Testing Thymol-Based DES for the Elimination of 11 Textile Dyes from Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of DES
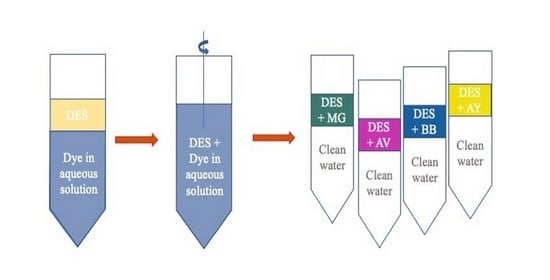
2.3. Liquid–Liquid Extraction Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. DES Formation and Characterization
3.2. Extraction Results
3.3. Influence of Aqueous:Organic Phase Ratio
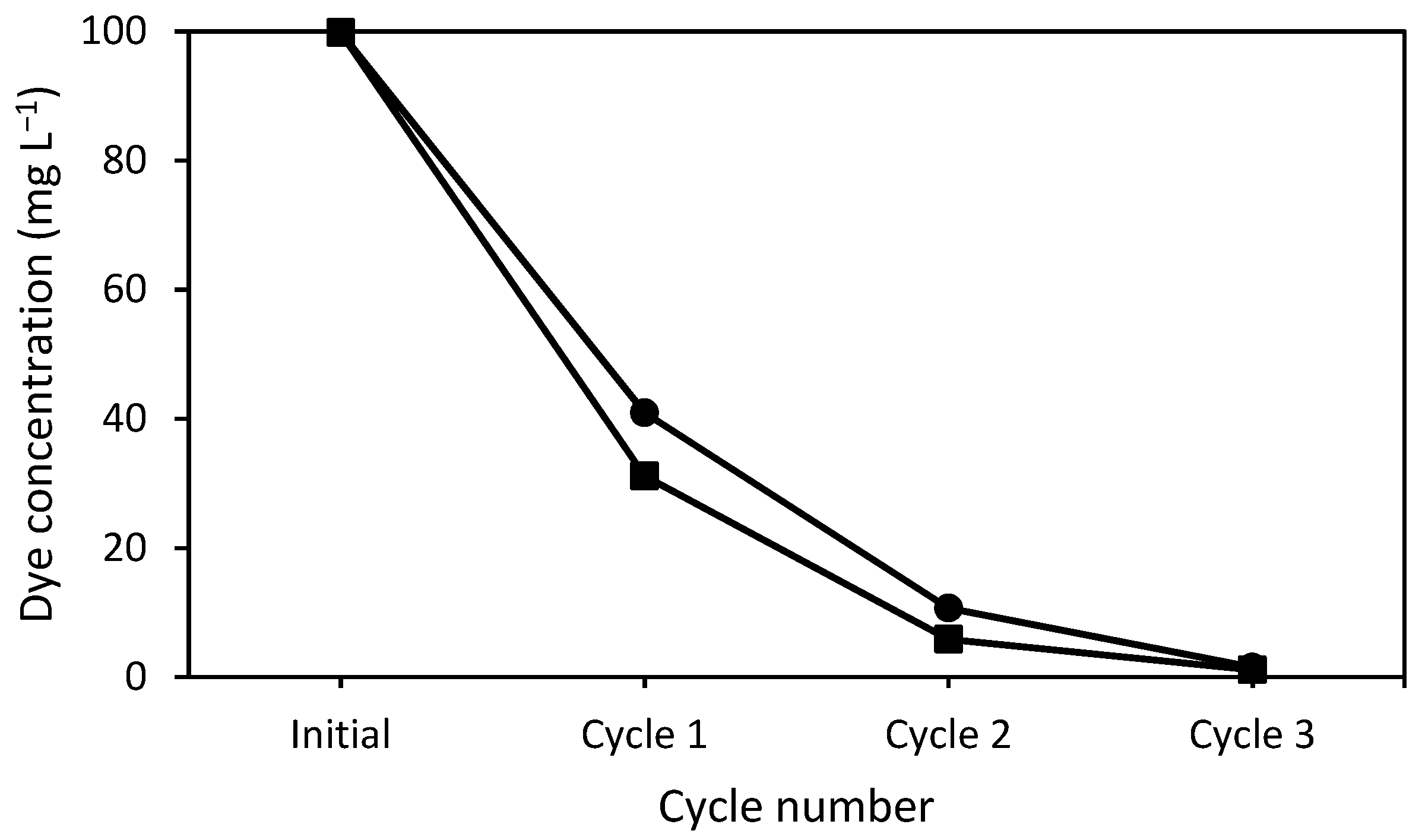
3.4. Number of Cycles
3.5. Comparison Study with Bibliographical Precedents
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Konsowa, A.H.; Abd El-Rahman, H.B.; Moustafa, M.A. Removal of azo dye acid orange 7 using aerobic membrane bioreactor. Alex. Eng. J. 2011, 50, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kaur, P.; Rajani, N.; Kumawat, P.; Singh, N.; Kushwaha, J.P. Performance and mechanism of dye extraction from aqueous solution using synthesized deep eutectic solvents. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 539, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuraman, G. Extractive removal of astacryl blue BG and astacryl golden yellow dyes from aqueous solutions by liquid-liquid extraction. Desalination 2011, 277, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcon, D.P.; Franco, F.C. All-fatty acid hydrophobic deep eutectic solvents towards a simple and efficient microextraction method of toxic industrial dyes. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 318, 114220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraghavan, R.; Vedaraman, N.; Surianarayanan, M.; MacFarlane, D.R. Extraction and recovery of azo dyes into an ionic liquid. Talanta 2006, 69, 1059–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shindhal, T.; Rakholiya, P.; Varjani, S.; Pandey, A.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Ng, H.Y.; Taherzadeh, M.J. A critical review on advances in the practices and perspectives for the treatment of dye industry wastewater. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal, I.A.; Dolla, T.H.; Pruessner, K.; Ndungu, P. Synthesis and characterization of deep eutectic solvent functionalized CNT/ZnCo2O4 nanostructure: Kinetics, isotherm and regenerative studies on Eosin Y adsorption. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 102877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Khalafy, S.H.; Hassanein, M.T.; Abd-Elal, M.F.; Atia, A.A. Oxidation of azo dye Orange II with hydrogen peroxide catalyzed by 5,10,15,20-tetrakis[4-(diethylmethylammonio)phenyl]porphyrinato-cobalt(II)tetraiodide in aqueous solution. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2020, 24, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovina, K.; Siddiquee, S.; Shaarani, S.M. Extraction, analytical and advanced methods for detection of Allura Red AC (E129) in food and beverages products. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.; Kong, C.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, J.; Li, W.; Li, D.; Cui, Z.; Xue, Y.; Lu, Y. Ultrasonic assisted electrochemical degradation of malachite green in wastewater. Microchem. J. 2021, 164, 106059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunelle, E.; Le, A.M.; Huynh, C.; Wingfield, K.; Halámková, L.; Agudelo, J.; Halámek, J. Coomassie Brilliant Blue G-250 Dye: An Application for Forensic Fingerprint Analysis. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 4314–4319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, J.; Wattoo, F.H.; Wattoo, M.H.S.; Malik, R.; Tirmizi, S.A.; Imran, M.; Ghangro, A.B. Adsorption of acid yellow dye on flakes of chitosan prepared from fishery wastes. Arab. J. Chem. 2011, 4, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Tappe, H.; Helmling, W.; Mischke, P.; Rebsamen, K.; Reiher, U.; Russ, W.L.; Schläfer, L.; Vermehren, P. Reactive Dyes. In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2005; ISBN 978-352-730-673-2. [Google Scholar]
