Abstract
This work successfully created a polypyrrole-polyethyleneimine (PPy-PEI) nano adsorbent for the elimination of the lead ion Pb2+ from an aqueous solution. An efficient conducting polymer-based adsorbent called as was created using ammonium persulfate (NH4)2S2O8 as an oxidant (PPy-PEI). The PEI hyper-branched polymer with terminal amino groups was added to the PPy adsorbent to offer heavy metals more effective chelating sites. Pb2+ removal from aqueous solution using polyethyleneimine micro adsorbent was successfully accomplished using a batch equilibrium technique (PPy-PEI). The generated water-insoluble polymer nanoadsorbent had enough nitrogen atoms; therefore, an effort was made to link PEI, a water-soluble PPy, with PPy, a conjugated polymer, for lead ion adsorption from an aqueous solution. The generated PPy-PEI nanoadsorbents were discovered to have average particle sizes of 18–34 nm and a Brunauer-Emmet-Teller surface area of 17 m2/g, respectively. The thermal behavior of the composites was investigated using thermo gravimetric and differential scanning calorimetric methods. The lead ion adsorption efficacy of pure polypyrrole was found to be 38%; however, a batch equilibrium technique employing nanoadsorbent revealed with the maximum adsorption capacity of 75.60 mg g−1. At pH 10 and 30 min of contact time at 50 °C, 0.2 g of adsorption was shown to be the ideal dosage. X-ray diffraction analysis, energy-dispersive ray spectroscopy, and Fourier transform infrared ray spectrum support the lead ion adsorption by PPy-PEI nanoadsorbents. The cauli-like structure was visible using field emission scanning electron microscopy. Studying the thermodynamic showed that the adsorption was endothermic as illustrated from the positive value of value of ΔH° is 1.439 kJ/mol which indicates that the uptake of Pb2+ onto nanoadsorbent PPy-PEI could be attributed to a physical adsorption process. According to the values of ΔG°, the adsorption process was spontaneous at all selected temperatures. The positive value of ΔS° value (43.52 j/mol) suggested an increase in the randomness at the solid/solution interface during the adsorption process. The adsorption data meet the pseudo-second-order kinetic model and suited the Langumuir isothermal model effectively.
1. Introduction
A significant environmental health issue has been raised from the pollution of the marine ecosystem with different heavy metals. The widest exposure is due to mining, metal smelting, battery production, and metal refining of various toxic metals such as cadmium, chrome, copper, arsenic, plum, zinc, and lead. These metals enter drinking water, domestic water, wetlands, waterways, streams, reservoirs, and oceans and pose a significant danger to all ecosystems because of their detrimental effects in humans and animals and it is very difficult to mitigate their toxicity [1,2,3,4,5]. The natural food chain is disrupted by the bioaccumulation of heavy metal ions including Ni2+, Pb2+, Hg2+, Co2+, and Cd2+ causing their ability to bind to nucleic acids, metabolisms, and proteins or accumulation in bone, a growing amount of wastewater containing heavy metal ions is discharged directly or indirectly into streams, lakes, rivers, or oceans, especially in developing countries, due to rapid urbanization and industrialization in sectors like metal plating, mining, tanneries, painting, batteries, paper industries, printing and photographic industries, pesticides and fertilizer industries, car radiator manufacturing, etc. These heavy metal ions are not biodegradable and tend to easily acclimate and cause a lot of health issues. A lot of efforts have been made to adsorb the heavy metals from wastewater [6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13].
Polymer adsorbents are emerging as alternatives to other forms of adsorbent because of their attractive mechanical features [14], moderate surface area, and favorable pore size distribution, viable regeneration under mild conditions, flexible surface chemical framework, and selectivity for heavy metal ions. Polymers containing mercapto, imino, and amino groups are of growing concern because of their strong range of heavy metal ions and their excellent adsorption capabilities over other light metal ions and dyes [3,15,16]. Among the most promising new materials for wastewater treatment are nanomaterials and polymers. They have unique functional characteristics that may be adjusted to fit the requirements of various wastewater treatment systems. A specific class of chemicals known as polymer nanocomposites enhance performance by fusing nanoparticles with beneficial properties of polymers. Of course, a full understanding of these materials’ essential characteristics and the underlying science is required for the development of these sorts of functional materials. Ecological wastewater remediation is increasingly considering polymers, such as polypyrrole (PPy) and polyaniline, as well as their composites due to the existence of certain functional groups that may mix well with various pollutants. Polymeric adsorbents made from polypyrrole and PEI was used to remove organic dyes from wastewater and achieved a 183.3 mg g−1 adsorption capacity, in another research, the adsorbent of polypyrrole and polyaniline was used in removal of Chromium6+ [17]. Various conducting polymers such as polyaniline, polypyrrole, and their composites have gained substantial research interest from polymer-based adsorbents owing to their possible uses in adsorption of different heavy metal ions and dyes and electronic pollution from wastewater [8,18,19]. The simplicity of synthesis, regeneration, mechanical stability, and low cost of these conducting polymer-based adsorbents are further advantages [20,21]. According to one study, polypyrrole can remove chromium (84 percent) from an aqueous solution when the pH is alkaline [22]. In an alkaline pH state, the effectiveness of eliminating heavy metals using fine polypyrrole powder has been studied [23,24]. In addition to pure polypyrrole, polypyrrole composites have been used to adsorb a number of heavy metal ions and dyes [25,26,27,28]. It was discovered that polypyrrole coated with rice husk ash, in addition to pure polypyrrole, was effective in removing nickel and copper ions from industrial effluents [29].
The remarkable adsorption characteristic of chelating resins for heavy metal ions makes them appear like potential adsorbents [30]. Although water-soluble polyethyleneimine (PEI) is a good candidate to adsorb heavy metal ions, it cannot be employed directly. Polypyrrole (PPy) and hyper-branched polymer (with terminal amino groups) polyethyleneimine (PEI) produced (PPy-PEI) adsorbent, which boosts the polymer composite adsorbent’s capacity to bind metal ions, may be joined with another polymer to create a polymer composite. N2 atoms are coupled to both PEI and PPy in the polymer nanoadsorbent structure, which is done in order to achieve the stimulatory effects for metal particle sorption from the aqueous solution. This has led to the flow research effort to plan (PPy-PEI) nanoadsorbent adsorbents for lead particle adsorption from aqueous solution [19]. The focused composite plan response surface approach was used for the improvement (CCD-RSM). This is done in order to validate the findings and give the common interactions of the Pb and PPy-PEI adsorption process appropriate consideration.
In this work, Pb is successfully removed from an aqueous media utilizing the highly porous and stable PPy-PEI. Insignificant runs that are essential for quickly, sensibly, and with a strong possibility for reuse are made using the experimental plan, expectation, and approval models.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The monomer and ammonium persulfate (NH4)2S2O8 (Merck) 99% was used for the oxidant of pyrrole (99%), (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA). To create PPy-PEI nanoadsorbents, polyethyleneimine (Merck, Kenilworth, NJ, USA) 99% was combined with PPy, (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA; MW: 1200–1300). Lead stock solutions have been formulated with deionized water (See Figure 1). For pH modification, HCl and NaOH (Merck, Kenilworth, NJ, USA) 99% have been used.
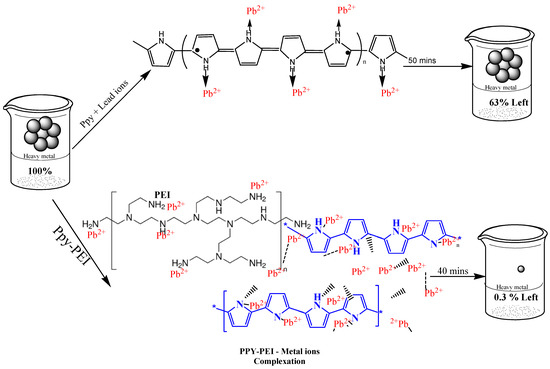
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of adsorption of polypyrrole and polypyrrole-polyethyleneimine.
2.2. Making Nanoadsorbents out of PPy and PPy-PEI
The primary quantity of oxidant was sonicated in deionized water for five minutes in order to thoroughly break it up, taking into account the mole ratio of pyrrole monomer to APS oxidant. The pyrrole arrangement was then consolidated and shaken for three hrs at room temperature to complete the polymerization, both with and without PEI. The transition from the original bright green solution to the dark one demonstrated how the product had developed (PPy-PEI and PPy). The black polymer solution was repeatedly washed with distilled H2O to eliminate the excess reactants, and the solution was then filtered to produce the black powder as the final polymer composite product [19]. After that, the polymer product was dried for 24 h at 65 °C in an oven. The synthesis scheme for the PPy-PEI adsorbent is shown in Figure 2.
