Design of a Nonhomogeneous Nonlinear Synchronizer and Its Implementation in Reconfigurable Hardware
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Preliminaries
2.1. The Generalized Lorenz System
2.2. Unstable Dissipative Systems
- (i)
- An UDS Type I, if one eigenvalue is negative real and the other two are complex conjugate with a positive real part.
- (ii)
- An UDS Type II, if one eigenvalue is positive real and the other two are complex conjugate with a negative real part.
3. Synchronization Scheme
3.1. Master UDS–Slave GLS
3.2. Master GLS–Slave UDS
3.3. Master GLS–Slave GLS
3.4. Master UDS–Slave UDS
4. Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FPGA | Field-Programmable Gate Array |
| GLS | Generalized Lorenz System |
| UDS | Unstable Dissipative System |
| DAC | Digital to Analogue Converter |
References
- Chua, L.; Komuro, M.; Matsumoto, T. The double scroll family. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 1986, 33, 1073–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mees, A.; Chapman, P. Homoclinic and heteroclinic orbits in the double scroll attractor. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 1987, 34, 1115–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaney, R. An Introduction to Chaotic Dynamical Systems, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, C. Shilnikov’s theorem—A tutorial. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 1993, 64, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikovsky, A.; Rosenblum, M.; Kurths, J. Synchronization: A Universal Concept in Nonlinear Sciences, 1st ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Fujisaka, H.; Yamada, T. Stability Theory of Synchronized Motions in Coupled–Oscillator Systems. Prog. Theor. Phys. 1983, 1983, 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecora, L.M.; Carroll, T.L. Synchronization in chaotic systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1990, 64, 821–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agiza, H.; Yassen, M. Synchronization of Rossler and Chen chaotic dynamical systems using active control. Phys. Lett. A 2001, 278, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassen, M. Chaos synchronization between two different chaotic systems using active control. Chaos Solit. Fractals 2005, 23, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J. Chaos synchronization between two different chaotic dynamical systems. Chaos Solit. Fractals 2006, 27, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, G.; Bountis, T.; Mahmoud, E. Active control and global synchronization of the complex Chen and Lü systems. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2007, 17, 4295–4308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Chen, G.; Cai, J. Chaos synchronization of the master–slave generalized Lorenz system via linear state error feedback control. Physica D 2007, 229, 52–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Feng, G. Output tracking of piecewise–linear systems via error feedback regulator with application to synchronization of nonlinear Chua’s circuit. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 2007, 54, 1852–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oancea, S.; Grosu, F.; Lazar, A.; Grosu, I. Master–slave synchronization of Lorenz systems using a single controller. Chaos Solit. Fractals 2009, 41, 2575–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mkaouar, H.; Boubaker, O. Chaos synchronization for master–slave piecewise linear systems: Application to Chua’s circuit. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2012, 17, 1292–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, J.H.; Figueroa, M.; López, A. Synchronization of chaotic Akgul system by means of feedback linearization and pole placement. IEEE Lat. Am. Trans. 2017, 15, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idowu, B.A.; Vincent, U.E. Synchronization and stabilization of chaotic dynamics in quasi–1D Bose–Einstein condensate. J. Chaos 2013, 2013, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vaidyanathan, S. Anti–synchronization of rikitake two–disk dynamo chaotic systems via adaptive control method. Int. J. ChemTech Res. 2015, 8, 393–405. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, G.; Zhang, X.; Wuang, Z. Generation and synchronization of feedback–induced chaos in semiconductor ring lasers by injection locking. Optik 2014, 125, 1950–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuang, L.; Wu, Z.; Wu, J.; Xia, G. Long–haul dual–channel bidirectional chaos communication based on polarization–resolved chaos synchronization between twin 1550 nM VCSELs subject to variable–polarization optical injection. Opt. Commun. 2015, 334, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klebanoff, A.; Hastings, A. Chaos in three species food chains. J. Math. Biol. 1994, 32, 427–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z. Chaos in the genesis and maintenance of cardiac arrhythmias. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2011, 105, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrego, F.J.; Moiola, J.L. Lyapunov exponents analysis applied to a hyperchaotic prey–predator model. IEEE Lat. Am. Trans. 2013, 11, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, J.A.; Booksh, K.S. Chaos theory in chemistry and chemometrics: A review. J. Chemom. 2006, 20, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidyanathan, S. Adaptive synchronization of chemical chaotic reactors. Int. J. ChemTech Res. 2015, 8, 612–621. [Google Scholar]
- Smaoui, N.; Karouma, A.; Zribi, M. Adaptive synchronization of hyperchaotic Chen systems with applications to secure communications. Int. J. Innov. Comput. Inf. Control 2013, 9, 1127–1144. [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasekaran, J.; Thiruvengadam, S.J. Ensemble of chaotic and naive approaches for performance enhancement in video encryption. Sci. World J. 2015, 2015, 