- Hunger, K.; Mischke, P.; Rieper, W.; Zhang, S. Azo Dyes, 2. Anionic Dyes. In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2005; ISBN 978-352-730-673-2. [Google Scholar]
- Hunger, K.; Mischke, P.; Rieper, W.; Zhang, S. Azo Dyes, 3. Direct (Substantive) Dyes. In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2005; ISBN 978-352-730-673-2. [Google Scholar]
- Bien, H.-S.; Stawitz, J.; Wunderlich, K. Anthraquinone Dyes and Intermediates. In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2005; ISBN 978-352-730-673-2. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, M.A.R.; Crespo, E.A.; Pontes, P.V.A.; Silva, L.P.; Bülow, M.; Maximo, G.J.; Batista, E.A.C.; Held, C.; Pinho, S.P.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Tunable Hydrophobic Eutectic Solvents Based on Terpenes and Monocarboxylic Acids. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 8836–8846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Bruinhorst, A.; Raes, S.; Maesara, S.A.; Kroon, M.C.; Esteves, A.C.C.; Meuldijk, J. Hydrophobic eutectic mixtures as volatile fatty acid extractants. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 216, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sas, O.G.; Sánchez, P.B.; González, B.; Domínguez, Á. Removal of phenolic pollutants from wastewater streams using ionic liquids. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 236, 116310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, X.; Tang, S.; Yang, Y. Emulsification liquid–liquid micro-extraction based on natural deep eutectic solvent for (triarylmethane) dyes determination. Chem. Pap. 2020, 74, 3617–3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraji, M.; Adeli, M.; Noormohammadi, F. Deep eutectic solvent-based dispersive liquid-liquid micro-extraction for extraction of malachite green and crystal violet in water samples prior their determination using high performance liquid chromatography. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2020, 102, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, F.; Yilmaz, E.; Soylak, M. A simple and novel deep eutectic solvent based ultrasound-assisted emulsification liquid phase microextraction method for malachite green in farmed and ornamental aquarium fish water samples. Microchem. J. 2017, 132, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiq, A.C.; Olasupo, A.; Rahim, N.Y.; Ngah, W.S.W.; Suah, F.B.M. Comparative removal of malachite green dye from aqueous solution using deep eutectic solvents modified magnetic chitosan nanoparticles and modified protonated chitosan beads. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiq, A.C.; Rahim, N.Y.; Suah, F.B.M. Adsorption and desorption of malachite green by using chitosan-deep eutectic solvents beads. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 3965–3973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawal, I.A.; Klink, M.; Ndungu, P. Deep eutectic solvent as an efficient modifier of low-cost adsorbent for the removal of pharmaceuticals and dye. Environ. Res. 2019, 179, 108837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, L.Y.; Chin, D.Z.B.; Lee, X.J.; Chemmangattuvalappil, N.; Gan, S. Evaluation of Abelmoschus esculentus (lady’s finger) seed as a novel biosorbent for the removal of Acid Blue 113 dye from aqueous solutions. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2015, 94, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirzad-Siboni, M.; Jafari, S.J.; Giahi, O.; Kim, I.; Lee, S.M.; Yang, J.K. Removal of acid blue 113 and reactive black 5 dye from aqueous solutions by activated red mud. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 1432–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xing, L.; Liang, H.; Ren, J.; Ding, W.; Wang, Q.; Geng, Z.; Xu, C. Efficient removal of Remazol Brilliant Blue R from water by a cellulose-based activated carbon. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 207, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirajudheen, P.; Poovathumkuzhi, N.C.; Vigneshwaran, S.; Chelaveettil, B.M.; Meenakshi, S. Applications of chitin and chitosan based biomaterials for the adsorptive removal of textile dyes from water: A comprehensive review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 273, 118604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, J.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, J.; Jeong, J.Y.; Jegal, J. Treatment of dye aqueous solutions using nanofiltration polyamide composite membranes for the dye wastewater reuse. Dye Pigment. 2008, 76, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toumi, K.H.; Bergaoui, M.; Khalfaoui, M.; Benguerba, Y.; Erto, A.; Dotto, G.L.; Amrane, A.; Nacef, S.; Ernst, B. Computational study of acid blue 80 dye adsorption on low cost agricultural Algerian olive cake waste: Statistical mechanics and molecular dynamic simulations. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 271, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, P.Y.; Ma, G.; Lei, Z. Synergic adsorption of acid blue 80 and heavy metal ions (Cu2+/Ni2+) onto activated carbon and its mechanisms. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 27, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khehra, M.S.; Saini, H.S.; Sharma, D.K.; Chadha, B.S.; Chimni, S.S. Decolorization of various azo dyes by bacterial consortium. Dye Pigment. 2005, 67, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkas, T.R.; Ediati, R.; Ersam, T.; Purnomo, A.S. Reactive Black 5 decolorization using immobilized Brown-rot fungus Gloeophyllum trabeum. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 65, 2934–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Kumar Dangi, L.; Kumar, S.; Rani, R. Microbial decolorization of Reactive Black 5 dye by Bacillus albus DD1 isolated from textile water effluent: Kinetic, thermodynamics & decolorization mechanism. Helyon 2022, 8, e08834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pazarlioglu, N.K.; Urek, R.O.; Ergun, F. Biodecolourization of Direct Blue 15 by immobilized Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Process. Biochem. 