Green Assessment of Chromatographic Methods Used for the Analysis of Four Methamphetamine Combinations with Commonly Abused Drugs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Methamphetamine and Captagon
3.2. Methamphetamine and Cannabis/Cannabinoids
3.3. Methamphetamine and Tramadol
3.4. Methamphetamine and Heroin
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zou, Z.; Wang, H.; Uquillas, F.D.; Wang, X.; Ding, J.; Chen, H. Definition of Substance and Non-substance Addiction. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 1010, 21–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, S.P.; Meisner, J.R.; Stewart, S.H. What constitutes prescription drug misuse? Problems and pitfalls of current conceptualizations. Curr. Drug Abus. Rev. 2008, 1, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saquib, N.; Rajab, A.M.; Saquib, J.; Almazrou, A. Substance use disorders in Saudi Arabia: A scoping review. Subst. Abus. Treat. Prev. Policy 2020, 15, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brackins, T.; Brahm, N.C.; Kissack, J.C.; Weber, S.S.; Biglow, M. Treatments for Methamphetamine Abuse. J. Pharm. Pract. 2011, 24, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Asmari, A.I. Methamphetamine-related postmortem cases in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Forensic Sci. Int. 2021, 321, 110746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabbagh, R.; Rawson, R. Captagon Use in Saudi Arabia: What Do We Know? Int. Addict. Rev. 2019, 2, 22–30. [Google Scholar]
- Alahmadi, T. Increased captagon tablets seizures in saudi arabia. Tech. Rom. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2020, 2, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rook, E.J.; Van Ree, J.M.; Brink, W.V.D.; Hillebrand, M.J.X.; Huitema, A.D.R.; Hendriks, V.M.; Beijnen, J.H. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of High Doses of Pharmaceutically Prepared Heroin, by Intravenous or by Inhalation Route in Opioid-Dependent Patients. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2006, 98, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A.; Shawoosh, M. Heroin Addiction in Saudi Arabia—Not Merely a Behavioural Problem. Ann. Saudi Med. 2003, 23, 419–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grond, S.; Sablotzki, A. Clinical Pharmacology of Tramadol. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2004, 43, 879–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassiony, M.M.; Youssef, U.M.; Hassan, M.S.; El-Deen, G.M.S.; El-Gohari, H.; Abdelghani, M.; Abdalla, A.; Ibrahim, D.H. Cognitive Impairment and Tramadol Dependence. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2017, 37, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, C.H. Pharmacology and effects of cannabis: A brief review. Br. J. Psychiatry 2001, 178, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abomughaid, M.; Mohamed, E.; Tayrab, A.; Alghamdi, A. Prevalence of Cannabis and Amphetamine in Aseer Region, Saudi Arabia: A Retrospective Study. Available online: https://www.iomcworld.org/articles/prevalence-of-cannabis-and-amphetamine-in-aseer-region-saudi-arabia-a-retrospective-study.pdf (accessed on 20 May 2022).
- Gałuszka, A.; Migaszewski, Z.; Konieczka, P.; Namiesnik, J. Analytical Eco-Scale for assessing the greenness of analytical procedures. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 37, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Płotka-Wasylka, J.; Namieśnik, J. Green Analytical Chemistry. In Green Chemistry and Sustainable Technology (GCST); Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacek Namieśnik, J. Green analytical chemistry—Some remarks. J. Sep. Sci. 2001, 24, 151–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamal, M.; Naguib, I.A.; Panda, D.S.; Abdallah, F.F. Comparative study of four greenness assessment tools for selection of greenest analytical method for assay of hyoscine N-butyl bromide. Anal. Methods 2020, 13, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd-ElSalam, H.-A.H.; Gamal, M.; Naguib, I.A.; Al-Ghobashy, M.A.; Zaazaa, H.E.; Abdelkawy, M. Development of Green and Efficient Extraction Methods of Quercetin from Red Onion Scales Wastes Using Factorial Design for Method Optimization: A Comparative Study. Separations 2021, 8, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pena-Pereira, F.; Wojnowski, W.; Tobiszewski, M. AGREE—Analytical GREEnness Metric Approach and Software. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 10076–10082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolmonen, M.; Leinonen, A.; Pelander, A.; Ojanperä, I. A general screening method for doping agents in human urine by solid phase extraction and liquid chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 585, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, K. One-Step Derivatization-Extraction Method for Rapid Analysis of Eleven Amphetamines and Cathinones in Oral Fluid by GC–MS. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2017, 41, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, C.A.; Weinmann, W.; Dresen, S.; Schreiber, A.; Gergov, M. Development of a multi-target screening analysis for 301 drugs using a QTrap liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry system and automated library searching. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 19, 1332–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauk, V.; Lemr, K. Forensic applications of supercritical fluid chromatography—Mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2018, 1086, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busardò, F.P.; Gottardi, M.; Pacifici, R.; Varì, M.R.; Tini, A.; Volpe, A.R.; Giorgetti, R.; Pichini, S. Nails Analysis for Drugs Used in the Context of Chemsex: A Pilot Study*. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2019, 44, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heltsley, R.; DePriest, A.; Black, D.L.; Robert, T.; Marshall, L.; Meadors, V.M.; Caplan, Y.H.; Cone, E.J. Oral Fluid Drug Testing of Chronic Pain Patients. I. Positive Prevalence Rates of Licit and Illicit Drugs. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2011, 35, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shin, Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Cheong, J.C.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, J.-H.; Lee, H.S. Liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry for the determination of three cannabinoids, two (−)-trans-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol metabolites, and six amphetamine-type stimulants in human hair. J. Chromatogr. B 2020, 1149, 122157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaiano, F.; Busardò, F.P.; Palumbo, D.; Kyriakou, C.; Fioravanti, A.; Catalani, V.; Mari, F.; Bertol, E. A novel screening method for 64 new psychoactive substances and 5 amphetamines in blood by LC–MS/MS and application to real cases. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 129, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crifasi, J.A.; Bruder, M.F.; Long, C.W.; Janssen, K. Performance Evaluation of Thermal Desorption System (TDS) for Detection of Basic Drugs in Forensic Samples by GC-MS. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2006, 30, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ristimaa, J.; Gergov, M.; Pelander, A.; Halmesmäki, E.; Ojanperä, I. Broad-spectrum drug screening of meconium by liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry and time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 398, 925–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrin, G.L.; McCurdy, H.H.; Wall, W.H. Investigation of an LC-MS-MS (QTrap(R)) Method for the Rapid Screening and Identification of Drugs in Postmortem Toxicology Whole Blood Samples. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2005, 29, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kronstrand, R.; Forsman, M.; Roman, M. Quantitative analysis of drugs in hair by UHPLC high resolution mass spectrometry. Forensic Sci. Int. 2018, 283, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelander, A.; Ristimaa, J.; Rasanen, I.; Vuori, E.; Ojanperä, I. Screening for Basic Drugs in Hair of Drug Addicts by Liquid Chromatography/Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. Ther. Drug Monit. 2008, 30, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberson, Z.R.; Goodpaster, J.V. Optimization of the qualitative and quantitative analysis of cocaine and other drugs of abuse via gas chromatography—Vacuum ultraviolet spectrophotometry (GC—VUV). Talanta 2020, 222, 121461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, T.; Zhao, X.; Luo, G.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Yao, B.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, J.; Yu, Z. Comparison of microemulsion electrokinetic chromatography and solvent modified micellar electrokinetic chromatography on rapid separation of heroin, amphetamine and their basic impurities. Talanta 2007, 71, 854–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postigo, C.; de Alda, M.J.L.; Barceló, D. Fully Automated Determination in the Low Nanogram per Liter Level of Different Classes of Drugs of Abuse in Sewage Water by On-Line Solid-Phase Extraction-Liquid Chromatography−Electrospray-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 3123–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lurie, I.S. High-performance liquid chromatography of seized drugs at elevated pressure with 1.7μm hybrid C18 stationary phase columns. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1100, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.; Zhang, L.; Feng, Q.; Xia, S.; Chi, Y.; Tong, P.; Chen, G. Pressure-assisted capillary electrochromatography with electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry based on silica-based monolithic column for rapid analysis of narcotics. Electrophoresis 2008, 29, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aturki, Z.; D’Orazio, G.; Rocco, A.; Bortolotti, F.; Gottardo, R.; Tagliaro, F.; Fanali, S. CEC-ESI ion trap MS of multiple drugs of abuse. Electrophoresis 2010, 31, 1256–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, L.H.; Gron, L.U.; Young, J.L. Green Analytical Methodologies. ChemInform 2007, 38, 2695–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2021-01/documents/ry_2020_tri_chemical_list_0_0.pdf (accessed on 15 December 2021).