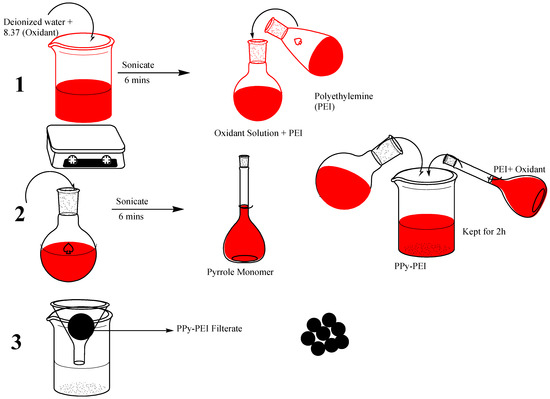
Figure 2.
Nanoadsorbent made of polypyrrole and polyethleneimine: Synthesis scheme.
2.3. Characterization of Polypyrrole and Polyethleneimine Nano Adsorbents
The surface morphology was investigated using the energy-dispersive ray-spectroscopy (EDS or EDX), Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FE-SEM Model SU 8220, Hitachi, Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). Surface analysis of polypyrrole and polyethleneimine adsorbents by surface analyzer Sorptomatic Thermo Finnigan 1990, USA, was carried out using the surface analyzer Brunauer-Emmet-Teller (BET) (1990, Sorptomatic Thermo Finnigan, Mundelein, IL, USA) by adsorbing N2 to 77.40 K. This adsorbent’s pore structure was described using the t-method. Inductive coupled plasma- mass spectroscopy (ICP-MS) (Model: ICPMS 7500, Brand: Agilent, NY, USA, was used to analyze ion samples from the metal ion solutions. For adsorbents used before and after adsorption, a differential calorimeter (DSC) was used (TA DCS Q20V24.10, (New Castle, DE, USA) in presence of N2 (20 cm3 min−1) at a temperature of 10 °C min−1. The TGA-DTA study was performed at the temperature range of 25 °C to 800 °C with a TGA analyzer (STA 6000 Perkin Elmer, Waltham, MA, USA). The experiment used a heating rate of 10 °C min−1 and a liquid flow rate of 50 mL min1 that were both influenced by the nitrogen (N2) environment.
2.4. Response Surface Methodology (RSM)
The goal of response surface methodology (RSM), a multi variant mathematical and statistical technique, is to maximize a response that is of relevance in a problem and is influenced by various variables. The central composite design (CCD), however, necessitates fewer experimental runs while producing an equivalent amount of information to the 3n complete factorial design. The CCD consists of axial points (2n), a two-level factorial design, a center point corresponding to the middle level of the factors, and axial points. The quantity of factors linked to the desired characteristics of the design (2n) determines the number of axial points [31]. The CCD may be classified into three categories based on the locations of the axial points: CCC (circumscribed central composite), CCI (inscribed central composite), and CCF (face centered composite). The comparison of the operable region and the region of interest is crucial in choosing the proper type of CCD. The most widely used technique for creating second-order response models for environmental applications is CCD. It offers sequential strategic experiment and may be effectively employed for up to five parameters utilizing parallel trials. Additionally, it can significantly forecast the effects of linear and quadratic interactions and optimize a huge number of variables.
A CCD with five independent variables—initial Pb concentration, PPy-PEI dose, contact time, pH, and temperature was the RSM used in the current study. Table 1 displays the variables together with their associated levels. The five-coded scale was used to evaluate the input values (−α, low, center, high, and +α). Pb elimination was the main focus of the experiments. Five separate process variables with strong Pb removal potential were tuned. A total of 50 sets of trials were used with a 25 complete factorial design. Included in the central composite design (CCD) experimentation set of 50 trials were 32 trials for factorial point design, 10 for axial point, and 8 for a replica of the midway. The outcomes are further examined with the aid of Design Expert Software(11 trial versions, Stat Ease, Minneapolis, MN, USA).

Table 1.
Matrix by RSM for the experimental Pb removal optimization.
Investigating alteration (ANOVA) based on the coefficient of determination, Fischer’s test value (F-value), and probability value are necessary to determine the applicability of the model (p-value). The ANOVA program from Design Expert was used to fully evaluate the outcomes. Based on the interaction between the levels of the five variables, three-dimensional plots and their corresponding contour plots were produced.
The model is defined by the following equation.
In Equation (1), i is the linear coefficient, j is the quadratic coefficient, mu and mv are independent variables, y is the expected response, βu is the constant, βv is the linear coefficient, βv is the interactive coefficient, and ɀ is the noise or error found in the response.
2.5. Batch Sorption Tests
The produced adsorbents of polypyrrole-polyetheleneimine nanoadsorbents were used in a batch process in a conical flask with magnetic stirring to adsorb Pb (II) ions. Adsorbent was brought to the solution in the necessary quantity. For some period of time, the solution was shaken. Adsorption was followed by filtering the solution. By using inductively coupled plasma-mass spectroscopy, the concentration of the filtrate and the original Pb (II) ions in the solution was found (ICP-MS). Equation (2) was used to determine the removal efficiency of Pb (II) ions during adsorption:
where, (mg/L) and Cf (mg/L) are the metal ion concentrations in the initial and final states, respectively.
Pb adsorption capacity (mg/g) = +86.68 − 0.1265A + 0.2415B − 0.2530C + 2.05D − 1.72E + 0.2487AB − 0.9413AC − 1.06AD − 0.9319AE − 0.2081BC − 0.6550BD − 1.29BE + 0.1900CD + 0.2850CE + 1.74DE − 2.10A2 − 0.1801B2 − 0.9464C2 + 0.0136D2 − 0.5426E2
The Langmuir isotherm model’s requirements are shown in Equation (4):
Equilibrium parameter without dimensions, RL, also known as the division factor:
The adsorption on a heterogeneous surface is the foundation of the linearized Freundlich adsorption isotherm
all calculated for the lead ions using the pseudo-first-order (PFO) rate model
all calculated for the lead ions using the pseudo-second-order (PSO) rate model
where is the pseudo-second-order rate constant.
RSM was used to determine the optimum parameters for these studies. Since the PEI is a water-soluble polymer, it cannot be used alone as an adsorbent, it must couple with PPy [24].
2.6. Determination of Adsorption Isotherms
The developed adsorbent, PPy-PEI, has been prepared for isothermal studies to assess its ability to adsorb lead ions from an aqueous solution. Different concentrations (1 ppm, 5 ppm, and 10 ppm) were made from the usual solutions. The ideal pH for lead ion adsorption was changed from the original pH to 10. The evenness state for adsorption was attained after 30 min at 50 °C and 150 rpm in an incubator shaker after adding 0.2 g of polypyrrole-polyethyleneimine for each of the flask. Following the establishment of equilibrium, the adsorbent was filtered, and the lead ion concentration was determined by ICP-MS.
2.7. Regeneration and Repeatability Test
Another crucial cost consideration was the adsorbent’s capacity to be reused. PPy-PEI nanoadsorbent sample tested for adsorption using Pb2+ that has been synthesized. With a solution of 0.5 N HCl, it was desorbed. After being separated, the PPy-PEI adsorbent was repeatedly rinsed with distilled water before being dried in a vacuum oven. The adsorption–desorption procedure was carried out five times under the identical circumstances in order to investigate its reusability, and we estimated the change in adsorption capacity.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. FTIR Spectra
The FTIR analysis was performed to pinpoint the functional groups and bonds that were present in polypyrrole-polyethyleneimine. When PPy-PEI was synthesized to be used in the adsorption of Pb ions, polypyrrole or polyethyleneimine was either the source of the functional groups and linkages. The FTIR was used to scan the PPy-PEI nano adsorbent at various wavenumbers and intensities. Figure 3 displays FTIR spectra at various elevated temperatures. The main characteristic peaks of pyrrole were assigned to the functional groups and stretches that could be seen on the apparent of polypyrrole-polyethyleneimine. These were 1587 cm−1, (Carbon-Carbon single bond and the Carbon-Carbon double bond stretching vibration), 1380 cm−1 (Carbon to Nitrogen stretching mode for PPy ring), 1306, 1190 cm−1 (in-plane vibrations of Carbon to Hydrogen), and 1041 cm−1 (Carbon to Hydrogen in-plane twisting). The broad peak of PEI was found to be at 3350 cm−1 for Nitrogen to Hydrogen stretching, 2980–2800 cm−1 for Carbon to Hydrogen stretching, 2100 cm−1 for Carbon to Nitrogen bending, 2008 cm−1 for Carbon to Hydrogen bending, and 1580 cm−1 for Nitrogen to Hydrogen bending (Carbon to Nitrogen stretching). When the Nitrogen to Hydrogen twisting of the PEI and the Carbon to Nitrogen stretching of the pyrrole ring are now shifted to 1440 cm−1 in the PPy-PEI composite, it is obviously showing the association between the amino-rich from polyethyleneimine and polypyrrole as well as the newly synthesized polypyrrole-polyethyleneimine nanoadsorbent with rich active groups of amine groups [19,21].