458272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderi, B.; Kheiri, H. Exponential synchronization of chaotic system and application in secure communication. Optik 2016, 127, 2407–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, T. A chaotic attractor from Chua’s circuit. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 1984, 31, 1055–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuomo, K.; Oppenheim, A. Circuit Implementation of Synchronized Chaos with Application to Communication. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1993, 71, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Li, Y.; Jiang, X. Simulation and Circuit Implementation of 12–Scroll Chaotic System. Chaos Solit. Fractals 2015, 75, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, R.; Mishra, S.; Madhekar, S. Electronic Circuit Implementation of Chaos Synchronization. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2013, 222, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fan, T.; Tuo, X.; Li, H.; He, P. Chaos Control and Circuit Implementation of Double–Wing Chaotic System. Int. J. Numer. Model. Electron. Netw. Devices Fields 2019, 32, e2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tlelo-Cuautle, E.; Rangel-Magdaleno, J.J.; Pano-Azucena, A.D.; Obseo-Rodelo, P.J.; Nunez-Perez, J.C. FPGA Realization of Multi–Scroll Chaotic Oscillators. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2015, 27, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yu, S.; Li, C.; Fang, X.; Guyeux, C.; Bahi, J.M. Theoritical design and FPGA–based implementation of higher–dimensional digital chaotic systems. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. 2016, 63, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tlelo-Cuautle, E.; Díaz-Muñoz, J.D.; González-Zapata, A.M.; Li, R.; León-Salas, W.D.; Fernández, F.V.; Guillén-Fernández, O.; Cruz-Vega, I. Chaotic Image Encryption Using Hopfield and Hindmarsh–Rose Neurons Implemented on FPGA. Sensors 2020, 20, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Čelikovský, S.; Chen, G. On a generalized Lorenz canonical form of chaotic systems. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2002, 12, 1789–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos-Cantón, E.; Barajas-Ramírez, J.G.; Solís-Perales, G.; Femat, R. Multiscroll attractors by switching systems. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2010, 20, 013116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos-Cantón, E.; Femat, R.; Chen, G. Attractor Generated from Switching Unstable Dissipative Systems. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2012, 22, 033121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, E.N. Deterministic nonperiodic flow. J. Atmos. Sci. 1963, 20, 130–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rössler, O.E. An Equation for Continuous Chaos. Phys. Lett. A 1976, 57, 397–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Ueta, T. Yet Another Chaotic Attractor. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 1999, 9, 1465–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-González, E.C.; Aguirre-Hernández, B.; López-Rentería, J.A.; Campos-Cantón, E.; Loredo-Villalobos, C.A. Stability and multiscroll attractors of control systems via the abscissa. Math. Probl. Eng. 2017, 2017, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

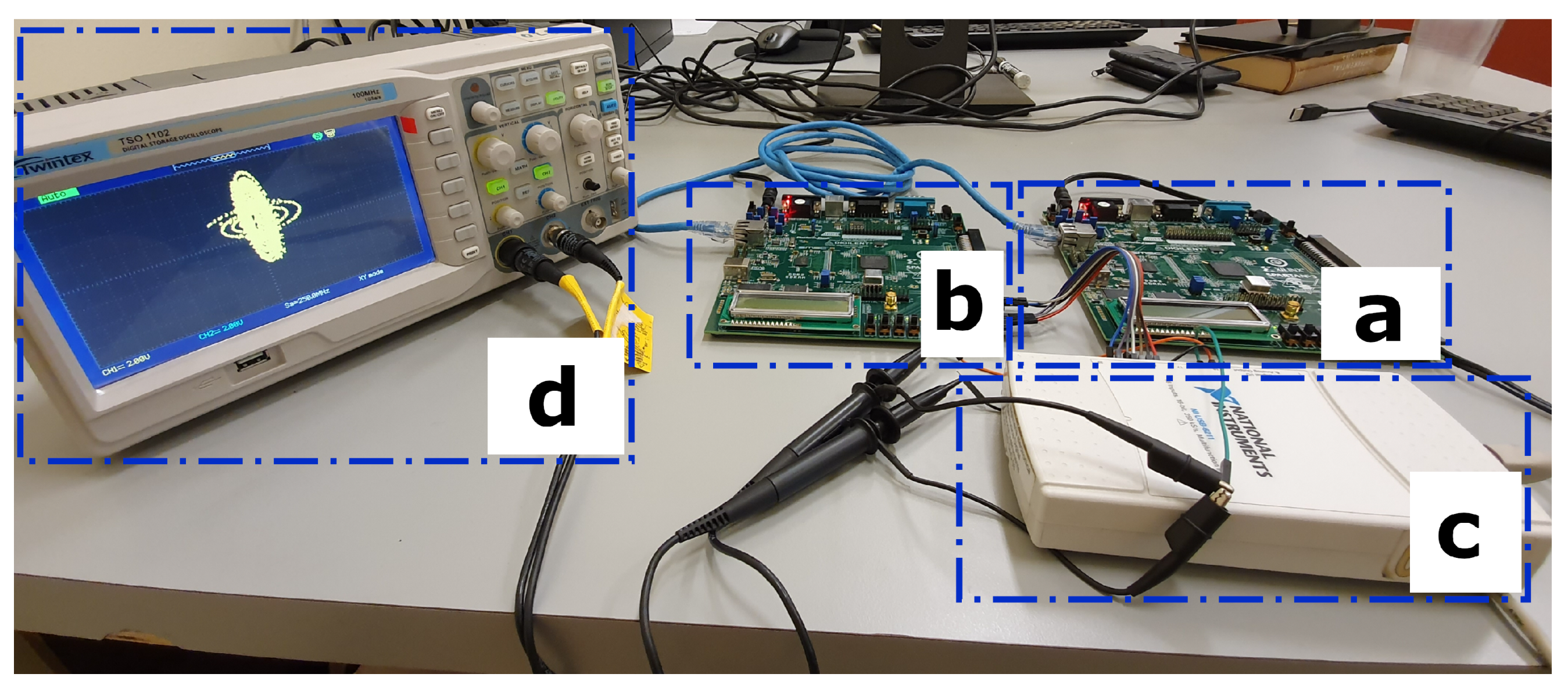

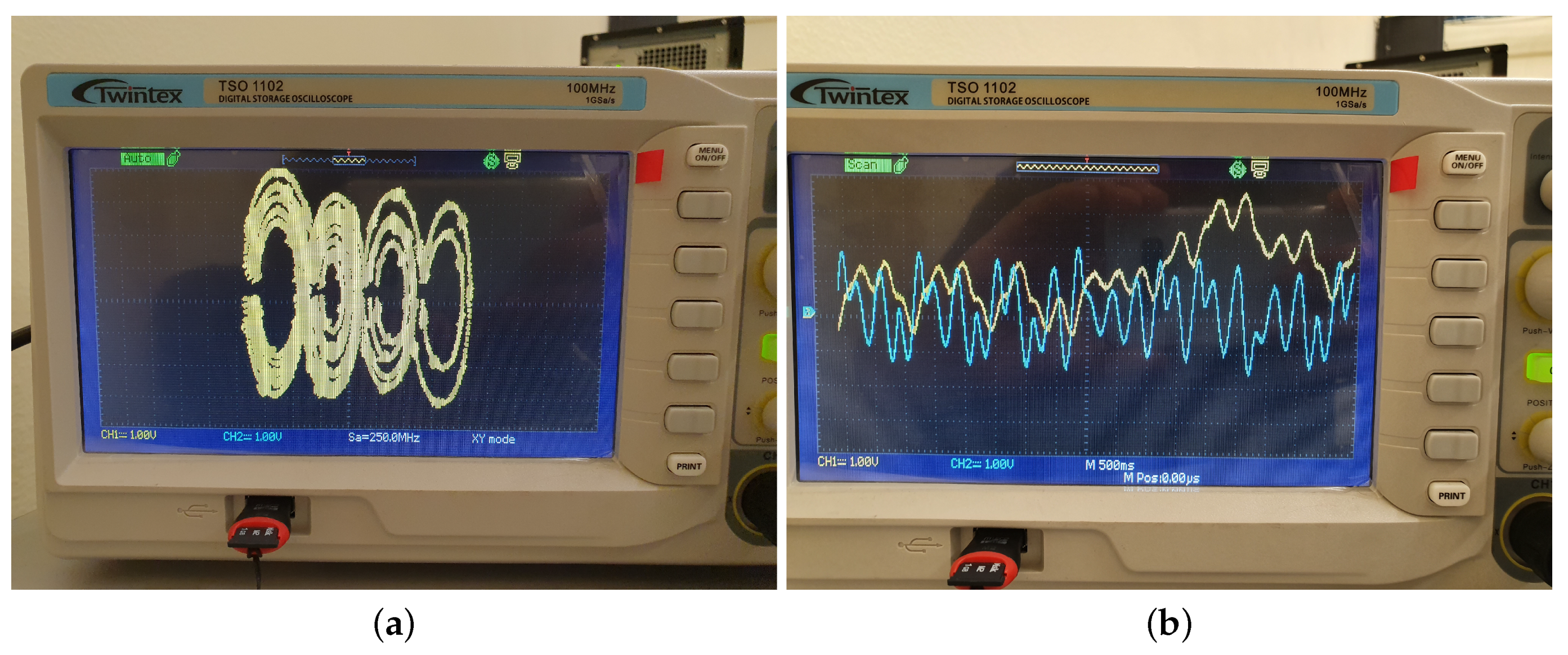
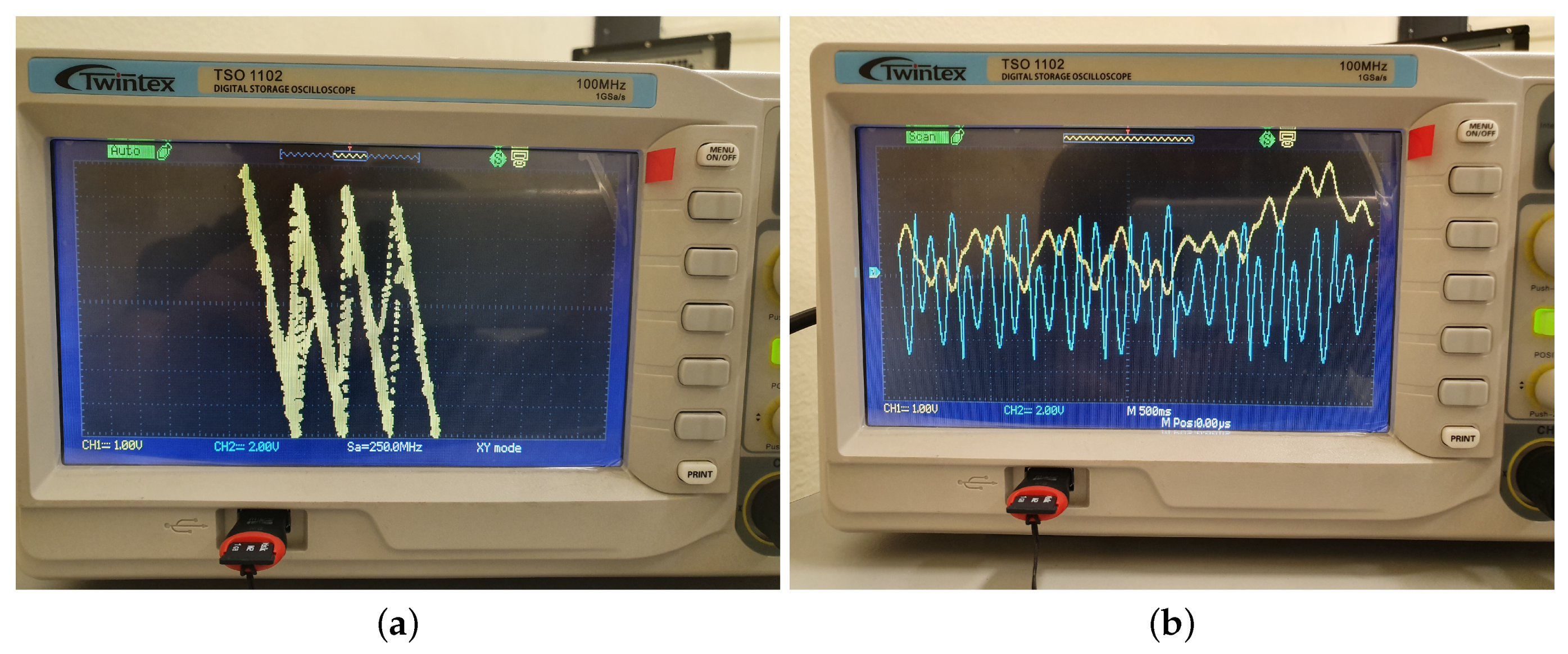
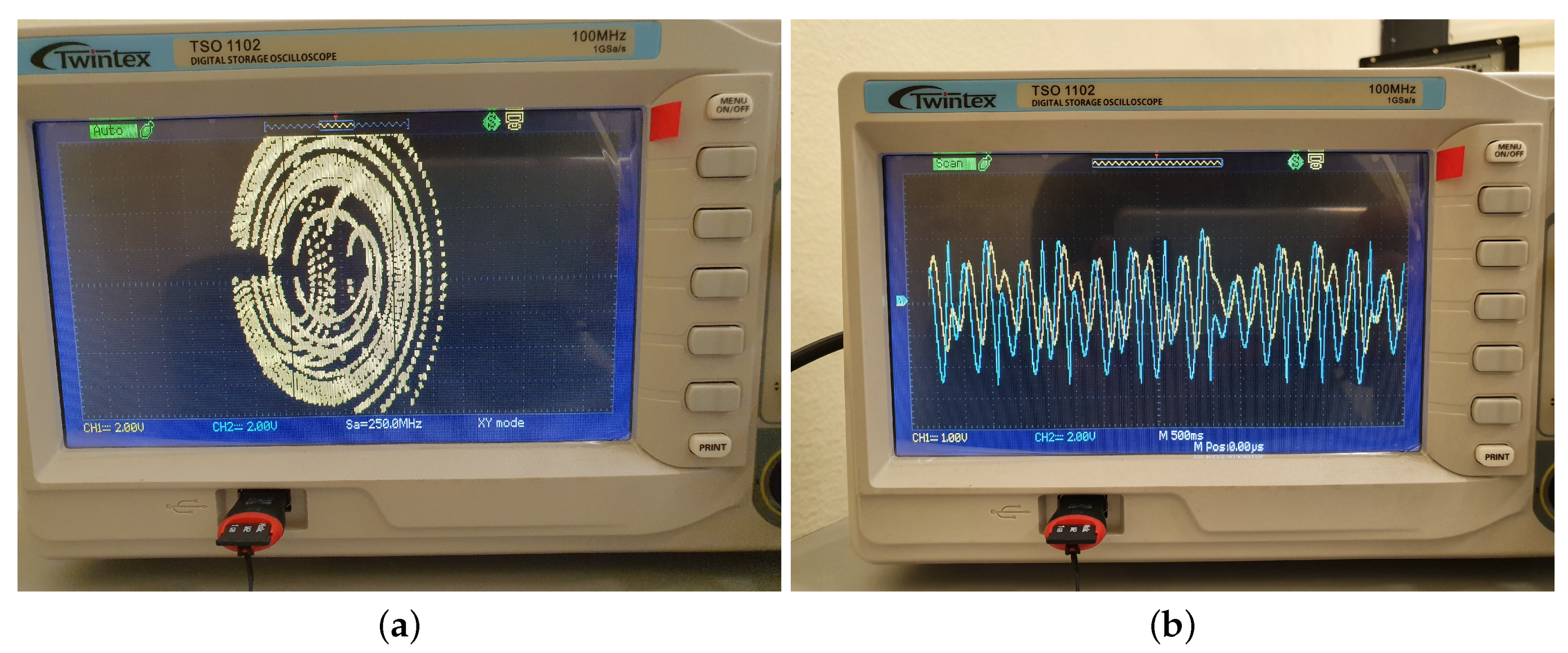
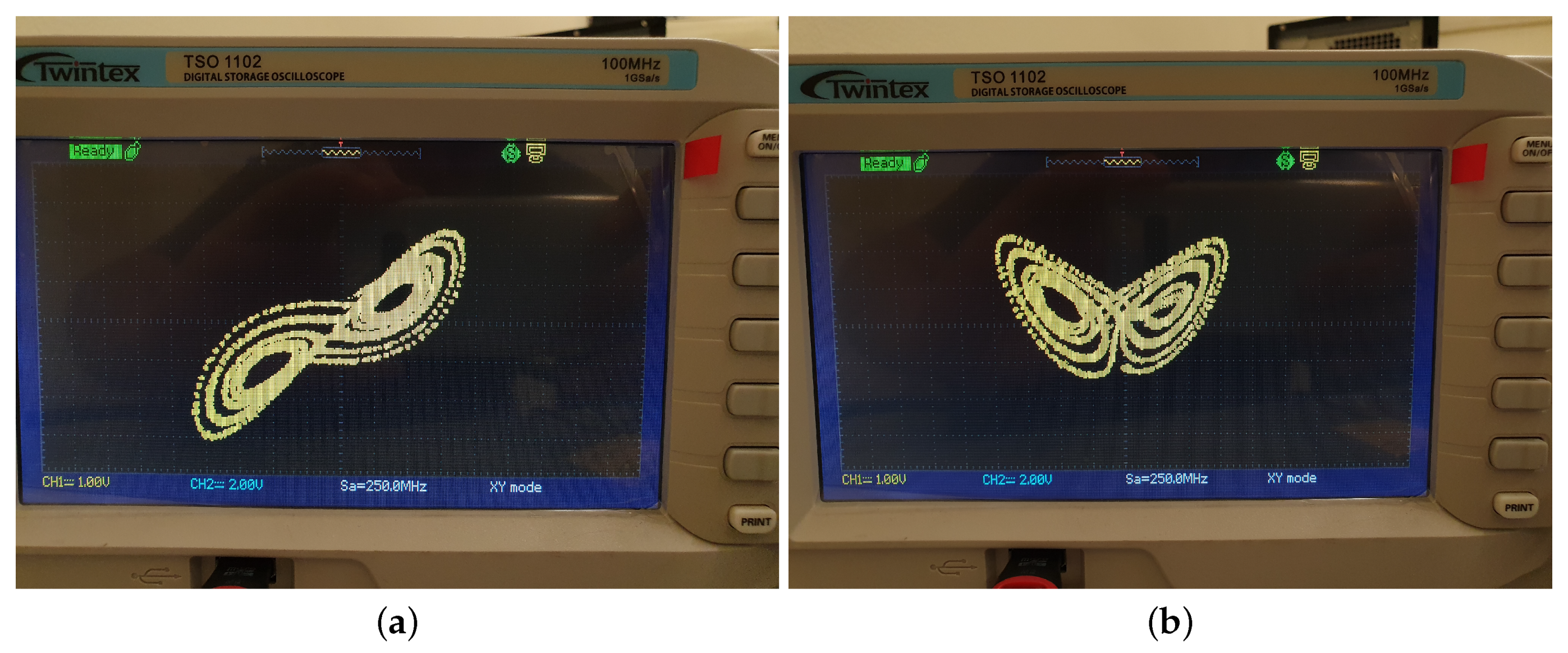

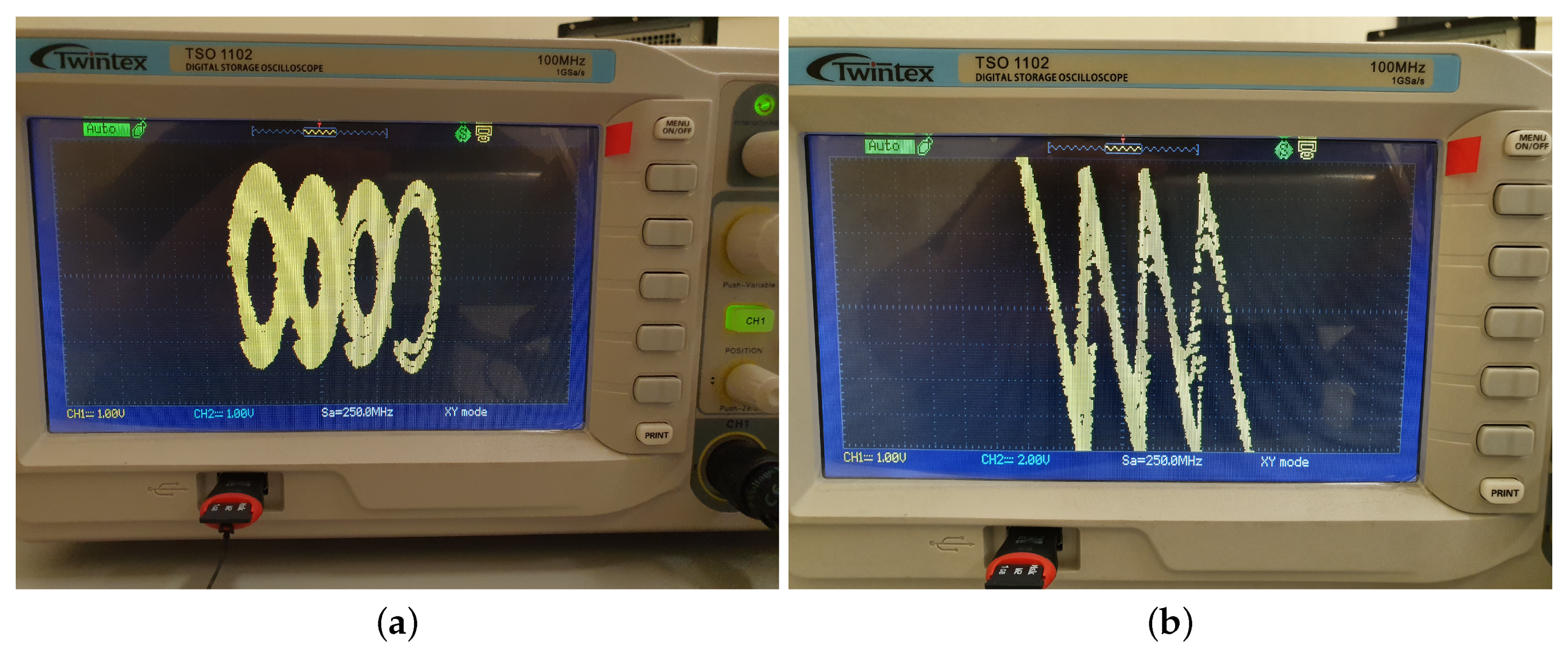
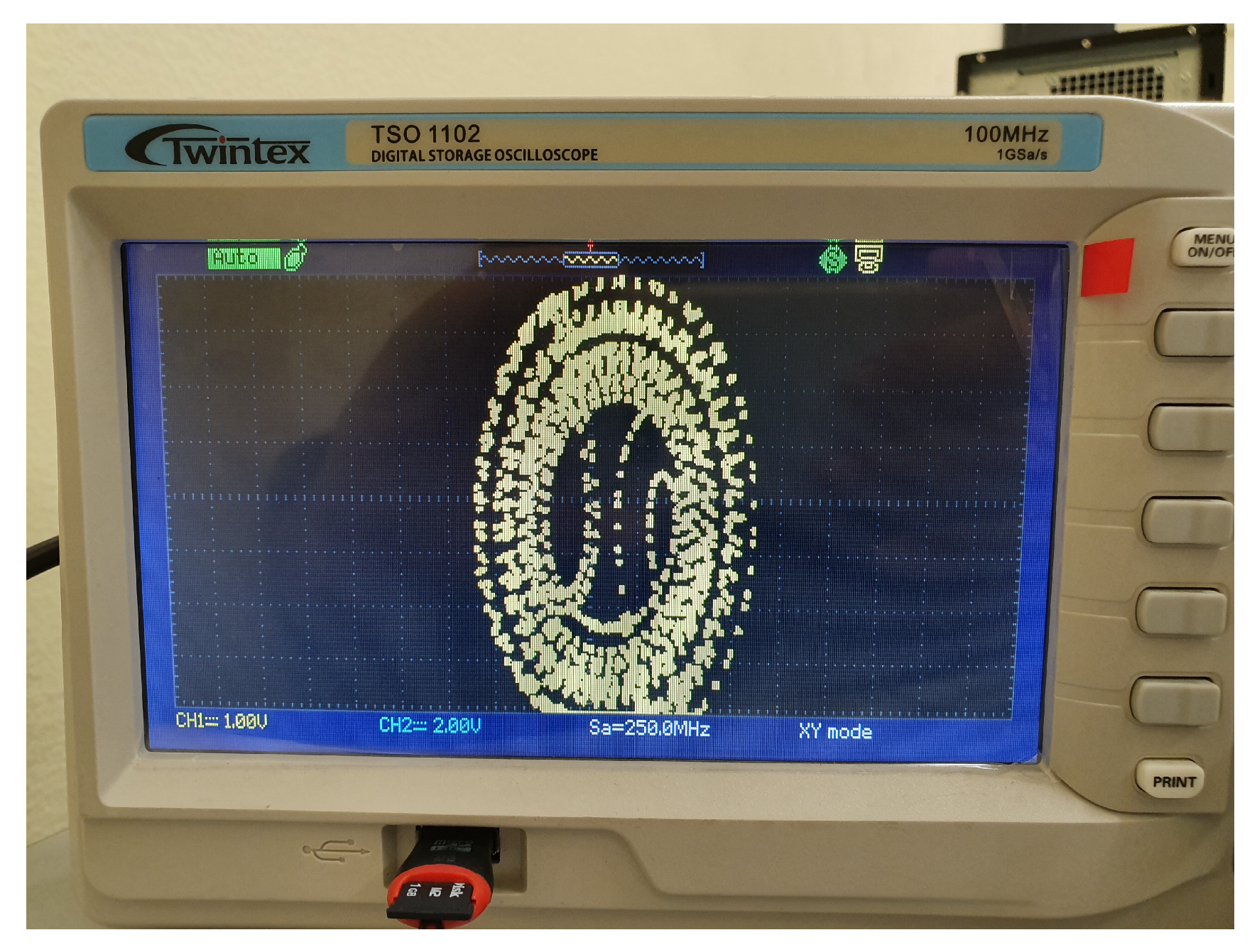
| Resources | Used | Available | Utilization |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Slice Flip Flops | 159 | 11,776 | |
| Number of 4 input LUTs | 4177 | 11,776 | |
| Number of occupied Slices | 2473 | 5888 | |
| Total Number of 4 input LUTs | 4467 | 11,776 | |
| Number of bounded IOBs | 145 | 372 | |
| Number of BUFGMUXs | 1 | 24 |
| Resources | Used | Available | Utilization |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Slice Flip Flops | 170 | 11,776 | |
| Number of 4 input LUTs | 2373 | 11,776 | |
| Number of occupied Slices | 1491 | 5888 | |
| Total Number of 4 input LUTs | 2677 | 11,776 | |
| Number of bounded IOBs | 53 | 372 | |
| Number of BUFGMUXs | 1 | 24 | |
| Number of MULT18X18SIOs | 18 | 20 |
| Resources | Used | Available | Utilization |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Slice Flip Flops | 332 | 11,776 | |
