Target Discovery of Flavonoids from Elymus nutans Griseb Using Medium- and High-Pressure Liquid Chromatography Combined with Online High-Performance Liquid Chromatography–1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Apparatus and Reagents
2.2. Sample Preparation, DPPH Suppressor Identification, and Active Fraction Enrichment
2.3. Identification and Isolation of Potential DPPH Suppressors Based on High-Pressure Liquid Chromatography Separation
2.4. Purity and Activity Evaluation of the Extracted DPPH Suppressors
3. Results and Discussion
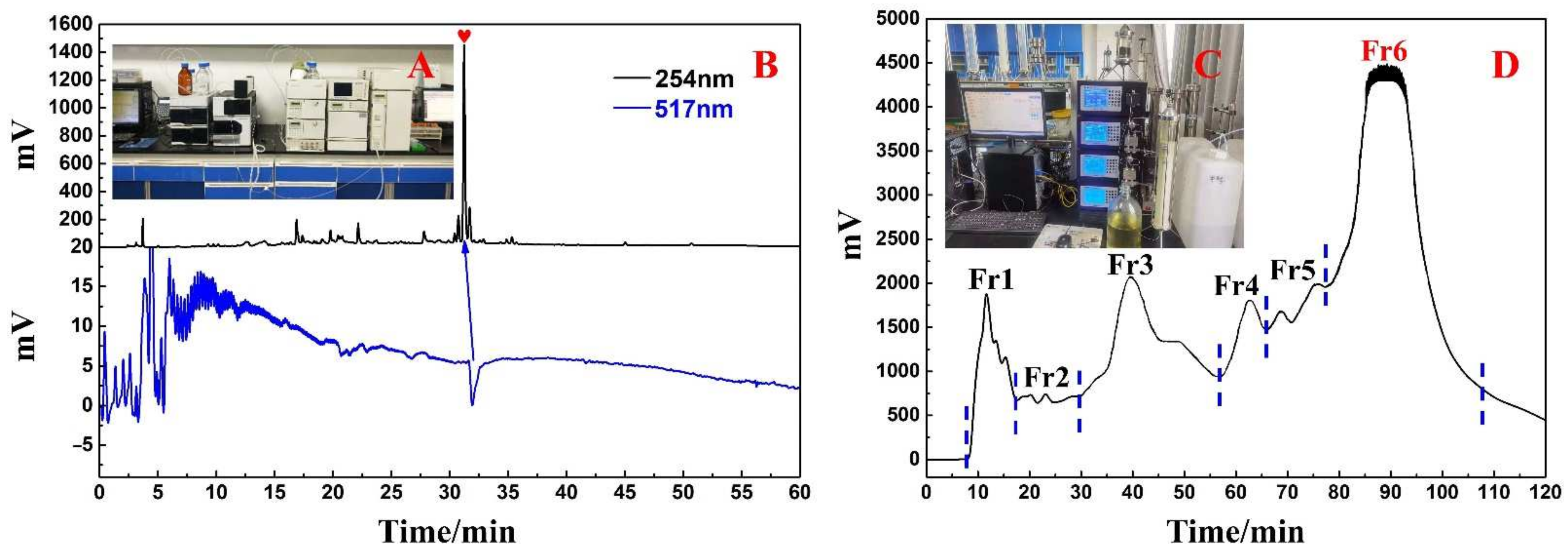
3.1. Sample Pretreatment, DPPH Suppressor Identification, and MCI GEL® CHP20P Medium Pressure Liquid Chromatography Enrichment
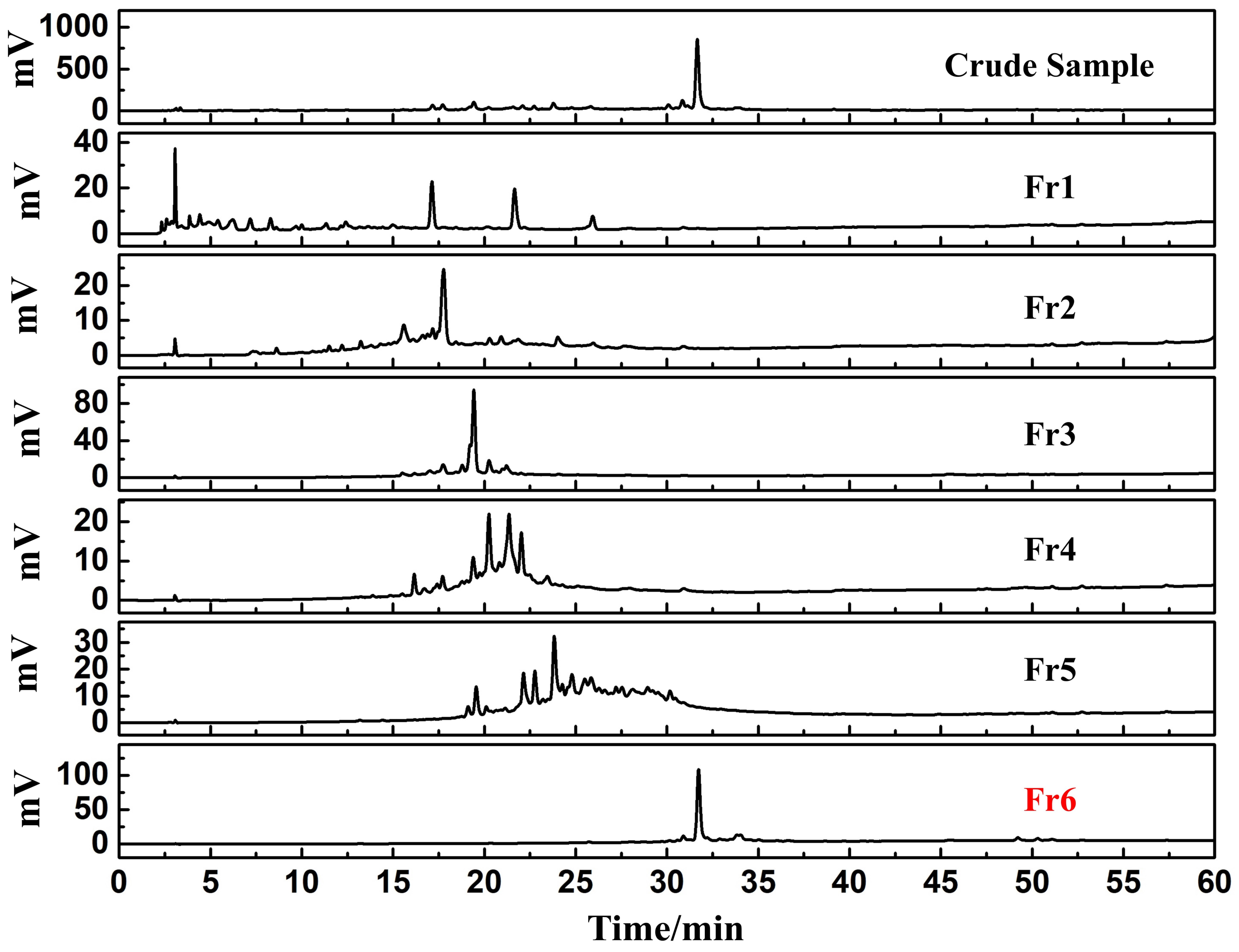
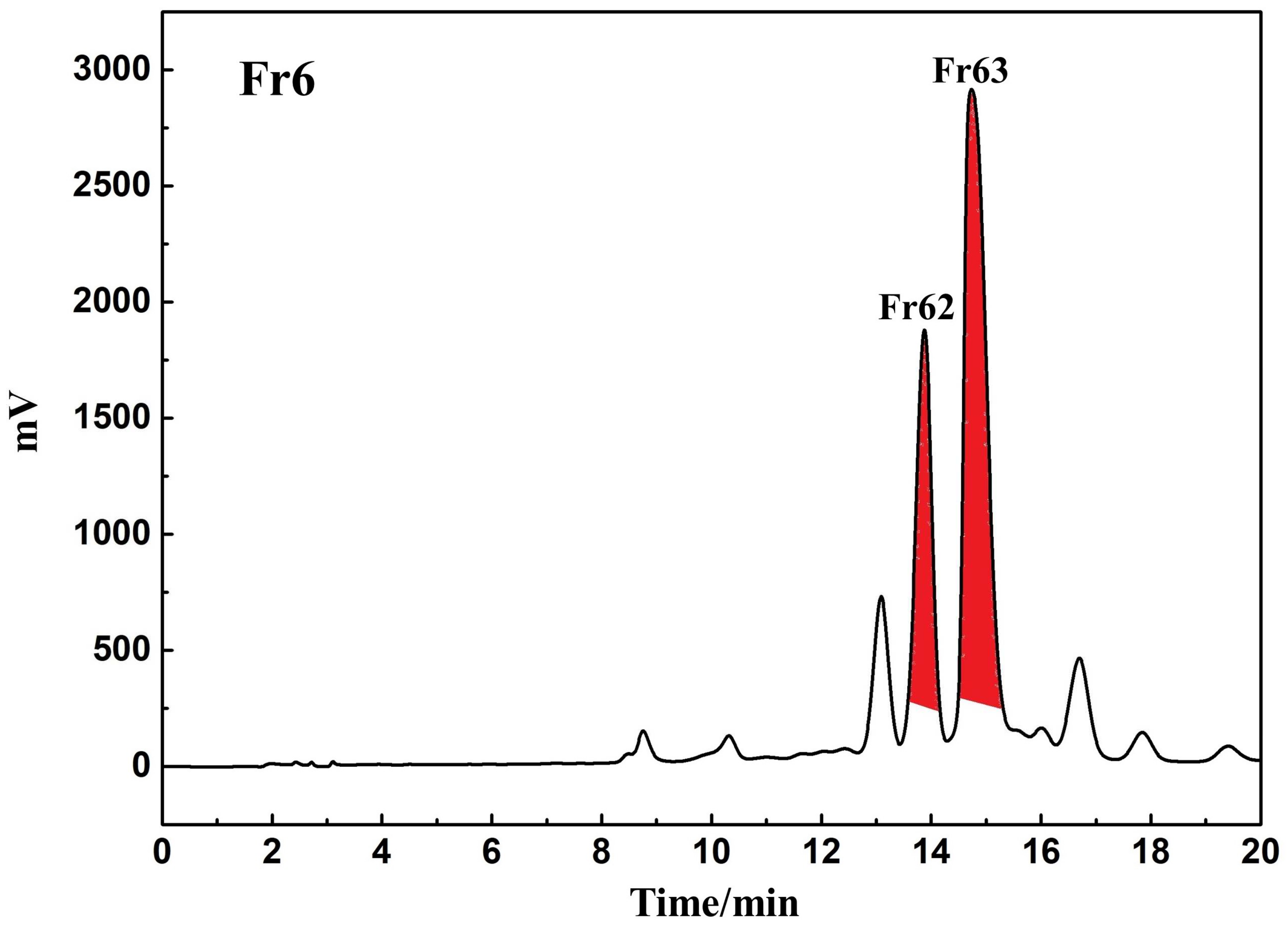
3.2. Identification and Extraction of Candidate DPPH Suppressors Based on High-Pressure Liquid Chromatography Separation
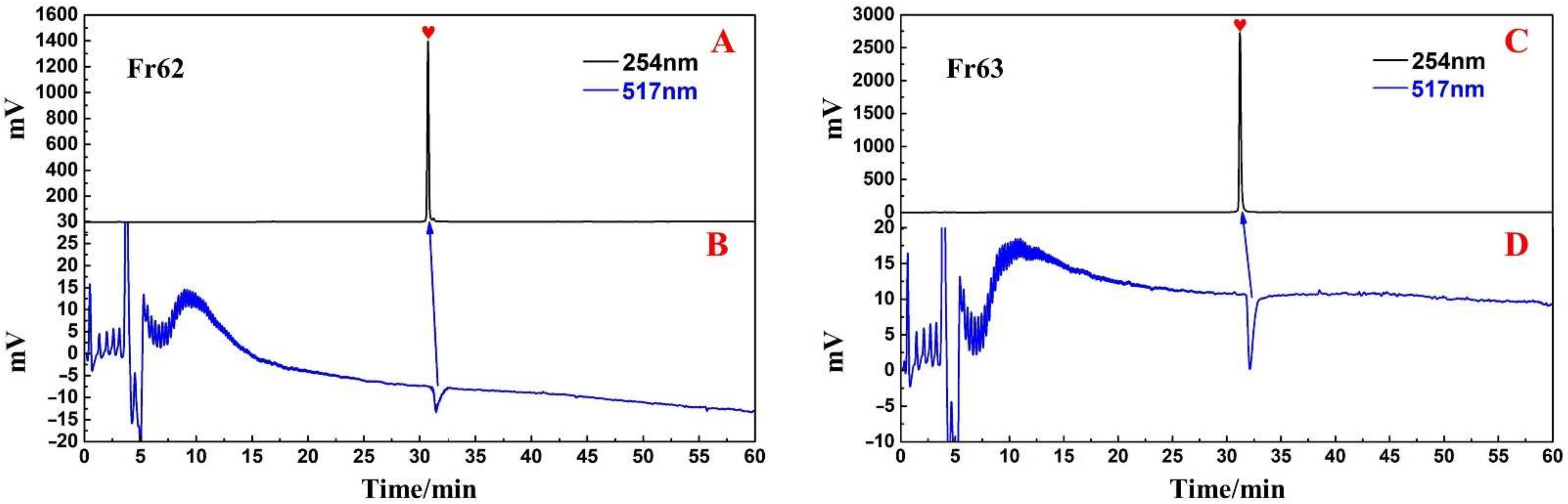
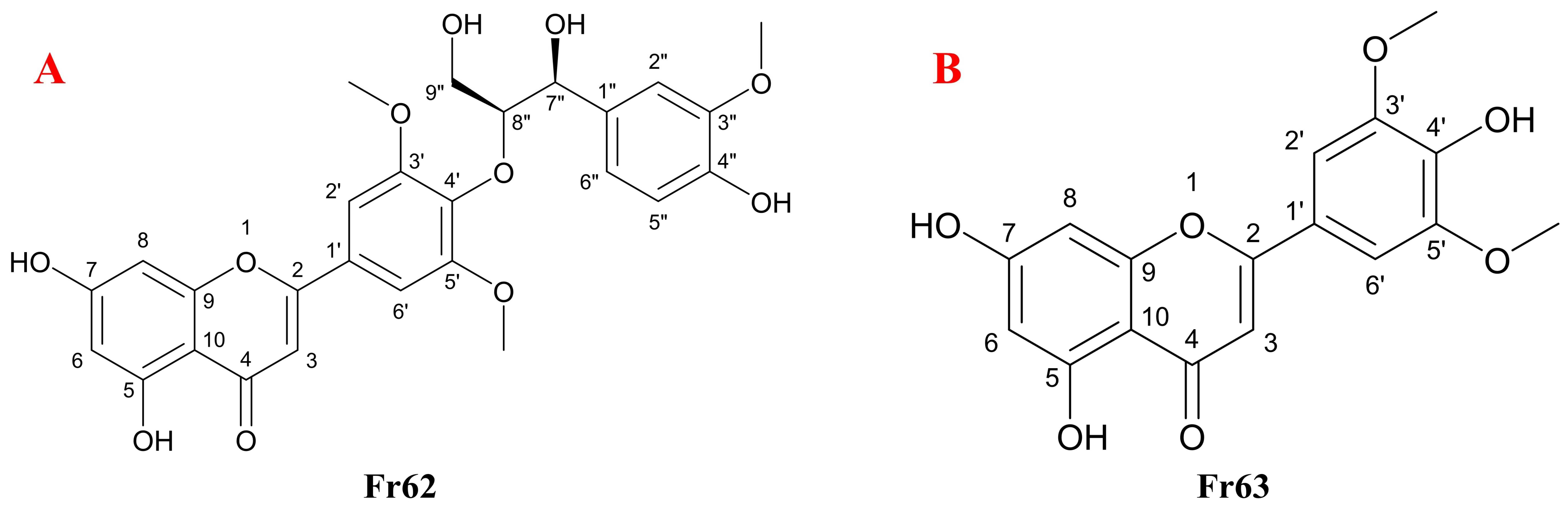
3.3. Purity, Activity and Structural Characterization of the Isolated DPPH Suppressors
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sies, H. Oxidative stress: A concept in redox biology and medicine. Redox. Biol. 2015, 4, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forman, H.J.; Zhang, H. Targeting oxidative stress in disease: Promise and limitations of antioxidant therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 2021, 20, 689–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senoner, T.; Dichtl, W. Oxidative Stress in Cardiovascular Diseases: Still a Therapeutic Target? Nutrients 2019, 11, 2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ighodaro, O.M. Molecular pathways associated with oxidative stress in diabetes mellitus. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 108, 656–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poprac, P.; Jomova, K.; Simunkova, M.; Kollar, V.; Rhodes, C.J.; Valko, M. Targeting Free Radicals in Oxidative Stress-Related Human Diseases. Trends. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 38, 592–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, B.L.; Norhaizan, M.E. Effect of High-Fat Diets on Oxidative Stress, Cellular Inflammatory Response and Cognitive Function. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Sengupta, P.; Slama, P.; Roychoudhury, S. Oxidative Stress, Testicular Inflammatory Pathways, and Male Reproduction. Int. J. Mol Sci. 2021, 22, 10043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarry, T.; Biniecka, M.; Veale, D.J.; Fearon, U. Hypoxia, oxidative stress and inflammation. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 125, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavangira, V.; Sordillo, L.M. Role of lipid mediators in the regulation of oxidative stress and inflammatory responses in dairy cattle. Res. Vet. Sci. 2018, 116, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; He, T.; Lu, S.; Huang, R.; Wang, Z. Records of Tibetan Medicine; Qinghai Publishing House: Qinghai, China, 1991; pp. 450–451. [Google Scholar]
- Capstaff, N.M.; Miller, A.J. Improving the Yield and Nutritional Quality of Forage Crops. Front. Plant. Sci. 2018, 9, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzanares, C.; Yates, S.; Ruckle, M.; Nay, M.; Studer, B. TILLING in forage grasses for gene discovery and breeding improvement. N. Biotechnol. 2016, 33, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macáková, K.; Afonso, R.; Saso, L.; Mladěnka, P. The influence of alkaloids on oxidative stress and related signaling pathways. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 134, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawa, Y.; Du, Y.; Wang, Q.; Chen, C.; Zou, D.; Qi, D.; Ma, J.; Dang, J. Targeted isolation of 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl inhibitors from Saxifraga atrata using medium- and high- pressure liquid chromatography combined with online high performance liquid chromatography-1,1-diphenyl-2- picrylhydrazyl detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1635, 461690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionita, P. The Chemistry of DPPH· Free Radical and Congeners. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulcin, İ. Antioxidants and antioxidant methods: An updated overview. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 94, 651–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Wei, L.; Sun, Z.; Gao, L.; Meng, Y.; Tang, Y.; Wu, Y. Production and transcriptional regulation of proanthocyanidin biosynthesis in forage legumes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 