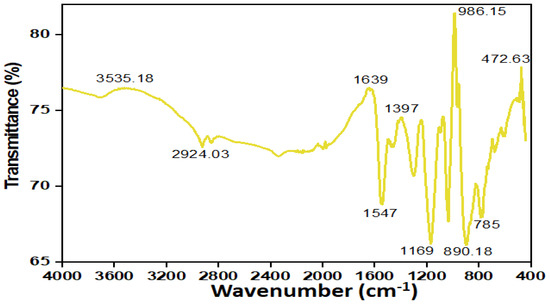
Figure 3.
FTIR spectra of synthesed polypyrrole-polyethyleneimine (PPy-PEI) nano-adsorbent.
3.2. Surface Area Analysis (BET)
The adsorption duration of various mixes is critically dependent on the surface area of the adsorbent. The nitrogen adsorption–desorption isothermal bends determined by Ppy-PEI are shown in Figure 4. According to IUPAC orders, it is discovered that the adsorption isotherm bend is mostly type II. This exemplifies how the choice of polymer fundamentally affects the physico-compound properties of the polimerized adsorbent. Accordingly, the BET surface area, pore volume, and pore size of the fine polypyrrole-polyethyleneimine nanoadsorbent powder discovered to be 13.9 m2, 0.025 cm3, and 73.4 (Å)a, respectively. The FESEM micrograph was used to determine the average particle size, which was estimated to range between 18 and 34 nm [19,23,24].
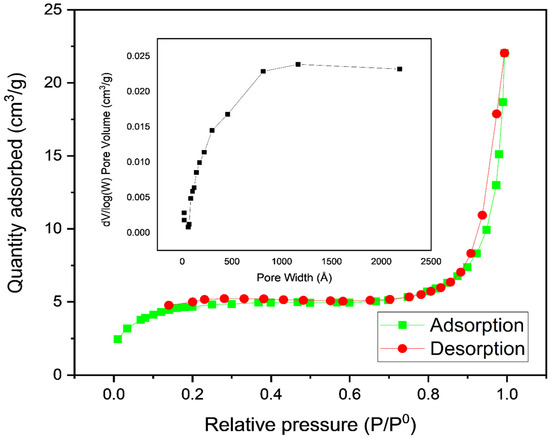
Figure 4.
BET isotherms of Polypyrrole-Polyethyleneimine for the adsorption–desorption of N2.
3.3. Thermo Gravimetric Analysis (TGA)
The mass loss of the Polypyrrole-Polyethyleneimine nanoadsorbent after heating at a temperature of 10 °C min−1 in a N2 enviroment is depicted in TGA Figure 5a. The samples start losing weight at about 50 °C and keep losing weight until 200 °C or so, which results in a loss of 8.03%. At 500 °C, the weight loss remained constant at 65%. This was caused by the polymer nano-hemicellulose composites of PPy-PEI decomposing, as well as the polymer nano-oligomeric adsorbents or unsaturated group breaking down under heat (thermal decomposition of PEI melting point at 500 °C). Less than 30% of the initial polymer’s weight was left after the final stage’s intense heat deterioration (500–800 °C) occurred, the sample’s residual mass following thermal degradation of the Ppy-PEI, which reveals the type of oxidant (ammonium persulphate) utilized during synthesis [19,21,23,24].
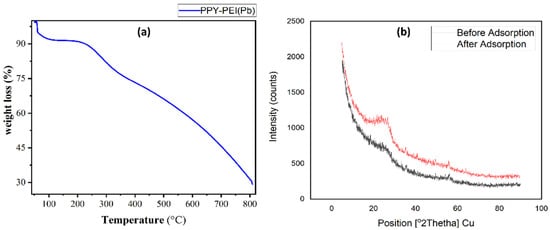
Figure 5.
(a) TGA graph showing the thermal degradation of Ppy-PEI, and (b) XRD graphs showing polypyrrole-polyethyleneimine before and after the adsorption of lead ion. (After adsorption in red lines and before adsorption in black lines).
3.4. The Study of X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
The study of the X-ray diffraction form of the polypyrrole-polyethyleneimine nanoadsorbent before and after Pb2+ adsorption is shown in Figure 5b. The polypyrrole-polythelimine composite displays a wide peak before Pb ion adsorption with a center at 2θ = 26.12°, demonstrating the substance’s amorphous nature, which is primarily caused by the periodicity running similar to the polymer chain. After lead ions were adsorbed, the polypyrrole-polythelimine adsorbent showed a nearly same wide peak, and it was found that it changed positions at 2θ = 25.04°. Even though the peaks were not significantly crystallized, the modification of the wide peak associated with PPy-PEI following adsorption indicated that lead ions were adsorbing on the PPy-PEI adsorbent [19,23,24] indicating that the adsorbent held the lead ions in place. Olatunji et al. [21] findings for polypyrrole adsorbent radioactive cesium absorption were identical.
3.5. Energy-Dispersive X-ray Analysis
Using EDX analysis, the PPy-PEI nanoadsorbent was evaluated for its ability to adsorb lead ions following the adsorption procedure as it can clearly be seen from Figure 6. The EDX pattern shown in Figure 6 illustrates how polypyrrole-polythelimine nanoadsorbents adsorb lead ions [32]. Figure 6 shows how the suggestive metallic signal manifests itself. Figure 6 displays the metallic signal evidence on the various polymer adsorbents. It has been determined that nitrogen lone pair bonds are responsible for coordinating with heavy metal ions from the aqueous solution of the effluent with the polymer nano adsorbent, and PPy-PEI oxidant with Ammonium persulphate (APS) had the largest number (33.5%). Another reason why APS oxidized PPy-PEI polymer performed better as an adsorbent for the heavy metals and dyes is that it is present in the nanoparticle.
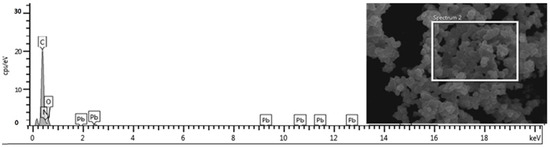
Figure 6.
Energy-dispersive X-ray analysis of polypyrrole-polyethylimine after adsorption with lead ion.
3.6. Morphology
Using FESEM, the shape of the synthesized PPy-PEI adsorbent was examined. A FESEM picture of the synthesized polypyrrole-polythelimine adsorbent, showing both the initial and final adsorption, is shown in Figure 7. Prior to the adsorption process, the polypyrrole-polythelimine nanoparticle powder was reported to have a cauliflower-like porous morphology (Figure 7a), which suggested a typical synthesis of polypyrrole. Figure 6a demonstrate the form of polypyrrole-polythelimine before adsorption, while Figure 7b represents the PPy-PEI after adsorption with the metal ion, demonstrating that the structure of the compound is buried with the metal ion, in [19,24,33] a similar trend was seen. The polypyrrole-polythelimine adsorbent’s range was between 18–34 nm with an average particle size estimated to be between 26 to 28 nm, as shown in Figure 7c.
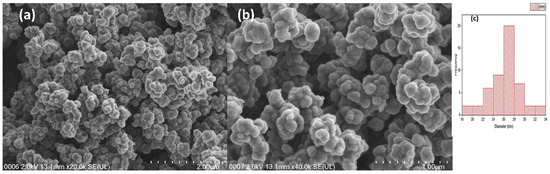
Figure 7.