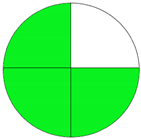
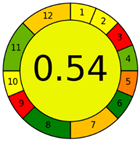
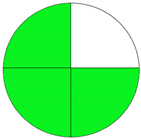
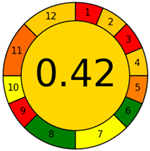
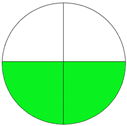
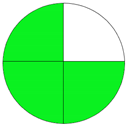
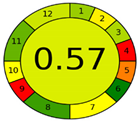
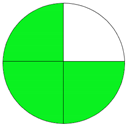
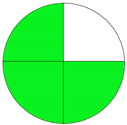
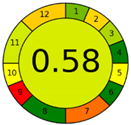
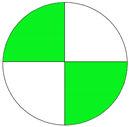
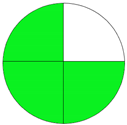
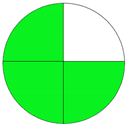
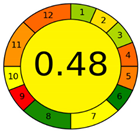
| Analytical Method | ESA [14] | NEMI Pictogram [39] | AGREE Pictogram [19] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Method 1.1 [20] | 69 | 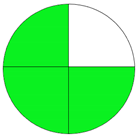 | 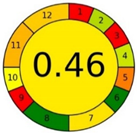 |
| Method 1.2 [21] | 79 | 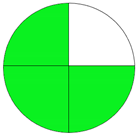 | 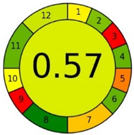 |
| Method 1.3 [22] | 51 |  | 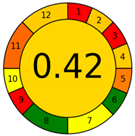 |
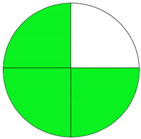
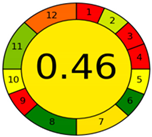
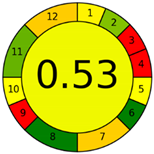
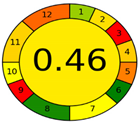
| Analytical Method | ESA [14] | NEMI Pictogram [39] | AGREE Pictogram [19] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Method 2.1 [20] | 69 | 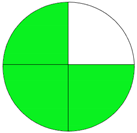 | 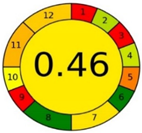 |
| Method 2.2 [23] | 70 |  |  |
| Method 2.3 [24] | 78 | 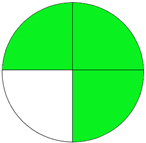 | 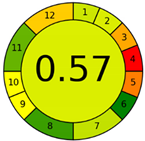 |
| Method 2.4 [25] | 69 | 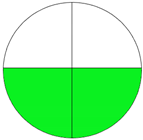 | 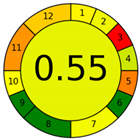 |
| Method 2.5 [26] | 70 | 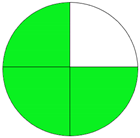 |  |
| Method 2.6 [27] | 74 | 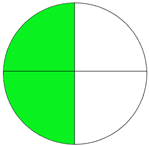 | 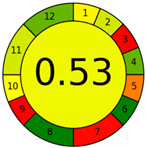 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alharthy, S.A.; Alharthi, M.A.; Almalki, S.A.; Alosaimi, S.H.; Aqeel, A.H.; Altowairqi, S.A.; Alsalahat, I.; Panda, D.S.; Alsheikh, M.Y.; Naguib, I.A. Green Assessment of Chromatographic Methods Used for the Analysis of Four Methamphetamine Combinations with Commonly Abused Drugs. Separations 2022, 9, 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9070156
Alharthy SA, Alharthi MA, Almalki SA, Alosaimi SH, Aqeel AH, Altowairqi SA, Alsalahat I, Panda DS, Alsheikh MY, Naguib IA. Green Assessment of Chromatographic Methods Used for the Analysis of Four Methamphetamine Combinations with Commonly Abused Drugs. Separations. 2022; 9(7):156. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9070156
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlharthy, Saif A., Muath A. Alharthi, Sultan A. Almalki, Sattam H. Alosaimi, Abdullah H. Aqeel, Sultan A. Altowairqi, Izzeddin Alsalahat, Dibya Sundar Panda, Mona Y. Alsheikh, and Ibrahim A. Naguib. 2022. "Green Assessment of Chromatographic Methods Used for the Analysis of Four Methamphetamine Combinations with Commonly Abused Drugs" Separations 9, no. 7: 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9070156
APA StyleAlharthy, S. A., Alharthi, M. A., Almalki, S. A., Alosaimi, S. H., Aqeel, A. H., Altowairqi, S. A., Alsalahat, I., Panda, D. S., Alsheikh, M. Y., & Naguib, I. A. (2022). Green Assessment of Chromatographic Methods Used for the Analysis of Four Methamphetamine Combinations with Commonly Abused Drugs. Separations, 9(7), 156. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9070156