3797–3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.R. Forage polyphenol oxidase and ruminant livestock nutrition. Front. Plant. Sci. 2014, 5, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Shen, N.; Yuan, X.; Dang, J.; Shao, Y.; Mei, L.; Tao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Z. Two-dimensional chromatography based on on-line HPLC-DPPH bioactivity-guided assay for the preparative isolation of analogue antioxidant compound from Arenaria kansuensis. J. Chromatogr. B. 2017, 1046, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Dawa, Y.; Wang, Q.; Lv, Y.; Yu, W.; Li, G.; Dang, J. Targeted isolation of 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl inhibitors from Saxifraga atrata and their antioxidant activities. J. Sep. Sci. 2022, 45, 2435–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.J.; Park, J.H.; Cho, J.G.; Seo, K.H.; Lee, D.S.; Kim, Y.C.; Kang, H.C.; Song, M.C.; Baek, N.I. Lignan and flavonoids from the stems of Zea mays and their anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective activities. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2015, 38, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Q.; Jiang, W.W.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.L.; Ye, W.C. A new phenylpropanoic acid derivatives from the roots of Ficus stenophylla. Yao. Xue. Xue. Bao. 2008, 43, 281–283. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gholami, A.; De Geyter, N.; Pollier, J.; Goormachtig, S.; Goossens, A. Natural product biosynthesis in Medicago species. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2014, 31, 356–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sheng, L.; Hou, Z.; Hu, Y. Target Discovery of Flavonoids from Elymus nutans Griseb Using Medium- and High-Pressure Liquid Chromatography Combined with Online High-Performance Liquid Chromatography–1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl Detection. Separations 2022, 9, 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9120437
Sheng L, Hou Z, Hu Y. Target Discovery of Flavonoids from Elymus nutans Griseb Using Medium- and High-Pressure Liquid Chromatography Combined with Online High-Performance Liquid Chromatography–1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl Detection. Separations. 2022; 9(12):437. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9120437
Chicago/Turabian StyleSheng, Lili, Zhaofei Hou, and Yufeng Hu. 2022. "Target Discovery of Flavonoids from Elymus nutans Griseb Using Medium- and High-Pressure Liquid Chromatography Combined with Online High-Performance Liquid Chromatography–1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl Detection" Separations 9, no. 12: 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9120437
APA StyleSheng, L., Hou, Z., & Hu, Y. (2022). Target Discovery of Flavonoids from Elymus nutans Griseb Using Medium- and High-Pressure Liquid Chromatography Combined with Online High-Performance Liquid Chromatography–1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl Detection. Separations, 9(12), 437. https://doi.org/10.3390/separations9120437





