Determination of Three Alkyl Camphorsulfonates as Potential Genotoxic Impurities Using GC-FID and GC-MS by Analytical QbD
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents, Materials and Standards
2.2. Analytical Condition and Equipments
2.2.1. GC-FID Condition
2.2.2. GC-MS Condition
2.3. Preparation of Standard Solution and Sample Solution
2.3.1. Internal Standard Solution Preparation
2.3.2. Standard Stock Solution Preparation (STD-2)
2.3.3. Standard Solution Preparation
2.3.4. Sample Solution Separation
2.4. In Silico Study
2.5. Method Screening
2.6. Method Optimization
2.7. Method Validation
2.7.1. Determination of Specificity
2.7.2. Determination of the Detection Limit and Quantitation Limit
2.7.3. Determination of Accuracy
2.7.4. Determination of Precision
2.7.5. Determination of Linearity
2.7.6. Determination of Robustness
3. Results
3.1. In Silico Study
3.2. Method Screening
3.3. Method Optimization by Analytical QbD
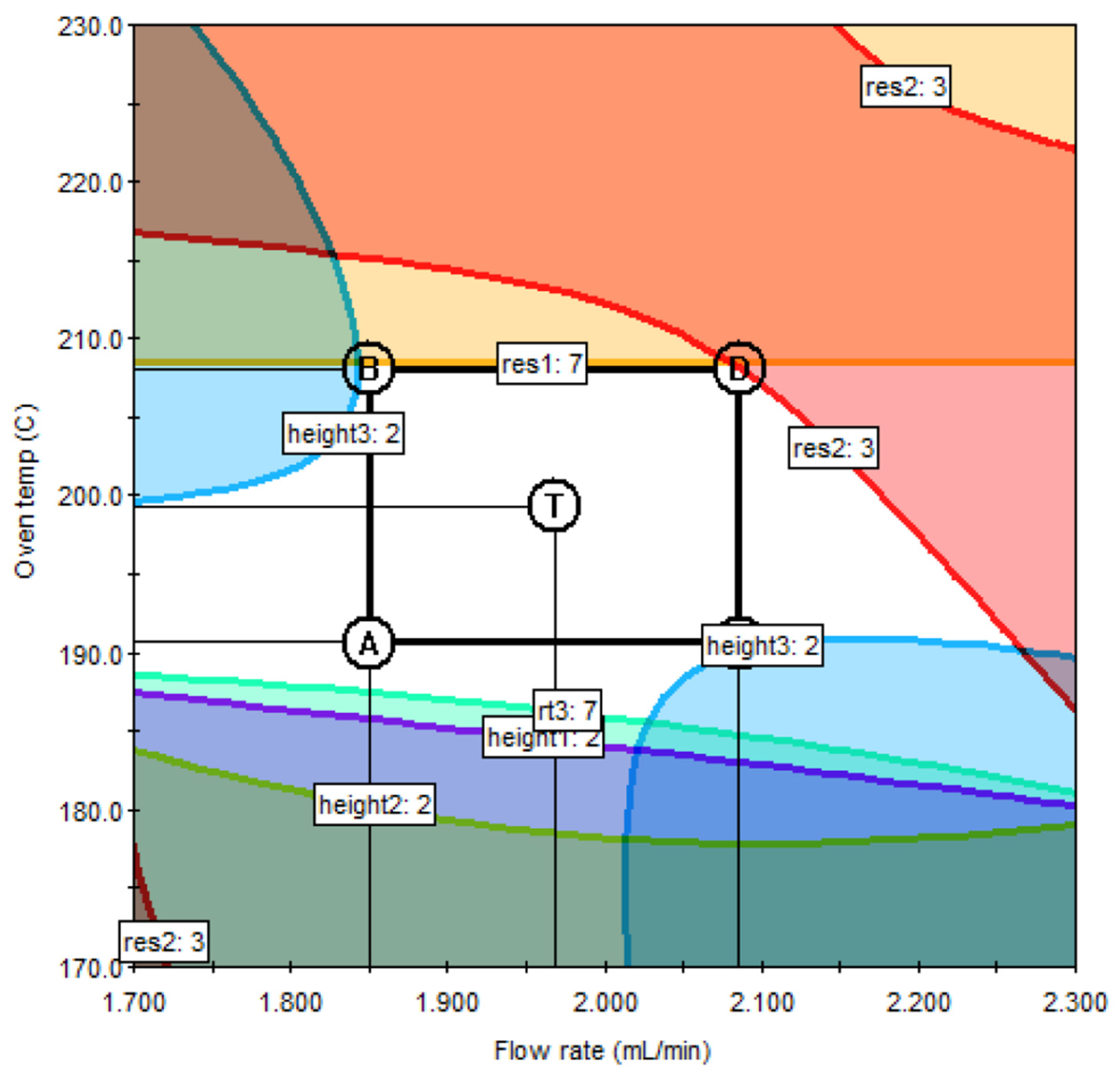
3.4. Design Space
3.5. Apply MS
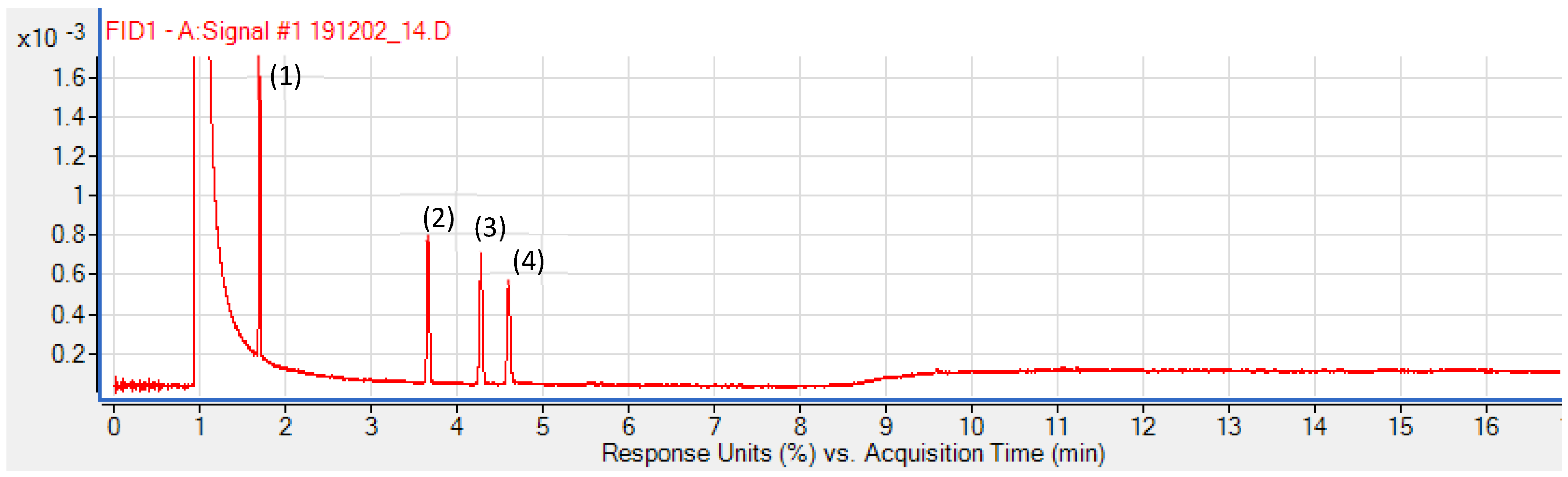
3.6. Applicability of the Method to Real Sample
3.7. Analytical Method Validation and Robustness Test
3.7.1. Limits of Detection and Quantification
3.7.2. Linearity and Range
3.7.3. Precision and Accuracy
3.7.4. Specificity
3.7.5. Robustness
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Serajuddin, A.T.M. Salt Formation to Improve Drug Solubility. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elder, D.P.; Holm, R.; de Diego, H.L. Use of Pharmaceutical Salts and Co crystals to Address the Issue of Poor Solubility. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 453, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berge, S.M.; Bighley, L.D.; Monkhouse, D.C. Pharmaceutical Salts. J. Pharm. Sci. 1977, 66, 417–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elder, D.P.; Delaney, E.; Teasdale, A.; Eyley, S.; Reif, V.D.; Jacq, K.; Facchine, K.L.; Oestrich, R.S.; Sandra, P.; David, F. The Utility of Sulfonate Salts in Drug Development. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 2948–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, D.; Bhatia, D.; Dave, V.; Sutariya, V.; Gupta, S.V. Salts of Therapeutic Agents: Chemical, Physicochemical, and Biological Considerations. Molecules 2018, 23, 1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teasdale, A.; Delaney, E.J.; Eyley, S.C.; Jacq, K.; Taylor-Worth, K.; Lipczynski, A.; Hoffmann, W.; Reif, V.; Elder, D.P.; Facchine, K.L.; et al. A Detailed Study of Sulfonate Ester Formation and Solvolysis Reaction Rates and Application toward Establishing Sulfonate Ester Control in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Processes. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2010, 14, 999–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snodin, D.; Teasdale, A. Mutagenic Alkyl-Sulfonate Impurities in Sulfonic Acid Salts: Reviewing the Evidence and Challenging Regulatory Perceptions. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2015, 19, 1465–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glowienke, S.; Frieauff, W.; Allmendinger, T.; Martus, H.J.; Suter, W.; Mueller, L. Structure-Activity Considerations and in Vitro Approaches to Assess the Genotoxicity of 19 Methane-, Benzene- and Toluenesulfonic Acid Esters. Mutat. Res.-Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagenesis 2005, 581, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobol, Z.; Engel, M.E.; Rubitski, E.; Ku, W.W.; Aubrecht, J.; Schiestl, R.H. Genotoxicity Profiles of Common Alkyl Halides and Esters with Alkylating Activity. Mutat. Res.-Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagenesis 2007, 633, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couch, D.B.; Forbes, N.L.; Hsie, A.W. Comparative Mutagenicity of Alkylsulfate and Alkanesulfonate Derivatives in Chinese Hamster Ovary Cells. Mutat. Res.-Fundam. Mol. Mech. Mutagenesis 1978, 57, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashby, J.; Basketter, D.A.; Paton, D.; Kimber, I. Structure Activity Relationships in Skin Sensitization Using the Murine Local Lymph Node Assay. Toxicology 1995, 103, 177–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, D.W.; Basketter, D.A. Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationships: Sulfonate Esters in the Local Lymph Node Assay. Contact Dermat. 2000, 42, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroes, R.; Kozianowski, G. Threshold of Toxicological Concern (TTC) in Food Safety Assessment. Toxicol. Lett. 2002, 127, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Council for Harmonisation Guideline M7 (R1) on Assessment and Control of DNA Reactive (Mutagenic) Impurities in Pharmaceuticals to Limit Potential Carcinogenic Risk Step 4 Version 2017. Available online: https://database.ich.org/sites/default/files/M7_R1_Guideline.pdf (accessed on 3 May 2022).
- Lee, C.R.; Hubert, M.; Nguyen Van Dau, C.; Peter, D.; Krstulovic, A.M. Determination of N,N-Dimethylaminoethyl Chloride and the Dimethylaziridinium Ion at Sub-Ppm Levels in Diltiazem Hydrochloride by LC-MS with Electrospray Ionisation. Analyst 2000, 125, 1255–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Dong, L.; Tang, K.; Lan, Z.; Liu, R.; Wang, Y.; Wang, R.; Lin, H. Simultaneous and Trace Level Quantification of Two Potential Genotoxic Impurities in Valsartan Drug Substance Using UPLC-MS/MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 212, 114630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.Q.; Sun, M.; Kord, A.S. Recent Advances in Trace Analysis of Pharmaceutical Genotoxic Impurities. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2010, 51, 999–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- al Azzam, K.M.; Aboul-Enein, H.Y. Recent Advances in Analysis of Hazardous Genotoxic Impurities in Pharmaceuticals by HPLC, GC, and CE. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2016, 39, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, A.V.B.; Jaafar, J.; Umar, K.; Majid, Z.A.; bin Aris, A.; Talib, J.; Madhavi, G. Identification, Control Strategies, and Analytical Approaches for the Determination of Potential Genotoxic Impurities in Pharmaceuticals: A Comprehensive Review. J. Sep. Sci. 2015, 38, 764–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elder, D.P.; Snodin, D.J. Drug Substances Presented as Sulfonic Acid Salts: Overview of Utility, Safety and Regulation. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2009, 61, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W. Trace Analysis of Residual Methyl Methanesulfonate, Ethyl Methanesulfonate and Isopropyl Methanesulfonate in Pharmaceuticals by Capillary Gas Chromatography with Flame Ionization Detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1046, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, N.V.V.S.S.; Reddy, K.R.; Prasad, A.V.S.S.; Ramakrishna, K. Development and Validation of a GC-MS Method for the Determination of Methyl and Ethyl Camphorsulfonates in Esomeprazole Magnesium. Chromatographia 2008, 68, 675–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacq, K.; Delaney, E.; Teasdale, A.; Eyley, S.; Taylor-Worth, K.; Lipczynski, A.; Reif, V.D.; Elder, D.P.; Facchine, K.L.; Golec, S.; et al. Development and Validation of an Automated Static Headspace Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (SHS-GC-MS) Method for Monitoring the Formation of Ethyl Methane Sulfonate from Ethanol and Methane Sulfonic Acid. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2008, 48, 1339–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Fan, H.; Zhou, Y.; Qian, X.; Tu, J.; Chen, B.; Duan, G. Development and Validation of a Sensitive Method for Alkyl Sulfonate Genotoxic Impurities Determination in Drug Substances Using Gas Chromatography Coupled to Triple Quadrupole Mass Spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 168, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szekely, G.; de Sousa, M.C.A.; Gil, M.; Ferreira, F.C.; Heggie, W. Genotoxic Impurities in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing: Sources, Regulations, and Mitigation. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 8182–8229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinh, N.P.; Shamshir, A.; Hulaj, G.; Jonsson, T. Validated Modernized Assay for Foscarnet in Pharmaceutical Formulations Using Suppressed Ion Chromatography Developed through a Quality by Design Approach. Separations 2021, 8, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozet, E.; Lebrun, P.; Hubert, P.; Debrus, B.; Boulanger, B. Design Spaces for Analytical Methods. TrAC-Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 42, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.N.; Kothari, C.S. Review on Implementation of Multivariate Approach for Forced Degradation Study and Impurity Profiling with Regulatory Considerations. Chromatographia 2018, 81, 105–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parr, M.K.; Schmidt, A.H. Life Cycle Management of Analytical Methods. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 147, 506–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tome, T.; Casar, Z. Development of a Unified Reversed-Phase HPLC Method for Efficient Determination of EP and USP Process-Related Impurities in Celecoxib Using Analytical Quality by Design Principles. Molecules 2020, 25, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlandini, S.; Pasquini, B.; del Bubba, M.; Pinzauti, S.; Furlanetto, S. Quality by Design in the Chiral Separation Strategy for the Determination of Enantiomeric Impurities: Development of a Capillary Electrophoresis Method Based on Dual Cyclodextrin Systems for the Analysis of Levosulpiride. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1380, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frederick, G.; Vogt, A.S.K. Development of Quality-By-Design Analytical Methods. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 101, 2271–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basso, J.; Mendes, M.; Cova, T.F.G.G.; Sousa, J.J.; Pais, A.A.C.C.; Vitorino, C. Analytical Quality by Design (AQbD) as a Multiaddressable Platform for Co-Encapsulating Drug Assays. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 5659–5671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Council for Harmonisation Guideline on Q14 Analytical Procedure Development Draft Version 2022. Available online: https://database.ich.org/sites/default/files/ICH_Q14_Document_Step2_Guideline_2022_0324.pdf (accessed on 3 May 2022).
- Elder, D.P.; White, A.; Harvey, J.; Teasdale, A.; Williams, R.; Covey-Crump, E. Mutagenic Impurities: Precompetitive/Competitive Collaborative and Data Sharing Initiatives. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2015, 19, 1476–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amberg, A.; Beilke, L.; Bercu, J.; Bower, D.; Brigo, A.; Cross, K.P.; Custer, L.; Dobo, K.; Dowdy, E.; Ford, K.A.; et al. Principles and Procedures for Implementation of ICH M7 Recommended (Q)SAR Analyses. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 77, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- International Council for Harmonisation Guideline on Q2 (R2) Validation of Analytical Procedures: Draft Version 24 March 2022. Available online: ICH_Q2-R2_Document_Step2_Guideline_2022_0324.pdf (accessed on 10 August 2022).
- Lhasa Website. Available online: https://www.lhasalimited.org (accessed on 20 July 2022).
- Vega Hub Website. Available online: https://www.vegahub.eu (accessed on 20 May 2022).
- S-Matrix Website. Available online: https://www.smatrix.com (accessed on 20 July 2022).




