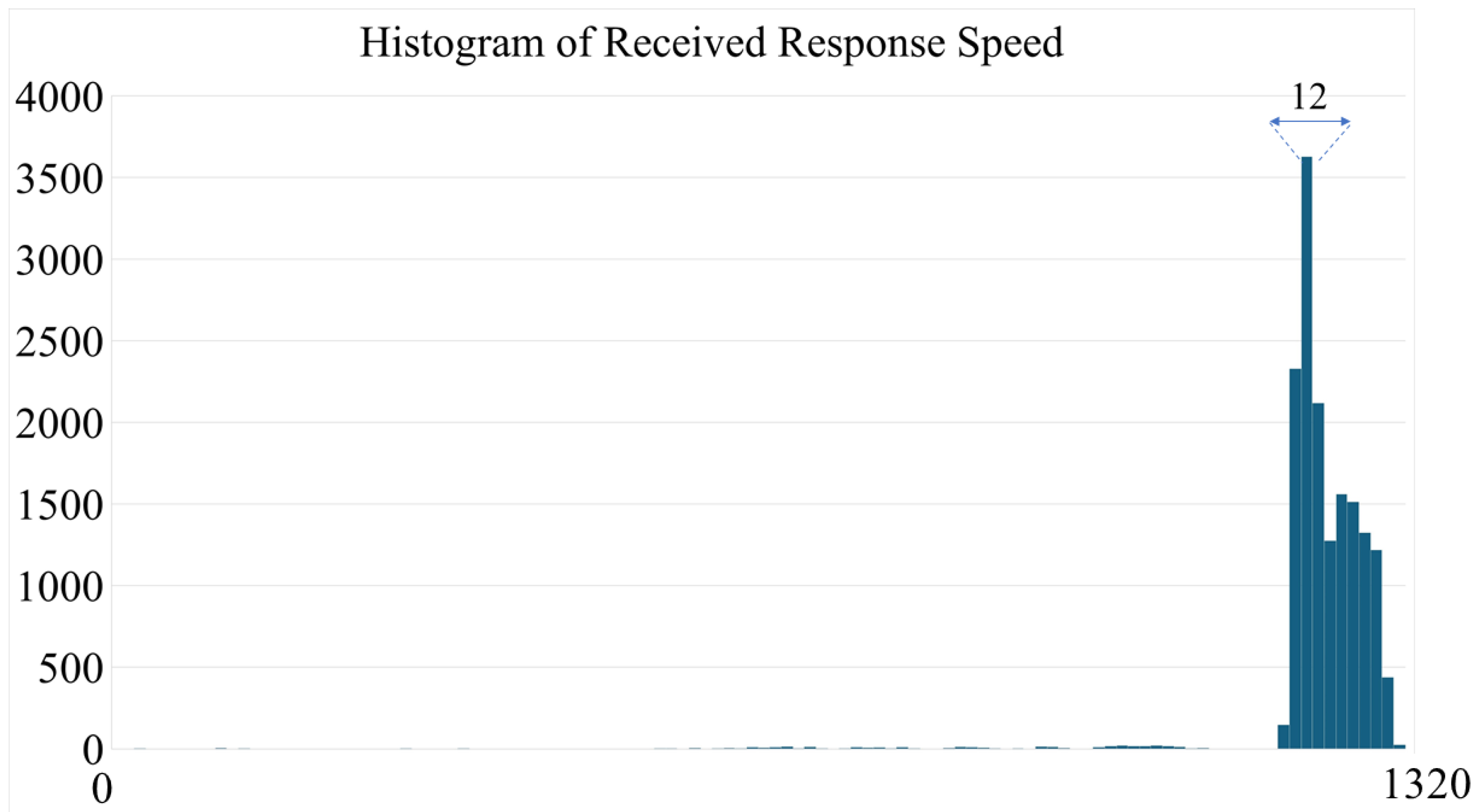
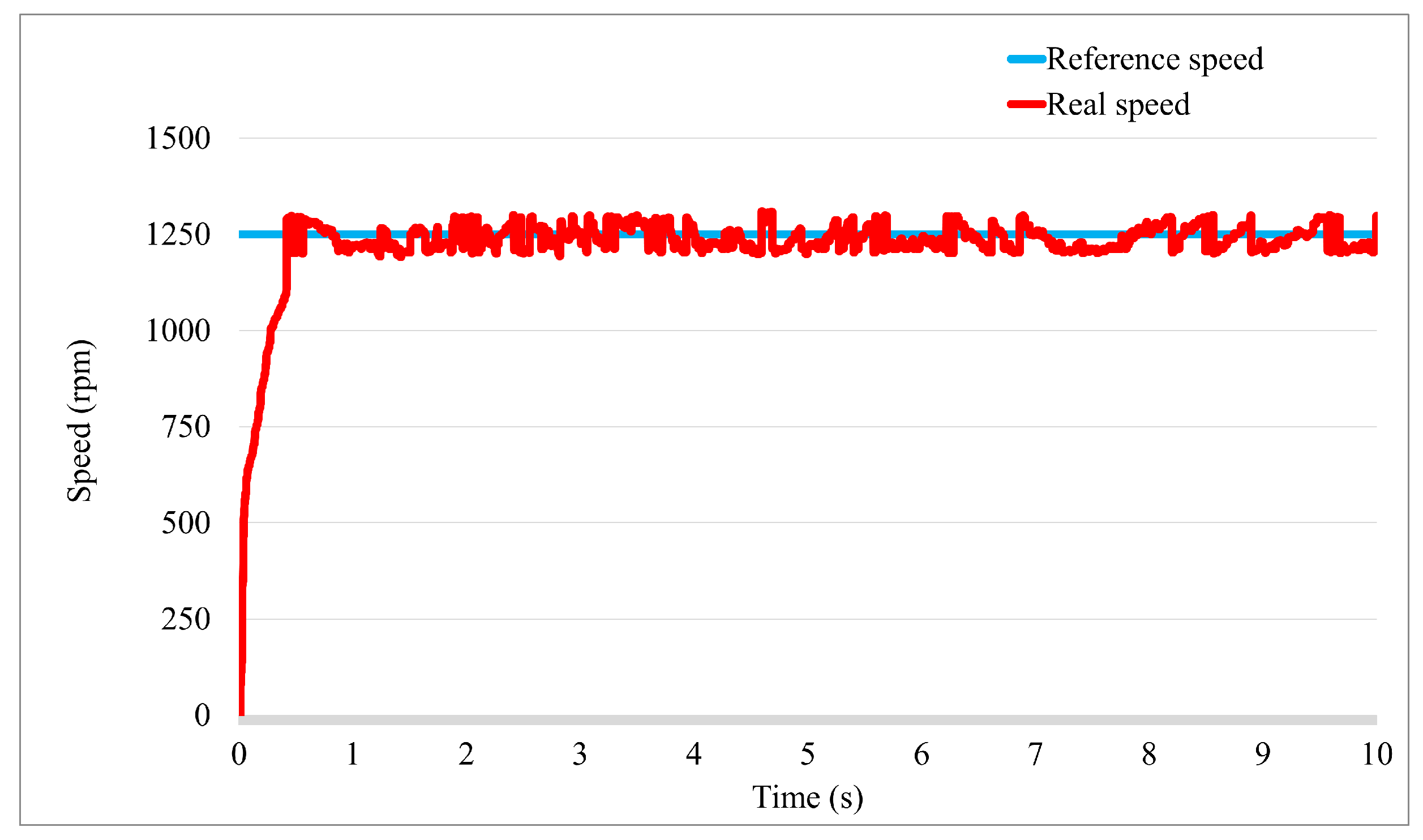
3. Simulation and Experimental Result
3.1. Simulation Study
3.2. Experiment Study
3.3. PI Controller
4. Conclusions
Limitations of the Study
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yan, J.J.; Shyu, K.K.; Lin, J.S. Adaptive variable-structure control for uncertain chaotic systems containing dead-zone non-linearity. Chaos Solit. Fractals 2005, 25, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-M.; Mon, Y.-J. Decoupling control by hierarchical fuzzy sliding-mode controller. IEEE Trans. Control. Syst. Technol. 2005, 13, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giap, V.N.; Nguyen, Q.D.; Pham, D.H.; Lin, C.M. Wireless secure communication of chaotic systems based on Takagi–Sugeno fuzzy optimal time-varying Disturbance Observer and sliding-mode control. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2023, 25, 2519–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giap, V.N. Text message secure communication based on fractional-order chaotic systems with Takagi–Sugeno fuzzy Disturbance Observer and sliding-mode control. Int. J. Dyn. Control. 2023, 11, 3109–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giap, V.-N.; Huang, S.-C.; Nguyen, Q.D. Synchronization of 3D Chaotic System Based on Sliding Mode Control: Electronic Circuit Implementation. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Eurasia Conference on IOT, Communication and Engineering (ECICE), Yunlin, Taiwan, 23–25 October 2020; pp. 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.M.; Ting, A.B.; Hsu, C.F.; Chung, C.M. Adaptive control for MIMO uncertain nonlinear systems using recurrent wavelet neural network. Int. J. Neural Syst. 2012, 22, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AL-Hussein, A.B.A. Neural Network-Based Adaptive Control of Robotic Manipulator: Application to a Three Links Cylindrical Robot. Iraqi J. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2017, 13, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, D.-H.; Lin, C.-M.; Giap, V.N.; Huynh, T.-T.; Cho, H.-Y. Wavelet Interval Type-2 Takagi-Kang-Sugeno Hybrid Controller for Time-Series Prediction and Chaotic Synchronization. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 104313–104327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.L.P.; Liu, Y.-J.; Wen, G.-X. Fuzzy Neural Network-Based Adaptive Control for a Class of Uncertain Nonlinear Stochastic Systems. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2014, 44, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-S. Robust Self-Organizing Neural-Fuzzy Control With Uncertainty Observer for MIMO Nonlinear Systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2011, 19, 694–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Chao, F.; Lin, C.M.; Yang, L.; Shang, C.; Zhou, C. An Improved Fuzzy Brain Emotional Learning Model Network Controller for Humanoid Robots. Front. Neurorobotics 2019, 13, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Fang, J.; Chen, C.; Li, Z.; Yu, F. A complex-valued time varying zeroing neural network model for synchronization of complex chaotic systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 2024, 113, 5471–5491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; He, S.; Yao, W.; Cai, S.; Xu, Q. Bursting Firings in Memristive Hopffeld Neural Network with Image Encryption and Hardware Implementation. IEEE Trans.-Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2025; early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marr, D. A theory of cerebellar cortex. J. Physiol. 1969, 202, 437–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albus, J.S. A new approach to manipulator control: The cerebellar model articulation controller (CMAC). J. Dyn. Syst. Meas. Control 1975, 97, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.-H. Adaptive fuzzy CMAC-based nonlinear control with dynamic memory architecture. J. Frankl. Inst. 2011, 348, 2480–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.-H. Adaptive output recurrent cerebellar model articulation controller for nonlinear system control. Soft Comput. 2010, 14, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.M.; Huynh, T.T.; Le, T.L. Adaptive TOPSIS fuzzy CMAC back-stepping control system design for nonlinear systems. Soft Comput. 2019, 23, 6947–6966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.M.; Li, H.Y. TSK Fuzzy CMAC-Based Robust Adaptive Backstepping Control for Uncertain Nonlinear Systems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2012, 20, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, F.; Yu, W.; Moreno-Armendariz, M.; Li, X. Recurrent Fuzzy CMAC for Nonlinear System Modeling. In Advances in Neural Networks; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; Volume 4491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.M.; Li, H.Y. Dynamic Petri Fuzzy Cerebellar Model Articulation Controller Design for a Magnetic Levitation System and a Two-Axis Linear Piezoelectric Ceramic Motor Drive System. IEEE Trans. Control. Syst. Technol. 2015, 23, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeDoux, J.E. Emotion and the amygdala: Fear, anxiety, and aggression. In The Amygdala: Neurobiological Aspects of Emotion, Memory, and Mental Dysfunction; Wiley-Liss: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1992; pp. 339–351. [Google Scholar]
- Balkenius, C.; Moren, J. Emotional learning: A computational model of the amygdala. Cybern. Syst. 2001, 32, 611–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, D.H.; Lin, C.M.; Giap, V.N. Intelligent control-system design for nonlinear systems using an improved TSK wavelet type-2 fuzzy brain-emotional controller. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2024, 26, 2632–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moren, J.; Balkenius, C. A computational model of emotional learning in the amygdala. In From Animals to Animats 7; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2002; pp. 115–124. [Google Scholar]