| Number of 4 input LUTs | 5550 | 11,776 | |
| Number of occupied Slices | 2964 | 5888 | |
| Total Number of 4 input LUTs | 7244 | 11,776 | |
| Number of bounded IOBs | 194 | 372 | |
| Number of BUFGMUXs | 2 | 24 | |
| Number of MULT18X18SIOs | 20 | 20 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pulido-Luna, J.R.; López-Rentería, J.A.; Cazarez-Castro, N.R. Design of a Nonhomogeneous Nonlinear Synchronizer and Its Implementation in Reconfigurable Hardware. Math. Comput. Appl. 2020, 25, 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/mca25030051
Pulido-Luna JR, López-Rentería JA, Cazarez-Castro NR. Design of a Nonhomogeneous Nonlinear Synchronizer and Its Implementation in Reconfigurable Hardware. Mathematical and Computational Applications. 2020; 25(3):51. https://doi.org/10.3390/mca25030051
Chicago/Turabian StylePulido-Luna, Jesus R., Jorge A. López-Rentería, and Nohe R. Cazarez-Castro. 2020. "Design of a Nonhomogeneous Nonlinear Synchronizer and Its Implementation in Reconfigurable Hardware" Mathematical and Computational Applications 25, no. 3: 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/mca25030051
APA StylePulido-Luna, J. R., López-Rentería, J. A., & Cazarez-Castro, N. R. (2020). Design of a Nonhomogeneous Nonlinear Synchronizer and Its Implementation in Reconfigurable Hardware. Mathematical and Computational Applications, 25(3), 51. https://doi.org/10.3390/mca25030051