| Name | Derek Prediction | Sarah Prediction | Vega Prediction | Overall In Silico * | ICH M7 Class * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSA | Negative | Negative | Negative | Negative | Class 5 |
| MCS | Positive | Negative | Negative | Positive | Class 3 |
| ECS | Positive | Equivocal | Positive | Positive | Class 3 |
| ICS | Positive | Positive | Positive | Positive | Class 3 |
| Run | Flow Rate (mL/min) | Oven Temp (°C) | Inlet Temp (°C) | Detector Temp (°C) | Inject Vol (µL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.5 | 170 | 340 | 330 | 2.2 |
| 2 | 1.5 | 230 | 340 | 330 | 1.8 |
| 3 | 1.5 | 170 | 180 | 330 | 1.8 |
| 4 | 2.5 | 170 | 340 | 270 | 2.2 |
| 5 | 2.5 | 170 | 180 | 330 | 2.2 |
| 6 | 2.5 | 170 | 180 | 270 | 1.8 |
| 7 | 2.5 | 230 | 180 | 330 | 1.8 |
| 8 | 2.5 | 230 | 340 | 270 | 1.8 |
| 9 | 2.0 | 200 | 280 | 300 | 2.0 |
| 10 | 2.0 | 200 | 280 | 300 | 2.0 |
| 11 | 2.5 | 230 | 340 | 330 | 2.2 |
| 12 | 1.5 | 230 | 340 | 270 | 2.2 |
| 13 | 2.5 | 230 | 180 | 270 | 2.2 |
| 14 | 1.5 | 230 | 180 | 270 | 1.8 |
| 15 | 1.5 | 230 | 180 | 330 | 2.2 |
| 16 | 2.0 | 200 | 280 | 300 | 2.0 |
| 17 | 1.5 | 170 | 340 | 270 | 1.8 |
| 18 | 1.5 | 170 | 180 | 270 | 2.2 |
| 19 | 2.5 | 170 | 340 | 330 | 1.8 |
| Run | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.06 | 1.75 | 0.46 | 14.34 | 6.74 |
| 2 | 4.15 | 4.26 | 0.59 | 4.28 | 1.98 |
| 3 | 1.57 | 1.32 | 1.14 | 14.08 | 6.61 |
| 4 | 2.75 | 2.25 | 0.83 | 13.46 | 6.19 |
| 5 | 2.72 | 2.19 | 2.00 | 12.92 | 5.95 |
| 6 | 2.32 | 1.89 | 1.68 | 13.31 | 6.21 |
| 7 | 5.28 | 5.39 | 3.57 | 3.93 | 1.97 |
| 8 | 5.43 | 5.67 | 1.37 | 4.05 | 1.94 |
| 9 | 4.20 | 3.93 | 3.09 | 8.08 | 3.94 |
| 10 | 4.23 | 3.96 | 3.14 | 8.15 | 3.97 |
| 11 | 6.39 | 6.60 | 1.64 | 3.91 | 1.87 |
| 12 | 4.48 | 4.67 | 0.65 | 4.03 | 1.84 |
| 13 | 5.89 | 5.90 | 3.85 | 3.73 | 1.87 |
| 14 | 3.60 | 3.72 | 2.01 | 4.05 | 2.02 |
| 15 | 4.45 | 4.60 | 2.47 | 4.04 | 2.02 |
| 16 | 4.27 | 4.00 | 3.12 | 8.28 | 4.03 |
| 17 | 1.68 | 1.40 | 0.38 | 14.61 | 6.85 |
| 18 | 1.92 | 1.65 | 1.42 | 14.04 | 6.65 |
| 19 | 2.28 | 1.84 | 0.72 | 13.56 | 6.20 |
| R2 | Adj. R2 | Sum of Squares | Degree of Freedom | Mean Square | F-Ratio | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCS | Height | 0.9995 | 0.9987 | 38.8914 | 10 | 3.8891 | 1334 | <0.0001 |
| ECS | Height | 0.9998 | 0.9995 | 51.1069 | 10 | 5.1107 | 3658 | <0.0001 |
| Resolution | 0.9999 | 0.9998 | 385.4958 | 7 | 55.0708 | 15098 | <0.0001 | |
| ICS | Height | 0.9999 | 0.9997 | 14.8934 | 12 | 1.2411 | 3349 | <0.0001 |
| Resolution | 0.9997 | 0.9995 | 81.2602 | 6 | 13.5434 | 5475.8411 | <0.0001 |