2005, 40, 1923–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saroj, S.; Kumar, K.; Pareek, N.; Prasad, R.; Singh, R.P. Biodegradation of azo dyes Acid Red 183, Direct Blue 15 and Direct Red 75 by the isolate Penicillium oxalicum SAR-3. Chemosphere 2014, 107, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuo, R.; Fan, F. A comprehensive insight into the application of white rot fungi and their lignocellulolytic enzymes in the removal of organic pollutants. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, S.U.; Jadhav, M.U.; Kagalkar, A.N.; Govindwar, S.P. Decolorization of Brilliant Blue G dye mediated by degradation of the microbial consortium of Galactomyces geotrichum and Bacillus sp. J. Chin. Inst. Chem. Eng. 2008, 39, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khambhaty, Y.; Mody, K.; Basha, S. Efficient removal of Brilliant Blue G (BBG) from aqueous solutions by marine Aspergillus wentii: Kinetics, equilibrium and process design. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 41, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, A.; Deive, F.J.; Rodríguez, A.; Álvarez, M.S. Towards the use of eco-friendly solvents as adjuvants in remediation processes. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 305, 112824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escudero, N.; Deive, F.J.; Sanromán, M.A.; Álvarez, M.S.; Rodríguez, A. Design of eco-friendly aqueous two-phase systems for the efficient extraction of industrial finishing dyes. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 284, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrijević, A.; Jocić, A.; Zec, N.; Tot, A.; Papović, S.; Gadžurić, S.; Vranes, M.; Trtic-Petrovic, T. Improved single-step extraction performance of aqueous biphasic systems using novel symmetric ionic liquids for the decolorisation of toxic dye effluents. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 76, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