FE-SEM micrograph of PPy-PEI Nano adsorbent (a) before adsorption, (b) after adsorption and (c) histogram showing frequency distribution of particle sizes of adsorption of lead ions.
3.7. Effects of Interactive Variables during Parameters Optimization by Response Surface Methodology (RSM)
The central composite design (CCD) was used for the experimental design data matrix for the statistical analysis in order to investigate the interaction impact of the independent variables on the Pb adsorption capacity. So, utilizing the CCD-RSM, the adsorption capability of PPy-PEI onto Pb was proven, both experimentally and theoretically. In accordance with the design matrix shown in Table 2, the impacts of the crucial adsorption parameters’ simultaneous optimization and interaction on the response were examined. Equation (3) represents the quadratic model derived from the coded components (20). The equation is shown as Initial Pb conc. (A), PPy-PEI dosage (B), Contact time (C), pH (D), and Temp. using the RSM model (E).

Table 2.
Design matrix for Pb removal.
Equation (3) stated in terms of coded factors allows one to predict the reaction for certain concentrations of each ingredient. The high levels of the components are by default expressed as +1 and the low levels as −1. The coded equation may be used to compare the factor coefficients and ascertain the relative weights of the components.
The Polypyrrole-Polyethyleneimine Adsorbent’s overall Adsorption Productivity was 89.7%. Due to the accessibility of NH2 in the nanoadsorbent structure from polyethyleneimine in the polypyrrole-polyethyleneimine structure, the rate at which Pb2+ particles are taken up has increased. The productivity of adsorption initially increases due to the obtainability of more reactive centers obtained from the NH2 of PEI. No further improvement in adsorption has been seen despite projected growth in the amount of the adsorbent [34]. All things considered, there was a little decrease in the adsorption of metal particles. This is because there is a large concentration of PPy-PEI particles in the construction, which is likely to obstruct the active site’s accessibility. As a consequence, the adsorption efficiency starts to decline after the immersion point of adsorption. Adsorption efficiency, PPy-PEI nanoadsorbent at 50 min, the maximum adsorption efficiency of 89.64% was observed, which is thought to occur as a result of physio-sorption. Because of how much the metal ions in the aqueous solution are ionized and how the functional groups at the adsorbent’s active sites are ionized or dissociated, pH has a significant impact in how well adsorbate molecules work. As the pH increases from 2 to 12, protons are released from the PPy-PEI adsorbent’s amine functional groups, increasing the number of active amine sites that are accessible for the adsorption of lead ions. Adsorption reaches its highest with a pH rise above 10 and at relatively low doses of adsorbent. The initial concentration of lead ions changed with an adsorbent dosage of 0.2 g at 20–60 °C and a pH range of 1–10 ppm. Adsorption efficiencies were high (83.2%) at 1.5 ppm and 73% at 7.5 ppm under the same circumstances, according to the influence of the initial metal ion concentration on adsorption. Lead ions quickly filled the available adsorption sites, increasing the effectiveness of adsorption. Additionally, it was discovered that when the initial lead ion concentration increased from 1 ppm to 10 ppm, the lead ion adsorption efficiency changed in all temperature zones. This is most likely caused by the higher concentration of adsorbent lead ions in relation to mass.
3.8. ANOVA
The model’s significance was assessed using the analysis of variance (ANOVA) in Table 3. The model may be significant as shown by the Model F-value of 1.95. An F-value of this size may result from noise just 4.90% of the time. When a model term’s p-value is less than 0.0500, it is regarded as significant. The relevant model terms here are D, E, DE, and A2. Model terms are not significant if the value is larger than 0.1000. If your model has a lot of unnecessary words, model reduction may help (except those needed to maintain hierarchy). The F-value for the lack of fit is 1.44, which indicates that the lack of fit is not significant when compared to the pure error. Noise has a 32.41% risk of causing a significant Lack of Fit F-value. In order to ensure that the model fits, we want a non-significant lack of fit. The statistical ANOVA statistics show significant interactions between the ideal input variables when the p-value is less than 0.05. Therefore, starting Pb concentration and pH, contact duration and initial Pb concentration, PPy-PEI dosage and pH are the relationships that matter most.

Table 3.
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) by RSM for Pb2+ removal efficiencies.
3.9. D Surface Plots
The contour and 3D surface plots in Figure 8a–f show the link between the independent variables’ definite and anticipated standards of Pb adsorption capacity (mg/g). Figure 8a,b illustrates the connection between the initial Pb concentration and the PPy-PEI dosage. 0.2 g of the adsorbent were utilized to get the best adsorption capacity. The adsorption capacity did not change significantly with further adsorbent addition. This pattern suggested that a tiny quantity of Pb might be effectively removed during the adsorption process. The common relationship between initial Pb concentration (1.5–7.5 ppm) and contact duration (15–75 min) is shown in Figure 8c,d, with all other parameters fixed at their ideal values. The effectiveness of Pb adsorption increased with contact duration while decreasing with an increase in starting Pb concentration. This is due to the fact that all of the Pb molecules are easily adsorbed onto the active sites of the PPy-PEI at lower concentrations [35]. Because the PPy-PEI has porous structure and both active and vacant adsorption sites, quick equilibration was accomplished with a short contact period of 15 min. The adsorption’s equilibration time is attained in 30 min and remains constant for the remaining 60 min without changing. Understanding the adsorbent’s surface energy and the ionization level of the adsorbate molecule, the influence of pH changing from 2 to 10 as illustrated in Figure 8e,f was investigated. The aqueous solution will switch to the anionic form as a result, becoming negatively charged due to deprotonation, resulting in a positively charged PPy-PEI surface, when the pH is low (2 to 6). At pH 4, the aqueous solution had a negative charge whereas the surface of the adsorbent had a positive charge. The possibility of electrostatic contact in this circumstance results in a large increase in adsorption capacity. The possibility of electrostatic interaction was altered by the deprotonated ionic conductivity of the adsorbent and molecule at high pH. As a result, the electrostatic repulsion caused the adsorption capacity to diminish. This may be brought on by the Pb and -OH molecules’ intense battle for active empty sites [36]. Additionally, some functional groups like carbonyl and hydroxyl will be in their protonated cationic state at higher pH levels, which slows down effective adoption. Thus, it can be said that the ideal adsorption conditions are contact duration of 30 min, starting Pb concentration of 3 ppm, dosage of 0.2 g PPy-PEI, pH 10, and temperature of 50 °C.
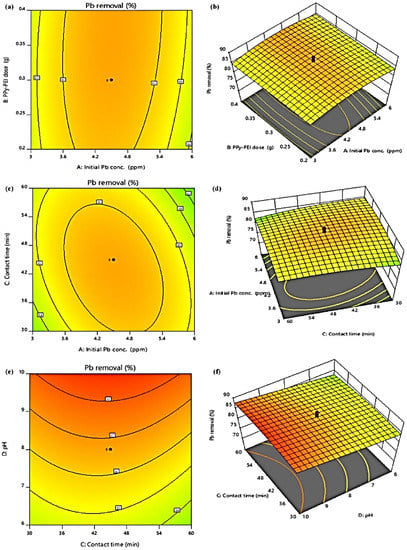
Figure 8.
Contour plots and 3D response surface plots of Pb removal showing the interactive effects of (a,b) Initial Pb conc. and PPy-PEI dose, (c,d) Initial Pb conc. and contact time, (e,f) pH and contact time.
3.10. Normal and Predicted Plots
The relationship between actual and predicted values were depicted in Figure 9. The experimental and anticipated reaction values are positively correlated. Figure 10 depicts the relationship between externally studentized residuals and Run Number for Pb removal. It also shows good correlation between the variables.
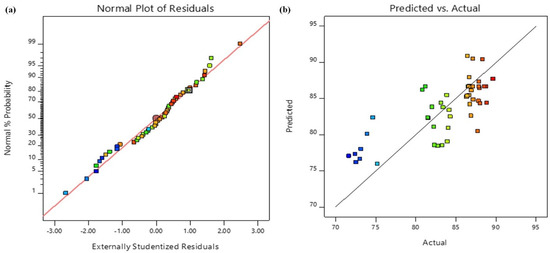
Figure 9.
Design-expert plots of (a) normal probability curve of the residuals and (b) relationship between actual values and predicted values for Pb removal.