| Run | Flow Rate (mL/min) | Oven Temp (°C) | Inlet Temp (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 220 | 280 |
| 2 | 2 | 200 | 300 |
| 3 | 2.2 | 220 | 300 |
| 4 | 1.8 | 180 | 300 |
| 5 | 1.8 | 200 | 280 |
| 6 | 2.2 | 180 | 260 |
| 7 | 2 | 200 | 260 |
| 8 | 2 | 180 | 280 |
| 9 | 1.8 | 220 | 300 |
| 10 | 2 | 200 | 280 |
| 11 | 2 | 200 | 280 |
| 12 | 2 | 200 | 280 |
| 13 | 2.2 | 180 | 300 |
| 14 | 1.8 | 220 | 260 |
| 15 | 2.2 | 200 | 280 |
| 16 | 2.2 | 220 | 260 |
| 17 | 1.8 | 180 | 260 |
| Run | R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3.22 | 4.11 | 2.68 | 4.91 | 2.43 | 2.95 |
| 2 | 2.74 | 3.35 | 2.23 | 8.21 | 3.96 | 4.60 |
| 3 | 3.53 | 4.58 | 2.67 | 5.16 | 2.53 | 2.75 |
| 4 | 1.75 | 1.98 | 3.19 | 12.32 | 4.92 | 8.46 |
| 5 | 2.46 | 3.04 | 2.06 | 8.37 | 4.04 | 4.96 |
| 6 | 1.99 | 2.24 | 1.68 | 11.81 | 5.50 | 7.58 |
| 7 | 2.69 | 3.31 | 2.43 | 8.47 | 4.09 | 4.61 |
| 8 | 1.84 | 2.12 | 2.04 | 12.09 | 6.36 | 8.10 |
| 9 | 3.09 | 4.03 | 2.07 | 5.46 | 2.65 | 3.17 |
| 10 | 2.60 | 3.21 | 2.15 | 8.27 | 4.00 | 4.60 |
| 11 | 2.75 | 3.34 | 2.25 | 8.60 | 4.11 | 4.60 |
| 12 | 2.69 | 3.28 | 2.29 | 8.36 | 4.10 | 4.60 |
| 13 | 1.98 | 2.25 | 1.46 | 12.01 | 5.54 | 7.57 |
| 14 | 2.90 | 3.74 | 2.18 | 5.22 | 2.58 | 3.17 |
| 15 | 2.71 | 3.24 | 2.38 | 8.05 | 3.86 | 4.03 |
| 16 | 3.73 | 4.70 | 3.23 | 5.55 | 2.72 | 2.76 |
| 17 | 1.74 | 1.97 | 3.94 | 12.23 | 4.84 | 8.46 |
| R2 | Adj. R2 | Sum of Squares | Degree of Freedom | Mean Square | F-Ratio | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | 0.9954 | 0.9908 | 5.7025 | 8 | 0.7128 | 215 | <0.0001 |
| R2 | 0.9934 | 0.9868 | 11.9727 | 8 | 1.4966 | 150 | <0.0001 |
| R3 | 0.9923 | 0.9824 | 5.7238 | 9 | 0.636 | 100 | <0.0001 |
| R4 | 0.9943 | 0.9935 | 117.0834 | 2 | 58.5417 | 1,224 | <0.0001 |
| R5 | 0.9971 | 0.9948 | 23.4002 | 7 | 3.3429 | 434 | <0.0001 |
| R6 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 9076.33 | 8 | 1,134.54 | 672,190 | <0.0001 |
| Present Amount in API (P) | Theoretical Spiked Amount (T) | Actual Detection Amount (A) | Recovery(%) ((A − P) /T × 100) | Precision (%RSD) | Effect of API | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FID | MCS | 0 ppm | 120 ppm | 120.5 ppm | 100.4% | ||
| 122.1 ppm | 101.8% | 0.76% | None | ||||
| 122.1 ppm | 101.8% | ||||||
| 0 ppm | 150 ppm | 152.4 ppm | 101.6% | 2.11% | None | ||
| 152.5 ppm | 101.7% | ||||||
| 146.9 ppm | 97.9% | ||||||
| 0 ppm | 180 ppm | 179.4 ppm | 99.7% | ||||
| 179.7 ppm | 99.8% | 0.73% | None | ||||
| 177.3 ppm | 98.5% | ||||||
| ECS | 123.5 ppm | 102.9% | |||||
| 0 ppm | 120 ppm | 118.6 ppm | 98.8% | 2.06% | None | ||
| 120.4 ppm | 100.3% | ||||||
| 0 ppm | 150 ppm | 150.5 ppm | 100.4% | 2.10% | None | ||
| 152.6 ppm | 101.7% | ||||||