- Lucas, C.; Salari, K.; Sheikholeslami, N. Introducing BELBIC: Brain emotional learning-based intelligent controller. Int. J. Intell. Autom. Soft Comput. 2004, 10, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouhani, H.; Jalili, M.; Araabi, B.N.; Eppler, W.; Lucas, C. Brain emotional learning based intelligent controller applied to neurofuzzy model of micro-heat exchanger. Expert Syst. Appl. 2007, 32, 911–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samimi, M.; Majidi, M.H.; Khorashadizadeh, S. Secure communication based on chaos synchronization using brain emotional learning. AEU—Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2020, 127, 153424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, M.C.; Giap, V.N.; Nguyen, Q.D.; Huang, S.-C. Electrocardiogram Signal Secure Transmission via a Wireless Communication Protocol of Chaotic Systems Based on Adaptive Sliding Mode Control and Disturbance Observer. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 145373–145385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, F.; Chen, C.; Broderick, N.G. Coupled Homogeneous Hopfield Neural Networks: Simplest Model Design, Synchronization, and Multiplierless Circuit Implementation. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Systems. 2025, 36, 11632–11639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Wang, C.; Yang, G.; Luo, D. Discrete Memristive Delay Feedback Rulkov Neuron Model: Chaotic Dynamics, Hardware Implementation, and Application in Secure Communication. IEEE Internet Things J. 2025, 12, 25559–25567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-M.; Pham, D.-H.; Huynh, T.-T. Encryption and Decryption of Audio Signal and Image Secure Communications Using Chaotic System Synchronization Control by TSK Fuzzy Brain Emotional Learning Controllers. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022, 52, 13684–13698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giap, V.N.; Vu, H.S.; Nguyen, Q.D.; Huang, S.C. Disturbance-and-uncertainty rejection based on fixed-time sliding-mode control for the secure communication of chaotic systems. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 133663–133685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.D.; Huang, S.C.; Giap, V.N. Lyapunov-based fractional-order Disturbance Observer and sliding-mode control for a secure communication of chaos-based system. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2023, 21, 3595–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.D.; Vu, D.D.; Huang, S.-C.; Giap, V.N. Fixed-time supper twisting Disturbance Observer and sliding mode control for a secure communication of fractional-order chaotic systems. J. Vib. Control. 2023, 30, 2568–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Deng, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, C. Secure image encryption scheme based on a new robust chaotic map and strong S-box. Math. Comput. Simul. 2023, 207, 322–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallav; Handa, H. Chaos synchronization for a class of hyper-chaotic systems using active SMC and PI SMC: A comparative analysis. J. Control Autom. Electr. Syst. 2022, 33, 1671–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, B.; Liu, C.; Yue, X. Integrated Predictor–Observer Feedback Control for Vibration Mitigation of Large-Scale Spacecraft With Unbounded Input Time Delay. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2025, 61, 4561–4572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yue, X.; Zhang, J.; Shi, K. Active Disturbance Rejection Control for Delayed Electromagnetic Docking of Spacecraft in Elliptical Orbits. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2022, 58, 2257–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, B.; Liu, C.; Yue, X. Hybrid nonfragile intermediate observer-based T-S fuzzy attitude control for flexible spacecraft with input saturation. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 2022, 128, 107753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadji, M.M.; Ladaci, S. A novel secure-communication-scheme design using a fractional-order adaptive observer-based synchronization. J. Control Autom. Electr. Syst. 2025, 36, 267–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Zhang, S.; Su, D.; Wu, Y.; Gracia, Y.M.; Yin, H. Dynamic Analysis and Implementation of FPGA for a New 4D Fractional-Order Memristive Hopfield Neural Network. Fractal Fract. 2025, 9, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Wang, C.; Sun, Y.; Yang, G. Discrete Memristive Conservative Chaotic Map: Dynamics, Hardware Implementation, and Application in Secure Communication. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2025; early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Q.; Yang, Q.; Liu, T.; Chen, C.; Shen, K. Single direction, grid and spatial multi-scroll attractors in Hopfield neural network with the variable number memristive self-connected synapses. Chaos Solit. Fractals 2024, 189, 115584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortigueira, M.D.; Machado, J.A.T. New discrete-time fractional derivatives based on the bilinear transformation: Definitions and properties. J. Adv. Res. 2020, 25, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.M.; Chung, C.C. Fuzzy Brain Emotional Learning Control System Design for Nonlinear Systems. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2015, 17, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Phan Thi, H.C.; Dang, N.Q.; Giap, V.N. Secure Communication of Electric Drive System Using Chaotic Systems Base on Disturbance Observer and Fuzzy Brain Emotional Learning Neural Network. Math. Comput. Appl. 2025, 30, 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/mca30040073
Phan Thi HC, Dang NQ, Giap VN. Secure Communication of Electric Drive System Using Chaotic Systems Base on Disturbance Observer and Fuzzy Brain Emotional Learning Neural Network. Mathematical and Computational Applications. 2025; 30(4):73. https://doi.org/10.3390/mca30040073
Chicago/Turabian StylePhan Thi, Huyen Chau, Nhat Quang Dang, and Van Nam Giap. 2025. "Secure Communication of Electric Drive System Using Chaotic Systems Base on Disturbance Observer and Fuzzy Brain Emotional Learning Neural Network" Mathematical and Computational Applications 30, no. 4: 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/mca30040073
APA StylePhan Thi, H. C., Dang, N. Q., & Giap, V. N. (2025). Secure Communication of Electric Drive System Using Chaotic Systems Base on Disturbance Observer and Fuzzy Brain Emotional Learning Neural Network. Mathematical and Computational Applications, 30(4), 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/mca30040073