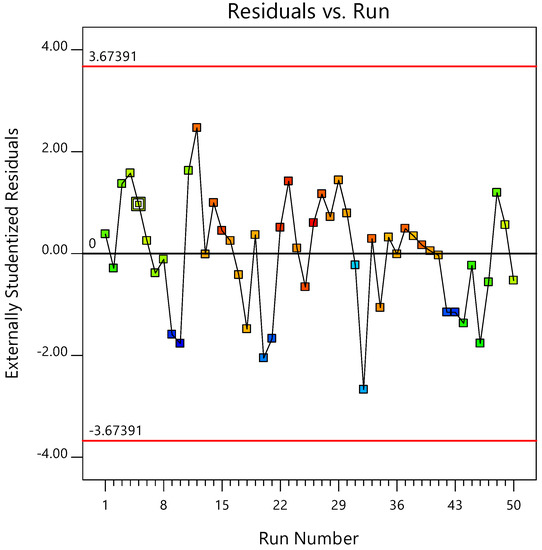
Figure 10.
Probability plot of externally studentized residuals vs. Run Number for Pb removal.
With values acquired during the Model comparison and fit statistics shown in Table 4, the outcome of the CCD-RSM multiple regression analysis provided a significant prediction. The model had strong R2 and Adjusted R2 correlation, and the confidence level was chosen at 95%. An unfavorable the overall mean may be a more accurate predictor of your reaction than the present model, according to predicted R2. In some circumstances, a higher order model could potentially be more accurate. Adeq Precision measures the ratio of signal to noise. Preferably, the ratio should be at least 4. The ratio of 5.293 shows a very strong signal. Use this model to navigate the design area.

Table 4.
Model comparison and fit statistics for Pb removal.
The coefficient estimates in terms of coded factors presented in Table 5 represent the projected change in response per unit change in factor value when all other variables are kept constant. In an orthogonal design, the intercept is the mean response over all runs. The coefficients alter the average in the vicinity of it depending on the factor values. The VIFs are 1 when the factors are orthogonal. The VIFs are greater than 1 when the factors are multi-colinear. The severity of the link between the components increases with the VIF. VIFs below 10 are often regarded as acceptable.

Table 5.
Coefficients in Terms of Coded Factors for the responses (Pb removal).
Table 6 displays a comparison of the efficiency of lead ion adsorption by several polymer-based materials.

Table 6.
The effectiveness of polymer-based compounds for adsorbing lead ions.
3.11. Isotherms of Adsorption
The Langmuir model (LM) predicts that lead particles will be taken up by monolayer adsorption on a homogenous surface as seen in (Figure 11a,b). The Langmuir isotherm model’s requirements are shown in Equation (4).
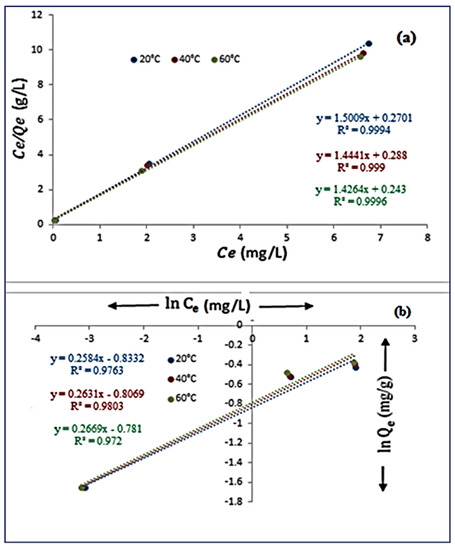
Figure 11.
The Langmuir (a) and Freundlich (b) isotherm plot for the adsorption of lead ions by polypyrrole-polyethyleneimine.
Qmax (mg/g) is the most stringent adsorption limit compared to the finished monolayer inclusion exposure, and kL (L/g) is a constant linked to the adsorption limit and adsorption energy. When Ce Qe was plotted versus Ce, a straight line was obtained. The inclines and captures were used to calculate the benefits of Qmax and kL between twenty and sixty degrees Celsius, they varied between 166 and 170 mg/g and 0.556 and 0.585 L mg−1 for both Qmax and kL, separately. The highest R2 connection coefficients (0.9996) were found at 60 °C, which proposes that the LM might be used to match the experimental data (Figure 11a). More research on the Langmuir condition was done to assess the situation using an equilibrium parameter without dimensions, RL, also known as the division factor, are shown in Equation (5).
This indicates that for advantageous (favorable) adsorption, 0 < < 1, > 1 denotes unfavorable adsorption, = 1 denotes linear adsorption, and = 0 denotes irreversible adsorption. According to study estimates, varied between 0.062 and 0.068, indicating that the adsorption is advantageous [41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48].
The adsorption on a heterogeneous surface is the foundation of the linearized Freundlich adsorption isotherm model. The phrase is provided in Equation (6).
Where the adsorption limit and adsorption intensity are shown, respectively, by the Freundlich constants KF (L/mg) and n. A straight line appeared when ln Qe and ln Ce were plotted against one another. Calculations of n and KF were done using the slope and inclination, respectively. The determined values of n and KF were 143.5 to 144.6 and 3.87 to 3.75 L/mg, respectively. The findings from both isotherm models show that the Freundlich isotherm model and the Langmuir isotherm are more closely connected to the lead ion adsorption by PPy-PEI adsorbent. Additionally, a rise in temperature raised the adsorption limit for Pb2+ particle evacuation by the adsorbent, proving the endothermic and homogeneous nature of the adsorption process, R2 values are all more than 0.9, indicating a combination mechanism was used to carry out the adsorption process [49,50,51,52].
3.12. Kinetics of Adsorption
To evaluate the rate and mechanism of the lead ions adsorption utilizing PFO and PSO kinetics, lead ion adsorption kinetic experiments were carried out at pH 10. (mg/g), also known as the Lagergren adsorption rate constant, is the amount of adsorption at equilibrium, the Lagergren adsorption rate constant, (min−1), and the amount of adsorption at time (min), (mg/g), were all calculated for the lead ions using the pseudo-first-order rate model, Equation (7).
From the intercepts and slope of the log ( − ) vs. t plot, the values of and were calculated. This is how the PSO rate model is put into words in Equation (8).
Because the estimated Qe is substantially lower than the actual value and the R2 value is low, it is clear that the PSO model does not adequately describe this adsorption process. The strong correlation coefficients of PSO rate model, as shown in (Figure 12a,b), and Table 7 suggest that the adsorption of Pb2+ onto the polypyrrole-polyethyleneimine nanoadsorbent matches the PSO kinetic model. As a result of the many connections between the metal ion and the active groups of the adsorbent, it also implies that PPy-PEI was used to adsorb Pb ions was followed by chemisorption [45,46,47].
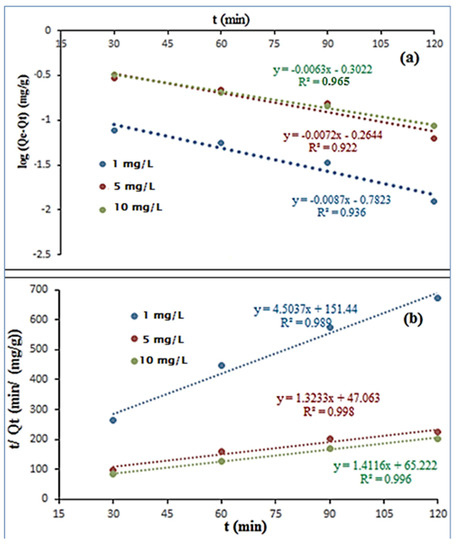
Figure 12.
(a) The pseudo-first-order and (b) pseudo-second-order kinetics for the adsorption of lead ions by PPy-PEI Nano adsorbent Pb2+.

Table 7.
Calculated kinetic parameters of the PFO and PSO kinetic for lead ion on polypyrrole-polyethhyleneimine Nano adsorbent at pH 10 and 50 °C.