| 146.4 ppm | 97.6% | ||||||
| 177.9 ppm | 98.9% | ||||||
| 0 ppm | 180 ppm | 179.9 ppm | 99.9% | 1.17% | None | ||
| 175.7 ppm | 97.6% | ||||||
| ICS | 122.6 ppm | 102.2% | |||||
| 0 ppm | 120 ppm | 121.6 ppm | 101.4% | 1.11% | None | ||
| 120.0 ppm | 100.0% | ||||||
| 0 ppm | 150 ppm | 155.7 ppm | 103.8% | 0.64% | None | ||
| 153.7 ppm | 102.5% | ||||||
| 154.8 ppm | 103.2% | ||||||
| 186.9 ppm | 103.8% | ||||||
| 0 ppm | 180 ppm | 18.3 ppm | 101.8% | 0.96% | None | ||
| 185.3 ppm | 102.9% | ||||||
| MS | 114.5 ppm | 95.4% | |||||
| 0 ppm | 120 ppm | 110.1 ppm | 91.8% | 4.06% | None | ||
| 105.5 ppm | 87.9% | ||||||
| MCS | 0 ppm | 150 ppm | 135.8 ppm | 90.5% | 0.83% | None | |
| 134.8 ppm | 89.9% | ||||||
| 133.6 ppm | 89.1% | ||||||
| 168.2 ppm | 93.5% | ||||||
| 0 ppm | 180 ppm | 167.0 ppm | 92.8% | 0.35% | None | ||
| 167.6 ppm | 93.1% | ||||||
| 117.0 ppm | 97.5% | ||||||
| 0 ppm | 120 ppm | 111.0 ppm | 92.5% | 4.94% | None | ||
| 106.0 ppm | 88.3% | ||||||
| ECS | 0 ppm | 150 ppm | 135.4 ppm | 90.3% | 0.93% | None | |
| 133.9 ppm | 89.3% | ||||||
| 132.9 ppm | 88.6% | ||||||
| 167.2 ppm | 92.9% | ||||||
| 0 ppm | 180 ppm | 166.0 ppm | 92.2% | 0.36% | None | ||
| 166.3 ppm | 92.4% | ||||||
| 139.9 ppm | 116.6% | ||||||
| 0 ppm | 120 ppm | 132.6 ppm | 110.5% | 5.79% | None | ||
| 124.6 ppm | 103.8% | ||||||
| ICS | 0 ppm | 150 ppm | 153.3 ppm | 102.2% | 2.47% | None | |
| 149.7 ppm | 99.8% | ||||||
| 145.9 ppm | 97.3% | ||||||
| 178.2 ppm | 99.0% | ||||||
| 0 ppm | 180 ppm | 174.8 ppm | 97.1% | 1.35% | None | ||
| 173.6 ppm | 96.5% |
| Validation Parameters | FID | MS | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCS | ECS | ICS | MCS | ECS | ICS | ||
| DL QL | DL | 1.5 ppm | 1.5 ppm | 1.9 ppm | 0.055 ppm | 0.069 ppm | 0.102 ppm |
| QL | 4.9 ppm | 5.1 ppm | 6.4 ppm | 0.185 ppm | 0.232 ppm | 0.340 ppm | |
| Linearity | R2 | 0.99953 | 0.99988 | 0.99983 | 0.99532 | 0.99412 | 0.99370 |
| Slope | 0.00501 | 0.00544 | 0.00494 | 0.00534 | 0.00547 | 0.00391 | |
| Y-intercept | 0.01200 | 0.00192 | 0.01838 | 0.07947 | 0.09033 | 0.06289 | |
| Accuracy | Low conc. (10 ppm) | 95.3% | 102.6% | 96.4% | 94.5% | 94.9% | 93.9% |
| Mid conc. (120 ppm) | 101.3% | 100.7% | 101.2% | 91.7% | 92.8% | 110.3% | |
| Mid conc. (150 ppm) | 100.4% | 99.9% | 103.2% | 89.8% | 89.4% | 99.8% | |
| High conc. (180 ppm) | 99.3% | 98.8% | 102.9% | 93.1% | 92.5% | 97.5% | |
| Precision Acceptance criteria (%RSD ≤ 10) | Low conc. (10 ppm) | 1.14% | 2.50% | 5.58% | 3.16% | 4.92% | 1.73% |
| Low conc. (30 ppm) | 7.79% | 6.97% | 6.64% | 3.14% | 3.36% | 2.49% | |
| Mid conc. (150 ppm) | 2.27% | 3.22% | 8.83% | 2.16% | 2.21% | 2.47% | |