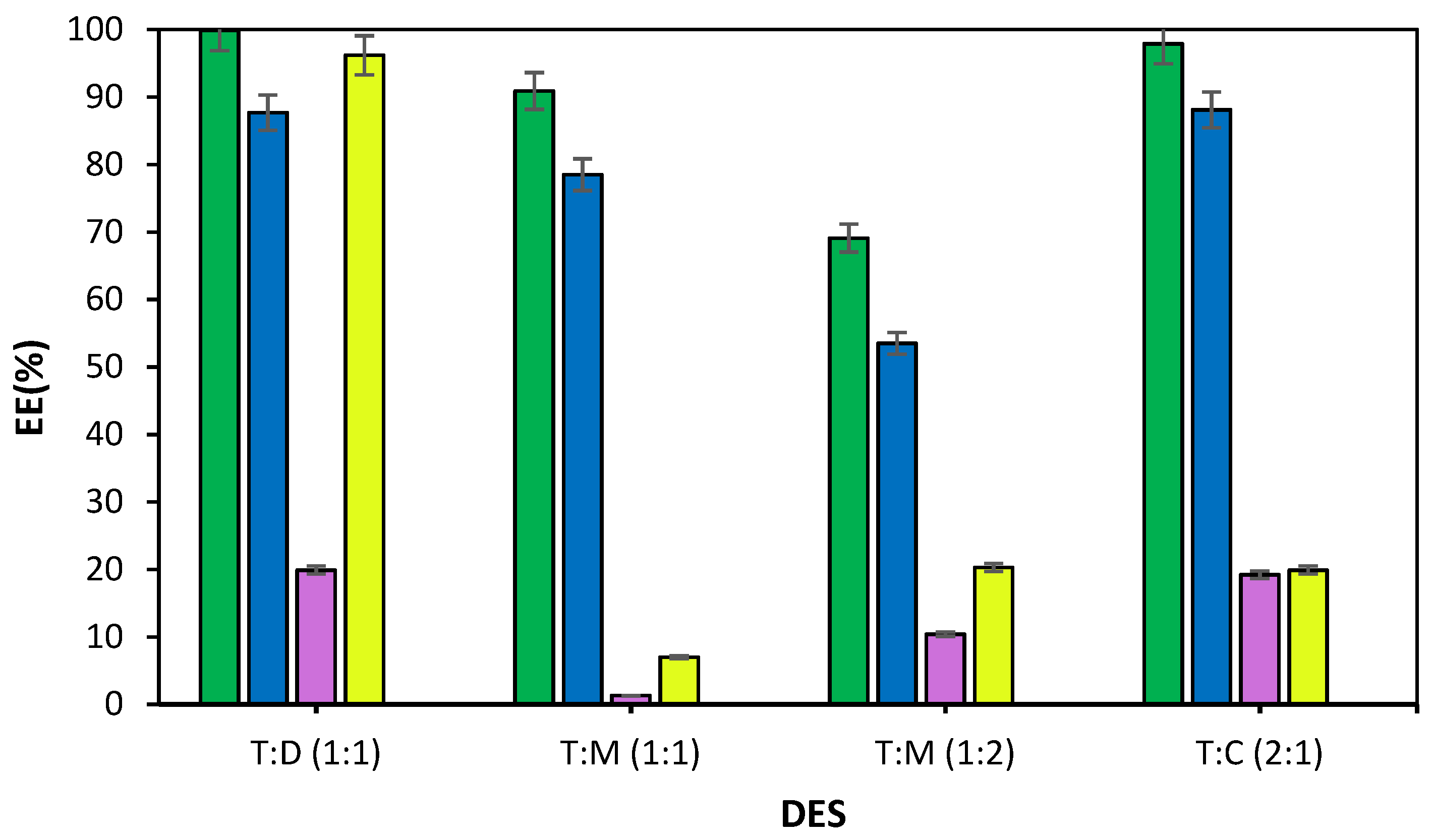
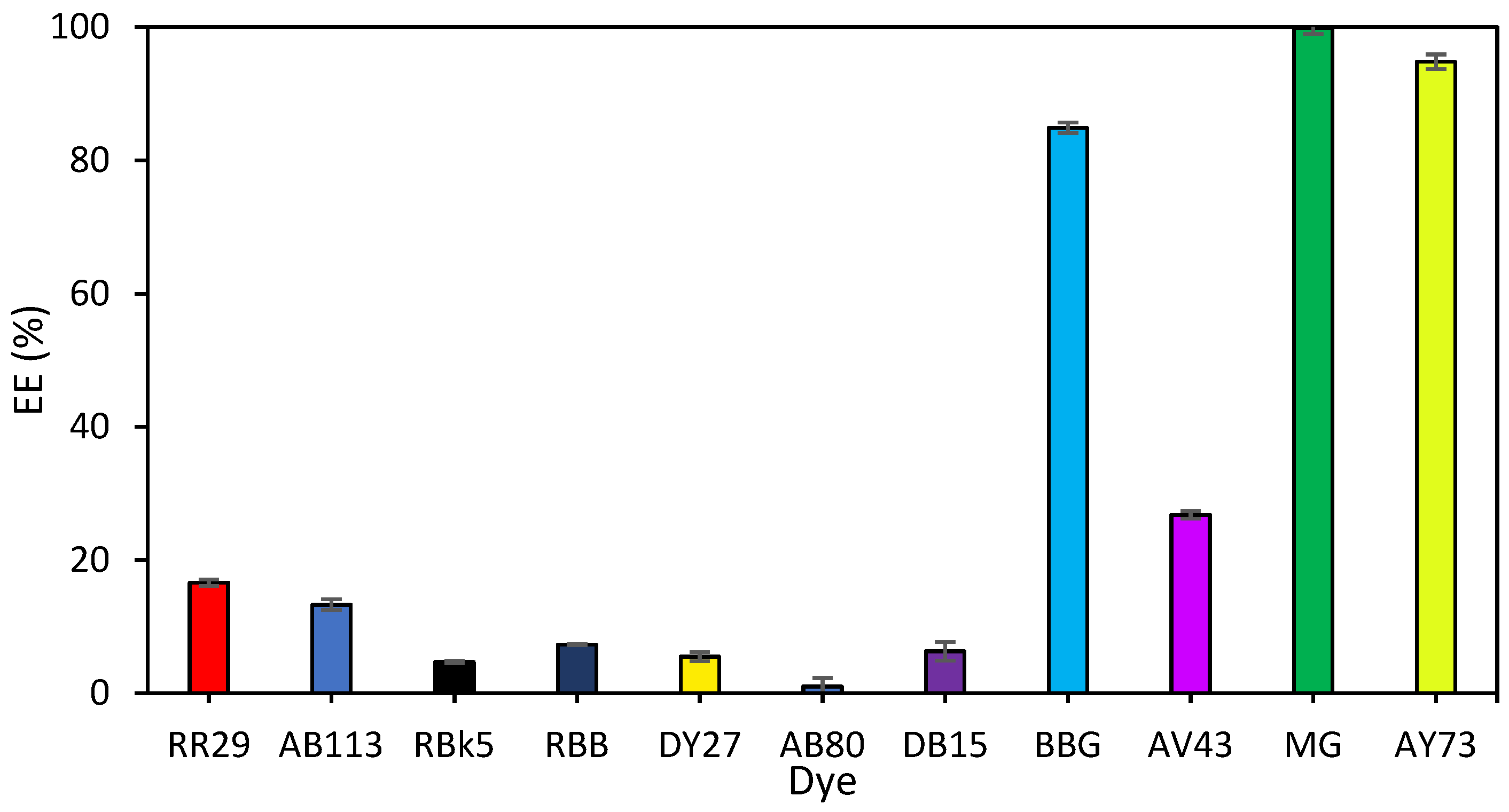
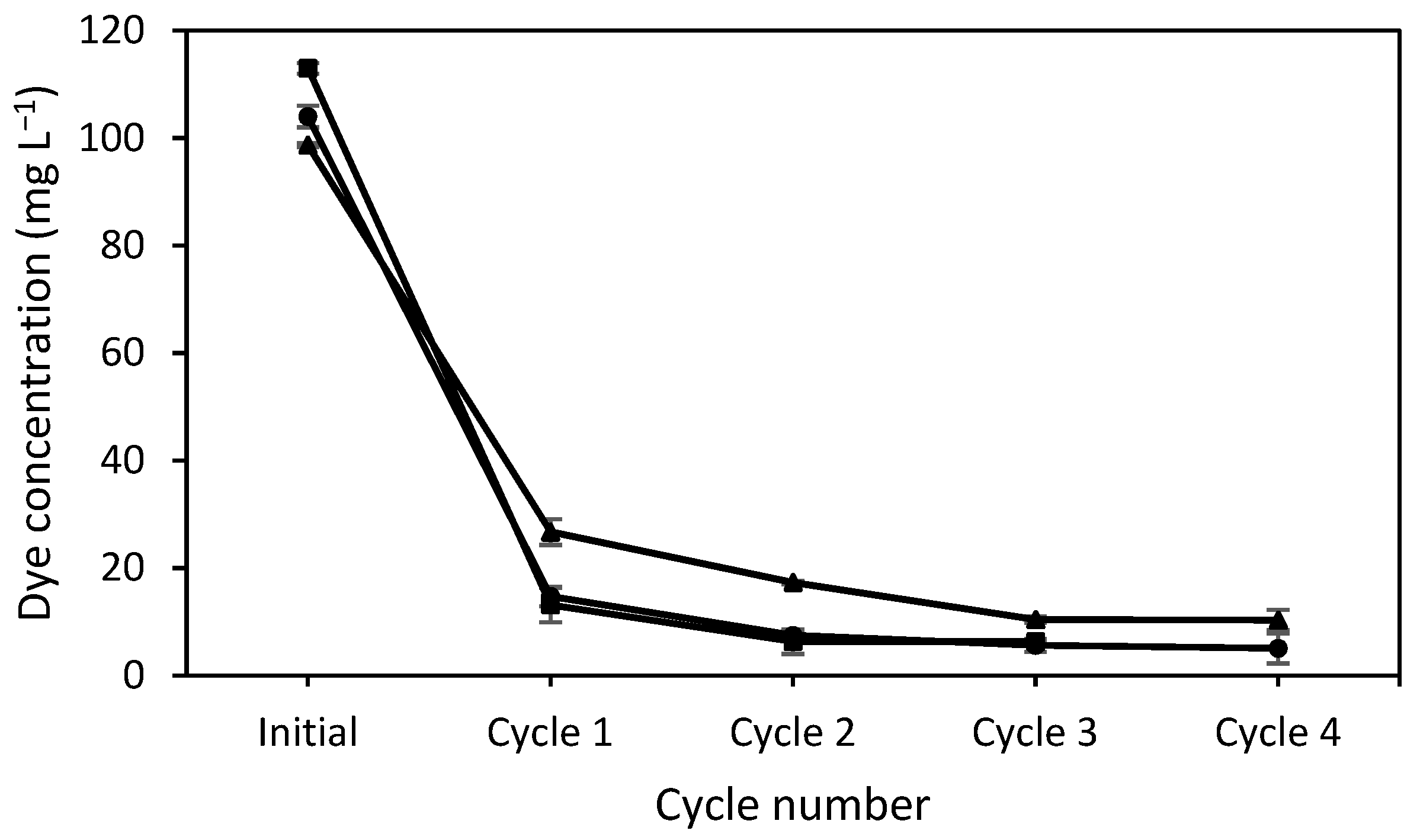
| DES | Ratio | T:D (1:1) | T:M (1:1) | T:M (1:2) | T:C (2:1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BBG | 1:1 | - | 72.9 | 62.8 | - |
| 2:1 | - | 84.6 | 56.2 | - | |
| 4:1 | - | 76.9 | 54.4 | - | |
| 5:1 | 87.7 | 78.5 | 53.5 | 84.2 | |
| AY73 | 1:1 | - | 39.9 | 95.2 | 67.5 |
| 2:1 | - | 22.9 | 63.6 | 40.9 | |
| 4:1 | - | 13.0 | 33.2 | 19.7 | |
| 5:1 | 94.3 | 7 | 20.3 | 19.9 | |
| MG | 1:1 | - | - | 84.9 | - |
| 2:1 | - | - | 77.7 | - | |
| 4:1 | - | - | 68.6 | - | |
| 5:1 | 99.9 | 89.3 | 70.0 | 99.6 | |
| AV43 | 1:1 | 68.8 | - | - | 59.0 |
| 2:1 | 41.8 | - | - | 35.8 | |
| 4:1 | 28.6 | - | - | 21.5 | |
| 5:1 | 19.9 | <3 | <3 | 19.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Villar, L.; Martínez-Rico, Ó.; Asla, A.; Domínguez, Á.; González, B. Testing Thymol-Based DES for the Elimination of 11 Textile Dyes from Water. Separations 2022, 9, 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9120442
Villar L, Martínez-Rico Ó, Asla A, Domínguez Á, González B. Testing Thymol-Based DES for the Elimination of 11 Textile Dyes from Water. Separations. 2022; 9(12):442. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9120442
Chicago/Turabian StyleVillar, Lorena, Óscar Martínez-Rico, Andrés Asla, Ángeles Domínguez, and Begoña González. 2022. "Testing Thymol-Based DES for the Elimination of 11 Textile Dyes from Water" Separations 9, no. 12: 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9120442
APA StyleVillar, L., Martínez-Rico, Ó., Asla, A., Domínguez, Á., & González, B. (2022). Testing Thymol-Based DES for the Elimination of 11 Textile Dyes from Water. Separations, 9(12), 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9120442