3.13. Adsorption Thermodynamics on Lead Ions
Thermodynamic considerations of an adsorption process are the key point to decide whether it has spontaneously occurred or not. The Gibbs free energy change, ΔG°, is an important parameter to evaluate the spontaneity of a process. If ΔG° is negative at a given temperature, then the reactions occur spontaneously. Moreover, the positive or negative changes of enthalpy ΔH° indicates the nature of the adsorption, whether it is endothermic or exothermic changes of entropy ΔS° indicates the interface sorption process [53,54,55]. A set of experiment is also carried out to determine the thermodynamic parameters of lead ions onto PPy-PEI nanoadsorbent at different temperatures in the range of 20–60 °C and the values of enthalpy change ΔH° and entropy change ΔS° were calculated from the slope and intercept of the plot ln Kd versus 1/T (Figure 13) and Table 8. Lead ions adsorption is endothermic and spontaneous onto PPy-PEI nanoadsorbents (Table 8), and positive ΔS° value (43.52 j/mol) suggested an increase in the randomness at the solid/solution interface during the adsorption process. The increase in sorption with rise in temperature may be due to the strengthening of adsorptive forces between the active sites of the adsorbents and adsorbate species and between the adjacent molecules of the adsorbed phase [56].
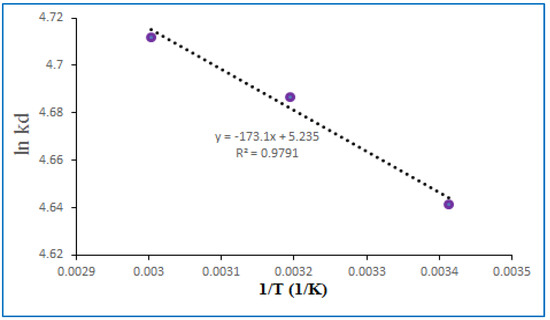
Figure 13.
Thermodynamic studies of the adsorption of lead ions onto PPy-PEI nanoadsorbent.

Table 8.
Thermodynamic parameters for the adsorption of lead ions onto PPy-PEI at different temperatures.
The value of ΔH° is 1.439 kJ/mol which indicates that the uptake of Pb2+ onto nanoadsorbent PPy-PEI could be attributed to a physical adsorption process, several researchers have conducted similar research and results aggress with the present finding [57].
3.14. Regeneration and Repeatability Studies
Before contemplating large-scale applications, it is essential to assess the adsorbent’s recyclability. Regeneration studies can aid in understanding the adsorption process between the adsorbent and adsorbate [58,59,60]. According to the adsorption experiment, lead2+ had to interact with the PPyPEI nanoadsorbent at an alkaline pH of (10). Therefore, it makes sense to utilize an acidic solution to remove the adsorbed lead from the PPyPEI nanoadsorbent. The lead ions were removed from the adsorbed polypyrrole-polyethyleneimine nano adsorbent using 0.5 N HCl (46). Figure 14 displays the repeatability of the polypyrrole-polyethyleneimine nanoadsorbent for the adsorption of lead ions. The results showed a success rate of 95% (with maximum adsorption capacity of 75.60 mg g−1) for the first cycle and a success rate of 55% for the fifth cycle. The declining trend might be the consequence of the heat treatment causing some of the adsorbent’s particles to agglomerate, which over time diminishes the surface area and block the available active site/binding area which might be chemical reaction which is not easily reversible. These results show that the composite’s greatest reusability performance was greater than five times [61,62,63].
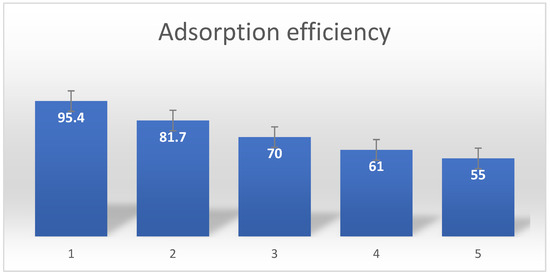
Figure 14.
Repeatability of the Pb2+ adsorbent made from polypyrrole-polyethyleneimine.
4. Conclusions
Polypyrrole/polyethyleneimine (PPy-PEI) Nano adsorbent was successfully synthesized in this study. The chemical oxidation of pyrrole occurs in the presence of polyethyleneimine. The adsorption of lead ion from aqueous solution was tested on the generated Nano adsorbent. This work shows that the lead ion adsorbs very well on conductive polymers like PPy-PEI. The adsorption process should approach equilibrium (with 89.6% removal) after 40 min at a temperature of 50 °C and a pH of 10. The results of the studies demonstrated that batch adsorption factors such adsorption dose, solution pH, and contact duration at 50 °C temperature had a significant impact on the efficiency of lead ion adsorption. The lead ion adsorption capability of the PPy-PEI Nano adsorbent peaked at a pH of 10. The presence of nitrogen atoms in PPy-PEI has been identified as the active sites in charge of lead ion adsorption. In isothermic testing at various temperatures, the adsorption data was well-fit to the Langmuir isothermal model and adopted the PSO kinetic model. The PSO rather than the PFO provided a more accurate representation of the adsorption data of the kinetics at various concentrations. Lead ions may be removed from aqueous solution by scraping a Nano adsorbent PPy-PEI acts as an excellent adsorbent. Future research should examine how it could be used to treat extremely acidic industrial wastewater that contains heavy metals and organic dyes, with the added benefit of higher adsorption and reduced impact on the environment. The created Nano adsorbent may also be used as a viable and reusable adsorbent for the removal of lead particles from wastewater. More attention should be paid to various altering specialists and amalgamation processes in order to improve the material’s fluid level stability and adsorption capabilities. Section concentrations and clump studies should be used to further handle the industrial effluents from wastewater and to concentrate on an adsorbent’s capacity for vast scope applications. In this manner, it is anticipated that additional research would encourage alternative desorption and recovery approaches that will reduce the underlying depreciation of top polymer adsorbents and lengthen their lifetime. Since conducting polymer adsorbents and their composites are preferred for practical applications, methods to increase their primary uprightness should be investigated. Others described labor- and energy-intensive preparation processes that could not be economically duplicated on a commercial scale. A portion of the examination that was reviewed produced inconsequential data. In several fields of study, using lead particles, other heavy metals, and dyes in combination with contaminated waste materials is important to reduce the danger of optional defilement due to the adsorption cycle.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.H.B. and H.N.M.E.M.; methodology, A.H.B. and H.N.M.E.M.; software, A.H.B., A.H.J., U.A. and M.A.; validation, S.R.M.K. and E.M.T.-E.; formal analysis, A.H.B. and H.N.M.E.M.; investigation, E.M.T.-E., H.M. and S.S.A.; resources, H.M., S.K. and S.R.M.K.; data curation, A.H.B., H.N.M.E.M., M.A. and U.A.; writing—original draft preparation, A.H.B. and H.N.M.E.M.; writing—review and editing, A.H.B., H.N.M.E.M. and H.M.; visualization, M.A., S.K., U.A. and S.S.A.; supervision, H.N.M.E.M. and H.M.; project administration, H.N.M.E.M., S.K. and E.M.T.-E.; funding acquisition, E.M.T.-E. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data are included in the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Deanship of Scientific Research at Umm Al-Qura University for supporting this work by Grant Code (22UQU4340549DSR05), and also wish to acknowledge the grants received from Tertiary Education Trust Fund (TETFUND) Nigeria.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hosseinzadeh, H.; Ramin, S. Fast and enhanced removal of mercury from aqueous solutions by magnetic starch-g-poly (acryl amide)/graphene oxide nanocomposite superabsorbents. Polym. Sci. Ser. B 2016, 58, 457–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadiri, A.; Benkhaled, A.; Choukchou-Braham, E. Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies of copper adsorption onto poly (n-vinylpyrrolidone) modified clay. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A 2018, 55, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezania, H.; Vatanpour, V.; Salehi, E.; Gavari, N.; Shockravi, A.; Ehsani, M. Wholly heterocycles-based polyamide–sulfide containing pyridine and thiazole rings: A super-adsorbent polymer for lead removal. J. Polym. Environ. 2019, 27, 1790–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Alharbi, N.S.; Rabah, S.O.; Wang, S.; Wang, X. Synthesis and fabrication of g-C3N4-based materials and their application in elimination of pollutants. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 731, 139054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagaba, A.H.; Kutty, S.R.M.; Hayder, G.; Baloo, L.; Noor, A.; Yaro, N.S.A.; Saeed, A.A.H.; Lawal, I.M.; Birniwa, A.H.; Usman, A.K. A systematic literature review on waste-to-resource potential of palm oil clinker for sustainable engineering and environmental applications. Materials 2021, 14, 4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahvi, A.H.; Balarak, D.; Bazrafshan, E. Remarkable reusability of magnetic Fe3O4-graphene oxide composite: A highly effective adsorbent for Cr (VI) ions. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazrafshan, E.; Sobhanikia, M.; Mostafapour, F.K.; Kamani, H.; Balarak, D. Chromium biosorption from aqueous environments by mucilaginous seeds of Cydonia oblonga: Thermodynamic, equilibrium and kinetic studies. Glob. NEST J. 2017, 19, 269–277. [Google Scholar]