| Specificity | Resolution | 9.51 | 4.53 | 10.21 | 4.78 | ||
| Condition | Parameter | FID | MS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCS | ECS | ICS | MCS | ECS | ICS | ||
| 1 | Precision (%RSD) | 2.27% | 3.22% | 8.83% | 2.16% | 2.21% | 2.47% |
| Precision (SDV) | 0.01558 | 0.02304 | 0.05539 | 0.01652 | 0.01706 | 0.01348 | |
| Resolution | 9.51 | 4.53 | 10.21 | 4.78 | |||
| Tailing factor | 0.90 | 0.91 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 1.00 | 0.95 | |
| 2 | Precision (%RSD) | 2.07% | 1.20% | 2.73% | 0.97% | 1.16% | 1.40% |
| Precision (SDV) | 0.01410 | 0.00855 | 0.01604 | 0.00733 | 0.00893 | 0.00804 | |
| Resolution | 9.07 | 4.43 | 9.97 | 4.66 | |||
| Tailing factor | 0.88 | 0.90 | 1.00 | 0.96 | 0.97 | 0.97 | |
| 3 | Precision (%RSD) | 1.84% | 1.63% | 9.06% | 3.03% | 3.49% | 3.83% |
| Precision (SDV) | 0.01249 | 0.01153 | 0.05802 | 0.02195 | 0.02570 | 0.02168 | |
| Resolution | 9.12 | 4.33 | 9.59 | 4.49 | |||
| Tailing factor | 0.87 | 0.94 | 1.02 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.99 | |
| 4 | Precision (%RSD) | 2.27% | 1.28% | 1.29% | 2.16% | 2.70% | 2.38% |
| Precision (SDV) | 0.01526 | 0.00909 | 0.00827 | 0.01635 | 0.02080 | 0.01496 | |
| Resolution | 10.03 | 4.68 | 10.56 | 4.93 | |||
| Tailing factor | 0.90 | 0.93 | 1.04 | 1.02 | 1.00 | 0.94 | |
| 5 | Precision (%RSD) | 1.24% | 0.96% | 1.68% | 2.91% | 3.49% | 3.86% |
| Precision (SDV) | 0.00833 | 0.00677 | 0.01120 | 0.02184 | 0.02707 | 0.02405 | |
| Resolution | 7.90 | 3.80 | 8.85 | 4.15 | |||
| Tailing factor | 0.85 | 0.90 | 0.97 | 0.90 | 0.97 | 0.95 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, K.; Yoo, W.; Jeong, J.H. Determination of Three Alkyl Camphorsulfonates as Potential Genotoxic Impurities Using GC-FID and GC-MS by Analytical QbD. Separations 2022, 9, 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9090246
Lee K, Yoo W, Jeong JH. Determination of Three Alkyl Camphorsulfonates as Potential Genotoxic Impurities Using GC-FID and GC-MS by Analytical QbD. Separations. 2022; 9(9):246. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9090246
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Kyoungmin, Wokchul Yoo, and Jin Hyun Jeong. 2022. "Determination of Three Alkyl Camphorsulfonates as Potential Genotoxic Impurities Using GC-FID and GC-MS by Analytical QbD" Separations 9, no. 9: 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9090246
APA StyleLee, K., Yoo, W., & Jeong, J. H. (2022). Determination of Three Alkyl Camphorsulfonates as Potential Genotoxic Impurities Using GC-FID and GC-MS by Analytical QbD. Separations, 9(9), 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9090246