- Balarak, D.; Azarpira, H. Isotherms and thermodynamics of Cd (II) ion removal by adsorption onto Azolla filiculoides. Int. J. Pharm. Technol. 2016, 8, 15780–15788. [Google Scholar]
- Jagaba, A.H.; Kutty, S.; Khaw, S.; Lai, C.; Isa, M.; Baloo, L.; Lawal, I.; Abubakar, S.; Umaru, I.; Zango, Z. Derived hybrid biosorbent for zinc (II) removal from aqueous solution by continuous-flow activated sludge system. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 34, 101152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagaba, A.H.; Kutty, S.R.M.; Noor, A.; Birniwa, A.H.; Affam, A.C.; Lawal, I.M.; Kankia, M.U.; Kilaco, A.U. A systematic literature review of biocarriers: Central elements for biofilm formation, organic and nutrients removal in sequencing batch biofilm reactor. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 42, 102178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balarak, D.; Azarpira, H.; Mostafapour, F.K. Thermodynamics of removal of cadmium by adsorption on Barley husk biomass. Der Pharma Chem. 2016, 8, 243–247. [Google Scholar]
- Azarpira, H.; Mahdavi, Y.; Balarak, D. Removal of Cd (II) by adsorption on agricultural waste biomass. Der Pharma Chem. 2016, 8, 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Jagaba, A.; Kutty, S.; Hayder, G.; Baloo, L.; Ghaleb, A.; Lawal, I.; Abubakar, S.; Al-dhawi, B.; Almahbashi, N.; Umaru, I. Degradation of Cd, Cu, Fe, Mn, Pb and Zn by Moringa-oleifera, zeolite, ferric-chloride, chitosan and alum in an industrial effluent. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2021, 12, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagaba, A.H.; Kutty, S.R.M.; Lawal, I.M.; Aminu, N.; Noor, A.; Al-dhawi, B.N.S.; Usman, A.K.; Batari, A.; Abubakar, S.; Birniwa, A.H.; et al. Diverse sustainable materials for the treatment of petroleum sludge and remediation of contaminated sites: A review. Clean. Waste Syst. 2022, 2, 100010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birniwa, A.H.; Abubakar, A.S.; Mahmud, H.N.M.E.; Kutty, S.R.M.; Jagaba, A.H.; Abdullahi, S.S.a.; Zango, Z.U. Application of Agricultural Wastes for Cationic Dyes Removal from Wastewater. In Textile Wastewater Treatment; Muthu, S.S., Khadir, A., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 239–274. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullahi, S.S.; Musa, H.; Habibu, S.; Mohammad, R.E.A. Facile synthesis and dyeing performance of some disperse monomeric and polymeric dyes on nylon and polyester fabrics. Bull. Chem. Soc. Ethiop. 2021, 35, 485–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, R.; Mosayebzadeh, Z.J.C.P. Application of polyaniline as an efficient and novel adsorbent for azo dyes removal from textile wastewaters. Chem. Pap. 2011, 65, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdinia, A.; Niroumand, R.; Jabbari, A. Removal of lead and copper ions from environmental water samples by nanorattle magnetic polypyrrole. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 17, 2721–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birniwa, A.H.; Mahmud, H.N.M.E.; Abdullahi, S.S.; Habibu, S.; Jagaba, A.H.; Ibrahim, M.N.M.; Ahmad, A.; Alshammari, M.B.; Parveen, T.; Umar, K. Adsorption Behavior of Methylene Blue Cationic Dye in Aqueous Solution Using Polypyrrole-Polyethylenimine Nano-Adsorbent. Polymers 2022, 14, 3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katal, R.; Ghiass, M.; Esfandian, H. Application of nanometer size of polypyrrole as a suitable adsorbent for removal of Cr (VI). J. Vinyl Addit. Technol. 2011, 17, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olatunji, M.A.; Khandaker, M.U.; Mahmud, H.N.M.E. Adsorption kinetics, equilibrium and radiation effect studies of radioactive cesium by polymer-based adsorbent. J. Vinyl Addit. Technol. 2018, 24, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekar, M.; Sakthi, V.; Rengaraj, S. Kinetics and equilibrium adsorption study of lead (II) onto activated carbon prepared from coconut shell. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 279, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huq, A.K.O.; Yahya, R.; Mahmud, H.N.M.E. Equilibrium, kinetics, and thermodynamics studies of polypyrrole adsorbent for arsenic ions. Water Supply 2018, 18, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birniwa, A.H.; Abubakar, A.S.; Huq, A.K.O. Polypyrrole-polyethyleneimine (PPy-PEI) nanocomposite: An effective adsorbent for nickel ion adsorption from aqueous solution. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A 2021, 58, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouthaman, A.; Azuradeen, R.S.; Gnanaprakasam, A.; Sivakumar, V.M.; Thirumarimurugan, M. Polymeric nanocomposites for the removal of Acid red 52 dye from aqueous solutions: Synthesis, characterization, kinetic and isotherm studies. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 160, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zare, E.N.; Motahari, A.; Sillanpää, M. Nanoadsorbents based on conducting polymer nanocomposites with main focus on polyaniline and its derivatives for removal of heavy metal ions/dyes: A review. Environ. Res. 2018, 162, 173–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagaba, A.H.; Kutty, S.R.M.; Baloo, L.; Birniwa, A.H.; Lawal, I.M.; Aliyu, M.K.; Yaro, N.S.A.; Usman, A.K. Combined treatment of domestic and pulp and paper industry wastewater in a rice straw embedded activated sludge bioreactor to achieve sustainable development goals. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2022, 6, 100261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasani, T.; Eisazadeh, H. Removal of Cd (II) by using polypyrrole and its nanocomposites. Synth. Met. 2013, 175, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, M.; Eisazadeh, H. Removal of COD, color, anions and heavy metals from cotton textile wastewater by using polyaniline and polypyrrole nanocomposites coated on rice husk ash. Compos. Part B Eng. 2013, 45, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liang, T.; Miao, P.; Chen, T.; Han, X.; Hu, G.; Gao, J. Green Preparation of Aminated Magnetic PMMA Microspheres via EB Irradiation and Its Highly Efficient Uptake of Ce (III). Materials 2022, 15, 6553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaleb, A.; Kutty, S.; Ho, Y.; Jagaba, A.; Noor, A.; Al-Sabaeei, A.; Kumar, V.; Saeed, A. Anaerobic Co-Digestion for Oily-Biological Sludge with Sugarcane Bagasse for Biogas Production under Mesophilic Condition; IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2020; p. 012084. [Google Scholar]
- Dandil, S.; Sahbaz, D.A.; Acikgoz, C. Adsorption of Cu (II) ions onto crosslinked chitosan/Waste Active Sludge Char (WASC) beads: Kinetic, equilibrium, and thermodynamic study. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 136, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawal, I.M.; Bertram, D.; White, C.J.; Jagaba, A.H.; Hassan, I.; Shuaibu, A. Multi-criteria performance evaluation of gridded precipitation and temperature products in data-sparse regions. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.; Mahmud, N.H.M.E.; Yahya, R.B.; Ibrahim, F.; Djordjevic, I. Polypyrrole conducting polymer and its application in removal of copper ions from aqueous solution. Mater. Lett. 2015, 149, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markandeya; Dhiman, N.; Shukla, S.P.; Kisku, G.C. Statistical optimization of process parameters for removal of dyes from wastewater on chitosan cenospheres nanocomposite using response surface methodology. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 149, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witek-Krowiak, A.; Chojnacka, K.; Podstawczyk, D.; Dawiec, A.; Pokomeda, K. Application of response surface methodology and artificial neural network methods in modelling and optimization of biosorption process. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 160, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, D.; Qiao, N.; Wang, N.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Ren, Z. Facile preparation of a nano-imprinted polymer on magnetite nanoparticles for the rapid separation of lead ions from aqueous solution. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2018, 20, 12870–12878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koushkbaghi, S.; Zakialamdari, A.; Pishnamazi, M.; Ramandi, H.F.; Aliabadi, M.; Irani, M. Aminated-Fe3O4 nanoparticles filled chitosan/PVA/PES dual layers nanofibrous membrane for the removal of Cr (VI) and Pb (II) ions from aqueous solutions in adsorption and membrane processes. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 337, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Gao, J.; Dai, J.; Han, J.; Wang, Y.; Xie, J.; Yan, Y. Selective adsorption behavior of Pb (II) by mesoporous silica SBA-15-supported Pb (II)-imprinted polymer based on surface molecularly imprinting technique. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, G.; Dabirian, F.; Mohammadi, P.; Rajabi, L.; Babaei, M.; Shiri, N. Electrospun fumarate ferroxane/polyacrylonitrile nanocomposite nanofibers adsorbent for lead removal from aqueous solution: Characterization and process optimization by response surface methodology. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2018, 129, 182–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagaba, A.H.; Kutty, S.R.M.; Noor, A.; Isah, A.S.; Lawal, I.M.; Birniwa, A.H.; Usman, A.K.; Abubakar, S. Kinetics of Pulp and Paper Wastewater Treatment by High Sludge Retention Time Activated Sludge Process. J. Hunan Univ. Nat. Sci. 2022, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagaba, A.H.; Kutty, S.R.M.; Noor, A.; Affam, A.C.; Ghfar, A.A.; Usman, A.K.; Lawal, I.M.; Birniwa, A.H.; Kankia, M.U.; Afolabi, H.K. Parametric optimization and kinetic modelling for organic matter removal from agro-waste derived paper packaging biorefinery wastewater. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2022, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagaba, A.H.; Kutty, S.R.M.; Naushad, M.; Lawal, I.M.; Noor, A.; Affam, A.C.; Birniwa, A.H.; Abubakar, S.; Soja, U.B.; Abioye, K.J. Removal of nutrients from pulp and paper biorefinery effluent: Operation, kinetic modelling and optimization by response surface methodology. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 114091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagaba, A.H.; Kutty, S.R.M.; Abubakar, S.; Birniwa, A.H.; Lawal, I.M.; Umaru, I.; Usman, A.K.; Yaro, N.S.A.; Al-Zaqri, N.; Al-Maswari, B.M. Synthesis, Characterization, and Performance Evaluation of Hybrid Waste Sludge Biochar for COD and Color Removal from Agro-Industrial Effluent. Separations 2022, 9, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birniwa, A.J.; Mohammad, R.E.A.; Ali, M.; Rehman, M.F.; Abdullahi, S.S.; Eldin, S.M.; Mamman, S.; Sadiq, A.C.; Jagaba, A.H. Synthesis of Gum Arabic Magnetic Nanoparticles for Adsorptive Removal of Ciprofloxacin: Equilibrium, Kinetic, Thermodynamics Studies, and Optimization by Response Surface Methodology. Separations 2022, 10, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagaba, A.H.; Kutty, S.R.M.; Isa, M.H.; Ghaleb, A.A.S.; Lawal, I.M.; Usman, A.K.; Birniwa, A.H.; Noor, A.; Abubakar, S.; Umaru, I.; et al. Toxic Effects of Xenobiotic Compounds on the Microbial Community of Activated Sludge. ChemBioEng Rev. 2022, 9, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullahi, S.S.; Musa, H.; Habibu, S.; Birniwa, A.H.; Mohammad, R.E.A. Comparative study and dyeing performance of as-synthesized azo heterocyclic monomeric, polymeric, and commercial disperse dyes. Turk. J. Chem. 2022, 46, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Jagabaa, A.H.; Kutty, S.R.M.; Lawal, I.M.; Birniwa, A.H.; Affam, A.C.; Yaro, N.S.A.; Usman, A.K.; Umaru, I.; Abubakar, S.; Noor, A. Circular economy potential and contributions of petroleum industry sludge utilization to environmental sustainability through engineered processes—A review. Clean. Circ. Bioecon. 2022, 3, 100029. [Google Scholar]
- Jagaba, A.H.; Kutty, S.R.M.; Baloo, L.; Noor, A.; Abubakar, S.; Lawal, I.M.; Umaru, I.; Usman, A.K.; Kumar, V.; Birniwa, A.H. Effect of hydraulic retention time on the treatment of pulp and paper industry wastewater by extended aeration activated sludge system. In Proceedings of the 2021 Third International Sustainability and Resilience Conference: Climate Change, Sakheer, Bahrain, 15–16 November 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 221–224. [Google Scholar]
- Birniwa, A.; Abdullahi, S. Study on physico-mechanical behaviour of acacia nilotica (gum tree) and glass fiber blend reinforced epoxy resin composite. ChemSearch J. 2019, 10, 46–53. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullahi, S.S.; Abu Bakar, N.H.H.; Iqbal, A.; Yusof, N.H. Facile Synthesis and Properties of Cu-Based Supported Halloysite Nanotube (HNT) Photocatalysts for Photocatalytic Degradation of Liquid Epoxidized Natural Rubber (LENR). Egypt. J. Chem. 2022, 65, 702–715. [Google Scholar]
- Jagaba, A.; Kutty, S.; Fauzi, M.; Razali, M.; Hafiz, M.; Noor, A. Organic and Nutrient Removal from Pulp and Paper Industry Wastewater by Extended Aeration Activated Sludge System; IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2021; p. 012021. [Google Scholar]
- Tsang, Y.F.; Chua, H.; Sin, S.; Tam, C. A novel technology for bulking control in biological wastewater treatment plant for pulp and paper making industry. Biochem. Eng. J. 2006, 32, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kankia, M.U.; Baloo, L.; Danlami, N.; Mohammed, B.S.; Haruna, S.; Abubakar, M.; Jagaba, A.H.; Sayed, K.; Abdulkadir, I.; Salihi, I.U. Performance of Fly Ash-Based Inorganic Polymer Mortar with Petroleum Sludge Ash. Polymers 2021, 13, 4143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baloo, L.; Isa, M.H.; Sapari, N.B.; Jagaba, A.H.; Wei, L.J.; Yavari, S.; Razali, R.; Vasu, R. Adsorptive removal of methylene blue and acid orange 10 dyes from aqueous solutions using oil palm wastes-derived activated carbons. Alex. Eng. J. 2021, 60, 5611–5629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mahbashi, N.M.Y.; Kutty, S.R.M.; Bilad, M.R.; Huda, N.; Kobun, R.; Noor, A.; Jagaba, A.H.; Al-Nini, A.; Ghaleb, A.A.S.; Al-dhawi, B.N.S. Bench-Scale Fixed-Bed Column Study for the Removal of Dye-Contaminated Effluent Using Sewage-Sludge-Based Biochar. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brink, A.; Sheridan, C.; Harding, K. A kinetic study of a mesophilic aerobic moving bed biofilm reactor (MBBR) treating paper and pulp mill effluents: The impact of phenols on biodegradation rates. J. Water Process Eng. 2017, 19, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooshyari, B.; Azimi, A.; Mehrdadi, N. Kinetic analysis of enhanced biological phosphorus removal in a hybrid integrated fixed film activated sludge process. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 6, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Mai, W.; Tang, J.; Wei, Y. Highly effective treatment of petrochemical wastewater by a super-sized industrial scale plant with expanded granular sludge bed bioreactor and aerobic activated sludge. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 360, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Iqbal, H.M.; Chandra, R. Evaluation of pollution parameters and toxic elements in wastewater of pulp and paper industries in India: A case study. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2022, 5, 100163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, R.E.A.; Gubartallah, E.A.; Elbashir, A.A.; Saad, B.; Yahaya, N.; Zain, N.N.M.; Rahim, N.Y.; Miskam, M. Simultaneous Determination of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Using Vortex-Assisted Liquid-Liquid Microextraction with Back Extraction Coupled with HPLC-UV. Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2021, 48, 1363–1373. [Google Scholar]
- Aigbe, U.O.; Das, R.; Ho, W.H.; Srinivasu, V.; Maity, A. A novel method for removal of Cr (VI) using polypyrrole magnetic nanocomposite in the presence of unsteady magnetic fields. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 194, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, R.E.A.; Elbashir, A.A.; Karim, J.; Yahaya, N.; Rahim, N.Y.; Miskam, M. Adsorptive performances of magnetic graphene oxide adsorbent for the removal of fluoroquinolones in the Langat River Basin, Malaysia. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 2021, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).